shaft FIAT 500 1973 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1973, Model line: 500, Model: FIAT 500 1973 1.GPages: 128, PDF Size: 9.01 MB
Page 24 of 128
sections of the air conveyor securing with seven
screws, seven toothed washers and five nuts.
22 Slide the fuel pump control rod into its seating,
assemble the insulator between oil wetted graphite
gaskets and fit the pump to the crankcase using nuts
and toothed washers.
23 Fit the air conveyor cover complete with the accelera-
tor control relay lever and rod. Secure using eight
mounting screws, eight toothed washers, eight plain
washers and eight nuts. Fit the fuel line retaining clip
which is secured by one of the air conveyor upper
screws. Install the generator and fan drive pulley
having first placed four adjusting rings between the
pulley halves and the thrust ring on the outside.
Secure the pulley to generator shaft using three
screws and three toothed washers. Fit the generator
fan drive belt.
24 Refit the carburetter having first positioned the
bakelite heat shield between the t w o oil moistened
graphite gaskets. Secure the carburetter using t w o
copper washers and t w o self-locking nuts. Fit the
exhaust silencer and secure to the exhaust manifolds
with nuts and spring washers. Place the t w o graphite
gaskets between the manifold joints. Fit both exhaust
silencer upper mounting brackets and secure them
on the top side to the brackets already in place w i t h
nuts and toothed washers on the bottom side w i t h
screws and toothed washers.
25 Carefully position the distributor at a 10 deg advance
setting and secure w i t h a
nut, plain washer and
spring washer. Fit the fuel pump to carburetter line
complete w i t h mounting bracket rubber lining and
secure the line with two clamps. If difficulty is
experienced in positioning the fuel line into the pump
or carburetter funnels it is suggested that the line
ends should be heated in hot water and thoroughly
dried before installing.
26 Install the air cleaner elbow and rubber hose assembly
on the top of the carburetter using a graphite gasket
in between and secure w i t h nuts, plain washers and
spring washers. Carefully position the air cleaner, line
and hose assembly and connect it to the elbow.
Secure the cleaner to air conveyor cover using screws
and toothed washers.
27 Fit the spark plug cables complete with the rubber
grommet for cable mounting bracket on engine
cowling and connect the cables to the distributor
and spark plugs. Fit the oil pressure gauge sender
unit together w i t h its sealing washer.
28 Install the cylinder head cover and oil breather pipe
assembly w i t h a cork gasket inserted between.
Secure w i t h self-locking nuts and fibre washers.
Connect the accelerator control relay lever rod to the
carburetter and secure with the clip.
29 Fill the oil pan with the correct grade and quantity of
oil, insert the dipstick and the engine is ready for
refitting.
1:18 Engine assembly (station wagon)
Reassembly of this engine is straightforward as it is
the reverse procedure to dismantling. It is recommended
that Sections 1 :5 and 1 :17 are studied as the assembly
technique is similar for both the horizontal and vertical
F50031 cylinder engines. The following points should however
be noted:
1 Refer to FIG 1 :45 for the correct positioning of the
connecting rod-piston assembly on the 120.000
engine.
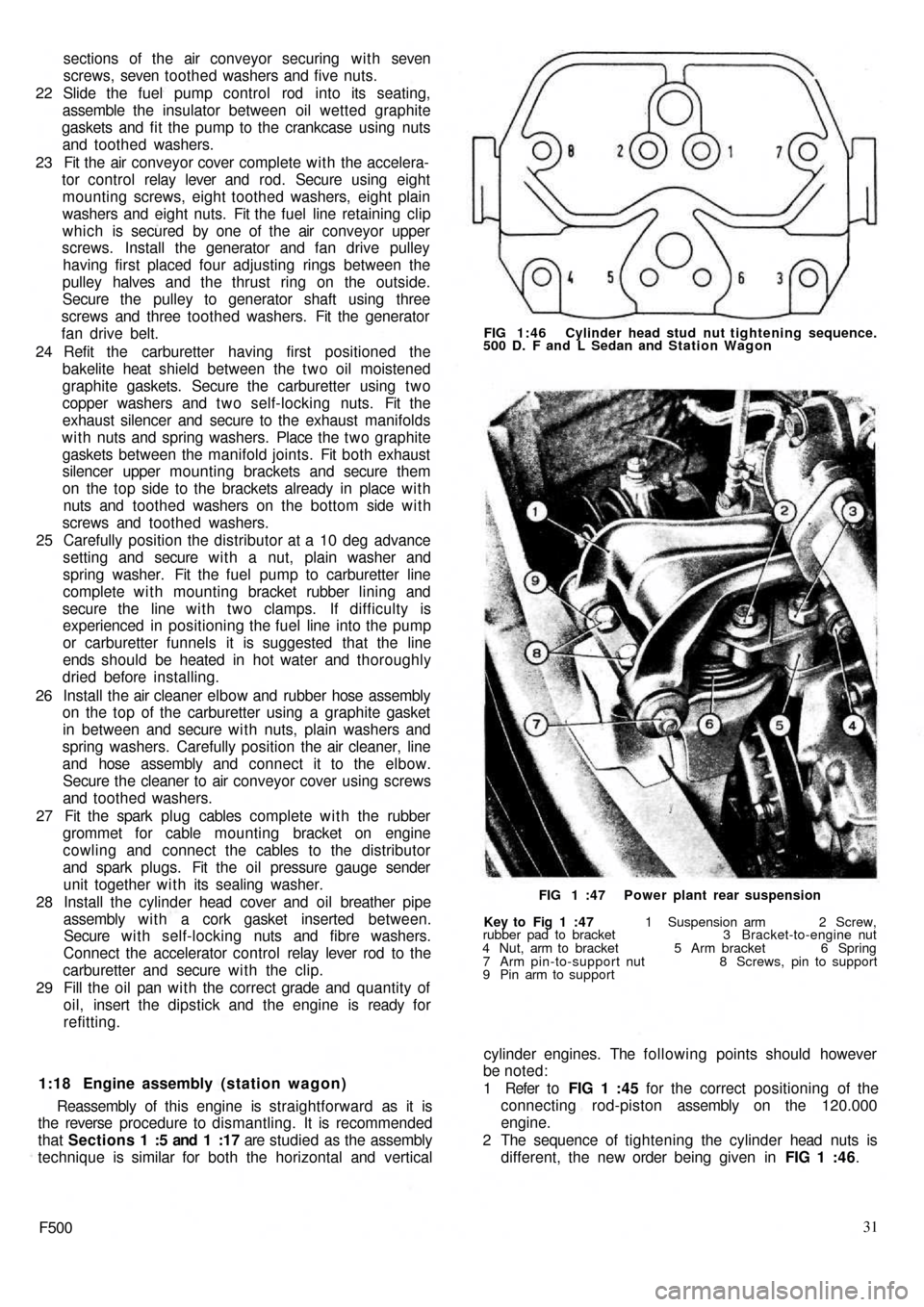
2 The sequence of tightening the cylinder head nuts is
different, the new order being given in FIG 1 :46.
Key to Fig 1 :47 1 Suspension arm 2 Screw,
rubber pad to bracket 3 Bracket-to-engine nut
4 Nut, arm to bracket 5 Arm bracket 6 Spring
7 Arm pin-to-support nut 8 Screws, pin to support
9 Pin arm to supportFIG 1 :47 Power plant rear suspension FIG 1:46 Cylinder head stud nut tightening sequence.
500 D. F and L Sedan and Station Wagon
Page 25 of 128
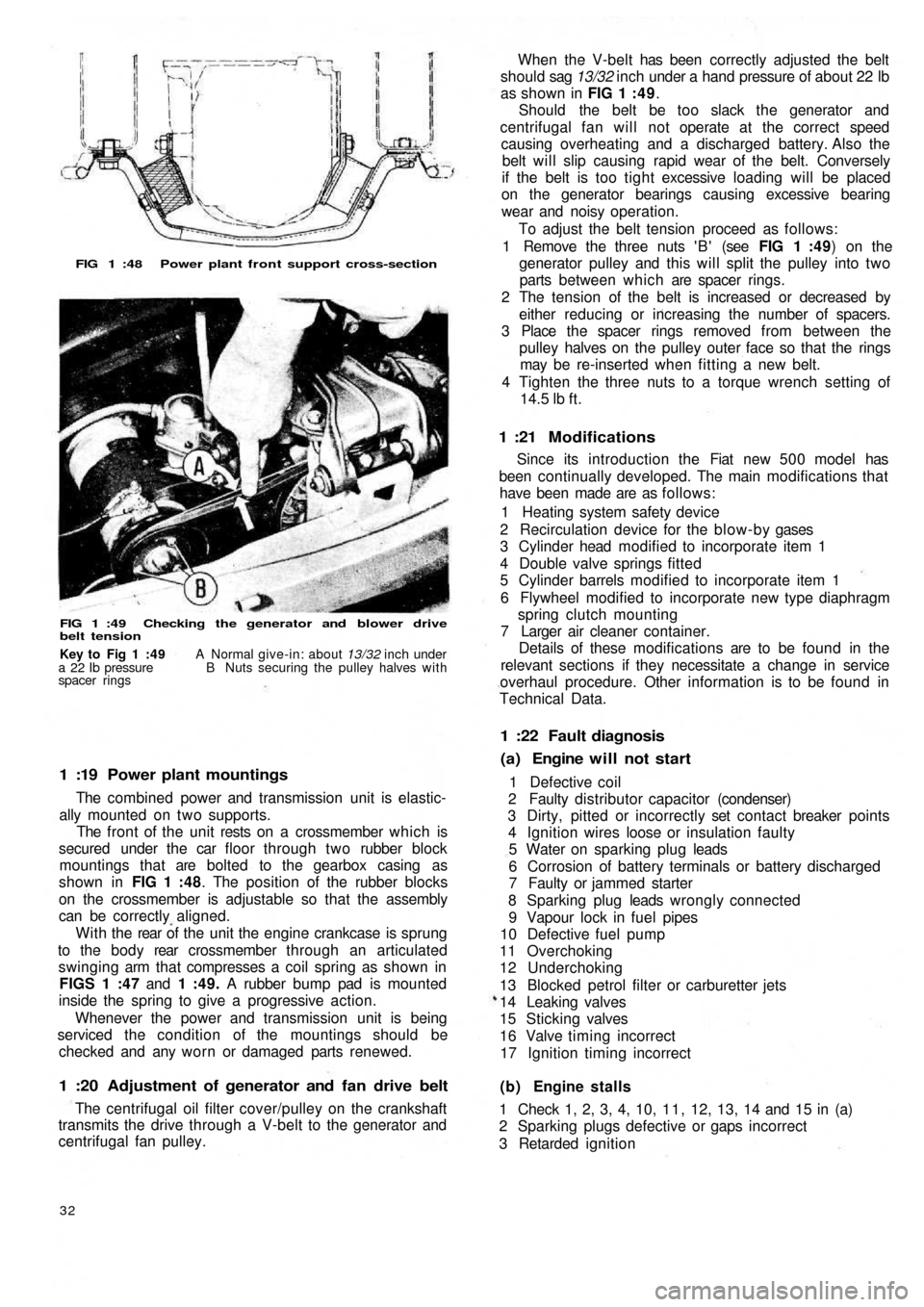
FIG 1 :48 Power plant front support cross-section
FIG 1 :49 Checking the generator and blower drive
belt tension
1 :19 Power plant mountings
The combined power and transmission unit is elastic-
ally mounted on two supports.
The front of the unit rests on a crossmember which is
secured under the car floor through two rubber block
mountings that are bolted to the gearbox casing as
shown in FIG 1 :48. The position of the rubber blocks
on the crossmember is adjustable so that the assembly
can be correctly aligned.
W i t h t h e rear of the unit the engine crankcase is sprung
to the b o d y rear crossmember through an articulated
swinging arm that compresses a coil spring as shown in
FIGS 1 :47 and 1 :49. A rubber bump pad is mounted
inside the spring to give a progressive action.
Whenever the power and transmission unit is being
serviced the condition of the mountings should be
checked and any worn or damaged parts renewed.
1 :20 Adjustment of generator and fan drive belt
The centrifugal oil filter cover/pulley on the crankshaft
transmits the drive through a V-belt to the generator and
centrifugal fan pulley.
32
(b) Engine stalls
1 Check 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 1 1 , 12, 13, 14 and 15 in (a)
2 Sparking plugs defective or gaps incorrect
3 Retarded ignition 1 Defective coil
2 Faulty distributor capacitor (condenser)
3 Dirty, pitted or incorrectly set contact breaker points
4 Ignition wires loose or insulation faulty
5 Water on sparking plug leads
6 Corrosion of battery terminals or battery discharged
7 Faulty or jammed starter
8 Sparking plug leads wrongly connected
9 Vapour lock in fuel pipes
10 Defective fuel pump
11 Overchoking
12 Underchoking
13 Blocked petrol filter or carburetter jets
14 Leaking valves
15 Sticking valves
16 Valve timing incorrect
17 Ignition timing incorrect
(a) Engine will not start 1 :22 Fault diagnosis
Since its introduction the Fiat new 5 0 0 model has
been continually developed. The main modifications that
have been made are as follows:
1 Heating system safety device
2 Recirculation device for the blow-by gases
3 Cylinder head modified to incorporate item 1
4 Double valve springs fitted
5 Cylinder barrels modified to incorporate item 1
6 Flywheel modified to incorporate new type diaphragm
spring clutch mounting
7 Larger air cleaner container.
Details of these modifications are to be found in the
relevant sections if they necessitate a change in service
overhaul procedure. Other information is to be found in
Technical Data.
1 :21 Modifications
When the V-belt has been correctly adjusted the belt
should sag 13/32 inch under a hand pressure of about 22 lb
as shown in FIG 1 : 4 9.
Should the belt be too slack the generator and
centrifugal fan will not operate at the correct speed
causing overheating and a discharged battery. Also the
belt will slip causing rapid wear of the belt. Conversely
if the belt is too tight excessive loading will be placed
on the generator bearings causing excessive bearing
wear and noisy operation.
To adjust the belt tension proceed as follows:
1 Remove the three nuts ' B ' (see FIG 1 :49) on the
generator pulley and this will split the pulley into two
parts between which are spacer rings.
2 The tension of the belt is increased or decreased by
either reducing or increasing the number of spacers.
3 Place the spacer rings removed from between the
pulley halves on the pulley outer face so that the rings
may be re-inserted when fitting a new belt.
4 Tighten the three nuts to a torque wrench setting of
14.5
lb ft.
Key to Fig 1 :49 A Normal give-in: about 13/32 inch under
a 22 Ib pressure B Nuts securing the pulley halves with
spacer rings
Page 26 of 128

4 Mixture too weak
5 Water in fuel system
6 Petrol tank vent blocked
7 Incorrect valve clearance
(c) Engine idles badly
1 Check 1 and 6 in (b)
2 Air leak at manifold joints
3 Slow-running jet blocked or out of adjustment
4 Air leak in carburetter
5 Over-rich mixture
6 Worn piston rings
7 Worn valve stems or guides
8 Weak exhaust valve springs
(d) Engine misfires
1 Check 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 13, 14, 1 5, 16, 17 in (a);
2, 3, 4 and 7 in (b)
2 Weak or broken valve springs
(e) Engine overheats
1 Generator and fan drive belt too loose
2 Shutter or thermostat seized in closed position
(f) Compression low
1 Check 14 and 15 in (a), 6 and 7 in (c) and 2 in (d)
2 Worn piston ring grooves
3 Scored or worn cylinder bores
(g) Engine lacks power
1 Check 3, 10, 1 1 , 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17 in (a), 2, 3, 4
and 7 in (b) 6 and 7 in (c) and 2 in (d). Also check (e)
and (f)
2 Leaking joint washers
3 Fouled sparking plugs
4 Automatic centrifugal advance not operating
(h) Burnt valves or seats
1 Check 14 and 15 in (a), 7 in (b) and 2 in (d). Alsocheck (e)
2 Excessive carbon around valve seat and head
(j) Sticking valves
1 Check 2 in (d)
2 Bent valve stem
3 Scored valve stem or guide
4 Incorrect valve clearance
(k) Excessive cylinder wear
1 Check 11 in (a) and see Chapter 4
2 Lack of oil
3 Dirty oil
4 Piston rings gummed up or broken
5 Badly fitting piston rings
6 Connecting rods bent
(l) Excessive oil consumption
1 Check 6 and 7 in (c) and check (k)
2 Ring gaps too wide
3 Oil return holes in piston choked with carbon
4 Scored cylinders
5 Oil level too high
6 External oil leaks
7 Ineffective valve stem oil seals
(m) Crankshaft and connecting rod bearing failure
1 Check 2 in (k)
2 Restricted oilways
3 Worn journals or crank pins
4 Loose bearing caps
5 Extremely low oil pressure
6 Bent connecting rod
(n) High fuel consumption (see Chapter 2)
(o) Engine vibration
1 Loose generator bolts
2 Blower blade assembly out-of-balance
3 Incorrect clearance for rear engine mounting rubber
F50033
Page 28 of 128

CHAPTER 2
THE FUEL SYSTEM
2:1 Description
2 : 2 Fuel pump operating principles
2 : 3 Routine maintenance
2 : 4 Pump removal, dismantling and examination
2 : 5 Reassembly, installation and adjustment
2 : 6 Carburetter operation and adjustment,
Weber 26.1MB2 : 7 Modifications
2 : 8 Carburetter operation and adjustment,
Weber 26.OC
2 :9 Air cleaner
2 : 1 0 B l o w - b y gases recirculation device
2:11 Fuel tank
2:12 Fault diagnosis
2:1 Description
All the new 500 models use a mechanical diaphragm
fuel feed pump as shown in FIG 2 : 1. Four types of
carburetter are fitted depending on the model to which
the engine is installed. Each carburetter operation and
adjustment is fully described, together with details of the
recirculation device for blow-by gases and o i l vapours.
2 : 2 Fuel pump operating principles
Refer to FIG 2 : 2. An eccentric on the rotating camshaft
actuates the operating rocker 21 via a pushrod 25 which
depresses the diaphragm 14 and so creates a depression
in the pumping chamber located in upper body 5. Under
atmospheric pressure, petrol passes through the pipeline
connection and inlet valve into the pumping chamber.
The return spring 15 then raises the diaphragm, expelling
the petrol through the outlet valve and pipeline to the
carburetter float chamber.
When the float chamber is full, the pressure in the pipe-
line and pumping chamber holds the diaphragm depressed
against the tension of the return spring.2 : 3 Routine maintenance
A poor delivery of fuel to the carburetter may be due to
a fault in the fuel pump or related lines. Periodically the
pump body screws 19 (see FIG 2 : 2) and upper cover
screw 1 should be checked for tightness. The fuel pump
lines should be disconnected and checked for freedom of
restriction, chafing and loose connections. The fuel pump
filter should be removed and cleaned periodically.
2:4 Pump removal, dismantling and examination
The pump is located on the carburetter side of the
engine crankcase (sedan) or under the generator at the
front of the crankcase (station wagon).
Removal:
1 Disconnect the fuel pipe from the tank to stop petrol
syphoning out of the tank and then release the fuel
inlet and outlet pipes from the pump body.
2 Remove the t w o nuts and washers holding pump to
crankcase.
3 Carefully lift away the pump, gaskets and insulating pad
from the crankcase (see FIG 2 : 3).
F50035
Page 30 of 128
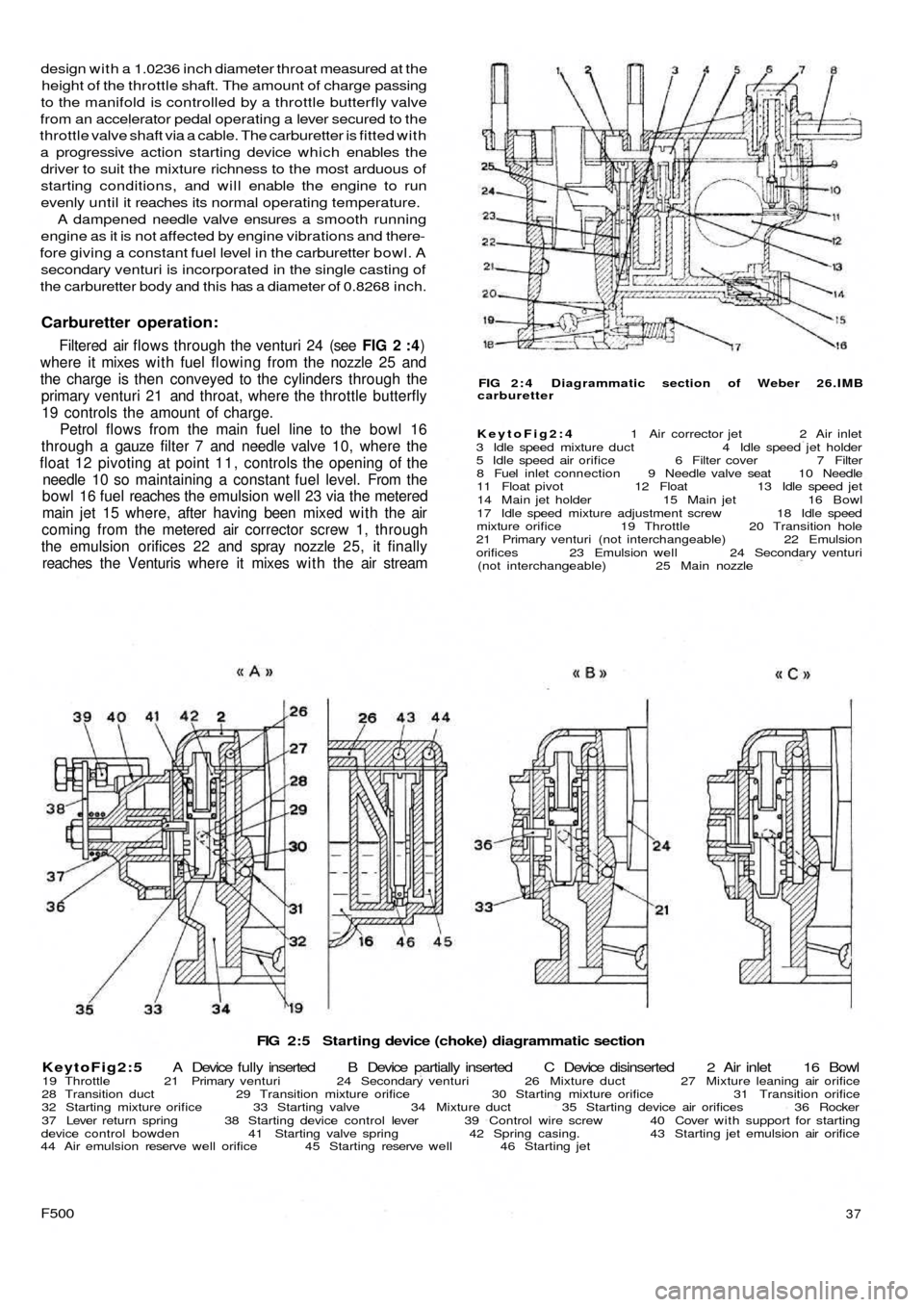
FIG 2:5 Starting device (choke) diagrammatic section
KeytoFig2:5 A Device fully inserted B Device partially inserted C Device disinserted 2 Air inlet 16 Bowl
19 Throttle 21 Primary venturi 24 Secondary venturi 26 Mixture duct 27 Mixture leaning air orifice
28 Transition duct 29 Transition mixture orifice 30 Starting mixture orifice 31 Transition orifice
32 Starting mixture orifice 33 Starting valve 34 Mixture duct 35 Starting device air orifices 36 Rocker
37 Lever return spring 38 Starting device control lever 39 Control wire screw 40 Cover with support for starting
device control bowden 41 Starting valve spring 42 Spring casing. 43 Starting jet emulsion air orifice
44 Air emulsion reserve well orifice 45 Starting reserve well 46 Starting jet
F50037
FIG 2 : 4 Diagrammatic section of Weber 26.IMB
carburetter
KeytoFig2:4 1 Air corrector jet 2 Air inlet
3 Idle speed mixture duct 4 Idle speed jet holder
5 Idle speed air orifice 6 Filter cover 7 Filter
8 Fuel inlet connection 9 Needle valve seat 10 Needle
11 Float pivot 12 Float 13 Idle speed jet
14 Main jet holder 15 Main jet 16 Bowl
17 Idle speed mixture adjustment screw 18 Idle speed
mixture orifice 19 Throttle 20 Transition hole
21 Primary venturi (not interchangeable) 22 Emulsion
orifices 23 Emulsion well 24 Secondary venturi
(not interchangeable) 25 Main nozzle
design with a 1.0236 inch diameter throat measured at the
height of the throttle shaft. The amount of charge passing
to the manifold is controlled by a throttle butterfly valve
from an accelerator pedal operating a lever secured to the
throttle valve shaft via a cable. The carburetter is fitted with
a progressive action starting device which enables the
driver to suit the mixture richness to the most arduous of
starting conditions, and will enable the engine to run
evenly until it reaches its normal operating temperature.
A dampened needle valve ensures a smooth running
engine as it is not affected by engine vibrations and there-
fore giving a constant fuel level in the carburetter bowl. A
secondary venturi is incorporated in the single casting of
the carburetter body and this has a diameter of 0.8268 inch.
Carburetter operation:
Filtered air flows through the venturi 24 (see FIG 2 :4)
where it mixes w i t h fuel flowing from the nozzle 25 and
the charge is then conveyed to the cylinders through the
primary venturi 21 and throat, where the throttle butterfly
19 controls the amount of charge.
Petrol flows from the main fuel line to the bowl 16
through a gauze filter 7 and needle valve 10, where the
float 12 pivoting at point 1 1 , controls the opening of the
needle 10 so maintaining a constant fuel level. From the
bowl 16 fuel reaches the emulsion well 23 via the metered
main jet 15 where, after having been mixed with the air
coming from the metered air corrector screw 1, through
the emulsion orifices 22 and spray nozzle 25, it finally
reaches the Venturis where it mixes w i t h the air stream
Page 31 of 128
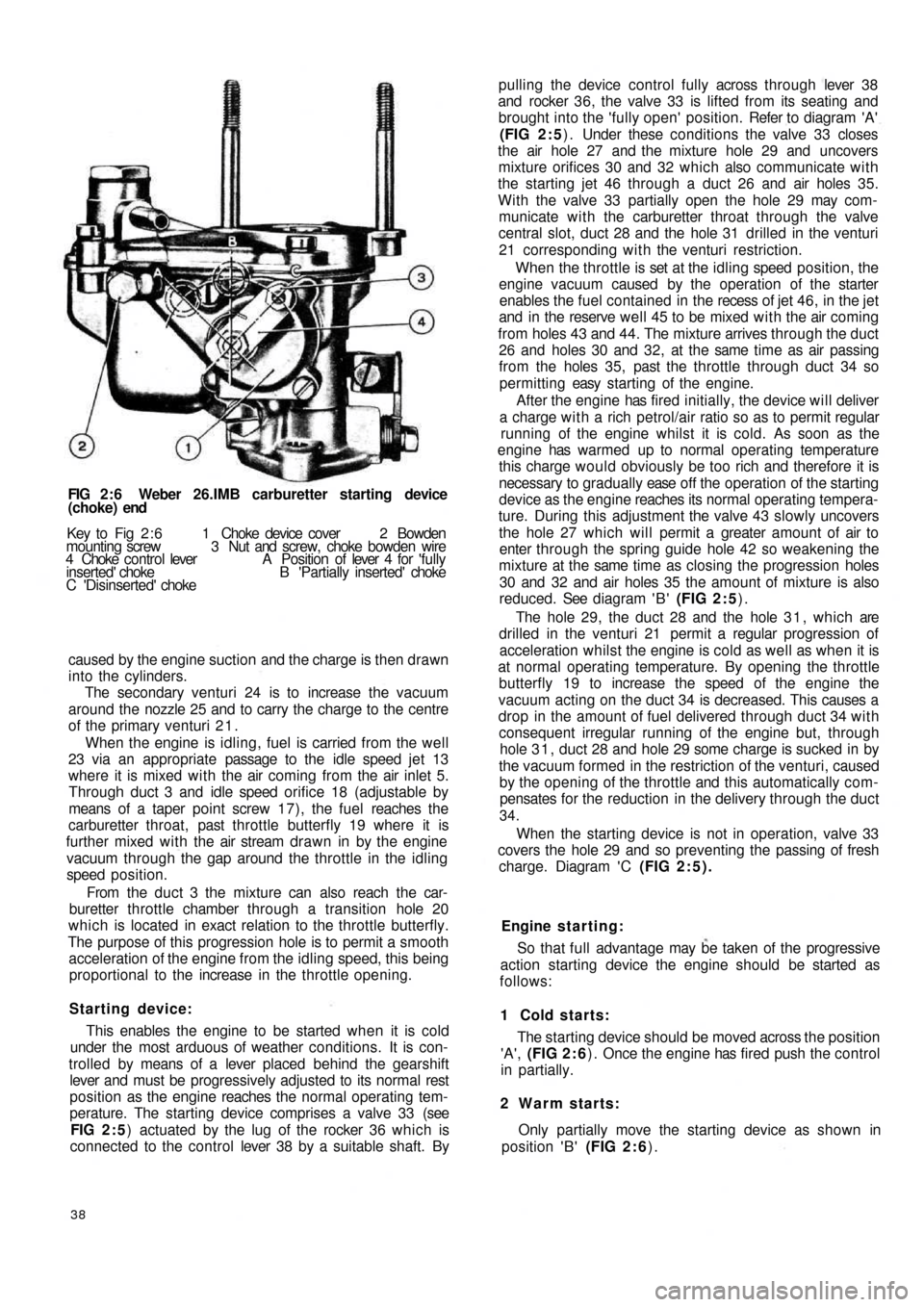
FIG 2 : 6 Weber 26.IMB carburetter starting device
(choke) end
Key to Fig 2 : 6 1 Choke device cover 2 Bowden
mounting screw 3 Nut and screw, choke bowden wire
4 Choke control lever A Position of lever 4 for 'fully
inserted' choke B 'Partially inserted' choke
C 'Disinserted' choke
caused by the engine suction and the charge is then drawn
into the cylinders.
The secondary venturi 24 is to increase the vacuum
around the nozzle 25 and to carry the charge to the centre
of the primary venturi 2 1 .
When the engine is idling, fuel is carried from the well
23 via an appropriate passage to the idle speed jet 13
where it is mixed with the air coming from the air inlet 5.
Through duct 3 and idle speed orifice 18 (adjustable by
means of a taper point screw 17), the fuel reaches the
carburetter throat, past throttle butterfly 19 where it is
further mixed with the air stream drawn in by the engine
vacuum through the gap around the throttle in the idling
speed position.
From the d u c t 3 the mixture can also reach the car-
buretter throttle chamber through a transition hole 20
which is located in exact relation to the throttle butterfly.
The purpose of this progression hole is to permit a smooth
acceleration of the engine from the idling speed, this being
proportional to the increase in the throttle opening.
Starting device:
This enables the engine to be started when it is cold
under the most arduous of weather conditions. It is con-
trolled by means of a lever placed behind the gearshift
lever and must be progressively adjusted to its normal
rest
position as the engine reaches the normal operating tem-
perature. The starting device comprises a valve 33 (see
FIG 2 : 5) actuated by the lug of the rocker 36 which is
connected to the control lever 38 by a suitable shaft. By
38
pulling the device control fully across through lever 38
and rocker 36, the valve 33 is lifted from its seating and
brought into the 'fully open' position. Refer to diagram 'A'
(FIG 2 : 5) . Under these conditions the valve 33 closes
the air hole 27 and the mixture hole 29 and uncovers
mixture orifices 30 and 32 which also communicate with
the starting jet 46 through a duct 26 and air holes 35.
With the valve 33 partially open the hole 29 may com-
municate with the carburetter throat through the valve
central slot, duct 28 and the hole 31 drilled in the venturi
21 corresponding with the venturi restriction.
When the throttle is set at the idling speed position, the
engine vacuum caused by the operation of the starter
enables the fuel contained in the recess of jet 4 6 , in the jet
and in the reserve well 45 to be mixed w i t h the air coming
from holes 43 and 44. The mixture arrives through the duct
26 and holes 30 and 32, at the same time as air passing
from the holes 35, past the throttle through duct 34 so
permitting easy starting of the engine.
After the engine has fired initially, the device will deliver
a charge with a rich petrol/air ratio so as to permit regular
running of the engine whilst it is cold. As soon as the
engine has warmed up to normal operating temperature
this charge would obviously be too rich and therefore it is
necessary to gradually ease o f f the operation of the starting
device as the engine reaches its normal operating tempera-
ture. During this adjustment the valve 43 slowly uncovers
the hole 27 which will permit a greater amount of air to
enter through the spring guide hole 42 so weakening the
mixture at the same time as closing the progression holes
30 and 32 and air holes 35 the amount of mixture is also
reduced. See diagram ' B ' (FIG 2 : 5).
The hole 29, the duct 28 and the hole 3 1 , which are
drilled in the venturi 21 permit a regular progression of
acceleration whilst the engine is cold as well as when it is
at normal operating temperature. By opening the throttle
butterfly 19 to increase the speed of the engine the
vacuum acting on the duct 34 is decreased. This causes a
drop in the amount of fuel delivered through duct 34 with
consequent irregular running of the engine but, through
hole 3 1 , duct 28 and hole 29 some charge is sucked in by
the vacuum formed in the restriction of the venturi, caused
by the opening of the throttle and this automatically com-
pensates for the reduction in the delivery through the duct
34.
When the starting device is not in operation, valve 33
covers the hole 29 and so preventing the passing of fresh
charge. Diagram ' C (FIG 2:5).
Engine s t a rting:
So that full advantage may be taken of the progressive
action starting device the engine should be started as
follows:
1 Cold starts:
The starting device should be moved across the position
'A', (FIG 2 : 6) . Once the engine has fired push the control
in partially.
2 Warm starts:
Only partially move the starting device as shown in
position 'B' (FIG 2 : 6).
Page 33 of 128
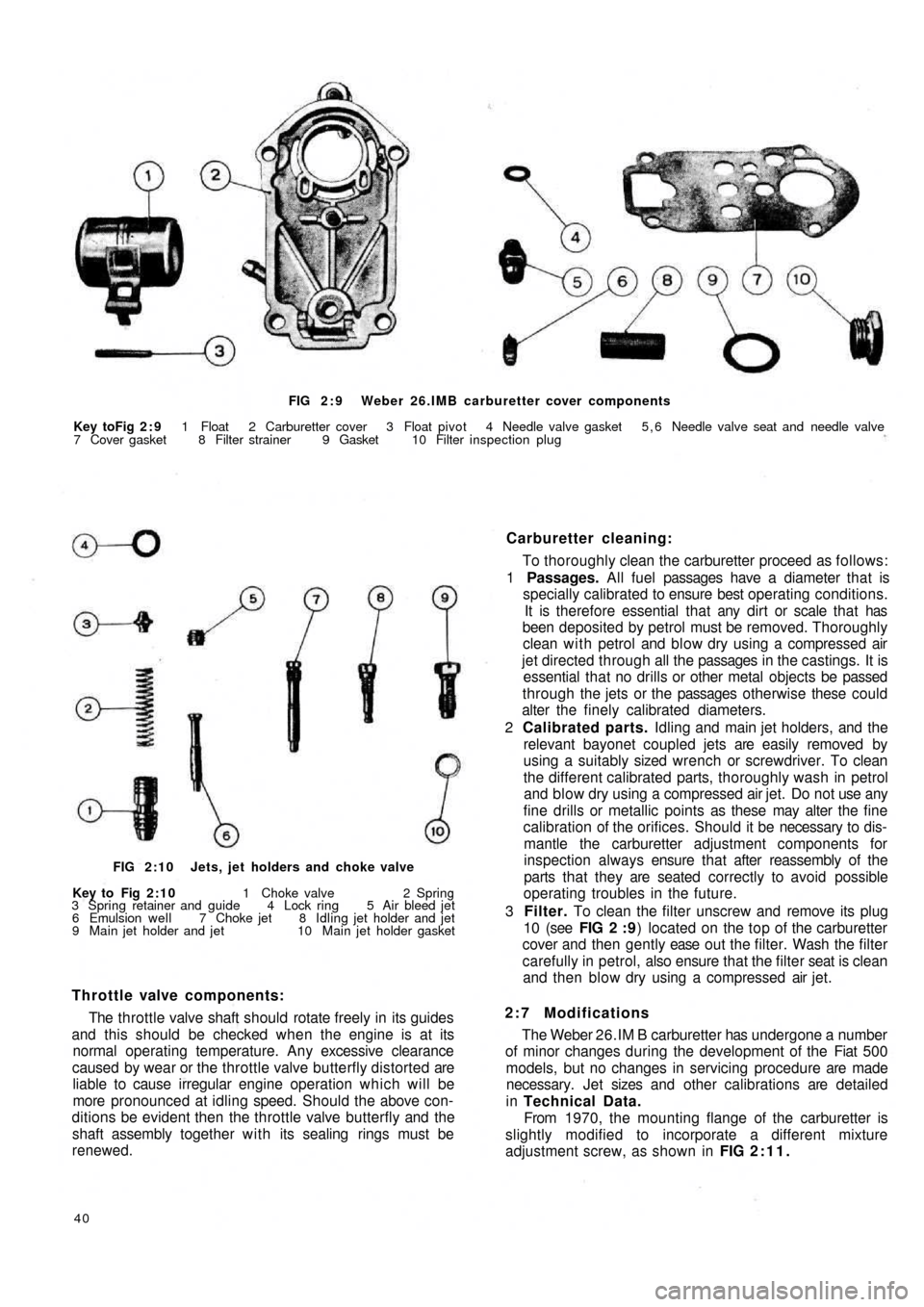
FIG 2 : 9 Weber 26.IMB carburetter cover components
Key toFig 2 : 9 1 Float 2 Carburetter cover 3 Float pivot 4 Needle valve gasket 5 , 6 Needle valve seat and needle valve
7 Cover gasket 8 Filter strainer 9 Gasket 10 Filter inspection plug
Carburetter cleaning:
To thoroughly clean the carburetter proceed as follows:
1 Passages. All fuel passages have a diameter that is
specially calibrated to ensure best operating conditions.
It is therefore essential that any dirt or scale that has
been deposited by petrol must be removed. Thoroughly
clean with petrol and blow dry using a compressed air
jet directed through all the passages in the castings. It is
essential that no drills or other metal objects be passed
through the jets or the passages otherwise these could
alter the finely calibrated diameters.
2 Calibrated parts. Idling and main jet holders, and the
relevant bayonet coupled jets are easily removed by
using a suitably sized wrench or screwdriver. To clean
the different calibrated parts, thoroughly wash in petrol
and blow dry using a compressed air jet. Do not use any
fine drills or metallic points as these may alter the fine
calibration of the orifices. Should it be necessary to dis-
mantle the carburetter adjustment components for
inspection always ensure that after reassembly of the
parts that they are seated correctly to avoid possible
operating troubles in the future.
3 Filter. To clean the filter unscrew and remove its plug
10 (see FIG 2 : 9) located on the top of the carburetter
cover and then gently ease o u t t h e filter. Wash the filter
carefully in petrol, also ensure that the filter seat is clean
and then blow dry using a compressed air jet.
2:7 Modifications
The Weber 26.IM B carburetter has undergone a number
of minor changes during the development of the Fiat 500
models, but no changes in servicing procedure are made
necessary. Jet sizes and other calibrations are detailed
in Technical Data.
From 1970, the mounting flange of the carburetter is
slightly modified to incorporate a different mixture
adjustment screw, as shown in FIG 2:11.
40
Throttle valve components:
The throttle valve shaft should rotate freely in its guides
and this should be checked when the engine is at its
normal operating temperature. Any excessive clearance
caused by wear or the throttle valve butterfly distorted are
liable to cause irregular engine operation which will be
more pronounced at idling speed. Should the above con-
ditions be evident then the throttle valve butterfly and the
shaft assembly together with its sealing rings must be
renewed.
FIG 2:10 Jets, jet holders and choke valve
Key to Fig 2:10 1 Choke valve 2 Spring
3 Spring retainer and guide 4 Lock ring 5 Air bleed jet
6 Emulsion well 7 Choke jet 8 Idling jet holder and jet
9 Main jet holder and jet 10 Main jet holder gasket
Page 40 of 128

3:1
3:2
3:3
3:4
3:5Description
Operation
Routine maintenance
Ignition faults
Removing and dismantling distributor (sedan
and sports)
CHAPTER 3
THE IGNITION SYSTEM
3:6
3:7
3:8
3:9
3:10
Removing and dismantling
(station wagon)
Timing the ignition
Sparking plugs
The distributor drive spindle
Fault diagnosisdistributor
3 :1 Description
The ignition system fitted to all the models covered by
this manual consists of an ignition coil, ignition distributor
fitted with contact breaker points, a centrifugal automatic
advance system, condenser, low- and high-tension
wiring, spark plugs and a power supply provided by a
generator and battery. The wiring diagram is shown in
FIG 3 : 1
1 The low-tension circuit which is sometimes called the
primary circuit includes the power supply, contact
breaker points, condenser and ignition coil primary
winding.
2 The high-tension circuit which is sometimes called the
secondary circuit includes the ignition coil secondary
winding, distributor rotor, distributor cap with terminals
and the central brush, high-tension cables and the spark
plugs.
3 : 2 Operation
The contact breaker unit in the distributor interrupts
the primary circuit by the points opening. The sudden stop
in the flow of current in the primary winding, does not cause
arcing at the contact breaker points because it discharges
into the condenser connected in parallel w i t h the contact
F50047
breaker points. With the sudden collapse of the primary
circuit, the intensity of the magnetic field drops causing
an induced high-tension current in the ignition coil
secondary winding. The high EMF is distributed to the
sparking plugs by the ignition distributor rotor.
The automatic advance mechanism comprises a plate
carrying t w o weights which are symmetrically pivoted on
the plate at one end. Also attached to the weights at
opposite ends to the pivots is the cam carrier shaft with
special tension return springs. Under the action of centri-
fugal force as the rotational speed increases, the weights
move outwards causing the cam carrier shaft to move
angularly compared to the distributor drive shaft thus
causing advancement of the ignition timing.
The contact breaker assembly comprises the cam on the
drive shaft and t w o contact points, one of which is
stationary while the other is under the influence of the
cam, the action of which is transmitted by a rubbing block.
The cam has t w o lobes to control the opening and closing
of contact points. The stationary contact point is mounted
on an adjustable support to enable the contact breaker
point gap to be adjusted.
The HT current reaches the distributor cap central
terminal, from the ignition coil and is distributed to each
of the spark plugs at the correct time by the rotor arm.
Page 41 of 128
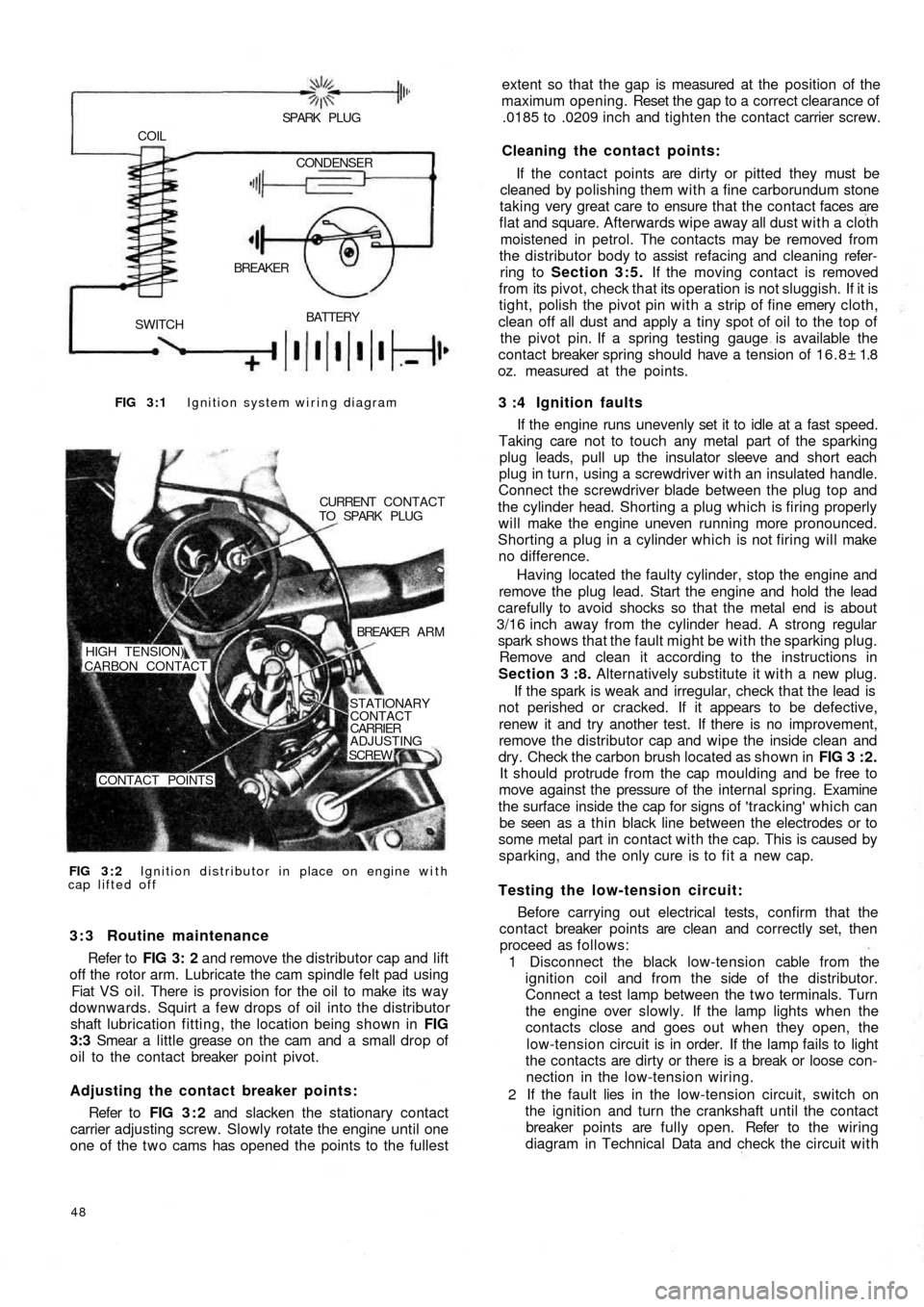
FIG 3 : 1 Ignition system wiring diagram
BATTERY
SWITCHBREAKER COIL
SPARK PLUG
CONDENSER
FIG 3 : 2 Ignition distributor in place on engine with
cap lifted offCURRENT CONTACT
TO SPARK PLUG
BREAKER A R M
STATIONARY
CONTACT
CARRIER
ADJUSTING
SCREW
CONTACT POINTS HIGH TENSION)
CARBON CONTACT
3 : 3 Routine maintenance
Refer to FIG 3: 2 and remove the distributor cap and lift
off the rotor arm. Lubricate the cam spindle felt pad using
Fiat VS oil. There is provision for the oil to make its way
downwards. Squirt a few drops of oil into the distributor
shaft lubrication fitting, the location being shown in FIG
3:3 Smear a little grease on the cam and a small drop of
oil to the contact breaker point pivot.
Adjusting the contact breaker points:
Refer to FIG 3 : 2 and slacken the stationary contact
carrier adjusting screw. Slowly rotate the engine until one
one of the t w o cams has opened the points to the fullest
48
extent so that the gap is measured at the position of the
maximum opening. Reset the gap to a correct clearance of
.0185 to .0209 inch and tighten the contact carrier screw.
Cleaning the contact points:
If the contact points are dirty or pitted they must be
cleaned by polishing them with a fine carborundum stone
taking very great care to ensure that the contact faces are
flat and square. Afterwards wipe away all dust with a cloth
moistened in petrol. The contacts may be removed from
the distributor body to assist refacing and cleaning refer-
ring to Section 3:5. If the moving contact is removed
from its pivot, check that its operation is not sluggish. If it is
tight, polish the pivot pin with a strip of fine emery cloth,
clean off all dust and apply a tiny spot of oil to the top of
the pivot pin. If a spring testing gauge is available the
contact breaker spring should have a tension of 16.8± 1.8
oz. measured at the points.
3 :4 Ignition faults
If the engine runs unevenly set it to idle at a fast speed.
Taking care not to touch any metal part of the sparking
plug leads, pull up the insulator sleeve and short each
plug in turn, using a screwdriver with an insulated handle.
Connect the screwdriver blade between the plug top and
the cylinder head. Shorting a plug which is firing properly
will make the engine uneven running more pronounced.
Shorting a plug in a cylinder which is not firing will make
no difference.
Having located the
faulty cylinder, stop the engine and
remove the plug lead. Start the engine and hold the lead
carefully to avoid shocks so that the metal end is about
3/16 inch away from the cylinder head. A strong regular
spark shows that the fault might be with the sparking plug.
Remove and clean it according to the instructions in
Section 3 :8. Alternatively substitute it with a new plug.
If the spark is weak and irregular, check that the lead is
not perished or cracked. If it appears to be defective,
renew it and try another test. If there is no improvement,
remove the distributor cap and wipe the inside clean and
dry. Check the carbon brush located as shown in FIG 3 : 2 .
It should protrude from the cap moulding and be free to
move against the pressure of the internal spring. Examine
the surface inside the cap for signs of 'tracking' which can
be seen as a thin black line between the electrodes or to
some metal part in contact with the cap. This is caused by
sparking, and the only cure is to fit a new cap.
Testing the low-tension circuit:
Before carrying out electrical tests, confirm that the
contact breaker points are clean and correctly set, then
proceed as follows:
1 Disconnect the black low-tension cable from the
ignition coil and from the side of the distributor.
Connect a test lamp between the t w o terminals. Turn
the engine over slowly. If the lamp lights when the
contacts close and goes out when they open, the
low-tension circuit is in order. If the lamp fails to light
the contacts are dirty or there is a break or loose con-
nection in the low-tension wiring.
2 If the fault lies in the
low-tension circuit, switch on
the ignition and turn the crankshaft until the contact
breaker points are fully open. Refer to the wiring
diagram in Technical Data and check the circuit with
Page 42 of 128

a n 0—20 v o ltmeter. If the circuit is in order the meter
should read approximately 12-volts.
3 Battery to fuse box terminal 30. Connect the volt-
meter between the terminal 30 and earth. No reading
indicates a faulty cable or loose connection.
4 Fuse box. Connect the voltmeter between the other
auxiliary terminal 30 and earth. No reading indicates a
broken or loose connection.
5 Fuse box auxiliary terminal 30 to terminal
number 30 on ignition switch. Connect the meter
between terminal number 30 on the ignition switch
and earth. No reading indicates a damaged cable or
loose connection.
6 Ignition switch. Connect the meter between termi-
nal 15/54 and earth. Switch onto the ignition position,
when no reading indicates a fault in the switch.
7 Ignition switch to low-tension cable connection
on the coil (blue cable). Connect the meter
between ignition coil terminal (blue cable) and earth.
No reading indicates a damaged cable or loose con-
nection.
8 Ignition coil. Disconnect the black low-tension cable
connecting the coil to the distributor side terminal at
the coil and connect the meter between this terminal
and earth. No reading indicates a fault in the primary
winding of the coil and a replacement coil must be
fitted. If the reading is correct remake the connections
to the coil.
9 Ignition coil to distributor. Disconnect the thin
black low-tension cable at the side of the distributor
and connect the meter between the end of this cable
and earth. No reading indicates a damaged cable or
loose connections.
10 Contact breaker and capacitor. Connect the
meter across the contact breaker points. No reading
indicates a faulty capacitor.
Capacitor:
The best method of testing a capacitor (condenser) is
by substitution. Disconnect the original capacitor and
connect a new one between the low-tension terminal on
the side of the distributor and earth.
If a new capacitor is needed, fit a new one complete
w i t h bracket, but if necessary unsolder the original bracket
and solder it onto the new capacitor using as little heat as
possible. Capacitor capacity is .15-.20 microfarads.
3 : 5 Removing and dismantling distributor (sedan
and sports)
To remove the distributor proceed as follows:
1 Rotate the engine slowly until the distributor rotor arm
is opposite the brass segment in the distributor cap
connected to No. 1 plug lead. This will provide a datum
for replacement.
2 Disconnect the cable from the low-tension terminal on
the side of the distributor body. Mark position of distri-
butor on support. Release the distributor retaining nut
and washer from the underside of the top flange of the
distributor support and carefully lift away the dis-
tributor.
3 Pull off the rotor arm. Remove the insulated terminal
assembly from the side of distributor body. Release the
contact breaker carrier plate retaining screws and con-
denser flange screw from the outside of the distributor
F50049 body. Carefully lift out the contact breaker plate
assembly.
4 Before further dismantling note the relative positions of
the driving dog and the rotor arm driving slot at the top
of the distributor cam spindle. The driving dog is offset
and can only engage its driving spindle in one position.
Then when the cam assembly is fitted to the centrifugal
weights during reassembly the timing is not 180 deg.
out.
5 Take out the cam lubrication felt pad recessed in the
rotor arm housing on the end of the cam spindle.
Remove the retaining screw, carefully disengage the
springs and lift out the cam spindle. It should be noted
that there is a small retaining ball and spring located in a
drilling nearly at the top of the drive shaft spindle.
Carefully lift away the weights.
6 Thoroughly clean all parts and inspect for excessive
wear. The distributor cap must not be cracked or show
signs of tracking. The cap terminals, rotor and contact
breaker points can be cleaned with a very fine file.
Emerypaper must not be used. If the clearance between
the rotor and distributor cap segments exceeds .0118
inch both the rotor and distributor cap must be replaced.
Inspect the contact breaker arm rubbing block for exces-
sive wear and also the points for wear so that if the gap
exceeds the last setting limit of .0209 inch and adjust-
ment through the stationary contact carrier screw is no
longer possible (see FIG 3 : 2) , the contact breaker set
must be renewed.
If the distributor drive shaft side or vertical movement is
excessive the distributor must be renewed.
Weak centri-
fugal weight springs or damaged weights must be
renewed using original Fiat spares otherwise the auto-
matic ignition advance characteristics could be altered.
FIG 3 : 3 Ignition distributor in place on engine SPARK PLUG CABLES
IGNITION COIL CABLE!
DISTRIBUTOR CAP
DISTRIBUTOR BODY
GROUND CABLE
CONDENSER
DISTRIBUTOR SHAFT
LUBRICATION FITTING
DISTRIBUTORSUPPORT-TO--CRANKCASE NUT
[MOUNTING SCREWDISTRIBUTOR
DISTRIBUTOR SUPPORT