exhaust DODGE NEON 2000 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 801 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE
EXHAUST NOISE
(UNDER HOOD)1. Exhaust manifold cracked or broken. 1. Replace manifold.
2. Manifold to cylinder head leak. 2. Tighten manifold and/or replace gasket.
3. Exhaust Flex joint to manifold leak. 3. Tighten fasteners or replace gasket.
4. Exhaust flex joint. 4. Replace catalytic converter assembly.
5. Pipe and shell noise from front exhaust
pipe.5. Characteristic of single wall pipes.
EXCESSIVE
EXHAUST NOISE1. Leaks at pipe joints. 1. Tighten or replace clamps at leaking
joints.
2. Burned, blown, or rusted out exhaust
pipe or muffler.2. Replace muffler or exhaust pipes.
3. Restriction in muffler or tailpipe. 3. Remove restriction, if possible or replace
as necessary.
4. Catalytic converter material in muffler. 4. Replace muffler and converter assembly.
Check fuel injection and ignition systems for
proper operation.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EXHAUST PIPE AND MUFFLER
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATING TIME.
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and apply penetrating oil
to band clamp fastener of component being removed.
NOTE: Do not use petroleum-based lubricants
when removing/installing muffler or exhaust pipe
isolators as it may compromise the life of the part.
A suitable substitute is a mixture of liquid dish
soap and water.
(2) Remove exhaust system ground strap.
(3) Loosen band clamp and remove support isola-
tors at muffler. Remove muffler from exhaust pipe
(Fig. 7).(4) Loosen band clamp at the catalytic converter to
intermediate pipe joint (Fig. 7)
(5) Remove intermediate pipe support isolator.
Separate at slip joint and remove intermediate pipe
(Fig. 7).
(6) Clean ends of pipes and muffler to assure mat-
ing of all parts. Discard broken or worn isolators,
rusted or overused clamps, supports, and attaching
parts.
NOTE: When replacement is required on any com-
ponent of the exhaust system, you must use origi-
nal equipment parts (or their equivalent).
INSTALLATION
When assembling exhaust systemdo nottighten
clamps until components are aligned and clearances
are checked.
(1) Assemble intermediate pipe to catalytic con-
verter and the isolator support to the underbody (Fig.
7).
(2) Install the muffler to intermediate pipe and the
isolator supports to the underbody.
(3) Working from the front of system; align each
component to maintain position and proper clearance
with underbody parts (Fig. 9). Tighten band clamps
to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 8).
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
Page 802 of 1285
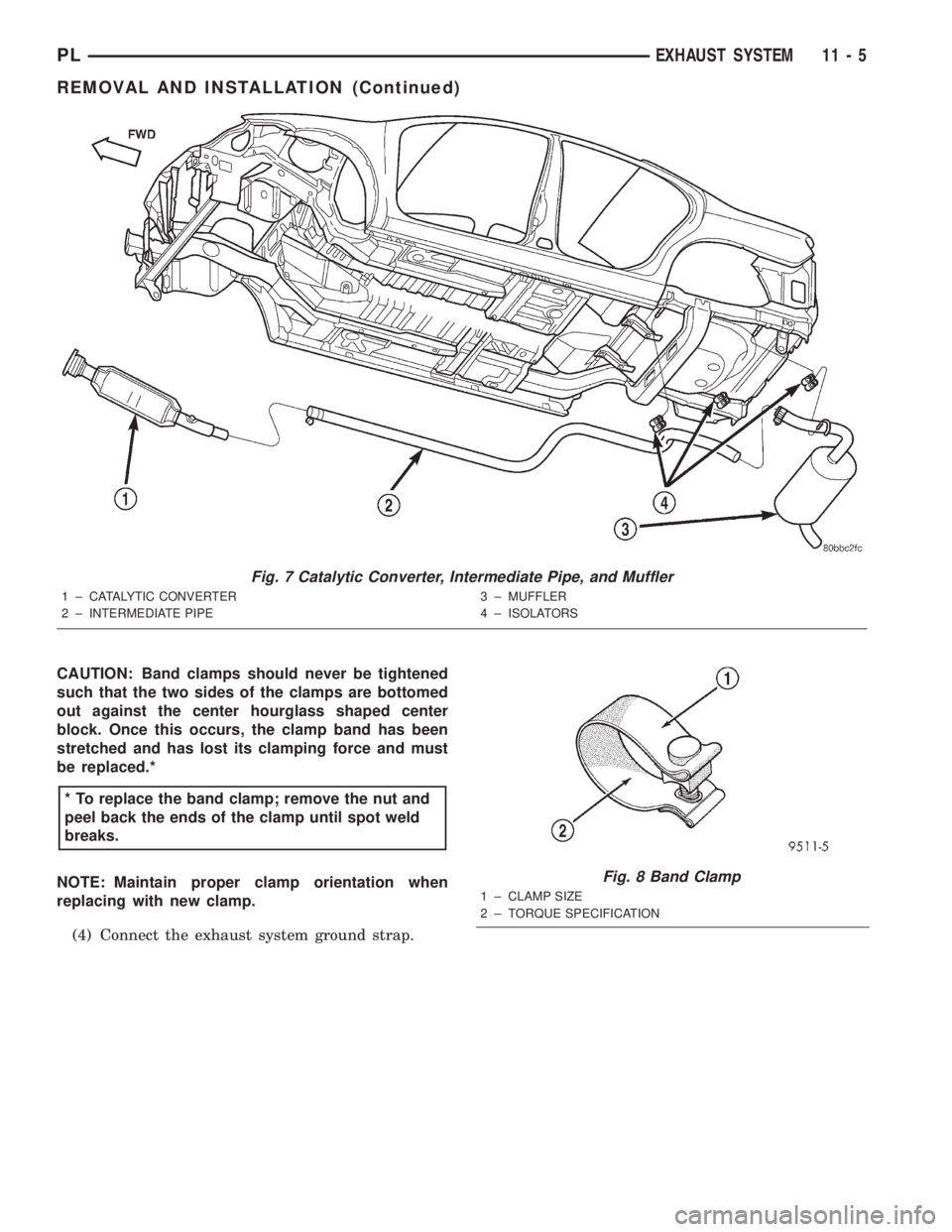
CAUTION: Band clamps should never be tightened
such that the two sides of the clamps are bottomed
out against the center hourglass shaped center
block. Once this occurs, the clamp band has been
stretched and has lost its clamping force and must
be replaced.*
NOTE: Maintain proper clamp orientation when
replacing with new clamp.
(4) Connect the exhaust system ground strap.
Fig. 7 Catalytic Converter, Intermediate Pipe, and Muffler
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 ± INTERMEDIATE PIPE3 ± MUFFLER
4 ± ISOLATORS
* To replace the band clamp; remove the nut and
peel back the ends of the clamp until spot weld
breaks.
Fig. 8 Band Clamp
1 ± CLAMP SIZE
2 ± TORQUE SPECIFICATION
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 5
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 803 of 1285
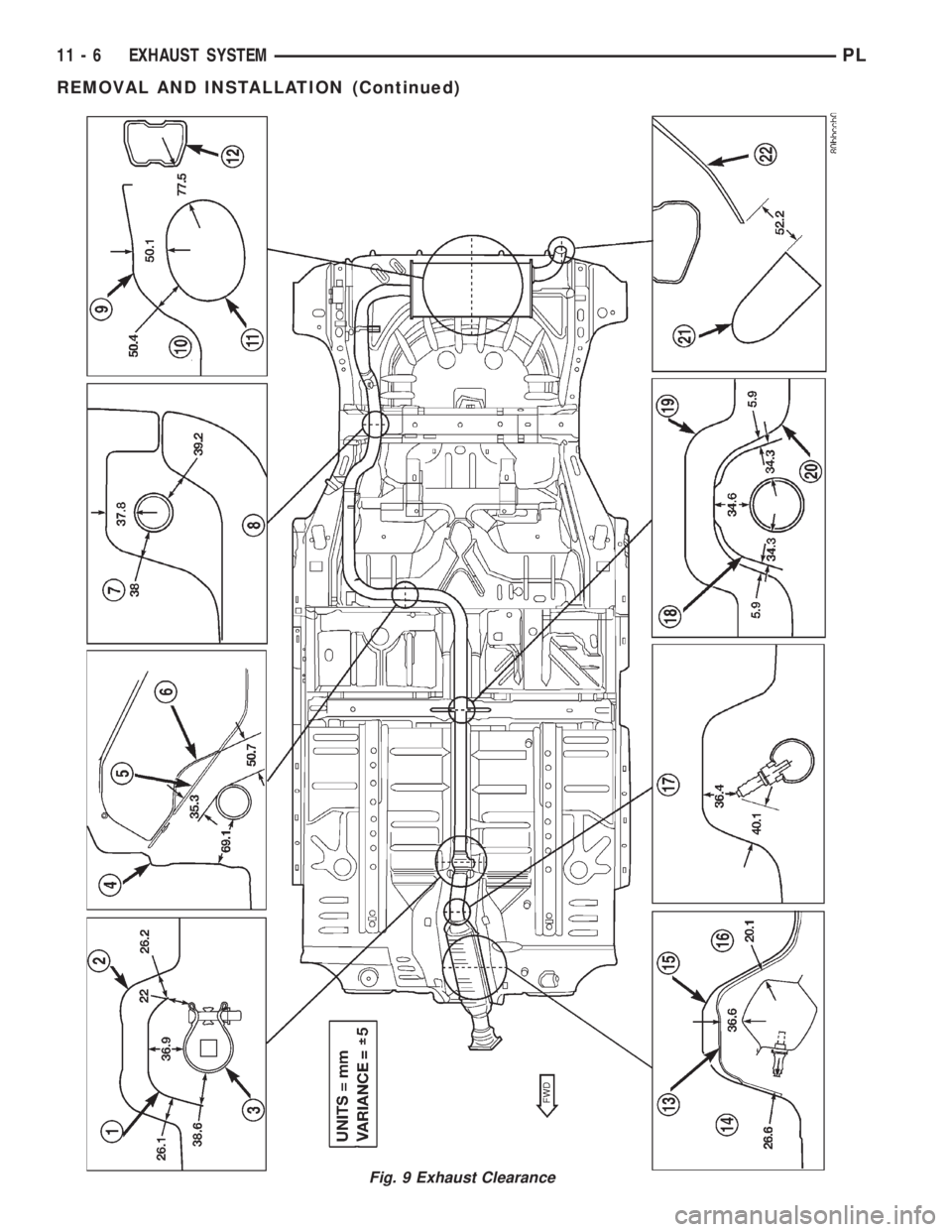
Fig. 9 Exhaust Clearance
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 804 of 1285

CATALYTIC CONVERTER
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER ATTEMPT TO SERVICE ANY
PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM UNTIL IT IS
COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN
WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC CON-
VERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CONVERTER
RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT PERIOD
OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
NOTE: Vehicles equipped with the ULEV emission
package are equipped with an additional catalytic
converter that is integral to the exhaust manifold.
