wheel alignment DODGE RAM 2003 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 48 of 2895

NOTE: Extreme pressure lubrication must be used
on the threaded portions of the tool. This will
increase the longevity of the tool and insure proper
operation during the removal and installation pro-
cess.
(7) Press the ball joint from the lower control arm
using special tools C-4212±F (PRESS), 8698-2
(RECEIVER) and 8698-3 (DRIVER) (Fig. 21).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Extreme pressure lubrication must be used on
the threaded portions of the tool. This will increase
the longevity of the tool and insure proper operation
during the removal and installation process.
(1) Install the ball joint into the control arm and
press in using special tools C-4212±F (press), 8698-1
(driver) and 8698-3 (receiver) (Fig. 22).
(2) Install the ball joint boot.
(3) Stake the ball joint flange in four evenly
spaced places around the ball joint flange, using a
chisel and hammer (LD only).
(4) Replace the snap ring (HD 4X2 only)
(5) Remove the support for the halfshaft and
install into position (If Equipped).
(6) Install the steering knuckle (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the tie rod end into the steering knuckle
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/LINKAGE/TIE ROD END -
INSTALLATION).
(8) Install and tighten the halfshaft nut to 251
N´m (185 ft. lbs.). (If Equipped).
(9) Install the brake caliper and rotor (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the tire and wheel assembly (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(11) Check the vehicle ride height (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(12) Perform a wheel alignment (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Fig. 20 LOWER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8677
Fig. 21 REMOVAL LOWER BALL JOINT
1 - PRESS - C-4212-F
2 - DRIVER - 8698-3
3 - BALL JOINT
4 - RECEIVER - 8698-2
Fig. 22 INSTALL LOWER BALL JOINT
1 - PRESS - C-4212-F
2 - DRIVER - 8698-1
3 - BALL JOINT
4 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
5 - RECEIVER - 8698-3
DRFRONT - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION 2 - 19
LOWER BALL JOINT (Continued)
Page 50 of 2895

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4X4 (LD)
(1) Position the lower control arm at the frame rail
brackets. Install the pivot bolts and nuts. Tighten the
nuts finger-tight.
CAUTION: The ball joint stud taper must be CLEAN
and DRY before installing the knuckle. Clean the
stud taper with mineral spirits to remove dirt and
grease.
(2) Insert the lower ball joint into the steering
knuckle. Install and tighten the retaining nut to 52
N´m (38 ft. lbs.)(on 1500 series only an additional 90É
turn is required).
(3) Install the torsion bar, (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/FRONT/TRACK BAR - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install shock absorber lower bolt and tighten to
135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install the front halfshaft, (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT -
INSTALLATION).
(6) Insert the upper ball joint into the steering
knuckle. Install and tighten the retaining nut to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.)(on 1500 series only an additional 90É
turn is required).
(7) Install the stabilizer bar link (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/STABILIZER LINK - INSTALLA-
TION).
(8) Tighten the lower control arm front pivot nut
to 204 N´m (150 ft. lbs.). Tighten rear pivot bolt to
204 N´m (150 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the wheel and tire assembly,(Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(10) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(11) Adjust the front suspension height and per-
form a wheel alignment (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/
WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - 4X2
(1) Install the lower control arm into place on the
vehicle.
(2) Install the front and rear control arm pivot
bolts finger tight.
(3) Install the coil spring into the frame pocket(Re-
fer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/SPRING - INSTAL-
LATION).
(4) Install the Spring Compressor DD-1278 up
through the lower suspension arm, coil spring and
shock hole in the frame.
(5) Tighten the tool nut to compress the coil
spring.
(6) Remove the support from the upper control
arm and steering knuckle.(7) Position the lower ball joint into the steering
knuckle.
(8) Install the retaining nut on the lower ball joint
and tighten to 52 N´m (38 ft. lbs.)(on 1500 series only
an additional 90É turn is required) or 135 N´m (100
ft. lbs.)(HD 4X2 only).
(9) Support the lower control arm at the outboard
side of the lower control arm to support vehicle
weight.
(10) Remove the spring compressor tool.
(11) Install the shock absorber. (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/SHOCK - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install the stabilizer link (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/STABILIZER LINK - INSTALLA-
TION).
(13) Remove the lower control arm support.
(14) Install the wheel and tire assembly and lower
the vehicle. (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(15) Lower the vehicle to the floor with vehicle
weight and Tighten the front and rear control arm
pivot bolts to 204 N´m (150 ft. lbs.)(LD) or 285 N´m
(210 ft. lbs.)(HD 4X2 only).
(16) Perform a wheel alignment (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
SPRING
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assembly.
(3)
Support the lower control arm at the outboard
side of the lower control arm to support vehicle weight.
(4) Remove the shock absorber (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/SHOCK - REMOVAL).
(5) Install Spring Compressor DD-1278 up through
the lower suspension arm, coil spring and shock hole
in the frame. The bell-shaped adapter goes against
the lower suspension arm. Install the nut on top of
the tool at the shock hole (Fig. 25).
(6) Tighten the spring compressor nut against bell-
shaped adapter finger tight then loosen 1/2 turn.
NOTE: This will hold the spring in place until the
lower suspension arm is separated from the steer-
ing knuckle.
(7) Remove the stabilizer link (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/STABILIZER LINK - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the lower ball joint nut at the steering
knuckle.
(9) Install Ball Joint Remover tool 8677 on the
lower ball joint and separate the ball joint from the
knuckle.
(10)
DRFRONT - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION 2 - 21
LOWER CONTROL ARM (Continued)
Page 51 of 2895

NOTE: Do not allow the upper control arm and
steering knuckle to rebound downwards they must
be supported.Support the upper control arm and
steering knuckle out of the way.
(11) Remove the lower control arm support.
(12) Tighten the spring compressor tool to allow
clearance for the lower ball joint to be removed out of
the knuckle.
NOTE: It may necessary to loosen the control arm
pivot bolt to allow downward swing.
(13) Loosen the tension on the spring compressor
tool slowly allowing the lower suspension arm to
pivot downward.
(14) Remove the spring compressor tool.
(15) Remove coil spring and isolator pad from the
vehicle (Fig. 26).
INSTALLATION
(1) Tape the isolator pad to the top of the coil
spring. Position the spring in the lower suspension
arm well. Be sure that the coil spring is seated in the
well.
(2) Install Spring Compressor DD-1278 up through
the lower suspension arm, coil spring and shock hole
in the frame.
(3) Tighten the tool nut to compress the coil
spring.(4) Remove the support from the upper control
arm and steering knuckle.
(5) Position the lower ball joint into the steering
knuckle.
(6) Install the retaining nut on the lower ball joint
and tighten to 52 N´m (38 ft. lbs.)(on 1500 series only
an additional 90É turn is required) or 135 N´m (100
ft. lbs.)(HD 4X2 only).
(7) Remove the spring compressor tool.
(8) Support the lower control arm at the outboard
side of the lower control arm to support vehicle
weight.
(9) Install the shock absorber. (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/SHOCK - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the stabilizer link (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/FRONT/STABILIZER LINK - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Remove the lower control arm support.
(12) Install the wheel and tire assembly and lower
the vehicle. (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(13) Lower the vehicle to the floor with vehicle
weight and Tighten the front and rear control arm
pivot bolts if loosened to 204 N´m (150 ft. lbs.)(LD) or
285 N´m (210 ft. lbs.)(HD 4X2 only).
(14) Perform a wheel alignment (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Fig. 25 SPRING COMPRESSOR TOOL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL DD-1278
2 - BELL-SHAPED ADAPTER
Fig. 26 COIL SPRING
1 - COIL SPRING
2 - STEERING KNUCKLE
3 - OUTER TIE ROD END
4 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
5 - SHOCK
2 - 22 FRONT - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSIONDR
SPRING (Continued)
Page 55 of 2895

INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The left and right side torsion bars are
NOT interchangeable. The bars are identified and
stamped R or L, for right or left. The bars do not
have a front or rear end and can be installed with
either end facing forward.
(1) Insert torsion bar ends into anchor and suspen-
sion arm.
(2) Position the anchor in the frame crossmember.
(3) Install Special Tool - 8686 to the anchor and
the crossmember (Fig. 30).
(4) Increase the tension on the anchor in order to
load the torsion bar.
(5) Install the adjustment bolt and the adjuster
nut.
(6) Turn adjustment bolt clockwise the recorded
amount of turns.
(7) Remove tool - 8686 from the torsion bar cross-
member (Fig. 30).
(8) Install the transfer case skid plate (Refer to 13
- FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - INSTALLATION).
(9) Lower vehicle and adjust the front suspension
height (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGN-
MENT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(10) Perform a wheel alignment (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
UPPER BALL JOINT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - UPPER BALL
JOINT
NOTE: If the ball joint is equipped with a lubrication
fitting, grease the joint then road test the vehicle
before performing test.
(1) Raise the front of the vehicle. Place safety floor
stands under both lower control arms as far outboard
as possible. Lower the vehicle to allow the stands to
support some or all of the vehicle weight.
(2) Remove the front tires.(3) Mount a dial indicator solidly to the frame and
then zero the dial indicator.
(4) Position dial indicator plunger on the topside of
the upper ball joint (Fig. 32).
NOTE: The dial indicator plunger must be perpen-
dicular to the machined surface of the ball joint
(Fig. 32).
NOTE: Use care not to pry or tear the ball joint
boot, when checking the free play.
(5) Position a pry bar between the steering
knuckle and the upper control arm. Pry upwards on
the upper control arm (Fig. 32).
(6) If the travel exceeds 0.5 mm (0.020 in.), replace
the upper control arm since the upper ball joint is
integral to the arm (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/
FRONT/UPPER CONTROL ARM - REMOVAL).
(7) If the upper ball joint is within specs reinstall
the front tires (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/
WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 32 UPPER BALL JOINT PLAY
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
3-PRYBAR
4 - KNUCKLE
5 - BALL JOINT BOOT
2 - 26 FRONT - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSIONDR
TORSION BAR (Continued)
Page 56 of 2895

UPPER CONTROL ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the nut from upper ball joint.
(4) Separate upper ball joint from the steering
knuckle with Remover 8677 (Fig. 33)
CAUTION: When installing Remover 8677 to sepa-
rate the ball joint, be careful not to damage the ball
joint seal.(5) Remove the control arm pivot bolts and remove
control arm (Fig. 34).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the control arm into the frame brack-
ets. Install bolts and tighten to 132 N´m (97 ft.
lbs.)(LD) or 170 N´m (125 ft. lbs.)(HD 4X2 only).
(2) Insert the ball joint in steering knuckle and
tighten the upper ball joint nut to 54 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.)(on 1500 series only an additional 90É turn is
required).
(3) Install the wheel and tire assembly,(Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(4) Remove the support and lower vehicle.
(5) Perform a wheel alignment, (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Fig. 33 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
Fig. 34 UPPER CONTROL ARM
1 - REAR PIVOT BOLT
2 - FRONT PIVOT BOLT
3 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
DRFRONT - INDEPENDENT FRONT SUSPENSION 2 - 27
Page 76 of 2895

(15) If the vibration remains unacceptable, apply
the same steps to the front end of the propeller shaft.
(16) Install the wheel and tires. Lower the vehicle.
PROPELLER SHAFT RUNOUT
(1) Remove dirt, rust, paint and undercoating from
the propeller shaft surface where the dial indicator
will contact the shaft.
(2) The dial indicator must be installed perpendic-
ular to the shaft surface.
(3) Measure runout at the center and ends of the
shaft sufficiently far away from weld areas to ensure
that the effects of the weld process will not enter into
the measurements.
(4) Refer to Runout Specifications chart.
(5) If the propeller shaft runout is out of specifica-
tion, remove the propeller shaft, index the shaft 180É,
and re-install the propeller shaft. Measure shaft
runout again.
(6) If the propeller shaft runout is now within
specifications, mark the shaft and yokes for proper
orientation.
(7) If the propeller shaft runout is not within spec-
ifications, verify that the runout of the transmission/
transfer case and axle are within specifications.
Correct as necessary and re-measure propeller shaft
runout.
(8) Replace the propeller shaft if the runout still
exceeds the limits.
RUNOUT SPECIFICATIONS
Front of Shaft 0.020 in. (0.50 mm)
Center of Shaft 0.025 in. (0.63 mm)
Rear of Shaft 0.020 in. (0.50 mm)
note:
Measure front/rear runout approximately 3 inches (76
mm) from the weld seam at each end of the shaft
tube for tube lengths over 30 inches. For tube lengths
under 30 inches, the maximum allowed runout is
0.020 in. (0.50 mm) for the full length of the tube.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
PROPELLER SHAFT ANGLE
This procedure applies to both the front/rear pro-
peller shafts. To obtain the front output angle (A) on
the front propeller shaft, place the inclinometer the
machined surface of the C/V joint.
(1) To check driveline alignment, raise and support
the vehicle at the axles as level as possible. Allow the
wheels and propeller shaft to turn.
(2) Remove any external bearing snap rings, if
equipped from universal joint so protractor base sits
flat.
Fig. 1 CLAMP SCREW AT POSITION 1
1 - CLAMP
2 - SCREWDRIVER
Fig. 2 TWO CLAMP SCREWS
Fig. 3 CLAMP SCREWS SEPARATED
1-1¤2INCH
DRPROPELLER SHAFT 3 - 3
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 84 of 2895

