check engine DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAM SRT-10, Model: DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006Pages: 5267, PDF Size: 68.7 MB
Page 1587 of 5267

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the engine, particularly at thearea of the suspected leak. If an oil leak
source is not readily identifiable, thefollowingstepsshouldbefollowed:
1. Do not clean or degrease the engine at this time because some solvents maycause rubber to swell, temporarily
stopping the leak.
2. Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for approximately 15
minutes. Check the oil dipstick to make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated with a bright yellow color
under a black light.
3. Using a black light, inspect the entire engine for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area of oil leak. If
the oil leak is found and identified, repair per service manual instructions.
4. If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at various speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and repeat inspec-
tion.If the oil leak source is not positively identified at this time, proceed with the air leak detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
1. Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap nipple.
2. Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valvegrommet.
3. Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to more than 20.6 kPa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
4. Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5 psi maximum while applyingsoapy water at the suspected source.
Adjust the regulator to the suitable test pressure that provide the best bubbles which will pinpoint the leak
source. If the oil leak is detected and identified, repair per service manual procedures.
5. If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area Leak.
6. If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps. Install the PCV
valve and breather cap hose.
7. Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various speeds approx-
imately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the engine for signs of an oil leak by usinga black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the source of an oil leak in therear seal area of the engine, a more
involved inspection is necessary. The following steps should be followedto help pinpoint the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal area:
1. Disconnect the battery.
2. Raise the vehicle.
3. Remove torque converter or clutch housing cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil. Use a black light
to check for the oil leak:
a. Circular spray pattern generally indicates seal leakage or crankshaftdamage.
b. Where leakage tends to run straight down, possible causes are a porous block, oil galley pipe plugs, oil filter
runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder block mating surfaces.
4. If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crankcase as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
5. If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the crankshaft and watch forleakage. If a leak is detected between
the crankshaft and seal while slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the crankshaft seal surface is damaged.
The seal area on the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches that canbe polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially machined to complement the function of the rear oil seal.
6. For bubbles that remain steady with shaft rotation, no further inspection can be done until disassembled.
Page 1588 of 5267

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
1. Remove oil pressure sending unit (2) and install
gauge assembly C-3292.
2. Run engine until thermostat opens.
3. Oil Pressure:
Curb Idle - 25 kPa (4 psi) minimum
3000 rpm - 170 - 758 kPa (25 - 110 psi)
4. If oil pressure is 0 at idle, shut off engine. Check
for a clogged oil pick-up screen or a pressure relief
valve stuck open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the source of an oil leak in therear seal area of the engine, a more
involved inspection is necessary. The following steps should be followedto help pinpoint the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal area:
1. Disconnect the battery.
2. Raise the vehicle.
3. Remove torque converter or clutch housing cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil. Use a black light
to check for the oil leak:
a. Circular spray pattern generally indicates seal leakage or crankshaftdamage.
b. Where leakage tends to run straight down, possible causes are a porous block, oil galley pipe plugs, oil filter
runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder block mating surfaces. See Engine, for proper repair procedures of
these items.
4. If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crankcase as outlined in the section, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks in
general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
5. If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the crankshaft and watch forleakage. If a leak is detected between
the crankshaft and seal while slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the crankshaft seal surface is damaged.
The seal area on the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches that canbe polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially machined to complement the function of the rear oil seal.
6. For bubbles that remain steady with shaft rotation, no further inspection can be done until disassembled. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING), under the Oil Leak row, for components inspections on possible
causes and corrections.
7. After the oil leak root cause and appropriate corrective action have been identified, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL).
Page 1590 of 5267

REMOVAL
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Install engine support fixture special tool # 8534.
Do not raise engine at this time.
3. Loosen both left and right side engine mount
through bolts. Do not remove bolts.
4. Remove the structural dust cover, if equipped.
5. Drain engine oil.
6. Remove the front crossmember (Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT CROSS-
MEMBER - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: Only raise the engine enough to pro-
vide clearance for oil pan removal. Check for
proper clearance at fan shroud to fan and cowl to
intake manifold.
7. Raise engine using special tool 8534 to provide
clearance to remove oil pan.
NOTE:Donotpryonoilpanoroilpangasket.
Gasket is integral to engine windage tray and does
not come out with oil pan.
8. Remove the oil pan mounting bolts and oil pan (1).
9. Unbolt oil pump pickup tube and remove tube.
10. Inspect the integral windage tray and gasket (2)
and replace as needed.
Page 1592 of 5267

1. If removed, install stud at position No. 9.
2. Position the oil pan and install the mounting bolts
and nut. Tighten the mounting bolts and nut to 15
Nꞏm (11 ft. lbs.) in the sequence shown .
3. Lower the engine into mounts using special tool
8534.
4. Install both the left and right side engine mount
through bolts. Tighten the nuts to 68 Nꞏm (50 ft.
lbs.).
5. Remove special tool 8534.
6. Install structural dust cover, if equipped.
7. Install the front crossmember (Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT CROSS-
MEMBER - INSTALLATION).
8. Fill engine oil.
9. Reconnect the negative battery cable.
10. Start engine and check for leaks.
Page 1593 of 5267

SWITCH-OIL PRESSURE
DESCRIPTION
The 3 wire, solid-state engine oil pressure sensor (sending unit) is located in an engine oil pressure gallery.
OPERATION
The oil pressure sensor uses three circuits. They are:
A 5 volt power supply from the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
A sensor ground through the PCM’s sensor return
A signal to the PCM relating to engine oil pressure
The oil pressure sensor has a 3 wire electrical function very much like the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sen-
sor. Meaning different pressures relate to different output voltages.
A 5 volt supply is sent to the sensor from the PCM to power up the sensor. The sensor returns a voltage signal
back to the PCM relating to engine oil pressure. This signal is then transferred (bussed) to the instrument panel on
either a CCD or PCI bus circuit (depending on vehicle line) to operate the oil pressure gauge and the check gauges
lamp. Ground for the sensor is provided by the PCM through a low-noise sensor return.
REMOVAL
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
2. Raise vehicle on hoist.
3. Remove front splash shield.
4. Disconnect oil pressure sender wire (4).
5. Remove the pressure sender (2).
INSTALLATION
1. Install oil pressure sender.
2. Connect oil pressure sender wire.
3. Install front splash shield.
4. Lower vehicle.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 1598 of 5267

OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL SERVICE
The engine oil level indicator (1) is located at the right
rear of the engine on the 3.7L/4.7L engines.
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil, pressure loss or oil foaming can result.
Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800 kilometers (500 miles).Unless the engine has exhibited loss of oil
pressure, run the engine for about five minutes before checking oil level.Checking engine oil level on a cold engine
is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level. The acceptable
levels are indicated between the ADD and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
1. Position vehicle on level surface.
2. With engine OFF, allow approximately ten minutes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove engine oil
dipstick.
3. Wipe dipstick clean.
4. Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the tube.
5. Remove dipstick, with handle held above the tip, take oil level reading.
6. Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals described in Maintenance Schedules.
Run engine until achieving normal operating temperature.
1. Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn engine off.
2. Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
3. Remove oil fill cap.
4. Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase drain.
5. Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow oil to drain into pan. Inspectdrain plug threads for stretching or
other damage. Replace drain plug if damaged.
6. Install drain plug in crankcase.
7. Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified type and amount of engine oil described in this section.
8. Install oil fill cap.
9. Start engine and inspect for leaks.
Page 1621 of 5267

CAUTION: Ensure the plate between the left sec-
ondary chain tensioner and block is correctly
installed.
15. Install both secondary chain tensioners. Tighten
boltsto28Nꞏm(250in.lbs.).
NOTE: Left and right secondary chain tensioners
are not common.
16. Remove all 3 locking pins from tensioners.
CAUTION: After pulling locking pins out of each
tensioner, DO NOT manually extend the tension-
er(s) ratchet. Doing so will over tension the
chains, resulting in noise and/or high timing chain
loads.
17. Using Special Tool 6958, Spanner with Adaptor
Pins 8346, (4) tighten left and right camshaft
sprocket bolts to 122 Nꞏm (90 ft. lbs.).
18. Rotate engine two full revolutions. Verify timing
marks are at the follow locations:
primary chain idler sprocket dot is at 12 o’clock
primary chain crankshaft sprocket dot is at 6
o’clock
secondary chain camshaft sprockets “V6” marks
are at 12 o’clock
counterbalancer shaft drive gear dot is aligned to
the idler sprocket gear dot
19. Lubricate all three chains with engine oil.
20. After installing all chains, it is recommended that
the idler gear end play be checked. The end play
must be within 0.10 -0.25 mm (0.004 - 0.010 in.).
If not within specification, the idler gear must be
replaced.
21. Install timing chain cover and crankshaft damper.
Refer to procedures.
22. Install cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
INSTALLATION).
Page 1624 of 5267

INSTALLATION ............................. 2394
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL ................................. 2395
INSTALLATION ............................. 2395
ROD - PISTON & CONNECTING
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2396
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING . 2396
REMOVAL ................................. 2397
CLEANING ................................. 2397
INSPECTION ............................... 2398
INSTALLATION ............................. 2398
RINGS - PISTON
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING .................................. 2400
DAMPER - CRANKSHAFT
REMOVAL ................................. 2403
INSTALLATION ............................. 2404
COVER - STRUCTURAL
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2405
OPERATION ............................... 2405
REMOVAL ................................. 2405
INSTALLATION ............................. 2405
MOUNT - FRONT
REMOVAL ................................. 2406
INSTALLATION ............................. 2408
MOUNT - REAR
REMOVAL ................................. 2410
INSTALLATION ............................. 2410
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION .............................. 2411
OPERATION ................................ 2411
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHECKING
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE.................. 2412
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK.................................... 2413
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
SERVICE ................................. 2414
FILTER - ENGINE OIL
REMOVAL ................................. 2416
INSTALLATION ............................. 2416
PAN - ENGINE OIL
REMOVAL ................................. 2417
INSTALLATION ............................. 2417
SWITCH - OIL PRESSURE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION ........................... 2418DESCRIPTION ........................... 2418
OPERATION
OPERATION ............................. 2418
OPERATION ............................. 2418
REMOVAL ................................. 2419
INSTALLATION ............................. 2419
PUMP - ENGINE OIL
REMOVAL ................................. 2420
DISASSEMBLY . ............................ 2420
