power FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1411 of 2057
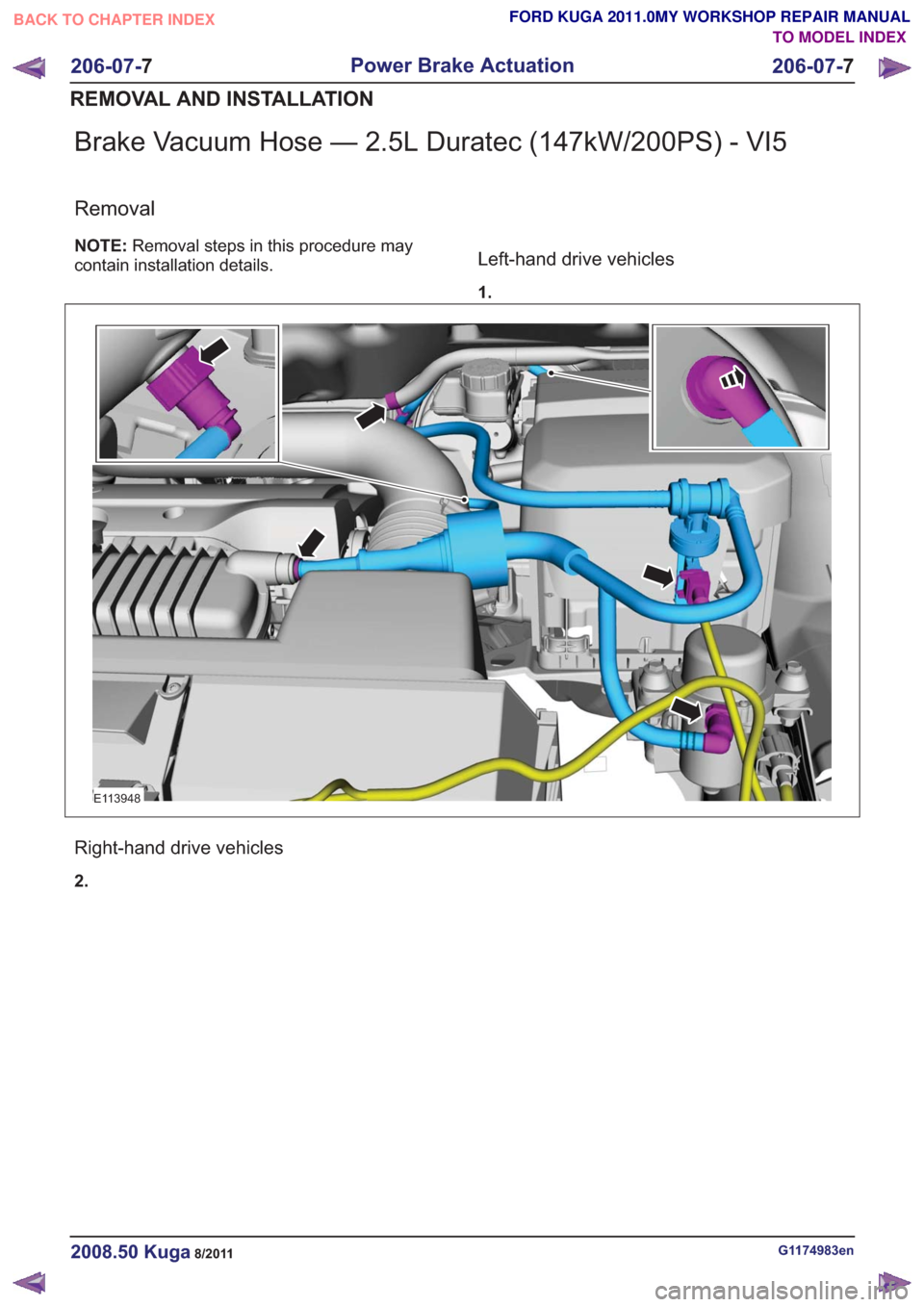
Brake Vacuum Hose — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
Removal
NOTE:Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.Left-hand drive vehicles
1.
E113948
Right-hand drive vehicles
2.
G1174983en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 7
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1412 of 2057
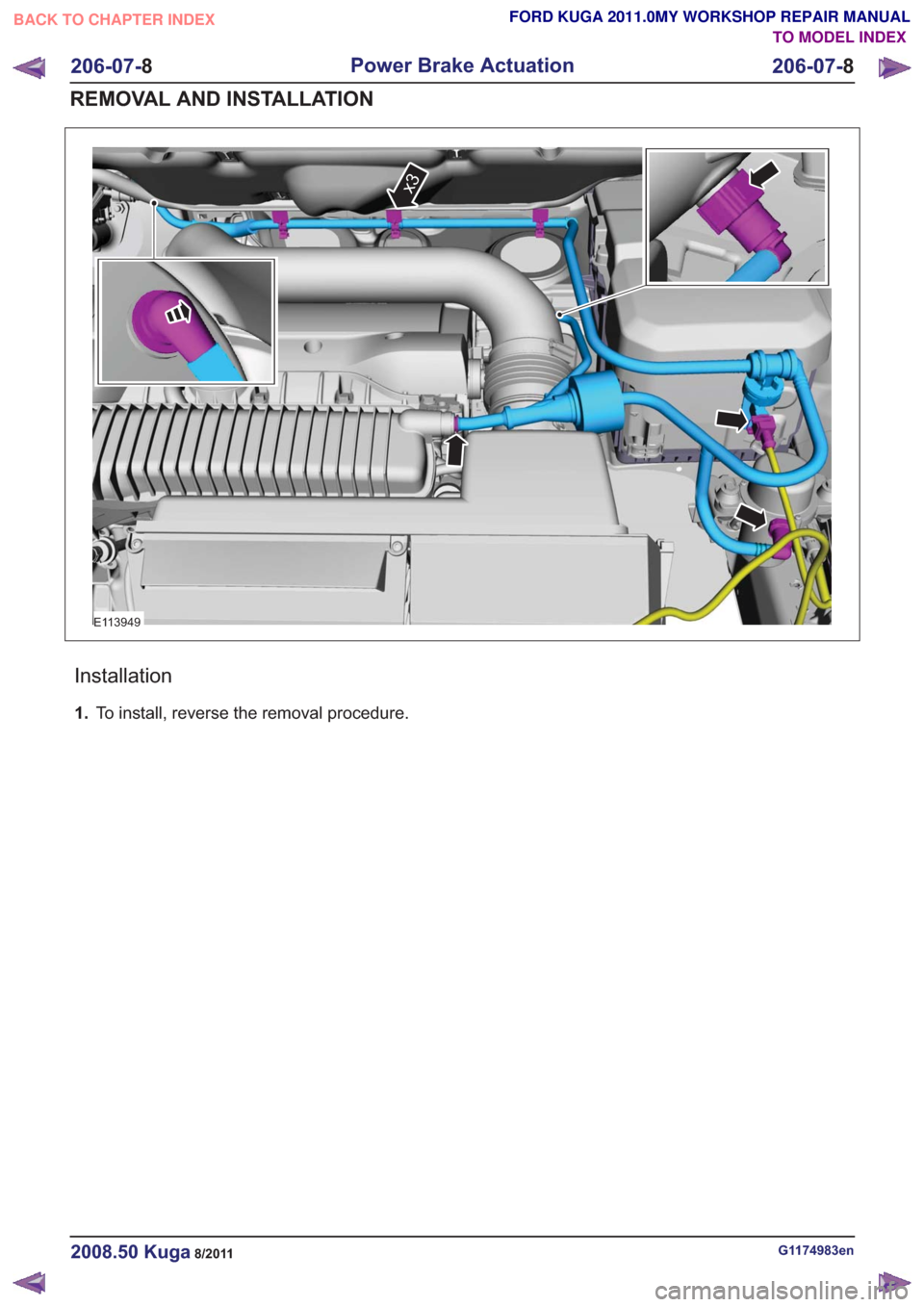
E113949
x3
Installation
1.To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G1174983en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 8
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 8
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1413 of 2057
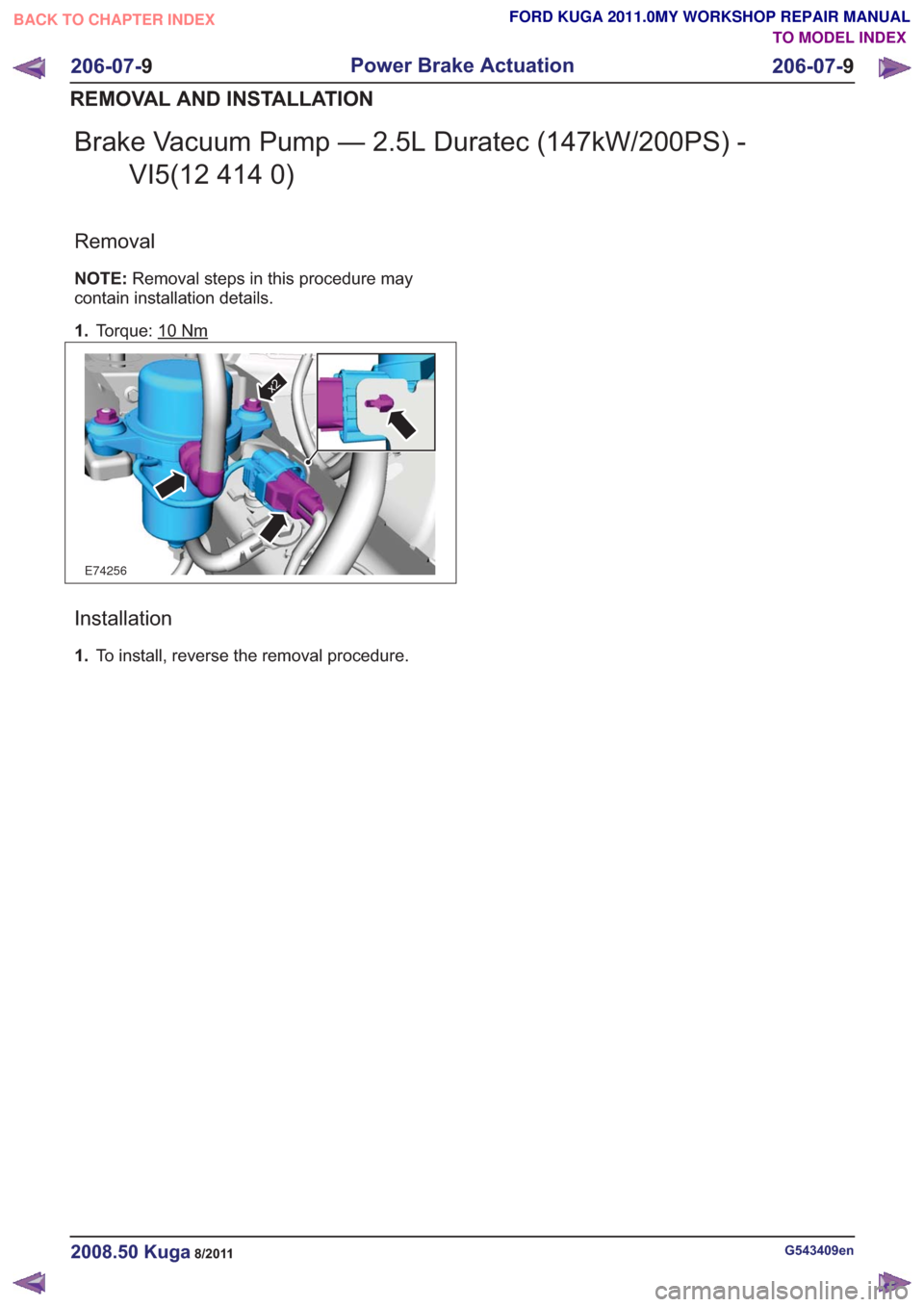
Brake Vacuum Pump — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) -VI5(12 414 0)
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Torque: 10
Nm
E74256
x2
Installation
1.To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G543409en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-07- 9
Power Brake Actuation
206-07- 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1428 of 2057

Description
Item
Battery
1
Battery junction box (BJB) in the engine
compartment
2
Generic electronic module (GEM)
3
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
4
Instrument cluster
5
Data link connector (DLC)
6
Steering Wheel Rotation Sensor
7
ABS/ESP module or hydraulic control unit
(HCU)
8Description
Item
Combined yaw rate sensor and lateral
acceleration sensor / longitudinal
acceleration sensor
9
Front wheel sensor
10
Rear wheel sensor
11
Rear wheel sensor
12
Front wheel sensor
13
ESP switch
14
Rear brakes
15
Front brake
16
The ABS monitors the different wheel speeds of
the vehicle with the aid of wheel speed sensors.
Using the data from all of the wheel speed sensors,
the ABS module calculates the so-called reference
speed, which is a measure of the actual road
speed. The ABS module compares the individual
circumferential wheel speeds with this reference
speed when the driver initiates braking. If one or
more of the circumferential wheel speeds deviates
too far from the reference speed, this means that
slip at the affected wheels is so great that steering
stability of the vehicle is no longer ensured. The
ABS module actuates electro-mechanical valves
which influence the brake pressure at the relevant
wheels.
Like the traction control system (TCS), the ESP
system uses a large proportion of the ABS
components. In addition, there are sensors which
pick up the steering angle, the acceleration forces
acting on the vehicle and the yaw rate or yaw
moment. The sensors transmit these signals to the
combined ABS/ESP module. Using the wheel
speed and steering angle data, the ABS/ESP
module calculates the direction of travel planned
by the driver and determines the corresponding
speed-dependent lateral acceleration and yaw
moment. These values are compared with those
actual measured. If the actual lateral acceleration
and the yaw moment deviate excessively from the
target values (unstable driving characteristics), the
ABS/ESP module actuates individual brakes
selectively via the HCU (hydraulic control unit). In
addition, the engine speed is reduced by
intervention in the engine management system.
How the system works for understeer: In the
event of understeer, brake intervention occurs at
the wheels on the inside of the curve. The rear
wheel is braked heavily, so that a high amount of slip is caused. In this way, the cornering force of
the rear axle is heavily reduced and the centrifugal
force that now becomes effective turns the rear of
the vehicle back into the curve. The front wheel is
not braked as hard. The braking force that is
transmitted via the front wheel to the road surface
generates a torque with the aid of the lever arm
(vertical tire force to the vehicle's centre of gravity),
which supports the yaw moment of the vehicle.
Both measures together result in the vehicle
reverting back to the curved path intended by the
driver.
How the system works for oversteer:
In the
event of oversteer the wheels on the outside of the
curve are braked. This time, the front wheel is
subjected to a high level of slip so that the
cornering force at the front axle is reduced. The
rear wheel is not braked as heavily and, together
with the effective lever arm, results in a reduction
in the vehicle yaw moment. Both measures
together result in the vehicle being stabilized and
reverting back to the curved path intended by the
driver.
If ESP control occurs, possible ABS interventions
will be overridden as the ESP works at higher slip
rates than the ABS.
Emergency brake assist (EBA): The emergency
brake assist helps drivers in emergency braking
situations by automatically applying the brakes with
the maximum possible braking force.
If the brake pedal is pressed very suddenly, the
ABS module increases the hydraulic pressure to
all of the brakes until the threshold for ABS
intervention is reached. This applies the maximum
braking effort for the available traction. The ABS
control unit monitors inputs from the brake pedal
switch and from the pressure sensor within the
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 10
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1432 of 2057

E53340
1
2
3
Description
Item
Tuning fork exciter
1
Suspension
2
Measuring side
3
Due to the special way in which it works. the
combined yaw rate sensor and lateral acceleration
sensor/longitudinal acceleration sensor must be
installed the right way up in the designated location
specified by the manufacturer. Any slight deviation
in the installation position and/or installation
location could lead to impaired functionality and
thereby possible failure of the stability assist.
Front wheel sensor
E96823
Active sensors are used to determine the rotational
speeds of the wheels at the hub. After the ignition
is switched on, the ABS module supplies the
sensors with power. The sensors work in
accordance with the Hall effect principle and
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 14
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 14
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1433 of 2057
generate a square wave output signal. The signal
acts in proportion to the rotational speed of the
sensor ring. The ABS sensor rings are built into
the seals in the front wheel bearings. The ABS
module evaluates the signals from all four sensors
to calculate a vehicle speed signal based on the
rotational speeds of all wheels. The road speed is
transmitted on the CAN bus. The powertrain controlmodule (PCM) uses this signal and the
programmed tire size to calculate the vehicle
speed. The calculated vehicle speed is forwarded
on the CAN bus and is requested by other control
units that need this input information.
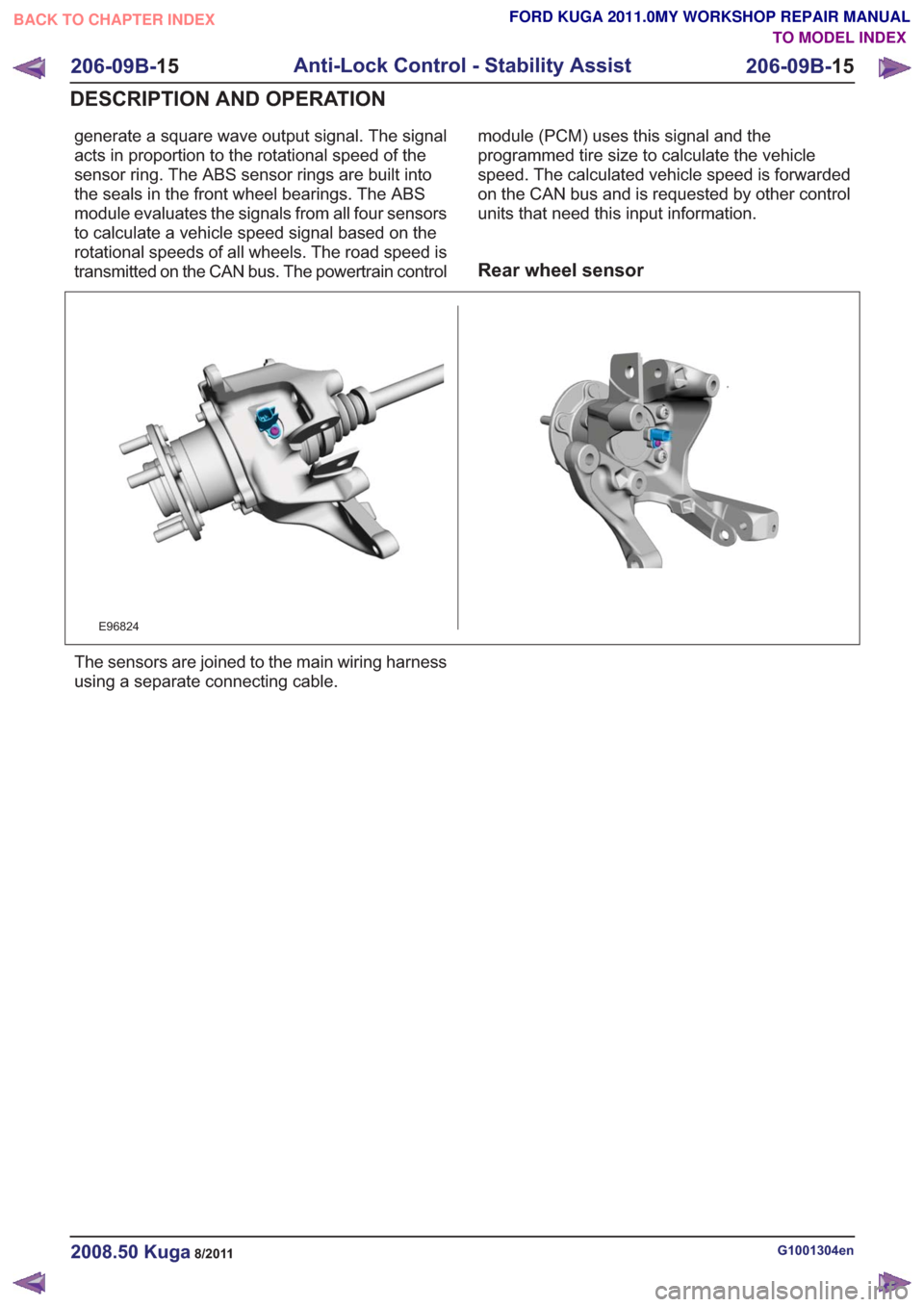
Rear wheel sensor
E96824
The sensors are joined to the main wiring harness
using a separate connecting cable.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-
15
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1442 of 2057

SECTION 211-00 Steering System - General
Information
VEHICLE APPLICATION:2008.50 Kuga
PA G E
CONTENTS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
211-00-2
Steering System ........................................................................\
.........................................
211-00-2
Inspection and Verification ........................................................................\
..........................
211-00-2
Components Tests ........................................................................\
......................................
211-00-6
Steering Gear Checks After a Collision ........................................................................\
......
GENERAL PROCEDURES 211-00-8
Power Steering System Flushing ........................................................................\
...............
211-00-9
Power Steering System Filling ........................................................................\
....................
211-00-10
Power Steering System Vacuum Bleeding ........................................................................\
.
211-00-1
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 1
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1443 of 2057

Steering System
Special Tool(s) / General EquipmentAlignment Pins, Subframe
205-316 (15-097A)
15097
Simulator, Driver and
Passenger Air Bags and Side
Air Curtains
501-073 (40-016)
501073
The Ford approved diagnostic tool
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanicalor electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart
Electrical
Mechanical
• Battery
• Battery cables
• Steering anglesensor electrical
connector
• Power steering pump control
module electrical
connectors
• Power steering pump control
module ground
cable
• Power steering pump control
module ground
cable retaining
screw
• Steering angle sensor warning
indicator
• Fuse(s)
• Tire pressure(s)
• Loose tie-rod end(s)
• Loose strut and
spring assemblies or
ball joints
• Loose pinch bolts on steering column
shaft flexible coup-
ling
• Wheels and tires
• Power steering line fluid leaks
• Steering gear bellows 3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported
concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the diagnostic tab within
the Ford approved diagnostic tool.
Components Tests
Steering Linkage
1. Grasp the steering wheel firmly and move it upand down and to the left and right without
turning the steering wheel to check the steering
column bearing for wear, steering column shaft
for wear, steering wheel for looseness and
steering column for looseness. If the steering
column bearing or the steering column shaft is
worn install a new steering column. If the
steering wheel or the steering column is loose,
tighten the steering wheel or the steering column
retaining bolts.
2. With the road wheels in the straight ahead position, gently turn the steering wheel to the
left and the right to check for free play in the
steering linkage.
3. There should be no excessive free play at the steering wheel rim. If there is excessive free
play, CHECK the tie-rod inner and outer ball
joints, REFER to Tie-Rod Component Test in
this procedure. CHECK the steering column
universal joint, REFER to Steering Column
Universal Joint Component Test in this
procedure. If there is no free play in the tie-rod
and the steering column, install a new steering
gear.
Tie-Rod
CAUTION: Steering gear boots must be
handled carefully to avoid damage. Use
new steering boot clamps when installing
the steering gear boots.
NOTE: Noises such as knocks, which may appear
to originate from the steering linkage, may also be
generated by front suspension components.
REFER to: Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH)
(100-04 Noise, Vibration and Harshness,
Diagnosis and Testing).
G1059437en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 2
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1445 of 2057

firmly grasp the road wheel and apply a rocking
motion checking for any free play in the steering
linkage.
E56375
10. Detach the steering gear boot from the steeringgear body and check for free play at the tie-rod
inner ball joint.
11. If there is free play at the tie-rod inner ball joint, install a new tie-rod.
REFER to: Tie Rod(211-03 Steering Linkage,
Removal and Installation).
12. Check the tie-rod end for free play. Install a new tie-rod end if necessary.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
Turning Effort Test
NOTE: Before carrying out this test, make sure
that the suspension components are serviceable.
NOTE: Before carrying out this test, make sure
that the steering column is serviceable.
NOTE: Before carrying out this test, make sure
that the toe adjustment and tire pressures are
correct.
1. Park the vehicle on a dry, even surface and apply the parking brake.
2. Remove the driver air bag module.
REFER to: Driver Air Bag Module (501-20
Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and
Installation).
3. Connect the air bag simulators to the sub-harnesses in place of the driver air bag
module at the top of the steering column.
4. Start the engine and turn the steering wheel from lock to lock several times until the power
steering fluid has reached normal operating
temperature. 5. Using a suitable torque wrench and socket,
check the steering wheel turning effort.
6. If the steering wheel turning effort is greater than the specification, install a new steering gear.
Steering Column Universal Joint
1.WARNING: Install a new steering column
to steering gear pinion retaining bolt. Failure
to follow this instruction may result in
personal injury.
Detach the steering column from the steering
gear pinion.• Discard the steering column to steering gear pinion retaining bolt.
TIE45919
1
2
2
2. Check for smooth movement of the steeringcolumn universal joint.
1. Hold the steering column universal joint yoke.
2. Articulate the free yoke in a figure of eight movement.
• If the movement is not smooth or resistance is felt, install a new steering column.
REFER to: Steering Column (211-04 Steering
Column, Removal and Installation).
TIE45918
3. Hold both of the steering column universal joint yokes and twist them clockwise and
counterclockwise.
G1059437en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 4
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1447 of 2057

Steering Gear Checks After a Collision
General EquipmentFeeler gauge
Straight edge
Items to be observed when checking the steering
system
The following list of steering gear conditions and
the methods of testing should be taken into account
when carrying out checks to the steering system:
• If the steering gear has no faults after completing the following checks, do not install
a new steering gear.
• Surface corrosion and marks on the tie-rod are acceptable.
• When checking for turning effort torque peaks in the steering gear, turn the steering wheel from
steering lock stop to steering lock stop in
approximately 15 seconds.
• A steady increase of turning effort torque from steering center to steering lock stop is
acceptable.
• When checking for power steering fluid leaks, turn the steering wheel to the steering lock stop
in approximately 10 seconds.
• Noises from the power steering, for example the power steering pump relief valve, are
acceptable.
STEERING GEAR HOUSING
1. Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
2. Visually inspect the steering gear housing for cracks and damage. If the steering gear housing
is cracked or damaged, install a new steering
gear.
REFER to: Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
TIE-RODS
1. Using a straight edge and feeler gauge, check the tie-rods to see if they are straight. If the
distance between the tie-rod and straight edge is greater than 0.5 mm, install a new steering
gear.
REFER to:
Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
2. Check the tightening torque of the tie-rod end to wheel knuckle nut.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
3. Check the tightening torque of the tie-rod end locking nut.
REFER to: Tie Rod End (211-03 Steering
Linkage, Removal and Installation).
CHECK FOR TURNING EFFORT TORQUE
PEAKS IN THE STEERING GEAR
1. Lower and support the vehicle making sure that the road wheels are just clear of the floor.
2. With the ignition switch in position I, slowly turn the steering wheel from steering lock stop to
steering lock stop. If a turning effort torque peak
or judder is felt while turning the steering wheel,
detach the tie-rods from the wheel knuckles.
3. Slowly turn the steering wheel from steering lock stop to steering lock stop. If a turning effort
torque peak or judder is felt while turning the
steering wheel, install a new steering gear.
REFER to: Steering Gear (211-02 Power
Steering, Removal and Installation).
CHECK FOR POWER STEERING FLUID LEAKS
1. Lower the vehicle.
2. Run the engine at a fast idle and slowly turn the steering wheel to the left-hand steering lock
stop. Hold the steering wheel in this position for
5 seconds with a turning effort torque of 15 Nm
at the steering wheel rim.
3. Turn the steering wheel away from the left-hand steering lock stop for 30 seconds.
4. Run the engine at a fast idle and slowly turn the steering wheel to the right-hand steering lock
stop. Hold the steering wheel in this position for
5 seconds with a turning effort torque of 15 Nm
at the steering wheel rim.
5. Turn the steering wheel away from the right-hand steering lock stop.
6. Check for power steering fluid leaks at the steering gear housing and the power steering
line connections to the steering gear. If there is
G538091en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
211-00- 6
Steering System - General Information
211-00- 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL