power FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1247 of 2057
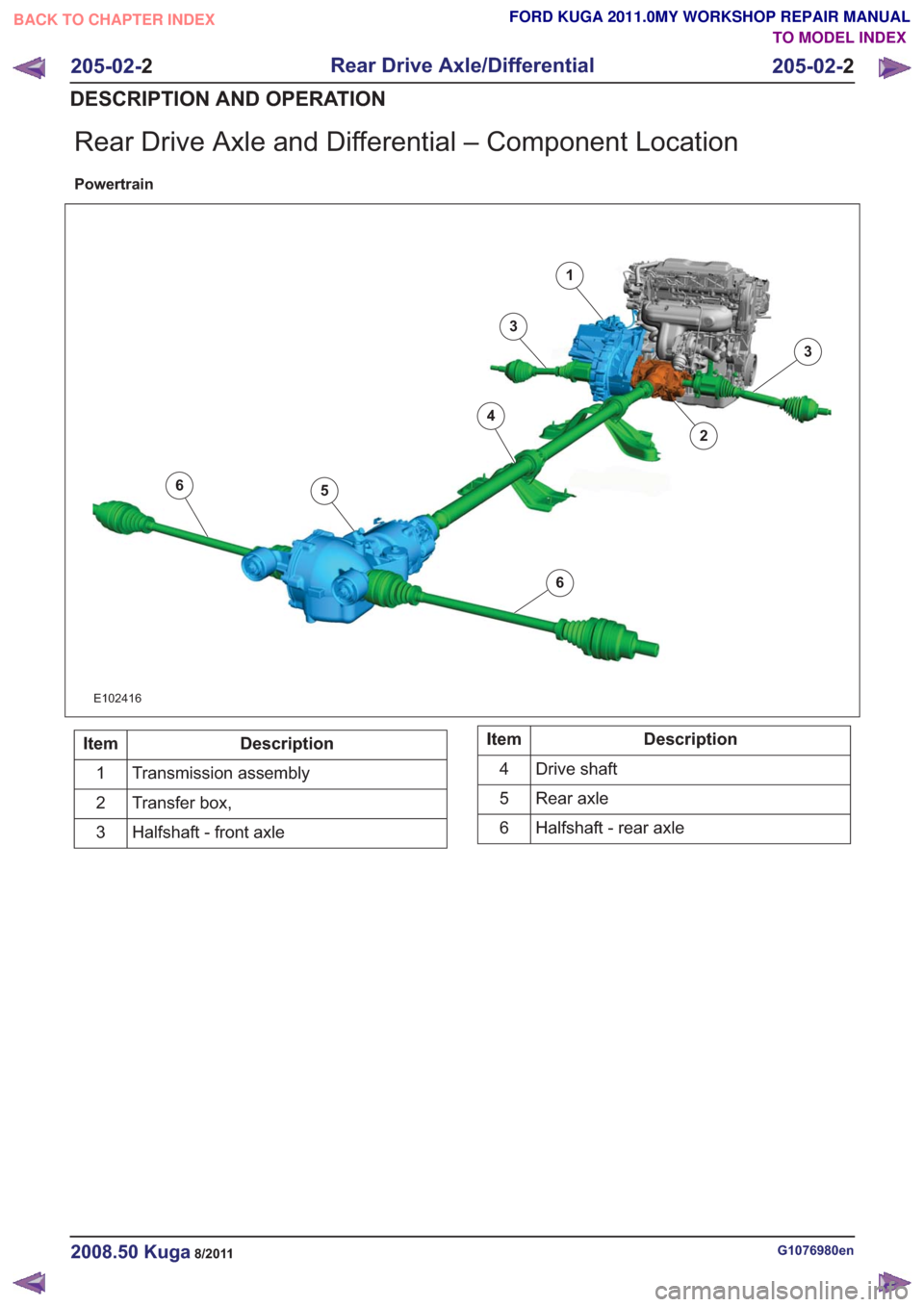
Rear Drive Axle and Differential – Component Location
Powertrain
6
6
1
2
3
3
4
5
6
6
E102416
Description
Item
Transmission assembly
1
Transfer box,
2
Halfshaft - front axle
3Description
Item
Drive shaft
4
Rear axle
5
Halfshaft - rear axle
6
G1076980en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
205-02- 2
Rear Drive Axle/Differential
205-02- 2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1251 of 2057

Rear Drive Axle and Differential – System Operation andComponent Description
System Operation
General Information
The powertrain with all-wheel drive consists of the
following main components:
• engine
• transaxle with front axle differential
• transfer box
• halfshafts and driveshafts
• Haldex clutch
• rear axle differential
The Haldex clutch guarantees continuous variable
torque transmission to the rear axle under all
driving conditions. The Haldex clutch reacts
immediately and equally quickly with slow or fast
wheel slip.
