HONDA CIVIC 2003 7.G Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 2003, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 2003 7.GPages: 1139, PDF Size: 28.19 MB
Page 231 of 1139
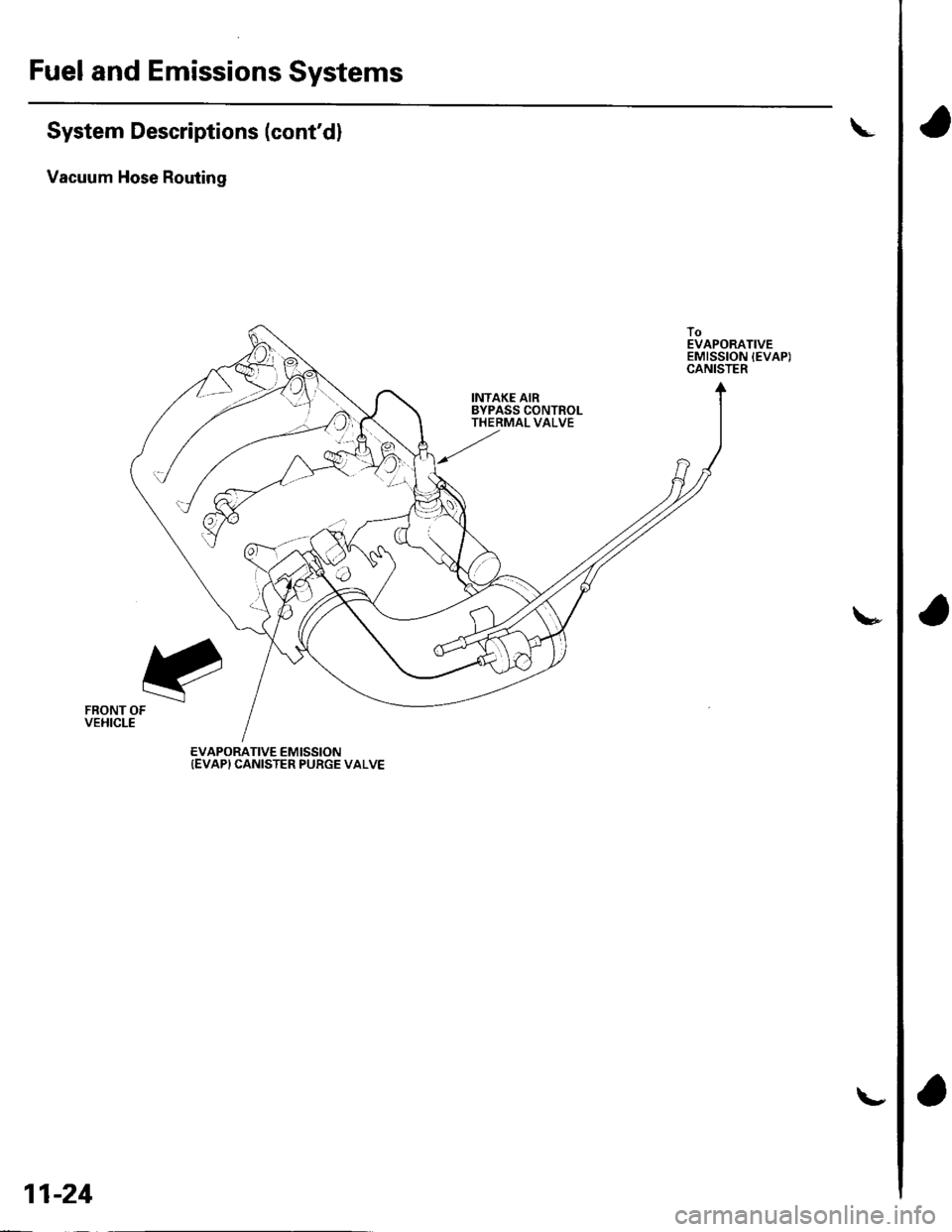
Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Descriptions (cont'dl
Vacuum Hose Routing
!
INTAKE AIRBYPASS CONTROLTHERMAL VALVE
\*
FRONT OFVEHICLE
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION{EVAP} CANISTER PURGE VALVE
11-24
\,
Page 232 of 1139
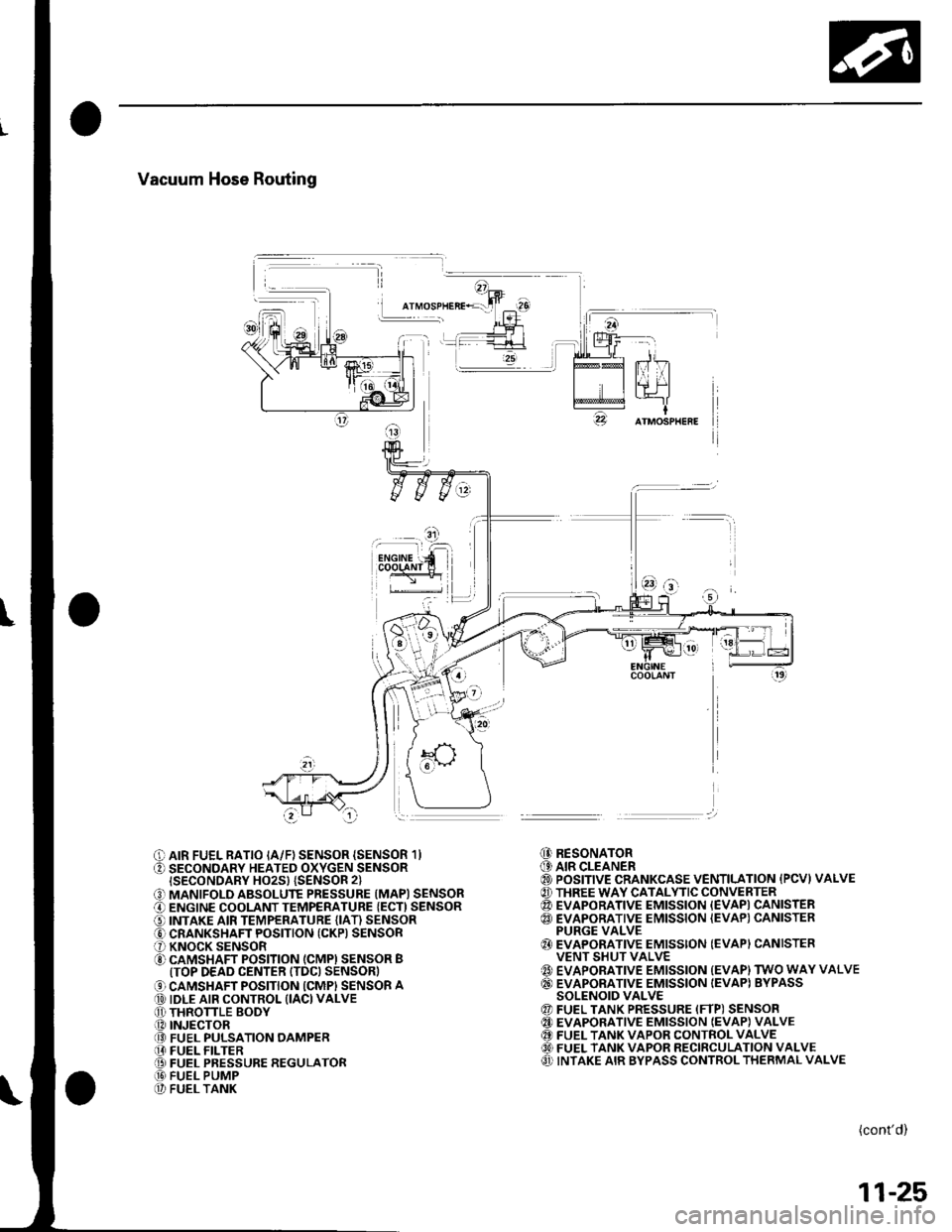
Vacuum Hose Routing
I
O AIR FUEL RATIO IA/F) SENSOR {SENSOR 1}O SECONDARY HEATED OXYGEN SENSORISECONDARY HO2S} {SENSOR 2}
O MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAPI SENSORO ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE {ECT) SENSORO INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSORO CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSORO KNOCK SENSORO CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMPI SENSOR BITOP DEAD CENTER ITDC) SENSOR)
