DODGE RAM 2003 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 1601 of 2895

CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL............................385
INSTALLATION........................385
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER
REMOVAL............................386
INSTALLATION........................386
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐHYDRAULIC
TAPPETS...........................386
REMOVAL............................387
CLEANING...........................388
INSTALLATION........................388
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION........................388
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐPISTON FITTING . 389
REMOVAL............................389
CLEANING...........................389
INSPECTION.........................389
INSTALLATION........................389
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐFITTING PISTON
RINGS.............................390
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL............................392
INSTALLATION........................392
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................392
INSTALLATION........................392
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL............................393
INSTALLATION........................393
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION........................393
OPERATION..........................393
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
LEAKS.............................394
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE.........................396OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL....396
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL............................397
INSTALLATION........................397
OIL PAN
REMOVAL............................397
CLEANING...........................397
INSPECTION.........................397
INSTALLATION........................398
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL............................398
CLEANING...........................398
INSPECTION.........................399
INSTALLATION........................400
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION........................401
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐINTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE.................401
REMOVAL............................401
CLEANING...........................402
INSPECTION.........................402
INSTALLATION........................402
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION........................403
OPERATION..........................403
REMOVAL............................404
CLEANING...........................404
INSPECTION.........................404
INSTALLATION........................404
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL............................404
INSTALLATION........................404
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL............................405
INSPECTIONÐMEASURING TIMING CHAIN
STRETCH..........................405
INSTALLATION........................406
9 - 352 ENGINE 8.0LDR
Page 1602 of 2895

ENGINE 8.0L
DESCRIPTION
The 8.0 Liter (488 CID) ten-cylinder engine is a
V-Type lightweight, single cam, overhead valve
engine with hydraulic roller tappets. This engine is
designed for unleaded fuel.
Engine lubrication system consists of a gerotor
type oil pump mounted in the timing chain cover and
driven by the crankshaft. The V-10 uses a full flow
oil filter.
The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7, 9 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 on the
right bank. The firing order is 1-10-9-4-3-6-5-8-7-2
(Fig. 1).
The engine serial number is located on the lower
left front of the cylinder block in front of the engine
mount (Fig. 2). When component part replacement is
necessary, use the engine type and serial number for
reference.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING - Preformance) or (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING - Mechanical). Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM for fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
²Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/HYDRAULIC LIFT-
ERS (CAM IN BLOCK) - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING)
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING)
Fig. 1 Firing Order
Fig. 2 Engine IdentificationÐ(Serial Number)
1 - ENGINE SERIAL NO.
2 - ENGINE MOUNT LOCATION
DRENGINE 8.0L 9 - 353
Page 1603 of 2895
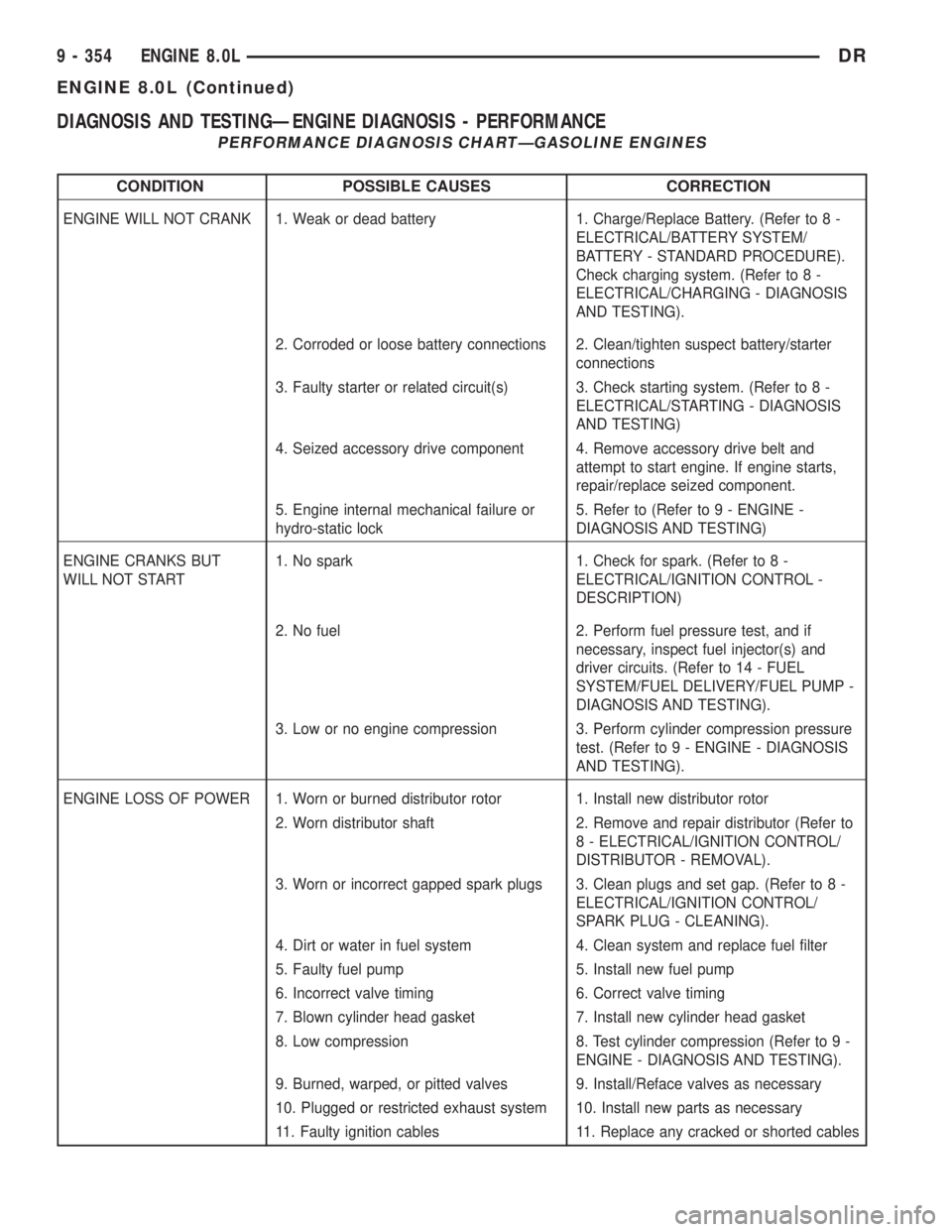
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS CHARTÐGASOLINE ENGINES
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT CRANK 1. Weak or dead battery 1. Charge/Replace Battery. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/
BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check charging system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
2. Corroded or loose battery connections 2. Clean/tighten suspect battery/starter
connections
3. Faulty starter or related circuit(s) 3. Check starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
4. Seized accessory drive component 4. Remove accessory drive belt and
attempt to start engine. If engine starts,
repair/replace seized component.
5. Engine internal mechanical failure or
hydro-static lock5. Refer to (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
ENGINE CRANKS BUT
WILL NOT START1. No spark 1. Check for spark. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL -
DESCRIPTION)
2. No fuel 2. Perform fuel pressure test, and if
necessary, inspect fuel injector(s) and
driver circuits. (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL PUMP -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
3. Low or no engine compression 3. Perform cylinder compression pressure
test. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Worn or burned distributor rotor 1. Install new distributor rotor
2. Worn distributor shaft 2. Remove and repair distributor (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
DISTRIBUTOR - REMOVAL).
3. Worn or incorrect gapped spark plugs 3. Clean plugs and set gap. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
SPARK PLUG - CLEANING).
