torque converter DODGE NEON 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 682 of 1285
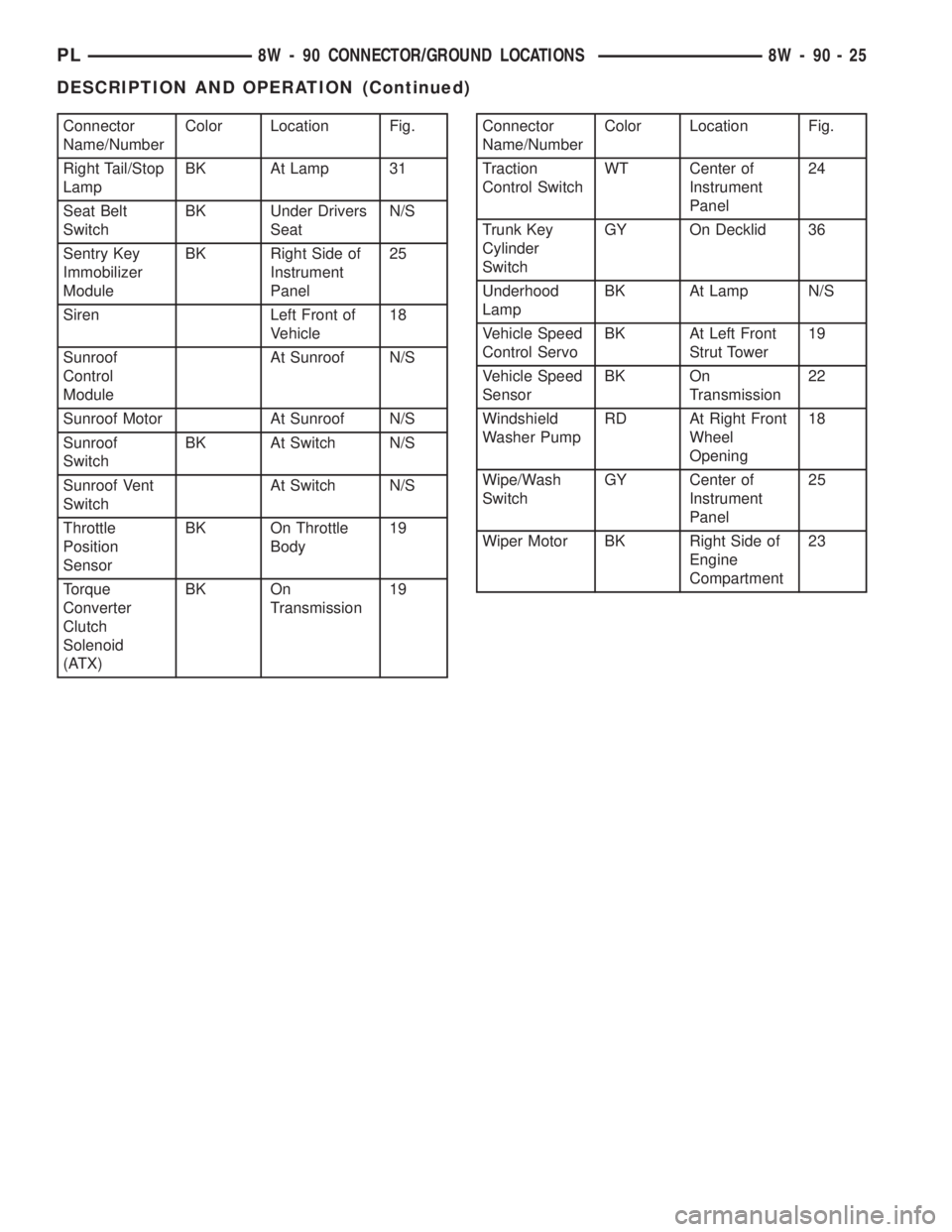
Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
Right Tail/Stop
LampBK At Lamp 31
Seat Belt
SwitchBK Under Drivers
SeatN/S
Sentry Key
Immobilizer
ModuleBK Right Side of
Instrument
Panel25
Siren Left Front of
Vehicle18
Sunroof
Control
ModuleAt Sunroof N/S
Sunroof Motor At Sunroof N/S
Sunroof
SwitchBK At Switch N/S
Sunroof Vent
SwitchAt Switch N/S
Throttle
Position
SensorBK On Throttle
Body19
Torque
Converter
Clutch
Solenoid
(ATX)BK On
Transmission19Connector
Name/NumberColor Location Fig.