Refer to Exhaust Manifold in Group 9, Engine for
procedure.
(1) Remove muffler and exhaust pipe. Refer to pro-
cedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect downstream oxygen sensor electri-
cal connector.
(3) Remove exhaust manifold support bracket
(Federal and LEV only) (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
attaching fasteners and remove converter from vehi-
cle (Fig. 11) or (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove and discard flange gasket.
NOTE: When replacement is required on any com-
ponent of the exhaust system, original equipment
parts (or equivalent) must be used.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: When assembling exhaust system do not
tighten clamps until all components are aligned and
clearances are checked.(1) Assemble catalytic converter to exhaust mani-
fold connection. Use a new flange gasket.
1 ± HEAT SHIELD
2 ± FLOOR PAN
3 ± BAND CLAMP
4 ± FLOOR PAN
5 ± TANK STRAP
6 ± FUEL TANK
7 ± SPARE TIRE TUB
8 ± REAR SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
9 ± FLOOR PAN
10 ± SPARE TIRE TUB
11 ± MUFFLER12 ± BUMPER BEAM
13 ± HEAT SHIELD
14 ± OXYGEN SENSOR CLEARANCE (LEV)
15 ± FLOOR PAN
16 ± FEDERAL & LEV
17 ± OXYGEN SENSOR CLEARANCE (FEDERAL)
18 ± HEAT SHIELD
19 ± FLOOR PAN
20 ± CROSSMEMBER
21 ± TAIL PIPE
22 ± FASCIA
Fig. 10 Exhaust Manifold Support BracketÐFederal
& LEV
1 ± BRACKET
2 ± BOLT (M10)
3 ± BOLT (M12)
4 ± NUT
Fig. 11 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
ConnectionÐFederal & LEV
1 ± PRESSED-IN STUDS
2 ± NUTS
3 ± GASKET
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 805 of 1285

(2) Install exhaust manifold support bracket (Fed-
eral and LEV only). Tighten M10 bolt to 54 N´m (40
ft. lbs.), M12 bolt to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.), and nut to
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Install bolt attaching manifold support bracket
to the heat shield (Federal and LEV only). Tighten
bolt to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(4) Assemble muffler and exhaust pipe to catalytic
converter. Install muffler and pipe support isolators
to the underbody.
(5) Tighten the catalytic converter to exhaust man-
ifold fasteners to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) (Fig. 11) or
(Fig. 12).
(6) Working from the front of the systemÐalign
each component to maintain position and proper
clearance with under body components. Tighten all
slip joint band clamps to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Band (Torca) clamps should never be
tightened such that the two sides of the clamps are
bottomed out against the center hourglass shaped
center block. Once this occurs, the clamp has lost
clamping force and must be replaced.
(7) If removed, install downstream oxygen sensor.
(8) Connect downstream oxygen sensor electrical
connector.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
EXHAUST SYSTEM
Inspect the exhaust pipes, catalytic converters,
muffler, and resonators for cracked joints, broken
welds and corrosion damage that would result in a
leaking exhaust system. Inspect the clamps, support
brackets, and insulators for cracks and corrosion
damage.
NOTE: Slip joint band clamps are spot welded to
exhaust system. If a band clamp must be replaced,
the spot weld must be ground off.
ADJUSTMENTS
EXHAUST SYSTEM ALIGNMENT
A misaligned exhaust system is usually indicated
by a vibration, rattling noise, or binding of exhaust
system components. These noises are sometimes hard
to distinguish from other chassis noises. Inspect
exhaust system for broken or loose clamps, heat
shields, insulators, and brackets. Replace or tighten
as necessary. It is important that exhaust system
clearances and alignment be maintained.
Perform the following procedures to align the
exhaust system. Refer to (Fig. 9) for clearance speci-
fications:
(1) Loosen clamps and support brackets.
(2) Align the exhaust system starting at the front,
working rearward.
(3) Tighten all clamps and brackets once align-
ment and clearances are achieved.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATION CHART
Fig. 12 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
ConnectionÐULEV
1 ± PRESSED-IN NUTS
2 ± GASKET
3 ± BOLTS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Band ClampsÐFastener 47 35 Ð
Catalytic Converter to Exhaust
Manifold FlangeÐFasteners28 Ð 250
11 - 8 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 843 of 1285

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INJECTION SYSTEM
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
MODES OF OPERATION
OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygensensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).
During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than 0.745
volts or less than 0.1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMPL
Page 844 of 1285

1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
If the PCM does not receive both signals within
approximately one second, it will not energize the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel
pump relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil and heated oxygen sen-
sors.
²The PCM energizes the injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within664 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If
the PCM does not detect a minimum difference
between the two values, it sets a MAP diagnostic
trouble code into memory.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated.
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Intake air temperature (IAT)²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch
²Battery voltage
²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²O2 sensors
²All diagnostics
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²A/C control positions
²Power steering pressure switch
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor
²Purge system monitor
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 23
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 845 of 1285

²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to the Emission
section for On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C pressure transducer
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in response to MAP
sensor feedback.
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
If decel fuel shutoff is detected, downstream oxy-
gen sensor diagnostics is performed.WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to the Emission sec-
tion for On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
OPERATION
The PCM can test many of its own input and out-
put circuits. If the PCM senses a fault in a major
system, the PCM stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in memory.
For DTC information see On-Board Diagnostics.
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
The Power Distribution Center (PDC) is located
next to the battery (Fig. 1). The PDC contains the
starter relay, radiator fan relay, A/C compressor
clutch relay, auto shutdown relay, fuel pump relay
and several fuses.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various
engine and vehicle operations through devices that
are referred to as PCM Outputs.
PCM Inputs:
14 - 24 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 846 of 1285

²Air Conditioning Controls
²Battery Voltage
²Inlet Air/Battery Temperature Sensor
²Brake Switch
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Fuel Level Sensor
²Ignition Switch
²Inlet Air/Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensors
²Power Steering Pressure Switch²SCI Receive
²Speed Control Switches
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Transmission Park/Neutral Switch (automatic
transmission)
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
²Air Conditioning WOT Relay
²Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay
²Charging Indicator Lamp
²Data Link Connector
²Proportional Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid
²Fuel Injectors
²Fuel Pump Relay
²Generator Field
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Ignition Coils
²Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
²Radiator Fan Relay
²Speed Control Solenoids
²Tachometer
²Torque Convertor Clutch Solenoid
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width, idle speed, ignition spark
advance, ignition coil dwell and EVAP canister purge
operation. The PCM regulates the cooling fan, air
conditioning and speed control systems. The PCM
changes generator charge rate by adjusting the gen-
erator field. The PCM also performs diagnostics.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel
ratio) based on the following inputs.
²Battery voltage
²Coolant temperature
²Inlet Air/Intake air temperature
²Exhaust gas content (oxygen sensor)
²Engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
²Coolant temperature
²Inlet Air/Intake air temperature
²Engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
²Transmission gear selection (park/neutral
switch)
The PCM also adjusts engine idle speed through
the idle air control motor based on the following
inputs.
²Air conditioning sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Brake switch
Fig. 1 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
Fig. 2 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 ± PCM
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 25
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 853 of 1285

HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (O2 SENSOR)Ð
PCM INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The upstream oxygen sensor threads into the out-
let flange of the exhaust manifold (Fig. 11).
The downstream heated oxygen sensor threads into
the system depending on emission package (Fig. 12).
Federal package the O2s is mounted after the cata-
lytic convertor, LEV package the O2s is mounted mid
catalytic convertor, ULEV package is mounted
between the catalytic convertor (Fig. 13).
OPERATION
The O2 sensors produce voltages from 0 to 1 volt,
depending upon the oxygen content of the exhaust
gas in the exhaust manifold (Fig. 14). When a large
amount of oxygen is present (caused by a lean air/
fuel mixture), the sensors produce a voltage below
450 mv. When there is a lesser amount present (rich
air/fuel mixture) it produces a voltage above 450 mv.
By monitoring the oxygen content and converting it
to electrical voltage, the sensors act as a rich- lean
switch.
The oxygen sensors are equipped with a heating
element that keeps the sensors at proper operating
temperature during all operating modes. Maintaining
correct sensor temperature at all times allows the
system to enter into closed loop operation sooner.
Also, it allows the system to remain in closed loop
operation during periods of extended idle.
In Closed Loop operation the PCM monitors the O2
sensor input (along with other inputs) and adjusts
the injector pulse width accordingly. During Open
Loop operation the PCM ignores the O2 sensor input.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based on pre-
programmed (fixed) values and inputs from other
sensors.
The Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to both the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The oxygen sensors are
equipped with a heating element. The heating ele-
ments reduce the time required for the sensors to
reach operating temperature.
UPSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR 1/1
The input from the upstream heated oxygen sensor
tells the PCM the oxygen content of the exhaust gas.
Based on this input, the PCM fine tunes the air-fuel
ratio by adjusting injector pulse width.
The sensor input switches from 0 to 1 volt, depend-
ing upon the oxygen content of the exhaust gas in
the exhaust manifold. When a large amount of oxy-
gen is present (caused by a lean air-fuel mixture), the
sensor produces voltage as low as 0.1 volt. When
there is a lesser amount of oxygen present (rich air-
fuel mixture) the sensor produces a voltage as high
as 1.0 volt. By monitoring the oxygen content and
converting it to electrical voltage, the sensor acts as
a rich-lean switch.
The heating element in the sensor provides heat to
the sensor ceramic element. Heating the sensor
allows the system to enter into closed loop operation
sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain in closed
loop operation during periods of extended idle.
In Closed Loop, the PCM adjusts injector pulse
width based on the upstream heated oxygen sensor
input along with other inputs. In Open Loop, the
PCM adjusts injector pulse width based on prepro-
Fig. 11 Upstream Heated Oxygen Sensor 1/1
1 ± OXYGEN SENSORS
2 ± EXHAUST MANIFOLD
Fig. 12 Downstream Heated Oxygen Sensor 1/2
14 - 32 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)