relay DODGE TRUCK 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1993, Model line: TRUCK, Model: DODGE TRUCK 1993Pages: 1502, PDF Size: 80.97 MB
Page 254 of 1502

CLUTCH
6 - 1
CLUTCH
CONTENTS
page
CLUTCH
DIAGNOSIS
2
CLUTCH
COMPONENTS
MECHANICAL COMPONENTS
The clutch mechanism
in
AD
models with
a gas or
diesel engine consists
of a
single, dry-type clutch disc and
a
diaphragm style clutch cover.
A
hydraulic
linkage
is
used
to
engage/disengage
the
clutch disc
and cover.
The transmission input shaft
is
supported
in the
crankshaft
by a
bearing.
A
sleeve type release bear
ing
is
used
to
operate
the
clutch cover pressure plate.
The release bearing
is
operated
by a
release fork
in
the clutch housing.
The
fork pivots
on a
ball stud
mounted inside
the
housing.
The
release fork
is
actu ated
by a
hydraulic slave cylinder mounted
in the
housing.
The
slave cylinder
is
operated
by a
clutch master cylinder mounted
on the
dash panel.
The
cyl
inder push
rod is
connected
to the
clutch pedal.
The clutch disc
has
cushion springs
in the
disc
hub.
The clutch disc facing
is
riveted
to the hub. The
fac ing
is
made from
a
non-asbestos material.
The
clutch
cover pressure plate
is a
diaphragm type with
a one-
piece spring
and
multiple release fingers.
The
pres sure plate release fingers
are
preset during
manufacture
and are not
adjustable.
A
265 mm
clutch disc
and
cover
are
used
in
models
with
a 3.9L
engine.
A 280 mm
clutch disc
and
cover are used
in
models with
a 5.2L, or
5.9L engine.
A
330 mm
clutch disc
and
cover
are
used
in
models
equipped with
the
optional
5.9L
Cummins diesel
en
gine.
Some diesel models
are
also equipped with
a
clutch pedal interlock switch.
The
switch
is in
circuit
with
the
starter relay
and is
actuated
by the
clutch
pedal
and
push
rod. The
clutch pedal must
be
fully depressed
in
order
to
start
the
engine.
HYDRAULIC LINKAGE COMPONENTS
The hydraulic linkage consists
of a
remote reser
voir, clutch master cylinder, clutch slave cylinder and interconnecting fluid lines.
The clutch master cylinder
is
connected
to the
clutch pedal
and the
slave cylinder
is
connected
to
the clutch release fork.
The
master cylinder
is
mounted
on the
drivers' side
of the
dash panel adja
cent
to the
brake master cylinder.
page
CLUTCH
SERVICE
11
CLUTCH LINKAGE FLUID
The clutch fluid reservoir, master cylinder, slave
cylinder
and
fluid lines
are
prefilled with fluid
at the
factory during assembly operations. The hydraulic system should
not
require additional
fluid under normal circumstances.
In
fact,
the
reser
voir fluid level will actually increase
as
normal clutch wear occurs.
For
this reason,
it is
impor
tant
to
avoid overfilling,
or
removing fluid from
the reservoir. If inspection
or
diagnosis indicates additional fluid
may
be
needed,
use
Mopar brake fluid,
or an
equiv
alent meeting
SAE and DOT
standards J1703
and
DOT
3. Do not use any
other type
of
fluid.
CLUTCH
COMPONENT LUBRICATION
Proper clutch component lubrication
is
important
to satisfactory operation.
The
correct lubricant
and
not overlubricating
are
equally important. Apply rec
ommended lubricant sparingly
to
avoid disc
and
pres sure plate contamination. Clutch
and
transmission components requiring
lu
brication
are:
• pilot bearing
• release lever pivot ball stud
• release lever contact surfaces
• clutch disc
hub
splines
• clutch pedal pivot shaft bore
• clutch pedal bushings
• input shaft splines
• input shaft pilot
hub
• transmission front bearing retainer slide surface Do
not
apply grease
to any
part
of the
clutch
cover,
or
disc.
RECOMMENDED LUBRICANTS
Use Mopar multi-purpose grease
for the
clutch
pedal bushings
and
pivot shaft.
Use
Mopar high tem
perature grease
(or
equivalent)
for all
other lubrica
tion requirements. Apply recommended amounts
and
do
not
over lubricate.
Page 330 of 1502
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 9
ENGINE STARTER MOTOR TEST PROCEDURES
GENERAL INFORMATION
The starting system consists of an:
• ignition switch
• starter relay
• park/neutral position switch (automatic transmis sion)
• clutch switch (diesel engine-manual transmission)
• wiring harness
• battery
• starter motor with an integral solenoid. These components form 2 separate circuits. A high
amperage circuit that feeds the starter motor up to
300+ amps-gas engine; 500+ amps-diesel engine,
and a control circuit that operates on less than 20
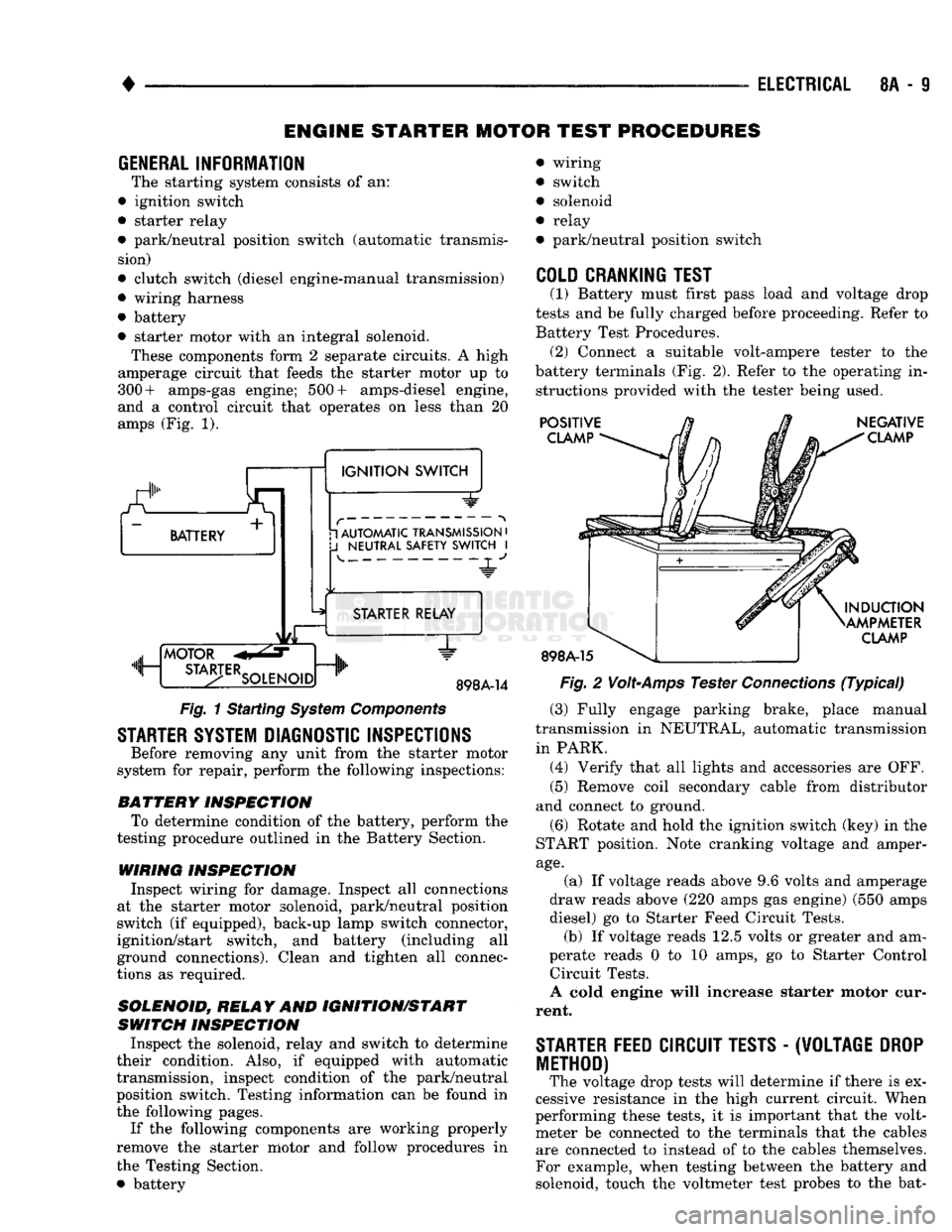
amps (Fig. 1).
a.
BATTERY +
1
IGNITION
SWITCH 1 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
•
J
NEUTRAL SAFETY SWITCH
I 4-
"JL"
MOTOR
m, ...
STA3-TERSOLENO,Dnlh
STARTER RELAY
1"
898A-14
Fig.
1 Starting
System
Components
STARTER SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC INSPECTIONS
Before removing any unit from the starter motor
system for repair, perform the following inspections:
BATTERY
INSPECTION
To determine condition of the battery, perform the
testing procedure outlined in the Battery Section.
WIRING INSPECTION
Inspect wiring for damage. Inspect all connections
at the starter motor solenoid, park/neutral position
switch (if equipped), back-up lamp switch connector,
ignition/start switch, and battery (including all
ground connections). Clean and tighten all connec
tions as required.
SOLENOID, RELAY
AND
IGNITION/START
SWITCH
INSPECTION
Inspect the solenoid, relay and switch to determine
their condition. Also, if equipped with automatic
transmission, inspect condition of the park/neutral position switch. Testing information can be found in
the following pages.
If the following components are working properly
remove the starter motor and follow procedures in
the Testing Section. • battery wiring
switch
solenoid
relay
park/neutral position switch
COLD CRANKING TEST
(1) Battery must first pass load and voltage drop
tests and be fully charged before proceeding. Refer to Battery Test Procedures. (2) Connect a suitable volt-ampere tester to the
battery terminals (Fig. 2). Refer to the operating in structions provided with the tester being used.
POSITIVE
CLAMP
898A-15
NEGATIVE
CLAMP
INDUCTION
AMPMETER
CLAMP
Fig.
2
Volt-Amps
Tester
Connections
(Typical)
(3) Fully engage parking brake, place manual
transmission in NEUTRAL, automatic transmission
in PARK. (4) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF. (5) Remove coil secondary cable from distributor
and connect to ground.
(6) Rotate and hold the ignition switch (key) in the
START position. Note cranking voltage and amper
age.
(a) If voltage reads above 9.6 volts and amperage
draw reads above (220 amps gas engine) (550 amps
diesel) go to Starter Feed Circuit Tests. (b) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and am-
perate reads 0 to 10 amps, go to Starter Control Circuit Tests.
A cold engine will increase starter motor cur
rent.
STARTER
FEED
CIRCUIT TESTS
-
(W0LTAGE
DROP
METHOD)
The voltage drop tests will determine if there is ex
cessive resistance in the high current circuit. When
performing these tests, it is important that the volt meter be connected to the terminals that the cables are connected to instead of to the cables themselves.
For example, when testing between the battery and
solenoid, touch the voltmeter test probes to the bat-
Page 331 of 1502
8A
- 10
ELECTRICAL
•
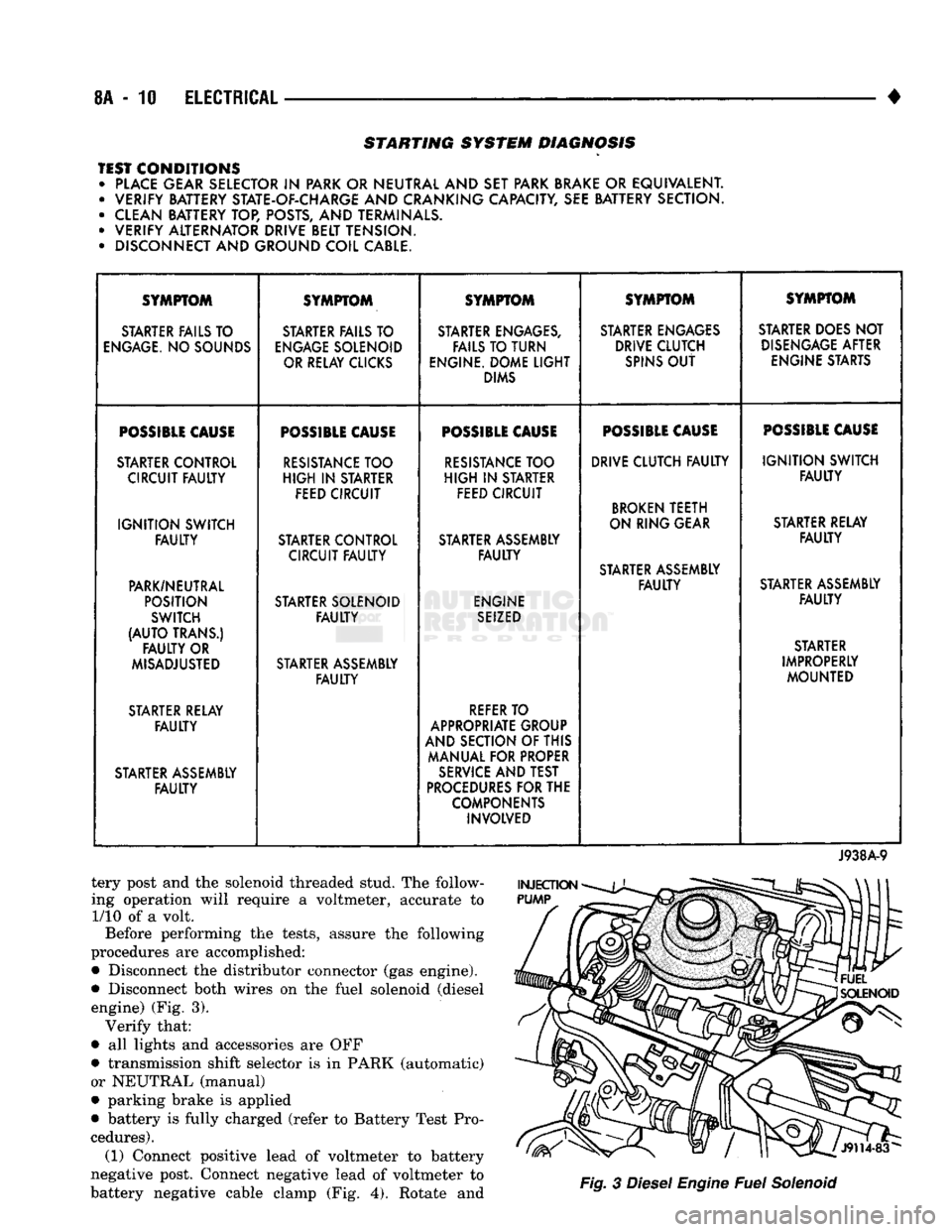
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
TEST CONDITIONS • PLACE GEAR SELECTOR
IN
PARK OR NEUTRAL AND SET PARK BRAKE
OR
EQUIVALENT. • VERIFY BATTERY STATE-OF-CHARGE AND CRANKING CAPACITY, SEE BATTERY SECTION.
• CLEAN BATTERY TOP, POSTS, AND TERMINALS.
• VERIFY ALTERNATOR DRIVE BELT TENSION.
• DISCONNECT AND GROUND COIL CABLE. SYMPTOM
SYMPTOM SYMPTOM SYMPTOM SYMPTOM
STARTER FAILS TO STARTER FAILS TO STARTER ENGAGES, STARTER ENGAGES STARTER DOES NOT
ENGAGE.
NO SOUNDS
ENGAGE
SOLENOID FAILS TO TURN DRIVE CLUTCH
DISENGAGE
AFTER
OR RELAY CLICKS ENGINE. DOME
LIGHT
SPINS
OUT
ENGINE STARTS
DIMS
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
STARTER CONTROL
RESISTANCE
TOO
RESISTANCE
TOO DRIVE CLUTCH
FAULTY
IGNITION
SWITCH
CIRCUIT
FAULTY
HIGH
IN
STARTER
HIGH
IN
STARTER
FAULTY
FEED CIRCUIT FEED CIRCUIT
BROKEN
TEETH
IGNITION
SWITCH ON RING GEAR
STARTER RELAY
FAULTY
STARTER CONTROL STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY
CIRCUIT
FAULTY FAULTY
STARTER ASSEMBLY
PARK/NEUTRAL
FAULTY
STARTER ASSEMBLY
POSITION STARTER SOLENOID ENGINE
FAULTY
SWITCH
FAULTY
SEIZED
(AUTO
TRANS.) STARTER
FAULTY
OR STARTER
MISADJUSTED STARTER ASSEMBLY IMPROPERLY
FAULTY
MOUNTED
STARTER RELAY
REFER
TO
FAULTY
APPROPRIATE GROUP
AND SECTION OF THIS
MANUAL FOR PROPER
STARTER ASSEMBLY
SERVICE
AND TEST
FAULTY
PROCEDURES
FOR THE
COMPONENTS INVOLVED
J938A-9
tery post and the solenoid threaded stud. The follow
ing operation will require a voltmeter, accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
Before performing the tests, assure the following
procedures are accomplished:
•
Disconnect the distributor connector (gas engine).
•
Disconnect both wires on the fuel solenoid (diesel engine) (Fig. 3). Verify that:
•
all lights and accessories are OFF
•
transmission shift selector is in PARK (automatic)
or NEUTRAL (manual)
•
parking brake is applied
•
battery is fully charged (refer to Battery Test Pro
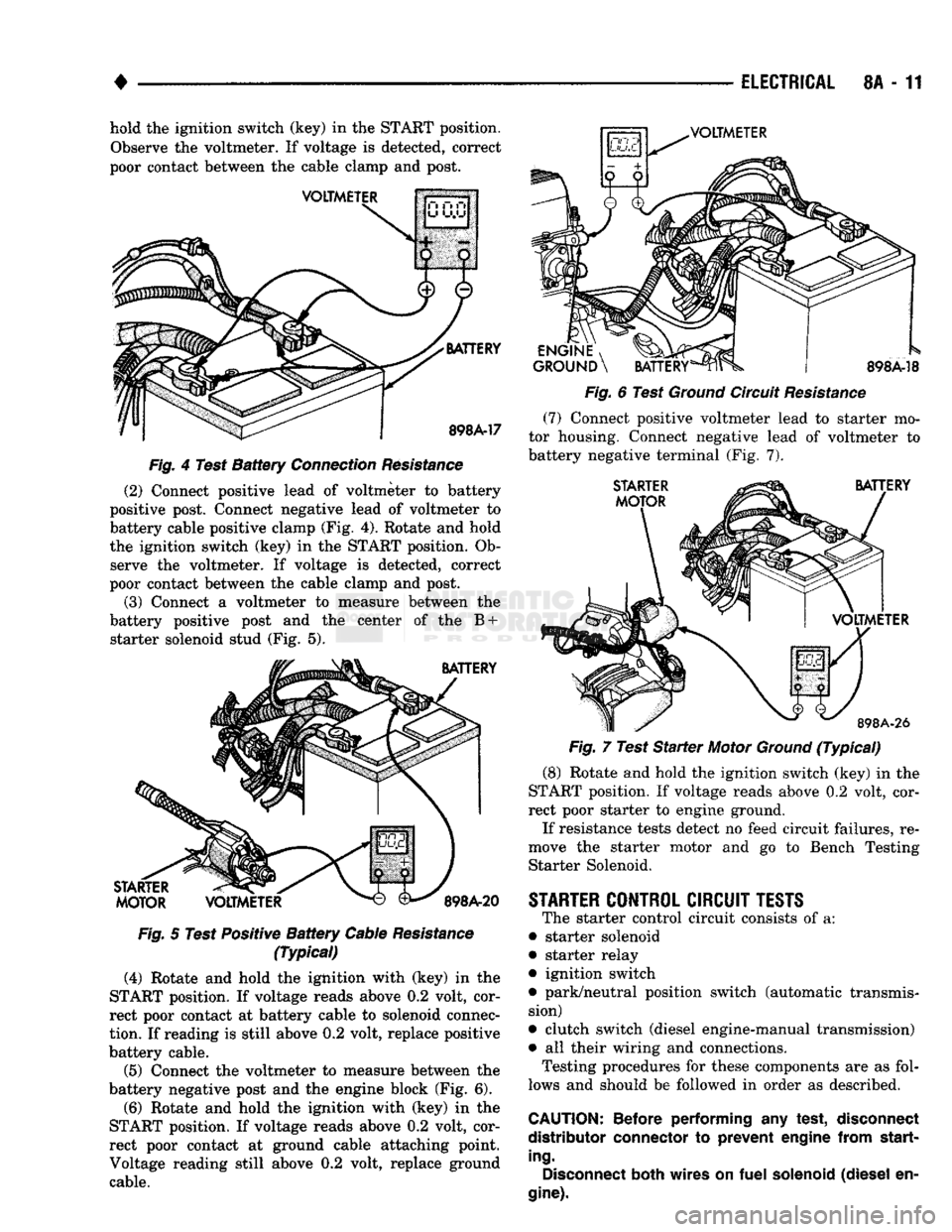
cedures). (1) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
negative post. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to
battery negative cable clamp (Fig. 4). Rotate and
Fig.
3
Diesel
Engine
Fuel
Solenoid
Page 332 of 1502
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 11 hold the ignition switch (key) in the START position.
Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct
poor contact between the cable clamp and post.
VOLTMETER
VOLTMETER
BATTERY
898A-17
Fig.
4 Test
Battery
Connection
Resistance
(2) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
positive post. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to
battery cable positive clamp (Fig. 4). Rotate and hold
the ignition switch (key) in the START position. Ob serve the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct
poor contact between the cable clamp and post.
(3) Connect a voltmeter to measure between the
battery positive post and the center of the B + starter solenoid stud (Fig. 5).
BATTERY
STARTER
MOTOR
VOLTMETER
898A-20
Fig.
5 Test Positive
Battery
Cable
Resistance
(Typical)
(4) Rotate and hold the ighition with (key) in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, cor
rect poor contact at battery cable to solenoid connec
tion.
If reading is still above 0.2 volt, replace positive
battery cable.
(5) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery negative post and the engine block (Fig. 6).
(6) Rotate and hold the ignition with (key) in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, cor
rect poor contact at ground cable attaching point.
Voltage reading still above 0.2 volt, replace ground cable.
ENGINE
, ^J^P
GROUND
\
BATTERY
898A-18
Fig.
6 Test
Ground
Circuit
Resistance
(7)
Connect positive voltmeter lead to starter mo
tor housing. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to
battery negative terminal (Fig. 7).
STARTER
MOTOR
BATTERY
VOLTMETER
898A-26
Fig.
7 Test
Starter
Motor
Ground
(Typical)
(8) Rotate and hold the ignition switch (key) in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, cor
rect poor starter to engine ground.
If resistance tests detect no feed circuit failures, re
move the starter motor and go to Bench Testing Starter Solenoid.
STARTER
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
TESTS
The starter control circuit consists of a:
• starter solenoid
• starter relay
• ignition switch
• park/neutral position switch (automatic transmis sion)
• clutch switch (diesel engine-manual transmission)
• all their wiring and connections.
Testing procedures for these components are as fol
lows and should be followed in order as described.
CAUTION:
Before
performing
any
test,
disconnect
distributor
connector
to
prevent
engine
from
start
ing.
Disconnect
both
wires
on
fuel
solenoid
(diesel
en
gine).
Page 333 of 1502
8A
- 12
ELECTRICAL
•
ENGINE
STARTER
RELAY
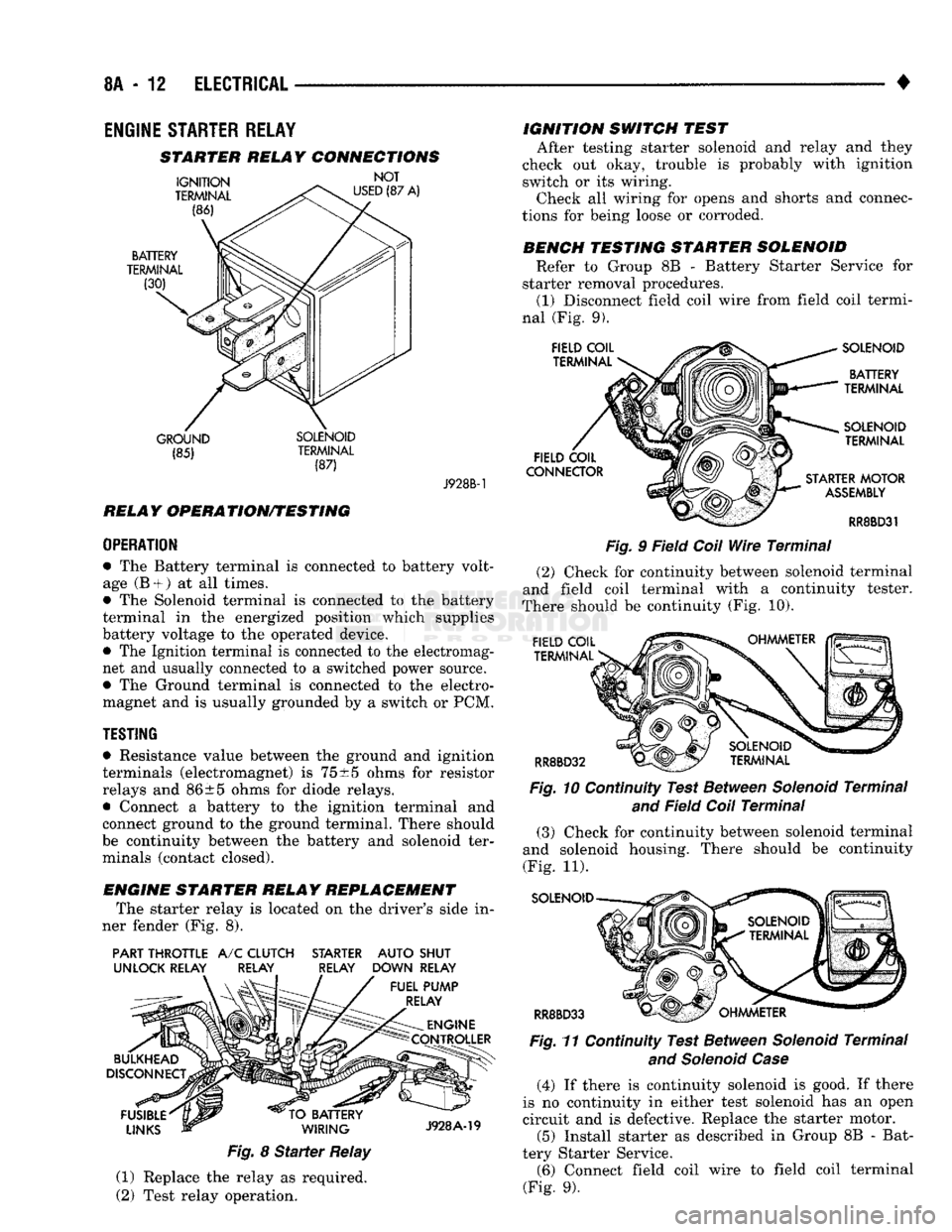
STARTER RELAY CONNECTIONS
GROUND SOLENOID (85) TERMINAL
(87) J928B-1
RELAY OPERATION/TESTING
OPERATION
• The Battery terminal is connected to battery volt
age (B +
)
at all times.
• The Solenoid terminal is connected to the battery
terminal in the energized position which supplies
battery voltage to the operated device. • The Ignition terminal is connected to the electromag
net and usually connected to a switched power source.
• The Ground terminal is connected to the electro
magnet and is usually grounded by a switch or PCM.
TESTING
• Resistance value between the ground and ignition
terminals (electromagnet) is
75
±5 ohms for resistor
relays and 86±5 ohms for diode relays.
• Connect a battery to the ignition terminal and
connect ground to the ground terminal. There should
be continuity between the battery and solenoid ter minals (contact closed).
ENGINE STARTER RELAY REPLACEMENT The starter relay is located on the driver's side in
ner fender (Fig. 8).
PART THROTTLE
A/C
CLUTCH STARTER AUTO SHUT
UNLOCK RELAY RELAY RELAY DOWN RELAY
Fig.
8
Starter
Relay
(1) Replace the relay as required.
(2) Test relay operation. IGNITION SWITCH TEST
After testing starter solenoid and relay and they
check out okay, trouble is probably with ignition
switch or its wiring. Check all wiring for opens and shorts and connec
tions for being loose or corroded.
BENCH TESTING STARTER SOLENOID Refer to Group 8B - Battery Starter Service for
starter removal procedures. (1) Disconnect field coil wire from field coil termi
nal (Fig. 9).
Fig.
9 Field
Coil
Wire
Terminal
(2) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and field coil terminal with a continuity tester.
There should be continuity (Fig. 10).
Fig.
10 Continuity Test Between
Solenoid
Terminal
and
Field
Coil
Terminal
(3) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and solenoid housing. There should be continuity
(Fig. 11).
SOLENOID
RR8BD33 Fig.
11 Continuity Test Between
Solenoid
Terminal
and Solenoid Case
(4) If there is continuity solenoid is good. If there
is no continuity in either test solenoid has an open
circuit and is defective. Replace the starter motor. (5) Install starter as described in Group 8B - Bat
tery Starter Service. (6) Connect field coil wire to field coil terminal
(Fig. 9).
Page 334 of 1502

•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 13 GENERATOR TEST PROCEDURES ON
VEHICLE
INDEX
page
Current
Output
Test
......................
14
Diagnostic Procedures
13
General
Information
13
Generator
Output
Wire Resistance Test
.......
13
page
How
to
Use
Malfunction
Indicator
(Check Engine) Lamp
for
Fault
Codes
17
Operational Check
with
Voltmeter
............
13
Using
On-Board Diagnostic System
15
GENERAL
INFORMATION
The generator
is
belt-driven
by the
engine.
All en
gines
use
serpentine drive. The amount
of DC
current produced
by the
gener
ator
is
controlled
by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
All vehicles
are
equipped with
On
Board Diagnos
tics (OBD).
All OBD
sensing systems
are
monitored
by
the PCM. The PCM
will store
in
electronic mem ory
any
detectable failure within
the
monitored cir
cuits.
Refer
to
USING ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
in
this group
for
more information.
OPERATIONAL CHECK
WITH
VOLTMETER
When
the
ignition switch
is
turned
to the RUN po
sition, battery potential will register
on the
voltme
ter. During engine cranking
a
lower voltage will appear
on the
meter. With
the
engine running,
a
voltage reading higher than
the
first reading (igni
tion
in RUN)
should register.
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
If
the
indicator does
not
operate properly,
or if an
undercharged
or
overcharged battery condition
oc
curs,
the
following procedures
may be
used
to
diag
nose
the
charging system. Remember that
an
undercharged battery
is
often
caused
by:
• accessories being left
on
overnight
•
or by a
defective switch which allows
a
bulb, such
as a
trunk
or
glove
box
light,
to
stay
on
(refer
to
Ignition
Off
Draw).
WISUAL
INSPECTION
• Inspect condition
of
battery cable terminals, bat
tery posts, connections
at
engine block, starter motor solenoid
and
relay. They should
be
clean
and
tight.
Repair
as
required.
• Inspect
all
fuses
in the
fuse block
for
tightness
in
receptacles. They should
be
properly installed
and
tight. Repair
or
replace
as
required.
• Inspect generator mounting bolts
for
tightness.
Re
place
or
torque bolt
as
required (refer
to
Torque Specifications).
• Inspect generator drive belt condition
and
tension.
Tension
or
replace belt
as
required. Refer
to
Belt
Tension Specifications. • Inspect connection
at
generator
B+
output.
It
should
be
clean
and
tight. Repair
as
required.
GENERATOR
OUTPUT
WIRE RESISTANCE TEST
(FIG.
1)
Generator output wire resistance test will show
amount
of
voltage drop across generator output wire
between generator
BAT
terminal
and
battery posi tive post.
PREPARATION
(1) Before starting test make sure vehicle
has a
fully charged battery. Test
and
procedures
on how to
check
for a
fully charged battery
are
shown
in
Bat
tery section
of
this Group.
(2) Turn
OFF
ignition switch.
(3)
Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4)
Disconnect generator output wire from genera
tor output Battery terminal. (5) Connect
a 0-150
ampere scale
D.C.
ammeter
in
series between generator
BAT
terminal
and
discon
nected generator output wire. Connect Positive lead
to generator
BAT
terminal
and
Negative lead
to
dis connected generator output wire. (6) Connect Positive lead
of a
test voltmeter
(Range
0-18
volts minimum)
to
disconnected genera
tor output wire. Connect negative lead
of
test voltme
ter
to
battery positive cable
at
positive post. (7) Connect
one end of a
Jumper Wire
to
ground
and with other
end
probe green
K20
lead wire
at
back
of
generator
(Fig. 1).
(This will generate
a
fault
code).
CAUTION:
Do not
connect blue
A142
lead
of
wiring
to ground. Refer
to
Group
8W
-
Wiring Diagrams
for
more information.
(8) Connect
an
engine tachometer
and
connect neg
ative cable
to
battery.
(9) Connect
a
variable carbon pile rheostat
be
tween battery terminals.
Be
sure carbon pile
is in
"Open"
or "Off
position before connecting leads.
See
Battery Section, Load Testing
for
instructions.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting,
re
duce engine speed
to
idle.
Page 335 of 1502
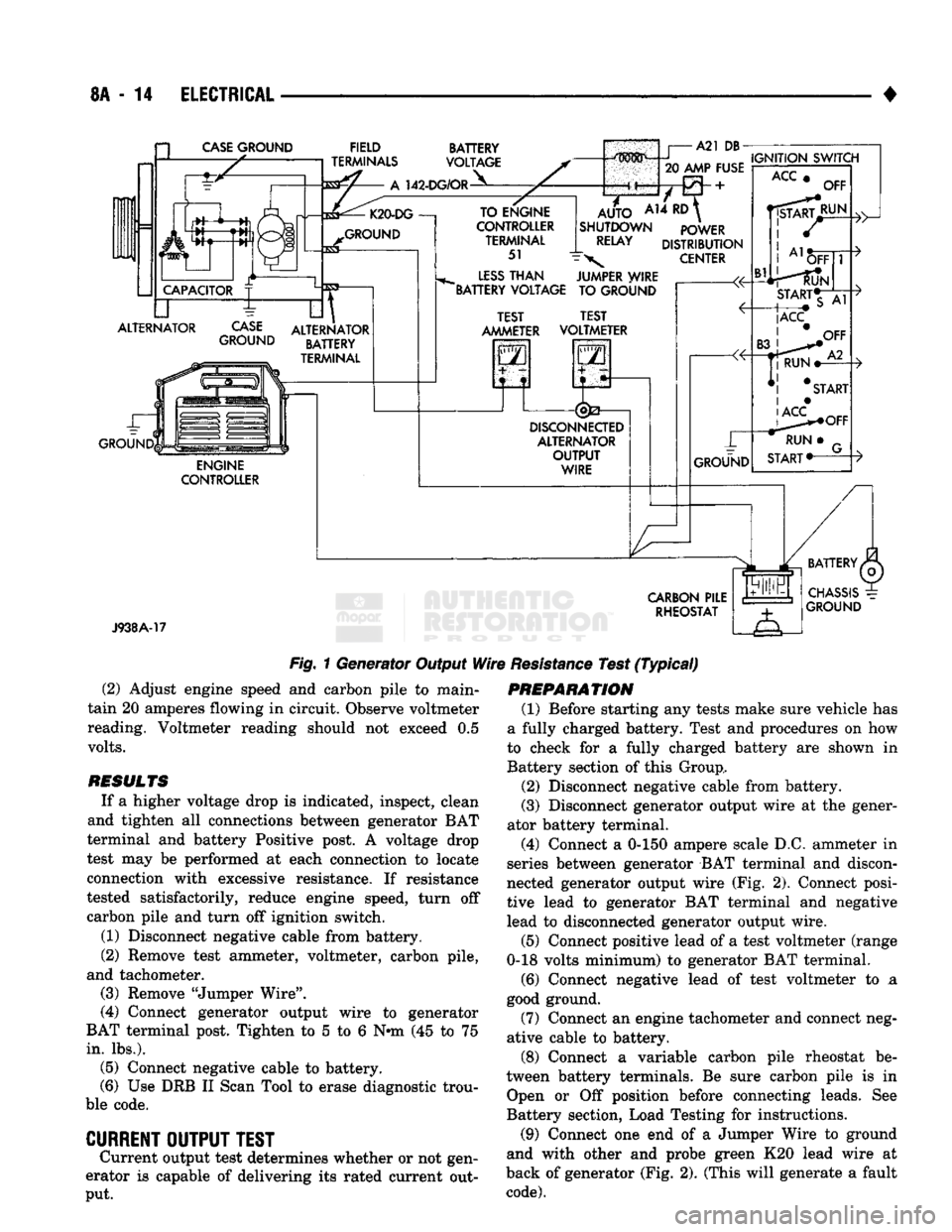
8A
- 14
ELECTRICAL
CASE
GROUND
FIELD
TERMINALS
142-DG/OR
BATTERY
VOLTAGE
ALTERNATOR
CASE
GROUND
GROUND ALTERNATOR
BATTERY
TERMINAL
ENGINE
CONTROLLER TO ENGINE
CONTROLLER TERMINAL
51
LESS
THAN
"BATTERY VOLTAGE
m^mm i
A21 DB-
20
AMP FUSE
A14
RD
AUTO
SHUTDOWN
RELAY
IGNITION
SWITCH
POWER
DISTRIBUTION
CENTER
JUMPER WIRE TO GROUND TEST
AMMETER TEST
VOLTMETER
2
i
DISCONNEaED
ALTERNATOR
OUTPUT
WIRE
ACC
OFF
J938A-17
CARBON
PILE
RHEOSTAT
Fig.
1 Generator Output
Wire
Resistance
Test
(Typical)
(2) Adjust engine speed and carbon pile to main
tain 20 amperes flowing in circuit. Observe voltmeter
reading. Voltmeter reading should not exceed 0.5
volts.
RESULTS
If a higher voltage drop is indicated, inspect, clean
and tighten all connections between generator BAT
terminal and battery Positive post. A voltage drop
test may be performed at each connection to locate
connection with excessive resistance. If resistance
tested satisfactorily, reduce engine speed, turn off carbon pile and turn off ignition switch.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove test ammeter, voltmeter, carbon pile,
and tachometer. (3) Remove "Jumper Wire".
(4) Connect generator output wire to generator
BAT terminal post. Tighten to 5 to 6 Nnn (45 to 75
in.
lbs.). (5) Connect negative cable to battery.
(6) Use DRB II Scan Tool to erase diagnostic trou
ble code.
CURRENT
OUTPUT
TEST
Current output test determines whether or not gen
erator is capable of delivering its rated current out
put.
PREPARATION
(1) Before starting any tests make sure vehicle has
a fully charged battery. Test and procedures on how
to check for a fully charged battery are shown in
Battery section of this Group,
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Disconnect generator output wire at the gener
ator battery terminal.
(4) Connect a 0-150 ampere scale D.C. ammeter in
series between generator BAT terminal and discon
nected generator output wire (Fig. 2). Connect posi
tive lead to generator BAT terminal and negative
lead to disconnected generator output wire.
(5) Connect positive lead of a test voltmeter (range
0-18 volts minimum) to generator BAT terminal.
(6) Connect negative lead of test voltmeter to a
good ground.
(7) Connect an engine tachometer and connect neg
ative cable to battery.
(8) Connect a variable carbon pile rheostat be
tween battery terminals. Be sure carbon pile is in Open or Off position before connecting leads. See
Battery section, Load Testing for instructions.
(9) Connect one end of a Jumper Wire to ground
and with other and probe green K20 lead wire at
back of generator (Fig. 2). (This will generate a fault
code).
Page 336 of 1502
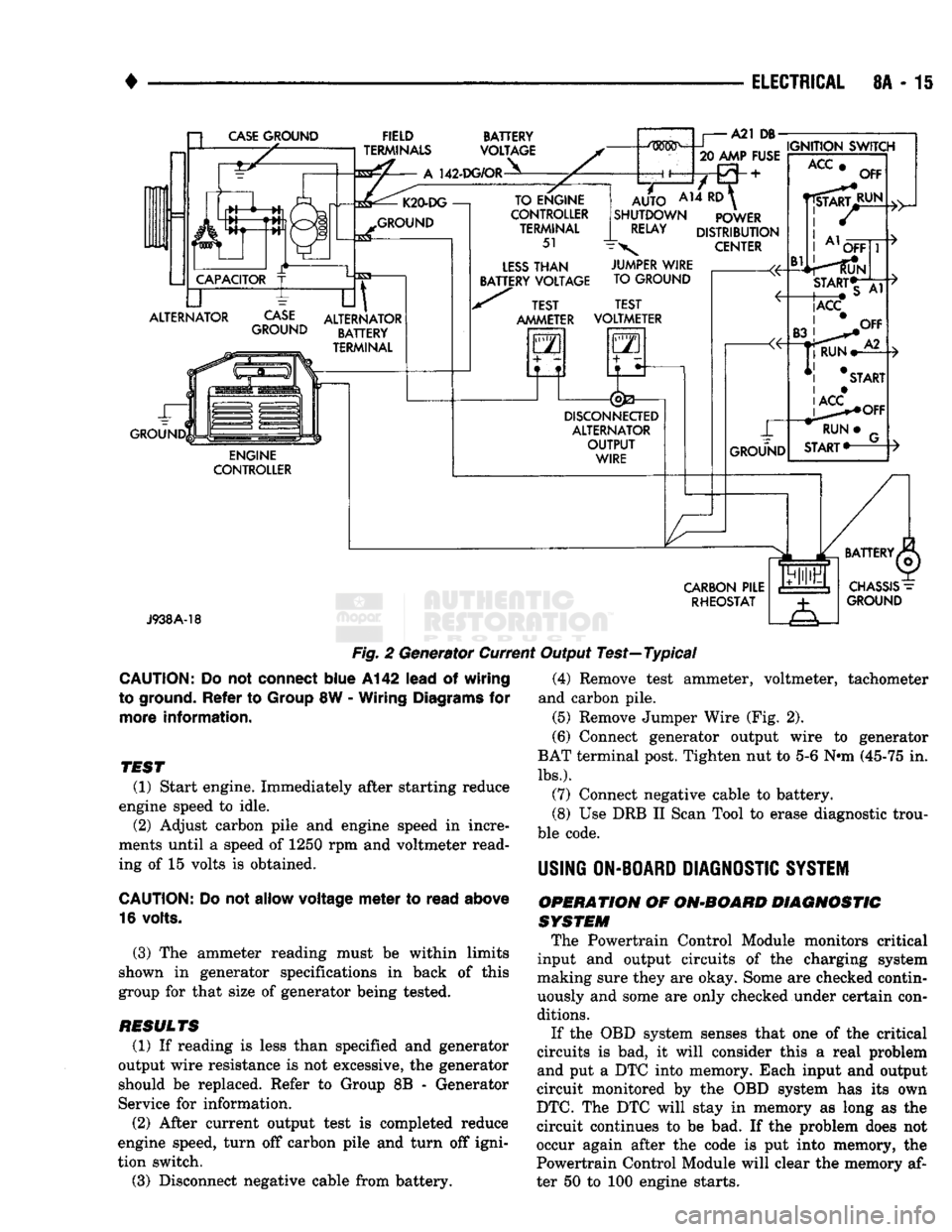
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 15 a
CASE
GROUND
CAPACITOR
ALTERNATOR ~L FIELD
TERMINALS
A
142-DG/OR BATTERY
VOLTAGE K20-DG
—!
GROUND
CASE
GROUND
til
ALTERNATOR BATTERY
TERMINAL ENGINE
CONTROLLER TO ENGINE
CONTROLLER TERMINAL
51
LESS
THAN
BATTERY VOLTAGE A21
DB-
.....
IGNITION SWITCH
20 AMP FUSE
AUTO
AH ^
SHUTDOWN POWER
RELAY
DISTRIBUTION
\
CENTER TEST
AMMETER JUMPER WIRE
TO GROUND
TEST
VOLTMETER
GO
5—n
DISCONNECTED
ALTERNATOR OUTPUT WIRE GROUND
ACC
Bl
OFF
RUN OFF
START*T
|ACC
CARBON
PILE RHEOSTAT
J938A-18
Fig.
2 Generator Current Output Test—Typical
CAUTION:
Do not
connect
blue
A142
lead
of
wiring
to ground.
Refer
to
Group
8W -
Wiring
Diagrams
for
more
information.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting reduce
engine speed to idle. (2) Adjust carbon pile and engine speed in incre
ments until a speed of 1250 rpm and voltmeter read
ing of 15 volts is obtained.
CAUTION:
Do not
allow
voltage
meter
to
read
above
16 volts.
(3) The ammeter reading must be within limits
shown in generator specifications in back of this
group for that size of generator being tested.
RESULTS
(1) If reading is less than specified and generator
output wire resistance is not excessive, the generator
should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B - Generator
Service for information.
(2) After current output test is completed reduce
engine speed, turn off carbon pile and turn off igni
tion switch.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery. (4) Remove test ammeter, voltmeter, tachometer
and carbon pile. (5) Remove Jumper Wire (Fig. 2).
(6) Connect generator output wire to generator
BAT terminal post. Tighten nut to 5-6 Nnn (45-75 in.
lbs.).
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
(8) Use DRB II Scan Tool to erase diagnostic trou
ble code.
USING
ON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTIC
SYSTEM
OPERATION
OF
ON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTIC
SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module monitors critical
input and output circuits of the charging system
making sure they are okay. Some are checked contin
uously and some are only checked under certain con
ditions.
If the OBD system senses that one of the critical
circuits is bad, it will consider this a real problem
and put a DTC into memory. Each input and output
circuit monitored by the OBD system has its own
DTC.
The DTC will stay in memory as long as the
circuit continues to be bad. If the problem does not
occur again after the code is put into memory, the
Powertrain Control Module will clear the memory af
ter 50 to 100 engine starts.
Page 345 of 1502
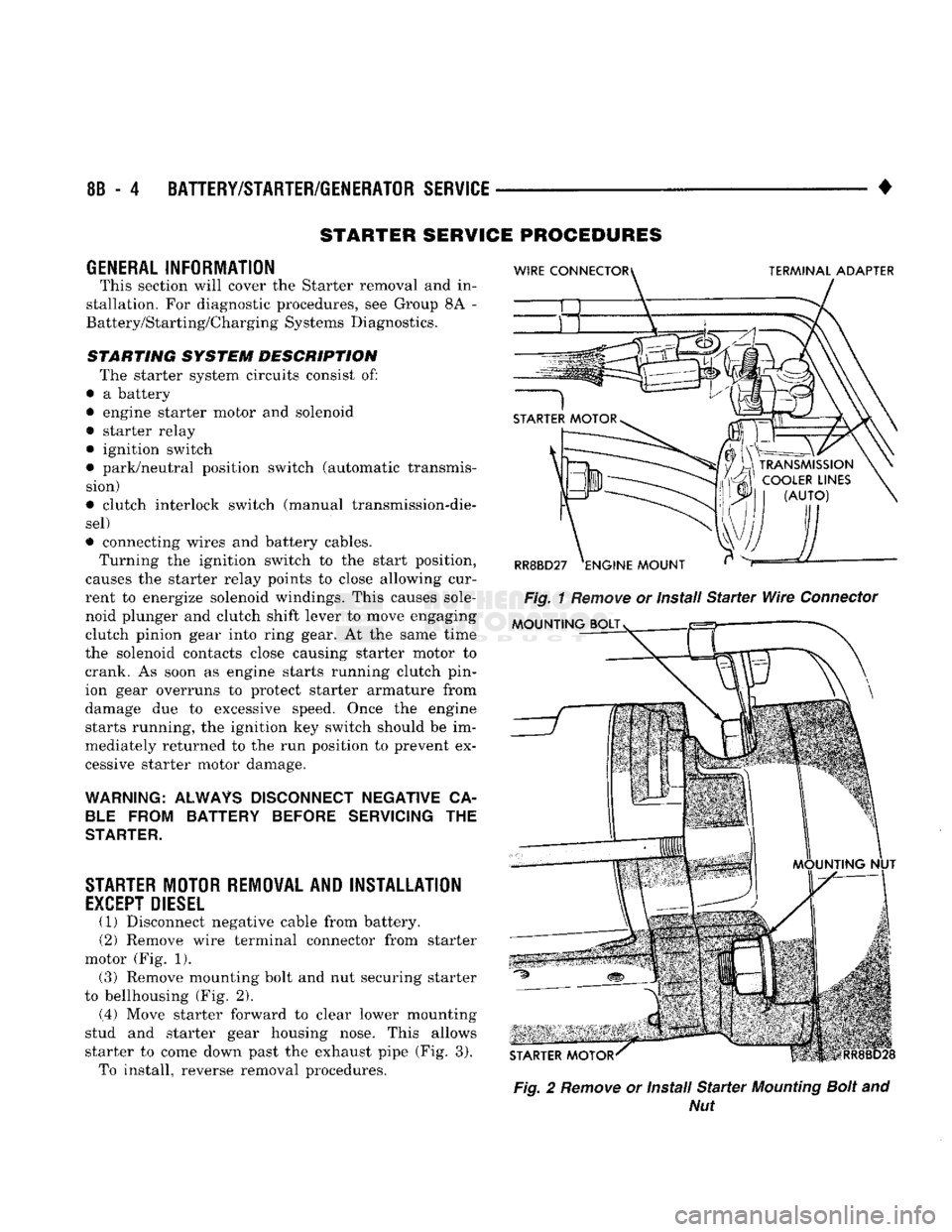
8B
- 4
BATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICE
•
STARTER SERVICE PROCEDURES
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section will cover the Starter removal and in
stallation. For diagnostic procedures, see Group 8A -
Battery/Starting/Charging Systems Diagnostics.
STARTING
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The starter system circuits consist of:
• a battery
• engine starter motor and solenoid
• starter relay
• ignition switch
© park/neutral position switch (automatic transmis sion)
• clutch interlock switch (manual transmission-die-
sel)
• connecting wires and battery cables. Turning the ignition switch to the start position,
causes the starter relay points to close allowing cur
rent to energize solenoid windings. This causes sole
noid plunger and clutch shift lever to move engaging
clutch pinion gear into ring gear. At the same time
the solenoid contacts close causing starter motor to
crank. As soon as engine starts running clutch pin ion gear overruns to protect starter armature from
damage due to excessive speed. Once the engine starts running, the ignition key switch should be im
mediately returned to the run position to prevent ex
cessive starter motor damage.
WARNING:
ALWAYS DISCONNECT NEGATIVE
CA
BLE FROM
BATTERY
BEFORE SERVICING
THE
STARTER.
STARTER
MOTOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION EXCEPT DIESEL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove wire terminal connector from starter
motor (Fig. 1). (3) Remove mounting bolt and nut securing starter
to bellhousing (Fig. 2).
(.4) Move starter forward to clear lower mounting
stud and starter gear housing nose. This allows
starter to come down past the exhaust pipe (Fig. 3). To install, reverse removal procedures.
Fig.
2
Remove
or Install
Starter
Mounting
Bolt
and
Nut
Page 352 of 1502

•
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
8D
- 1
CONTENTS
page page
COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS/SERVICE PROCEDURES
7
OPERATION
1
IGNITION SWITCH
25
COMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
..... 18
SPECIFICATIONS
28
COMPONENT
IDENTIFICATION/SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page
Automatic
Shut Down (ASD) Relay
1
Camshaft Position Sensor
2
Crankshaft Position Sensor
2
Distributors
3
Engine Coolant
Temperature
Sensor
...........
4
General
Information
1
page
Ignition
Coil
3
Intake
Manifold Charge
Air
Temperature
Sensor
. . 4
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
4
Powertrain
Control
Module (PCM)
. 5
Throttle
Position Sensor
5
GENERAL
INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references
are
made
to
par
ticular vehicle models
by
alphabetical designation
or
by
the
particular vehicle nameplate.
A
chart showing a breakdown
of
alphabetical designations
is
included
in
the
Introduction group
at the
beginning
of
this
manual. 5.9L
gas
powered engines will
be
referred
to as ei
ther: LDC (Light Duty Cycle),
or
HDC (Heavy Duty Cycle). This section
of the
group, Component Identifica
tion/System Operation, will discuss ignition system operation
and
will identify ignition system compo
nents.
For diagnostic procedures
and
adjustments, refer
to
the Diagnostics/Service Procedures section
of
this
group.
For removal
and
installation
of
ignition system
components, refer
to the
Component Removal/Instal
lation section
of
this group. For other useful information, refer
to
On-Board
Di
agnostics
in the
General Diagnosis sections
of
Group
14,
Fuel System
in
this manual. For operation
of the DRB II
Diagnostic Scan Tool,
refer
to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce
dures service manual.
An Ignition specifications section
is
included
at the
end
of
this group.
A
general Maintenance Schedule (mileage intervals)
for
ignition related items
can be
found
in
Group
0,
Lubrication and Maintenance. This
schedule
can
also
be
found
in the
Owners Manual.
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
The ignition systems used
on all
engines
are
basi
cally identical. Similarities
and
differences between
the systems will
be
discussed.
A sequential multi-port fuel injection system
is
used
on all gas
powered engines.
The ignition system
is
controlled
by the
powertrain
control module (PCM)
on all
engines.
The
PCM
was
formerly referred
to as the
SBEC
or
engine control ler.
The ignition system consists
of:
• Spark Plugs
• Ignition Coil
• Secondary Ignition Cables
• Ignition distributor. Contains rotor
and
camshaft
position sensor • Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
• Crankshaft Position Sensor
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN (ASD) RELAY
The automatic shut down (ASD) relay
is
located
in
the engine compartment (Fig.
1). As one of its
func
tions,
the ASD
relay will supply battery voltage
to
the ignition coil.
The
ground circuit
for the
ASD
re
lay
is
controlled
by the
powertrain control module (PCM).
The PCM
regulates
ASD
relay operation
by
switching
the
ground circuit on-and-off.
IGNITION
SYSTEMS