O CAMSHAFT POSITION ICMPI SENSOR A@ IDLE AIR CONTROL (IACI VALVEO THRONLE BODY.O INJECTOR@ FUEL PULSATION OAMPER[I FUEL FILTER@ FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR@ FUEL PUMP@ FUEL TANK
@ RESONATOR(9 AIR CLEANER@ POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION {PCVI VALVE@ THREE WAY CATALYTIC CONVERTER@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION {EVAPI CANISTER@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION {EVAP) CANISTERPURGE VALVE{} EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAPI CANISTERVENT SHUT VALVE{' EVAPORATIVE EMISSION {EVAP) TWO WAY VALVE@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION IEVAPI BYPASSSOLENOID VALVE@ FUEL TANK PRESSURE (FTP) SENSOR@ EVAPORATIVE EMISSION IEVAP} VALVE@ FUEL TANK VAPOR CONTROL VALVE60) FUEL TANK VAPOR RECIRCULATION VALVEO INTAKE AIR BYPASS CONTROL THERMAL VALVE
(cont'd)
11-25
Page 233 of 1139
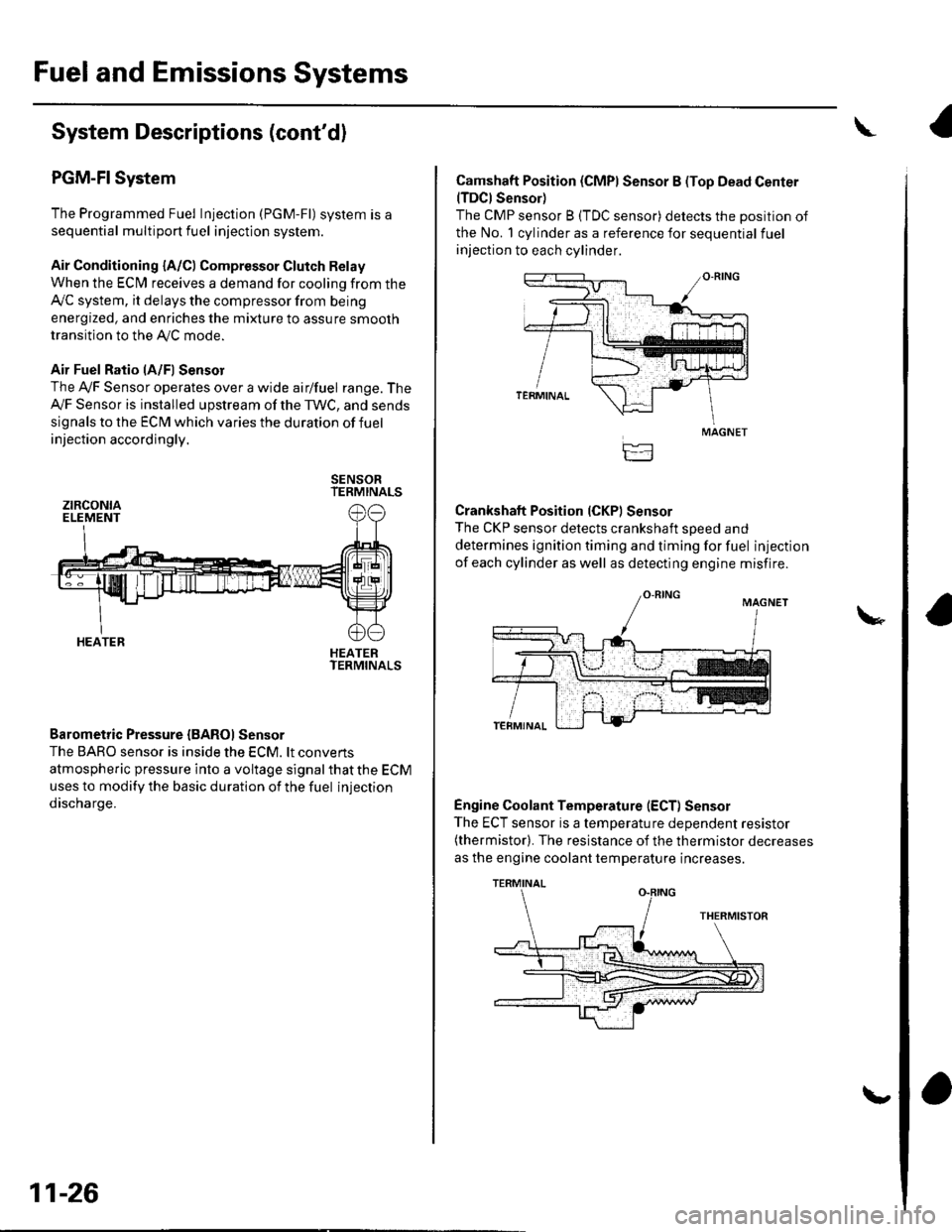
Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Descriptions (cont'd)
PGM-FI System
The Programmed Fuel Injection (PGM-Fl) system is a
sequential multiport fuel injection system.
Air Conditioning {A/C) Compressor Glutch Relay
When the ECfM receives a demand for cooling from the
Ay'C system, it delays the compressor from being
energized, and enriches the mixture to assure smooth
transition to the AVC mode.
Air Fuel Ratio lA/Fl Sensor
The Ay'F Sensor operates over a wide airlfuel range. The
Ay'F Sensor is installed upstream of the TWC, and sends
signals to the ECM which varies the duration of fuel
injection accordingly.
SENSORTERMINALS
HEATERTERMINALS
Barometric Pressure {BAROI Sensor
The BARO sensor is inside the ECM. lt convens
atmospheric pressure into a voltage signal that the ECM
uses to modify the basic duration of the fuel injection
discharge.
ztRcoNtaELEMENT
HEATER
11-26
\,
Camshaft Position (CMPI Sensor B (Top Dead Center(TDCI Sensor)
The CMP sensor B (TDC sensor) detects the position of
the No. 1 cylinder as a reference for sequential fuel
injection to each cylinder.
Crankshaft Position (CKPI Sensor
The CKP sensor detects crankshaft soeed and
determines ignition timing and timing for fuel injection
of each cylinder as well as detecting engine misfire.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The ECT sensor is a temperature dependent resistor(thermistor). The resistance of the thermistor decreases
as the engine coolant temperature increases.
MAGNET
TERMINAL
Page 234 of 1139
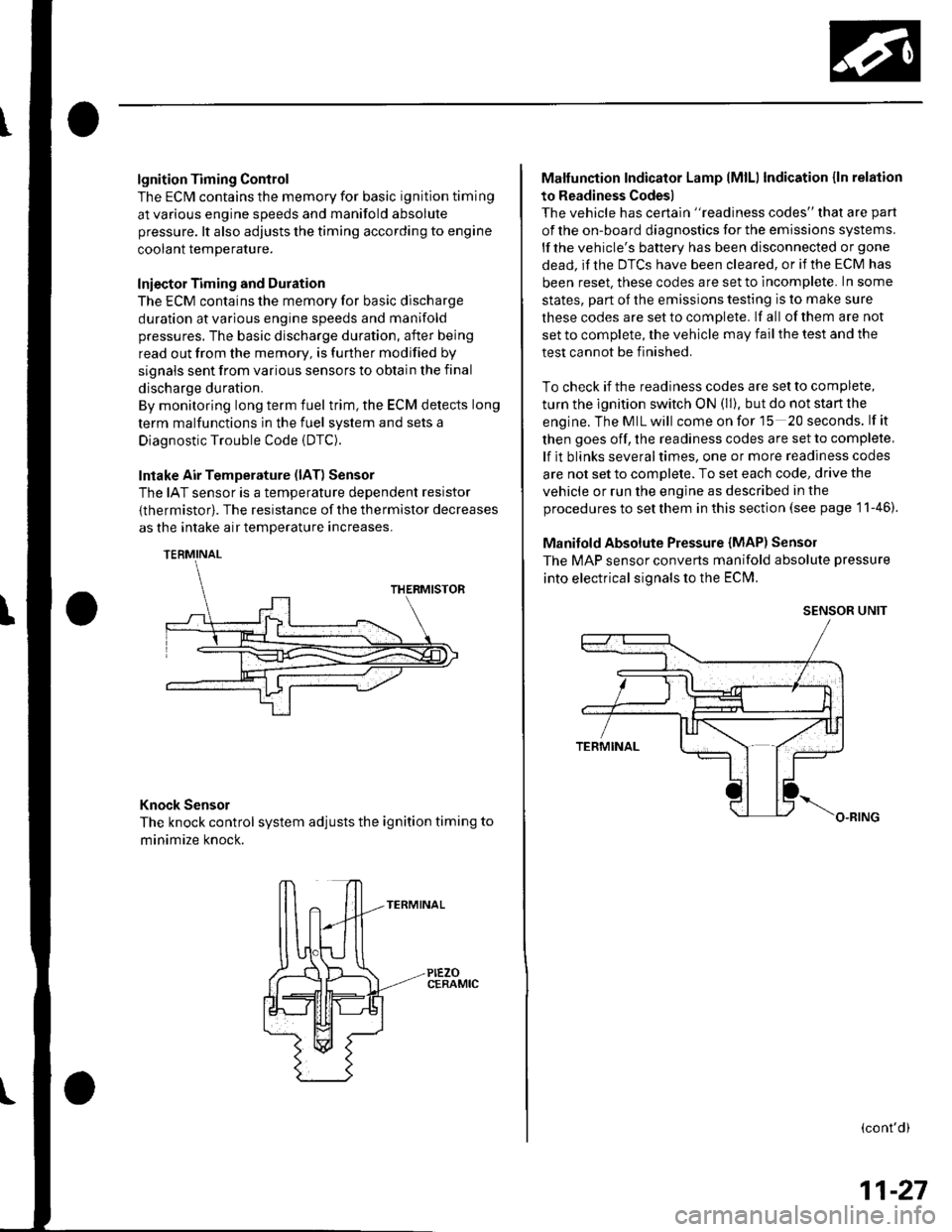
lgnition Timing Control
The ECM contains the memory for basic ignition timing
at various engine speeds and manifold absolute
pressure. lt also adjusts the timing according to engine
coolant temperature.
Iniector Timing and Duration
The ECM contains the memory for basic discharge
duration at various engine speeds and manifold
pressures. The basic discharge duration, after being
read out from the memory, is further modified by
signals sent from various sensors to obtain the final
discharge duration.
By monitoring long term fuel trim, the ECM detects long
term malfunctions in the fuel system and sets a
Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC).
Intake Air Temperature (lAT) Sensor
The IAT sensor is a temperature dependent resistor
{thermistor). The resistance of the thermistor decreases
as the intake air temDerature increases.
Knock Sensor
The knock control system adjusts the ignition timing to
minimize knock.
PIEZOCERAMIC
Malfunction Indicator Lamp lMlLl Indication {ln relation
to Readiness Codes)
The vehicle has certain "readiness codes" that are part
of the on-board diagnostics for the emissions systems.
lf the vehicle's baftery has been disconnected or gone
dead. if the DTCS have been cleared, or if the ECM has
been reset. these codes are set to incomplete. In some
states, part of the emissions testing is to make sure
these codes are set to comDlete. lf all of them are not
set to complete, the vehicle may fail the test and the
test cannot be finished.
To check if the readiness codes are set to complete,
turn the ignition switch ON (ll). but do not start the
engine.TheMILwill comeonforlS 20seconds. lf it
then goes off, the readiness codes are set to complete,
lf it blinks severaltimes, one or more readiness codes
are not set to comolete. To set each code, drive the
vehicle or run the engine as described in the
procedures to set them in this section (see page 1 1-46).
Manifold Absolute Pressure {MAP) Senso]
The MAP sensor converts manifold absolute pressure
into electrical signals to the ECM.
SENSOR UNIT
(cont'd)
11-27
Page 235 of 1139
Fuel and Emissions Systems
(
(
(
System Descriptions (cont'dl
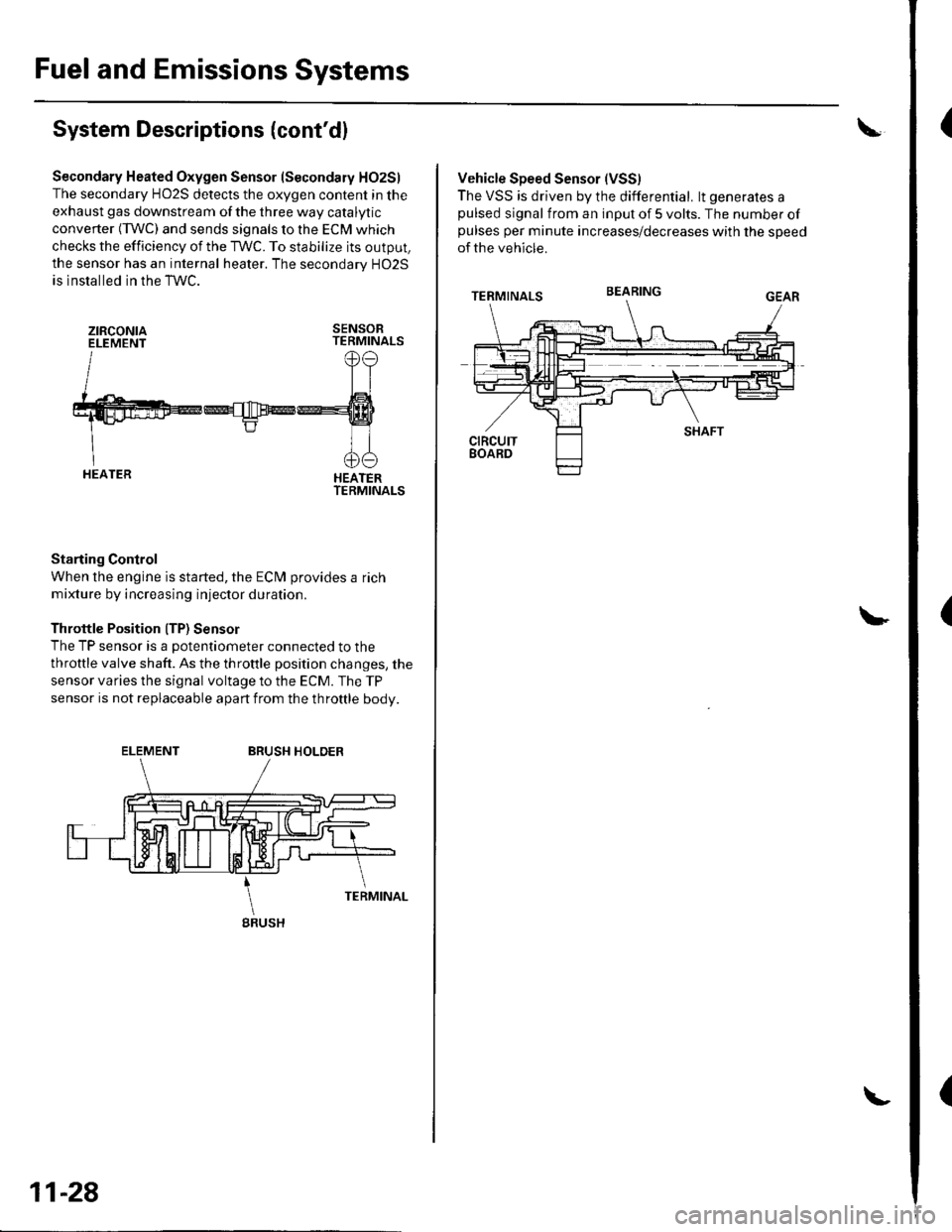
Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S)
The secondary HO2S detects the oxygen content in the
exhaust gas downstream of the three way catalytic
converter (TWC) and sends signals to the ECM which
checks the efficiency of the TWC. To stabilize its output,
the sensor has an internal heater. The secondarv HO2S
is installed in the TWC.
ztRcoNtaELEMENTSENSORTERMINALS
HEATERTERMINALS
Starting Control
When the engine is started, the ECM provides a rich
mixture by increasing injector duration.