A difference in angle of rotation of 90° between the
input and output shafts is required to build up
maximum pressure at the multi-plate clutch or to
transmit maximum torque.
The advantage of vehicles with all-wheel drive is
that they distribute the drive between all four
wheels. They therefore have a higher tractive
power. They feature improved cornering behaviour,
as the grip at all four wheels can be better utilised.
Thus, the wheels contribute to a greater degree
towards cornering stability.
The engine torque is transmitted from the transfer
box to the rear axle via a driveshaft. The driveshaft
is flange-mounted to the input side of the Haldex
clutch.
Driving situations
Pulling away and accelerating
• When pulling away and accelerating, as muchall-wheel drive as necessary must be available
immediately in the short-term. During
acceleration, the electronic system detects slip
at the front axle. This slip is counter-controlled
and thus the propulsive force optimally
distributed to the two axes.
Cornering • A sporty driving style, in particular dynamic
cornering, demands stable cornering behaviour.
The all-wheel system distributes the propulsive
force to all four wheels and by so doing boosts
the high cornering forces so that the vehicle
makes optimum contact with the road surface.
Snow and black ice
• Snow and black ice require particularly high grip. Under these conditions, the Haldex clutch
always distributes the propulsive force to the
axle with the better traction. The all-wheel
system reacts intelligently and quickly to all
driving situations.
Trailer operation
• When driving with a trailer, the trailer weight (support load) is transmitted to the rear axle via
the towbar. This reduces the load on the front
wheels, which means they can slip. The
electronic system detects this difference and
distributes most of the propulsive force to the
rear axle.
Haldex clutch
E100642
G1076981en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
205-02- 6
Rear Drive Axle/Differential
205-02- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1350 of 2057

DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS
TEST CONDITIONS
D2: CHECK THE BRAKE BOOSTER FOR LEAKS
1 Run the engine at approximately 1000 rpm,
release the accelerator pedal and turn the
engine off. Wait 90 seconds and apply the
brakes. Two or more brake applications should
be power assisted.
• Does the brake booster work?
zYe s VERIFY the customer concern.
zNoGO to D4 .
D3: CHECK THE BRAKE PEDAL LINKAGE
1 Disconnect the actuator rod from the pedal pin
and fully depress the brake pedal.
• Did the pedal move freely?
zYe s VERIFY the customer concern.
zNoINSTALL new brake pedal bushings. TEST
the system for normal operation.
D4: CHECK THE BRAKE BOOSTER CHECK VALVE
1 Disconnect the brake booster check valve
vacuum hose at the manifold.
2Blow into the hose attached to the brake booster
check valve.
• Does air pass through the valve?
zYe s INSTALL a new brake booster check valve.
TEST the system for normal operation.
zNoGO to D5 .
D5: CHECK THE BRAKE BOOSTER CHECK VALVE VACUUM
1 Run the engine at idle.
G1058975en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-00-
14
Brake System - General Information
206-00- 14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1354 of 2057

4. Remove the vacuum hose from the brakebooster. Manifold vacuum should be available
at the brake booster end of the hose with the
engine at idle speed and the transaxle in the
NEUTRAL position. Make sure that all unused
vacuum outlets are correctly capped, hose
connectors are correctly secured and vacuum
hoses are in good condition. When it is
established that manifold vacuum is available
to the brake booster, connect the vacuum hose
to the brake booster and repeat Step 3. If no
downward movement of the brake pedal is felt,
install a new brake booster.
5. Operate the engine a minimum of 10 seconds at approximately 1200 rpm. Stop the engine and
let the vehicle stand for 10 minutes. Then, apply
the brake pedal with approximately 89 N (20 lb)
force. The pedal feel (brake application) should
be the same as that noted with the engine
operating. If the brake pedal feels hard (no
power assist), install a new vacuum check valve
and then repeat the test. If the brake pedal still
feels hard, install a new brake booster. If the
brake pedal movement feels spongy, bleed the
brake system. REFER to: (206-00 Brake System
- General Information)
Brake System Bleeding (General Procedures),
Brake System Pressure Bleeding (General
Procedures),
Component Bleeding (General Procedures).
Brake Master Cylinder
Usually, the first and strongest indicator of anything
wrong with the braking system is a feeling through
the brake pedal. In diagnosing the condition of the
brake master cylinder, check pedal feel as
evidence of a brake concern. Check for the red
brake warning indicator illumination and the fluid
level in the master cylinder reservoir.
Normal Conditions
The following conditions are considered normal
and are not indications that the brake master
cylinder is in need of service.
– Modern brake systems are not designed to
produce as hard a pedal effort as in the past.
Complaints of light pedal efforts should be compared to pedal efforts of another vehicle, of
the same model and year.
– During normal operation of the brake pedal, the fluid level in the reservoir will rise during brake
pedal application and fall during release. The
net fluid level (i.e., after brake pedal application
and release) will remain unchanged.
– A trace of brake fluid will exists on the brake booster shell below the master cylinder
mounting flange. This results from the normal
lubricating action of the master cylinder bore
end seal.
– The fluid level will fall with brake shoe and lining wear.
Abnormal Conditions
NOTE: Prior to performing any diagnosis, make
sure the brake system warning indicator is
functional.
Changes in brake pedal feel or travel are indicators
that something could be wrong with the braking
system. The diagnostic procedure and techniques
use brake pedal feel, warning indicator illumination
and low brake fluid level as indicators in diagnosing
braking system concerns. The following conditions
are considered abnormal and indicate that the
brake master cylinder is in need of service.
– The brake pedal goes down fast. This could be caused by an external or internal leak.
– The brake pedal eases down slowly. This could be caused by an external or internal leak.
– The brake pedal is low and or feels spongy. This condition may be caused by no fluid in the brake
master cylinder reservoir, reservoir cap vent
holes clogged or air in the hydraulic system.
– The brake pedal effort is excessive. This may be caused by a bind or obstruction in the pedal
or linkage, clogged fluid control valve or
insufficient booster vacuum.
– The rear brakes lock up during light pedal force. This may be caused by incorrect tire pressures,
grease or fluid on the brake shoes and linings,
damaged brake shoes and linings, incorrectly
adjusted parking brake, or damaged or
contaminated brake pressure control valves.
– The brake pedal effort is erratic. This condition could be caused by a brake booster malfunction,
extreme caliper piston knock back or incorrectly
installed brake shoes and linings.
– The red brake warning indicator is ON. This may be caused by low fluid level, ignition wire routing
G1058975en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-00- 18
Brake System - General Information
206-00- 18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1405 of 2057

SECTION 206-07 Power Brake Actuation
VEHICLE APPLICATION:2008.50 Kuga
PA G E
CONTENTS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
206-07-2
(12 451 0)
Brake Booster — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5, RHD 4WD/RHD FWD .
206-07-7
Brake Vacuum Hose — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 ..............................................
206-07-9
(12 414 0)
Brake Vacuum Pump — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 ........................
206-07-1
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 1
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1406 of 2057

Brake Booster — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5, RHD4WD/RHD FWD(12 451 0)
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Brake System Health and Safety
Precautions (100-00 General Information,
Description and Operation).
2. Torque: 24
Nm
E69829
x4
1
2
3.Refer to: Air Conditioning (A/C) System
Recovery, Evacuation and Charging (412-00
Climate Control System - General Information,
General Procedures).
Refer to: Brake Master Cylinder - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5 (206-06 Hydraulic Brake
Actuation, Removal and Installation).
Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
4.
E65299
5. Torque:
• Stage 1: 10
Nm
• Stage 2: 25Nm
E99866
x6
6.
G1185955en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 2
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 2
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1407 of 2057
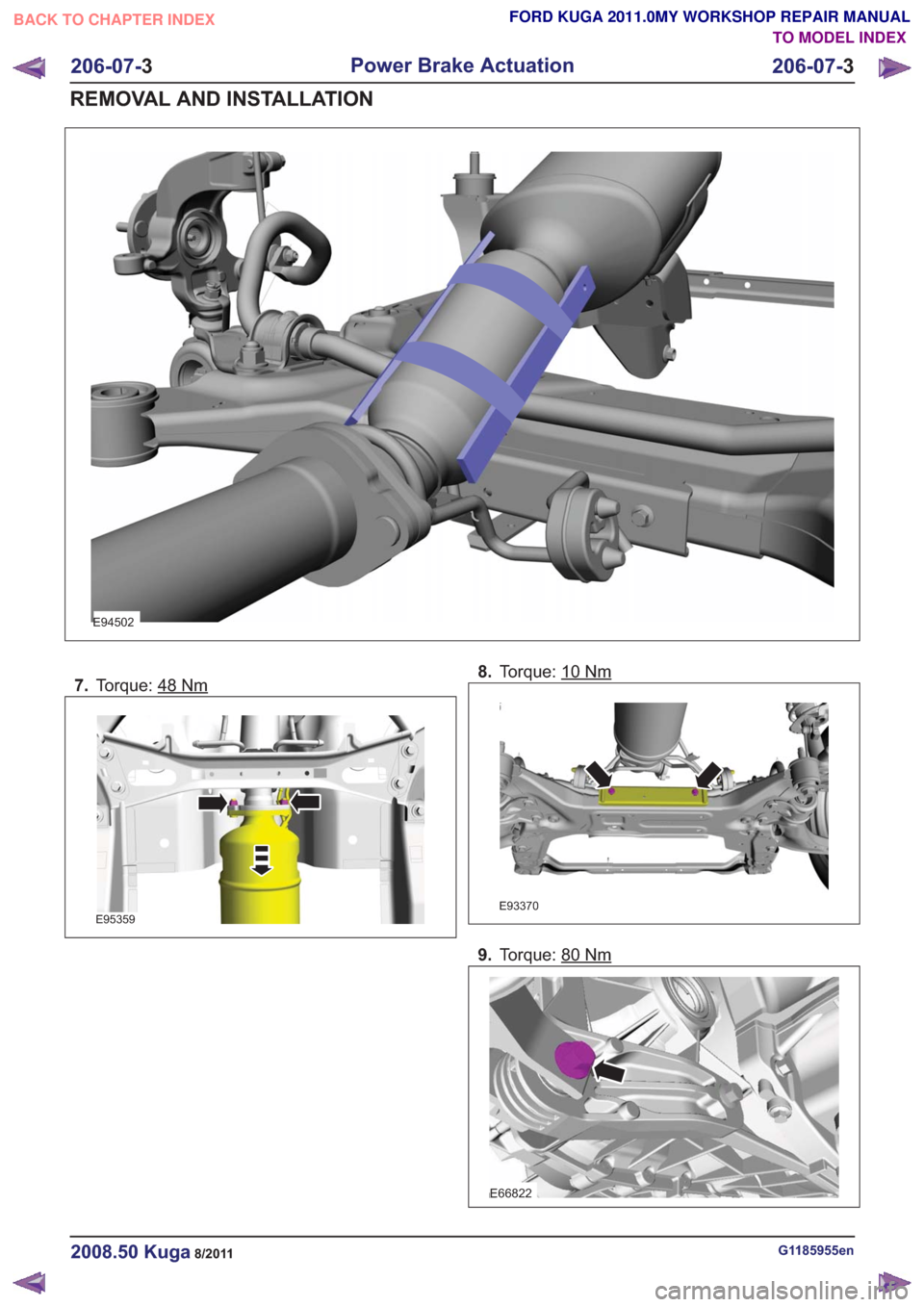
E94502
7.Torque: 48Nm
E95359
8.Torque: 10Nm
E93370
9.Torque: 80Nm
E66822
G1185955en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 3
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 3
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1408 of 2057

10.Torque: 35Nm1. Torque: 10Nm2.
E99862
11
2
11 .Torque: 80Nm
G1185955en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 4
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1409 of 2057
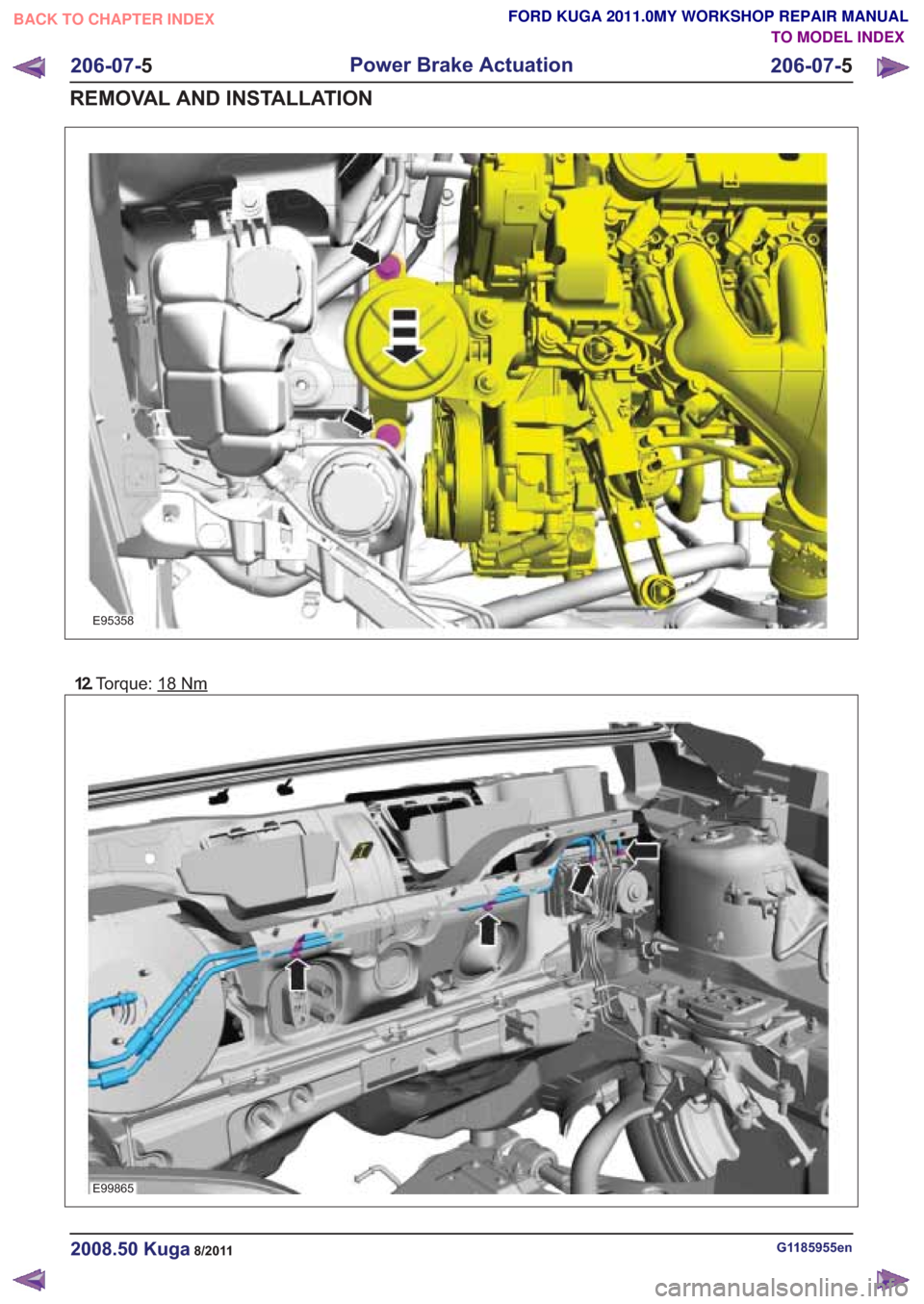
12.Torque: 18Nm
G1185955en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 5
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 5
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
E95358
E99865
Page 1410 of 2057
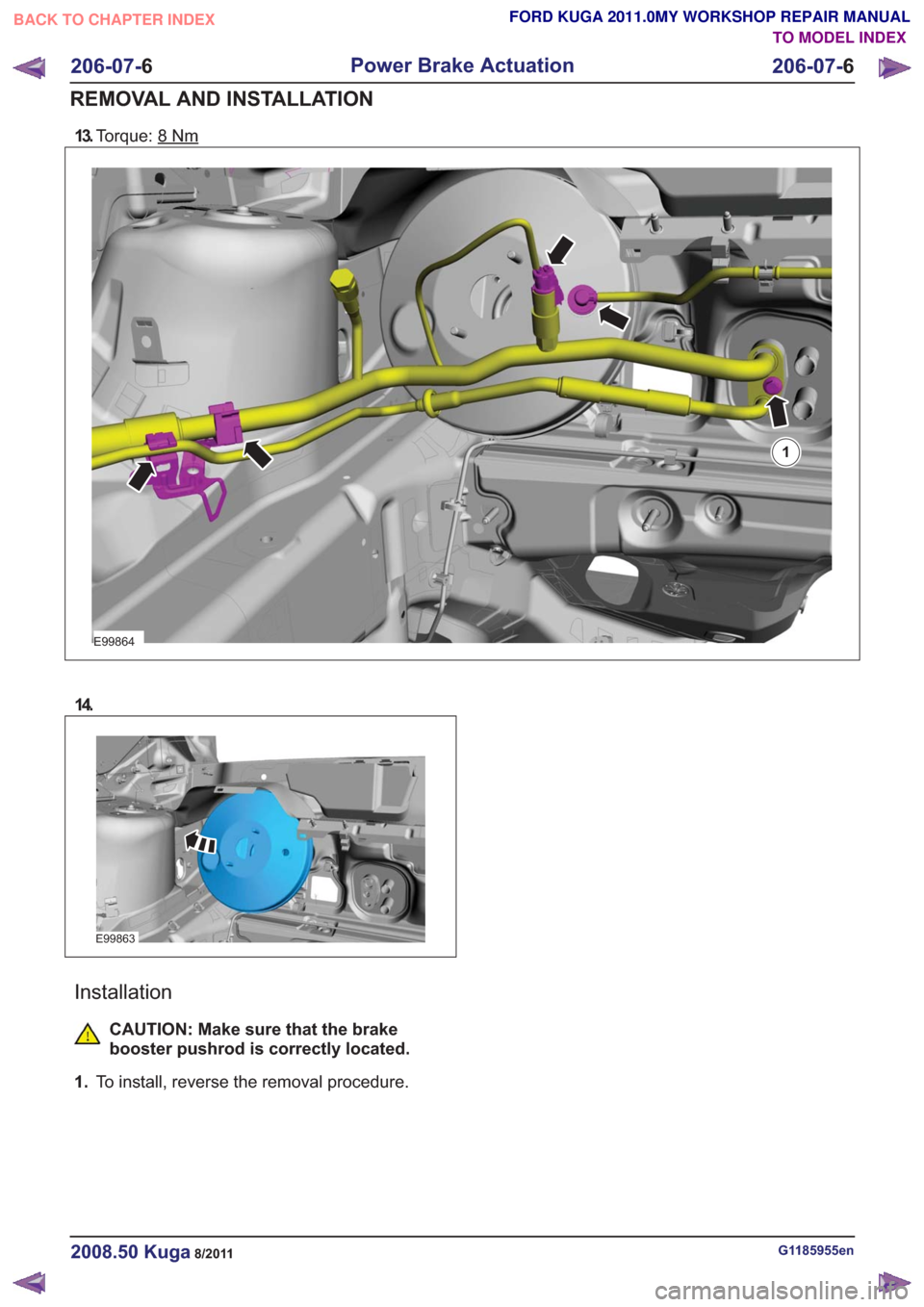
13.Torque: 8Nm
E99864
1
14.
E99863
Installation
CAUTION: Make sure that the brake
booster pushrod is correctly located.
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G1185955en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 6
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 6
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL