control arm DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 15 of 2889

It is even more important to look for gasoline with-
out MMT in Canada because MMT can be used at
levels higher than allowed in the United States.
MMT is prohibited in Federal and California refor-
mulated gasoline.
SULFUR IN GASOLINE
If you live in the northeast United States, your
vehicle may have been designed to meet California
low emission standards with Cleaner-Burning Cali-
fornia reformulated gasoline with low sulfur. If such
fuels are not available in states adopting California
emission standards, your vehicles will operate satis-
factorily on fuels meeting federal specifications, but
emission control system performance may be
adversely affected. Gasoline sold outside of California
is permitted to have higher sulfur levels which may
affect the performance of the vehicle's catalytic con-
verter. This may cause the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL), Check Engine or Service Engine Soon
light to illuminate. We recommend that you try a dif-
ferent brand of unleaded gasoline having lower sulfur
to determine if the problem is fuel related prior to
returning your vehicle to an authorized dealer for
service.
CAUTION: If the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL),
Check Engine or Service Engine Soon light is flash-
ing, immediate service is required; see on-board
diagnostics system section.
MATERIALS ADDED TO FUEL
All gasoline sold in the United States and Canada
are required to contain effective detergent additives.
Use of additional detergents or other additives is not
needed under normal conditions.
FUEL SYSTEM CAUTIONS
CAUTION: Follow these guidelines to maintain your
vehicle's performance:
²The use of leaded gas is prohibited by Federal
law. Using leaded gasoline can impair engine perfor-
mance, damage the emission control system, and
could result in loss of warranty coverage.
²An out-of-tune engine, or certain fuel or ignition
malfunctions, can cause the catalytic converter to
overheat. If you notice a pungent burning odor or
some light smoke, your engine may be out of tune or
malfunctioning and may require immediate service.
Contact your dealer for service assistance.²When pulling a heavy load or driving a fully
loaded vehicle when the humidity is low and the tem-
perature is high, use a premium unleaded fuel to
help prevent spark knock. If spark knock persists,
lighten the load, or engine piston damage may result.
²The use of fuel additives which are now being
sold as octane enhancers is not recommended. Most
of these products contain high concentrations of
methanol. Fuel system damage or vehicle perfor-
mance problems resulting from the use of such fuels
or additives is not the responsibility of Daimler-
Chrysler Corporation and may not be covered under
the new vehicle warranty.
NOTE: Intentional tampering with emissions control
systems can result in civil penalties being assessed
against you.
DESCRIPTION - FUEL REQUIREMENTS -
DIESEL ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Do not use alcohol or gasoline as a fuel
blending agent. They can be unstable under certain
conditions and hazardous or explosive when mixed
with diesel fuel.
Use good quality diesel fuel from a reputable sup-
plier in your Dodge truck. For most year-round ser-
vice, number 2 diesel fuel meeting ASTM
specification D-975 will provide good performance. If
the vehicle is exposed to extreme cold (below 0ÉF/-
18ÉC), or is required to operate at colder-than-normal
conditions for prolonged periods, use climatized No. 2
diesel fuel or dilute the No. 2 diesel fuel with 50%
No. 1 diesel fuel. This will provide better protection
from fuel gelling or wax-plugging of the fuel filters.
Diesel fuel is seldom completely free of water. To
prevent fuel system trouble, including fuel line freez-
ing in winter, drain the accumulated water from the
fuel/water separator using the fuel/water separator
drain provided. If you buy good-quality fuel and fol-
low the cold-weather advice above, fuel conditioners
should not be required in your vehicle. If available in
your area, a high cetane ªpremiumº diesel fuel may
offer improved cold starting and warm-up perfor-
mance.