4. Dirt or water in fuel system 4. Clean system and replace fuel filter
5. Faulty fuel pump 5. Install new fuel pump
6. Incorrect valve timing 6. Correct valve timing
7. Blown cylinder head gasket 7. Install new cylinder head gasket
8. Low compression 8. Test cylinder compression (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
9. Burned, warped, or pitted valves 9. Install/Reface valves as necessary
10. Plugged or restricted exhaust system 10. Install new parts as necessary
11. Faulty ignition cables 11. Replace any cracked or shorted cables
9 - 354 ENGINE 8.0LDR
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1604 of 2895
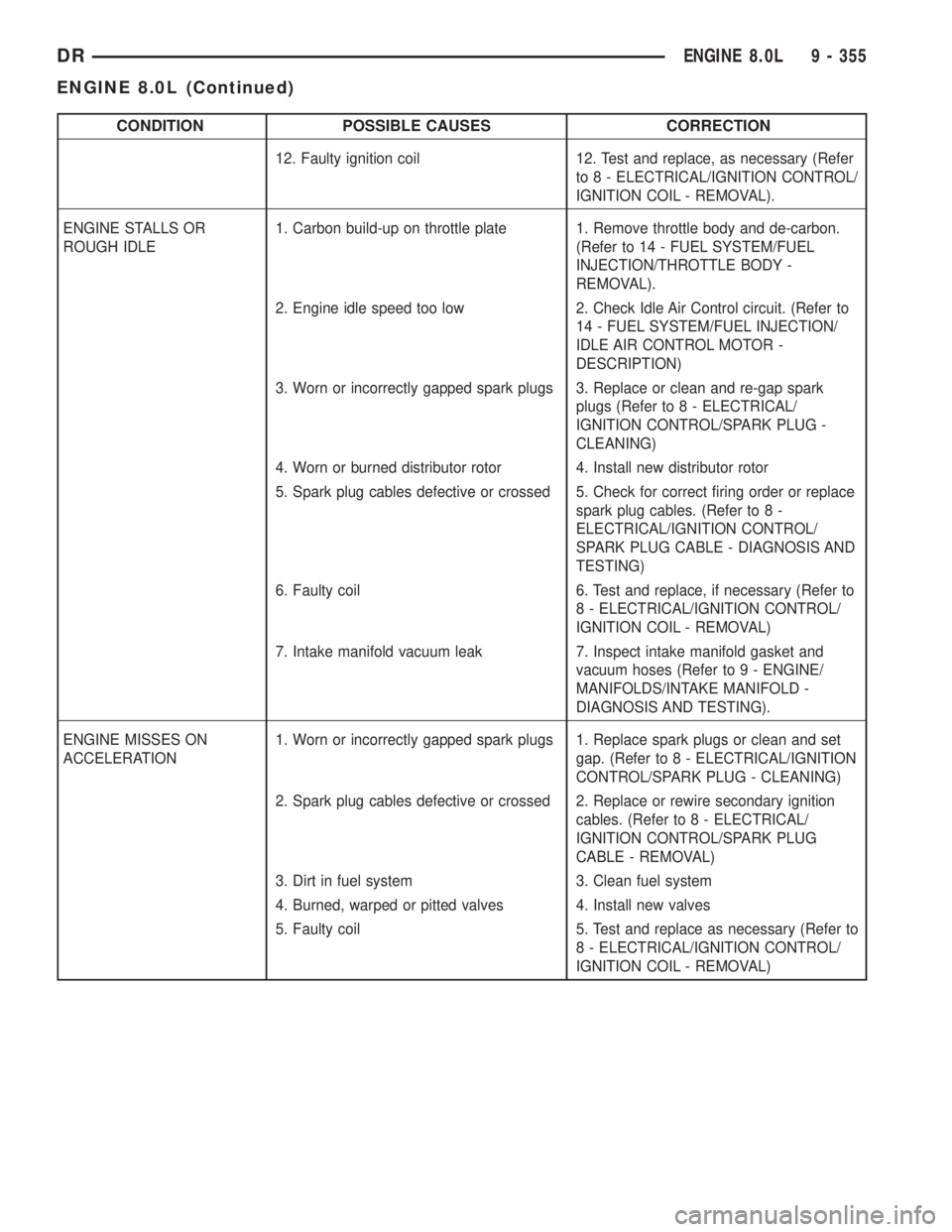
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
12. Faulty ignition coil 12. Test and replace, as necessary (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL).
ENGINE STALLS OR
ROUGH IDLE1. Carbon build-up on throttle plate 1. Remove throttle body and de-carbon.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/THROTTLE BODY -
REMOVAL).
2. Engine idle speed too low 2. Check Idle Air Control circuit. (Refer to
14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR -
DESCRIPTION)
3. Worn or incorrectly gapped spark plugs 3. Replace or clean and re-gap spark
plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING)
4. Worn or burned distributor rotor 4. Install new distributor rotor
5. Spark plug cables defective or crossed 5. Check for correct firing order or replace
spark plug cables. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
SPARK PLUG CABLE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
6. Faulty coil 6. Test and replace, if necessary (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL)
7. Intake manifold vacuum leak 7. Inspect intake manifold gasket and
vacuum hoses (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Worn or incorrectly gapped spark plugs 1. Replace spark plugs or clean and set
gap. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/SPARK PLUG - CLEANING)
2. Spark plug cables defective or crossed 2. Replace or rewire secondary ignition
cables. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
CABLE - REMOVAL)
3. Dirt in fuel system 3. Clean fuel system
4. Burned, warped or pitted valves 4. Install new valves
5. Faulty coil 5. Test and replace as necessary (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL)
DRENGINE 8.0L 9 - 355
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1605 of 2895
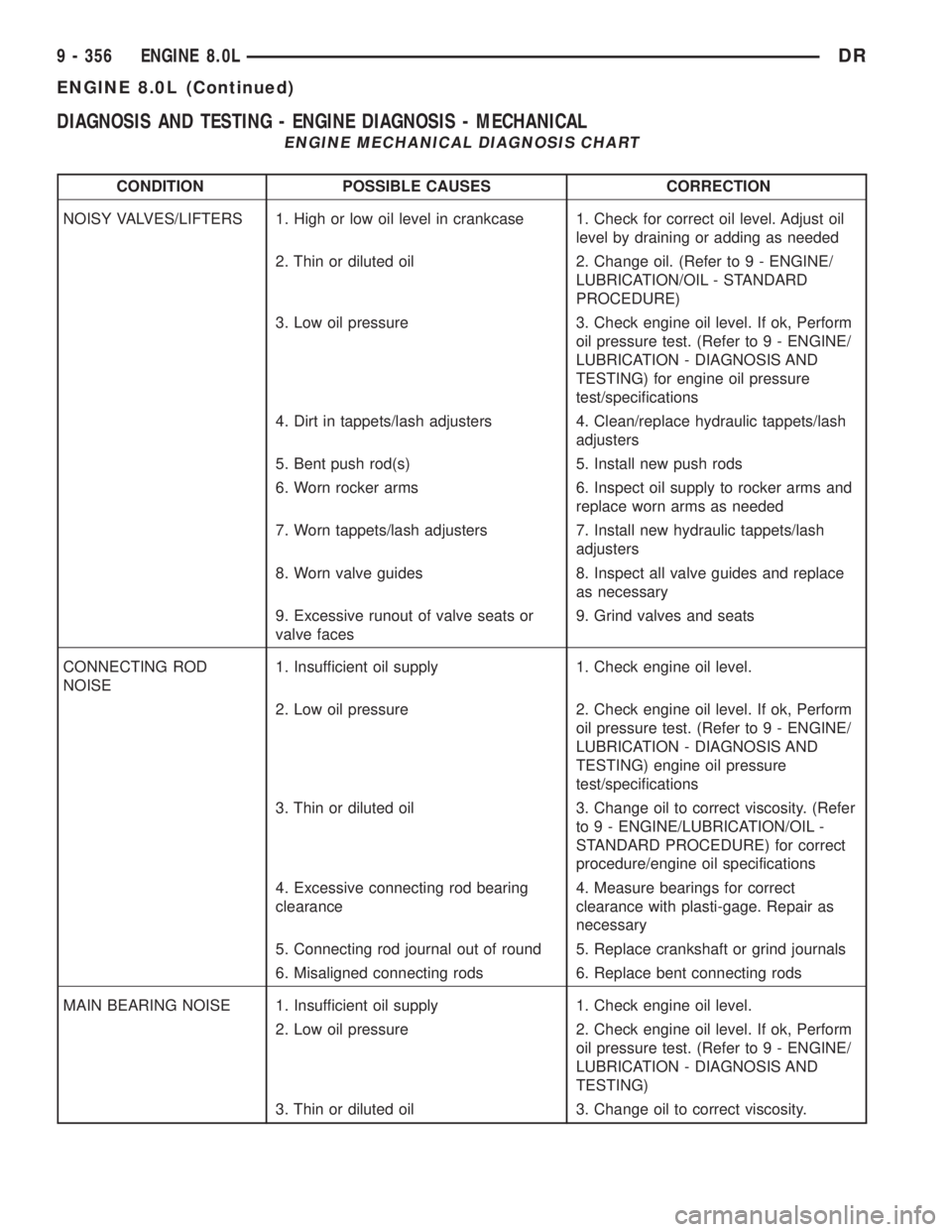
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES/LIFTERS 1. High or low oil level in crankcase 1. Check for correct oil level. Adjust oil
level by draining or adding as needed
2. Thin or diluted oil 2. Change oil. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
3. Low oil pressure 3. Check engine oil level. If ok, Perform
oil pressure test. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) for engine oil pressure
test/specifications
