service FORD MUSTANG 1969 Volume One Chassis
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1969, Model line: MUSTANG, Model: FORD MUSTANG 1969Pages: 413, PDF Size: 75.81 MB
Page 233 of 413
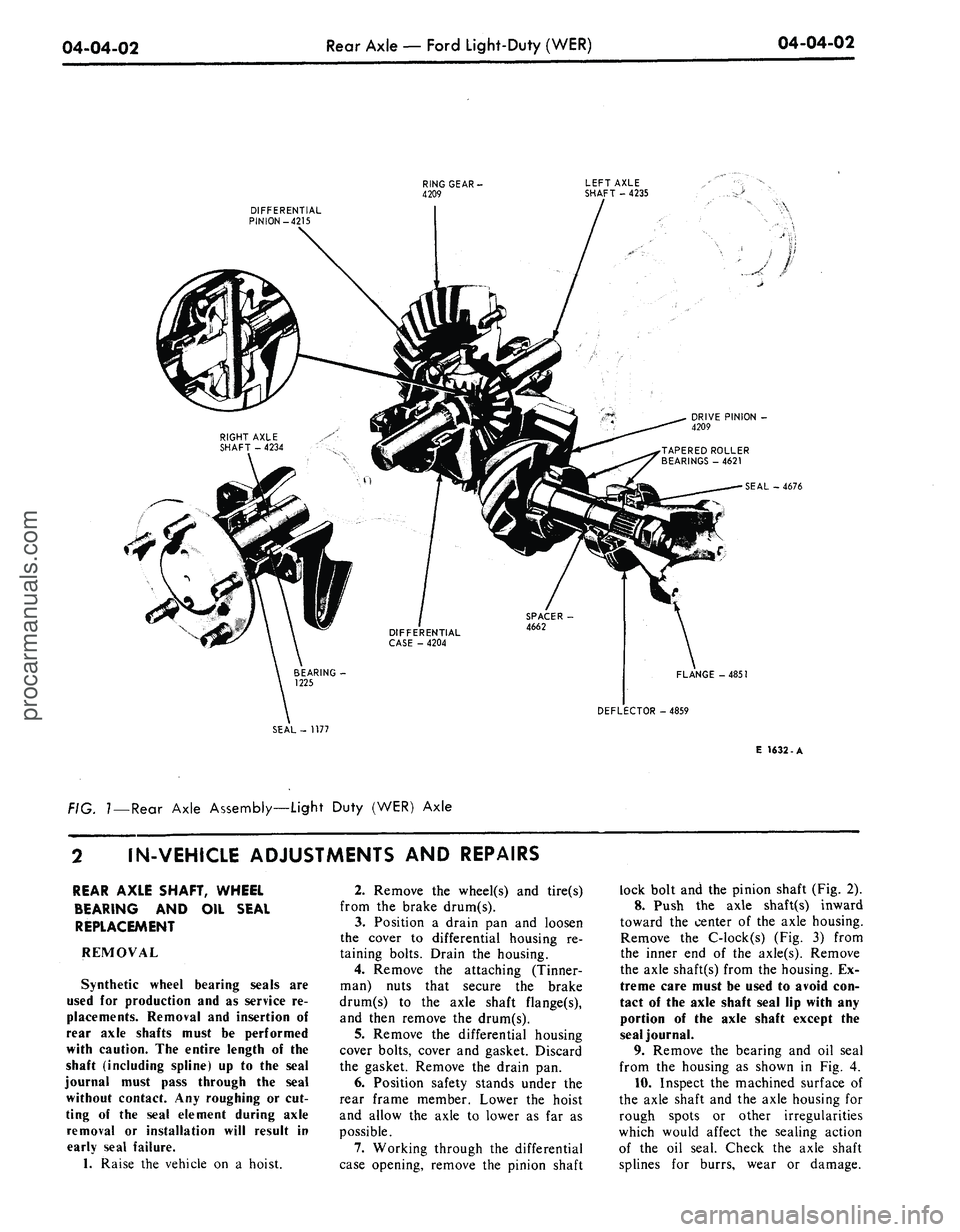
04-04-02
Rear Axle
—
Ford Light-Duty (WER)
04-04-02
DIFFERENTIAL
PINION-4215
RING GEAR
-
4209
LEFT AXLE
SHAFT
-
4235
1
DRIVE PINION
-
4209
SEAL
-
4676
FLANGE-4851
DEFLECTOR -4859
SEAL-
1177
f\G.
7
—Rear Axle Assembly—Light Duty
(WER)
Axle
E 1632-A
IN-VEHICLE ADJUSTMENTS AND REPAIRS
REAR AXLE SHAFT, WHEEL
BEARING
AND OIL
SEAL
REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
Synthetic wheel bearing seals
are
used
for
production
and as
service
re-
placements. Removal
and
insertion
of
rear axle shafts must
be
performed
with caution.
The
entire length
of the
shaft (including spline)
up to the
seal
journal must pass through
the
seal
without contact.
Any
roughing
or cut-
ting
of the
seal element during axle
removal
or
installation will result
in
early seal failure.
1.
Raise
the
vehicle
on a
hoist.
2.
Remove
the
wheel(s)
and
tire(s)
from
the
brake drum(s).
3.
Position
a
drain
pan and
loosen
the cover
to
differential housing
re-
taining bolts. Drain
the
housing.
4.
Remove
the
attaching (Tinner-
man) nuts that secure
the
brake
drum(s)
to the
axle shaft flange(s),
and then remove
the
drum(s).
5.
Remove
the
differential housing
cover bolts, cover
and
gasket. Discard
the gasket. Remove
the
drain
pan.
6. Position safety stands under
the
rear frame member. Lower
the
hoist
and allow
the
axle
to
lower
as far as
possible.
7.
Working through
the
differential
case opening, remove
the
pinion shaft
lock bolt
and the
pinion shaft
(Fig. 2).
8. Push
the
axle shaft(s) inward
toward
the
center
of the
axle housing.
Remove
the
C-lock(s)
(Fig. 3)
from
the inner
end of the
axle(s). Remove
the axle shaft(s) from
the
housing.
Ex-
treme care must
be
used
to
avoid
con-
tact
of the
axle shaft seal
lip
with
any
portion
of the
axle shaft except
the
seal journal.
9. Remove
the
bearing
and oil
seal
from
the
housing
as
shown
in Fig. 4.
10.
Inspect
the
machined surface
of
the axle shaft
and the
axle housing
for
rough spots
or
other irregularities
which would affect
the
sealing action
of
the oil
seal. Check
the
axle shaft
splines
for
burrs, wear
or
damage.procarmanuals.com
Page 238 of 413
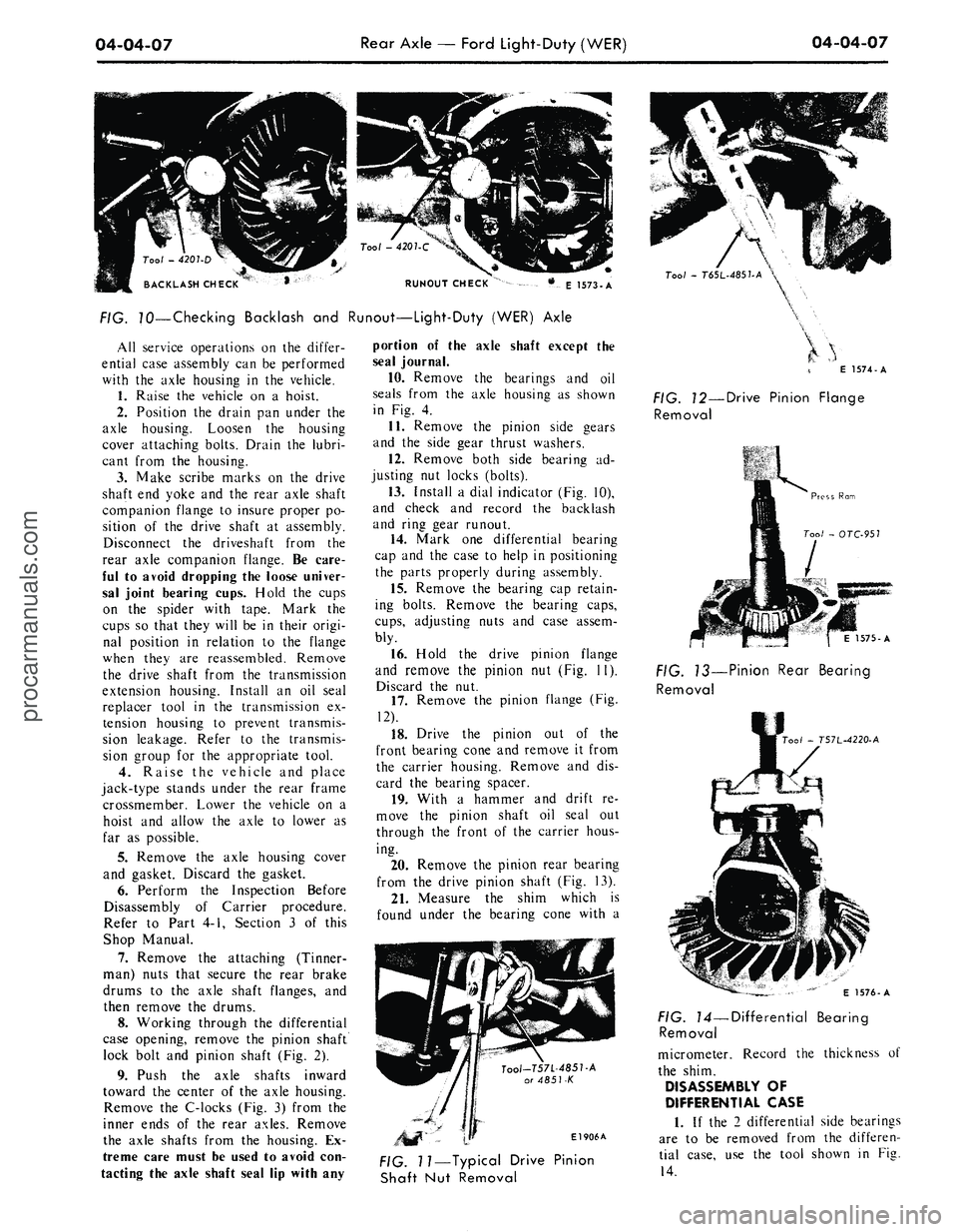
04-04-07
Rear Axle — Ford Light-Duty (WER)
04-04-07
RUNOUT CHECK
E 1573-A
FIG. 70—Checking Backlash and Runout—Light-Duty (WER) Axle
All service operations on the differ-
ential case assembly can be performed
with the axle housing in the vehicle.
1.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
2.
Position the drain pan under the
axle housing. Loosen the housing
cover attaching bolts. Drain the lubri-
cant from the housing.
3.
Make scribe marks on the drive
shaft end yoke and the rear axle shaft
companion flange to insure proper po-
sition of the drive shaft at assembly.
Disconnect the driveshaft from the
rear axle companion flange. Be care-
ful to avoid dropping the loose univer-
sal joint bearing cups. Hold the cups
on the spider with tape. Mark the
cups so that they will be in their origi-
nal position in relation to the flange
when they are reassembled. Remove
the drive shaft from the transmission
extension housing. Install an oil seal
replacer tool in the transmission ex-
tension housing to prevent transmis-
sion leakage. Refer to the transmis-
sion group for the appropriate tool.
4.
Raise the vehicle and place
jack-type stands under the rear frame
crossmember. Lower the vehicle on a
hoist and allow the axle to lower as
far as possible.
5.
Remove the axle housing cover
and gasket. Discard the gasket.
6. Perform the Inspection Before
Disassembly of Carrier procedure.
Refer to Part 4-1, Section 3 of this
Shop Manual.
7.
Remove the attaching (Tinner-
man) nuts that secure the rear brake
drums to the axle shaft flanges, and
then remove the drums.
8. Working through the differential
case opening, remove the pinion shaft
lock bolt and pinion shaft (Fig. 2).
9. Push the axle shafts inward
toward the center of the axle housing.
Remove the C-locks (Fig. 3) from the
inner ends of the rear axles. Remove
the axle shafts from the housing. Ex-
treme care must be used to avoid con-
tacting the axle shaft seal lip with any
portion of the axle shaft except the
seal journal.
10.
Remove the bearings and oil
seals from the axle housing as shown
in Fig. 4.
11.
Remove the pinion side gears
and the side gear thrust washers.
12.
Remove both side bearing ad-
justing nut locks (bolts).
13.
Install a dial indicator (Fig. 10),
and check and record the backlash
and ring gear runout.
14.
Mark one differential bearing
cap and the case to help in positioning
the parts properly during assembly.
15.
Remove the bearing cap retain-
ing bolts. Remove the bearing caps,
cups,
adjusting nuts and case assem-
bly.
16.
Hold the drive pinion flange
and remove the pinion nut (Fig. 11).
Discard the nut.
17.
Remove the pinion flange (Fig.
12).
18.
Drive the pinion out of the
front bearing cone and remove it from
the carrier housing. Remove and dis-
card the bearing spacer.
19.
With a hammer and drift re-
move the pinion shaft oil seal out
through the front of the carrier hous-
ing.
20.
Remove the pinion rear bearing
from the drive pinion shaft (Fig. 13).
21.
Measure the shim which is
found under the bearing cone with a
Tool-T57L-485T-A
or 4851-K
El 906A
Tool
-
T6SL-485UA
\
E 1574-A
FIG. 12—Drive Pinion Flange
Removal
1575-A
FIG. 13—Pinion Rear Bearing
Removal
00/
- T57L-4220-A
FIG. 11—Typical Drive Pinion
Shaft Nut Removal
E 1576-A
FIG. 14—Differential Bearing
Removal
micrometer. Record the thickness of
the shim.
DISASSEMBLY OF
DIFFERENTIAL CASE
1.
If the 2 differential side bearings
are to be removed from the differen-
tial case, use the tool shown in Fig.
14.procarmanuals.com
Page 244 of 413
04-05-03
Specifications
04-05-03
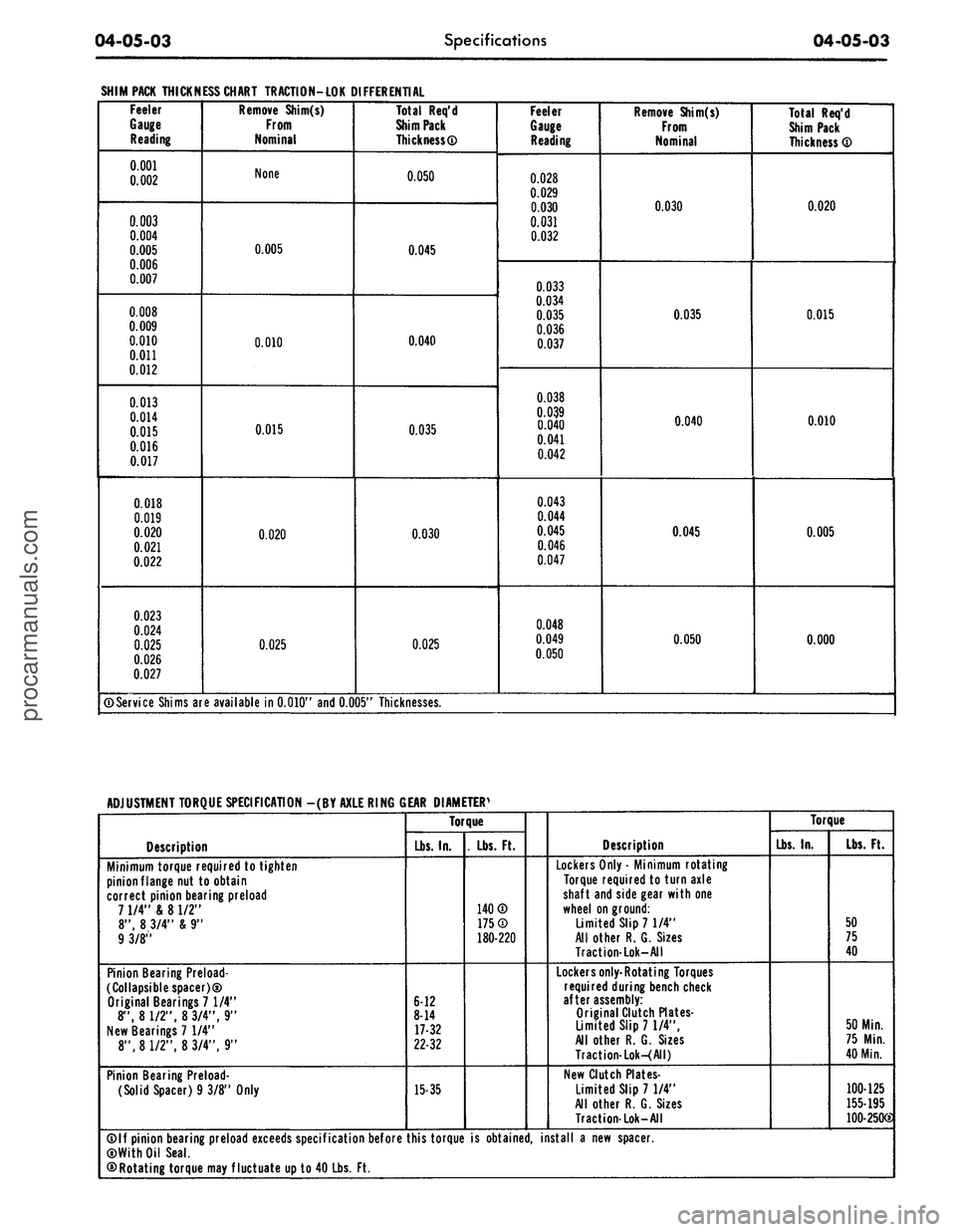
SHIM PACK THICKNESS CHART TRACTION-LOK DIFFERENTIAL
Feeler
Gauge
Reading
0.001
0.002
0.003
0.004
0.005
0.006
0.007
0.008
0.009
0.010
0.011
0.012
0.013
0.014
0.015
0.016
0.017
0.018
0.019
0.020
0.021
0.022
0.023
0.024
0.025
0.026
0.027
Remove Shim(s)
From
Nominal
None
0.005
0.010
0.015
0.020
0.025
Total Req'd
Shim Pack
Thickness®
0.050
0.045
0.040
0.035
0.030
0.025
Feeler
Gauge
Reading
0.028
0.029
0.030
0.031
0.032
0.033
0.034
0.035
0.036
0.037
0.038
0.039
0.040
0.041
0.042
0.043
0.044
0.045
0.046
0.047
0.048
0.049
0.050
Remove Shim(s)
From
Nominal
0.030
0.035
0.040
0.045
0.050
Total Req'd
Shim Pack
Thickness ®
0.020
0.015
0.010
0.005
0.000
©Service Shims are available in 0.010" and 0.005" Thicknesses.
ADJUSTMENT TORQUE SPECIFICATION -(BY AXLE RING GEAR DIAMETERS
Description
Minimum torque required to tighten
pinion flange nut to obtain
correct pinion bearing preload
7 1/4" & 8 1/2"
8", 8 3/4" & 9"
9 3/8"
Pinion Bearing Preload-
collapsible spacer)®
Original Bearings 7 1/4"
8", 8 1/2", 8 3/4", 9"
New Bearings 7 1/4"
8", 8 1/2", 8 3/4", 9"
Pinion Bearing Preload-
(Solid Spacer) 9 3/8" Only
Torque
Lbs.
In.
6-12
8-14
17-32
22-32
15-35
. Lbs. Ft.
140®
175®
180-220
Description
Lockers Only • Minimum rotating
Torque required to turn axle
shaft and side gear with one
wheel on ground:
Limited Slip 7 1/4"
All other R. G. Sizes
Traction-Lok-All
Lockers only-Rotating Torques
required during bench check
after assembly:
Original Clutch Plates-
Limited Slip 71/4",
All other R. G. Sizes
Traction-Lok-(All)
New Clutch Plates-
Limited Slip 7 1/4"
All other R. G. Sizes
Traction-Lok-All
Torque
Lbs.
In.
Lbs.
Ft.
50
75
40
50 Min.
75 Min.
40 Min.
100-125
155-195
100-250G
©If pinion bearing preload exceeds specification before this torque is obtained, install a new spacer.
©With Oil Seal.
©Rotating torque may fluctuate up to 40 Lbs. Ft.procarmanuals.com
Page 248 of 413
05-01-01
05-01-01
Clutch
GROUP
5
PART
5-1
PAGE
Drive Shaft 05-01-01
PART
5-2
General Clutch Service 05-02-01
PART
5-3
Clutch
PART
5-4
Specifications
PAGE
05-03-01
05-04-01
PART
5-1
Drive Shaft
COMPONENT INDEX
DESCRIPTION
DRIVE SHAFT ANGLE CHECK
DRIVE SHAFT BALANCE CHECK
DRIVE SHAFT BALANCING
(Single Universal Joint)
DRIVE SHAFT DISASSEMBLY
AND
OVERHAUL
Single Universal Joint — Ford Design
Double Cardan Joint — Dana Design
Double Cardan Joint — Saginaw Design
DRIVE SHAFT REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
DRIVE SHAFT RUNOUT CHECK
MODEL APPLICATION
All
Models
01-01
01-01
01-01
01-02
01-01
Ford
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Mercury
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Meteor
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Cougar
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Fairlane
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Falcon
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Montego
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Mustang
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Lincoln-
Continental
N/A
N/A
01-04
N/A
Thunderbird
N/A
N/A
N/A
01-05
Continental-
Mark
III
N/A
N/A
N/A
01-05
A page number indicates that the item
is for the
vehicle listed
at the
head
of
the column.
N/A indicates that
the
item
is not
applicable
to the
vehicle listed.
DRIVE SHAFT TESTS
DRIVE LINE BALANCE CHECK
If detailed parts
of the
drive shaft
are replaced
and
shaft vibration
is en-
countered after installation, disconnect
the shaft
at the
slip yoke. Rotate
the
slip yoke
180
degrees; then, reconnect
the shaft
to the
slip yoke.
If the
vibra-
tion persists, disconnect
the
shaft
at
the rear axle companion flange.
Ro-
tate
the
companion flange
180
degrees
and reconnect
the
shaft
to the
flange.
DRIVE LINE ANGLE CHECK
Vibration
or
"shudder" which
is no-
ticeable either
on
fast acceleration
or
when coasting, using
the
engine
for a
brake,
may be
caused
by the
rear axle
housing being loose
on the
rear
springs
or by
improper pinion angle.
Refer
to
Group
3,
Part
2 for
pinion
angle checking procedures.
If the
rear
axle U-bolts (Fairlane, Montego,
Mustang, Cougar, Falcon models
only)
are
loose, torque
the
nuts
to
specification.
DRIVE SHAFT RUNOUT CHECK
Using
a
dial indicator, check
the
runout
at
each
end and in the
middle
of
the
driveshaft.
The
rear check
should
be
made
on the
small tube
sec-
tion
of the
shaft between
the
balance
weights
and the
yoke welds. Drive-
shaft runout should
not
exceed 0.035
inch
at any one
point.
DESCRIPTION
The drive shaft
is the
means
of
transferring power from
the
engine,
through
the
transmission,
to the dif-
ferential
in the
rear axle,
and
then
to
the rear wheels.
The
drive shaft incor-
porates
two
universal joints
and a
slip
yoke
(Fig. 1) or two
double cardan
universal joints,
one at
each
end of the
shaft (Figs.
2 and 3).
Each double
procarmanuals.com
Page 253 of 413

05-01-06
Drive Shaft
05-01-06
procedures, a sharp rap on the yokes
with a brass hammer will seat the
bearings needles and usually provide
freedom of movement. Care must be
taken to support the shaft end during
this operation, as well as preventing
blows to the bearings themselves. Do
not install the drive shaft unless the
universal joints are free of bind.
DISASSEMBLY (DOUBLE
CARDAN JOINT — LINCOLN
CONTINENTAL — DANA DESIGN)
1.
Mark the position of the spiders,
the center yoke, and the centering
socket yoke as related to the stud
yoke which is welded to the front of
the drive shaft tube. The spiders must
be assembled with the bosses in their
original position to provide proper
clearance.
2.
Remove the snap rings that se-
cure the bearings in the front of the
center yoke.
3.
Position the tool as shown in
Fig. 11. Thread the tool clockwise
until the bearing protrudes approxi-
mately 3/8 inch out of the yoke.
4.
Remove the drive shaft from the
vise.
5.
Tighten the bearing in the vise
and drive on the center yoke as shown
in Fig. 12 to free it from the bearing.
CENTER
YOKE
C 2066-A
FIG. 15—Removing Bearing from
Rear of Center Yoke
SLINGER RING
CENTER YOKE
6. Lift the two bearings (Fig. 13)
from the spider at this time.
7.
Reposition the tool on the yoke
and move the remaining bearing in the
opposite direction so that it protrudes
approximately 3/8 inch out of the
yoke.
8. Grip the bearing in a vise. Drive
on the center yoke to free it from the
bearing (Fig. 12).
9. Remove the spider from the cen-
ter yoke.
10.
Pull the centering socket yoke
off the center stud (Fig. 14). Remove
the rubber seal from the centering ball
stud.
11.
Remove the snap rings from the
center yoke and from the drive shaft
yoke.
12.
Position the tool on the drive
shaft yoke (Fig. 15) and press the
bearing outward until the inside of the
center yoke almost contacts the sling-
er ring at the front of the drive shaft
yoke. Pressing beyond this point can
distort the slinger ring. The arrow in
Fig. 16 illustrates the interference
point.
13.
Clamp the exposed end of the
bearing in a vise and drive on the cen-
ter yoke with a soft-faced hammer to
free it from the bearing.
14.
Reposition the tool and press
on the spider to remove the opposite
bearing.
Tool-CJ91B
C1772-A
FIG. 17—Partially Pressing Bearing
From Center Yoke
C 2067-A
FIG. 16—Center Yoke Interference
Point
C1771-A
FIG. 18—Removing Bearing From
Center Yoke
15.
Remove the center yoke from
the spider.
16.
Remove the spider from the
drive shaft yoke in the same manner.
17.
Clean all serviceable parts in
cleaning solvent. If using a repair kit,
install all of the parts supplied in the
kit. If the drive shaft is damaged, re-
place the complete shaft to be assured
of a balanced assembly.
ASSEMBLY (DOUBLE
CARDON JOINT —
LINCOLN CONTINENTAL —
DANA DESIGN)
1.
To assemble the double cardan
joints,
position the spider in the drive
shaft yoke. Make sure the spider boss-
es (or lubrication plugs on kits) will be
in the same position as originally in-
stalled. Press in the bearing cups. In-
stall the snap rings.
2.
Position the center yoke over the
spider ends and press in the bearing
cups.
Install the snap rings.
3.
Install a new seal on the cen-
tering ball stud. Position the centering
socket yoke on the stud.
4.
Place the front spider in the cen-
ter yoke. Make sure the spider bosses
(or lubrication plugs on kits) are prop-
erly positioned. Press in the bearing
cups and install the snap rings.
5.
Apply pressure on the centering
socket yoke and install the remaining
bearing cup.
6. On kits, remove the plug from
each spider and lubricate the universal
joints.
Reinstall the plug in each spi-
der.
DISASSEMBLY (DOUBLE
CARDAN JOINT — CONTINENTAL
MARK III, THUNDERBORD —
SAGINAW DESIGN)
1.
Working at the rear axle end of
the shaft, mark the position of the spi-
ders,
the center yoke, and the cen-
tering socket yoke as related to the
companion flange. The spiders must
be assembled with the bosses in their
original position to provide proper
clearance.
2.
Position tool CJ91B as shown in
Fig. 17. Thread the tool clockwise
until the injected nylon moulding
snaps and the bearing protrudes ap-
proximately 3/8 inch out of the yoke.
3.
Remove the driveshaft from the
vise.
4.
Tighten the bearing in the vise
and tap on the weld yoke to free the
bearing from the center yoke (Fig.
18).
Do not tap on the driveshaft tube.procarmanuals.com
Page 255 of 413

05-02-01
General Clutch Service
05-02-01
PART
5-2
General Clutch Service
COMPONENT INDEX
MODEL APPLICATION
3
a>
1
o>
il
•U
i
!-
II
CLUTCH DISC
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
CHECKING FLYWHEEL HOUSING
ALIGNMENT
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
N/A
N/A
N/A
CORRECTING FLYWHEEL HOUSING
ALIGNMENT
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
N/A
N/A
N/A
PILOT BUSHING
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
PRESSURE PLATE AND COVER
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
RELEASE BEARING
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
A page number indicates that the item is for the vehicle listed at the head of the column.
N/A indicates that the item is not applicable to the vehicle listed.
l
FLYWHEEL HOUSING ALIGNMENT
Alignment of the flywheel housing
bore and rear face with the engine
should be checked as a possible cause
of any of the following troubles- ex-
cessive transmission gear wear, ..ans-
mission jumping out of gear, especial-
ly third gear, drive line vibration, ex-
cessive pilot bushing wear, noisy re-
lease bearing, or excessive clutch spin
time.
INSPECTION
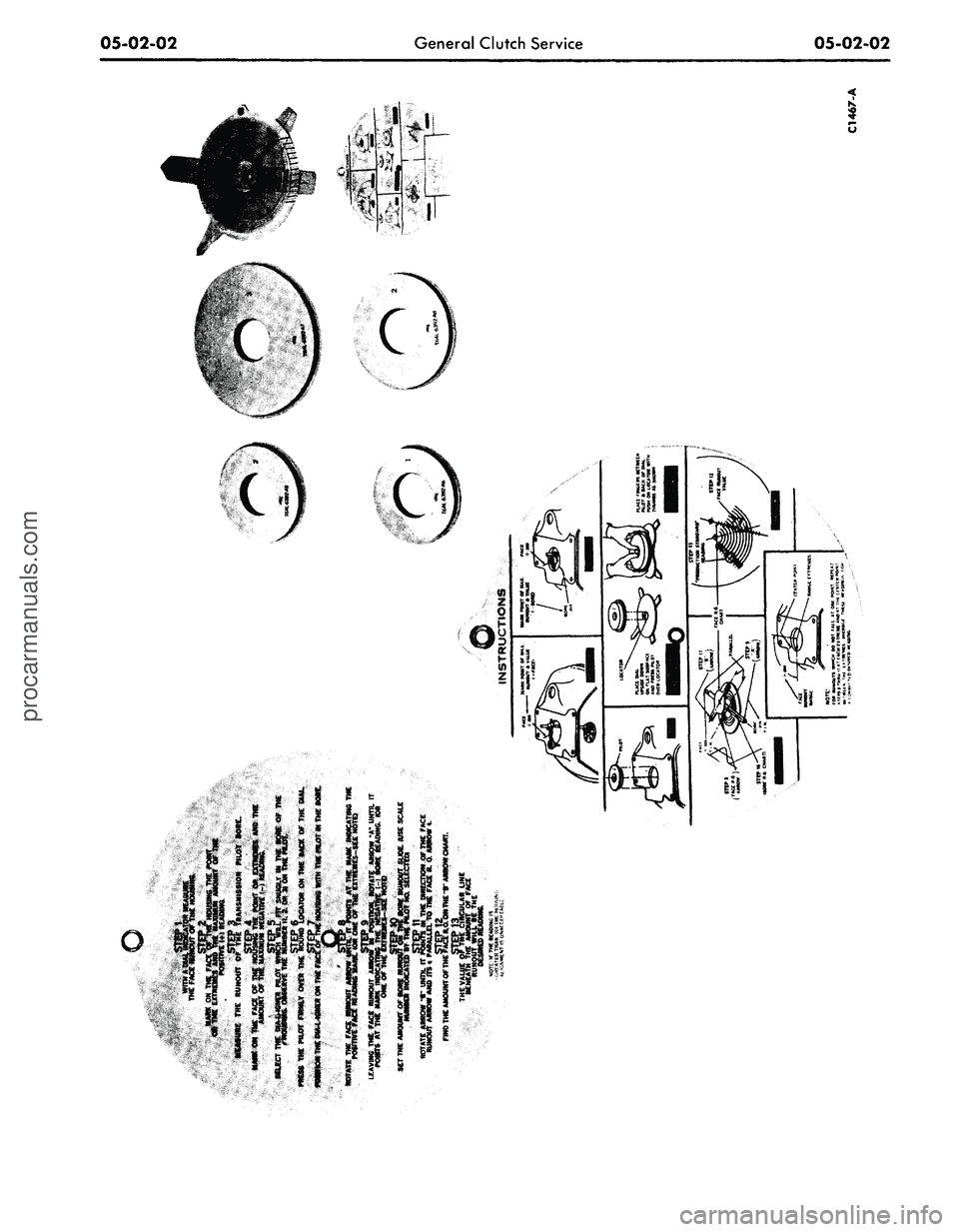
1. With the clutch release bearing
removed, install the indicator pilot
tool shown in Fig. 1.
2.
Clean the faces of the flywheel
housing bolt bosses, and remove all
burrs, nicks, and paint from the
mounting face of the housing.
3.
Install the dial indicator on the
pilot and adjust the holder so the but-
ton will contact a circumference just
inside of the transmission mounting
holes.
4.
Push the flywheel forward to re-
move crankshaft end play. Set the dial
indicator face to read zero.
5.
Remove the spark plugs to alle-
viate compression.
6. Pull the engine crankshaft
through one revolution. The crank-
shaft must be held in the forward po-
sition while rotating it.
7. Note the indicator reading and
mark the maximum point of runout
on the face of the housing (Fig. 1).
8. Position the dial indicator to
check bore alignment (Fig. 1). The
bore must be clean and free of burrs,
nicks and paint.
9. Pull the crankshaft through one
revolution. Note the indicator reading
and mark the maximum point of run-
out on the face of the housing as
shown in Fig. 1.
10.
Remove the dial indicator from
the crankshaft and the housing.
11.
Select the Dia-L-lgner pilot
(Fig. 2) which will fit snugly in the
bore of the flywheel housing.
12.
Press the pilot into place on the
locator on the back of the dial.
13.
Position the Dia-L-lgner on the
face of the housing (Fig. 3) with the
pilot in the bore.
14.
Rotate the face runout arrow to
the positive face runout mark on the
housing.
15.
Without moving the face runout
arrow, rotate arrow A until it is at the
negative bore reading.
16.
Slide arrow A to register the
amount of bore runout on the .010-
line of the white scale. Use the
scale No. to coincide with the pilot
being used.
17.
Rotate arrow B until it points
CHECKING
FACE
RUN OUT
CHECKING
BORE
RUN OUT
C
1783-
A
FIG.
1—Flywheel
Housing Alignment Checkprocarmanuals.com
Page 256 of 413
05-02-02
General Clutch Service
05-02-02procarmanuals.com
Page 257 of 413
05-02-03
General Clutch Service
05-02-03
in the direction of the face runout
arrow and its center line is parallel to
the center line of the face runout
arrow.
18.
Determine the amount of the
face runout on the B arrow scale.
19.
The value of the circular line
beneath the amount of face runout
will be the desired reading. If the
reading is in excess of 0.014 inch the
housing alignment is unacceptable.
20.
Remove the Dia-L-lgner gauge
from the flywheel housing.
21.
Install the spark plugs and con-
nect the wires.
ENGINE IN VEHICLE
Since any change in face alignment
will change bore alignment, it may be
possible to correct bore alignment by
changing face alignment. Face align-
ment can be changed by shimming be-
tween the flywheel housing and en-
gine.
Fig. 4 shows the type of shim
which can be fabricated.
Not more than 0.010 inch thickness
shims may be used between the fly-
wheel housing and engine. If a 0.010-
inch shim will not bring face and bore
alignment within limits, replace the
flywheel housing.
The shim required is one half the
maximum (—) indicator reading, and
should be located at the point of max-
imum minus (—) indicator reading.
If both the bore and face alignment
are out of limits, shim between the
flywheel housing and engine to bring
face alignment within limits. Check
the bore alignment.
If the bore alignment is out of lim-
its and the face alignment is within
limits,
shim the flywheel housing to
the limit of face misalignment and
check the bore alignment. If it is not
within limits, replace the housing.
ENGINE OUT OF VEHICLE
The same procedure to correct
alignment may be used with the en-
gine out of the vehicle or in the vehi-
cle,
up to the point of replacing the
flywheel housing. If the bore align-
ment cannot be brought within limits
by shimming, follow this procedure:
dure:
1.
Remove the flywheel housing
from the engine and remove the dowel
pins.
Install the flywheel housing and
tighten the attaching bolts.
2.
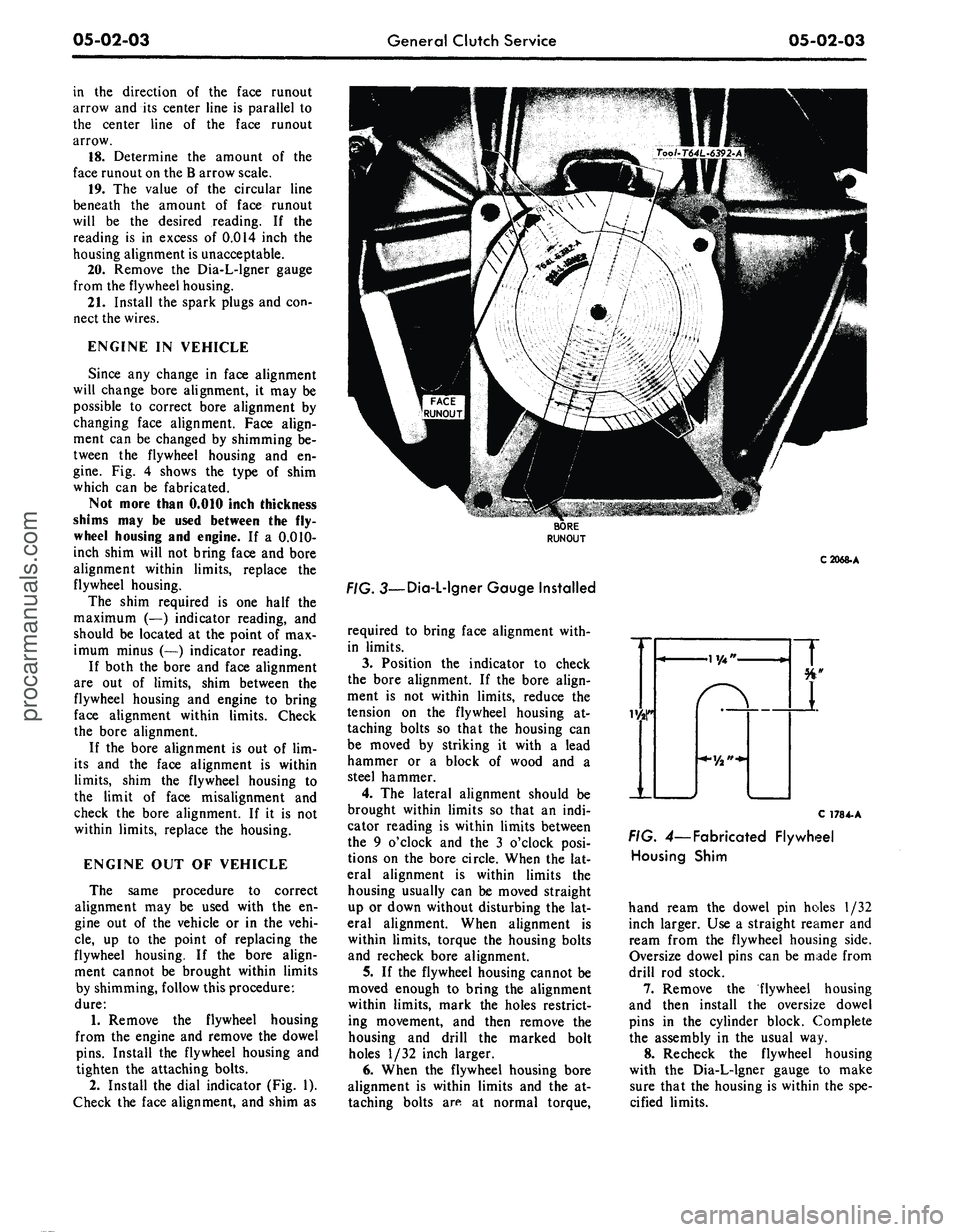
Install the dial indicator (Fig. 1).
Check the face alignment, and shim as
C2068-A
. 3—Dia-L-lgner Gauge Installed
required to bring face alignment with-
in limits.
3.
Position the indicator to check
the bore alignment. If the bore align-
ment is not within limits, reduce the
tension on the flywheel housing at-
taching bolts so that the housing can
be moved by striking it with a lead
hammer or a block of wood and a
steel hammer.
4.
The lateral alignment should be
brought within limits so that an indi-
cator reading is within limits between
the 9 o'clock and the 3 o'clock posi-
tions on the bore circle. When the lat-
eral alignment is within limits the
housing usually can be moved straight
up or down without disturbing the lat-
eral alignment. When alignment is
within limits, torque the housing bolts
and recheck bore alignment.
5.
If the flywheel housing cannot be
moved enough to bring the alignment
within limits, mark the holes restrict-
ing movement, and then remove the
housing and drill the marked bolt
holes 1/32 inch larger.
6. When the flywheel housing bore
alignment is within limits and the at-
taching bolts are at normal torque,
C 178 4-A
FIG. 4— Fabricated Flywheel
Housing Shim
hand ream the dowel pin holes 1/32
inch larger. Use a straight reamer and
ream from the flywheel housing side.
Oversize dowel pins can be made from
drill rod stock.
7.
Remove the flywheel housing
and then install the oversize dowel
pins in the cylinder block. Complete
the assembly in the usual way.
8. Recheck the flywheel housing
with the Dia-L-lgner gauge to make
sure that the housing is within the spe-
cified limits.procarmanuals.com
Page 258 of 413

05-02-04
General Clutch Service
05-02-04
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
RELEASE BEARING
Wipe all oil and dirt off the release
bearing. The bearing is prelubricated
and should not be cleaned with sol-
vent.
Inspect the bearing retainer for
loose spring clips and rivets.
Inspect the release bearing assembly
for burrs which may cause the assem-
bly to drag on the transmission bear-
ing retainer. Any such burrs should be
cleaned up with fine crocus cloth. If
burrs are found, inspect the transmis-
sion input shaft bearing retainer for
evidence of scoring. Any scoring
should be polished out with crocus
cloth. Coat the bearing retainer with a
thin film of lithium-base grease
(C3VY-19586-A). Prior to release
bearing installation, apply a light film
of lithium base grease (C3VY-
19586-A) on both sides of the release
lever fork where it contacts the release
bearing hub and retaining springs.
Apply a light film of lithium base
grease (C3VY-19586-A) plate to the
release bearing surface that contacts
the pressure plate fingers. Carefully
fill the grease groove inside the bear-
ing hub with lithium base grease (no
polyethylene). Clean all excess grease
from the bore of the bearing hub. Ex-
cess grease will be forced onto the
spline by the transmission input shaft
bearing retainer and will contaminate
the clutch disc. Also, care must be
exercised when applying lubricants to
the release bearing, release bearing
hub and the release lever fork to avoid
excessive grease from contaminating
the clutch disc.
Hold the bearing inner race and ro-
tate the outer race while applying
pressure to it. If the bearing rotation
is rough or noisy, replace the bearing.
Most release bearing failures are
caused by improper clutch pedal ad-
justments. If the clutch linkage does
not have enough free travel, the re-
lease bearing will constantly touch the
release fingers and will spin whenever
the engine is running.
When installing a release bearing on
vehicles equipped with separate hub
and bearing, use the tool shown in
Fig. 5.
Release bearing failure can be
caused by the release lever contact
points being out of plane. Check the
wear on the release bearing assembly
where the release lever contacts it.
If one side of the assembly shows
more wear than the other, the release
lever is bent out of plane, or is not
centering on the bracket on the fly-
wheel housing.
Misalignment between the engine
and transmission can cause release
bearing failure. Other symptoms of
misalignment are transmission jump-
ing out of gear, especially third gear,
drive line vibration; excessive wear in
the pilot bushing, excessive clutch disc
spin time resulting in gear clash, and
excessive transmission gear wear.
PRESSURE PLATE AND COVER
Inspect the surface of the pressure
plate for burn marks, scores, or rid-
ges.
Generally, pressure plate resur-
facing is not recommended. However
minor burn marks, scores, or ridges
may be removed. During the resurfac-
ing process, the flatness of the pres-
sure plate must be maintained. If the
pressure plate is badly heat-checked or
deeply scored, replace the pressure
plate and cover assembly. Clean pres-
sure plate and flywheel surfaces with a
suitable solvent, such as alcohol to be
sure the surfaces are free from any oil
film. Do not use cleaners with petrole-
um base, and do not immerse the
pressure plate in the solvent.
Place the plate on the floor, being
careful not to score or scratch the sur-
face.
Force each individual finger
down, then release quickly. If the fin-
ger does not return quickly, a binding
condition is indicated, and the pres-
sure plate should be replaced.
The pressure plate should be lubri-
cated with a lithium-base grease be-
tween the driving lugs and the edges
of the pressure plate openings, as
shown in Fig. 6. Depress the pressure
plate fingers fully, apply the lubricant,
and then move the fingers up and
down until the lubricant is worked in.
Do not apply excessive lubricant.
CLUTCH DISC
Inspect the clutch disc facings for
oil or grease. Eliminate the source of
any oil or grease before replacing the
disc. An excessive amount of grease in
the pilot bushing or release bearing
hub will find its way to the disc fac-
ings.
Too much lubricant in the trans-
mission or a plugged transmission
vent will force the transmission lubri-
cant out the input shaft and onto the
disc facings. Also, rear main bearing
oil seal leaks or oil leaks from the fly-
wheel mounting bolts can contaminate
the clutch disc.
Inspect the clutch disc for worn or
loose facings. Check the disc for worn
or loose facings. Check the disc for
distortion and for loose rivets at the
hub.
Check for broken springs.
Springs loose enough to rattle will not
cause noise when the car is operating.
Replace the disc assembly if any of
these defects are present. Be especially
careful when installing a new disc to
avoid dropping it or contaminating it
with oil or grease.
PILOT BUSHING
Check the fit of the clutch pilot
bushing in the bore of the crankshaft.
The bushing is pressed into the
crankshaft and should not be loose.
Inspect the inner surface of the bush-
ing for wear or a bell-mouthed condi-
tion. If the bushing is worn or dam-
aged, replace the bushing with a new
service bearing. Refer to the applica-
ble engine for the replacement proce-
dure.
C 1785-A
FIG. 5—Installing Clutch Release
Bearing on Hub
PRESSURE PLATE
AND COVER
DRIVING
LUG
FLYWHEEL
C2048-A
FIG. 6—Pressure Plate Lubrication
Pointsprocarmanuals.com
Page 267 of 413
06-01-01
06-01-01
ual Shift
GROUP
6
PART
6-1
PAGE
General Transmission Service
06-01-01
PART 6-2
Ford Design Three-Speed
Transmission
06-02-01
PART 6-3
Ford Design Four-Speed
Transmission
PART
6-4
Specifications
PAGE
.06-03-01
.06-04-01
Part 6-1 General
Transmission
Service
COMPONENT INDEX
REAR SEAL
Removal and Installation
REAR BUSHING AND SEAL
Removal and Installation
TRANSMISSION
Cleaning
Inspection
Lubrication
MODEL APPLICATION
All
Models
Ford
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Mercury
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Meteor
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Cougar
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Fairlane
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Falcon
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Montego
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Mustang
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
01-02
Lincoln-
Continental
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Thunderbird
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Continental-
Mark
III
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
A page number indicates that the item
is for
the vehicle listed
at
the head
of
the column.
N/A indicates that the item
is
not applicable
to
the vehicle listed.
COMMON ADJUSTMENTS
AND
REPAIRS
54E
M IB I2H 33
CODE
1
5
6
TRANSMISSION
THREE-SPEED
FOUR-SPEED (WIDE RATIO)
FOUR-SPEED (CLOSE RATIO)
C2086-A
FIG.
1—Typical
Warranty Plate—Transmission Identification
procarmanuals.com