0 - 2 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEBR/BE
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE (Continued)
Page 50 of 2889

FRONT - 2WD
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT - 2WD
DESCRIPTION............................7
SPECIFICATIONS.........................8
SPECIAL TOOLS..........................9
HUB / BEARING
REMOVAL...............................9
INSTALLATION............................9
JOUNCE BUMPER
DESCRIPTION............................9
OPERATION.............................9
KNUCKLE
DESCRIPTION............................9
OPERATION.............................10
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................10
LOWER BALL JOINT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................10
LOWER BALL JOINT....................10
LOWER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL..............................10
INSTALLATION...........................10
SHOCK
DESCRIPTION...........................11OPERATION.............................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................11
SHOCK...............................11
REMOVAL..............................11
INSTALLATION...........................11
SPRING
DESCRIPTION...........................11
OPERATION.............................11
REMOVAL..............................11
INSTALLATION...........................12
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION...........................12
OPERATION.............................12
REMOVAL..............................12
INSTALLATION...........................12
UPPER BALL JOINT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................12
UPPER BALL JOINT.....................12
UPPER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL..............................13
INSTALLATION...........................13
FRONT - 2WD
DESCRIPTION
The independent front suspension (IFS) is com-
prised of (Fig. 1) and (Fig. 2):
²Shock absorbers
²Coil springs
²Upper and lower suspension arms
²Stabilizer bar
²Steering Knuckles
²Hub/Bearing
²Ball Joints
²Jounce Bumpers
CAUTION: Components attached with a nut and cot-
ter pin must be torqued to specification. Then if the
slot in the nut does not line up with the cotter pin
hole, tighten nut until it is aligned. Never loosen the
nut to align the cotter pin hole.
Fig. 1 Independent Front Suspension
1 - KNUCKLE
2 - SUSPENSION ARM
3 - COIL SPRING
4 - STABILIZER BAR
5 - SUSPENSION ARM
6 - LINK
BR/BEFRONT - 2WD 2 - 7
Page 53 of 2889

OPERATION
The steering knuckles pivots between the upper
and lower ball joints. The steering linkage is
attached to the knuckles controls vehicle steering.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the brake caliper and rotor, (Refer to 5
- BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the tie-rod
end. Remove the tie rod end from the knuckle with
Puller C-3894-A.
(5) Remove the cotter pins and nuts from the
upper and lower ball joints. Separate upper ball joint
from knuckle with remover MD-990635. Separate
lower ball joint with remover C-4150A and remove
knuckle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the knuckle on the ball joints and
install the ball joint nuts.
(2) Tighten the upper ball joint nut to 81 N´m (60
ft. lbs.) and install cotter pin.
(3) Tighten the lower ball joint nut to:
²LD: 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.)
²HD: 149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.)
(3) Install the cotter pin.
(4) Install the tie rod end on the steering knuckle
and tighten the nut to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.). Install
cotter pin.
(5) Install the brake rotor and caliper, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install wheel and tire assembly (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(7) Remove support and lower vehicle.
LOWER BALL JOINT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LOWER BALL
JOINT
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle. Place safety floor
stands under both lower suspension arms as far out-
board as possible. Lower the vehicle to allow the
stands to support some or all of the vehicle weight.
NOTE: The upper suspension arms must not be in
maximum rebound position.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Mount a dial indicator solidly under the lower
suspension arm.(4) Position indicator plunger against the bottom
of the steering knuckle lower ball joint boss.
NOTE: The dial Indicator plunger must be perpen-
dicular to the machined surface of the steering
knuckle lower ball joint boss.
(5) Position a pry bar over the top of the upper
suspension arm and under the pivot bar of the upper
suspension arm. Pry down on the upper suspension
arm and then zero the dial indicator.
(6) Reposition the pry bar under the upper suspen-
sion arm and on top of the frame rail. Pry up on the
upper suspension arm and record the dial indicator
reading.
(7) If the travel exceeds 0.8 mm (0.030 in.) replace
the suspension arm.
LOWER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the brake caliper assembly and rotor,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the tie rod.
Remove the tie rod end from the steering knuckle
with Puller C-3894-A.
(5) Remove the stabilizer bar link from lower sus-
pension arm.
(6) Support the lower suspension arm outboard
end with jack. Place a jack under the arm in the
front of the shock mount.
(7) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the lower
ball joint. Separate the ball joint with Remover
C-4150A.
(8) Remove the lower shock bolt from the suspen-
sion arm.
(9) Lower the jack and suspension arm until
spring tension is relieved. Remove spring and rubber
isolator (Fig. 5).
(10) Remove bolts mounting suspension arm to
crossmember and remove arm.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the suspension arm on the crossmem-
ber and install the bolts and nuts snug.
(2) Install the rubber isolator on top of the spring.
Position the spring into upper spring seat.
(3) Raise the lower suspension arm with a jack
and position the spring into the lower suspension
arm mount.
(4) Install the lower shock bolt and tighten to 142
N´m (105 ft. lbs.).
2 - 10 FRONT - 2WDBR/BE
KNUCKLE (Continued)
Page 54 of 2889

(5) Install the steering knuckle on the lower ball
joint. Install the lower ball joint nut and tighten to:
²LD: 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.)
²HD: 136 N´m (110 ft. lbs.)
(5) Install the lower ball joint cotter pin.
(6) Install the stabilizer bar link on the lower sus-
pension arm. Install the grommet, retainer and nut
and tighten to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install the tie rod end on the steering knuckle
and tighten nut to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.). Install cotter
pin.
(8) Install the brake rotor and caliper assembly,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the tire and wheel assembly, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(10) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(11) Tighten the suspension arm crossmember
nuts to 169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
SHOCK
DESCRIPTION
The top of the shocks mounts on frame brackets
using grommets. The bottom of the shock is bolted to
the lower suspension arms.
OPERATION
The shock absorbers dampen jounce and rebound
of the vehicle over various road conditions.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The shock absorber bushings do not require any
type of lubrication. Do not attempt to stop bushing
noise by lubricating them. Grease and mineral oil-
base lubricants will deteriorate the bushing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove shock upper nut and remove retainer
and grommet.
(3) Remove lower mounting bolt from suspension
arm and remove shock (Fig. 4).
INSTALLATION
(1) Extend shock fully, install retainer and grom-
met on top of shock absorber. Check grommets and
retainer for wear.
(2) Guide shock up through upper suspension arm
bracket. Install top grommet, retainer and nut.
Tighten nut to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(3) Align bottom end of shock into lower suspen-
sion arm and install mounting bolt. Tighten bolt to
142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.).
(4) Remove support and lower vehicle.
SPRING
DESCRIPTION
The springs mount between the lower suspension
arms and the front cross member spring seats. A rub-
ber isolator seats on top off the spring to help pre-
vent noise.
OPERATION
The coil springs control ride quality and maintain
proper ride height.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
Fig. 4 Shock
1 - SHOCK
2 - JOUNCE BUMPER
BR/BEFRONT - 2WD 2 - 11
LOWER CONTROL ARM (Continued)
Page 56 of 2889

(3) Position the indicator plunger against the
upper ball stud boss of the steering knuckle.
(4) Grasp the top of the tire and apply force in and
out. Look for movement at the ball joint between the
upper suspension arm and steering knuckle.
(5) If lateral movement is greater than 0.8 mm
(0.030 in.), replace the suspension arm.
UPPER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Support lower suspension arm at outboard end
with jack stand.(4) Remove upper ball joint cotter pin and nut.
(5) Separate ball joint from knuckle with remover
MB-990635.
(6) Remove pivot bar bolts from upper suspension
arm bracket and remove arm from vehicle (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the upper suspension arm on the
bracket and install the pivot bar bolts. Tighten to
169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install the ball joint in the knuckle. Install the
nut and tighten to 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.) and replace-
ment the cotter pin.
(3) Remove the jack from the lower suspension
arm.