4. Dirt in tappets/lash adjusters 4. Clean/replace hydraulic tappets/lash
adjusters
5. Bent push rod(s) 5. Install new push rods
6. Worn rocker arms 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms and
replace worn arms as needed
7. Worn tappets/lash adjusters 7. Install new hydraulic tappets/lash
adjusters
8. Worn valve guides 8. Inspect all valve guides and replace
as necessary
9. Excessive runout of valve seats or
valve faces9. Grind valves and seats
CONNECTING ROD
NOISE1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok, Perform
oil pressure test. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) engine oil pressure
test/specifications
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL -
STANDARD PROCEDURE) for correct
procedure/engine oil specifications
4. Excessive connecting rod bearing
clearance4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance with plasti-gage. Repair as
necessary
5. Connecting rod journal out of round 5. Replace crankshaft or grind journals
6. Misaligned connecting rods 6. Replace bent connecting rods
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure 2. Check engine oil level. If ok, Perform
oil pressure test. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
3. Thin or diluted oil 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
9 - 356 ENGINE 8.0LDR
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1606 of 2895
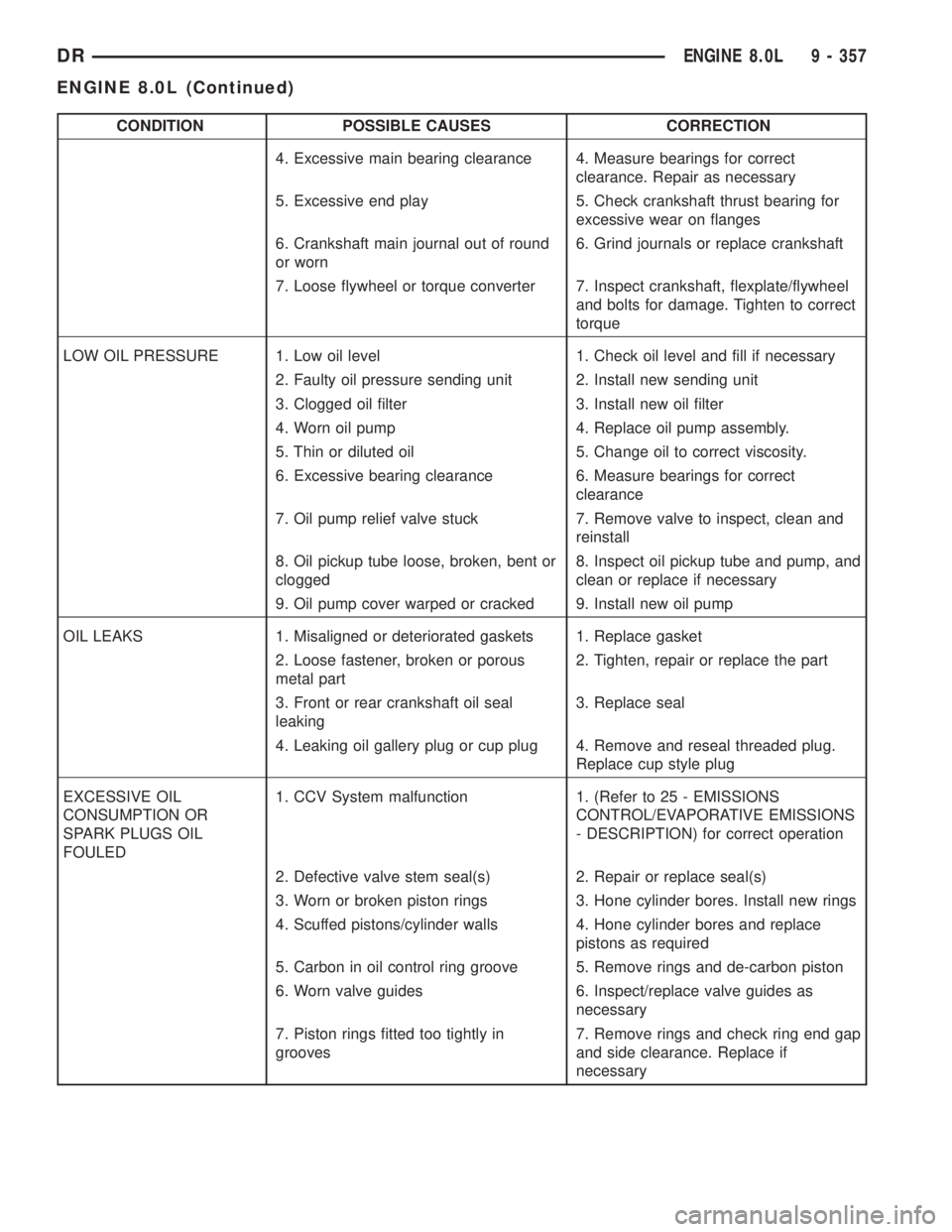
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
4. Excessive main bearing clearance 4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary
5. Excessive end play 5. Check crankshaft thrust bearing for
excessive wear on flanges
6. Crankshaft main journal out of round
or worn6. Grind journals or replace crankshaft
7. Loose flywheel or torque converter 7. Inspect crankshaft, flexplate/flywheel
and bolts for damage. Tighten to correct
torque
