DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 1821 of 2889
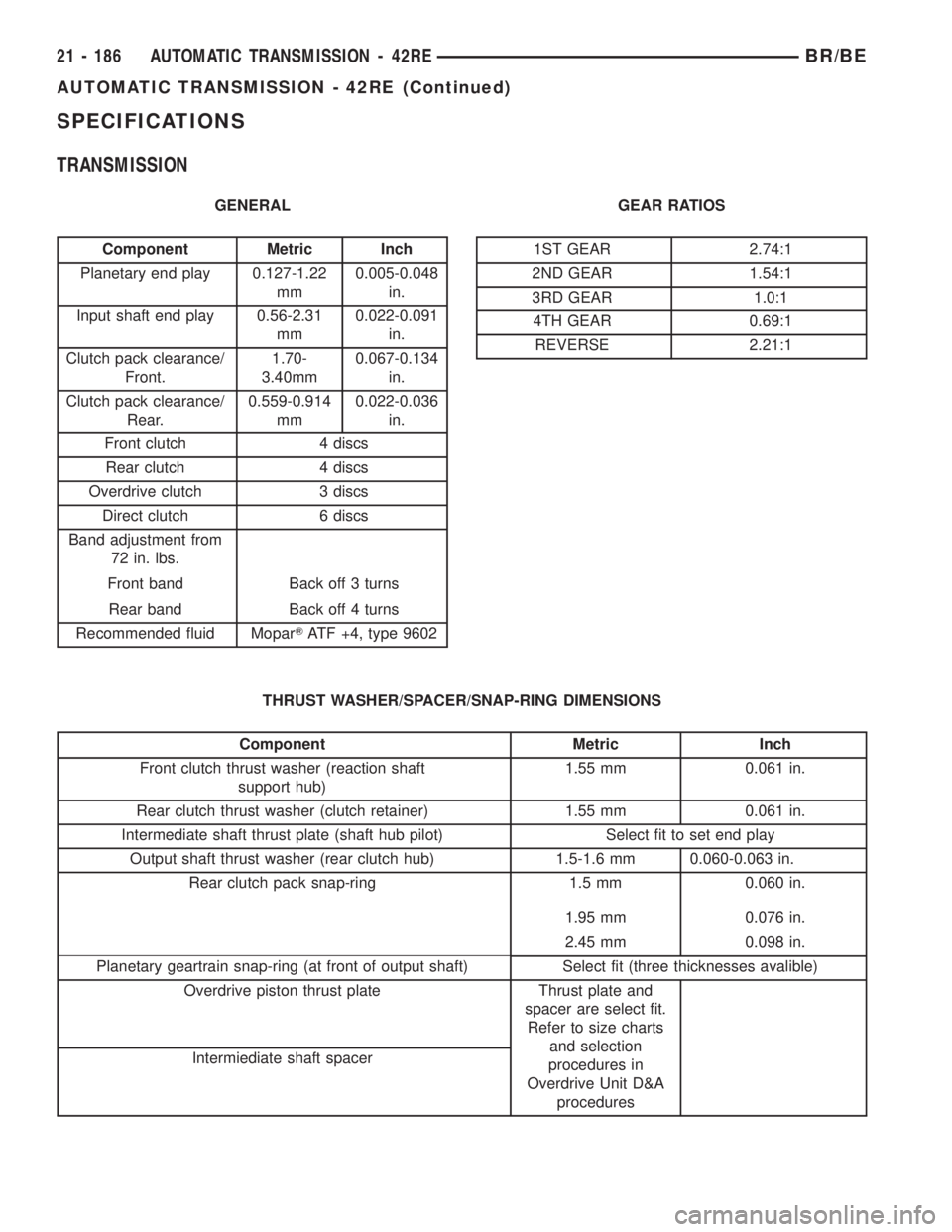
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION
GENERAL
Component Metric Inch
Planetary end play 0.127-1.22
mm0.005-0.048
in.
Input shaft end play 0.56-2.31
mm0.022-0.091
in.
Clutch pack clearance/
Front.1.70-
3.40mm0.067-0.134
in.
Clutch pack clearance/
Rear.0.559-0.914
mm0.022-0.036
in.
Front clutch 4 discs
Rear clutch 4 discs
Overdrive clutch 3 discs
Direct clutch 6 discs
Band adjustment from
72 in. lbs.
