flat tire DODGE NEON 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 353 of 1285

INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Ensure that the red locking tab is in the lock position
after installing the connector. Tighten trim screws to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the three module
retaining nuts to 22 to 34 N´m (200 to 300 in. lbs.)
torque. Do not connect battery negative cable. Refer
to Diagnosis and Testing for Airbag System Test pro-
cedures.
DEPLOYED MODULE
REMOVAL
When removing a deployed module, rubber gloves,
eye protection, and a long-sleeved shirt should be
worn, as there may be deposits on the surface which
could irritate the skin and eyes.
(1) Roll/fold airbag towards instrument panel.
(2) Close door over folded airbag and tape door
closed.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove instrument panel top cover. Refer to
Group 8E Instrument Panel Systems, Instrument
Panel Top Cover Removal and Installation.
(5) Remove three screws to glove box door and
remove door from instrument panel.
(6) Remove three passenger airbag cover screws
attaching cover to top of instrument panel (Fig. 9).
(7) Remove two passenger airbag cover screws
attaching cover to front lower instrument panel.
(8) Remove three module attaching nuts from the
support structure.
(9) Lift module up until the wire connector is visi-
ble and disconnect the 4-way wire connector from
module. Unlock the red locking tab and compress
lock to release the connector (Fig. 10).
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Ensure that the red locking tab is in the lock position
after installing the connector. Tighten trim screws to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the module nuts to
22 to 34 N´m (200 to 300 in. lbs.) torque. Do not con-
nect battery negative cable. Refer to Diagnosis and
Testing for Airbag System Test procedures.
STEERING WHEEL
WARNING: DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BAT-
TERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE BEFORE
BEGINNING ANY AIRBAG SYSTEM COMPONENT
REMOVAL OR INSTALLATION PROCEDURE. THIS
WILL DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO
DISCONNECT BATTERY COULD RESULT IN ACCI-DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
ALLOW SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
FOR 1 MINUTE BEFORE REMOVING ANY AIRBAG
COMPONENTS.
REMOVAL
(1) Adjust the steering wheel so that the tires are
in the straight ahead position. Then:
(a) Rotate the steering wheel half turn (180
degrees) to the right (clockwise).
(b) Lock column with the ignition cylinder lock.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable (Fig. 4).
(3) Remove the speed control switches and discon-
nect the wire connectors or covers (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the Driver Airbag Module attaching
bolts from the back of steering wheel.
(5) Lift module and disconnect the airbag and horn
wire connectors.
(6) Remove steering wheel retaining nut.
(7) Remove the steering wheel with a steering
wheel puller (Fig. 12). While removing the steering
wheel take care to feed the wires gently through the
holes in the steering wheel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Confirm that:
(a) The steering wheel position is a half turn
(180 degrees) to the right (clockwise).
(b) The column is locked with the ignition cylin-
der lock.
(c) Check that the turn signal stalk is in the
neutral position.
(2) Install the steering wheel ensuring the flats on
hub align with the clockspring. Pull the horn lead,
airbag and speed control leads through the larger
Fig. 11 Steering Wheel Remove/Install
8M - 8 PASSIVE RESTRAINT SYSTEMSPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 728 of 1285

²When checking #2 main bearing shim #1 & #3
main bearing.
²When checking #3 main bearing shim #2 & #4
main bearing.
²When checking #4 main bearing shim #3 main
bearing.
NOTE: REMOVE ALL SHIMS BEFORE REASSEM-
BLING ENGINE
ALTERNATIVE METHOD
The weight of the crankshaft can be supported by a
jack under the counterweight adjacent to the bearing
being checked.
PLASTIGAGE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 5). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 6) with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Refer to Engine Specifications.Plastigage gener-
ally is accompanied by two scales. One scale is
in inches, the other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. Thefollowing is the recommended procedure for the use
of Plastigage:
(1) Rotate the crankshaft until the connecting rod
to be checked is at the bottom of its stroke.
(2) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the bearing cap approx-
imately 6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from
the oil hole (Fig. 5). In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing plastigage in that area.
(4) Assemble the rod cap with Plastigage in place.
Tighten the rod cap to the specified torque.Do not
rotate the crankshaft while assembling the cap
or the Plastigage may be smeared, giving inac-
curate results.
(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 6) with the scale pro-
vided on the package. Locate the band closest to the
same width. This band indicates the amount of oil
clearance. Differences in readings between the ends
indicate the amount of taper present. Record all
readings taken. Refer to Engine Specifications.Plas-
tigage generally is accompanied by two scales.
One scale is in inches, the other is a metric
scale. If the bearing clearance exceeds wear
limit specification, replace the bearing.
REPAIR OF DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (including aluminum
head spark plug threads) can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of drilling out worn or
damaged threads, tapping the hole with a special
Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing an insert
into the tapped hole. This brings the hole back to its
original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original centerline.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
Fig. 6 Clearance Measurement
PLENGINE 9 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 877 of 1285
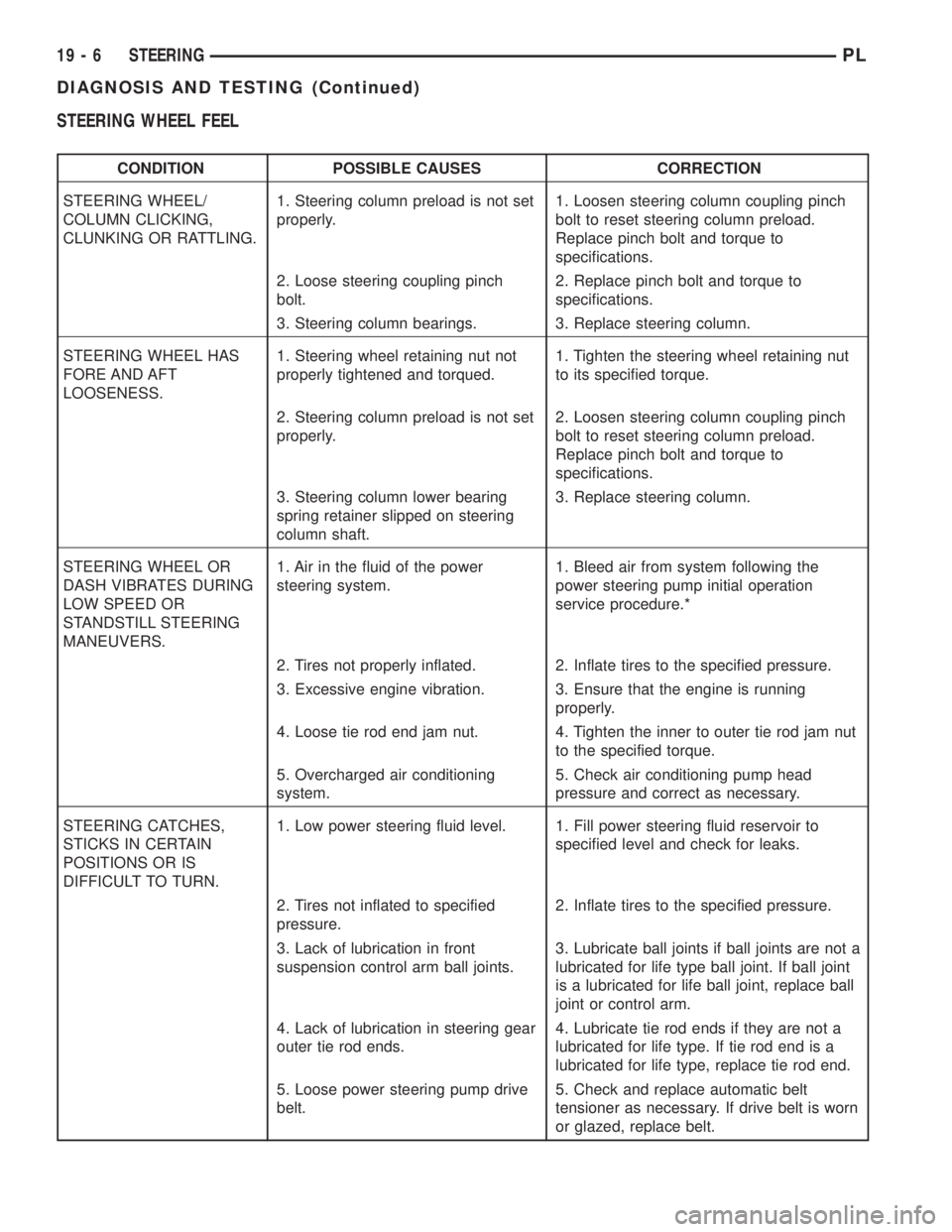
STEERING WHEEL FEEL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STEERING WHEEL/
COLUMN CLICKING,
CLUNKING OR RATTLING.1. Steering column preload is not set
properly.1. Loosen steering column coupling pinch
bolt to reset steering column preload.
Replace pinch bolt and torque to
specifications.
2. Loose steering coupling pinch
bolt.2. Replace pinch bolt and torque to
specifications.
3. Steering column bearings. 3. Replace steering column.
STEERING WHEEL HAS
FORE AND AFT
LOOSENESS.1. Steering wheel retaining nut not
properly tightened and torqued.1. Tighten the steering wheel retaining nut
to its specified torque.
2. Steering column preload is not set
properly.2. Loosen steering column coupling pinch
bolt to reset steering column preload.
Replace pinch bolt and torque to
specifications.
3. Steering column lower bearing
spring retainer slipped on steering
column shaft.3. Replace steering column.
STEERING WHEEL OR
DASH VIBRATES DURING
LOW SPEED OR
STANDSTILL STEERING
MANEUVERS.1. Air in the fluid of the power
steering system.1. Bleed air from system following the
power steering pump initial operation
service procedure.*
2. Tires not properly inflated. 2. Inflate tires to the specified pressure.
3. Excessive engine vibration. 3. Ensure that the engine is running
properly.
4. Loose tie rod end jam nut. 4. Tighten the inner to outer tie rod jam nut
to the specified torque.
5. Overcharged air conditioning
system.5. Check air conditioning pump head
pressure and correct as necessary.
STEERING CATCHES,
STICKS IN CERTAIN
POSITIONS OR IS
DIFFICULT TO TURN.1. Low power steering fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
specified level and check for leaks.
2. Tires not inflated to specified
pressure.2. Inflate tires to the specified pressure.
3. Lack of lubrication in front
suspension control arm ball joints.3. Lubricate ball joints if ball joints are not a
lubricated for life type ball joint. If ball joint
is a lubricated for life ball joint, replace ball
joint or control arm.
4. Lack of lubrication in steering gear
outer tie rod ends.4. Lubricate tie rod ends if they are not a
lubricated for life type. If tie rod end is a
lubricated for life type, replace tie rod end.
5. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.5. Check and replace automatic belt
tensioner as necessary. If drive belt is worn
or glazed, replace belt.
19 - 6 STEERINGPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 878 of 1285
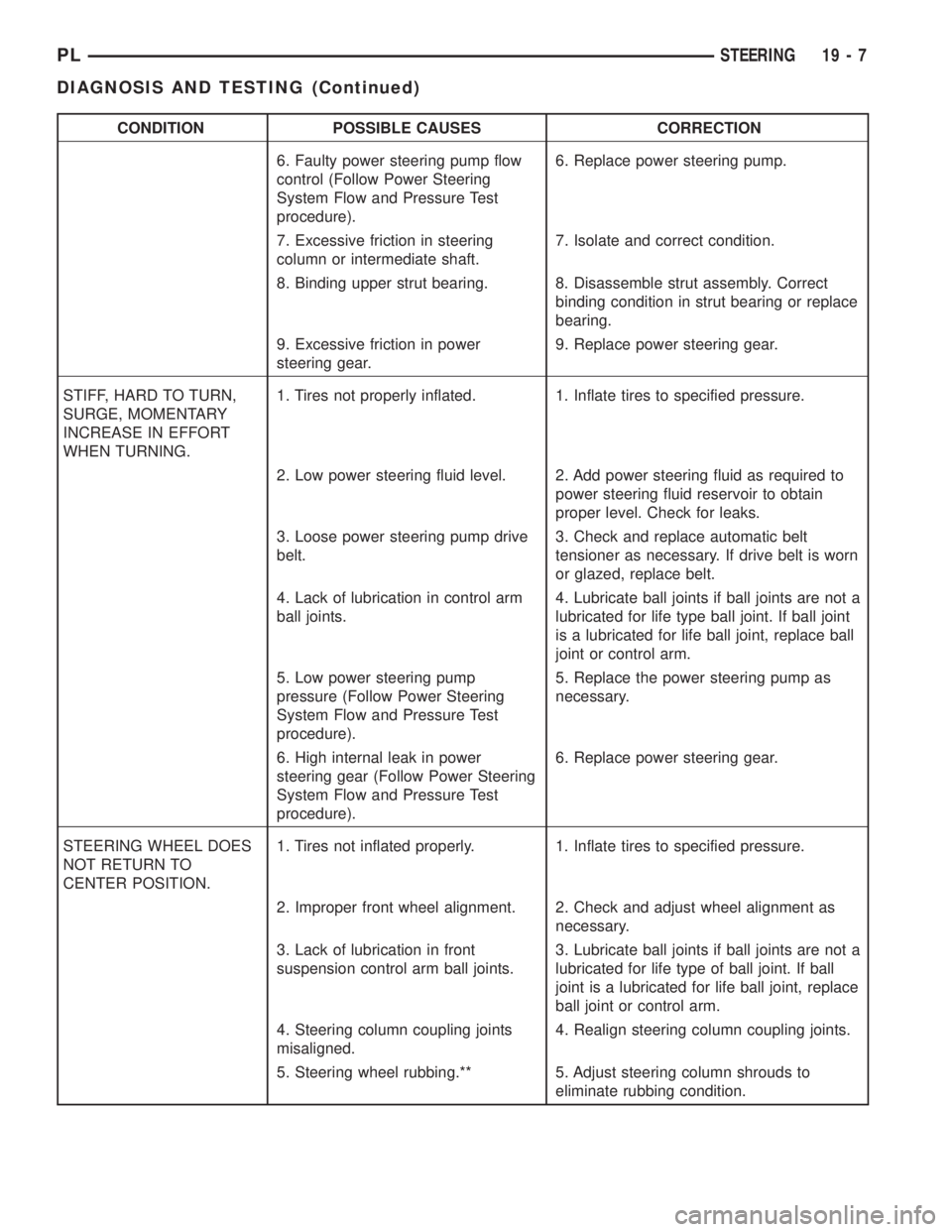
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
6. Faulty power steering pump flow
control (Follow Power Steering
System Flow and Pressure Test
procedure).6. Replace power steering pump.
7. Excessive friction in steering
column or intermediate shaft.7. Isolate and correct condition.
8. Binding upper strut bearing. 8. Disassemble strut assembly. Correct
binding condition in strut bearing or replace
bearing.
9. Excessive friction in power
steering gear.9. Replace power steering gear.
STIFF, HARD TO TURN,
SURGE, MOMENTARY
INCREASE IN EFFORT
WHEN TURNING.1. Tires not properly inflated. 1. Inflate tires to specified pressure.
2. Low power steering fluid level. 2. Add power steering fluid as required to
power steering fluid reservoir to obtain
proper level. Check for leaks.
3. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.3. Check and replace automatic belt
tensioner as necessary. If drive belt is worn
or glazed, replace belt.
4. Lack of lubrication in control arm
ball joints.4. Lubricate ball joints if ball joints are not a
lubricated for life type ball joint. If ball joint
is a lubricated for life ball joint, replace ball
joint or control arm.
5. Low power steering pump
pressure (Follow Power Steering
System Flow and Pressure Test
procedure).5. Replace the power steering pump as
necessary.
6. High internal leak in power
steering gear (Follow Power Steering
System Flow and Pressure Test
procedure).6. Replace power steering gear.
STEERING WHEEL DOES
NOT RETURN TO
CENTER POSITION.1. Tires not inflated properly. 1. Inflate tires to specified pressure.
2. Improper front wheel alignment. 2. Check and adjust wheel alignment as
necessary.
3. Lack of lubrication in front
suspension control arm ball joints.3. Lubricate ball joints if ball joints are not a
lubricated for life type of ball joint. If ball
joint is a lubricated for life ball joint, replace
ball joint or control arm.
4. Steering column coupling joints
misaligned.4. Realign steering column coupling joints.
5. Steering wheel rubbing.** 5. Adjust steering column shrouds to
eliminate rubbing condition.
PLSTEERING 19 - 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 898 of 1285
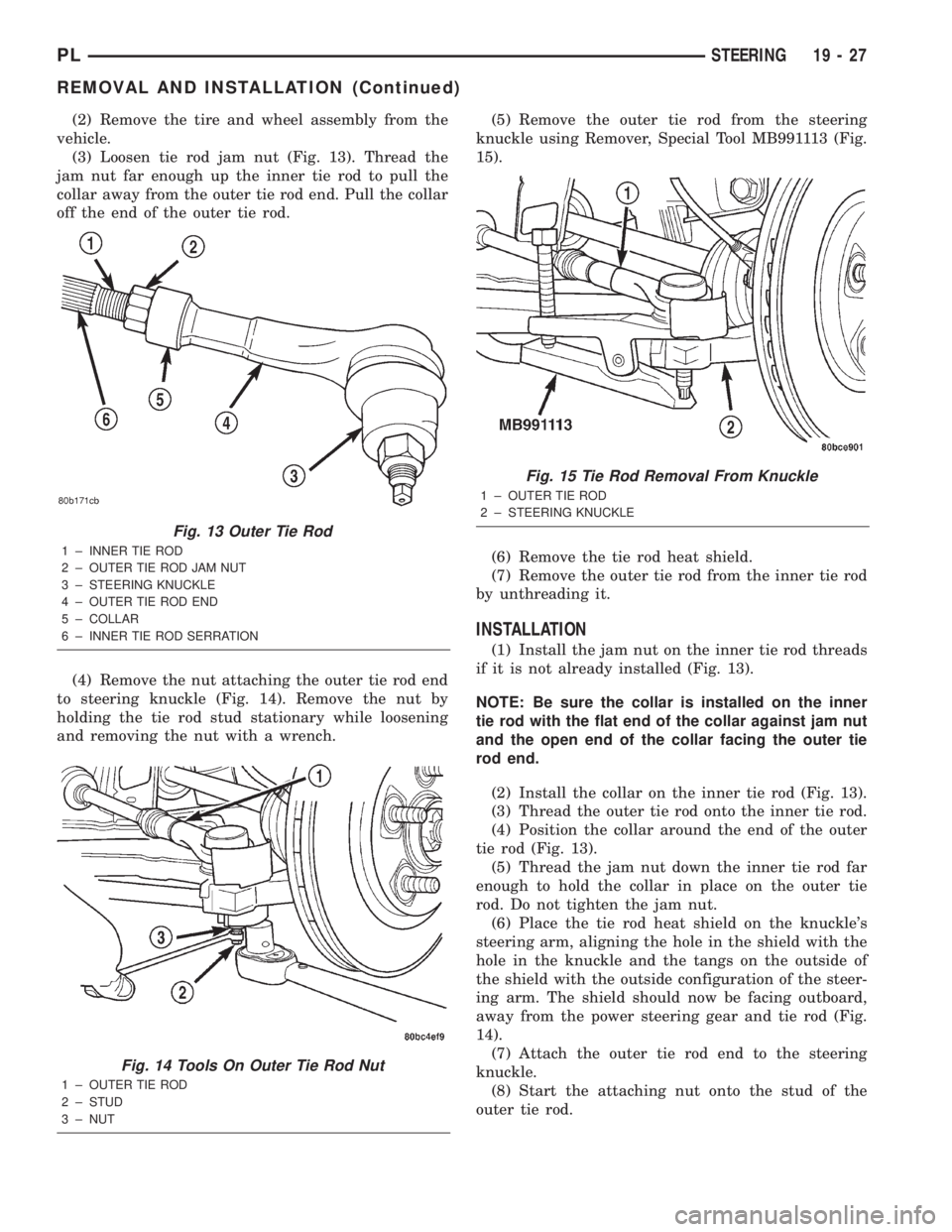
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly from the
vehicle.
(3) Loosen tie rod jam nut (Fig. 13). Thread the
jam nut far enough up the inner tie rod to pull the
collar away from the outer tie rod end. Pull the collar
off the end of the outer tie rod.
(4) Remove the nut attaching the outer tie rod end
to steering knuckle (Fig. 14). Remove the nut by
holding the tie rod stud stationary while loosening
and removing the nut with a wrench.(5) Remove the outer tie rod from the steering
knuckle using Remover, Special Tool MB991113 (Fig.
15).
(6) Remove the tie rod heat shield.
(7) Remove the outer tie rod from the inner tie rod
by unthreading it.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the jam nut on the inner tie rod threads
if it is not already installed (Fig. 13).
NOTE: Be sure the collar is installed on the inner
tie rod with the flat end of the collar against jam nut
and the open end of the collar facing the outer tie
rod end.
(2) Install the collar on the inner tie rod (Fig. 13).
(3) Thread the outer tie rod onto the inner tie rod.
(4) Position the collar around the end of the outer
tie rod (Fig. 13).
(5) Thread the jam nut down the inner tie rod far
enough to hold the collar in place on the outer tie
rod. Do not tighten the jam nut.
(6) Place the tie rod heat shield on the knuckle's
steering arm, aligning the hole in the shield with the
hole in the knuckle and the tangs on the outside of
the shield with the outside configuration of the steer-
ing arm. The shield should now be facing outboard,
away from the power steering gear and tie rod (Fig.
14).
(7) Attach the outer tie rod end to the steering
knuckle.
(8) Start the attaching nut onto the stud of the
outer tie rod.
Fig. 13 Outer Tie Rod
1 ± INNER TIE ROD
2 ± OUTER TIE ROD JAM NUT
3 ± STEERING KNUCKLE
4 ± OUTER TIE ROD END
5 ± COLLAR
6 ± INNER TIE ROD SERRATION
Fig. 14 Tools On Outer Tie Rod Nut
1 ± OUTER TIE ROD
2 ± STUD
3 ± NUT
Fig. 15 Tie Rod Removal From Knuckle
1 ± OUTER TIE ROD
2 ± STEERING KNUCKLE
PLSTEERING 19 - 27
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1070 of 1285

TIRES AND WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES................................... 1WHEELS................................ 10
TIRES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TIRE...................................1
RADIAL-PLY TIRES........................2
SPARE TIRE±TEMPORARY..................3
REPLACEMENT TIRES.....................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS.................3
TIRE WEAR PATTERNS.....................4
TIRE NOISE OR VIBRATION.................4
VEHICLE LEAD DIAGNOSIS AND
CORRECTION..........................4
SERVICE PROCEDURES
PRESSURE GAUGES......................6TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES...............6
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION............................6
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION................6
REPAIRING TIRE LEAKS....................7
TIRE AND WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING.........7
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLEANING TIRES.........................9
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRE SPECIFICATIONS.....................9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TIRE
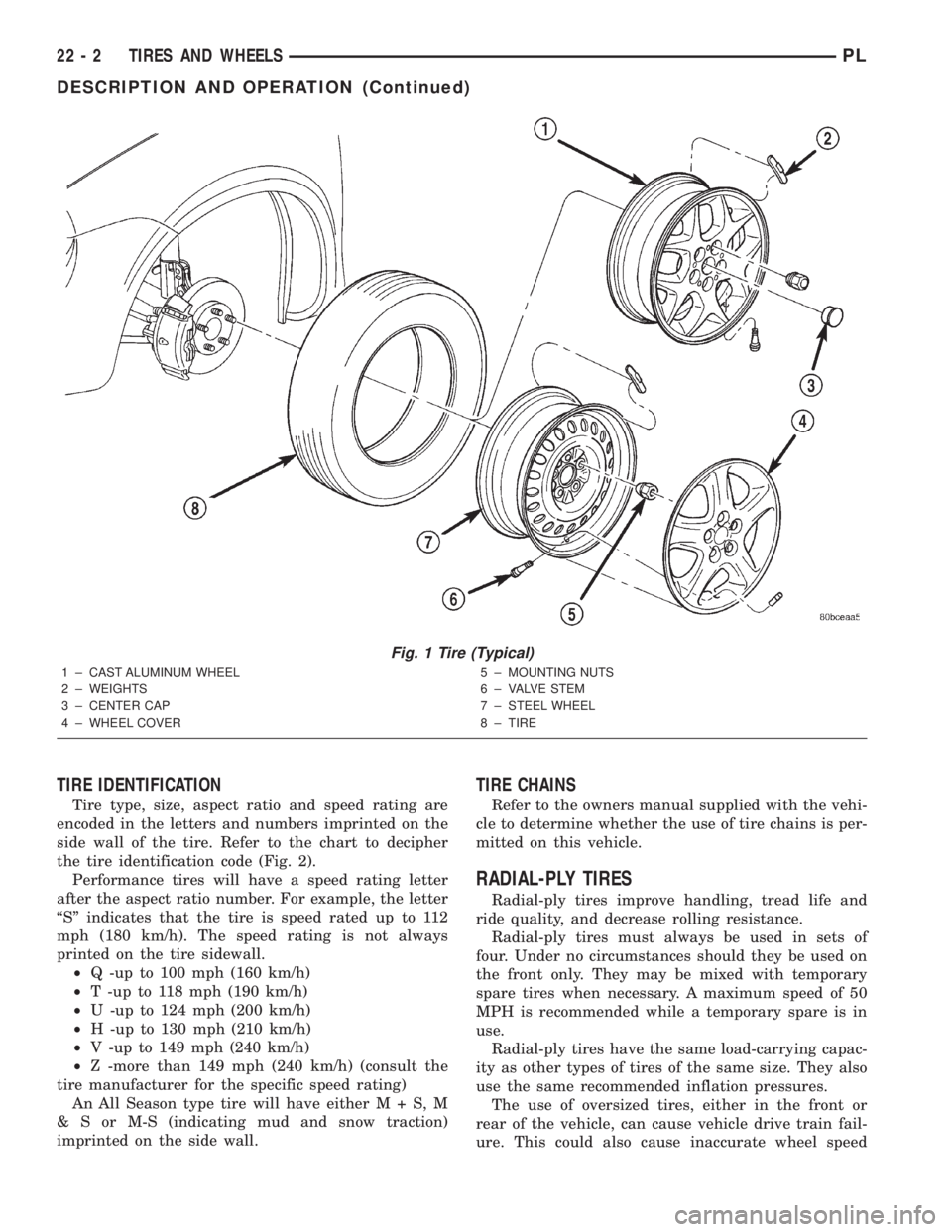
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle (Fig. 1). They provide the best overall perfor-
mance for normal operation. The ride and handling
characteristics match the vehicle's requirements.
With proper care they will give excellent reliability,
traction, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:²Rapid acceleration
²Severe application of brakes
²High-speed driving
²Taking turns at excessive speeds
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
²Operating vehicle with over or under inflated
tire pressures
Radial ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation. This will
help to achieve a greater tread-life potential.
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 1
Page 1071 of 1285
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 2).
Performance tires will have a speed rating letter
after the aspect ratio number. For example, the letter
ªSº indicates that the tire is speed rated up to 112
mph (180 km/h). The speed rating is not always
printed on the tire sidewall.
²Q -up to 100 mph (160 km/h)
²T -up to 118 mph (190 km/h)
²U -up to 124 mph (200 km/h)
²H -up to 130 mph (210 km/h)
²V -up to 149 mph (240 km/h)
²Z -more than 149 mph (240 km/h) (consult the
tire manufacturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
& S or M-S (indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Refer to the owners manual supplied with the vehi-
cle to determine whether the use of tire chains is per-
mitted on this vehicle.
RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
Fig. 1 Tire (Typical)
1 ± CAST ALUMINUM WHEEL
2 ± WEIGHTS
3 ± CENTER CAP
4 ± WHEEL COVER5 ± MOUNTING NUTS
6 ± VALVE STEM
7 ± STEEL WHEEL
8 ± TIRE
22 - 2 TIRES AND WHEELSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1073 of 1285

TIRE WEAR PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 4).
Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 4).
TIRE NOISE OR VIBRATION
Radial-ply tires are sensitive to force impulses
caused by improper mounting, vibration, wheel
defects, or possibly tire imbalance.To find out if tires are causing the noise or vibra-
tion, drive the vehicle over a smooth road at varying
speeds. Note the noise level during acceleration and
deceleration. The engine, differential and exhaust
noises will change as speed varies, while the tire
noise will usually remain constant.
VEHICLE LEAD DIAGNOSIS AND CORRECTION
Use the following chart to diagnose a vehicle that
has a complaint of a drift or lead condition. The use
of this chart will help to determine if the lead condi-
tion is the result of a bad tire or is caused by the
wheel alignment.
Fig. 4 Tire Wear Patterns
22 - 4 TIRES AND WHEELSPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1075 of 1285
SERVICE PROCEDURES
PRESSURE GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
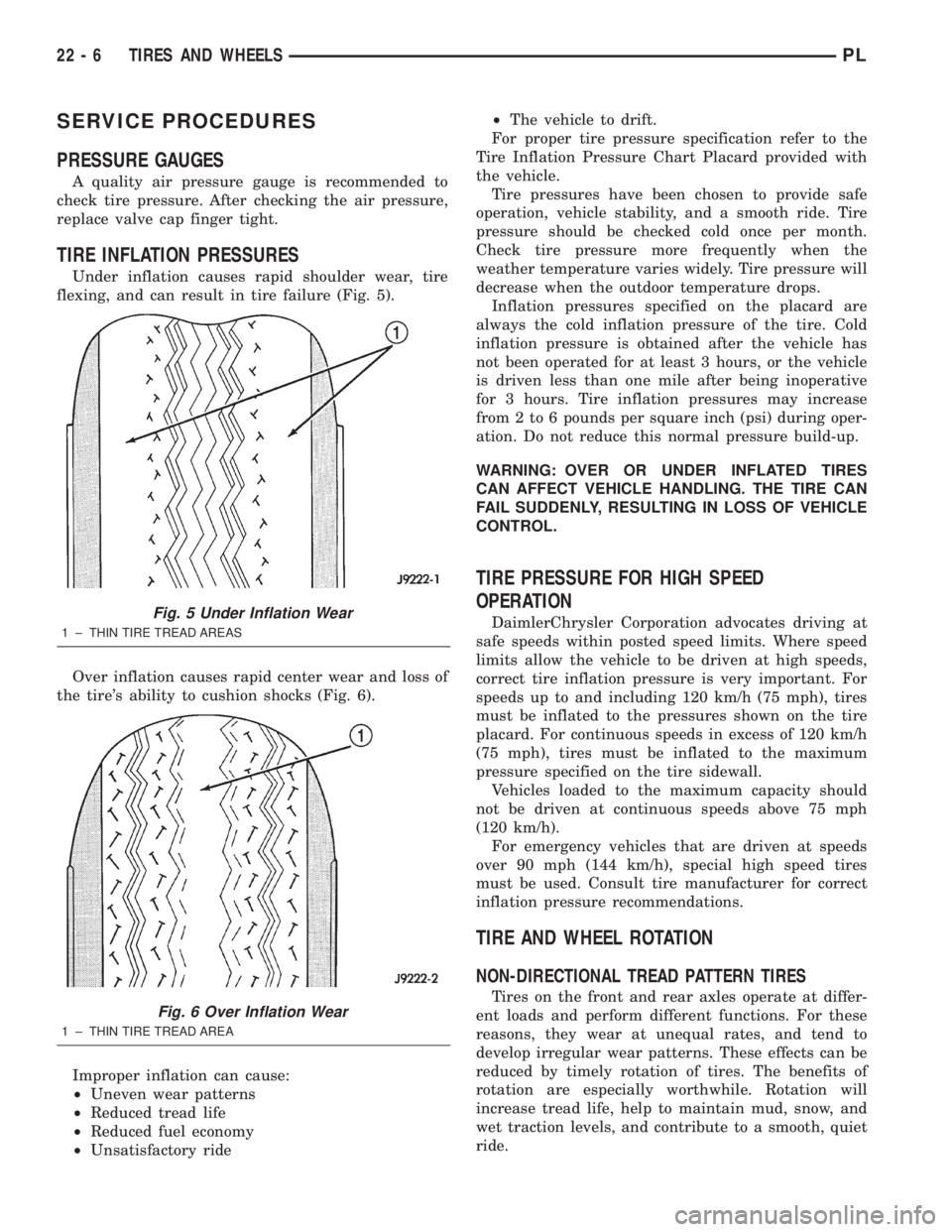
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and can result in tire failure (Fig. 5).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 6).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride²The vehicle to drift.
For proper tire pressure specification refer to the
Tire Inflation Pressure Chart Placard provided with
the vehicle.
Tire pressures have been chosen to provide safe
operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth ride. Tire
pressure should be checked cold once per month.
Check tire pressure more frequently when the
weather temperature varies widely. Tire pressure will
decrease when the outdoor temperature drops.
Inflation pressures specified on the placard are
always the cold inflation pressure of the tire. Cold
inflation pressure is obtained after the vehicle has
not been operated for at least 3 hours, or the vehicle
is driven less than one mile after being inoperative
for 3 hours. Tire inflation pressures may increase
from 2 to 6 pounds per square inch (psi) during oper-
ation. Do not reduce this normal pressure build-up.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES
CAN AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN
FAIL SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
CONTROL.
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION
DaimlerChrysler Corporation advocates driving at
safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed
limits allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds,
correct tire inflation pressure is very important. For
speeds up to and including 120 km/h (75 mph), tires
must be inflated to the pressures shown on the tire
placard. For continuous speeds in excess of 120 km/h
(75 mph), tires must be inflated to the maximum
pressure specified on the tire sidewall.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
For emergency vehicles that are driven at speeds
over 90 mph (144 km/h), special high speed tires
must be used. Consult tire manufacturer for correct
inflation pressure recommendations.
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION
NON-DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Tires on the front and rear axles operate at differ-
ent loads and perform different functions. For these
reasons, they wear at unequal rates, and tend to
develop irregular wear patterns. These effects can be
reduced by timely rotation of tires. The benefits of
rotation are especially worthwhile. Rotation will
increase tread life, help to maintain mud, snow, and
wet traction levels, and contribute to a smooth, quiet
ride.
Fig. 5 Under Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREAS
Fig. 6 Over Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREA
22 - 6 TIRES AND WHEELSPL
Page 1076 of 1285

The suggested rotation method is the forward-cross
tire rotation method (Fig. 7). This method takes
advantage of current tire industry practice which
allows rotation of radial-ply tires. Other rotation
methods may be used, but may not have all the ben-
efits of the recommended method.
NOTE: Only the 4 tire rotation method may be used
if the vehicle is equipped with a low mileage or tem-
porary spare tire.
DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Some vehicles are fitted with special high-perfor-
mance tires having a directional tread pattern. These
tires are designed to improve traction on wet pave-
ment. To obtain the full benefits of this design, the
tires must be installed so that they rotate in the cor-
rect direction. This is indicated by arrows on the tire
sidewalls.
When wheels and tires are being installed, extra
care is needed to ensure that this direction of rota-
tion is maintained.
Refer to Owner's Manual for rotation schedule.
REPAIRING TIRE LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 8). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.Deflate tire completely before attempting to dis-
mount the tire from the wheel.Use a lubricant
such as a mild soap solution when dismounting
or mounting tire.Use tools free of burrs or sharp
edges which could damage the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and progressively tighten
the 5 wheel nuts to a torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
TIRE AND WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING
Wheels and tires are match mounted at the factory.
This means that the high spot of the tire is matched
to the low spot on the wheel rim. This technique is
used to reduce run-out in the wheel/tire assembly.
The high spot on the tire is marked with a paint
mark or a bright colored adhesive label on the out-
board sidewall. The low spot on the rim is identified
with a label on the outside of the rim and a dot or
line in the drop well on the tire side of the rim. If the
outside label has been removed the tire will have to
be removed to locate the dot or line on the inside of
the rim.
Before dismounting a tire from its wheel, a refer-
ence mark should be placed on the tire at the valve
stem location. This reference will ensure that it is
remounted in the original position on the wheel.
Fig. 7 Forward-Cross Tire Rotation Method
Fig. 8 Tire Repair Area
1 ± REPAIRABLE AREA
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 7
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)