LOW OIL PRESSURE 1. Low oil level 1. Check oil level and fill if necessary
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit 2. Install new sending unit
3. Clogged oil filter 3. Install new oil filter
4. Worn oil pump 4. Replace oil pump assembly.
5. Thin or diluted oil 5. Change oil to correct viscosity.
6. Excessive bearing clearance 6. Measure bearings for correct
clearance
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck 7. Remove valve to inspect, clean and
reinstall
8. Oil pickup tube loose, broken, bent or
clogged8. Inspect oil pickup tube and pump, and
clean or replace if necessary
9. Oil pump cover warped or cracked 9. Install new oil pump
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated gaskets 1. Replace gasket
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part2. Tighten, repair or replace the part
3. Front or rear crankshaft oil seal
leaking3. Replace seal
4. Leaking oil gallery plug or cup plug 4. Remove and reseal threaded plug.
Replace cup style plug
EXCESSIVE OIL
CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL
FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
- DESCRIPTION) for correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end gap
and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
DRENGINE 8.0L 9 - 357
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1607 of 2895
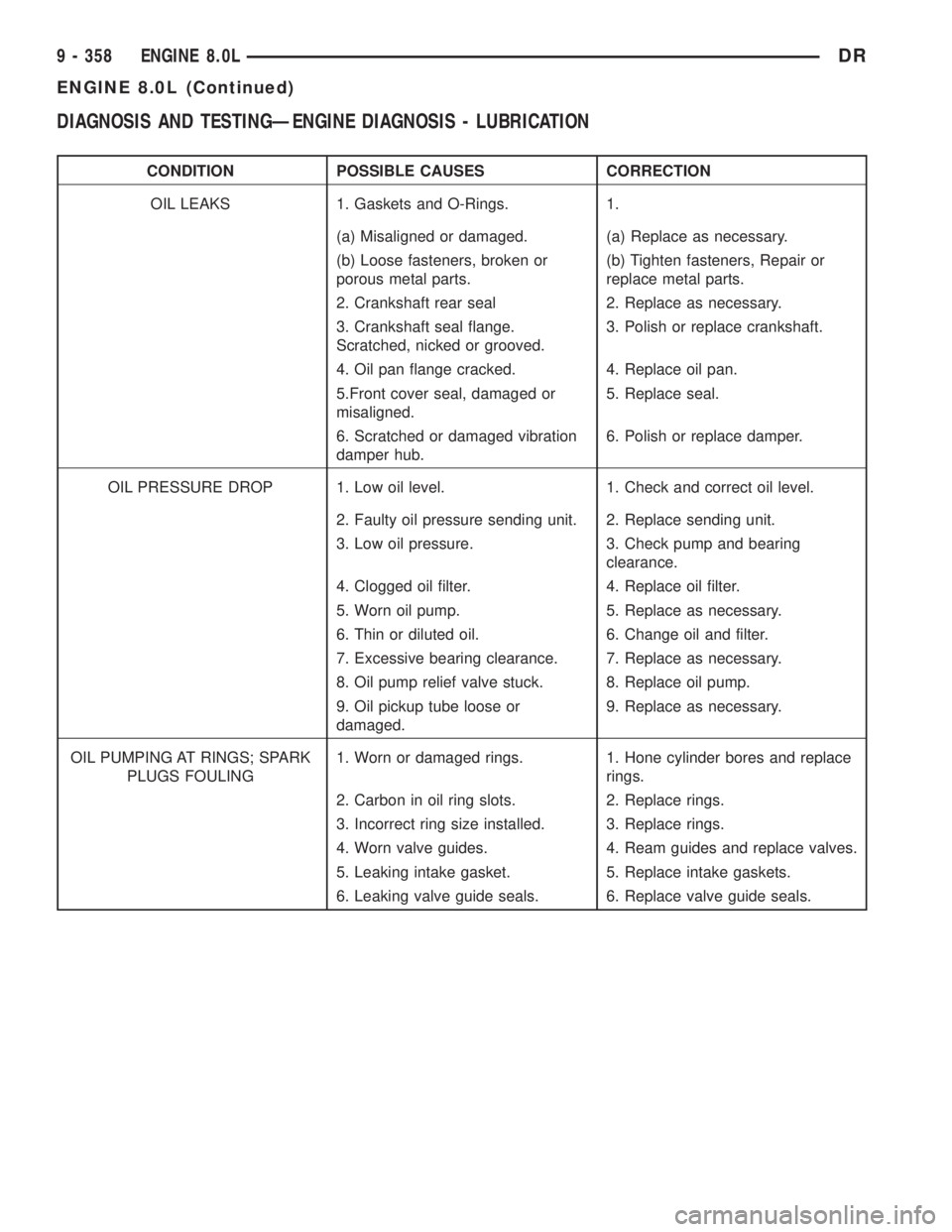
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL LEAKS 1. Gaskets and O-Rings. 1.
(a) Misaligned or damaged. (a) Replace as necessary.
(b) Loose fasteners, broken or
porous metal parts.(b) Tighten fasteners, Repair or
replace metal parts.
2. Crankshaft rear seal 2. Replace as necessary.
3. Crankshaft seal flange.
Scratched, nicked or grooved.3. Polish or replace crankshaft.
4. Oil pan flange cracked. 4. Replace oil pan.
5.Front cover seal, damaged or
misaligned.5. Replace seal.
6. Scratched or damaged vibration
damper hub.6. Polish or replace damper.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter.
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump.
9. Oil pickup tube loose or
damaged.9. Replace as necessary.
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings.
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings.
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves.
5. Leaking intake gasket. 5. Replace intake gaskets.
6. Leaking valve guide seals. 6. Replace valve guide seals.
9 - 358 ENGINE 8.0LDR
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1608 of 2895

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
REMOVAL).
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.
(4) Disconnect the ignition coil.
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the third
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the
correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing)
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM HOT COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn OFF the
engine.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedure on each cylinder accord-
ing to the tester manufacturer's instructions. While
testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through
the throttle body, tailpipe or oil filler cap opening.
Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
DRENGINE 8.0L 9 - 359
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1609 of 2895

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60
strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 50É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Toothin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
9 - 360 ENGINE 8.0LDR
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1610 of 2895

MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier than using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
DRENGINE 8.0L 9 - 361
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)