HALF SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION.............................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................11
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
SPECIFICATIONS.......................12
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................12CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
CV JOINT-INNER
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
HALF SHAFT
CAUTION
CAUTION:: Never grasp half shaft assembly by the
boots. This may cause the boot to pucker or crease
and reduce the service life of the boot.
Avoid over angulating or stroking the C/V joints
when handling the half shaft.
Half shafts exposed to battery acid, transmission
fluid, brake fluid, differential fluid or gasoline may
cause the boots to deteriorate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Check for grease at the inboard and outboard C/V
joint. This is a sign of boot or boot clamp damage.
NOISE/VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise or a vibration in turns could be
caused by a damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint
seal boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the
loss/contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint. Noise could also
be caused by another component of the vehicle com-
ing in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a result of a damaged or worn
C/V joint. A torn boot or loose/missing clamp on the
inner/outer joint which has allowed the grease to be
lost will damage the C/V joint.
SHUDDER/VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This problem could be a result of a worn/damaged
inner tripod joint or a sticking tripod joint. Improper
wheel alignment may also cause a shudder or vibra-
tion.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of out of balance
front tires or tire/wheel runout. Foreign material
(mud, etc.) packed on the backside of the wheel(s)
will also cause a vibration.
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen lug nuts and hub nut while the with
the vehicle brakes applied.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove wheel and tire assembly
(4) Remove half shaft hub nut.
(5) Remove brake caliper and rotor.
(6) Position hydraulic jack under lower suspension
arm and raise jack to unload rebound bumper.
(7) Remove lower shock absorber bolt.
(8) Remove upper ball joint nut and seperate ball
with Remover 8677 (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 UPPER BALL JOINT SEPARATION
1 - UPPER CONTROL ARM
2 - REMOVER
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
DRHALF SHAFT 3 - 11
Page 86 of 2895

CV JOINT-OUTER
REMOVAL
(1) Clamp shaft in a vise (with soft jaws) and sup-
port C/V joint.
(2) Remove clamps with a cut-off wheel or grinder
(Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Do not damage C/V housing or half
shaft.
(3) Slide the boot down the shaft.
(4) Remove lubricant to expose the C/V joint snap
ring.
(5) Spread snap ring and slide the joint off the
shaft (Fig. 5).
(6) Slide boot off the shaft and discard old boot.
(7) Mark alignment marks on the inner race/hub,
bearing cage and housing with dabs of paint (Fig. 6).
(8) Clamp C/V joint in a vertical position in a soft
jawed vise.
(9) Press down one side of the bearing cage to gain
access to the ball at the opposite side.
NOTE: If joint is tight, use a hammer and brass drift
to loosen the bearing hub. Do not contact the bear-
ing cage with the drift.
(10) Remove ball from the bearing cage (Fig. 7).
(11) Repeat step above until all six balls are
removed from the bearing cage.
(12) Lift cage and inner race upward and out from
the housing (Fig. 8).
(13) Turn inner race 90É in the cage and rotate the
inner race/hub out of the cage (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If C/V joint is worn, replace entire C/V joint
and boot.
(1) Clean all C/V joint components and shaft.
(2) Apply a light coat of grease supplied with the
joint/boot to the C/V joint components before assem-
bling them.
(3) Align the inner race, cage and housing accord-
ing to the alignment reference marks.
(4) Insert the inner race into the cage (Fig. 10) and
rotate race into the cage.
(5) Rotate the inner race/hub in the cage (Fig. 11).
Fig. 4 BOOT CLAMP LOCATIONS
1 - C/V HOUSING
2 - CLAMP
3 - HALF SHAFT
4 - CLAMP
5 - C/V BOOT
Fig. 5 OUTER C/V JOINT
1 - SNAP RING
2 - SNAP RING GROVE
3 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 6 BEARING ACCESS
1 - ALIGNMENT MARKS
2 - BEARING HUB
3 - BEARING CAGE
4 - HOUSING
DRHALF SHAFT 3 - 13
Page 92 of 2895

tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load
information and correct as
necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash
between the ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring
gear and pinion backlash. Correct
as necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion
gear bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings
pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact
surfaces.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
DRFRONT AXLE - C205F 3 - 19
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)
Page 93 of 2895
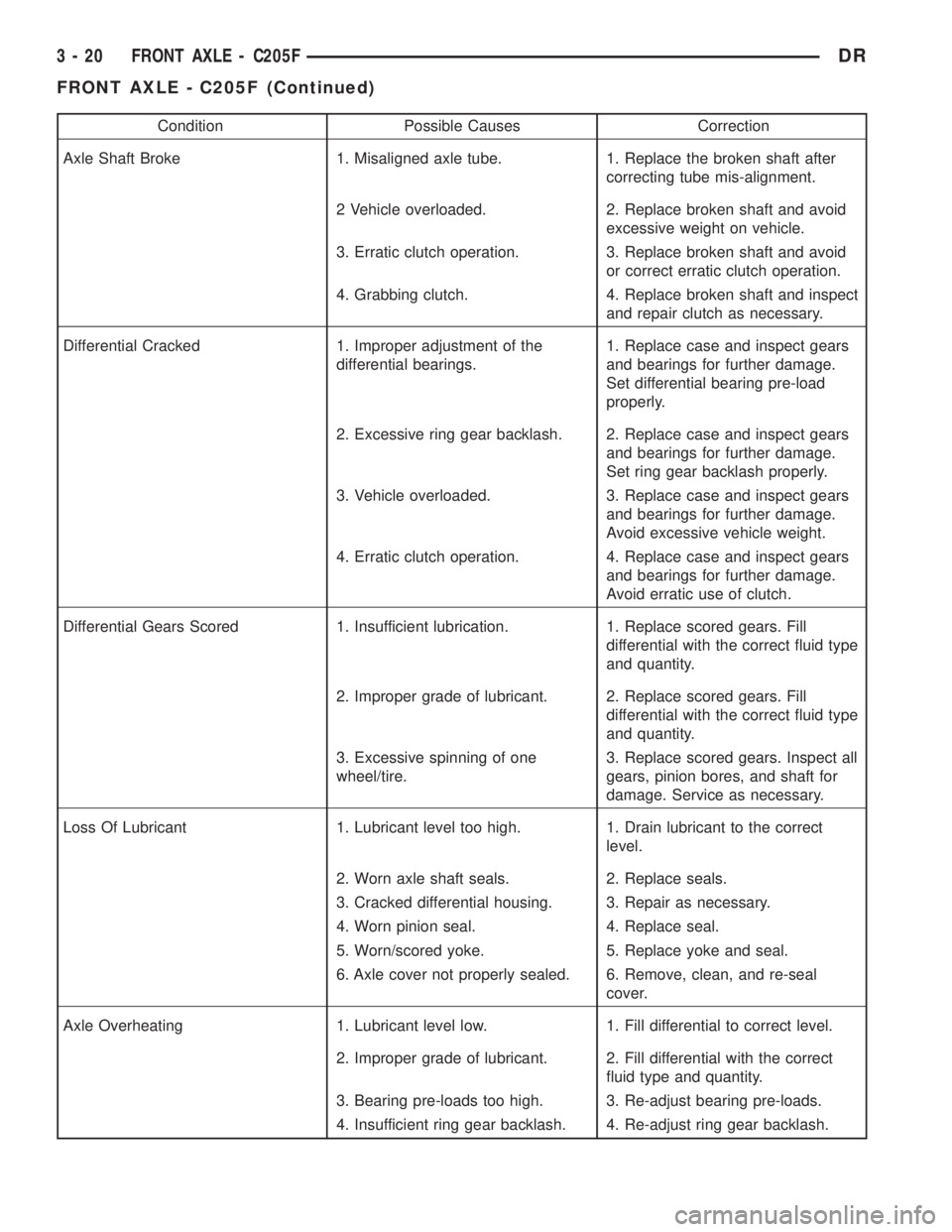
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
3 - 20 FRONT AXLE - C205FDR
FRONT AXLE - C205F (Continued)