HONDA CIVIC COUPE 1998 Owners Manual
Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: CIVIC COUPE, Model: HONDA CIVIC COUPE 1998Pages: 251, PDF Size: 2.04 MB
Page 231 of 251
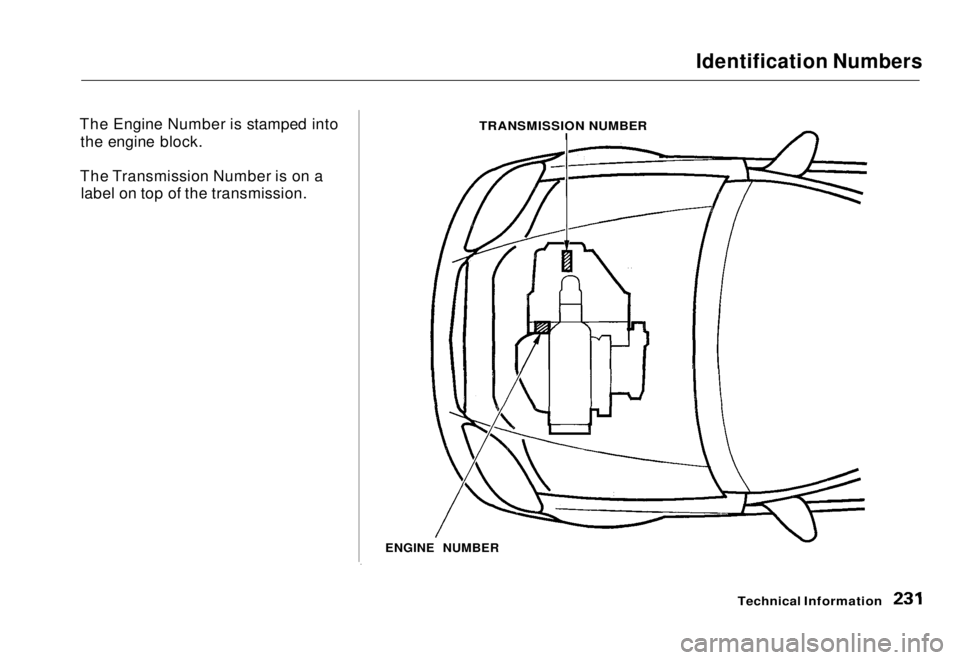
Identification Numbers
The Engine Number is stamped into the engine block.
The Transmission Number is on a label on top of the transmission.
Technical Information
ENGINE NUMBER
TRANSMISSION NUMBERMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 232 of 251
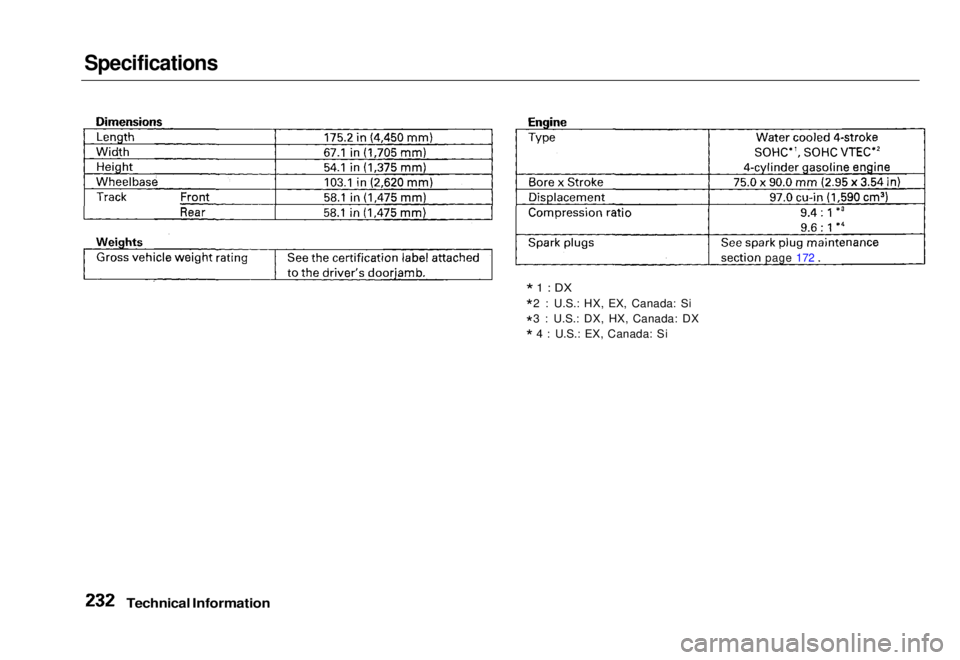
Specifications
*1 : DX
* 2 : U.S.: HX, EX, Canada: Si
* 3 : U.S.: DX, HX, Canada: DX
* 4: U.S.: EX, Canada: Si
Technical Information
page 172Main Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 233 of 251
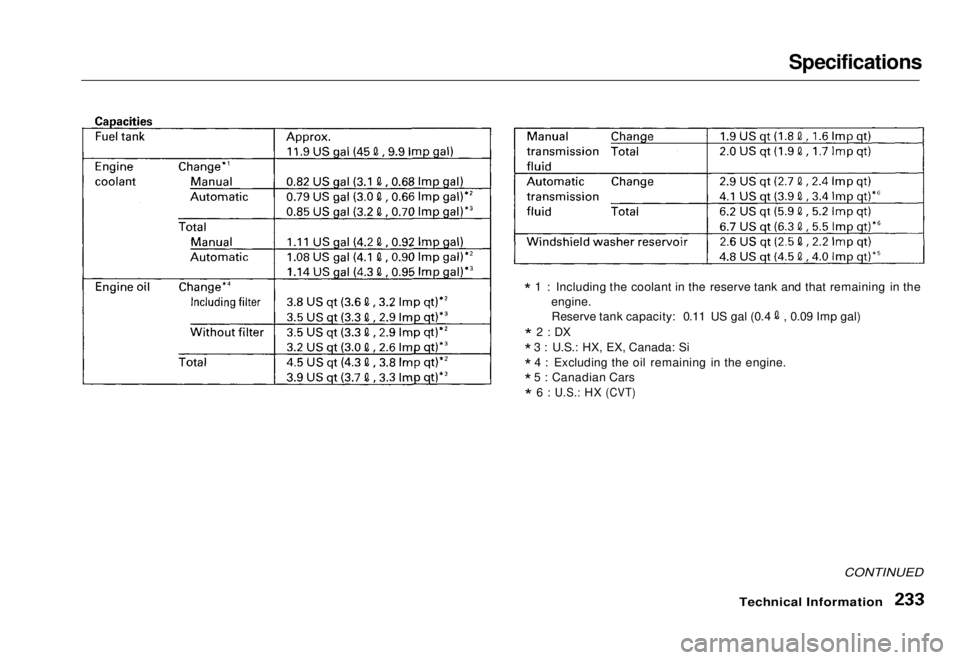
Specifications
* 1 : Including the coolant in the reserve tank and that remaining in the
engine. Reserve tank capacity: 0.11 US gal (0.4 , 0.09 Imp gal)
*
2
:
DX
* 3 : U.S.: HX, EX, Canada: Si
* 4 : Excluding the oil remaining in the engine.
* 5 : Canadian Cars
*
6
:
U.S.:
HX
(CVT)
CONTINUED
Technical InformationMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 234 of 251
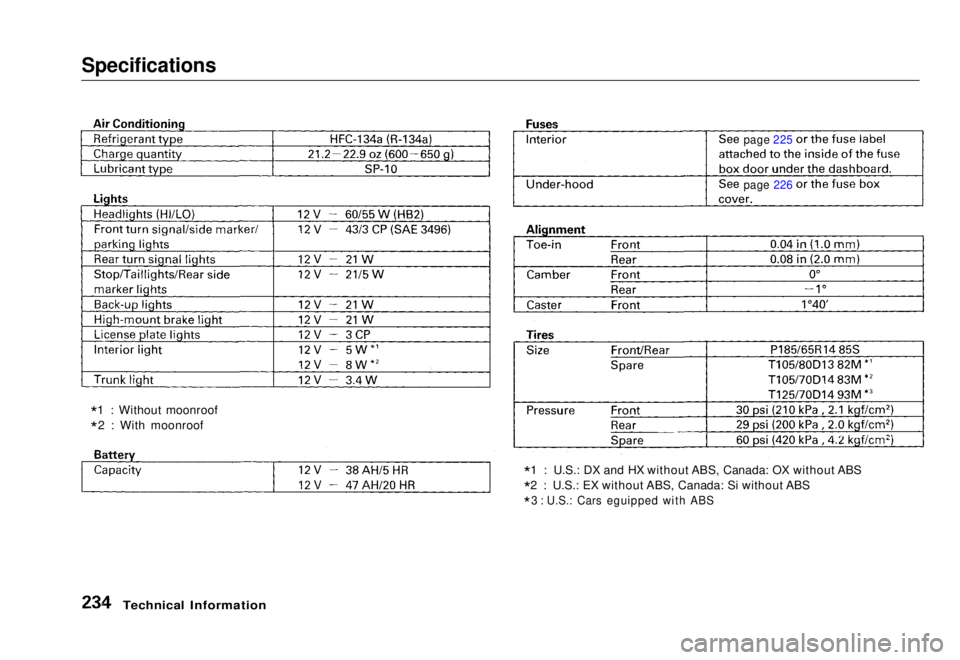
Specifications
*1 : U.S.: DX and HX without ABS, Canada: OX without ABS
* 2 : U.S.: EX without ABS, Canada: Si without ABS
* 3 : U.S.: Cars eguipped with ABS
Technical Information
*
1 : Without moonroof
* 2 : With moonroof
page 226 page 225Main Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 235 of 251
Tire Information
Tire Size Designation
A tire's sidewall is marked with a tire size designation. You will need this
information when selecting replace-
ment tires for your vehicle. The
following explains what the letters and numbers in the tire size
designation mean.
(Example tire size designation)
P185/65R14 85S
P — Applicable vehicle type (tires
marked with the prefix "P" are
intended for use on passenger
vehicles; however, not all tires have this marking).
185 — Tire width in millimeters.
65 — Aspect ratio. The tire's section
height as a percentage of its width.
R — Tire construction code (Radial).
14 — Rim diameter in inches. 85 — Load Index, a numerical code
associated with the maximum load
the tire can carry.
S — Speed Symbol. See the speed
rating chart in this section foradditional information.
Wheel Size Designation
Wheels are also marked with important information that you need
if you ever have to replace one. The
following explains what the letters and numbers in the wheel size
designation mean.
(Example wheel size designation)
14 x 5J
14 — Ri
m diameter in inches.
5 — Rim width in inches.
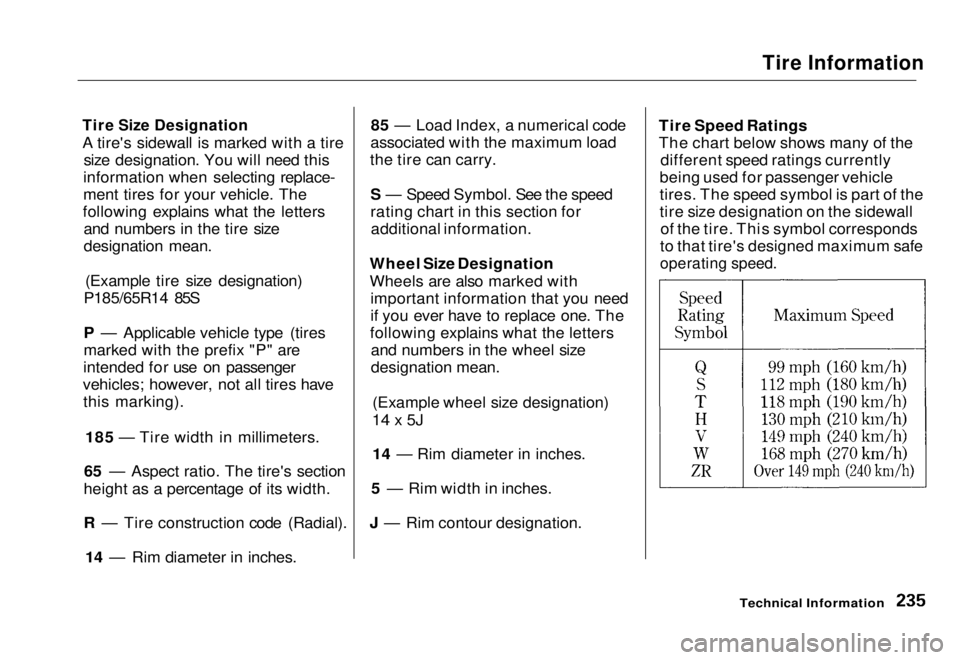
J — Rim contour designation. Tire Speed Ratings
The chart below shows many of the
different speed ratings currently
being used for passenger vehicle
tires. The speed symbol is part of the
tire size designation on the sidewall of the tire. This symbol corresponds
to that tire's designed maximum safe
operating speed.
Technical InformationMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 236 of 251

Tire Information
Tire Pressure Adjustment For
High Speed Driving
Honda strongly recommends that
you not drive faster than posted speed limits and conditions allow. If
you decide it is safe to drive at high speeds, be sure to adjust the cold tire
pressures as shown below. If you do
not adjust the tire pressure, exces- sive heat can build up and cause
sudden tire failure.
Be sure to readjust the pressure for
normal driving speeds. You should
wait until the tires are cold before
adjusting the tire pressure (see page
180).
DOT Tire Quality Grading
(U.S. Cars)
The tires on your car meet all U.S. Federal Safety Requirements. All
tires are also graded for treadwear, traction, and temperature perform-ance according to Department of
Transportation (DOT) standards.
The following explains these gradings.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a compara- tive rating based on the wear rate of
the tire when tested under controlledconditions on a specified government
test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and one
half (1-1/2) times as well on the
government course as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of
tires depends upon the actual condi-
tions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the normdue to variations in driving habits,
service practices, and differences in
road characteristics and climate.
Technical InformationMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 237 of 251
Tire Information
Traction
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are A, B, and C, and they
represent the tire's ability to stop on
wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified
government test surfaces of asphaltand concrete. A tire marked C may
have poor traction performance.
Warning: The traction grade as- signed to this tire is based on brak-
ing (straight ahead) traction tests
and does not include cornering (turning) traction.
Temperature
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing the
tire's resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability to dissipate heat
when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor
laboratory test wheel. Sustained high
temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce
tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The
grade C corresponds to a level of
performance which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal
Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent
higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the
minimum required by law. Warning: The temperature grade for
this tire is established for a tire that
is properly inflated and not over-
loaded. Excessive speed, underinfla- tion, or excessive loading eitherseparately or in combination, can
cause heat build-up and possible tire
failure.
Technical InformationMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 238 of 251
Oxygenated Fuels
Some conventional gasolines are
being blended with alcohol or an
ether compound. These gasolines
are collectively referred to as
oxygenated fuels. To meet clean air
standards, some areas of the United
States and Canada use oxygenated
fuels to help reduce emissions.
If you use an oxygenated fuel, be
sure it is unleaded and meets the
minimum octane rating requirement.
Before using an oxygenated fuel, try
to confirm the fuel's contents. Some
states/provinces require this
information to be posted on the
pump.
The following are the EPA-approved
percentages of oxygenates:
ETHANOL (ethyl or grain alcohol)
You may use gasoline containing up to 10 percent ethanol by volume.Gasoline containing ethanol may be
marketed under the name "Gasohol.''
MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether)
You may use gasoline containing up to 15 percent MTBE by volume.
METHANOL (methyl or wood
alcohol)
You may use gasoline containing up to 5 percent methanol by volume aslong as it also contains cosolvents
and corrosion inhibitors to protect
the fuel system. Gasoline containing more than 5 percent methanol by
volume may cause starting and/or performance problems. It may alsodamage metal, rubber and plastic
parts of your fuel system. If you notice any undesirable
operating symptoms, try another
service station or switch to another
brand of gasoline.
Fuel system damage or performance
problems resulting from the use of
an oxygenated fuel containing more
than the percentages of oxygenates
given above are not covered under
warranty.
Technical InformationMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 239 of 251
Driving In Foreign Countries
Technical Information
If you are planning to take your
Honda outside the U.S. or Canada,
contact the tourist bureaus in the
areas you will be traveling in to find out about the availability of unleaded
gasoline with the proper octane
rating.
If unleaded gasoline is not available,
be aware that using leaded gasoline in your Honda will affect perfor-
mance and fuel mileage, and damage
its emissions controls. It will no
longer comply with U.S. and Canadian emissions regulations, and
will be illegal to operate in North
America. To bring your vehicle back into compliance will require the re-
placement of several components, such as the oxygen sensors and the
three way catalytic converter. These
replacements are not covered under
warranty.Main Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 240 of 251
Emissions Controls
The burning of gasoline in your vehicle's engine produces several by-products. Some of these are carbon
monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC).
Gasoline evaporating from the tank
also produces hydrocarbons. Con-
trolling the production of NOx, CO, and HC is important to the environ-
ment. Under certain conditions ofsunlight and climate, NOx and HC
react to form photochemical "smog." Carbon monoxide does not contri-
bute to smog creation, but it is a
poisonous gas.
The Clean Air Act
The United States Clean Air Act*
sets standards for automobile
emissions. It also requires that
automobile manufacturers explain toowners how their emissions controls
work and what to do to maintain
them. This section summarizes how the emissions controls work.
Scheduled maintenance is on page
142.
* In Canada, Honda vehicles comply
with the Canadian Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (CMVSS) for
Emissions valid at the time they are
manufactured. Crankcase Emissions Control
System
Your vehicle has a Positive Crankcase Ventilation System. This
keeps gasses that build up in the engine's crankcase from going into
the atmosphere. The Positive Crank-
case Ventilation valve routes them
from the crankcase back to the intake manifold. They are thendrawn into the engine and burned.
Evaporative Emissions Control
System
As gasoline evaporates in the fuel tank, an evaporative emissions
control canister filled with charcoaladsorbs the vapor. It is stored in this
canister while the engine is off. After
the engine is started and warmed up, the vapor is drawn into the engine
and burned during driving.
Technical InformationMain Menu Table of Contents s t