tra DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 1092 of 1285

MISFIRE
²Same Misfire Warm-Up StateÐ Indicates if
the misfire occurred when the engine was warmed up
(above 160É F).
²In Similar Misfire WindowÐ An indicator
that 'Absolute MAP When Misfire Occurred' and
'RPM When Misfire Occurred' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Misfire OccurredÐ
The stored MAP reading at the time of failure.
Informs the user at what engine load the failure
occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Misfire OccurredÐ The stored
RPM reading at the time of failure. Informs the user
at what engine RPM the failure occurred.
²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM uti-
lizes both Short Term Compensation and Long Term
Adaptive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor
for total fuel correction.
²200 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±100 720 degree
cycles.
²SCW Cat 200 Rev CounterÐ Counts when in
similar conditions.
²SCW FTP 1000 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±4
when in similar conditions.
²Misfire Good Trip CounterÐ Counts up to
three to turn OFF the MIL.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)
OPERATION
As a functional test, the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) illuminates at key-on before engine
cranking. Whenever the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) sets a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that
affects vehicle emissions, it illuminates the MIL. If a
problem is detected, the PCM sends a message over
the PCI Bus to the instrument cluster to illuminate
the lamp. The PCM illuminates the MIL only for
DTC's that affect vehicle emissions. The MIL stays
on continuously when the PCM has entered a
Limp-In mode or identified a failed emission compo-
nent or system. The MIL remains on until the DTC
is erased. Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Code
charts in this group for emission related codes.
Also, the MIL either flashes or illuminates contin-
uously when the PCM detects active engine misfire.
Refer to Misfire Monitoring in this section.Additionally, the PCM may reset (turn off) the MIL
when one of the following occur:
²PCM does not detect the malfunction for 3 con-
secutive trips (except misfire and fuel system moni-
tors).
²PCM does not detect a malfunction while per-
forming three successive engine misfire or fuel sys-
tem tests. The PCM performs these tests while the
engine is operating within6375 RPM of and within
10 % of the load of the operating condition at which
the malfunction was first detected.
DRB III STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
OPERATION
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. From
the state display screen, access either State Display
Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
DRB III CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
OPERATION
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
DESCRIPTION
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.
Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1097 of 1285

(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
P0456 Evap Leak Monitor Small Leak
Detected
P0460 Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
MilesNo movement of fuel level sender detected.
P0461 Fuel Level Unit No Changeover
TimeNo level of fuel level sender detected.
P0462 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
LowFuel level sensor input below acceptable voltage.
P0463 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighFuel level sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P0500 (M) No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal No vehicle speed sensor signal detected during road
load conditions.
P0505 (M) Idle Air Control Motor Circuits Replace
P0522 Oil Pressure Sens Low Oil pressure sensor input below acceptable voltage.
P0523 Oil Pressure Sens High Oil pressure sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P0551 (M) Power Steering Switch Failure Incorrect input state detected for the power steering
switch circuit. PL: High pressure seen at high speed.
P0600 (M) PCM Failure SPI Communications No communication detected between co-processors in
the control module.
P0601 (M) Internal Controller Failure Internal control module fault condition (check sum)
detected.
P0604 Internal Trans Controller Transmission control module RAM self test fault
detected. -Aisin transmission.
P0605 Internal Trans Controller Transmission control module ROM self test fault
detected -Aisin transmission.
P0622 (G) Generator Field Not Switching
ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the generator
field control circuit.
P0645 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C clutch
relay control circuit.
P0700 (M) EATX Controller DTC Present This SBEC III or JTEC DTC indicates that the EATX or
Aisin controller has an active fault and has illuminated
the MIL via a CCD (EATX) or SCI (Aisin) message. The
specific fault must be acquired from the EATX via CCD
or from the Aisin via ISO-9141.
P0703 (M) Brake Switch Stuck Pressed or
ReleasedIncorrect input state detected in the brake switch circuit.
(Changed from P1595).
P0711 Trans Temp Sensor, No Temp Rise
After StartRelationship between the transmission temperature and
overdrive operation and/or TCC operation indicates a
failure of the Transmission Temperature Sensor. OBD II
Rationality.
P0712 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too
LowTransmission fluid temperature sensor input below
acceptable voltage.
P0713 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too
HighTransmission fluid temperature sensor input above
acceptable voltage.
P0720 Low Output SPD Sensor RPM,
Above 15 MPHThe relationship between the Output Shaft Speed
Sensor and vehicle speed is not within acceptable
limits.
25 - 10 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1098 of 1285
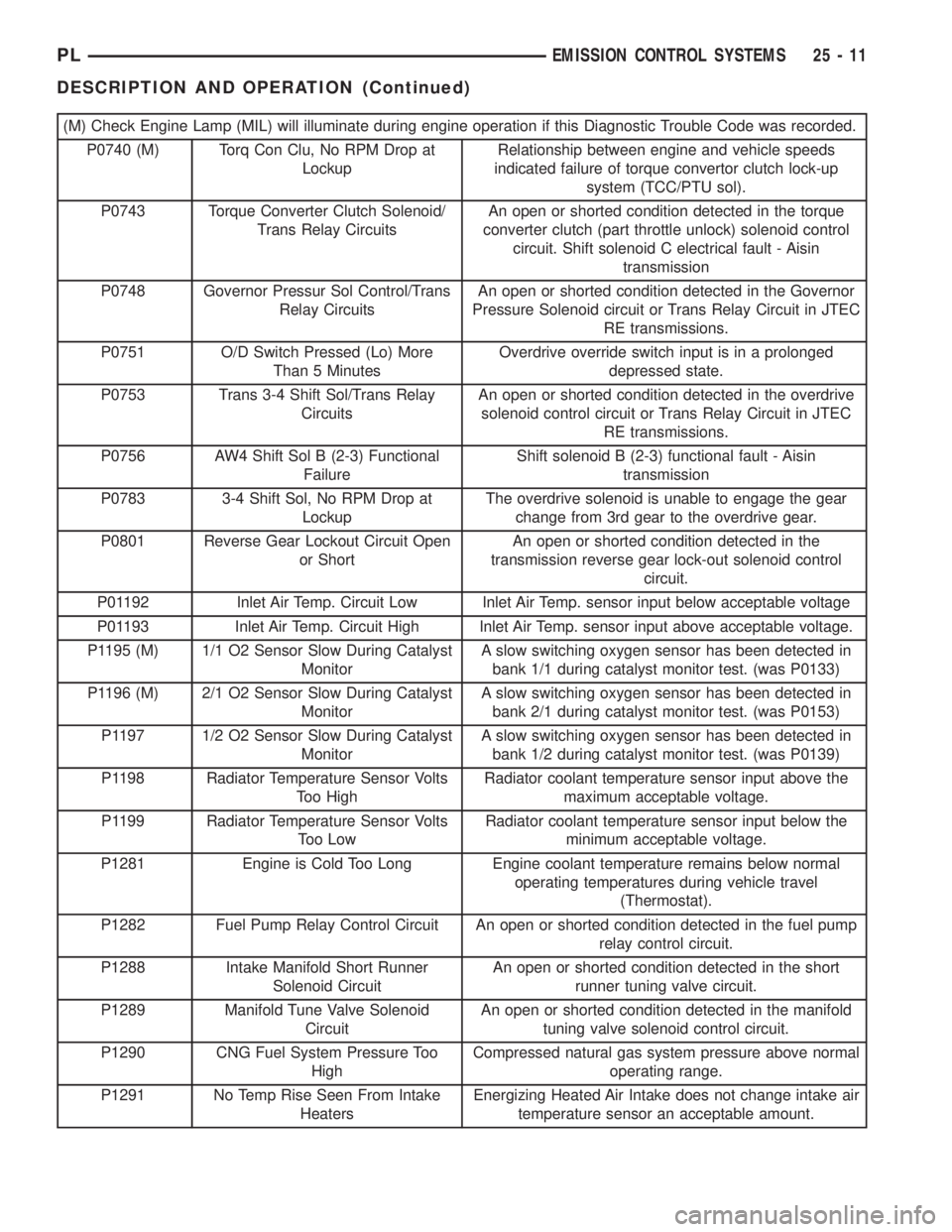
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
P0740 (M) Torq Con Clu, No RPM Drop at
LockupRelationship between engine and vehicle speeds
indicated failure of torque convertor clutch lock-up
system (TCC/PTU sol).
P0743 Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter clutch (part throttle unlock) solenoid control
circuit. Shift solenoid C electrical fault - Aisin
transmission
P0748 Governor Pressur Sol Control/Trans
Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Governor
Pressure Solenoid circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC
RE transmissions.
P0751 O/D Switch Pressed (Lo) More
Than 5 MinutesOverdrive override switch input is in a prolonged
depressed state.
P0753 Trans 3-4 Shift Sol/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the overdrive
solenoid control circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC
RE transmissions.
P0756 AW4 Shift Sol B (2-3) Functional
FailureShift solenoid B (2-3) functional fault - Aisin
transmission
P0783 3-4 Shift Sol, No RPM Drop at
LockupThe overdrive solenoid is unable to engage the gear
change from 3rd gear to the overdrive gear.
P0801 Reverse Gear Lockout Circuit Open
or ShortAn open or shorted condition detected in the
transmission reverse gear lock-out solenoid control
circuit.
P01192 Inlet Air Temp. Circuit Low Inlet Air Temp. sensor input below acceptable voltage
P01193 Inlet Air Temp. Circuit High Inlet Air Temp. sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P1195 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0133)
P1196 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 2/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0153)
P1197 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/2 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0139)
P1198 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too HighRadiator coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P1199 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too LowRadiator coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P1281 Engine is Cold Too Long Engine coolant temperature remains below normal
operating temperatures during vehicle travel
(Thermostat).
P1282 Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the fuel pump
relay control circuit.
P1288 Intake Manifold Short Runner
Solenoid CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the short
runner tuning valve circuit.
P1289 Manifold Tune Valve Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the manifold
tuning valve solenoid control circuit.
P1290 CNG Fuel System Pressure Too
HighCompressed natural gas system pressure above normal
operating range.
P1291 No Temp Rise Seen From Intake
HeatersEnergizing Heated Air Intake does not change intake air
temperature sensor an acceptable amount.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1099 of 1285
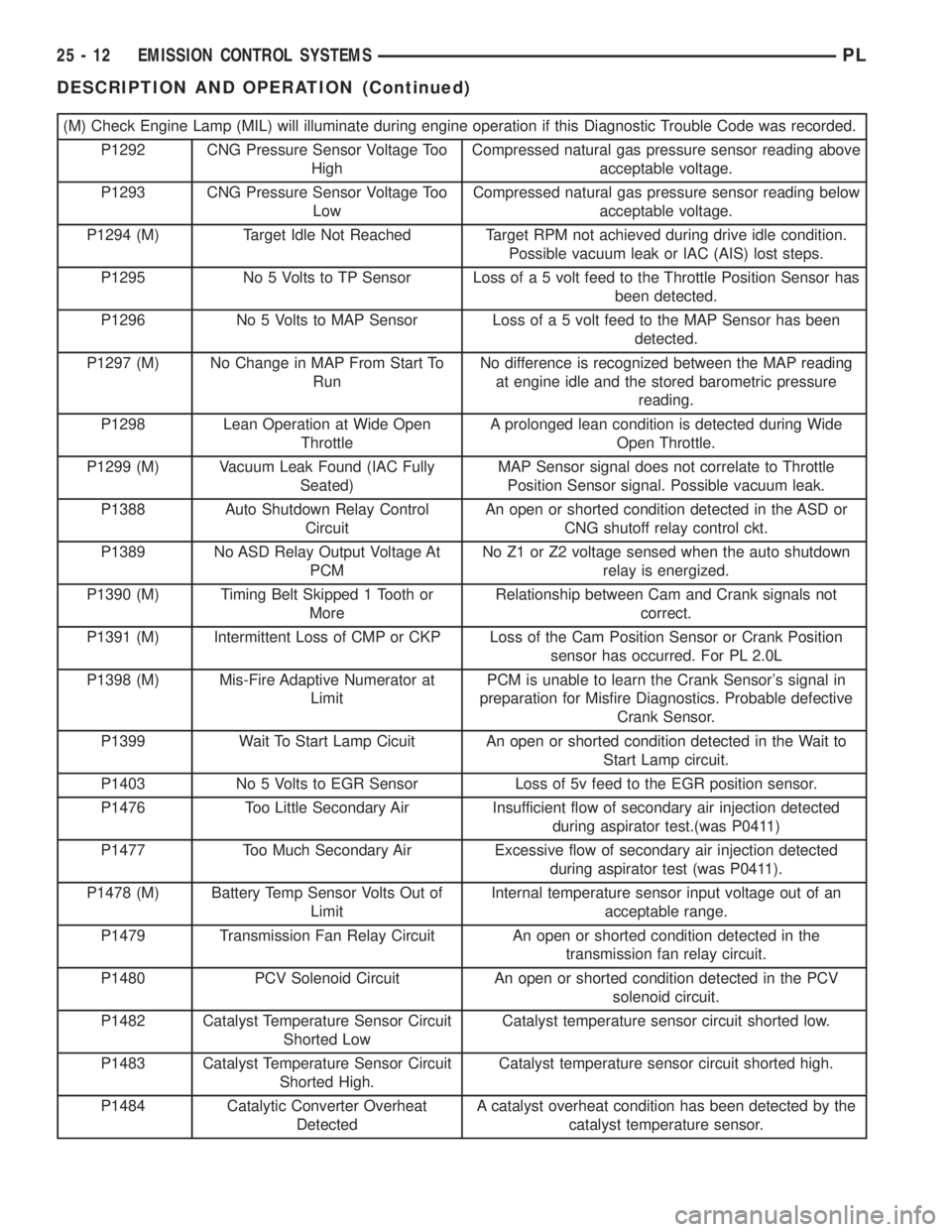
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
P1292 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
HighCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading above
acceptable voltage.
P1293 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
LowCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading below
acceptable voltage.
P1294 (M) Target Idle Not Reached Target RPM not achieved during drive idle condition.
Possible vacuum leak or IAC (AIS) lost steps.
P1295 No 5 Volts to TP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the Throttle Position Sensor has
been detected.
P1296 No 5 Volts to MAP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the MAP Sensor has been
detected.
P1297 (M) No Change in MAP From Start To
RunNo difference is recognized between the MAP reading
at engine idle and the stored barometric pressure
reading.
P1298 Lean Operation at Wide Open
ThrottleA prolonged lean condition is detected during Wide
Open Throttle.
P1299 (M) Vacuum Leak Found (IAC Fully
Seated)MAP Sensor signal does not correlate to Throttle
Position Sensor signal. Possible vacuum leak.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the ASD or
CNG shutoff relay control ckt.
P1389 No ASD Relay Output Voltage At
PCMNo Z1 or Z2 voltage sensed when the auto shutdown
relay is energized.
P1390 (M) Timing Belt Skipped 1 Tooth or
MoreRelationship between Cam and Crank signals not
correct.
P1391 (M) Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Loss of the Cam Position Sensor or Crank Position
sensor has occurred. For PL 2.0L
P1398 (M) Mis-Fire Adaptive Numerator at
LimitPCM is unable to learn the Crank Sensor's signal in
preparation for Misfire Diagnostics. Probable defective
Crank Sensor.
P1399 Wait To Start Lamp Cicuit An open or shorted condition detected in the Wait to
Start Lamp circuit.
P1403 No 5 Volts to EGR Sensor Loss of 5v feed to the EGR position sensor.
P1476 Too Little Secondary Air Insufficient flow of secondary air injection detected
during aspirator test.(was P0411)
P1477 Too Much Secondary Air Excessive flow of secondary air injection detected
during aspirator test (was P0411).
P1478 (M) Battery Temp Sensor Volts Out of
LimitInternal temperature sensor input voltage out of an
acceptable range.
P1479 Transmission Fan Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the
transmission fan relay circuit.
P1480 PCV Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the PCV
solenoid circuit.
P1482 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit
Shorted LowCatalyst temperature sensor circuit shorted low.
P1483 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit
Shorted High.Catalyst temperature sensor circuit shorted high.
