brake HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: INTEGRA, Model: HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.GPages: 1681, PDF Size: 54.22 MB
Page 343 of 1681
t"iI
Emission Gontrol System
System Description
Three Way Catalytic Converter (TWCI
\
t
The emission control system includes a Three Way
Catalytic Converter (TWC), Positive Crankcase Ventilation
(PCV) system and Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control
system. The emission control system is designed to meet
tederal and state emission standards.
InsDeciion
!@@ Do not smoke during this procedure. Keep
any open llame away from your work area.
1. Start the engine. Hold the engine at 3,000 rpm with
no load {in Park or neutral) until the radiator fan
comes on, then let it idle.
2. Connect a tachometer.
Check and adjust the idle speed, if necessary (see
page '11-11 ! ).
Warm up and calibrate the CO meter according to the
meter manufacturer's instructions.
Check idle CO with rhe headlights, heater blower,
rear window defogger, cooling fan, and air condition-
er off.
NOTE: {Canada) Pull the parking brake lever up.
Start the engine, then check that the headlights are
olf.
CO meter should indicste 0.17o maximum.
DescriDtion
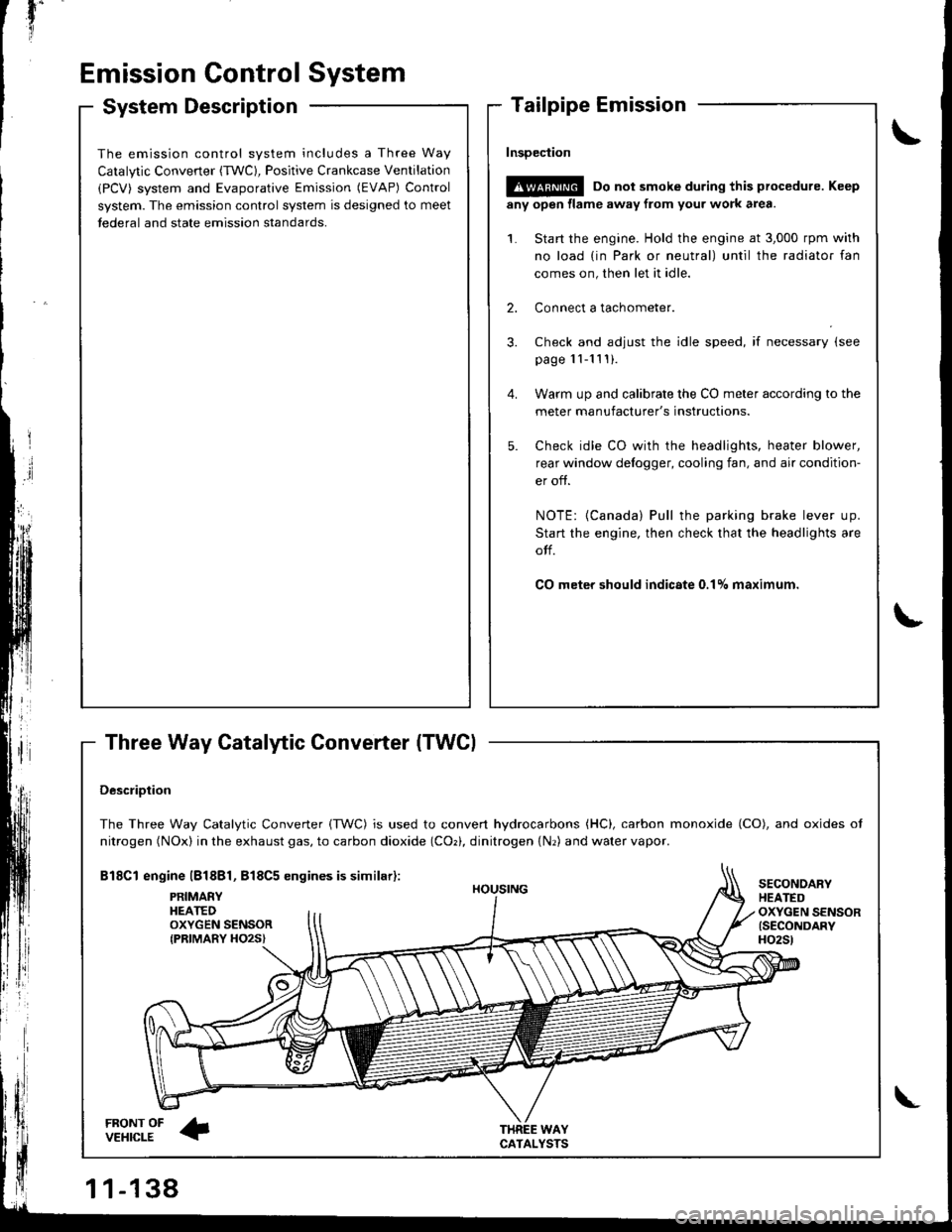
The Three Way Catalytic Converter {TWC) is used to convert hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of
nitrogen (NOx) in the exhaust gas, to carbon dioxide (COr), dinitrogen {Nr) and water vapor.
Bl8Cl engine l818Bl, 818C5 engines is similar):
FRONT OFVEHICLE
PRIMAEYHEATEDOXYGEN SENSORIPRIMARY HO2S}
HOUSING
WAYCATALYSTS
SECONOARYHEATEDOXYGEN SENSOR{SECONDARYH02St
\
Page 353 of 1681
Emission Control System
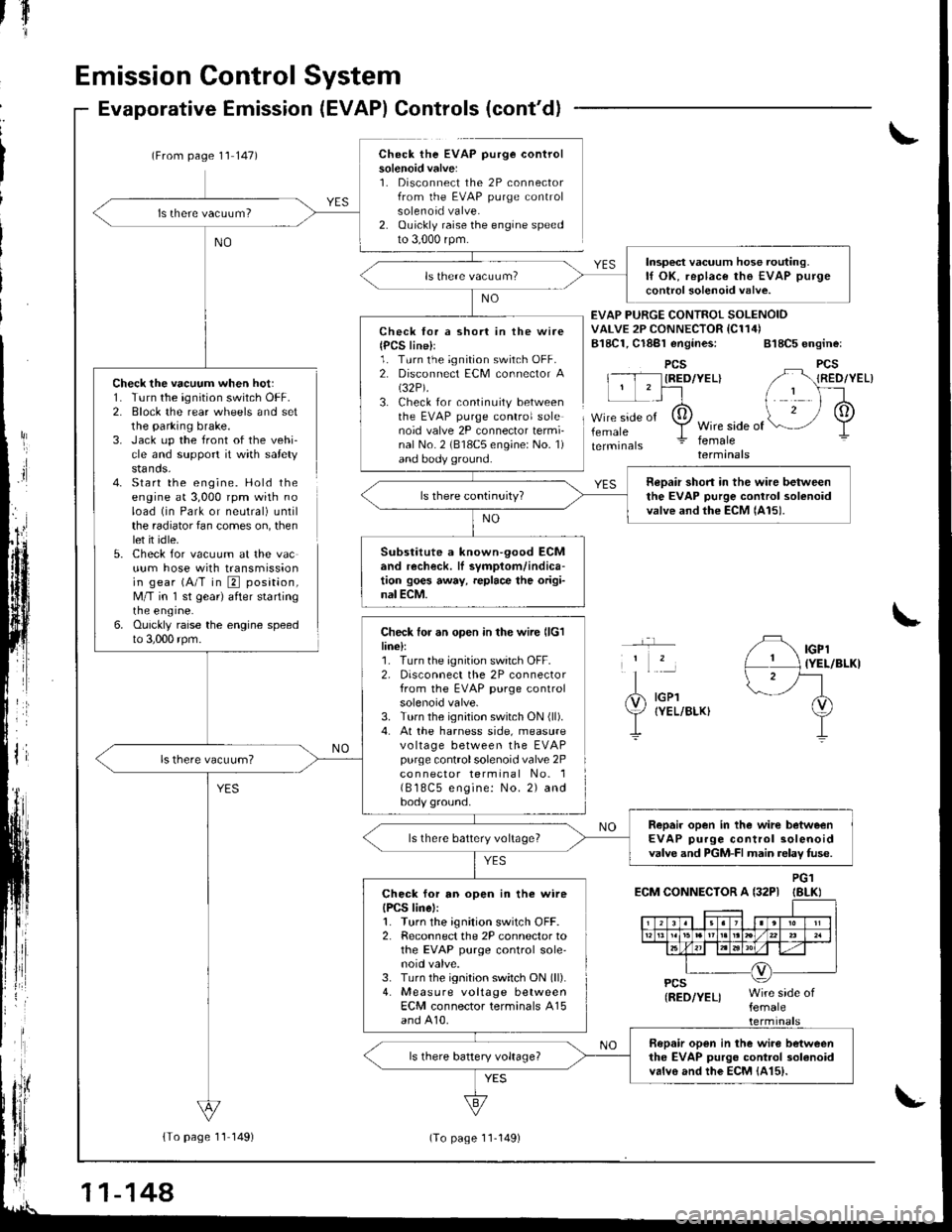
Check the vacuum when hot:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Block the rear wheels and setthe parking brake.3. Jack up the front of the vehi-cle and support it with safetystands.4- Start the engine. Hold theengine at 3,000 rpm with noload (in Park or neutral) untilthe radiator fan comes on, thenlet it idle.5. Check for vacuum at the vacuum hose with transmissionin gear (A/T in E position,M/T in 'l st gear) after startingrne engrne.6. Ouickly raise the engine speedto 3,000 rpm.
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls (cont'd)
(From page 1'l 147)Check the EVAP purge controlsolenoid valve:1. Disconnect the 2P connectorfrom the EVAP purge controlsolenoid valve.2. Ouickly raise the engine speedto 3,000 rpm.
{To page 11 149)
tfl'I
Check lor a short in the wire{PCS line}l1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect ECM connector A(32P).
3. Check for continuity betweenthe EVAP purge control solenoid valve 2P connector termi-nal No. 2 (818C5 engine: No. 1)and body ground.
Check for an open in the wire llclline):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2, Disconnect the 2P connectorfrom the EVAP purge controlsolenoid valve.3. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll).
4. At the harness side, measurevo ltage between the EVAPpurge controlsolenoid valve 2Pco n nector terminal No. 1( B 18C5 engine: No. 2) andbody ground.
EVAP PURGE CONTROI SOLENOIDVALVE 2P CONNECTOR IC114)B18C1, Cl8Bl engines: 818C5 engine:
PCSIRED/YEL}
femaleWire side offemaleterminals
YES
IGPl{YEL/BLKI
IGPlIYEL/BLKI
ECM CONNECTOR A {32PIPG1IBLKI
Insp€ct vacuum hose routing.lf OK, replace the EVAP purge
control solenoid valve.
neDair short in the wire betweenthe EVAP purge control solenoidvalve and the ECM lAl5).
Substitute a known-90od ECMand recheck. lI symptom/indica-tion goes away, replace the origi-nal ECM.
Repair open in the wirc betweenEVAP purge control solenoidvalve and PGM-FI main relav fuse.ls there battery voltage?
Check for an open in the wireIPCS linel:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Reconnect the 2P connector tothe EVAP purge control sole'noid valve.3. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll).
4. Measure voltage betweenECM connector terminals A15and A10.
Bopair open in the wiro betweenthe EVAP purgo control 3olanoidvalvo and the EcM {415).
11-144
(To page 11-149)
Page 362 of 1681
CAUTION:
a Do not 3pill brakefluid on the vehicle; it may damege
th€ paid; if brake fluid do63 contact th€ paint. wa3h
it otf immediately with water.
a Plug the end of the clutch pipe and reservoir hose with
a shop towel to prevent brake fluid from coming out.
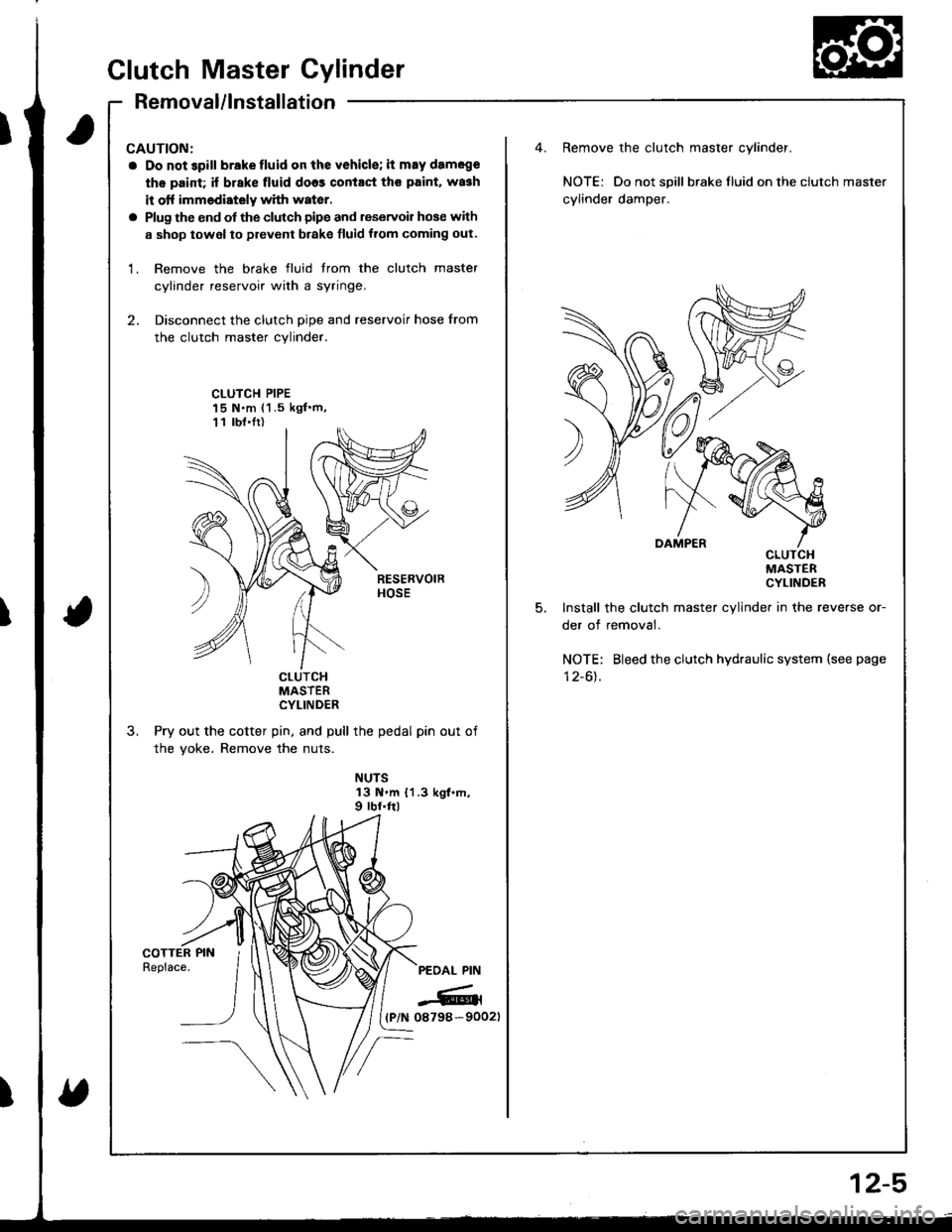
1. Remove the brake fluid trom the clutch master
cylinder reservoir with a syringe,
2. Disconnect the clutch pipe and reservoir hose from
the clutch master cylinder.
Remove the clutch master cylinder.
NOTE: Do not spill braketluid ontheclutch master
cylinder damper.
CLUTCH PIPE15 N.m {1 .5 kgf'm,11 lbt.Ir)
5.
cLulcHMASTERCYLINDER
Install the clutch master cylinder in the reverse or-
der of removal.
NOTE: Bleed the clutch hydraulic system {see page
I z-ol.cturcHMASTERCYLINDER
Pry out the cotter pin, and pull the pedal pin out of
the yoke. Remove the nuts.
NUTS13 N.m {1.3 kgt.m,9 rbf.ftl
PEOAL PIN
-6rl(P/N 08798-90021
Clutch Master Cylinder
Removal/lnstallation
2-5
Page 363 of 1681
T
fi
;ill
Slave Cylinder
Removal/lnstallation
CAUTION:
a Do not spill brakelluid onthe vehicle; it may dameg€
the paint; if brake fluid does coniaqt the paint, wash
it otf immodiaioly wilh w8ter.
a Plug the end of the clutch pipe with a shop towel to
prevent brake fluid from coming out.
-6|1, Super High Temp Urea Grease (P/N
4==? 08798- 9OO2).-='aii^5Fi: Brake Assembly Lube or equivalent rubber
grease.
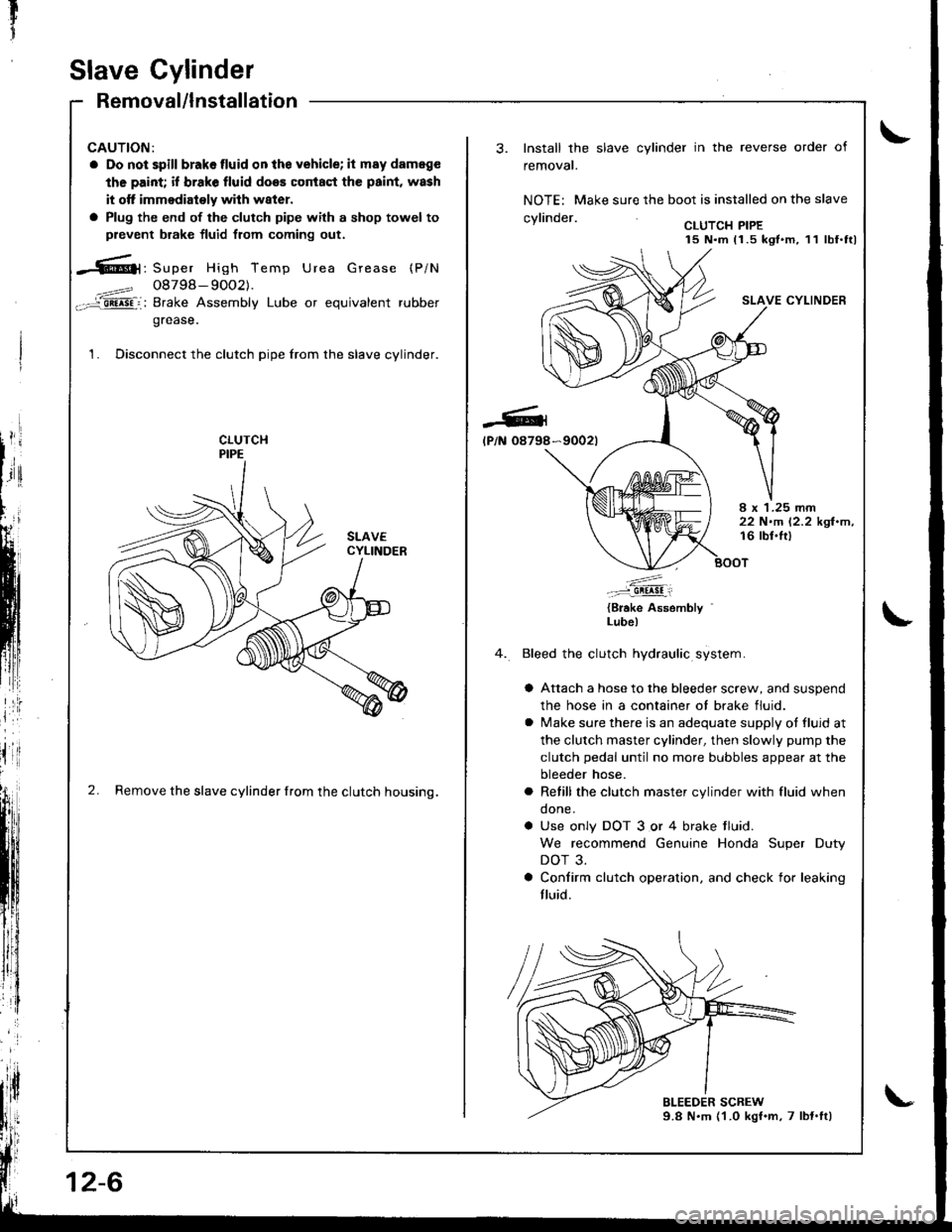
1. Disconnect the clutch pipe from the slave cylinder.
2. Remove the slave cylinder from the clutch housing.
12-6
-Gl
lP/N 08798
Install the slave cylinder in the reverse order of
removal.
NOTE: Make sure the boot is installed on the slave
.wlin.larCLUTCH PIPE15 N.m 11.5 kgt.m, 11 lbf.ttl
SLAVE CYLINDER
*9002t
I x 1.25 rnm22 N.m 12.2 kgl.m,16 lbl.lt)
.'....-..-:::-9!!!!!i
{Brake Assembly '
Lube)
Bleed the clutch hydraulic system.
a Attach a hose to the bleeder screw, and suspend
the hose in a container ot brake fluid.
a lvlake sure there is an adequate supply ot fluid at
the clutch master cylinder, then slowly pump the
clutch pedal until no more bubbles appear at the
bleeder hose.
a Refill the clutch master cylinder with fluid when
done.
a Use only DOT 3 or 4 brake tluid.
We recommend Genuine Honda Super Duty
DOT 3.
a Confirm clutch operation. and check for leaking
fluid.
Page 373 of 1681
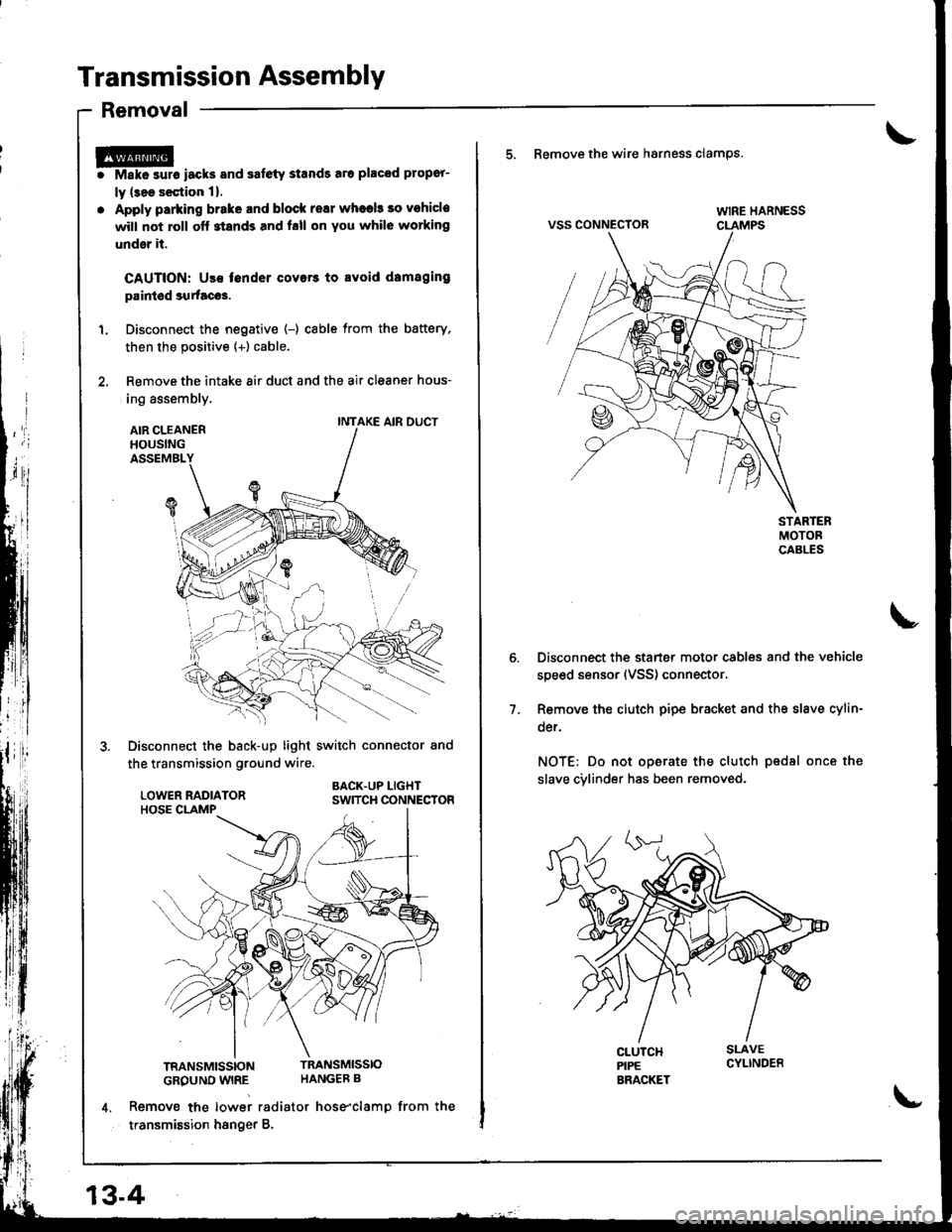
Transmission Assembly
Removal
r@i Make surs iacks and safety stands sro placod propor-
ly (3ee s€ction 1).
. Apply parking brake and block resr whaeb 30 vohicle
will not roll off stands and hll on You whil6 working
under it.
CAUTION: Use fender covers to svoid damaging
paintod surtacos.
1. Disconnect the negative (-) cable from the battery,
then the positive {+) cable.
2. Remove the intake 8ir duct and the air cleaner hous-
ing assembly,
AIR CLEANERHOUSINGASSEMBL
Disconnect the back-up light switch connector and
the transmission ground wire.
BACK.UP LIGHTSWITCH CONNECTOR
TRANSMISSIONTRANSMISSIO
GROUND WIRE HANGEB B
4. Remove tne lowei radiator hose"clamp from the
transmission hsnger B.
INTAKE AIR DUCT
13-4
\-
5. Remove the wire hsrness clamps.
VSS CONNECTOR
Disconnect the starter motor cables and the vehicle
speed sensor (VSS) connector.
Remove the clutch pipe bracket and the slave cylin-
der.
NOT€: Do not operate the clutch pedsl once the
slave cvlinder has been removed.
7.
Page 418 of 1681

Automatic Transmission
Special Tools ................ '14-2
Descraption .................... 14-3
Clutches ............ ...... 14-6
Power Flow ..,........... 14-8
Electronic Control System ..................... 1 4-1 8
Hydraulic Control ...... 14-23
Hydraulic Flow .........- 14-28
Lock-up System ........ 14-38
Electrical System
Component Location -................................ 1 4-45
Circuit Diagram ............. 14-46
TCM Terminal Voltage/
Measuring Conditions ......,.................... 1 4-48
Troubleshooting Procedures .. . ... ........ ...... ... 14-50
Symptom-to-Component Chart
Electrical System ...... 14-54
Electrical Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Flowcharts .......... ... ...,.. 14-56
Lock-up Control Solenoid Valve A/B Assembly
Test .................. ...... 14-A7
Replacement ............. 14-a7
Shilt Control Solenoid Valve A/B Assembly
Test .................. ...... '14-88
Replacement .,..,........ 14-88
lvlainshaf t/Countershaft Speed Sensors
Replacement ....-......,. 14-89
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Replacement ............. 14-89
Hydraulic System
Symptom-to-Component Chart
Hydraulic System ...... 14-90
Road Test ,................... 14-94
Stall Speed
Test .................. ...... 14-97
Fluid Level
Checking/Changing .... 14-98
Pressure Testing ........... 14-99
Transmission
Transmission
Removal ............. ...... 14-10�4
lllustrated lndex
Transmission/Right Side Cover ............... 1 4-1 08
Transmission Housin9 ................,..,....... 1 4-1'1 O
Torque Converter Housing/ValveBody .................. .. 14-112
Right Side Cover
Removal ............. ...... 14-114
Transmission Housing
Removal ............. ...... 14-1 l6
Torque Converter Housing/Valve Body
Removal ............. ...... l4-1 18
Valve Caps
Description ...........-... 14-120
Valve Body
Repair ................ ...... 14-12'l
Valve
Assembly
ATF Pump
Inspeclton
Main Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Regulator Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Lock-up Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Secondary Valve Body
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly
Servo Body
....... 14-124
....... 14-126
....... 14-127
....... 14 124
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly .......
1st-hold Accumulator/Right Side Cover
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly .......
Mainsha{t
14-130
14-132
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ....... 14-133
Inspection ................. 14-134
Countershaft
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly,..,.., l4-136
Disassembly/Reassembly ..,...,..,.........,,.. 1 4-1 37
Inspection ......,...,..,... 14-138
One-way Clutch
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ....,.. 14-141
Sub-shaft
Disassembly/lnspection/Reassembly ...,,..'14-142
Disassembly/Reassembly ....................... 1 4- l 43
Sub-shaft Bearings
Replacement ,..,,.,,..,.. 14-144
Clutch
lllustrated Index ................................... I 4-1 45
Disassembly ............. 14-144
Reassembly .............. 14-150
Torque Converter Housing Bearings
Mainshaft Bearing/Oil Seal
Replacement ......... 14-154
Countershaft Bearing Replacement ......... 1 4- 1 55
Transmission Housing Bearings
Mainshaft/Countershaft BearingReplacement ......,.. 14-'156
Sub-shaft Bearing Replacement .,............ 1 4-1 57
Reverse ldler Gear
Installation .........-..... 14-158
Parking Brake Stop
Inspection/Adjustment .......................... 1 4-1 58
Transmission
Reassembly .............. 14-160
Torque Converler/Drive Plate ..............,.,,.,, 1 4-1 67
Transmission
Installation ............... 14-168
Cooler Flushing ......... 14-172
ATF Cooler Hoses
Connection ,..,,,....,,.,, '14-'174
*shift cable
Removal/lnstallation . . .. .... ... .... ... .... .. . ... .. 14-'l75
Adjustment ,..,...,,,,.,, 14-'116*Shilt lever
Disassembly/Reassembly ....................... 1 4-'17 7'Shift Indicator Panel
Adjustment .............. 14-178
\l
)g
Page 421 of 1681

Description
{cont'd)
Gsar Selection
The shift lever has seven positions; @ PARK, E REVERSE, N NEUTRAL. [Dt l st through 4th ranges, @ 1st through
3rd ranges, @ 2nd gear and [ 1sr gear.
Starting is possible only in @ and N positions through use of a slide-type, neutral-safety switch.
Automatic Transaxle (A/T) Gear Position Indicator
A/T gear position indicator in the instrument panel shows what gear has been selected without having look down at
the console.
PositionDescription
E PARK
E REVERSE
N NEUTRAL
[p"l DRrvE
('lst through 4th)
I p3l DRrvE
(1st through 3rd)
E sEcoND
E FIRST
F.ont wheels locked; parking brake pawl engaged with parking gear on countershaft. All clutches
released.
Reverse; reverse selector engaged with countershatt reverse gear and 4th clutch locked.
All clulches released.
General driving; sta.ts o{f in 1st, shitts automatically to 2nd, 3rd, then 4th, depending on vehicle
speed and throttle positlon. Downshifts through 3rd, 2nd and 1st on deceleration to stop.
The lock-up mechanism comes into operation in @ in Zna, 3rd and 4th gear.
For rapid acceleration at highway speeds and general driving; starts otf in 1st, shifts automatical-
ly to 2nd then 3rd, depending on vehicle speed and throttle position. Downshifts through lowe.gears on deceleration to stop. The lock-up mechanism comes into operation in 3rd gear.
Driving in 2nd geat; stays in 2nd gear. does not shift up and down.
For engine braking or better traction starting otl on loose or slippery surlece.
Driving in 1st gear; stays in 1st gear, does not shift up.
For engine braking.
14-4
{
Page 426 of 1681
![HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.G User Guide l
t
LNI Position
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft.
[] Position
Hydrsulic pressure is not applied 10 the clutches. Power is not transmitt HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.G User Guide l
t
LNI Position
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft.
[] Position
Hydrsulic pressure is not applied 10 the clutches. Power is not transmitt](/img/13/6069/w960_6069-425.png)
l'
t
LNI Position
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft.
[] Position
Hydrsulic pressure is not applied 10 the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft.
The countershaft is locked by the parking brake pawl interlocking the parking gear.
TOROUE CONVERTEB
PARKING GEAR
REVERSE SELECTOR
REVERSE GEAR
REVERSE SEI.ECTORHUB
SERVO VALVE/SHIFT FORK SHAFT
{cont'd)
14-9
Page 438 of 1681
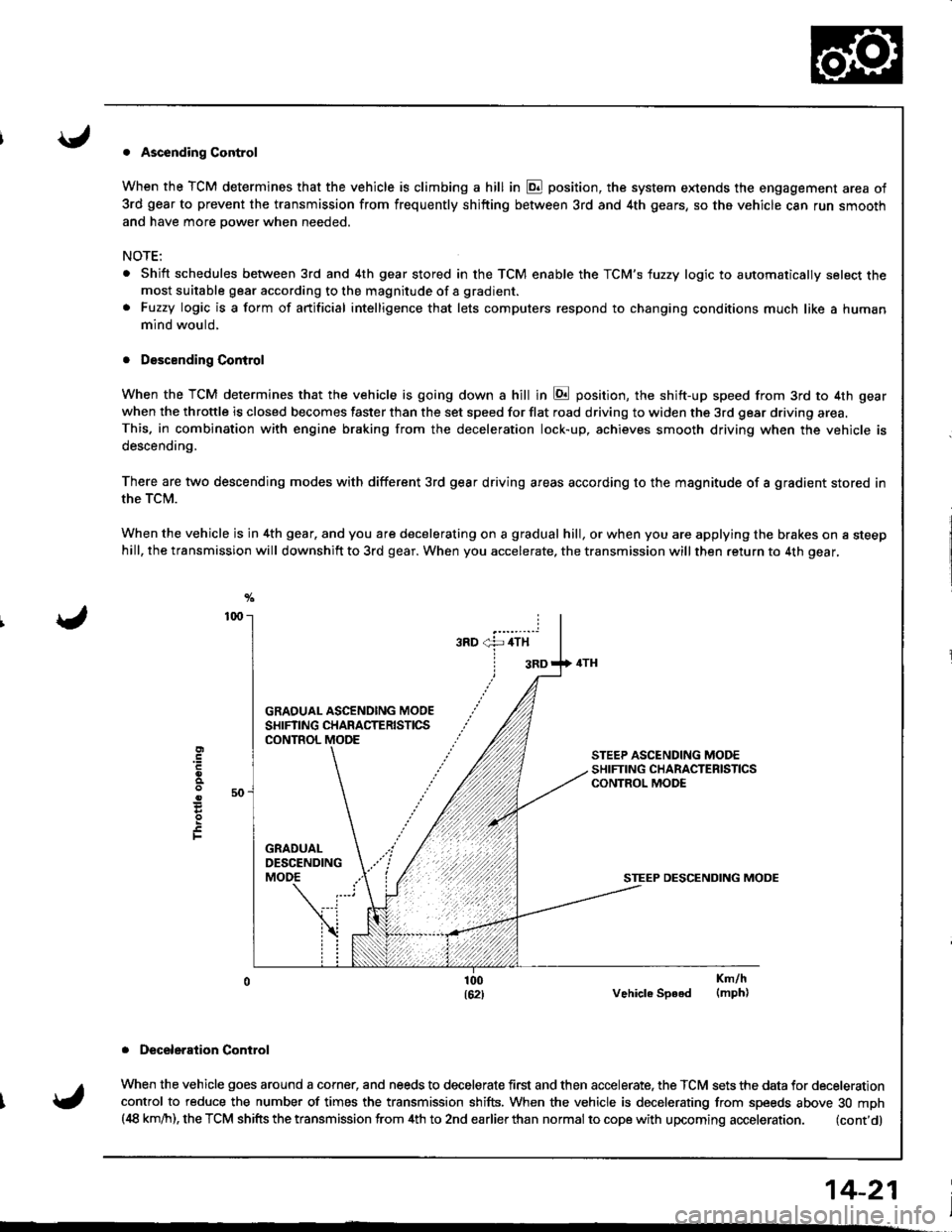
. Ascending Control
When the TCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E position, the system extends the engagement area of
3rd gear to prevent the transmission from frequently shifting between 3rd and 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth
and have more power when needed,
NOTE:
Shift schedules between 3rd and 4th gear stored in the TCM enable the TCM'S fuzzy logic to automatically select themost suitable gear according to the magnitude of a gradient.
Fuzzy logic is a form of artificial intelligence that lets computers respond to changing conditions much like a human
mind would,
. Descending Control
When the TCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in E position, the shift-up speed from 3rd to 4th gear
when the throttle is closed becomes faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear driving area.This. in combination with engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle is
descending,
There are two descending modes with different 3rd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradient stored in
the TCM.
When the vehicle js in 4th gear, and you are decelerating on a gradual hill, or when you are applying the brakes on a steephill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear. When you accelerate, the transmission will then return to 4th gear,
GRAOUAL ASCENOING MOOESHIFTING CHARACTERISTICSCONTROL
STEEP DESCENDING MODE
Vehicle Speed
. Deceleraiion Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner, and needs to decelerate first and then accelerate. the TCM sets the data for deceleration
control to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 30 mph(,18 km/h), the TCM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlierthan normal to cope with upcoming acceleration. (cont'd)
E
F
Km/h(mph)
14-21
Page 465 of 1681
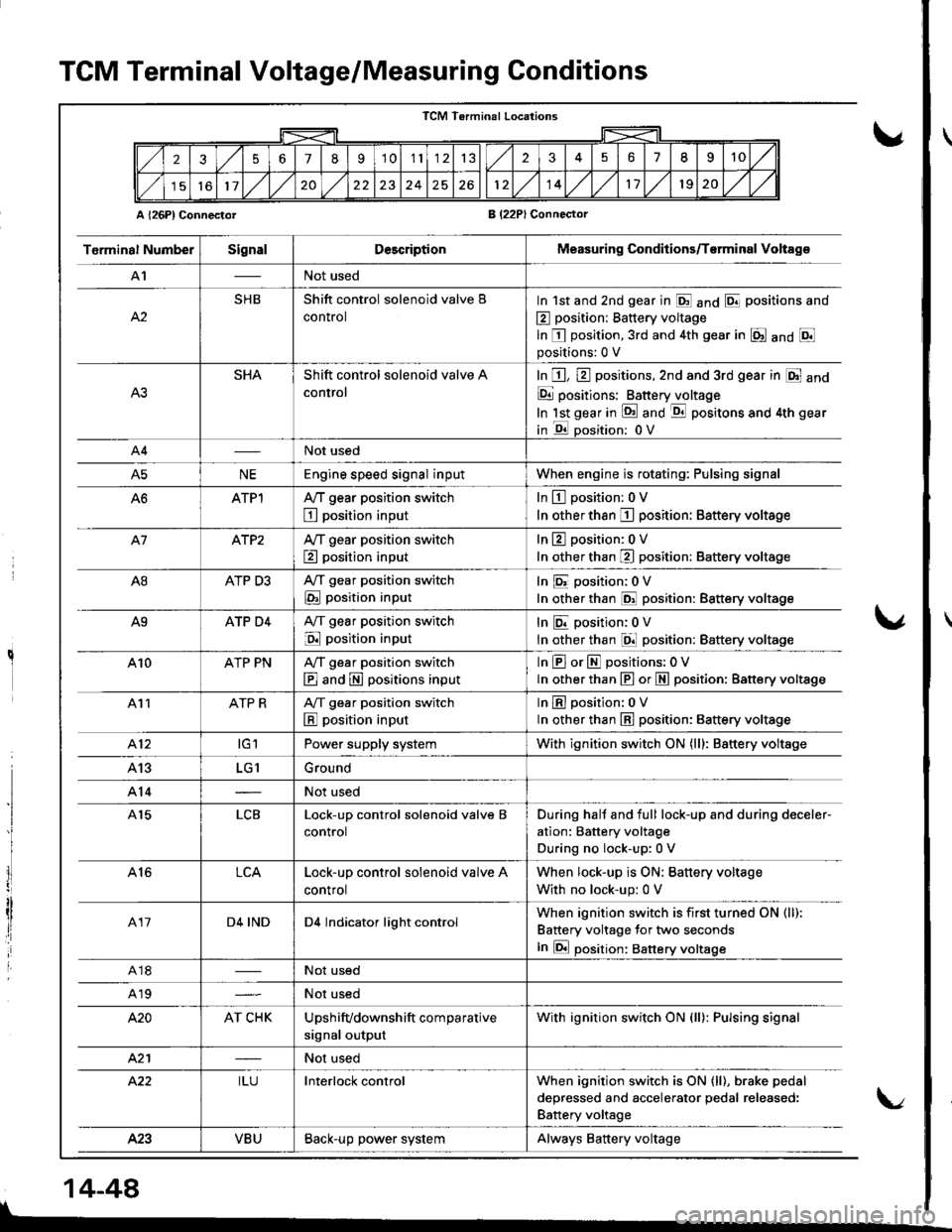
TCM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Conditions
A l26Pl ConnectorB (22PlConnector
TCM Terminal Locations
256789'1011132351II10
11,/l/2024261214,/l/1120,/1,/
T6rminal NumberSignalDescriptionMeasuring Conditions/T€rminal Voltag€
A'INot used
A2
SHBShift control solenoid valve B
control
In 1st and 2nd gear in E anO E positions and
E position: Battery voltage
ln E position,3rd and 4th gear in E anO Epositions:0 V
SHAShift control solenoid valve A
control
In E, E positions,2nd and 3rd gear in E and
E positions: Batteryjloltage
In lst gear in !d and -qtl positons and 4th gear
in E oosition: 0V
A4Not used
A5NEEngine speed signal inputWhen engine is rotating: Pulsing signal
ATPlA,/T gear position switch
E position input
In L!-l position: 0 V
In other than I position: Battery voltage
A7ATP2Ay'T gear position switch
E position input
In 13 position:0 V
In other than E position: Battery voltage
A8ATP D3A,/T gear position switch
E position input
In E position:0V
In other than @ position: Battery voltage
A9ATP D4A,/T gear position switch
E position input
InEposition;0V
In other than El position: Battery voltage
410ATP PNA,/T gear position switch
E and E positions input
InEorEpositions:OV
In other than E or N position: Battery vottage
411ATP RA/T gear position switch
E position input
lnEposition: oV
ln other than E position: 8attery voltage
412tGlPower supply systemWith ignition switch ON (lll: Battery voltage
413LG1Ground
A14Not used
A15LCBLock-up control solenoid valve B
control
During hall and full lock-up and during deceler-
ation: Battery voltage
During no lock-up:0 V
A16LCALock-up control solenoid valve A
control
When lock-up is ON; Battery voltage
With no lock-up: 0 V
417D4 INDD4 Indicator light controlWhen ignition switch is first turned ON (ll):
Battery voltage for two seconds
In E position: Battery voltsge
A18Not used
A19Not used
420AT CHKUpshifvdownshift comparative
signal output
With ignition switch ON (ll): Pulsing signal
421Not used
422ILUInterlock controlWhen ignition switch is ON (ll), brake pedal
deoressed and accelerator oedal released:
Battery voltage
423VBUBack-up power systemAlways Battery voltage
I
lI
I
14-44
\/