Traction
Control SwitchWT Center of
Instrument
Panel24
Trunk Key
Cylinder
SwitchGY On Decklid 36
Underhood
LampBK At Lamp N/S
Vehicle Speed
Control ServoBK At Left Front
Strut Tower19
Vehicle Speed
SensorBK On
Transmission22
Windshield
Washer PumpRD At Right Front
Wheel
Opening18
Wipe/Wash
SwitchGY Center of
Instrument
Panel25
Wiper Motor BK Right Side of
Engine
Compartment23
PL8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONS 8W - 90 - 25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 733 of 1285

make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
²Disconnect the fresh air hose (makeup air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the nipple on
the cover.
²Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve nipple on the
cover.
²Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and reg-
ulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and CCV hose. Proceed to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of theengine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil galley cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, refer to Crank-
shaft Oil SealÐRear for proper replacement proce-
dures.
9 - 10 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 736 of 1285
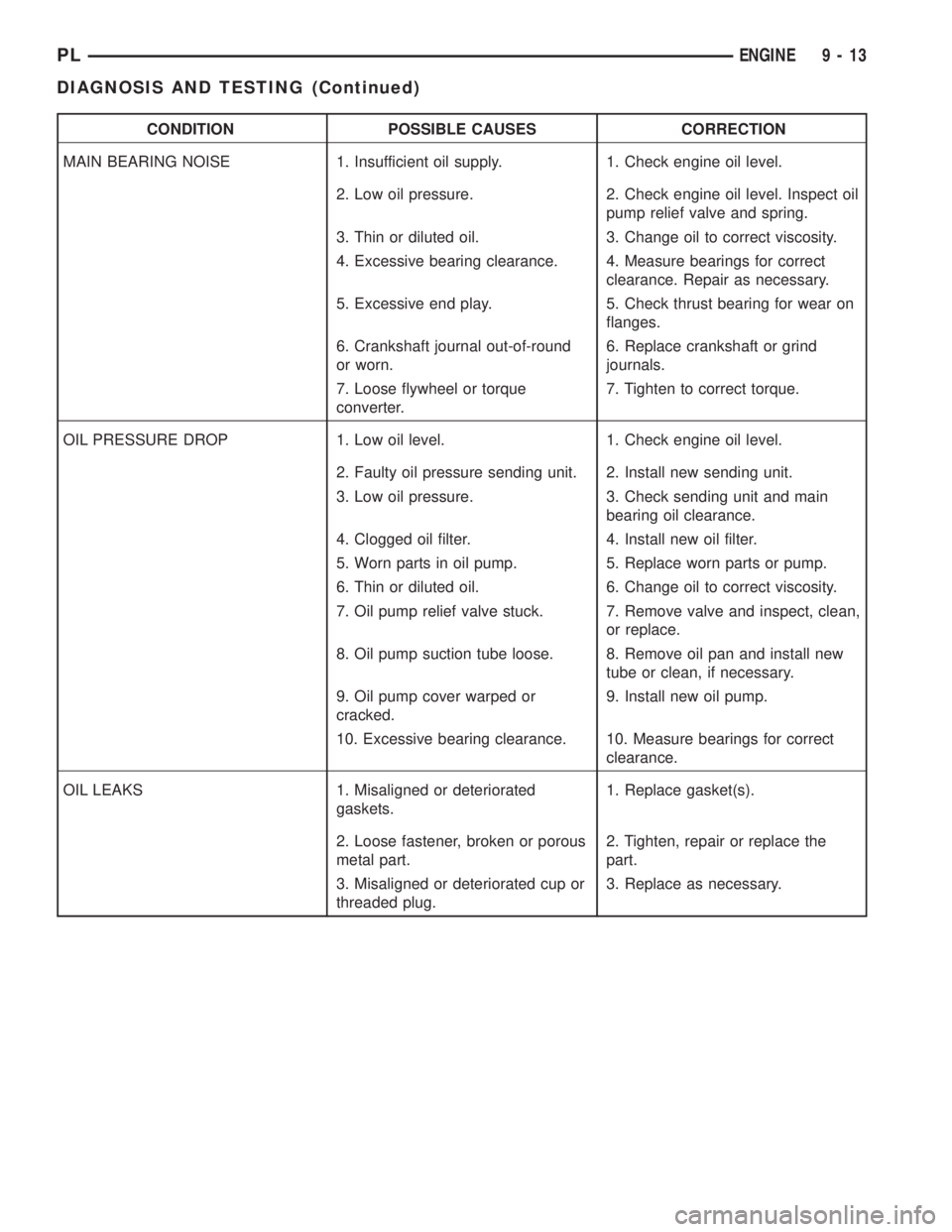
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust bearing for wear on
flanges.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of-round
or worn.6. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Install new sending unit.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check sending unit and main
bearing oil clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Install new oil filter.
5. Worn parts in oil pump. 5. Replace worn parts or pump.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil to correct viscosity.
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 7. Remove valve and inspect, clean,
or replace.
8. Oil pump suction tube loose. 8. Remove oil pan and install new
tube or clean, if necessary.
9. Oil pump cover warped or
cracked.9. Install new oil pump.
10. Excessive bearing clearance. 10. Measure bearings for correct
clearance.
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets.1. Replace gasket(s).
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part.2. Tighten, repair or replace the
part.
3. Misaligned or deteriorated cup or
threaded plug.3. Replace as necessary.
PLENGINE 9 - 13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 798 of 1285
EXHAUST SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
EXHAUST SYSTEM........................1
EXHAUST FLEX-JOINT COUPLING............1
CATALYTIC CONVERTER....................1
EXHAUST HEAT SHIELDS..................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART.......4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EXHAUST PIPE AND MUFFLER..............4CATALYTIC CONVERTER....................7
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
EXHAUST SYSTEM........................8
ADJUSTMENTS
EXHAUST SYSTEM ALIGNMENT.............8
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATION CHART.............8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
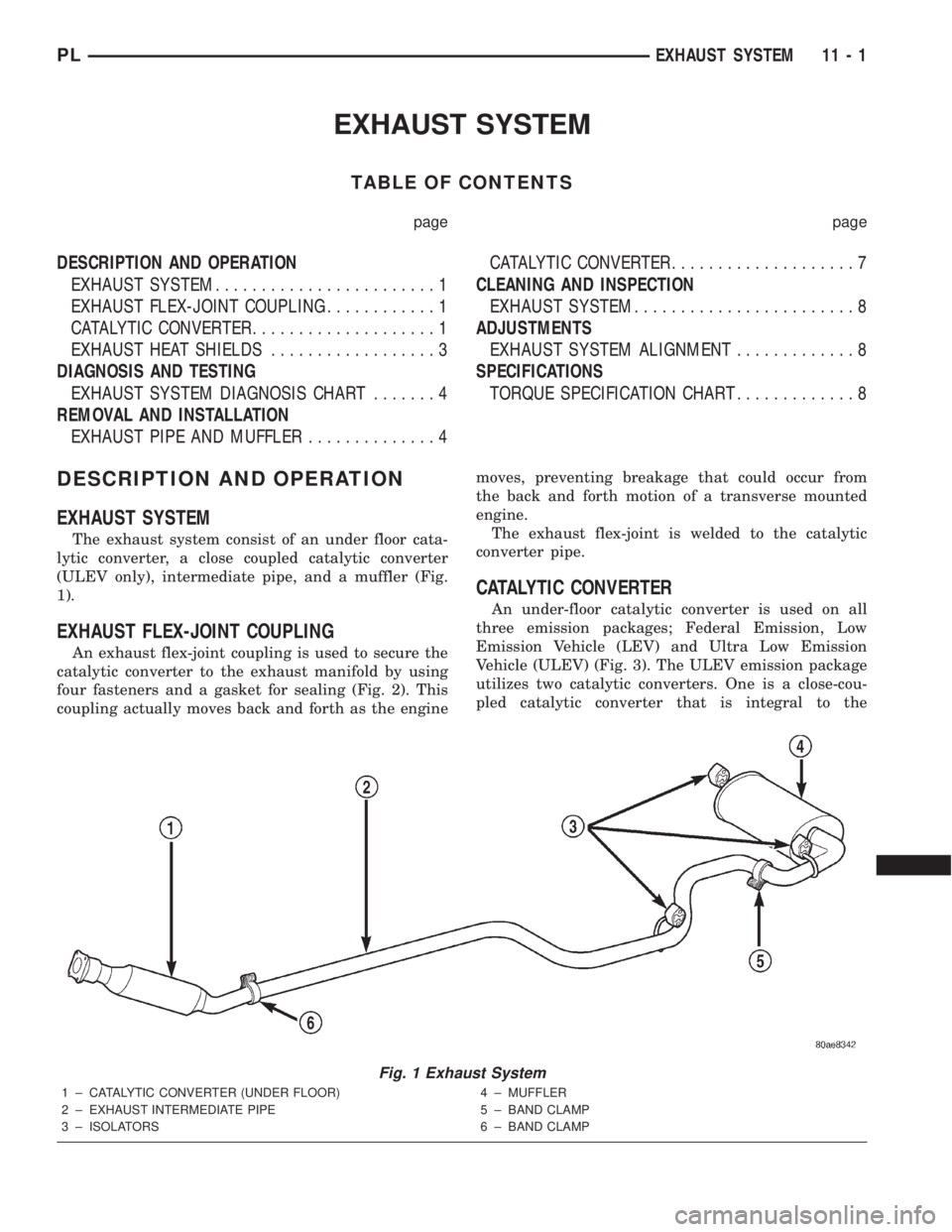
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The exhaust system consist of an under floor cata-
lytic converter, a close coupled catalytic converter
(ULEV only), intermediate pipe, and a muffler (Fig.
1).
EXHAUST FLEX-JOINT COUPLING
An exhaust flex-joint coupling is used to secure the
catalytic converter to the exhaust manifold by using
four fasteners and a gasket for sealing (Fig. 2). This
coupling actually moves back and forth as the enginemoves, preventing breakage that could occur from
the back and forth motion of a transverse mounted
engine.
The exhaust flex-joint is welded to the catalytic
converter pipe.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
An under-floor catalytic converter is used on all
three emission packages; Federal Emission, Low
Emission Vehicle (LEV) and Ultra Low Emission
Vehicle (ULEV) (Fig. 3). The ULEV emission package
utilizes two catalytic converters. One is a close-cou-
pled catalytic converter that is integral to the
Fig. 1 Exhaust System
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER (UNDER FLOOR)
2 ± EXHAUST INTERMEDIATE PIPE
3 ± ISOLATORS4 ± MUFFLER
5 ± BAND CLAMP
6 ± BAND CLAMP
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 1
Page 802 of 1285
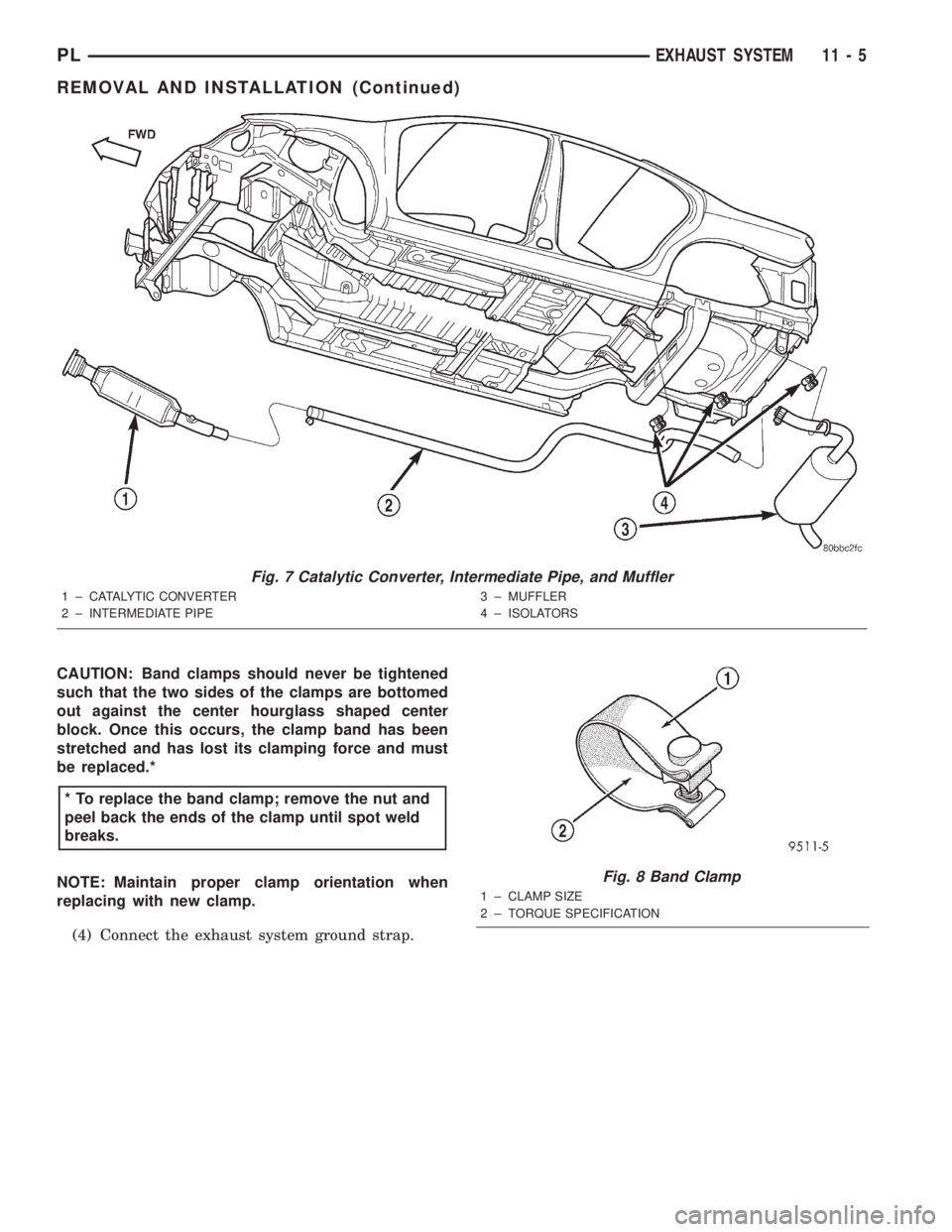
CAUTION: Band clamps should never be tightened
such that the two sides of the clamps are bottomed
out against the center hourglass shaped center
block. Once this occurs, the clamp band has been
stretched and has lost its clamping force and must
be replaced.*
NOTE: Maintain proper clamp orientation when
replacing with new clamp.
(4) Connect the exhaust system ground strap.
Fig. 7 Catalytic Converter, Intermediate Pipe, and Muffler
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 ± INTERMEDIATE PIPE3 ± MUFFLER
4 ± ISOLATORS
* To replace the band clamp; remove the nut and
peel back the ends of the clamp until spot weld
breaks.
Fig. 8 Band Clamp
1 ± CLAMP SIZE
2 ± TORQUE SPECIFICATION
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 5
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 805 of 1285

(2) Install exhaust manifold support bracket (Fed-
eral and LEV only). Tighten M10 bolt to 54 N´m (40
ft. lbs.), M12 bolt to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.), and nut to
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Install bolt attaching manifold support bracket
to the heat shield (Federal and LEV only). Tighten
bolt to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(4) Assemble muffler and exhaust pipe to catalytic
converter. Install muffler and pipe support isolators
to the underbody.
(5) Tighten the catalytic converter to exhaust man-
ifold fasteners to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) (Fig. 11) or
(Fig. 12).
(6) Working from the front of the systemÐalign
each component to maintain position and proper
clearance with under body components. Tighten all
slip joint band clamps to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Band (Torca) clamps should never be
tightened such that the two sides of the clamps are
bottomed out against the center hourglass shaped
center block. Once this occurs, the clamp has lost
clamping force and must be replaced.
(7) If removed, install downstream oxygen sensor.
(8) Connect downstream oxygen sensor electrical
connector.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
EXHAUST SYSTEM
Inspect the exhaust pipes, catalytic converters,
muffler, and resonators for cracked joints, broken
welds and corrosion damage that would result in a
leaking exhaust system. Inspect the clamps, support
brackets, and insulators for cracks and corrosion
damage.
NOTE: Slip joint band clamps are spot welded to
exhaust system. If a band clamp must be replaced,
the spot weld must be ground off.
ADJUSTMENTS
EXHAUST SYSTEM ALIGNMENT
A misaligned exhaust system is usually indicated
by a vibration, rattling noise, or binding of exhaust
system components. These noises are sometimes hard
to distinguish from other chassis noises. Inspect
exhaust system for broken or loose clamps, heat
shields, insulators, and brackets. Replace or tighten
as necessary. It is important that exhaust system
clearances and alignment be maintained.
Perform the following procedures to align the
exhaust system. Refer to (Fig. 9) for clearance speci-
fications:
(1) Loosen clamps and support brackets.
(2) Align the exhaust system starting at the front,
working rearward.
(3) Tighten all clamps and brackets once align-
ment and clearances are achieved.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATION CHART
Fig. 12 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
ConnectionÐULEV
1 ± PRESSED-IN NUTS
2 ± GASKET
3 ± BOLTS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Band ClampsÐFastener 47 35 Ð
Catalytic Converter to Exhaust
Manifold FlangeÐFasteners28 Ð 250
11 - 8 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 863 of 1285

Control Module (PCM) receives data from the DRB
through the SCI Receive circuit.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
OPERATION
The PCM operates the tachometer on the instru-
ment panel. The PCM calculates engine RPM from
the crankshaft position sensor input. Sends the infor-
mation to the cluster across the bus.
TORQUE CONVERTOR CLUTCH SOLENOIDÐ
PCM OUTPUT
OPERATION
Three-speed automatic transaxles use a torque con-
verter clutch solenoid. The PCM controls the engage-
ment of the torque converter clutch through the
solenoid (Fig. 28). The torque converter clutch is
engaged up only in direct drive mode. Refer to the
Transmission section for information.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
THROTTLE BODY
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable (Fig. 29).
(2) Remove the air cleaner box cover.
(3) Remove the air cleaner element (Fig. 30). Pull
up on element, past the lip in the box, to remove it
from the air cleaner box.
(4) Disconnect the electrical connection at the
throttle body.
(5) Loosen the clamp on throttle body outlet hose.(6) Remove the bolts holding the throttle body to
the air cleaner box (Fig. 31).
(7) Remove cable's from throttle body cam (Fig.
32).INSTALLATION
(1) Install cable's into throttle cam and clip cable's
into throttle cable bracket.
(2) Install throttle body onto air cleaner box.
Tighten mounting bolts.
(3) Install and tighten the clamp on throttle body
outlet hose.
(4) Connect the electrical connectors to the throttle
body.
Fig. 28 Torque Convertor Clutch Solenoid
1 ± TORQUE CONVERTOR CLUTCH SOLENOID
2 ± AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE HOUSING
3 ± PARK/NEUTRAL SWITCH
Fig. 29 Battery Negative Cable
Fig. 30 Air Cleaner Element
1 ± LIP
14 - 42 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 921 of 1285
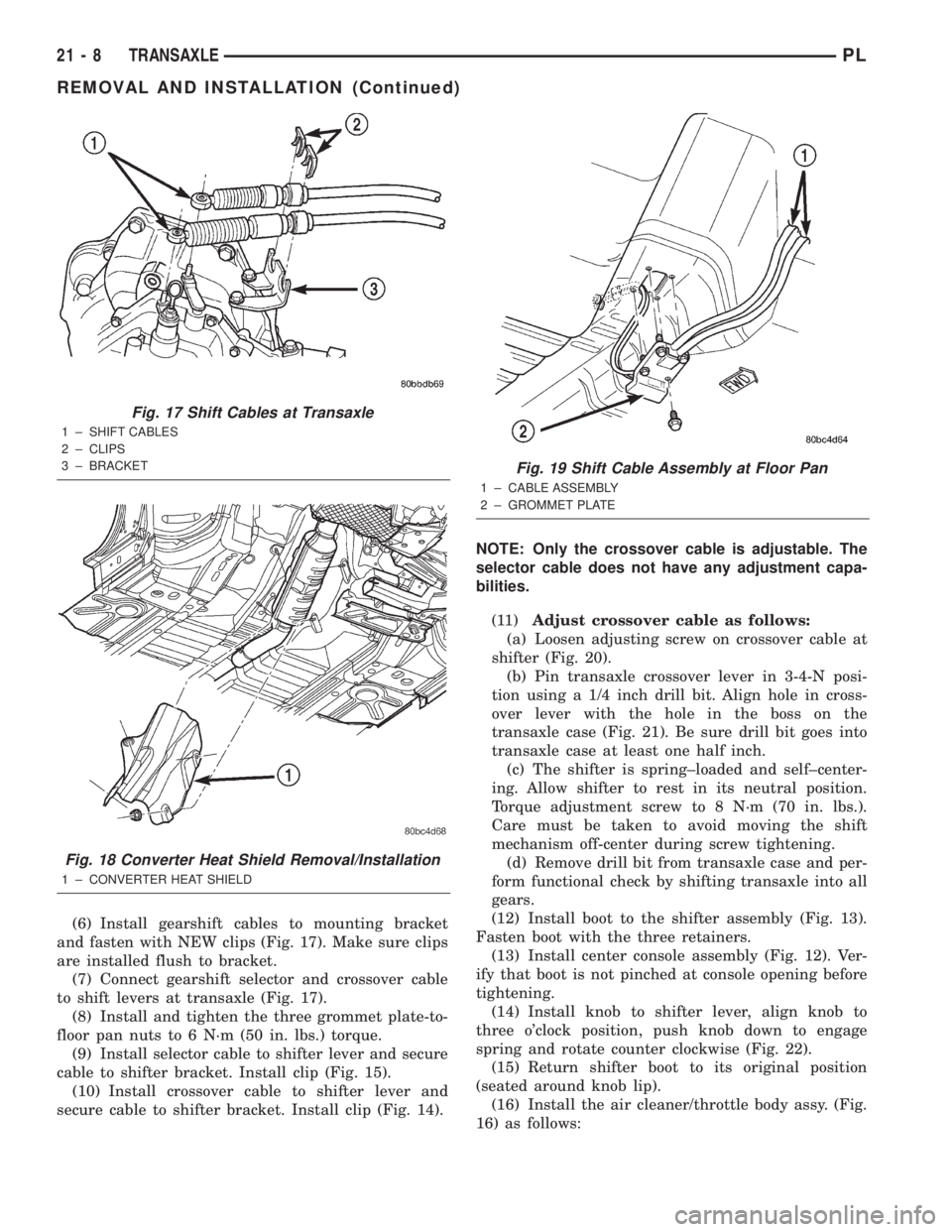
(6) Install gearshift cables to mounting bracket
and fasten with NEW clips (Fig. 17). Make sure clips
are installed flush to bracket.
(7) Connect gearshift selector and crossover cable
to shift levers at transaxle (Fig. 17).
(8) Install and tighten the three grommet plate-to-
floor pan nuts to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install selector cable to shifter lever and secure
cable to shifter bracket. Install clip (Fig. 15).
(10) Install crossover cable to shifter lever and
secure cable to shifter bracket. Install clip (Fig. 14).NOTE: Only the crossover cable is adjustable. The
selector cable does not have any adjustment capa-
bilities.
(11)Adjust crossover cable as follows:
(a) Loosen adjusting screw on crossover cable at
shifter (Fig. 20).
(b) Pin transaxle crossover lever in 3-4-N posi-
tion using a 1/4 inch drill bit. Align hole in cross-
over lever with the hole in the boss on the
transaxle case (Fig. 21). Be sure drill bit goes into
transaxle case at least one half inch.
(c) The shifter is spring±loaded and self±center-
ing. Allow shifter to rest in its neutral position.
Torque adjustment screw to 8 N´m (70 in. lbs.).
Care must be taken to avoid moving the shift
mechanism off-center during screw tightening.
(d) Remove drill bit from transaxle case and per-
form functional check by shifting transaxle into all
gears.
(12) Install boot to the shifter assembly (Fig. 13).
Fasten boot with the three retainers.
(13) Install center console assembly (Fig. 12). Ver-
ify that boot is not pinched at console opening before
tightening.
(14) Install knob to shifter lever, align knob to
three o'clock position, push knob down to engage
spring and rotate counter clockwise (Fig. 22).
(15) Return shifter boot to its original position
(seated around knob lip).
(16) Install the air cleaner/throttle body assy. (Fig.
16) as follows:
Fig. 17 Shift Cables at Transaxle
1 ± SHIFT CABLES
2 ± CLIPS
3 ± BRACKET
Fig. 18 Converter Heat Shield Removal/Installation
1 ± CONVERTER HEAT SHIELD
Fig. 19 Shift Cable Assembly at Floor Pan
1 ± CABLE ASSEMBLY
2 ± GROMMET PLATE
21 - 8 TRANSAXLEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 967 of 1285

31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
IN VEHICLE SERVICE.....................55
FLUID REQUIREMENTS...................55
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
31TH GENERAL INFORMATION..............55
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION..............56
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH.............56
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM.............56
PRESSURE SUPPLY SYSTEM...............56
PRESSURE REGULATING VALVES...........56
FLOW CONTROL VALVES..................56
CLUTCHES, BAND SERVOS, AND
ACCUMULATOR........................57
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM..............................57
GEARSHIFT AND PARKING LOCK CONTROLS . . 57
COOLER BYPASS VALVE..................57
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
WIRING CONNECTOR...................58
GOVERNOR.............................58
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TRANSAXLE PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS.......58
ROAD TEST.............................65
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS.............66
CLUTCH AND SERVO AIR PRESSURE TESTS . . 68
FLUID LEAKAGE-TRANSAXLE TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA.............70
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK....70
SERVICE PROCEDURES
TRANSAXLE FLUID AND FILTER SERVICE.....70
ALUMINUM THREAD REPAIR...............71
FLUSHING COOLERS AND TUBES...........72
OIL PUMP VOLUME CHECK................72
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
GEARSHIFT CABLE.......................73
GEARSHIFT MECHANISM..................76
THROTTLE VALVE (KICKDOWN) CABLE.......77
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
CABLE...............................79
INTERLOCK MECHANISM..................82
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR PINION GEAR......83
PARK/NEUTRAL STARTING AND BACK-UP
LAMP SWITCH.........................84TRANSAXLE AND TORQUE CONVERTER......84
PUMP OIL SEAL.........................88
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
TRANSAXLE............................89
VALVE BODY............................91
OIL PUMP.............................104
FRONT CLUTCH........................105
REAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY................108
FRONT PLANETARY AND ANNULUS
GEAR-RECONDITION...................110
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) SERVO-
RECONDITION........................112
ACCUMULATOR-RECONDITION............113
KICKDOWN SERVO (CONTROLLED LOAD)-
RECONDITION........................113
TRANSFER SHAFT REPAIR................114
PARKING PAWL.........................121
OUTPUT SHAFT REPAIR..................121
DIFFERENTIAL REPAIR...................129
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
VALVE BODY...........................135
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE......................135
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE.........................136
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM.............................137
BAND ADJUSTMENT.....................138
HYDRAULIC CONTROL PRESSURE
ADJUSTMENTS.......................138
BEARING ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES......138
OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING................139
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING.................139
TRANSFER SHAFT BEARING..............140
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
31TH TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATIC . . 142
SPECIFICATIONS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.............150
31TH TRANSAXLE TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS . 150
SPECIAL TOOLS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.............151
21 - 54 TRANSAXLEPL
Page 968 of 1285

GENERAL INFORMATION
IN VEHICLE SERVICE
The following components are serviceable in the
vehicle without transaxle removal:
²Valve Body Assembly
²Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Governor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor & Pinion
²Park/Neutral & Back-up Lamp Switch
²Transfer Gears and Transfer Shaft
²Low/Reverse Servo
²Kickdown Servo
²Accumulator
FLUID REQUIREMENTS
NOTE: The transmission and differential have a
common oil sump with an opening between the
two.
TRANSMISSION/DIFFERENTIAL
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid
Type 9602) is required in this transaxle. Substitute
fluids must meet fluid specification MS-9602.
FLUID ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation strongly recommends against
the addition of any fluids to the transmission, other
than those automatic transmission fluids listed
above. Exceptions to this policy are the use of special
dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks.
Various ªspecialº additives and supplements exist
that claim to improve shift feel/quality and converter
clutch operation, inhibit overheating, oxidation, var-
nish and sludge. These claims have not been sup-
ported to Chrysler's satisfaction and these additives
must not be used. The use of transmission ªsealersº
should also be avoided, since they may adversely
affect the integrity of tranmission seals.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
31TH GENERAL INFORMATION
NOTE: Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on these transaxles.
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system.
NOTE: Transaxle operation requirements are differ-
ent for each vehicle and engine combination. Some
internal parts will be different to provide for this.Therefore, when replacing parts, refer to the seven
digit part number stamped on rear of the transaxle
oil pan flange.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
Center distances between the main rotating parts
in these three areas are held precise to maintain a
low noise level.
The torque converter, transaxle area, and differen-
tial are housed in an integral aluminum die casting.
The differential oil sump is common with the
transaxle sump. Separate filling of the differen-
tial is NOT necessary.
The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through a remote cooler. There are two types of
coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler located in
the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to-air heat
exchanger. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assembly.
Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter and then through the input shaft to multiple-
disc clutches in the transaxle. The power flow
depends on the application of the clutches and bands.
Refer to Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and
Tests section.
The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands
²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The driving shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor in the
transaxle final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also car-
ries the governor and parking sprag. An integral heli-
cal gear on the transfer shaft drives the differential
ring gear.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 55