wheel DODGE NEON 2000 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 65 of 1285
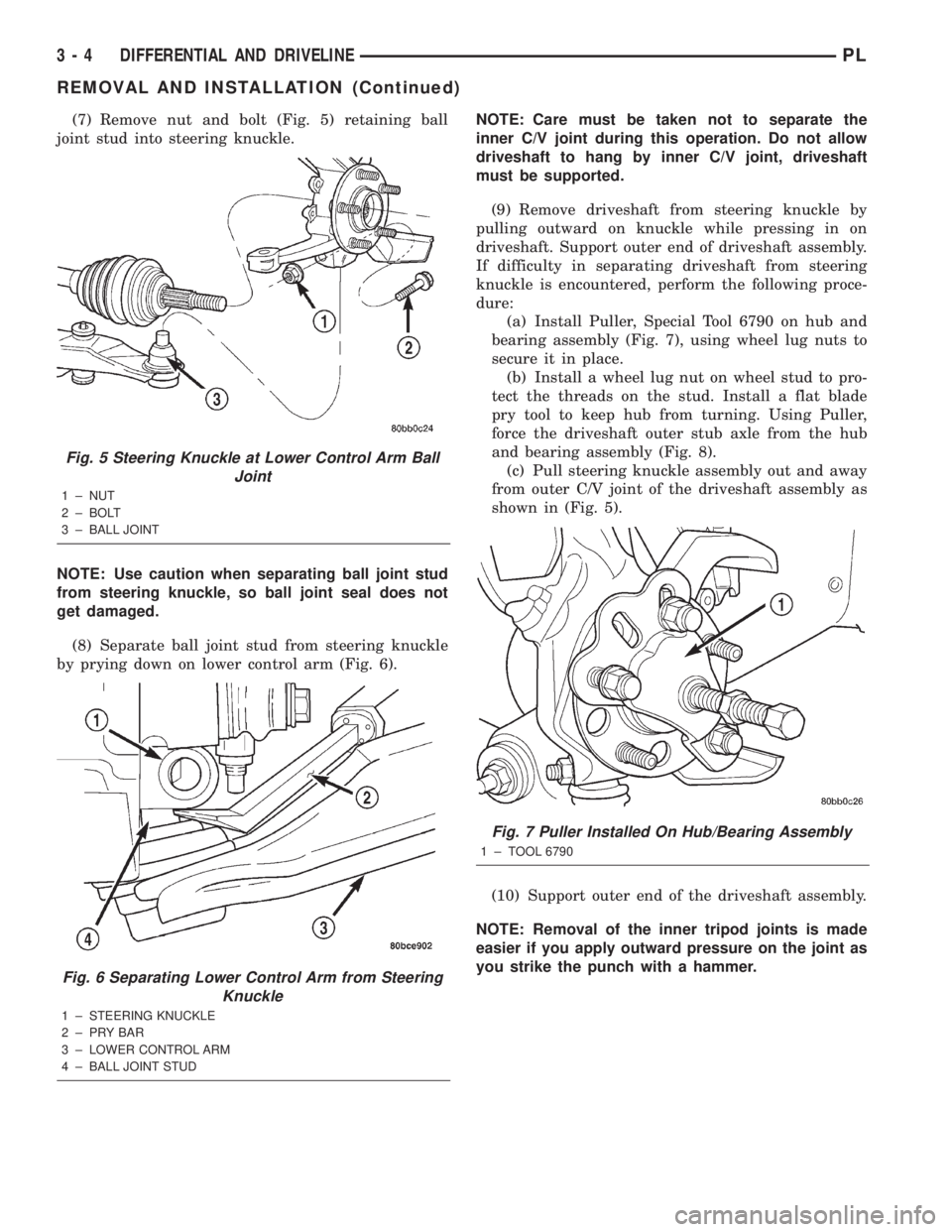
(7) Remove nut and bolt (Fig. 5) retaining ball
joint stud into steering knuckle.
NOTE: Use caution when separating ball joint stud
from steering knuckle, so ball joint seal does not
get damaged.
(8) Separate ball joint stud from steering knuckle
by prying down on lower control arm (Fig. 6).NOTE: Care must be taken not to separate the
inner C/V joint during this operation. Do not allow
driveshaft to hang by inner C/V joint, driveshaft
must be supported.
(9) Remove driveshaft from steering knuckle by
pulling outward on knuckle while pressing in on
driveshaft. Support outer end of driveshaft assembly.
If difficulty in separating driveshaft from steering
knuckle is encountered, perform the following proce-
dure:
(a) Install Puller, Special Tool 6790 on hub and
bearing assembly (Fig. 7), using wheel lug nuts to
secure it in place.
(b) Install a wheel lug nut on wheel stud to pro-
tect the threads on the stud. Install a flat blade
pry tool to keep hub from turning. Using Puller,
force the driveshaft outer stub axle from the hub
and bearing assembly (Fig. 8).
(c) Pull steering knuckle assembly out and away
from outer C/V joint of the driveshaft assembly as
shown in (Fig. 5).
(10) Support outer end of the driveshaft assembly.
NOTE: Removal of the inner tripod joints is made
easier if you apply outward pressure on the joint as
you strike the punch with a hammer.
Fig. 5 Steering Knuckle at Lower Control Arm Ball
Joint
1 ± NUT
2 ± BOLT
3 ± BALL JOINT
Fig. 6 Separating Lower Control Arm from Steering
Knuckle
1 ± STEERING KNUCKLE
2±PRYBAR
3 ± LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 ± BALL JOINT STUD
Fig. 7 Puller Installed On Hub/Bearing Assembly
1 ± TOOL 6790
3 - 4 DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 67 of 1285

CAUTION: The driveshaft, when installed, acts as a
bolt and secures the front hub/bearing assembly. If
vehicle is to be supported or moved on its wheels
with a driveshaft removed, install a PROPER±SIZED
BOLT AND NUT through front hub. Tighten bolt and
nut to 203 N´m (150 ft. lbs.). This will ensure that
the hub bearing cannot loosen.
INSTALLATION
(1) Thoroughly clean spline and oil seal sealing
surface, on tripod joint. Lightly lubricate oil seal
sealing surface on tripod joint with fresh clean trans-
mission lubricant.
(2) Holding driveshaft assembly by tripod joint and
interconnecting shaft, install tripod joint into tran-
saxle side gear as far as possible by hand.
(3) Carefully align tripod joint with transaxle side
gears. Then grasp driveshaft interconnecting shaft
and push tripod joint into transaxle side gear until
fully seated.Test that snap ring is fully engaged
with side gear by attempting to remove tripod
joint from transaxle by hand. If snap ring is
fully engaged with side gear, tripod joint will
not be removable by hand.
(4) Clean all debris and moisture out of steering
knuckle (Fig. 12).
(5) Ensure that front of outer C/V joint, which fits
into steering knuckle (Fig. 13), is free of debris and
moisture before assembling into steering knuckle.(6) Slide driveshaft back into front hub. Install
steering knuckle onto the ball joint stud (Fig. 14).
NOTE: At this point, the outer joint will not seat
completely into the front hub. The outer joint will be
pulled into hub and seated when the hub nut is
installed and torqued.
(7) Install aNEWsteering knuckle to ball joint
stud bolt and nut (Fig. 14). Tighten the nut and bolt
to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 12 Steering Knuckle to C/V Joint Sealing Area
1 ± STEERING KNUCKLE
2 ± WHEEL BEARING
3 ± FRONT HUB
4 ± THIS AREA OF THE STEERING KNUCKLE IS TO BE FREE
OF ALL DEBRIS AND MOISTURE BEFORE INSTALLING
DRIVE SHAFT IN STEERING KNUCKLE
Fig. 13 Outer C/V Joint Inspection
1 ± OUTER C/V JOINT
2 ± THIS AREA OF OUTER C/V JOINT MUST BE FREE OF ALL
DEBRIS AND MOISTURE, BEFORE INSTALLATION INTO
STEERING KNUCKLE.
Fig. 14 Driveshaft Installation Into Hub And Steering
Knuckle
1 ± NUT
2 ± BOLT
3 ± BALL JOINT
3 - 6 DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 68 of 1285

(8) Clean all foreign matter from threads of drive-
shaft outer stub axle. Install hub nut onto the
threads of the stub axle and tighten nut to 244 N´m
(180 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 15).
(9) Install front wheel and tire assembly. Install
front wheel lug nuts (Fig. 16) and tighten to 128 N´m
(95 ft. lbs.).(10) Check for correct fluid level in transaxle
assembly. Refer to Group 21 Transaxle, for the cor-
rect fluid level checking procedure for the type of
transaxle being checked.
(11) Lower vehicle.
(12) Connect battery negative cable.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
DRIVESHAFT RECONDITION
NOTE: The only service that is to be performed on
the driveshaft assemblies is the replacement of the
driveshaft seal boots.
If any failure of internal driveshaft components is
diagnosed during a vehicle road test or disassembly
of the driveshaft, the driveshaft will need to be
replaced as an assembly.
NOTE: Lubricant requirements and quantities are
different for inner joints than for outer joints. Use
only the recommended lubricants in the required
quantities when servicing driveshaft assemblies.
See (Fig. 17) for the exploded view of the front
driveshaft components.
INNER TRIPOD JOINT SEAL BOOT
REMOVAL
To remove sealing boot from driveshaft for replace-
ment, the driveshaft assembly must be removed from
the vehicle. See Driveshaft Removal and Installation
in this section for the required driveshaft removal
and replacement procedure.
The inner tripod joints use no internal retention in
the tripod housing to keep the spider assembly in the
housing. Therefore, do not pull on the interconnect-
ing shaft to disengage tripod housing from transmis-
sion stub shaft. Removal in this manner will cause
damage to the inboard joint sealing boots.
(1) Remove the driveshaft requiring boot replace-
ment from the vehicle. See Driveshaft Removal and
Installation in this section for the required driveshaft
removal procedure.
(2) Remove large boot clamp that retains inner tri-
pod joint sealing boot to tripod joint housing (Fig. 18)
and discard. Then remove small clamp that retains
inner tripod joint sealing boot to interconnecting
shaft and discard. Remove the sealing boot from the
tripod housing and slide it down the interconnecting
shaft.
Fig. 15 Driveshaft Retaining Nut Installation
1 ± DRIVESHAFT
2 ± HUB
3 ± HUB NUT
Fig. 16 Wheel and Tire Installation
1 ± WHEEL/TIRE ASSY.
2 ± LUG NUT (5)
3 ± HUB
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 78 of 1285

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Driveshaft-to-Hub/Bearing
Nut................... 244N´m(180 ft. lbs.)
Knuckle-to-Ball Joint
Bolt/Nut................. 95N´m(70ft.lbs.)
Wheel/Tire-to-Hub/Bearing
Lug Nuts............... 128N´m(95ft.lbs.)
SPECIAL TOOLS
DRIVESHAFT
Boot Clamp Installer C-4975A
Puller 6790
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 17
Page 80 of 1285
BRAKES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM...................... 1ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM................. 65
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION...........2
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS.........2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS....9
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER.................11
DRUM BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER........12
BRAKE ROTOR..........................12
BRAKE DRUM...........................15
PROPORTIONING VALVE..................15
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION.............17
SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL CHECKING............17
BASE BRAKE BLEEDING...................17
MASTER CYLINDER BLEEDING.............19
BRAKE TUBE REPAIR.....................19
BRAKE ROTOR MACHINING................21
BRAKE DRUM MACHINING.................22
PARKING BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER
LOCK OUT............................22
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS........23
BRAKE PEDAL...........................24
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH....................27
MASTER CYLINDER......................28
BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR.................29
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH..............30
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER.................30
PROPORTIONING VALVE..................32
BRAKES TUBES AND HOSES...............33
DISC BRAKE CALIPER (FRONT).............33
DISC BRAKE SHOES (FRONT)..............35BRAKE ROTOR (FRONT)...................37
DISC BRAKE CALIPER (REAR)..............38
DISC BRAKE SHOES (REAR)...............39
BRAKE ROTOR (REAR)....................41
DRUM BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER (REAR).....41
DRUM BRAKE SHOES (REAR)..............43
BRAKE DRUM (REAR).....................45
DRUM BRAKE SHOE SUPPORT PLATE
(REAR)...............................46
PARKING BRAKE LEVER...................48
PARKING BRAKE CABLE (REAR)............49
PARKING BRAKE SHOES (REAR DISC
BRAKE)...............................53
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
DISC BRAKE CALIPER (FRONT AND REAR)....55
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES................59
DISC BRAKES (FRONT)....................59
DISC BRAKES (REAR).....................60
DRUM BRAKES (REAR)....................60
ADJUSTMENTS
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH....................61
DRUM BRAKE SHOES.....................61
PARKING BRAKE SHOES (REAR DISC
BRAKES).............................62
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID...........................63
BRAKE ACTUATION SYSTEM...............63
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS.......................63
SPECIAL TOOLS
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM....................64
PLBRAKES 5 - 1
Page 81 of 1285

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION
When a vehicle needs to be stopped, the driver
applies the brake pedal. The brake pedal pushes the
input rod of the power brake booster into the booster.
The booster uses vacuum to ease pedal effort as force
is transferred through the booster to the master cyl-
inder. The booster's output rod pushes in the master
cylinder's primary and secondary pistons applying
hydraulic pressure through the chassis brake tubes
and proportioning valves (rear only) to the brakes at
each tire and wheel assembly.
Front disc brakes control the braking of the front
wheels; rear braking is controlled by rear drum
brakes as standard equipment. Rear disc brakes and
an antilock brake system (ABS) with traction control
are optional.
The hydraulic brake system is diagonally split on
both the non-antilock and antilock braking systems.
This means the left front and right rear brakes are
on one hydraulic circuit and the right front and left
rear are on the other.
Vehicles equipped with the optional antilock brake
system (ABS) use a system designated Mark 20e.
This system shares most base brake hardware used
on vehicles without ABS. A vehicle equipped with
ABS, however, uses a different master cylinder and
brake tubes. Also included in the ABS system is an
integrated control unit (ICU) and four wheel speed
sensors. These components are described in detail in
the ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM section in this
group of the service manual. All vehicles with ABS
come standard with four-wheel-disc brakes and trac-
tion control.
The parking brakes are hand-operated. When
applied, the parking brake lever pulls on cables that
actuate brake shoes at each rear wheel. The parking
brake lever has an automatic adjusting feature that
takes up any excessive slack in the parking brake
cable system.
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
BRAKE PEDAL
A suspended-type brake pedal is used on this vehi-
cle. The pedal pivots on a shaft mounted in the pedal
support bracket under the instrument panel. The
pedal connects to the power brake booster input rod
and pushes it in when the pedal is applied.
The brake pedal and it's pad are serviceable sepa-
rately.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
There are two different power brake booster
designs, although externally they appear the same.
All vehicles use a 205 mm tandem diaphragm power
brake booster. The two boosters are internally tuned
differently depending on whether the vehicle is
equipped with the standard front disc/rear drum
brake combination or the optional front disc/rear disc
(four-wheel disc) brake combination. If the power
brake booster requires replacement, be sure it is
replaced with the correct part.
The power brake booster can be identified by the
tag attached to the body of the booster assembly (Fig.
1). This tag contains the following information: The
production part number of the power brake booster,
the date it was built and who manufactured it.
The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop the vehicle.
The power brake booster is vacuum-operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through the power brake booster check valve
(Fig. 2).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power booster
input rod moves forward. This opens and closes
valves in the power brake booster, allowing atmo-
spheric pressure to enter on one side of a diaphragm.
Engine vacuum is always present on the other side.
This difference in pressure forces the output rod of
the power booster out against the primary piston of
the master cylinder. As the pistons in the master cyl-
inder move forward, hydraulic pressure is created in
the brake system.
Fig. 1 Master Cylinder and Power Brake Booster
1 ± POWER BRAKE BOOSTER PARTS IDENTIFICATION TAG
2 ± POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
3 ± BRAKE FLUID PRESSURE SWITCH
4 ± MASTER CYLINDER
5 - 2 BRAKESPL
Page 83 of 1285

Proportioning valves balance front to rear braking
by controlling the brake fluid hydraulic pressure to
the rear brakes. Under light pedal application, the
proportioning valve allows normal fluid flow to the
rear brakes. Under higher pedal effort, the valve
reduces fluid pressure to the rear brakes.
The non-antilock master cylinder is a four-outlet
design with two screw-in proportioning valves
attached directly to the master cylinder housing (Fig.
3). One proportioning valve controls each rear brake.
BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The purpose of the brake tubes and flex hoses is to
transfer the pressurized brake fluid developed by the
master cylinder to the brakes at each wheel of the
vehicle. The flex hoses connect the chassis brake
tubes, which are mounted to the vehicle's underbody,
to the brake at each wheel, allowing for movement of
the vehicle's suspension. The brake tubes are steel
with a corrosion-resistant nylon coating applied to
the external surfaces. The flex hoses are made of
reinforced rubber.
DISC BRAKES (FRONT)
The front disc brakes consist of the following com-
ponents (Fig. 4):
²Brake caliper - single-piston, floating type
²Brake shoes and linings
²Brake rotorWhen the brakes are applied, fluid pressure is sent
to each brake caliper. The pressure at the caliper is
exerted equally against the caliper piston. The pres-
sure applied to the piston is transmitted directly to
the inboard brake shoe. This forces the shoe lining
against the inner surface of the brake rotor. At the
same time, fluid pressure within the caliper piston
bore forces the caliper to slide inward on its guide
pins. This action brings the outboard shoe lining into
contact with the outer surface of the brake rotor.
This pressure on both sides of the brake rotor causes
friction, bringing the vehicle to a stop.
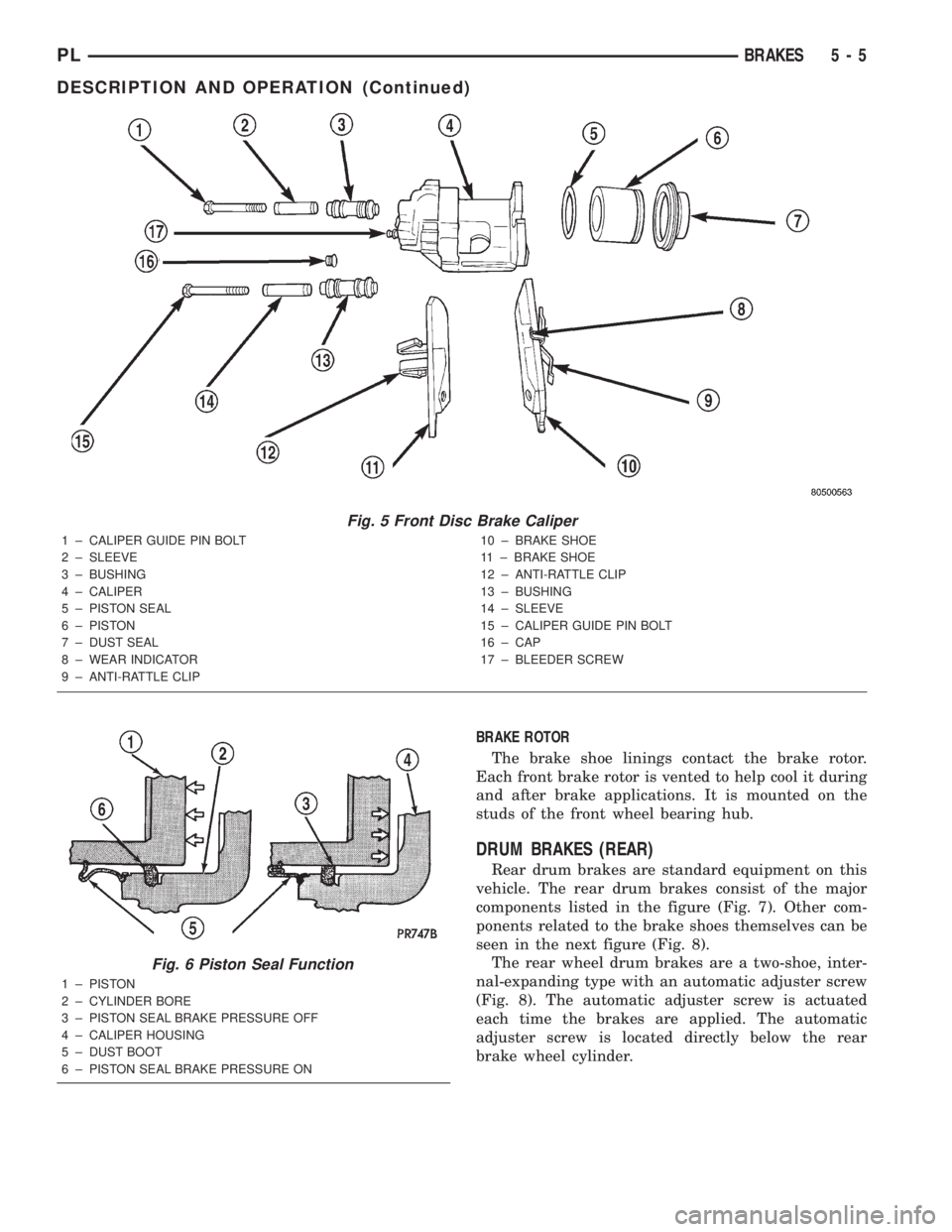
BRAKE CALIPER
The caliper is a one-piece casting with the inboard
side containing a single piston cylinder bore (Fig. 5).
The front disc brake caliper piston, is manufac-
tured from a phenolic compound. The outside diame-
ter of the caliper piston is 54 mm.
A square-cut rubber piston seal is located in a
machined groove in the caliper cylinder bore. This
provides a hydraulic seal between the piston and the
cylinder wall (Fig. 6). The piston seal is designed to
pull the piston back into the bore of the caliper when
the brake pedal is released. This maintains the
proper brake shoe-to-rotor clearance.
A rubber dust boot is installed in the cylinder bore
opening and in a groove in the piston (Fig. 6). This
prevents contamination in the bore area.
The caliper is mounted to the steering knuckle
using bushings, sleeves and two guide pin bolts (Fig.
5). The guide pin bolts thread directly into bosses on
the steering knuckle.
Two machined abutments on the steering knuckle
position the caliper. The guide pin bolts, sleeves, and
bushings control the side-to-side movement of the
caliper. All of the front brake force generated during
braking of the vehicle is taken up directly by the
steering knuckles of the vehicle.
BRAKE SHOES AND LININGS
There are two brake shoes mounted to each caliper,
one inboard and one outboard (Fig. 5). When brake
shoes are replaced, only brake shoes meeting the
original equipment manufacturer (OEM) formulation
(such as Mopartreplacement parts) should be used.
As front disc brake shoe linings wear, master cyl-
inder reservoir brake fluid level will drop. Fluid level
should be checked after replacing shoes.
Front disc brakes are equipped with an audible
wear indicator on the outboard brake pad (Fig. 5).
This sensor emits a sound when the brake lining
may need inspection or replacement.
Fig. 4 Front Disc Brakes
1 ± STEERING KNUCKLE
2 ± BRAKE PADS AND LININGS
3 ± BRAKE ROTOR
4 ± DRIVING HUB
5 ± CALIPER ASSEMBLY
5 - 4 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 84 of 1285
BRAKE ROTOR
The brake shoe linings contact the brake rotor.
Each front brake rotor is vented to help cool it during
and after brake applications. It is mounted on the
studs of the front wheel bearing hub.
DRUM BRAKES (REAR)
Rear drum brakes are standard equipment on this
vehicle. The rear drum brakes consist of the major
components listed in the figure (Fig. 7). Other com-
ponents related to the brake shoes themselves can be
seen in the next figure (Fig. 8).
The rear wheel drum brakes are a two-shoe, inter-
nal-expanding type with an automatic adjuster screw
(Fig. 8). The automatic adjuster screw is actuated
each time the brakes are applied. The automatic
adjuster screw is located directly below the rear
brake wheel cylinder.
Fig. 5 Front Disc Brake Caliper
1 ± CALIPER GUIDE PIN BOLT
2 ± SLEEVE
3 ± BUSHING
4 ± CALIPER
5 ± PISTON SEAL
6 ± PISTON
7 ± DUST SEAL
8 ± WEAR INDICATOR
9 ± ANTI-RATTLE CLIP10 ± BRAKE SHOE
11 ± BRAKE SHOE
12 ± ANTI-RATTLE CLIP
13 ± BUSHING
14 ± SLEEVE
15 ± CALIPER GUIDE PIN BOLT
16 ± CAP
17 ± BLEEDER SCREW
Fig. 6 Piston Seal Function
1 ± PISTON
2 ± CYLINDER BORE
3 ± PISTON SEAL BRAKE PRESSURE OFF
4 ± CALIPER HOUSING
5 ± DUST BOOT
6 ± PISTON SEAL BRAKE PRESSURE ON
PLBRAKES 5 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 85 of 1285

DISC BRAKES (REAR)
Rear disc brakes are optional equipment on some
models of this vehicle (Fig. 9). The rear disc brakes
are similar to the front disc brakes; however, there
are several distinctive features that require different
service procedures. The rear disc brakes consist of
the following components:
²Brake caliper - single-piston, floating type
²Brake caliper adapter
²Brake shoe and linings
²Brake rotor - drum-in-hat type
All vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes have a
small duo-servo drum brake mounted to the caliper
adapter. This is part of the parking brake system.
The drum brake shoes expand out against a braking
surface (hat section) on the inside area of the disc
brake rotor.
BRAKE CALIPER
Vehicles are equipped with a caliper assembly that
has a 34 mm (1.43 in.) piston and uses a solid non-
vented rotor.
The caliper assembly for all applications floats on
rubber bushings using internal metal sleeves that
are attached to the adapter using threaded guide pin
bolts.
BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER
The brake caliper adapter and rotor shield are
mounted to the rear suspension knuckles of vehicle.
Fig. 7 Rear Drum Brakes
1 ± DUST CAP
2 ± NUT
3 ± DRUM
4 ± HUB AND BEARING
5 ± WHEEL CYLINDER
6 ± SEAL
7 ± SUPPORT PLATE
8 ± BRAKE SHOES
9 ± RETAINER CLIP
Fig. 8 Drum Brake Shoes (Left Side Shown)
1 ± WHEEL CYLINDER
2 ± AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER SCREW ASSEMBLY
3 ± RETURN SPRING
4 ± HOLD DOWN CLIP
5 ± HOLD DOWN CLIP
6 ± AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER LEVER AND SPRING
7 ± PARK BRAKE LEVER
8 ± PARK BRAKE CABLE
9 ± FRONT BRAKE SHOE
10 ± BRAKE SHOE TO ANCHOR SPRING
11 ± BRAKE ANCHOR PLATE
12 ± REAR BRAKE SHOE
Fig. 9 Rear Disc Brakes
1 ± DISC BRAKE CALIPER
2 ± DISC BRAKE ADAPTER
3 ± GUIDE PIN BOLTS
4 ± HUB AND BEARING
5 ± BRAKE ROTOR
6 ± RETAINER CLIP
7 ± DUST CAP
8 ± NUT
5 - 6 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 86 of 1285

The adapter is used to mount the brake caliper to the
vehicle (Fig. 9). The adapter has two machined abut-
ments, which are used to position and align the cal-
iper and brake pads for movement inboard and
outboard. The adapter also mounts the parking brake
shoes and actuating cables to the vehicle.
PARKING BRAKES
The parking brakes (Fig. 4) consist of the following
components:
²Hand-operated park brake lever - automatic-ad-
justing
²Parking brake cables
²Actuation levers and struts
²Duo-servo parking brake assembly (rear disc
only)
PARKING BRAKE LEVER
All vehicles are equipped with a center-mounted,
hand-operated parking brake lever mounted between
the front seats (Fig. 10). This lever is an automatic-
adjusting type that continuously applies minimal
tension to the parking brake cables to keep them in
adjustment at all times. Due to this feature, the
parking brake cable system does not require adjust-
ment. Proper parking brake system adjustment is
obtained by proper drum brake or drum-in-hat brake
shoe adjustment. When service is needed, the lever
auto-adjust mechanism must be reloaded and locked
out before service can be performed.
The parking brake lever has a short output cable
with an equalizer bracket attached to it that connects
to the parking brake cables (Fig. 10). The output
cable can only be serviced as part of the parking
brake lever.PARKING BRAKE CABLES
There is an individual parking brake cable for each
rear wheel that joins a parking cable equalizer,
attached to the parking brake lever, to the rear park-
ing brakes. The parking brake cables are made of
flexible steel cable. Both drum rear brakes and disc
rear brakes use the same parking brake cable config-
uration, but the cables are different.
PARKING BRAKES
On vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, the
rear wheel service brakes also act as the vehicle's
parking brakes. The rear drum brake shoes, when
acting as parking brakes, are mechanically operated
using an internal actuating lever and strut connected
to the flexible steel parking brake cable.
The parking brakes on vehicles equipped with rear
disc brakes consist of a small duo-servo brake assem-
bly mounted to the disc brake caliper adapter (Fig.
11). The hat (center) section of the rear brake rotor
serves as the braking surface (drum) for the parking
brakes (Fig. 12). This parking brake application uses
the same operating cable configuration as the drum
brake equipped vehicles, but different cables.
Fig. 10 Parking Brake Lever
1 ± PARKING BRAKE LEVER
2 ± PARKING BRAKE WARNING LAMP SWITCH
3 ± OUTPUT CABLEFig. 11 Parking Brake Assembly With Rear Disc
Brakes
1 ± DISC BRAKE ADAPTER
2 ± PARKING BRAKE BRAKE SHOES
3 ± HUB/BEARING ASSEMBLY
4 ± BRAKING DISC STONE SHIELD
5 ± PARKING BRAKE ACTUATING STRUT
PLBRAKES 5 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)