tra DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 1068 of 1285

Bearing Splitter P-334
Bearing Cone Remover 5048
Bearing Installer 5052
Bearing Cup Remover 6062-A
Bearing Installer 6536-A
Cooling System Tester 7700
Seal Remover 7794-a
End Play SetÐ8266
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 155
SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
Page 1070 of 1285

TIRES AND WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES................................... 1WHEELS................................ 10
TIRES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TIRE...................................1
RADIAL-PLY TIRES........................2
SPARE TIRE±TEMPORARY..................3
REPLACEMENT TIRES.....................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS.................3
TIRE WEAR PATTERNS.....................4
TIRE NOISE OR VIBRATION.................4
VEHICLE LEAD DIAGNOSIS AND
CORRECTION..........................4
SERVICE PROCEDURES
PRESSURE GAUGES......................6TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES...............6
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION............................6
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION................6
REPAIRING TIRE LEAKS....................7
TIRE AND WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING.........7
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLEANING TIRES.........................9
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRE SPECIFICATIONS.....................9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TIRE
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle (Fig. 1). They provide the best overall perfor-
mance for normal operation. The ride and handling
characteristics match the vehicle's requirements.
With proper care they will give excellent reliability,
traction, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:²Rapid acceleration
²Severe application of brakes
²High-speed driving
²Taking turns at excessive speeds
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
²Operating vehicle with over or under inflated
tire pressures
Radial ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation. This will
help to achieve a greater tread-life potential.
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 1
Page 1071 of 1285
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 2).
Performance tires will have a speed rating letter
after the aspect ratio number. For example, the letter
ªSº indicates that the tire is speed rated up to 112
mph (180 km/h). The speed rating is not always