(4) Install the tire and wheel assembly, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(5) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(6) Align the front suspension, (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Fig. 6 STABILIZER BAR
1 - STABILIZER BAR
2 - GROMMET
3 - GROMMET
4 - LINK
Fig. 7 Upper Suspension Arm
1 - PIVOT BAR
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - SUSPENSION ARM FRAME MOUNT
4 - ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
BR/BEFRONT - 2WD 2 - 13
UPPER BALL JOINT (Continued)
Page 57 of 2889

FRONT - 4WD
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT - 4WD
DESCRIPTION...........................14
SPECIFICATIONS........................15
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................16
HUB / BEARING
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................18
KNUCKLE
DESCRIPTION...........................20
OPERATION.............................20
REMOVAL..............................20
INSTALLATION...........................20
LOWER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL..............................20
INSTALLATION...........................20
SHOCK
DESCRIPTION...........................21
OPERATION.............................21
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................21
SHOCK..............................21
REMOVAL..............................21
INSTALLATION...........................21
SPRING
DESCRIPTION...........................22OPERATION.............................22
REMOVAL..............................22
INSTALLATION...........................22
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION...........................22
OPERATION.............................22
REMOVAL..............................22
INSTALLATION...........................23
TRACK BAR
DESCRIPTION...........................23
OPERATION.............................23
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................23
TRACK BAR...........................23
REMOVAL..............................23
INSTALLATION...........................23
UPPER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL..............................23
INSTALLATION...........................24
LOWER BALL JOINT
REMOVAL..............................24
INSTALLATION...........................25
UPPER BALL JOINT
REMOVAL..............................25
INSTALLATION...........................25
FRONT - 4WD
DESCRIPTION
The link/coil suspension allows each wheel to adapt
to different road surfaces. The suspension is com-
prised of (Fig. 1) :
²Shock absorbers
²Coil springs
²Upper and lower suspension arms
²Stabilizer bar
²Track bar
²Steering Knuckles
²Hub/Bearing
²Ball Joints
²Jounce Bumpers
CAUTION: Components attached with a nut and cot-
ter pin must be torqued to specification. Then if the
slot in the nut does not line up with the cotter pin
hole, tighten nut until it is aligned. Never loosen the
nut to align the cotter pin hole.CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings (except stabilizer bar) should be tightened
with the vehicle at normal height. It is important to
have the springs supporting the weight of the vehi-
cle when the fasteners are torqued. If springs are
not at their normal ride position, vehicle ride com-
fort could be affected and premature bushing wear
may occur.
DESCRIPTION
The upper and lower suspension arms use bush-
ings to isolate road noise. The suspension arms are
bolted to the frame and axle through the rubber
bushings. The lower suspension arm uses cam bolts
at the axle to allow for caster and pinion angle
adjustment.
2 - 14 FRONT - 4WDBR/BE
Page 63 of 2889

(8) Install a new cotter pin in hub nut. Tighten the
nut as needed to align cotter pin hole in shaft with
the opening in the nut.
(9) Install the rotor, brake caliper with adapter,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the ABS wheel speed sensor if
equipped, (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/ELECTRICAL/
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Install the wheel and tire assemblies, (Refer
to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(12) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(13) Apply the brakes several times to seat the
brake shoes and the caliper piston. Do not move the
vehicle until a firm brake pedal is obtained.
KNUCKLE
DESCRIPTION
The knuckles are a single casting with legs
machined for the upper and lower ball joints. The
knuckles also has machined mounting locations for
the front brake calipers adapters and hub bearing
assembly.
OPERATION
The steering knuckles pivots between the upper
and lower ball joints. The steering linkage is
attached to the knuckles controls vehicle steering.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearing and axle shaft.
(2) Remove tie-rod or drag link end from the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(3) Remove the ABS sensor wire and bracket from
knuckle.
(4) Remove the cotter pin from the upper ball stud
nut. Remove the upper and lower ball stud nuts.
(5) Strike the steering knuckle with a brass ham-
mer to loosen. Remove knuckle from axle tube yokes.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearing and axle shaft.
(2) Remove tie-rod or drag link end from the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(3) Remove the ABS sensor wire and bracket from
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedures.
(4) Remove the cotter pin from the upper ball stud
nut. Remove the upper and lower ball stud nuts.