Throttle Position ITP) Sensor
The TP sensor is a potentiometer connected to the
throttle valve shaft. As the throttle position changes, the
sensor varies the signal voltage to the ECM. The TP
sensor is not replaceable apart from the throftle body.
ELEMENTBRUSH HOLDER
gRUSH
11-28
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The VSS is driven by the differential. lt generates apulsed signal from an input of 5 volts. The number ofpulses per minute increases/decreases with the speed
of the vehicle.
BEARING
Page 236 of 1139
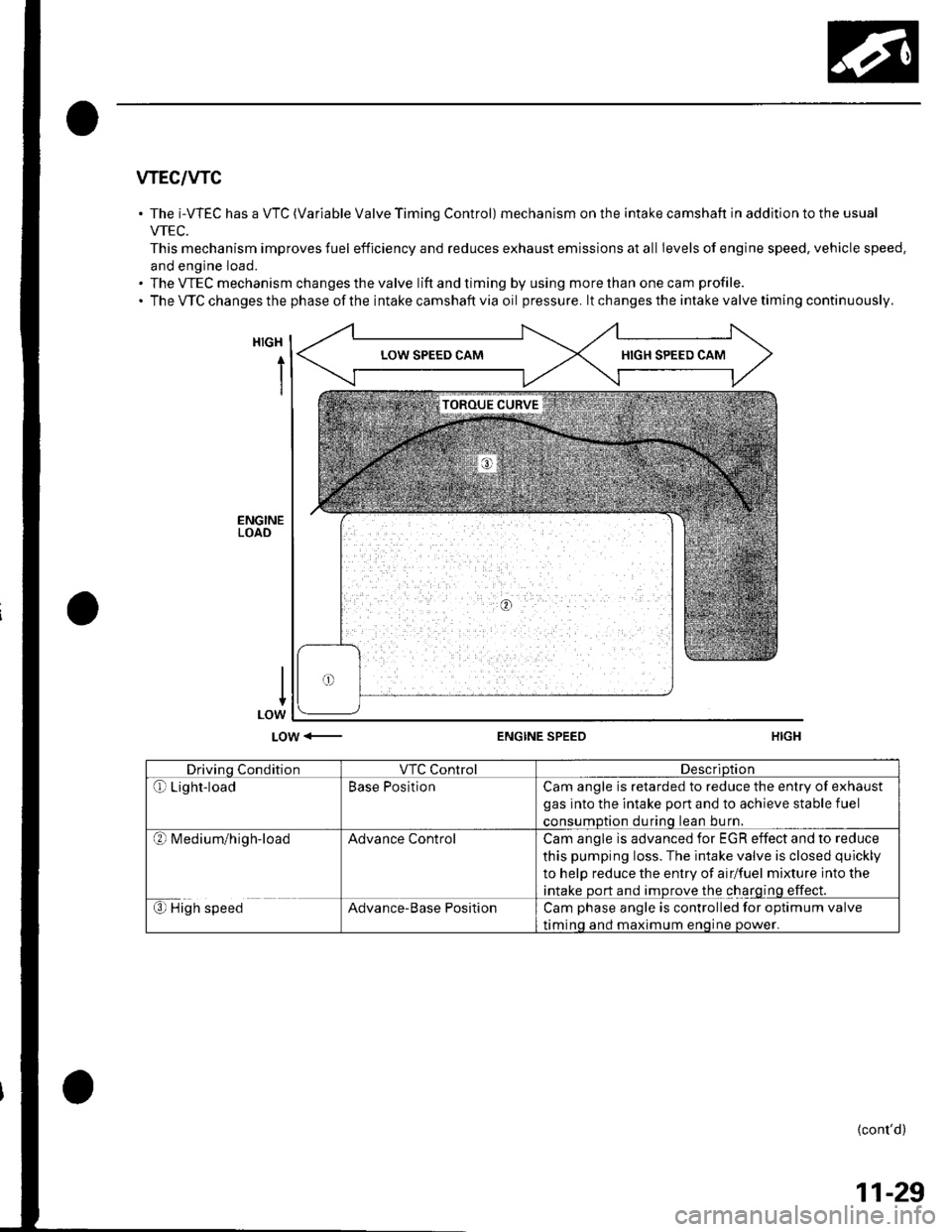
wEc/wc
The i-WEC has a VTC (Variable Valve Timing Control) mechanism on the intake camshaft in addition to the usual
VTEC.
This mechanism improves fuel efficiency and reduces exhaust emissions at all Ievels of engine speed, vehicle speed.
and engine load.
The VTEC mechanism changes the valve lift and timing by using more than one cam profile.
The VTC changes the phase of the intake camshaft via oil pressure. lt changes the intake valve timing continuously.
HIGH
i
LOW <-ENGINE SPEED
Drivino ConditionVTC ControlDescriDtion
Qr Light-loadBase PositionCam angle is retarded to reduce the entry of exhaust
gas into the intake port and to achieve stable fuel
consumDtion durinq lean bu rn.
?l M ed iu m/h ig h-loadAdvance ControlCam angle is advanced for EGR effect and to reduce
this pumping loss. The intake valve is closed quickly
to help reduce the entry of airlfuel mixture into the
intake port and improve the charging effect.
€) High speedAdvance-Base PositionCam phase angle is controlled for optimum valve
timinq and maximum enoine oower.
{cont'd)
11-29
Page 237 of 1139
Fuel and Emissions Systems
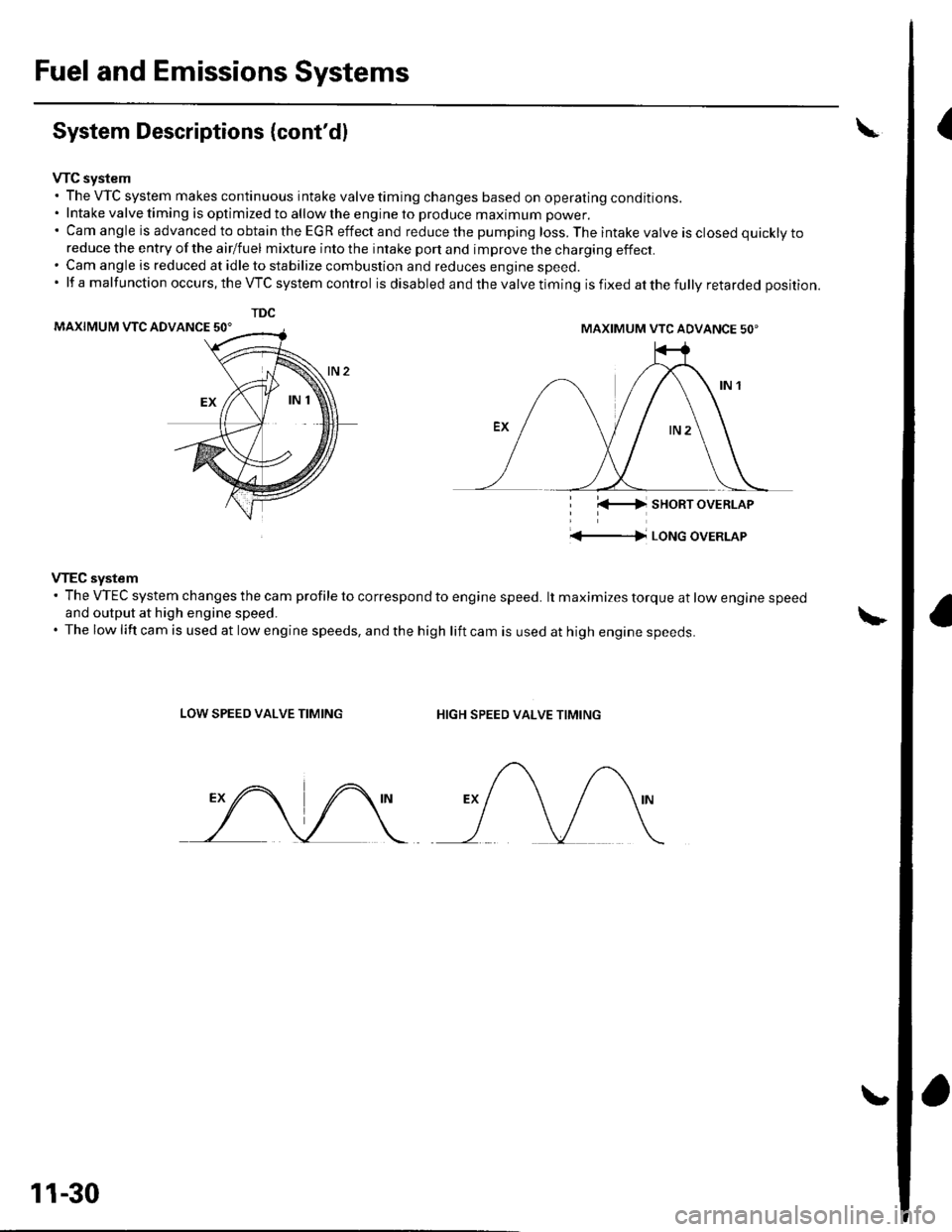
(System Descriptions (cont'dl
VTC system. The VTC system makes continuous intake valve timing changes based on operating conditions.. Intake valve timing is optimized to allow the engine to produce maximum power.'CamangleisadvancedtoobtaintheEGReffectandreducethepumpingloss.Theintakevalveisclosedquicklyto
reduce the entry of the airlfuel mixture into the intake port and improve the charging effect.. Cam angle is reduced at idle to stabilize combustion and reduces engine speed.'lfamalfunctionoccurs,theVTCsystemcontrol is disabled and the valve timing is fixed at the fully retarded position.
MAXIMUM VTC ADVANCE 50'
i l(-4 sHoRT oVERLAP
'+-|l LoNG oVERLAP
VTEC system' The VTEC system changes the cam profile to correspond to engine speed. lt maximizes torque at low engine speedand output at high engine speed.. The low lift cam is used at low engine speeds, and the high lift cam is used at high engine speeds.
LOW SPEED VALVE TIMINGHIGH SPEED VALVE TIMING
TDC
MAXIMUM VTC ADVANCE 50'
11-30
Page 238 of 1139
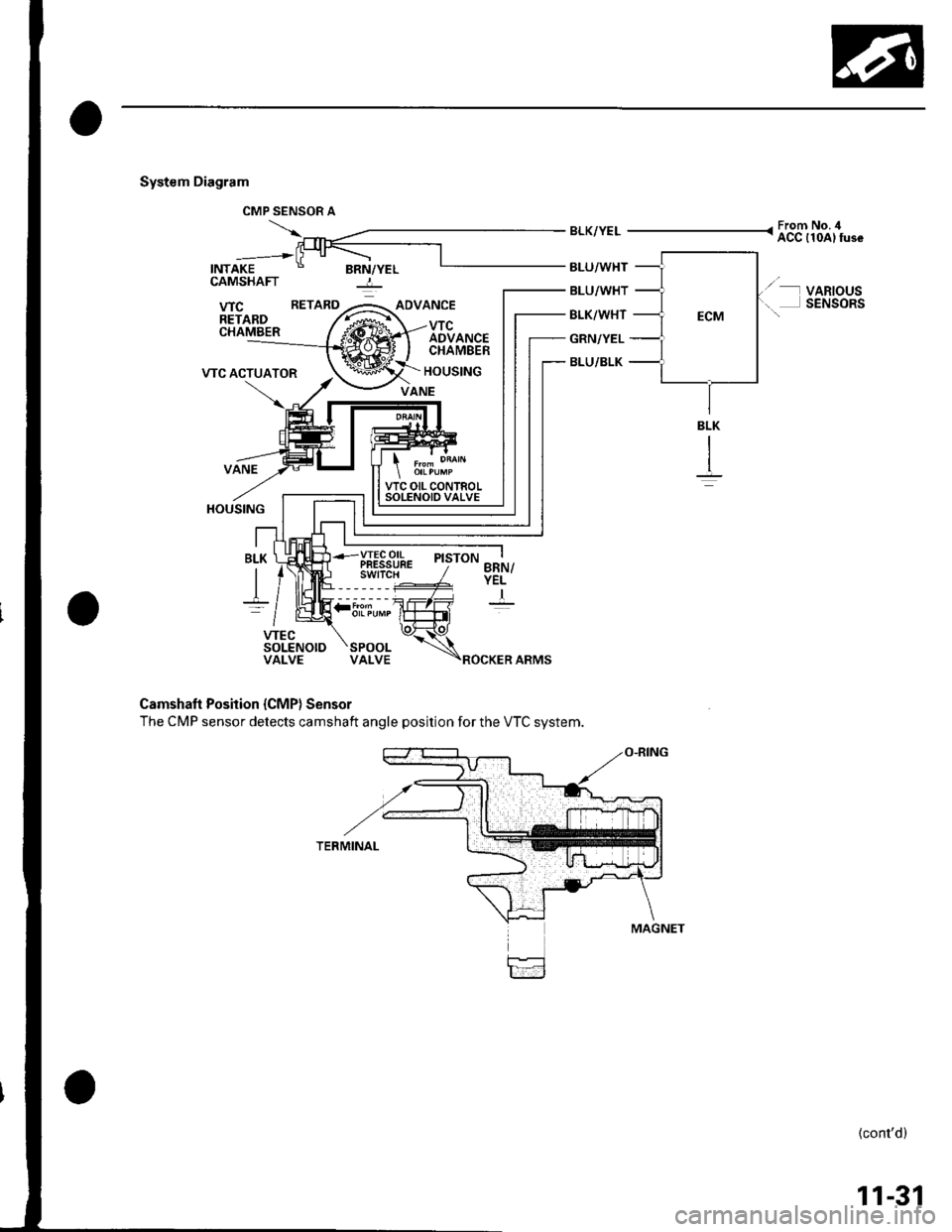