P1484 Catalytic Converter Overheat
DetectedA catalyst overheat condition has been detected by the
catalyst temperature sensor.
25 - 12 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1101 of 1285

(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
P1684 The battery has been disconnected within the last 50
starts.
P1685 Skim Invalid Key The engine controler has received an invalid key from
the SKIM.
P1686 No SKIM BUS Messages Received No CCD/J1850 messages received from the Smart Key
Immobilizer Module (SKIM).
P1687 No MIC BUS Message No CCD/J1850 messages received from the Mechanical
Instrument Cluster (MIC) module.
P1693 DTC Detected in Companion
ModuleA fault has been generated in the companion engine
control module.
P1694 Fault In Companion Module No CCD/J1850 messages received from the powertrain
control module-Aisin transmission.
P1695 No CCD/J1850 Message From
Body Control ModuleNo CCD/J1850 messages received from the body
control module.
P1696 (M) PCM Failure EEPROM Write
DeniedUnsuccessful attempt to write to an EEPROM location
by the control module.
P1697 (M) PCM Failure SRI Mile Not Stored Unsuccessful attempt to update Service Reminder
Indicator (SRI or EMR) mileage in the control module
EEPROM.
P1698 (M) No CCD/J1850 Message From TCM No CCD/J1850 messages received from the electronic
transmission control module (EATX) or the Aisin
transmission controller.
P1719 Skip Shift Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the
transmission 2-3 gear lock-out solenoid control circuit.
P1756 GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control
System which is used to regulate governor pressure to
control shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear. (Mid Pressure
Malfunction)
P1757 GOV Press Not Equal to Target @
15-20 PSIThe requested pressure and the actual pressure are not
within a tolerance band for the Governor Control
System which is used to regulate governor pressure to
control shifts for 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gear (Zero Pressure
Malfunction)
P1762 Gov Press Sen Offset Volts Too Lo
or HighThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is greater than a
calibration limit or is less than a calibration limit for 3
consecutive park/neutral calibrations.
P1763 Governor Pressure Sensor Volts
To o H iThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is above an
acceptable voltage level.
P1764 Governor Pressure Sensor Volts
Too LowThe Governor Pressure Sensor input is below an
acceptable voltage level.
P1765 Trans 12 Volt Supply Relay CTRL
CircuitAn open or shorted condition is detected in the
Transmission Relay control circuit. This relay supplies
power to the TCC>
P1899 (M) P/N Switch Stuck in Park or in Gear Incorrect input state detected for the Park/Neutral
switch.
25 - 14 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1102 of 1285

MONITORED SYSTEMS
DESCRIPTION
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator (Check
Engine) Lamp will be illuminated. These monitors
generate Diagnostic Trouble Codes that can be dis-
played with the check engine lamp or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the monitored systems:
²EGR Monitor
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Evaporative Emissions Monitor
Following is a description of each system monitor,
and its DTC.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
EGR MONITOR
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) performs
an on-board diagnostic check of the EGR system.
The EGR system consists of two main components:
a vacuum solenoid back pressure transducer and a
vacuum operated valve. The EGR monitor is used to
test whether the EGR system is operating within
specifications. The diagnostic check activates only
during selected engine/driving conditions. When the
conditions are met, the EGR is turned off (solenoid
energized) and the O2S compensation control is mon-
itored. Turning off the EGR shifts the air fuel (A/F)
ratio in the lean direction. Oxygen sensor voltage
then indicates increased oxygen in the exhaust. Con-
sequently, Short Term Compensation shifts to rich
(increased injector pulse width). By monitoring the
shift, the PCM can indirectly monitor the EGR sys-
tem. While this test does not directly measure the
operation of the EGR system, it can be inferred from
the shift in the O2S data whether the EGR system is
operating correctly. Because the O2S is being used,
the O2S test must pass its test before the EGR test.
Enabling ConditionsÐ
²Engine Temperature
²Engine Run Time
²Engine RPM²MAP Sensor
²TPS
²Vehicle Speed
²Short Term Compensation
Pending ConditionsÐThe EGR Monitor does
not run when any of the following example faults
have illuminated the MIL:
²Misfire
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Fuel System Rich/Lean
²Limp in for MAP, TPS or ECT
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Cam or Crank Sensor
²EGR Electrical
²EVAP Electrical
²Fuel Injector
²Ignition Coil
²Idle Speed
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
²MAP Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
Conflict ConditionsÐThe EGR Monitor typi-
cally does not run if any of the following conditions
are present:
²Fuel System Monitor
²Purge Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Low Fuel Level
²High Altitude
²Low Ambient Air Temperature
The EGR Monitor does not run if any of the follow-
ing example DTCs are present:
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
²Upstream Oxygen Sensor Heater, Priority 1
²Fuel System Monitor, Priority 2
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Priority 1
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
OBD II regulations for misfire monitoring require
two different tests for misfire. The first is a Catalyst
Damage level of misfire test. The second is for emis-
sions greater than 1.5 times the Federal Tailpipe
(FTP) standards. The tests are monitored by two dif-
ferent counters. These counters are:
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1105 of 1285

Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º H20.
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the
system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at.040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicatedby a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
Enabling Conditions for Systems with LDP
²Ambient Air Temperature
²Barometric Pressure
²Fuel level
²Engine Temperature
²No stalling
²Battery voltage
NON-LDP VEHICLESÐOn a vehicle without an
EVAP leak detection pump system, changes in short
term memory and movement in target IAC at idle or
idle speed change, are used to monitor the system.
There are two stages for this test.
Stage OneÐStage one is a non-intrusive test.
The PCM compares adaptive memory values between
purge and purge-free cells. The PCM uses these val-
ues to determine the amount of fuel vapors entering
the system. If the difference between the cells
exceeds a predetermined value, the test passes. If
not, then the monitor advances to state two.
Stage TwoÐOnce the enabling conditions are
met, the PCM de-energizes the Duty Cycle Purge
(DCP) solenoid. The PCM then waits until engine
RPM, Short Term Compensation and Idle Air Control
have all stabilized. Once stable, the PCM increments
the DCP solenoid cycle rate approximately 6% every
8 engine revolutions. If during the test any one of
three conditions occur before the DCP cycle reaches
100%, the EVAP system is considered to be opera-
tional and the test passes. These conditions are as
follows:
²RPM rises by a predetermined amount
²Short Term drops by a predetermined amount
²Idle Air Control closes by a predetermined
amount
When none of the previous conditions occur, the
test fails and the PCM increments a counter by one.
When the PCM runs the test three times during a
trip, and the counter has been incremented to three,
the monitor fails and a Freeze Frame is stored.
Enabling Conditions (Stage Two)ÐThe follow-
ing conditions must be met to enable the EVAP Mon-
itor (without LDP)
²Ambient Air Temperature
²Barometric Pressure
²Fuel level
²Engine Temperature
²Engine run time
²RPM stable
²MAP
²Generator, radiator fans, A/C clutch
Pending Conditions-With or Without LDPÐ
The EVAP Monitor is suspended and does not run,
25 - 18 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1106 of 1285

when the MIL is illuminated due to any of the fol-
lowing faults:
²Misfire
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Fuel System Rich
²Fuel System Lean
²EGR Monitor
²MAP
²TPS
²ECT
²DCP Solenoid
Conflict Conditions-With or Without LDPÐ
The EVAP Monitor does not run if any of the follow-
ing tests are in progress:
²Catalyst
²EGR
²Fuel System
²Misfire
TRIP DEFINITION
OPERATION
A ªTripº means vehicle operation (following an
engine-off period) of duration and driving mode such
that all components and systems are monitored at
least once by the diagnostic system. The monitors
must successfully pass before the PCM can verify
that a previously malfunctioning component is meet-
ing the normal operating conditions of that compo-
nent. For misfire or fuel system malfunction, the
MIL may be extinguished if the fault does not recur
when monitored during three subsequent sequential
driving cycles in which conditions are similar to
those under which the malfunction was first deter-
mined.
Anytime the MIL is illuminated, a DTC is stored.
The DTC can self erase only when the MIL has been
extinguished. Once the MIL is extinguished, the
PCM must pass the diagnostic test for the most
recent DTC for 40 warm-up cycles (80 warm-up
cycles for the Fuel System Monitor and the Misfire
Monitor). A warm-up cycle can best be described by
the following:
²The engine must be running
²A rise of 40ÉF in engine temperature must occur
from the time when the engine was started
²Engine coolant temperature must reach at least
160ÉF
²A ªdriving cycleº that consists of engine start up
and engine shut off.
Once the above conditions occur, the PCM is con-
sidered to have passed a warm-up cycle. Due to the
conditions required to extinguish the MIL and erase
the DTC, it is most important that after a repair has
been made, all DTC's be erased and the repair veri-
fied.
MONITORED COMPONENT
DESCRIPTION
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum
and 1600 rpm.
Any component that has an associated limp in will
set a fault after 1 trip with the malfunction present.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
The following is a list of the monitored compo-
nents:
²Comprehensive Components
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS
Along with the major monitors, OBD II requires
that the diagnostic system monitor any component
that could affect emissions levels. In many cases,
these components were being tested under OBD I.
The OBD I requirements focused mainly on testing
emissions-related components for electrical opens and
shorts.
However, OBD II also requires that inputs from
powertrain components to the PCM be tested for
rationality, and that outputs to powertrain compo-
nents from the PCM be tested forfunctionality.
Methods for monitoring the various Comprehensive
Component monitoring include:
(1) Circuit Continuity
²Open
²Shorted high
²Shorted to ground
(2) Rationality or Proper Functioning
²Inputs tested for rationality
²Outputs tested for functionality
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 19
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1107 of 1285

NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch
²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Leak Detection Pump Switch
²P/N Switch
²Trans Controls
Output FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
put component, it can verify that the command was
carried out by monitoring specific input signals for
expected changes. For example, when the PCM com-
mands the Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor to a specific
position under certain operating conditions, it expects
to see a specific (target) idle speed (RPM). If it does
not, it stores a DTC.
PCM outputs monitored for functionality include:
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coils
²Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Idle Air Control
²Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid
²LDP Solenoid
²Radiator Fan Control
²Trans Controls
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐEffective control of exhaust
emissions is achieved by an oxygen feedback system.
The most important element of the feedback system
is the O2S. The O2S is located in the exhaust path.
Once it reaches operating temperature 300É to 350ÉC
(572É to 662ÉF), the sensor generates a voltage that
is inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen inthe exhaust. When there is a large amount of oxygen
in the exhaust caused by a lean condition, the sensor
produces a low voltage, below 450 mV. When the oxy-
gen content is lower, caused by a rich condition, the
sensor produces a higher voltage, above 450mV.
The information obtained by the sensor is used to
calculate the fuel injector pulse width. This main-
tains a 14.7 to 1 air fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture
ratio, the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons
(HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrous oxide (NOx)
from the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
EGR, Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S may fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²Slow response rate (Big Slope)
²Reduced output voltage (Half Cycle)
²Heater Performance
Slow Response Rate (Big Slope)ÐResponse
rate is the time required for the sensor to switch
from lean to rich signal output once it is exposed to a
richer than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As
the PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio, the sensor must
be able to rapidly detect the change. As the sensor
ages, it could take longer to detect the changes in the
oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The rate of
change that an oxygen sensor experiences is called
'Big Slope'. The PCM checks the oxygen sensor volt-
age in increments of a few milliseconds.
Reduced Output Voltage (Half Cycle)ÐThe
output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1 volt. A
good sensor can easily generate any output voltage in
this range as it is exposed to different concentrations
of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F mixture (lean
or rich), the output voltage has to change beyond a
threshold value. A malfunctioning sensor could have
difficulty changing beyond the threshold value. Each
time the voltage signal surpasses the threshold, a
counter is incremented by one. This is called the Half
Cycle Counter.
Heater PerformanceÐThe heater is tested by a
separate monitor. Refer to the Oxygen Sensor Heater
Monitor.
OPERATIONÐAs the Oxygen Sensor signal
switches, the PCM monitors the half cycle and big
slope signals from the oxygen sensor. If during the
test neither counter reaches a predetermined value, a
malfunction is entered and a Freeze Frame is stored.
Only one counter reaching its predetermined value is
needed for the monitor to pass.
The Oxygen Sensor Monitor is a two trip monitor
that is tested only once per trip. When the Oxygen
Sensor fails the test in two consecutive trips, the
MIL is illuminated and a DTC is set. The MIL is
extinguished when the Oxygen Sensor monitor
passes in three consecutive trips. The DTC is erased
25 - 20 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1108 of 1285

from memory after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles
without test failure.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met for the PCM to run the oxygen
sensor monitor:
²Battery voltage
²Engine temperature
²Engine run time
²Engine run time at a predetermined speed
²Engine run time at a predetermined speed and
throttle opening
²Transmission in gear (automatic only)
²Fuel system in Closed Loop
²Long Term Adaptive (within parameters)
²Power Steering Switch in low PSI (no load)
²Engine at idle
²Fuel level above 15%
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure
²Engine RPM within acceptable range of desired
idle
²Closed throttle speed
Pending ConditionsÐThe Task Manager typi-
cally does not run the Oxygen Sensor Monitor if over-
lapping monitors are running or the MIL is
illuminated for any of the following:
²Misfire Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor and Heater Monitor
²MAP Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Engine Controller Self Test Faults
²Cam or Crank Sensor
²Injector and Coil
²Idle Air Control Motor
²EVAP Electrical
²EGR Solenoid Electrical
²Intake Air Temperature
²5 Volt Feed
ConflictÐThe Task Manager does not run the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor if any of the following condi-
tions are present:
²A/C ON (A/C clutch cycling temporarily sus-
pends monitor)
²Purge flow in progress
SuspendÐThe Task Manager suspends maturing
a fault for the Oxygen Sensor Monitor if an of the fol-
lowing are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor, Priority 1
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐIf there is an oxygen sensor
(O2S) DTC as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. After the O2S fault isrepaired, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S are very
temperature sensitive. The readings are not accurate
below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S is done to allow the
engine controller to shift to closed loop control as
soon as possible. The heating element used to heat
the O2S must be tested to ensure that it is heating
the sensor properly.
The heater element itself is not tested. The sensor
output is used to test the heater by isolating the
effect of the heater element on the O2S output volt-
age from the other effects. The resistance is normally
between 100 ohms and 4.5 megaohms. When oxygen
sensor temperature increases, the resistance in the
internal circuit decreases. The PCM sends a 5 volts
biased signal through the oxygen sensors to ground
this monitoring circuit. As the temperature increases,
resistance decreases and the PCM detects a lower
voltage at the reference signal. Inversely, as the tem-
perature decreases, the resistance increases and the
PCM detects a higher voltage at the reference signal.
an The O2S circuit is monitored for a drop in voltage.
OPERATIONÐThe Oxygen Sensor Heater Moni-
tor begins after the ignition has been turned OFF
and the O2 sensors have cooled. The PCM sends a 5
volt bias to the oxygen sensor every 1.6 seconds. The
PCM keeps it biased for 35 ms each time. As the sen-
sor cools down, the resistance increases and the PCM
reads the increase in voltage. Once voltage has
increased to a predetermined amount, higher than
when the test started, the oxygen sensor is cool
enough to test heater operation.
When the oxygen sensor is cool enough, the PCM
energizes the ASD relay. Voltage to the O2 sensor
begins to increase the temperature. As the sensor
temperature increases, the internal resistance
decreases. The PCM continues biasing the 5 volt sig-
nal to the sensor. Each time the signal is biased, the
PCM reads a voltage decrease. When the PCM
detects a voltage decrease of a predetermined value
for several biased pulses, the test passes.
The heater elements are tested each time the
engine is turned OFF if all the enabling conditions
are met. If the monitor fails, the PCM stores a
maturing fault and a Freeze Frame is entered. If two
consecutive tests fail, a DTC is stored. Because the
ignition is OFF, the MIL is illuminated at the begin-
ning of the next key cycle.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must be met for the PCM to run the oxygen sensor
heater test:
²Engine run time of at least 5.1 minutes
²Key OFF power down
²Battery voltage of at least 10 volts
²Sufficient Oxygen Sensor cool down
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)