printed on the tire sidewall.
²Q -up to 100 mph (160 km/h)
²T -up to 118 mph (190 km/h)
²U -up to 124 mph (200 km/h)
²H -up to 130 mph (210 km/h)
²V -up to 149 mph (240 km/h)
²Z -more than 149 mph (240 km/h) (consult the
tire manufacturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
& S or M-S (indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Refer to the owners manual supplied with the vehi-
cle to determine whether the use of tire chains is per-
mitted on this vehicle.
RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
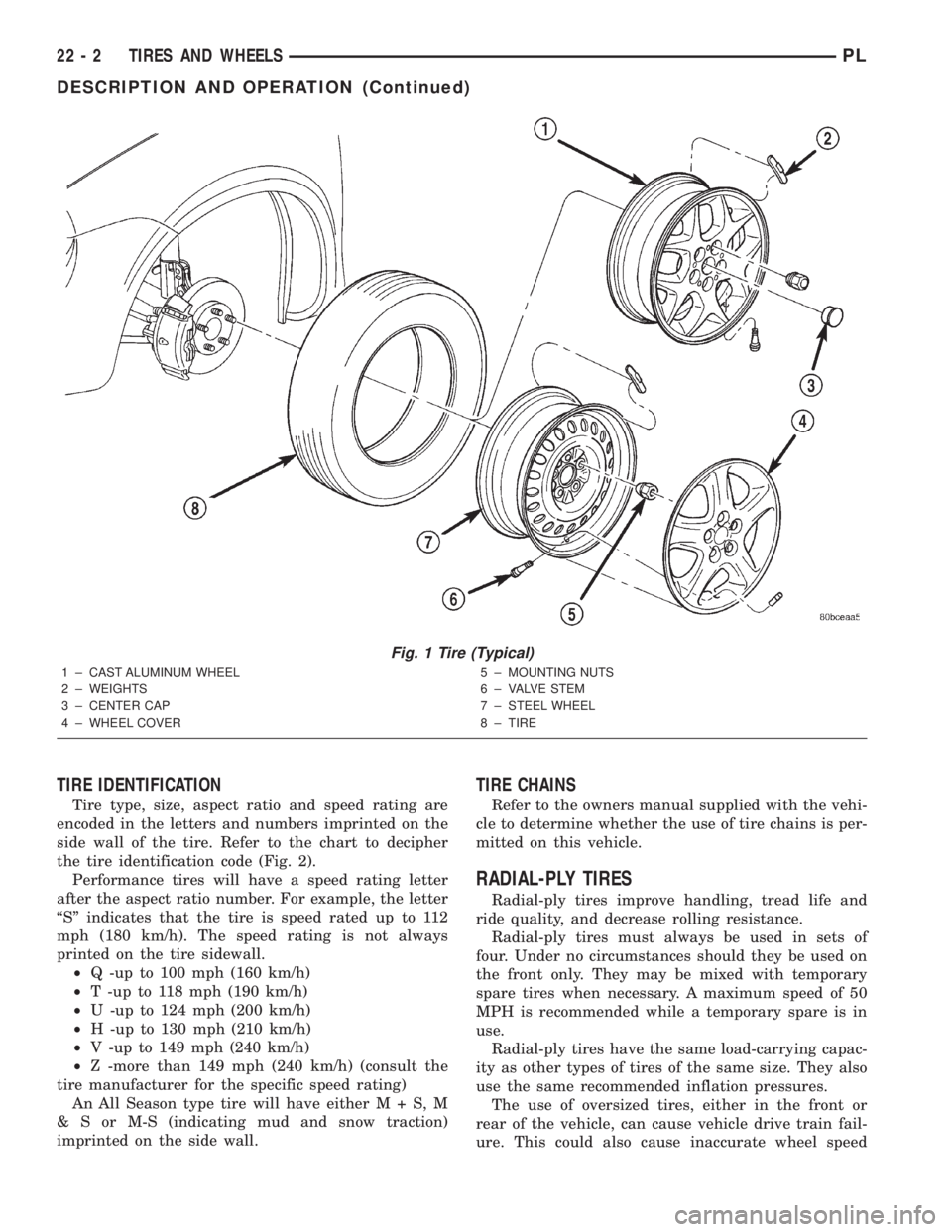
Fig. 1 Tire (Typical)
1 ± CAST ALUMINUM WHEEL
2 ± WEIGHTS
3 ± CENTER CAP
4 ± WHEEL COVER5 ± MOUNTING NUTS
6 ± VALVE STEM
7 ± STEEL WHEEL
8 ± TIRE
22 - 2 TIRES AND WHEELSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1072 of 1285

signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
SPARE TIRE±TEMPORARY
The temporary spare tire is designed for emer-
gency use only. The original tire should be repaired
or replaced at the first opportunity, then reinstalled.
Do not exceed speeds of 50 M. P. H. when using the
temporary spare tire. Refer to Owner's Manual for
complete details.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
The original equipment tires provide a proper bal-
ance of many characteristics such as:
²Ride
²Noise
²Handling
²Durability
²Tread life
²Traction
²Rolling resistance
²Speed capabilityIt is recommend that tires equivalent to the origi-
nal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed.
Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehi-
cle.
The use of oversize tires may cause interference
with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspen-
sion and steering travel, interference with vehicle
components may cause tire damage.
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 3).
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
Fig. 2 Tire Identification
Fig. 3 Tread Wear Indicators
1 ± TREAD ACCEPTABLE
2 ± TREAD UNACCEPTABLE
3 ± WEAR INDICATOR
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1075 of 1285
SERVICE PROCEDURES
PRESSURE GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
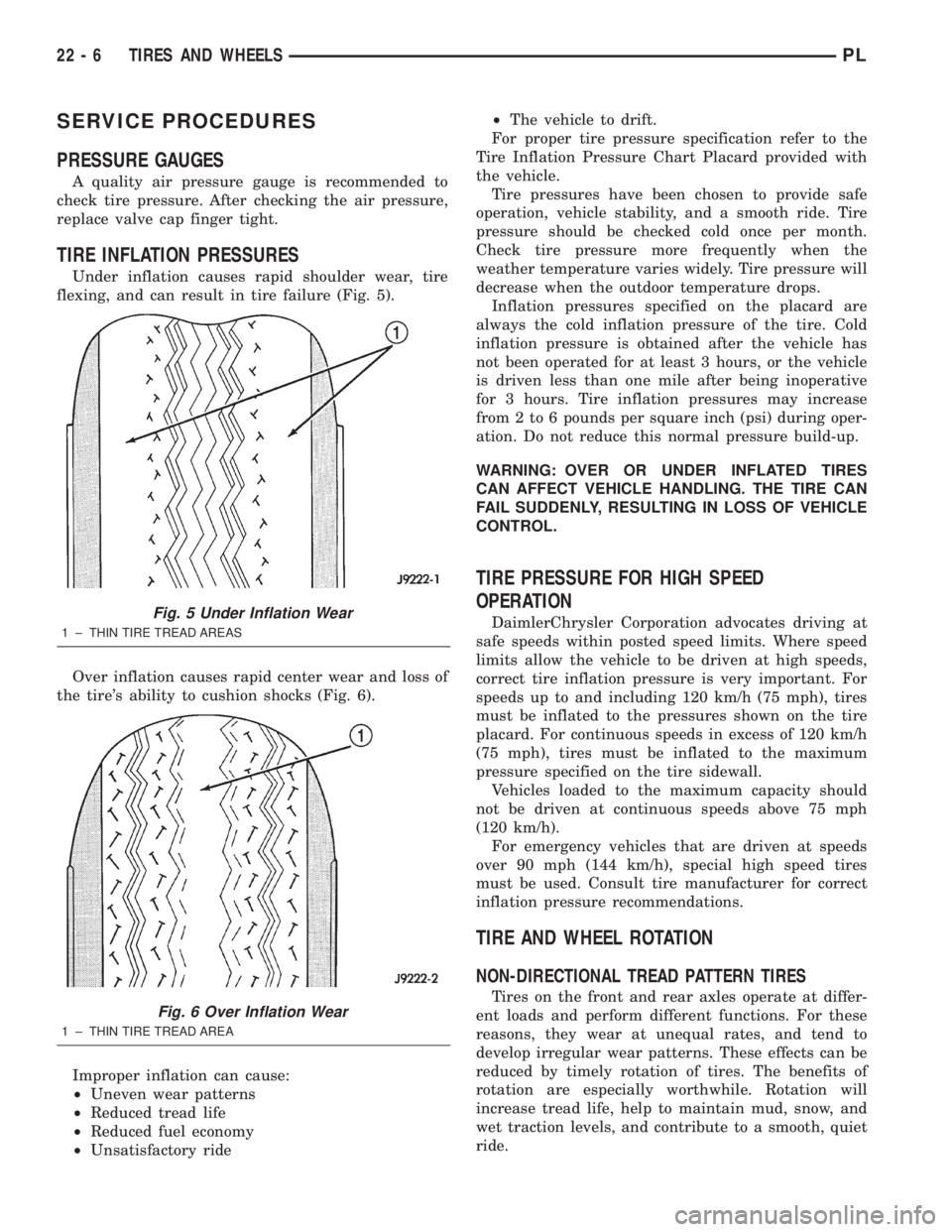
Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and can result in tire failure (Fig. 5).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 6).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride²The vehicle to drift.
For proper tire pressure specification refer to the
Tire Inflation Pressure Chart Placard provided with
the vehicle.
Tire pressures have been chosen to provide safe
operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth ride. Tire
pressure should be checked cold once per month.
Check tire pressure more frequently when the
weather temperature varies widely. Tire pressure will
decrease when the outdoor temperature drops.
Inflation pressures specified on the placard are
always the cold inflation pressure of the tire. Cold
inflation pressure is obtained after the vehicle has
not been operated for at least 3 hours, or the vehicle
is driven less than one mile after being inoperative
for 3 hours. Tire inflation pressures may increase
from 2 to 6 pounds per square inch (psi) during oper-
ation. Do not reduce this normal pressure build-up.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES
CAN AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN
FAIL SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
CONTROL.
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION
DaimlerChrysler Corporation advocates driving at
safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed
limits allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds,
correct tire inflation pressure is very important. For
speeds up to and including 120 km/h (75 mph), tires
must be inflated to the pressures shown on the tire
placard. For continuous speeds in excess of 120 km/h
(75 mph), tires must be inflated to the maximum
pressure specified on the tire sidewall.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
For emergency vehicles that are driven at speeds
over 90 mph (144 km/h), special high speed tires
must be used. Consult tire manufacturer for correct
inflation pressure recommendations.
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION
NON-DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Tires on the front and rear axles operate at differ-
ent loads and perform different functions. For these
reasons, they wear at unequal rates, and tend to
develop irregular wear patterns. These effects can be
reduced by timely rotation of tires. The benefits of
rotation are especially worthwhile. Rotation will
increase tread life, help to maintain mud, snow, and
wet traction levels, and contribute to a smooth, quiet
ride.
Fig. 5 Under Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREAS
Fig. 6 Over Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREA
22 - 6 TIRES AND WHEELSPL
Page 1076 of 1285

The suggested rotation method is the forward-cross
tire rotation method (Fig. 7). This method takes
advantage of current tire industry practice which
allows rotation of radial-ply tires. Other rotation
methods may be used, but may not have all the ben-
efits of the recommended method.
NOTE: Only the 4 tire rotation method may be used
if the vehicle is equipped with a low mileage or tem-
porary spare tire.
DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Some vehicles are fitted with special high-perfor-
mance tires having a directional tread pattern. These
tires are designed to improve traction on wet pave-
ment. To obtain the full benefits of this design, the
tires must be installed so that they rotate in the cor-
rect direction. This is indicated by arrows on the tire
sidewalls.
When wheels and tires are being installed, extra
care is needed to ensure that this direction of rota-
tion is maintained.
Refer to Owner's Manual for rotation schedule.
REPAIRING TIRE LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 8). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.Deflate tire completely before attempting to dis-
mount the tire from the wheel.Use a lubricant
such as a mild soap solution when dismounting
or mounting tire.Use tools free of burrs or sharp
edges which could damage the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and progressively tighten
the 5 wheel nuts to a torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
TIRE AND WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING
Wheels and tires are match mounted at the factory.
This means that the high spot of the tire is matched
to the low spot on the wheel rim. This technique is
used to reduce run-out in the wheel/tire assembly.
The high spot on the tire is marked with a paint
mark or a bright colored adhesive label on the out-
board sidewall. The low spot on the rim is identified
with a label on the outside of the rim and a dot or
line in the drop well on the tire side of the rim. If the
outside label has been removed the tire will have to
be removed to locate the dot or line on the inside of
the rim.
Before dismounting a tire from its wheel, a refer-
ence mark should be placed on the tire at the valve
stem location. This reference will ensure that it is
remounted in the original position on the wheel.
Fig. 7 Forward-Cross Tire Rotation Method
Fig. 8 Tire Repair Area
1 ± REPAIRABLE AREA
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 7
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1083 of 1285
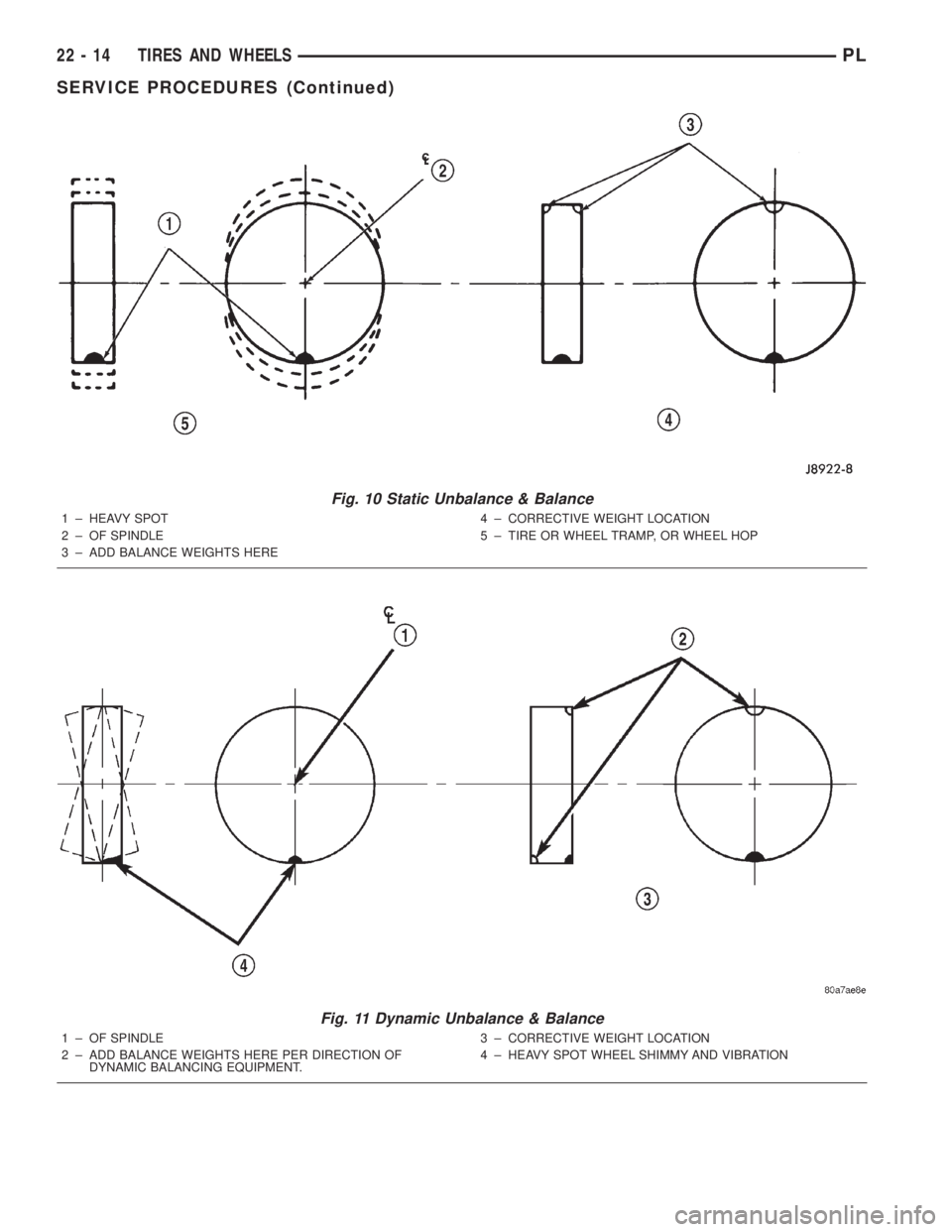
Fig. 10 Static Unbalance & Balance
1 ± HEAVY SPOT
2 ± OF SPINDLE
3 ± ADD BALANCE WEIGHTS HERE4 ± CORRECTIVE WEIGHT LOCATION
5 ± TIRE OR WHEEL TRAMP, OR WHEEL HOP
Fig. 11 Dynamic Unbalance & Balance
1 ± OF SPINDLE
2 ± ADD BALANCE WEIGHTS HERE PER DIRECTION OF
DYNAMIC BALANCING EQUIPMENT.3 ± CORRECTIVE WEIGHT LOCATION
4 ± HEAVY SPOT WHEEL SHIMMY AND VIBRATION
22 - 14 TIRES AND WHEELSPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1084 of 1285

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WHEEL COVER (LOCK-ON)
REMOVE
NOTE: When unthreading the wheel cover retaining
nuts (Fig. 12) from the wheel nuts it is recom-
mended that a hand wrench be used and not an
impact wrench. Use of an impact wrench could
result in damage to the lock-on wheel cover retain-
ing nuts.
(1) Un-thread the 5 nuts (Fig. 12) attaching the
wheel cover to the wheel nuts.
(2) Grasp the wheel cover and pull straight out-
ward from the wheel. This will remove the wheel
cover from the wheel.
INSTALL
(1) Align the valve notch in the wheel cover with
the valve stem on the wheel (Fig. 12). Align the
wheel cover retaining nuts with the externally
threaded wheel nuts.
(2) By hand, start to thread all 5 of the wheel
cover retaining nuts onto the externally threaded
wheel nuts.
NOTE: When tightening the wheel cover retaining
nuts it is recommended that a hand wrench be used
and not an impact wrench. Use of an impact wrenchcould result in damage to the lock-on wheel cover
retaining nuts.
(3) Tighten each of the wheel cover retaining nuts.
If the retaining nut ªjumpsº a thread (slips), which is
an override feature of the retaining nut, retighten
the retaining nut to a point just prior to this occur-
ring. To avoid rattling of the wheel cover be sure all
five retaining nuts are correctly tightened.
WHEEL COVER RETAINING NUT
If a retaining nut for the lock-on wheel cover is
damaged, it can be replaced as a separate component
of the wheel cover. Use the following procedure for
replacing a wheel cover retaining nut.
REMOVE
(1) If required, remove the wheel cover from the
wheel. Refer to Wheel Cover Lock-On in the Removal
And Installation Section in this group of the service
manual for the procedure.
NOTE: The retaining nut flange can not be forced
past the large retaining tab. When removing retain-
ing nut from wheel cover, the flange on the retain-
ing nut must be forced past the 2 small retaining
tabs on wheel cover.
(2) From the back side of the wheel cover, push
outward and tilt the retaining nut sideways forcing
the flange on the retaining nut past the 2 small
retaining tabs in the retaining nut hole of the wheel
cover (Fig. 13).
Fig. 12 Wheel Cover Retaining Nuts
1 ± TIRE
2 ± VALVE STEM
3 ± LOCK-ON WHEEL COVER
4 ± WHEEL
5 ± WHEEL COVER RETAINING NUTS
Fig. 13 Wheel Cover Retaining Nut Retention
1 ± WHEEL COVER
2 ± WHEEL COVER RETAINING NUT
3 ± SMALL RETAINING TABS
4 ± LARGE RETAINING TAB
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 15
Page 1086 of 1285

(3) Grasp the wheel cover and pull straight out-
ward. This will remove the wheel cover from the
wheel.
(4) Remove the wheel mounting nuts from the
studs (Fig. 16).
(5) Remove the tire and wheel assembly from the
hub.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Installing the wheel mounting nuts with-
out having good metal-to-mental contact between
the back of the wheel and the hub mounted brake
disc or drum could cause the wheel to bind and
eventually cause loosening of the wheel mounting
nuts.
(1) Install the tire and wheel assembly on the hub
studs against the hub mounted brake disc or drum
using the hub pilot as a guide.
CAUTION: When installing the tire and wheel
assembly, never use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
(2) Install and lightly tighten the wheel nuts in
the proper sequence (Fig. 17).
(3) Lower the vehicle.
(4) Progressively tighten the 5 wheel nuts in the
proper sequence until tightened to half of the speci-
fied torque (Fig. 17). Finally, tighten the wheel nutsin the proper sequence to a torque of 135 N´m (100
ft. lbs.).
(5) Align the valve notch in the wheel cover with
the valve stem on the wheel (Fig. 15). Align the
wheel cover retaining nuts with the externally
threaded wheel nuts.
(6) By hand, start to thread all 5 of the wheel
cover retaining nuts onto the externally threaded
wheel nuts.
NOTE: When tightening the wheel cover retaining
nuts it is recommended that a hand wrench be used
and not an impact wrench. Use of an impact wrench
could result in damage to the lock-on wheel cover
retaining nuts.
(7) Tighten each of the wheel cover retaining nuts.
If the retaining nut ªjumpsº a thread (slips), which is
an override feature of the retaining nut, retighten
the retaining nut to a point just prior to this occur-
ring. To avoid rattling of the wheel cover be sure all
five retaining nuts are correctly tightened.
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL SPECIFICATIONS
Wheel:
Wheel Mounting Stud Size...... M12x1.5mm
Wheel Mounting Nut Hex Size......... 19mm
Wheel Mounting Nut Torque..... 115±155 N´m
(85 to 115 ft. lbs.)
Fig. 16 Wheel Nuts
1 ± WHEEL
2 ± EXTERNALLY THREADED WHEEL NUTS
3 ± TIRE
Fig. 17 Wheel Nut Tightening Sequence
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1088 of 1285

EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS................... 1 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROLS......... 25
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION....................1
TASK MANAGER..........................2
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)........5
DRB III STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE..........5
DRB III CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE......5
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES..............5
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DESCRIPTIONS.........................6MONITORED SYSTEMS....................15
TRIP DEFINITION........................19
MONITORED COMPONENT.................19
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS...............23
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS....................24
LOAD VALUE............................24
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
OBD II requires that vehicles falling under OBD II
guidelines utilize the following system monitors:
²Comprehensive Component Monitor (inputs/out-
puts for powertrain management that affect emis-
sions, but do not have a specific major monitor)
²Fuel Control Monitor (fuel compensation
required to maintain stoichiometric ratio rich/lean)
²Misfire Monitor (change in crankshaft speed)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor (response and
performance of oxygen sensors)
²Catalyst Monitor (Performance and efficiency of
catalyst)
²Evaporative Emissions Monitor (performance of
and leaks from EVAP system)
²Exhaust Gas Recirculation Monitor (flow perfor-
mance of EGR system)
The software was rewritten to enable the PCM to
carry out the responsibilities to meet these required
guidelines. The PCM now contains a Task Manager.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a
problem with a monitored circuit often enough to
indicate an actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the
code applies to a non-emissions related component or
system, and the problem is repaired or ceases to
exist, the PCM cancels the code after 40 warmup
cycles. Diagnostic trouble codes that affect vehicle
emissions illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL). Refer to Malfunction Indicator Lamp in this
section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored
circuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This
may happen because one of the DTC criteria for the
circuit has not been met.For example, assume the
diagnostic trouble code criteria requires the PCM to
monitor the circuit only when the engine operates
between 750 and 2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor's
output circuit shorts to ground when engine operates
above 2400 RPM (resulting in 0 volt input to the
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 1