System Diagram
INTAKE
CMP SENSOR A
BRN/YELBLU/WHT
BLU/WHT
BLK/WHT
GRN/YEL
BLU/BLK
From No. ilACC {10A) fuse
VARIOUSSENSORS
CAMSHAFT -:-
BLK
It
Camshaft Position {CMP} Sensor
The CMP sensor detects camshaft angle position for the VTC system.
{cont'd}
11-31
:5i.T,""
Page 239 of 1139
Fuel and Emissions Systems
(
{
System Descriptions (cont'd)
ldle Control System
When the engine is cold, the Ay'C compressor is on, the
transmission is in gear, the brake pedal is pressed. thepower steering load is high, or the alternator is
charging, the ECIM controls current to the ldle Air
Control (lAC) valve to maintain the correct idle speed.
Refer to the System Diagram to see the functional
layout of the system.
Brake Pedal Position Switch
The brake pedal position switch signals the ECM when
the brake pedal is oressed.
Electrical Power Steering (EPS) Senser
The EPS sensor signals the ECM when the power
steering load is high.
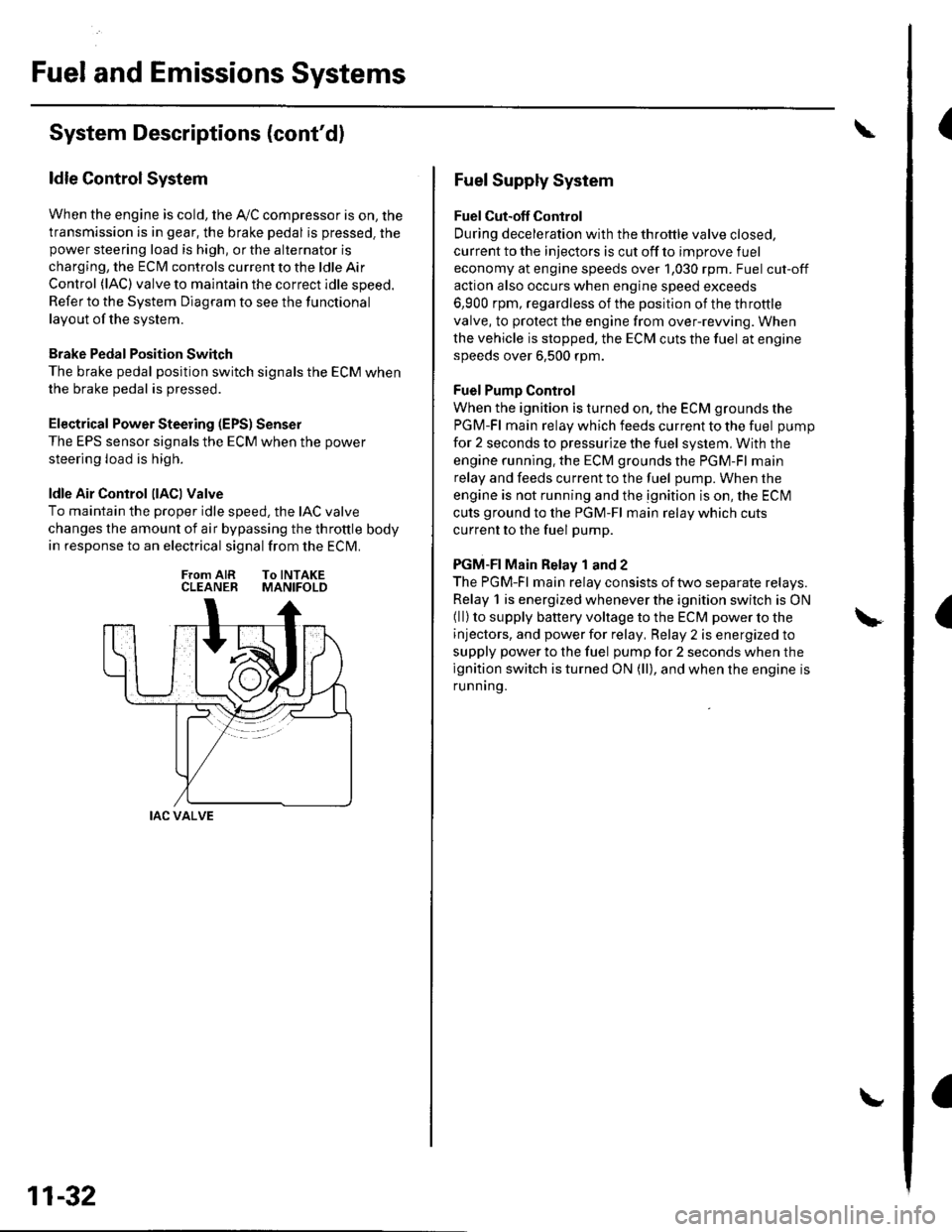
ldle Air Control llACl Valve
To maintain the proper idle speed, the IAC valve
changes the amount of air bypassing the throttle body
in response to an electrical signal from the ECM.
From AIR To INTAKECLEANER MANIFOLD
IAC VALVE
11-32
Fuel Supply System
Fuel Cut-off Control
During deceleration with the throttle valve closed,
current to the injectors is cut off to improve fuel
economy at engine speeds over 1,030 rpm. Fuel cut-off
action also occurs when engine speed exceeds
6,900 rpm, regardless of the position of the throttle
valve, to protect the engine from over-rewing. When
the vehicle is stopped. the ECM cuts the fuel at engine
speeds over 6,500 rpm.
Fuel Pump Control
When the ignition is turned on, the ECM grounds the
PGM-Fl main relay which feeds current to the fuel pump
for 2 seconds to pressurize the fuel system, With the
engine running. the ECM grounds the PGM-Fl main
relay and feeds current to the fuel pump. When the
engine is not running and the ignition is on, the ECI\4
cuts ground to the PGM-Fl main relay which cuts
current to the fuel pump.
PGM-FI Main Relay 1 and 2
The PGM-Fl main relay consists of two separate relays.
Relay 1 is energized whenever the ignition switch is ON(ll) to supply battery voltage to the ECM power to the
injectors, and power for relay, Relay 2 is energized to
supply power to the fuel pump for 2 seconds when the
ignition switch is turned ON (ll), and when the engine is
runnrng.
Page 240 of 1139
Intake Air System
Refer to the System Diagram to see the functional
layout of the system.
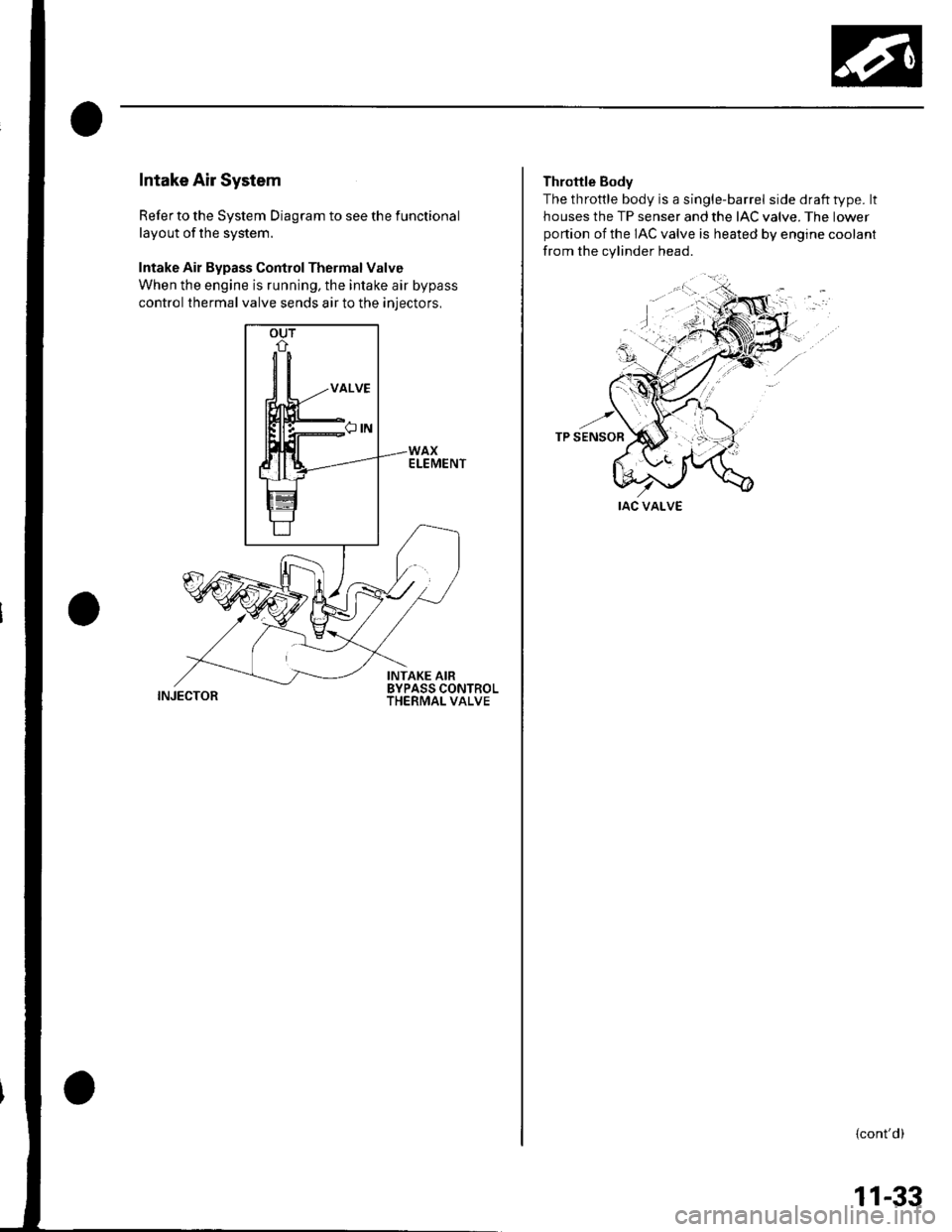
Intake Air Bypass Control Thermal Valve
When the engine is running, the intake air bypass
control thermal valve sends air to the iniectors,
INJECTOR
Throttle Body
The throttle body is a single-barrel side draft type. lt
houses the TP senser and the IAC valve. The lower
portion of the IAC valve is heated by engine coolant
from the cylinder head.
IAC VALVE
{cont'd)
11-33