(5) Strike the steering knuckle with a brass ham-
mer to loosen.
(6) Remove knuckle from axle tube yokes.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering knuckle on the ball studs.
(2) Install and tighten lower ball stud nut to 108
N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(3) Install and tighten upper ball stud nut to 101
N´m (75 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(4) Install the hub bearing and axle shaft.
(5) Install tie-rod or drag link end onto the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(6) Install the ABS sensor wire and bracket to the
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedures.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering knuckle on the ball studs.
(2) Install and tighten lower ball stud nut to 47
N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque. Do not install cotter pin at
this time.
(3) Install and tighten upper ball stud nut to 94
N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(4) Retorque lower ball stud nut to 190±217 N´m
(140±160 ft. lbs.) torque. Advance nut to next slot to
line up hole and install new cotter pin.
(5) Install the hub bearing and axle shaft.
(6) Install tie-rod or drag link end onto the steer-
ing knuckle arm.
(7) Install the ABS sensor wire and bracket to the
knuckle. Refer to Brakes, for proper procedure.
LOWER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Paint or scribe alignment marks on the cam
adjusters and suspension arm for installation refer-
ence (Fig. 15).
(3) Remove the lower suspension arm nut, cam
and cam bolt from the axle.
(4) Remove the nut and bolt from the frame rail
bracket and remove the lower suspension arm (Fig.
22).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the lower suspension arm at the axle
bracket and frame rail bracket.
(2) Install the rear bolt and finger tighten the nut.
(3) Install the cam bolt, cam and nut in the axle
and align the reference marks.
(4) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
(5) Tighten cam nut at the axle bracket to 190
N´m (140 ft. lbs.). Tighten rear nut at the frame
bracket to 190 N´m (140 ft. lbs.).
2 - 20 FRONT - 4WDBR/BE
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
Page 64 of 2889
SHOCK
DESCRIPTION
The shocks are mounted inside the springs and
attached at the top to brackets with grommets. These
brackets are bolted on the frame with three studs on
a ring. The shock is mounted at the bottom of the
axle below the spring seat.
OPERATION
The shock absorbers dampen the jounce and
rebound of the vehicle over various road conditions.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorbermust be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The shock absorber bushings do not require any
type of lubrication. Do not attempt to stop bushing
noise by lubricating them. Grease and mineral oil-
base lubricants will deteriorate the bushing.
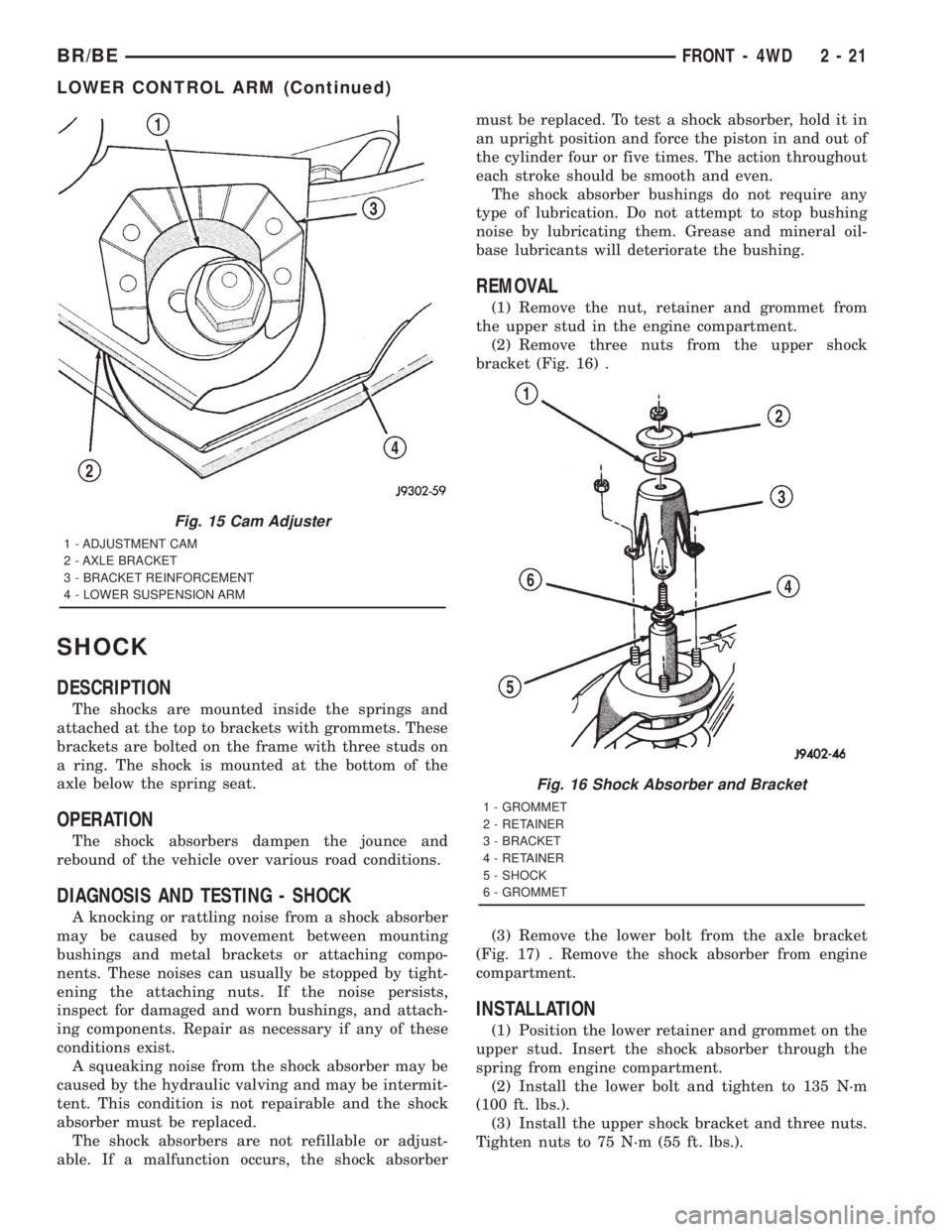
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the nut, retainer and grommet from
the upper stud in the engine compartment.
(2) Remove three nuts from the upper shock
bracket (Fig. 16) .
(3) Remove the lower bolt from the axle bracket
(Fig. 17) . Remove the shock absorber from engine
compartment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the lower retainer and grommet on the
upper stud. Insert the shock absorber through the
spring from engine compartment.
(2) Install the lower bolt and tighten to 135 N´m
(100 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install the upper shock bracket and three nuts.
Tighten nuts to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 15 Cam Adjuster
1 - ADJUSTMENT CAM
2 - AXLE BRACKET
3 - BRACKET REINFORCEMENT
4 - LOWER SUSPENSION ARM
Fig. 16 Shock Absorber and Bracket
1 - GROMMET
2 - RETAINER
3 - BRACKET
4 - RETAINER
5 - SHOCK
6 - GROMMET
BR/BEFRONT - 4WD 2 - 21
LOWER CONTROL ARM (Continued)
Page 65 of 2889

(4) Install upper grommet and retainer. Install
upper shock nut and tighten to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs).
SPRING
DESCRIPTION
The springs use a rubber isolators between the
frame bracket and spring. The isolators help prevent
road noise. The bottom of the spring sits on a seat
mounted to the axle.
OPERATION
The coil springs control ride quality and maintain
proper ride height.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle. Position a
hydraulic jack under the axle to support it.
(2) Paint or scribe alignment marks on lower sus-
pension arm cam adjusters and axle bracket for
installation reference.
(3) Remove the upper suspension arm and loosen
lower suspension arm bolts.
(4) Mark and disconnect the front propeller shaft
from the axle 4x4 models.
(5) Disconnect the track bar from the frame rail
bracket.
(6) Disconnect the drag link from pitman arm.
(7) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link and shock
absorber from the axle.(8) Lower the axle until the spring is free from the
upper mount. Remove the coil spring.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the coil spring on the axle pad.
(2) Raise the axle into position until the spring
seats in the upper mount.
(3) Connect the stabilizer bar links and shock
absorbers to the axle bracket. Connect the track bar
to the frame rail bracket.
(4) Install the upper suspension arm.
(5) Install the front propeller shaft to the axle 4x4
model.
(6) Install drag link to pitman arm and tighten
nut to specifications. Install new cotter pin.
(7) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(8) Tighten the following suspension components
to specifications:
²Link to stabilizer bar nut.
²Lower shock bolt.
²Track bar bolt at axle shaft tube bracket.
²Upper suspension arm nut at axle bracket.
²Upper suspension nut at frame bracket.
²Align lower suspension arm reference marks and
tighten cam nut.
²Lower suspension nut at frame bracket.
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION
The stabilizer bar extends across the front under-
side of the chassis and connects to the frame rails.
Links are connected from the bar to the axle brack-
ets. Stabilizer bar mounts are isolated by teflon lined
rubber bushings.
OPERATION
The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle front
sway during turns. The spring steel bar helps to con-
trol the vehicle body in relationship to the suspen-
sion.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Hold the stabilizer link shafts with a wrench
and remove the link nuts at the stabilizer bar.
(3) Remove the retainers and grommets from the
stabilizer bar links.
(4) Remove the stabilizer bar link nuts from the
axle brackets.
(5) Remove the links from the axle brackets with
Puller C-3894-A (Fig. 18).
(6) Remove the stabilizer bar clamps from the
frame rails and remove the stabilizer bar.
Fig. 17 Shock Absorber Axle Mount
1 - SHOCK
2 - SPRING
3 - FLAG NUT
4 - SHOCK BOLT
2 - 22 FRONT - 4WDBR/BE
SHOCK (Continued)
Page 66 of 2889

INSTALLATION
(1) Position the stabilizer bar on the frame rail
and install the clamps and bolts. Ensure the bar is
centered with equal spacing on both sides.
(2) Tighten the clamp bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install links to the axle bracket and tighten
nut to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install links, retainers, grommets and nuts to
the stabilizer bar. Hold the link shaft with a wrench
and tighten the nuts to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(5) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
TRACK BAR
DESCRIPTION
The bar is attached to a frame rail bracket with a
ball stud and is isolated with a bushing at the axle
bracket.
OPERATION
The track bar is used to control front axle side-to-
side movement.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRACK BAR
(1) Turn the front wheel 90É to the left of center.
(2) Mount a dial indicator to the left frame rail in
front of the track bar ball joint (Fig. 19).
(3) Position the dial indicator plunger on the ball
joint end cap next to the grease fitting and zero the
indicator.
NOTE: Dial indicator plunger must be perpendicular
to the ball joint end cap.(4) Turn the front wheel 180É to the right and
record the dial indicator reading. Repeat this step
three times and record all readings.
(5) If any of the readings exceed 2.03 mm (0.080
in) replace the track bar.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the ball
stud end at the frame rail bracket (Fig. 20) .
(3) Remove ball stud from bracket with Puller
C-4150A (Fig. 21) .
(4) Remove the bolt and flag nut from the axle
bracket and remove the track bar (Fig. 20) .
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the track bar at axle bracket. Loosely
install the retaining bolt and flag nut.
(2) Pry the axle assembly over to install the track
bar at the frame rail bracket.
(3) Install the retaining nut on the stud. Tighten
the ball stud nut to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.). Install a new
cotter pin.
(4) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(5) Tighten the bolt at the axle bracket to 176 N´m
(130 ft. lbs.).
UPPER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the upper suspension arm nut and bolt
at the axle bracket (Fig. 22) .
Fig. 18 Stabilizer Link
1 - PULLER
2 - LINK
Fig. 19 Dial Indicator Location
1 - TRACK BAR BALL JOINT
BR/BEFRONT - 4WD 2 - 23
STABILIZER BAR (Continued)