CLEANING ................................. 2420
INSPECTION............................... 2420
ASSEMBLY................................ 2422
INSTALLATION ............................. 2422
MANIFOLD - INTAKE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2423
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE ..................... 2423
REMOVAL ................................. 2423
CLEANING ................................. 2424
INSPECTION............................... 2424
INSTALLATION ............................. 2425
MANIFOLD - EXHAUST
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2426
REMOVAL ................................. 2426
CLEANING ................................. 2428
INSPECTION............................... 2428
INSTALLATION ............................. 2428
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM ..... 2430
OPERATION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM....... 2430
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
TIMING CHAIN WEAR..................... 2431
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE TIMING
- VERIFICATION.......................... 2431
COVER - TIMING
REMOVAL ................................. 2436
INSTALLATION ............................. 2437
TIMING CHAIN & SPROCKETS
REMOVAL ................................. 2438
INSPECTION............................... 2441
INSTALLATION ............................. 2442
SHAFT - IDLER
REMOVAL ................................. 2446
INSTALLATION ............................. 2446
Page 1627 of 5267
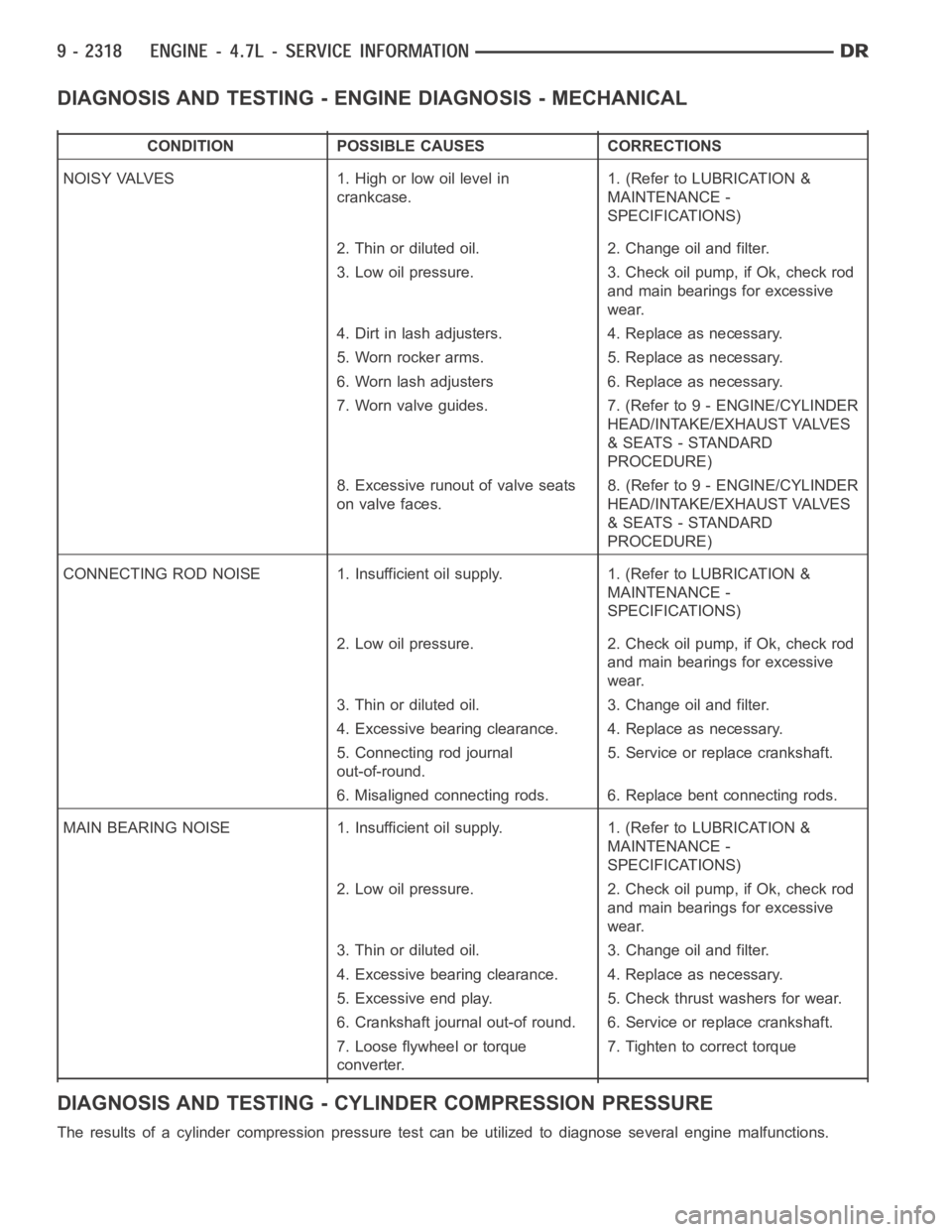
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION&
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compressionpressure test can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunctions.
Page 1628 of 5267

Ensurethebatteryiscompletelychargedandtheenginestartermotorisingood operating condition. Otherwise the
indicated compression pressures may not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
1. Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed air.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
4. Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUTDOWNRELAY-
REMOVAL).
5. Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate the engine with the engine starter motor for three revolutions.
6. Record the compression pressure on the 3rd revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylinders.
7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDERCOMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seating).
Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water jacket.
Any causes for combustion/compression pressure loss.
1. Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO NOT install the radiatorcap.
2. Start and operate the engine until it attains normal operating temperature, then turn the engine OFF.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Remove the oil filler cap.
5. Remove the air cleaner hose.
6. Calibrate the tester according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The shop air source for testing should maintain
483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379 kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recommended.
7. Perform the test procedures on each cylinder according to the tester manufacturer’s instructions. Set piston of
cylinder to be tested at TDC compression,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through the throttle
body, tailpipe and oil filler cap opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal, with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pressure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be maintained in the
cylinder.
Refer to CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary