port GMC SAVANA 1998 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GMC, Model Year: 1998, Model line: SAVANA, Model: GMC SAVANA 1998Pages: 388, PDF Size: 20.04 MB
Page 166 of 388

Defensive Driving
The best advice anyone can give about driving is:
Drive defensively.
Please start with a very important safety device
in your
vehicle: Buckle up. (See “Safety Belts’’ in the Index.) Defensive driving really means “be ready
for anything.”
On city streets, rural roads or freeways, it means
“always expect the unexpected.”
Assume that pedestrians or other drivers are going to be
careless and make mistakes. Anticipate what they might
do. Be ready for their mistakes.
Rear-end collisions are about the most preventable of
accidents. Yet they are common. Allow enough
following distance. It’s the best defensive driving
maneuver, in both city and rural driving.
You never
know when the vehicle in front of you is going to brake
or turn suddenly.
Defensive driving requires that a driver concentrate
on the driving task. Anything that distracts from the
driving task
-- such as concentrating on a cellular
telephone call, reading, or reaching for something on the
floor
-- makes proper defensive driving more difficult
and can even cause
a collision, with resulting injury. Ask
a passenger
to help do things like this, or pull off the road
in a safe place to do them yourself. These simple
defensive driving techniques could save your life.
4-2
ProCarManuals.com
Page 170 of 388

Braking
Braking action involves perception time and
reaction time.
First, you have to decide to push on the brake pedal.
That’s
perception time. Then you have to bring up your
foot and do it. That’s
reaction time.
Average reaction time is about 3/4 of a second. But
that’s only an average. It might be less with one driver
and as long as two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition, alertness, coordination
and eyesight all play a part.
So do alcohol, drugs and
frustration. But even
in 3/4 of a second, a vehicle
moving at
60 mph ( 100 kdh) travels 66 feet (20 m).
That could be a lot of distance in an emergency, so
keeping enough space between your vehicle and others
is important.
And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of the road (whether it’s pavement or
gravel); the condition
of the road (wet, dry, icy); tire
tread; the condition
of your brakes; the weight of the
vehicle and the amount of brake force applied. Avoid needless heavy braking.
Some
people drive in
spurts
-- heavy acceleration followed by heavy
braking
-- rather than keeping pace with traffic. This is a
mistake. Your brakes may not have time to cool between
hard stops. Your brakes will wear
out much faster if you
do
a lot of heavy braking. If you keep pace with the
traffic and allow realistic following distances, you will
eliminate a lot
of unnecessary braking. That means
better braking and longer brake life.
If your engine ever stops while you’re driving, brake
normally but don’t pump your brakes.
If you do, the
pedal may get harder to push down. If your engine
stops, you will still have some power brake assist.
But
you will use it when you brake. Once the power assist is
used up, it may take longer
to stop and the brake pedal
will be harder
to push.
4-6
ProCarManuals.com
Page 173 of 388

Speed Sensitive Steering
Your vehicle is equipped with a speed sensitive steering
system.
This system automatically varies the amount of
steering effort in proportion to your vehicle speed. The
required steering effort increases as your speed increases.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of
us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves. The
traction of the tires against the road surface makes
it
possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels.
If there’s no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going in the same direction. If you’ve ever
tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface,
the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control. Suppose
you’re steering through a sharp curve.
Then you suddenly accelerate. Both control
systems
-- steering and acceleration -- have to do
their work where the tires meet the road. Adding the
sudden acceleration can demand too much
of those
places. You can lose control.
What should you do if this ever happens? Ease up on the
accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want it
to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves
warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds are
based on good weather and road conditions. Under less
favorable conditions you’ll want to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach
a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed
so you can “drive” through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait to
accelerate until you are out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into the straightaway.
4-9
ProCarManuals.com
Page 176 of 388

0 Do not get too close to the vehicle you want to
pass while you’re awaiting an opportunity. For one
thing, following too closely reduces your area
of
vision, especially if you’re following a larger
vehicle. Also,
you won’t have adequate space if the
vehicle ahead suddenly slows or stops. Keep back a
reasonable distance.
When it looks like a chance to pass is coming up,
start
to accelerate but stay in the right lane and don’t
get too close. Time your move
so you will be
increasing speed as the time comes
to move into the
other lane. If the way is clear to pass,
you will have a
“running start” that more than makes up for the
distance you would lose by dropping back. And if
something happens
to cause you to cancel your pass,
you need only slow down and drop back again and
wait for another opportunity.
0 If other cars are lined up to pass a slow vehicle, wait
your turn. But take care that someone isn’t trying
to
pass you as you pull out to pass the slow vehicle.
Remember to glance over your shoulder and check
the blind spot.
0 Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder and
start your left lane change signal before moving out
0
0
0
of the right lane to pass. When you are far enough
ahead of the passed vehicle
to see its front in your
inside mirror, activate your right lane change signal
and move back into the right lane. (Remember that
your right outside mirror is convex. The vehicle you
just passed may seem
to be farther away from you
than it really is.)
Try
not to pass more than one vehicle at a time
on two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake
a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps
are not flashing, it may
be slowing down or starting to turn.
If you’re being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little
to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes, steering
and acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the
tires meet
the road to do what the driver has asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to steer and
constantly seek
an escape route or area of less danger.
4-12
ProCarManuals.com
Page 177 of 388

In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not
“overdriving” those conditions. But skids
are
always possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels aren’t rolling. In the steering
or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires
to slip and
lose cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving wheels
to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid
are best
handled by easing your foot off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide,
ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want the
vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid if it occurs. Of
course, traction is reauced when water, snow, ice,
gravel or other material is on the road. For safety, you’ll
want to slow down and adjust your driving to these
conditions.
It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving
on a surface with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration or
braking (including engine braking by shifting to a lower
gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires to
slide. You may not realize the surface is slippery until
your vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning
clues
-- such as enough water, ice or packed snow on
the road to make a “mirrored surface”
-- and slow
down when you have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock brake system (ABS) helps
avoid only the braking skid.
4-13
ProCarManuals.com
Page 183 of 388

Freeway Driving
Mile for mile, freeways (also called thruways, parkways,
expressways, turnpikes or superhighways) are the safest
of all roads. But they have their own special rules.
The most important advice on freeway driving is: Keep
up with traffic and keep
to the right. Drive at the same
speed most of the other drivers are driving. Too-fast
or
too-slow driving breaks a smooth traffic flow. Treat the
left lane on
a freeway as a passing lane. At the
entrance, there
is usually a ramp that leads to the
freeway. If you have
a clear view of the freeway as you
drive along the entrance ramp, you should begin to
check traffic. Try to determine where you expect to
blend with
the flow. Try to merge into the gap at close to
the prevailing speed. Switch on your turn signal, check
your mirrors and glance over your shoulder
as often as
necessary. Try to blend smoothly with the traffic flow.
Once you are on the freeway, adjust your speed to the
posted limit or to the prevailing rate if it’s slower. Stay
in the right lane unless you want to pass.
Before changing lanes, check your mirrors. Then use
your turn signal.
Just before you leave the lane, glance quickly over your
shoulder to make sure there isn’t another vehicle
in your
“blind” spot.
Once you are moving
on the freeway, make certain you
allow
a reasonable following distance. Expect to move
slightly slower at night.
When you want to leave the freeway, move to the proper
lane well
in advance. If you miss your exit, do not,
under any circumstances, stop and back
up. Drive on to
the next exit.
The exit ramp can be curved, sometimes quite sharply.
4-19
ProCarManuals.com
Page 184 of 388

The exit speed is usually posted.
Reduce your speed according to your speedometer,
not
to your sense of motion. After driving for any distance
at higher speeds, you
may tend to think you are going
slower than you actually are.
Before Leaving on a Long Trip
Make sure you’re ready. Try to be well rested. If you
must start when you’re not fresh
-- such as after a day’s
work
-- don’t plan to make too many miles that first part
of the journey. Wear comfortable clothing and shoes you
can easily drive
in.
Is your vehicle ready for a long trip? If you keep it
serviced and maintained, it’s ready to go. If it needs
service, have
it done before starting out. Of course,
you’ll find experienced and able service experts
in GM
dealerships all across North America. They’ll be ready
and willing to help if you need
it.
Here are some things you can check before a trip:
0
0
0
0
0
0
a
Windshield Washer Fluid: Is the reservoir full? Are
all windows clean inside and outside?
Wiper Blades: Are they in good shape?
Fuel, Engine Oil, Other Fluids: Have you checked
all levels?
Lamps: Are they all working? Are the lenses clean?
Tires: They are vitally important to a safe,
trouble-free trip.
Is the tread good enough for
long-distance driving? Are the tires all inflated
to the
recommended pressure?
Weather Forecasts: What’s the weather outlook
along your route?
Should you delay your trip a short
time to avoid a major storm system?
Maps: Do you have up-to-date maps?
4-20
ProCarManuals.com
Page 186 of 388

If you drive regularly in steep country, or if you’re
planning to visit there, here are some tips that can make
your trips safer and more enjoyable.
0 Keep your vehicle in good shape. Check all fluid
levels and also the brakes, tires, cooling system and
transmission. These parts can work hard on
mountain roads.
0 Know how to go down hills. The most important
thing
to know is this: let your engine do some of the
slowing down. Shift to
a lower gear when you go
down a steep or long hill.
/r CAUTION:
If’ you don’t shift down, your brakes could get so
hot that they wouldn’t work well. You would then
have poor braking
or even none going down a hill.
You could crash. Shift down to let your engine
assist your brakes
on a steep downhill slope.
1
A CAUTION:
Coasting downhill in NEUTRAL (N) or with the
ignition
off is dangerous. Your brakes will have to
do all the work of slowing down. They could get
so
hot that they wouldn’t work well. You would then
have poor braking or even none going down a hill.
You could crash.
Always have your engine running
and your vehicle in gear when you
go downhill.
a
0
0
0
Know how to go uphill. You may want to shift down
to a lower gear. The lower gears help cool your engine
and transmission, and
you can climb the hill better.
Stay
in your own lane when driving on two-lane
roads in hills or mountains. Don’t swing wide or
cut
across the center of the road. Drive at speeds that let
you stay in your own lane.
As you go over the top of a hill, be alert. There could be
something
in your lane, like a stalled car or an accident.
You may see highway signs on mountains that warn
of
special problems. Examples are long grades, passing or
no-passing zones,
a falling rocks area or winding
roads. Be alert to these and take appropriate action.
4-22
ProCarManuals.com
Page 193 of 388

NOTICE:
Pulling a trailer improperly can damage your
vehicle and result in costly repairs not covered by
your warranty.
To pull a trailer correctly, follow
the advice in this part, and see your dealer for important information about towing a trailer
with your vehicle.
Your vehicle can tow a trailer. To identify what the
vehicle trailering capacity is for your vehicle, you
should read the information in “Weight
of the Trailer”
that appears later in this section. But trailering is
different than just driving your vehicle by itself.
Trailering means changes in handling, durability and
fuel economy. Successful, safe trailering takes correct
equipment, and it has
to be used properly.
That’s the reason for this section. In it are many
time-tested, important trailering tips and safety rules.
Many of these are important for your safety and that
of
your passengers. So please read this section carefully
before you pull a trailer.
If You Do Decide To Pull A Trailer
If you do, here are some important points:
There are many different laws, including speed limit
restrictions, having to
do with trailering. Make sure
your rig will be legal, not only where you live but
also where you’ll be driving.
A good source for this
information can be state or provincial police.
Consider using a sway control if your trailer will
weigh
4,000 lbs. (1 800 kg) or less. You should
always use a sway control if your trailer will weigh
more than
4,000 Ibs. (1 800 kg). You can ask a hitch
dealer about sway controls.
Don’t tow a trailer at all during the first 500 miles
(800 km) your new vehicle is driven. Your engine,
axle or other parts could be damaged.
Then, during the first 500 miles (800 km) that you
tow a trailer, don’t drive over
50 mph (80 kmh) and
don’t make starts at full throttle. This helps your
engine and other parts of your vehicle wear
in at the
heavier loads.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 194 of 388
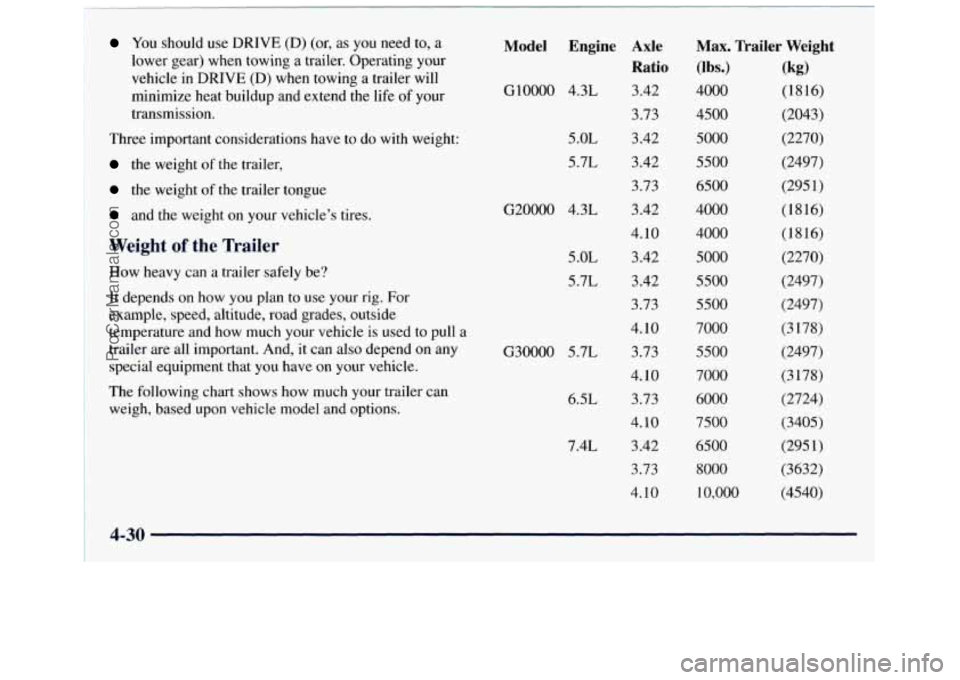
You should use DRIVE (D) (or, as you need to, a
lower gear) when towing a trailer. Operating your
vehicle in
DRIVE (D) when towing a trailer will
minimize heat buildup and extend the life
of your
transmission.
Three important considerations have to do with weight:
the weight of the trailer,
the weight of the trailer tongue
and the weight on your vehicle’s tires.
Weight of the Trailer
How heavy can a trailer safely be?
It depends on how
you plan to use your rig. For
example, speed, altitude, road grades, outside
temperature and how much your vehicle is used to pull a
trailer are all important. And, it can also depend on any
special equipment that
you have on your vehicle.
The following chart shows how much your trailer
can
weigh, based upon vehicle model and options.
Model Engine
GlOOOO 4.3L
5 .OL
5.7L
G20000 4.3L
5 .OL
5.7L
G30000 5.7L
6.5L
7.4L
Axle
Ratio
3.42
3.73
3.42 3.42
3.73
3.42
4.10 3.42
3.42
3.73
4.10 3.73
4.10
3.73
4.10 3.42
3.73
4.10
Max. Trailer Weight
(lbs.)
4000
4500
5000
5500
6500
4000
4000
5000
5500
5500
7000
5500
7000
6000
7500
6500
8000 10,000
(kg)
(1816)
(2043)
(2270)
(2497)
(295 1)
(1816)
(1816)
(2270)
(2497)
(2497)
(3 178)
(2497)
(3 178)
(2724)
(3405)
(295 1)
(3632)
(4540)
4-30
ProCarManuals.com