Front band Back off 3 turns
Rear band Back off 4 turns
Recommended fluid MoparTATF +4, type 9602GEAR RATIOS1ST GEAR 2.74:1
2ND GEAR 1.54:1
3RD GEAR 1.0:1
4TH GEAR 0.69:1
REVERSE 2.21:1
THRUST WASHER/SPACER/SNAP-RING DIMENSIONS
Component Metric Inch
Front clutch thrust washer (reaction shaft
support hub)1.55 mm 0.061 in.
Rear clutch thrust washer (clutch retainer) 1.55 mm 0.061 in.
Intermediate shaft thrust plate (shaft hub pilot) Select fit to set end play
Output shaft thrust washer (rear clutch hub) 1.5-1.6 mm 0.060-0.063 in.
Rear clutch pack snap-ring 1.5 mm 0.060 in.
1.95 mm 0.076 in.
2.45 mm 0.098 in.
Planetary geartrain snap-ring (at front of output shaft) Select fit (three thicknesses avalible)
Overdrive piston thrust plate Thrust plate and
spacer are select fit.
Refer to size charts
and selection
procedures in
Overdrive Unit D&A
procedures Intermiediate shaft spacer
21 - 186 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1822 of 2889
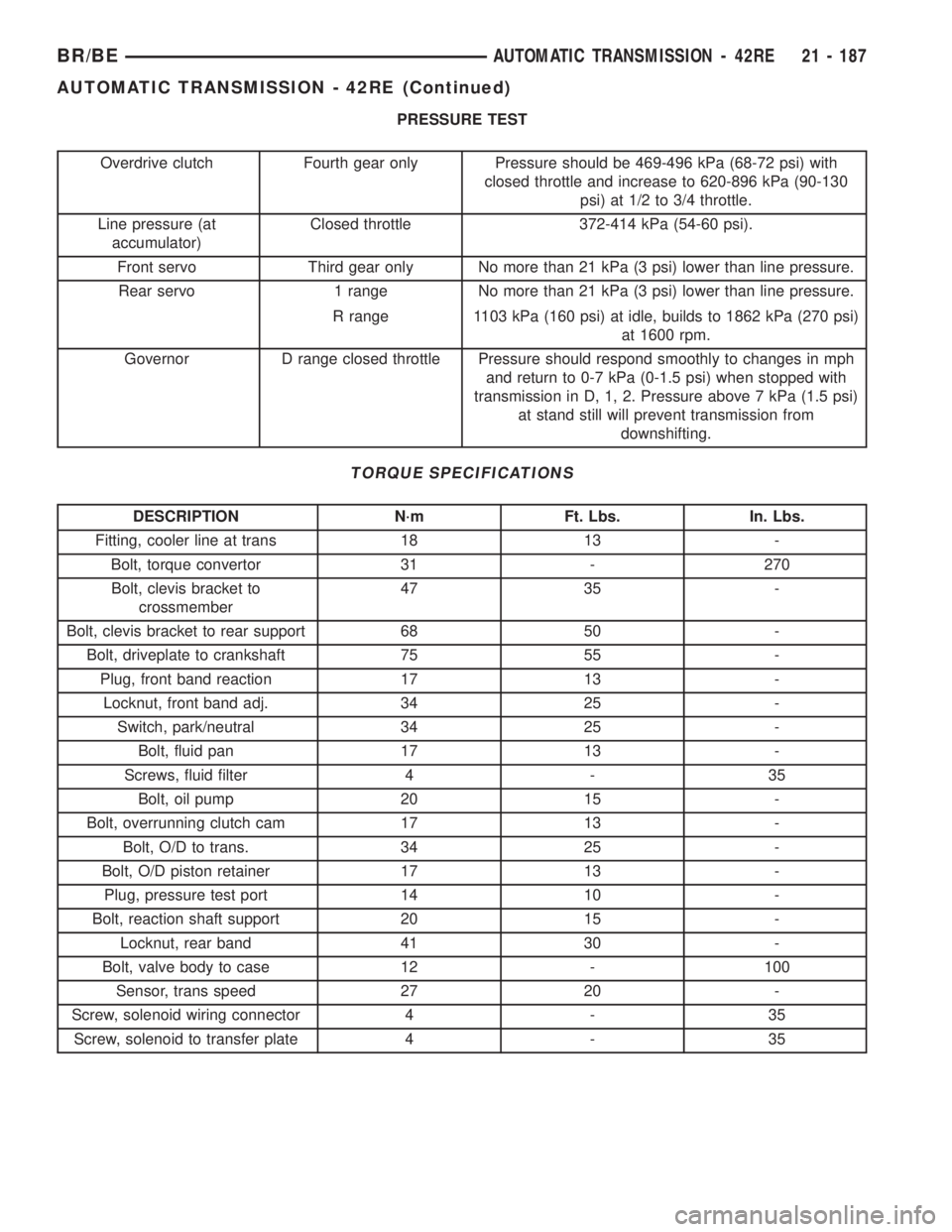
PRESSURE TEST
Overdrive clutch Fourth gear only Pressure should be 469-496 kPa (68-72 psi) with
closed throttle and increase to 620-896 kPa (90-130
psi) at 1/2 to 3/4 throttle.
Line pressure (at
accumulator)Closed throttle 372-414 kPa (54-60 psi).
Front servo Third gear only No more than 21 kPa (3 psi) lower than line pressure.
Rear servo 1 range No more than 21 kPa (3 psi) lower than line pressure.
R range 1103 kPa (160 psi) at idle, builds to 1862 kPa (270 psi)
at 1600 rpm.
Governor D range closed throttle Pressure should respond smoothly to changes in mph
and return to 0-7 kPa (0-1.5 psi) when stopped with
transmission in D, 1, 2. Pressure above 7 kPa (1.5 psi)
at stand still will prevent transmission from
downshifting.
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fitting, cooler line at trans 18 13 -
Bolt, torque convertor 31 - 270
Bolt, clevis bracket to
crossmember47 35 -
Bolt, clevis bracket to rear support 68 50 -
Bolt, driveplate to crankshaft 75 55 -
Plug, front band reaction 17 13 -
Locknut, front band adj. 34 25 -
Switch, park/neutral 34 25 -
Bolt, fluid pan 17 13 -
Screws, fluid filter 4 - 35
Bolt, oil pump 20 15 -
Bolt, overrunning clutch cam 17 13 -
Bolt, O/D to trans. 34 25 -
Bolt, O/D piston retainer 17 13 -
Plug, pressure test port 14 10 -
Bolt, reaction shaft support 20 15 -
Locknut, rear band 41 30 -
Bolt, valve body to case 12 - 100
Sensor, trans speed 27 20 -
Screw, solenoid wiring connector 4 - 35
Screw, solenoid to transfer plate 4 - 35
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 187
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1823 of 2889
SPECIAL TOOLS
RE TRANSMISSIONS
Shaft, Spring Compressor and Alignment - 6227
Bar, Gauge - 6311
Pilot, Extension Housing - C-3288-B
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3292
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3293SP
Dial Indicator - C-3339
Compressor, Spring - C-3422-C
Puller, Slide Hammer - C-3752
Gauge, Throttle Setting - C-3763
Installer, Seal - C-3860-A
21 - 188 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1824 of 2889
Remover, Seal - C-3985-B
Installer, Seal - C-3995-A
Handle, Universal - C-4171
Installer, Seal - C-4193-A
Dial Caliper - C-4962
Kit, Bushing Remover/Installer - C-3887-J
Nut, Bushing Remover - SP-1191, From kit C-3887-J
Cup, Bushing Remover - SP-3633, From kit C-3887-J
Remover, Bushing - SP-3551
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 189
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1825 of 2889
Installer, Bushing - SP-5117
Remover, Bushing - SP-5324
Installer, Bushing - SP-5325
Compressor, Spring - C-3575-A
Gauge - 6312
Adapter, Band Adjuster - C-3705
Flusher, Oil Cooler - 6906-B
Installer, Piston - 8114
Remover, Bushing - 6957
Installer, Bushing - 6951
Retainer, Detent Ball and Spring - 6583
21 - 190 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1826 of 2889
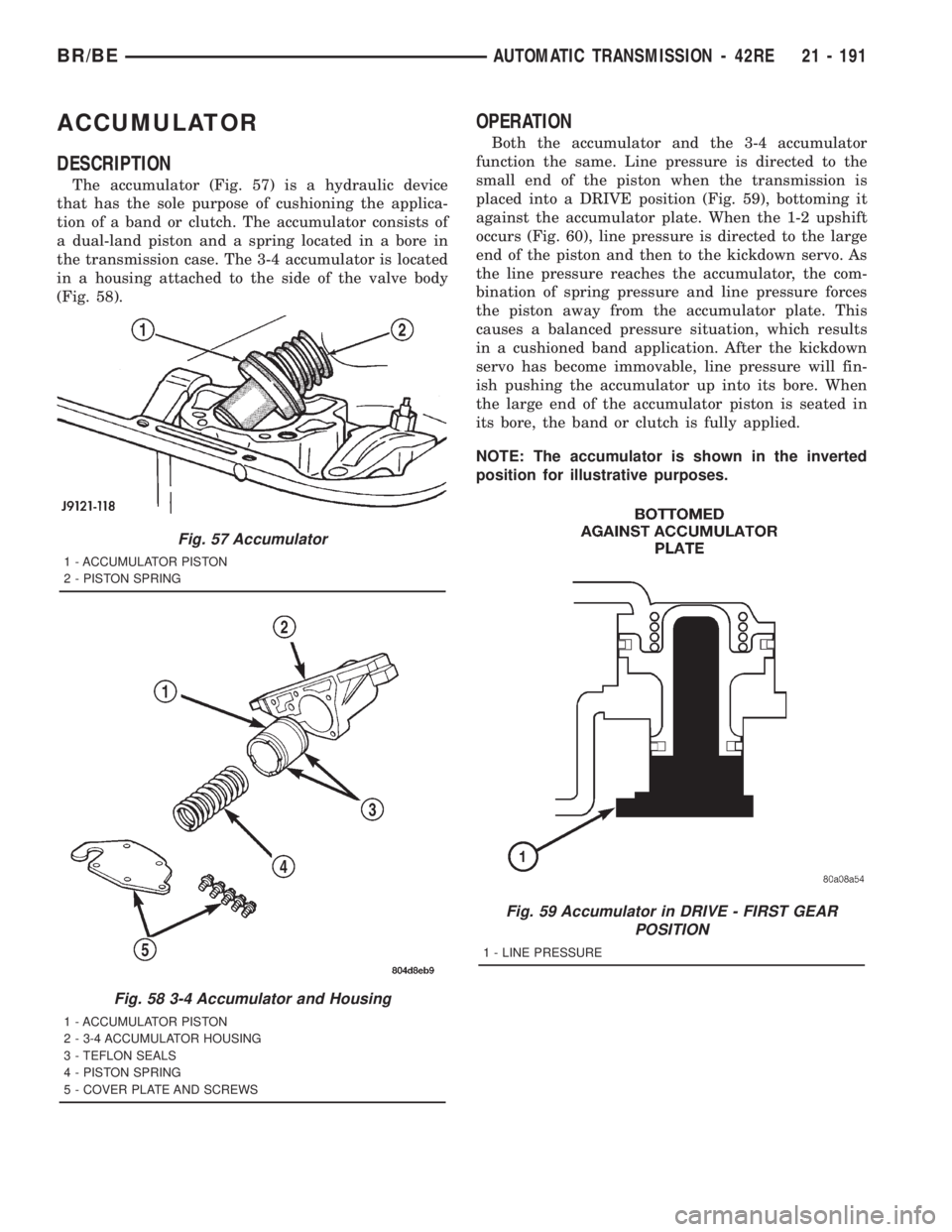
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The accumulator (Fig. 57) is a hydraulic device
that has the sole purpose of cushioning the applica-
tion of a band or clutch. The accumulator consists of
a dual-land piston and a spring located in a bore in
the transmission case. The 3-4 accumulator is located
in a housing attached to the side of the valve body
(Fig. 58).
OPERATION
Both the accumulator and the 3-4 accumulator
function the same. Line pressure is directed to the
small end of the piston when the transmission is
placed into a DRIVE position (Fig. 59), bottoming it
against the accumulator plate. When the 1-2 upshift
occurs (Fig. 60), line pressure is directed to the large
end of the piston and then to the kickdown servo. As
the line pressure reaches the accumulator, the com-
bination of spring pressure and line pressure forces
the piston away from the accumulator plate. This
causes a balanced pressure situation, which results
in a cushioned band application. After the kickdown
servo has become immovable, line pressure will fin-
ish pushing the accumulator up into its bore. When
the large end of the accumulator piston is seated in
its bore, the band or clutch is fully applied.
NOTE: The accumulator is shown in the inverted
position for illustrative purposes.
Fig. 57 Accumulator
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - PISTON SPRING
Fig. 58 3-4 Accumulator and Housing
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
3 - TEFLON SEALS
4 - PISTON SPRING
5 - COVER PLATE AND SCREWS
Fig. 59 Accumulator in DRIVE - FIRST GEAR
POSITION
1 - LINE PRESSURE
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 191
Page 1827 of 2889
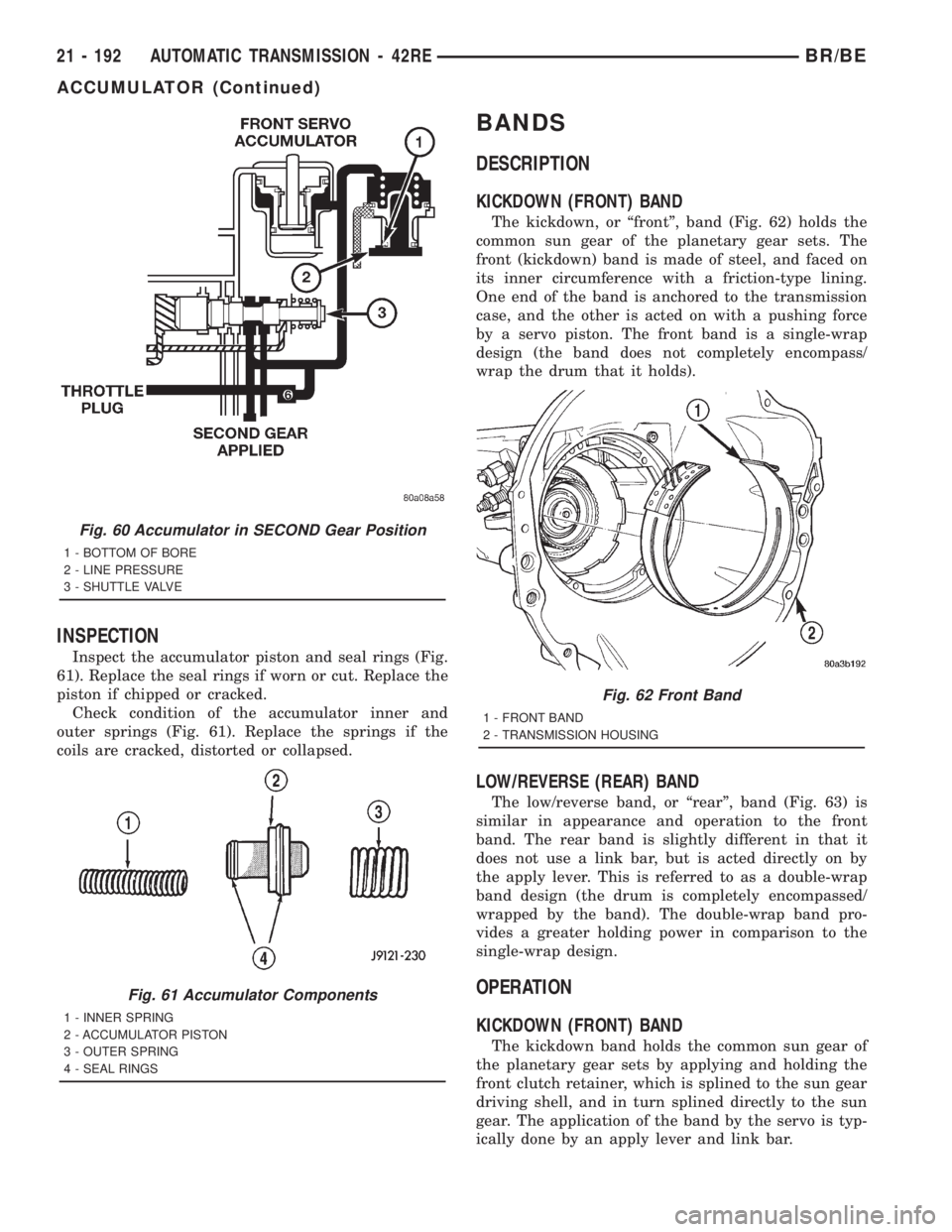
INSPECTION
Inspect the accumulator piston and seal rings (Fig.
61). Replace the seal rings if worn or cut. Replace the
piston if chipped or cracked.
Check condition of the accumulator inner and
outer springs (Fig. 61). Replace the springs if the
coils are cracked, distorted or collapsed.
BANDS
DESCRIPTION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) BAND
The kickdown, or ªfrontº, band (Fig. 62) holds the
common sun gear of the planetary gear sets. The
front (kickdown) band is made of steel, and faced on
its inner circumference with a friction-type lining.
One end of the band is anchored to the transmission
case, and the other is acted on with a pushing force
by a servo piston. The front band is a single-wrap
design (the band does not completely encompass/
wrap the drum that it holds).
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) BAND
The low/reverse band, or ªrearº, band (Fig. 63) is
similar in appearance and operation to the front
band. The rear band is slightly different in that it
does not use a link bar, but is acted directly on by
the apply lever. This is referred to as a double-wrap
band design (the drum is completely encompassed/
wrapped by the band). The double-wrap band pro-
vides a greater holding power in comparison to the
single-wrap design.
OPERATION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) BAND
The kickdown band holds the common sun gear of
the planetary gear sets by applying and holding the
front clutch retainer, which is splined to the sun gear
driving shell, and in turn splined directly to the sun
gear. The application of the band by the servo is typ-
ically done by an apply lever and link bar.
Fig. 60 Accumulator in SECOND Gear Position
1 - BOTTOM OF BORE
2 - LINE PRESSURE
3 - SHUTTLE VALVE
Fig. 61 Accumulator Components
1 - INNER SPRING
2 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
3 - OUTER SPRING
4 - SEAL RINGS
Fig. 62 Front Band
1 - FRONT BAND
2 - TRANSMISSION HOUSING
21 - 192 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 1828 of 2889
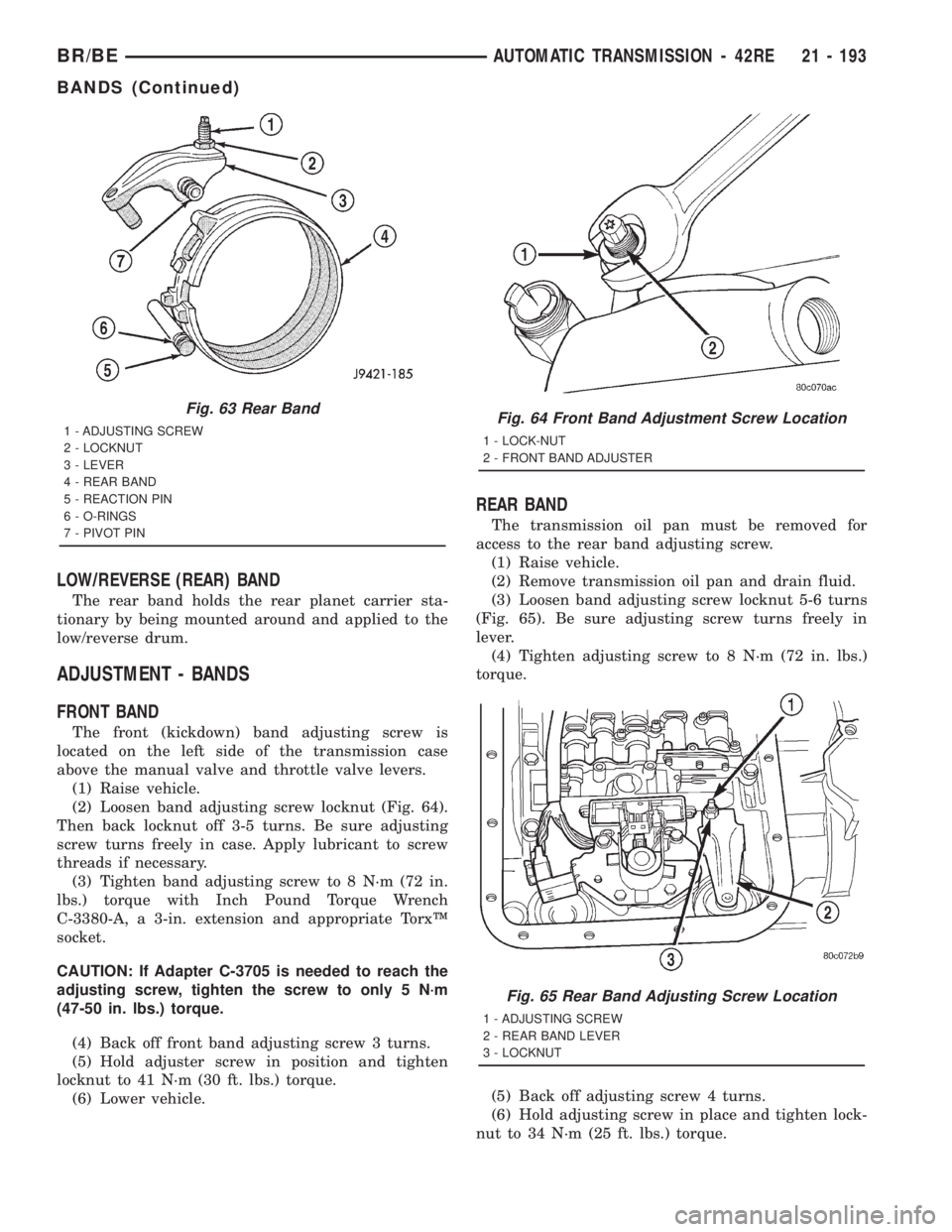
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) BAND
The rear band holds the rear planet carrier sta-
tionary by being mounted around and applied to the
low/reverse drum.
ADJUSTMENT - BANDS
FRONT BAND
The front (kickdown) band adjusting screw is
located on the left side of the transmission case
above the manual valve and throttle valve levers.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut (Fig. 64).
Then back locknut off 3-5 turns. Be sure adjusting
screw turns freely in case. Apply lubricant to screw
threads if necessary.
(3) Tighten band adjusting screw to 8 N´m (72 in.
lbs.) torque with Inch Pound Torque Wrench
C-3380-A, a 3-in. extension and appropriate TorxŸ
socket.
CAUTION: If Adapter C-3705 is needed to reach the
adjusting screw, tighten the screw to only 5 N´m
(47-50 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Back off front band adjusting screw 3 turns.
(5) Hold adjuster screw in position and tighten
locknut to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Lower vehicle.
REAR BAND
The transmission oil pan must be removed for
access to the rear band adjusting screw.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove transmission oil pan and drain fluid.
(3) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut 5-6 turns
(Fig. 65). Be sure adjusting screw turns freely in
lever.
(4) Tighten adjusting screw to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Back off adjusting screw 4 turns.
(6) Hold adjusting screw in place and tighten lock-
nut to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 63 Rear Band
1 - ADJUSTING SCREW
2 - LOCKNUT
3 - LEVER
4 - REAR BAND
5 - REACTION PIN
6 - O-RINGS
7 - PIVOT PINFig. 64 Front Band Adjustment Screw Location
1 - LOCK-NUT
2 - FRONT BAND ADJUSTER
Fig. 65 Rear Band Adjusting Screw Location
1 - ADJUSTING SCREW
2 - REAR BAND LEVER
3 - LOCKNUT
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 193
BANDS (Continued)
Page 1829 of 2889

(7) Position new gasket on oil pan and install pan
on transmission. Tighten pan bolts to 17 N´m (13 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and refill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602, fluid.
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION
Governor pressure is controlled electronically. Com-
ponents used for governor pressure control include:
²Governor body
²Valve body transfer plate
²Governor pressure solenoid valve
²Governor pressure sensor
²Fluid temperature thermistor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Transmission speed sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid valve is a duty-cycle solenoid which
regulates the governor pressure needed for upshifts
and downshifts. It is an electro-hydraulic device
located in the governor body on the valve body trans-
fer plate (Fig. 66).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output
pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
67).
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmis-
sion line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid
valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in
the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower
side of the transfer plate (Fig. 67).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absence
of sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Fig. 66 Governor Pressure Solenoid Valve
1 - SOLENOID FILTER
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
Fig. 67 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 194 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REBR/BE
BANDS (Continued)
Page 1830 of 2889

Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
tial setting for the WOT upshift is below the opti-
mum engine speed. As WOT shifts are repeated, the
PCM learns the time required to complete the shifts
by comparing the engine speed when the shifts occur
to the optimum speed. After each shift, the PCM
adjusts the shift point until the optimum speed is
reached. The PCM also considers vehicle loading,
grade and engine performance changes due to high
altitude in determining when to make WOT shifts. It
does this by measuring vehicle and engine accelera-
tion and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 195
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)