light ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2201 of 6020
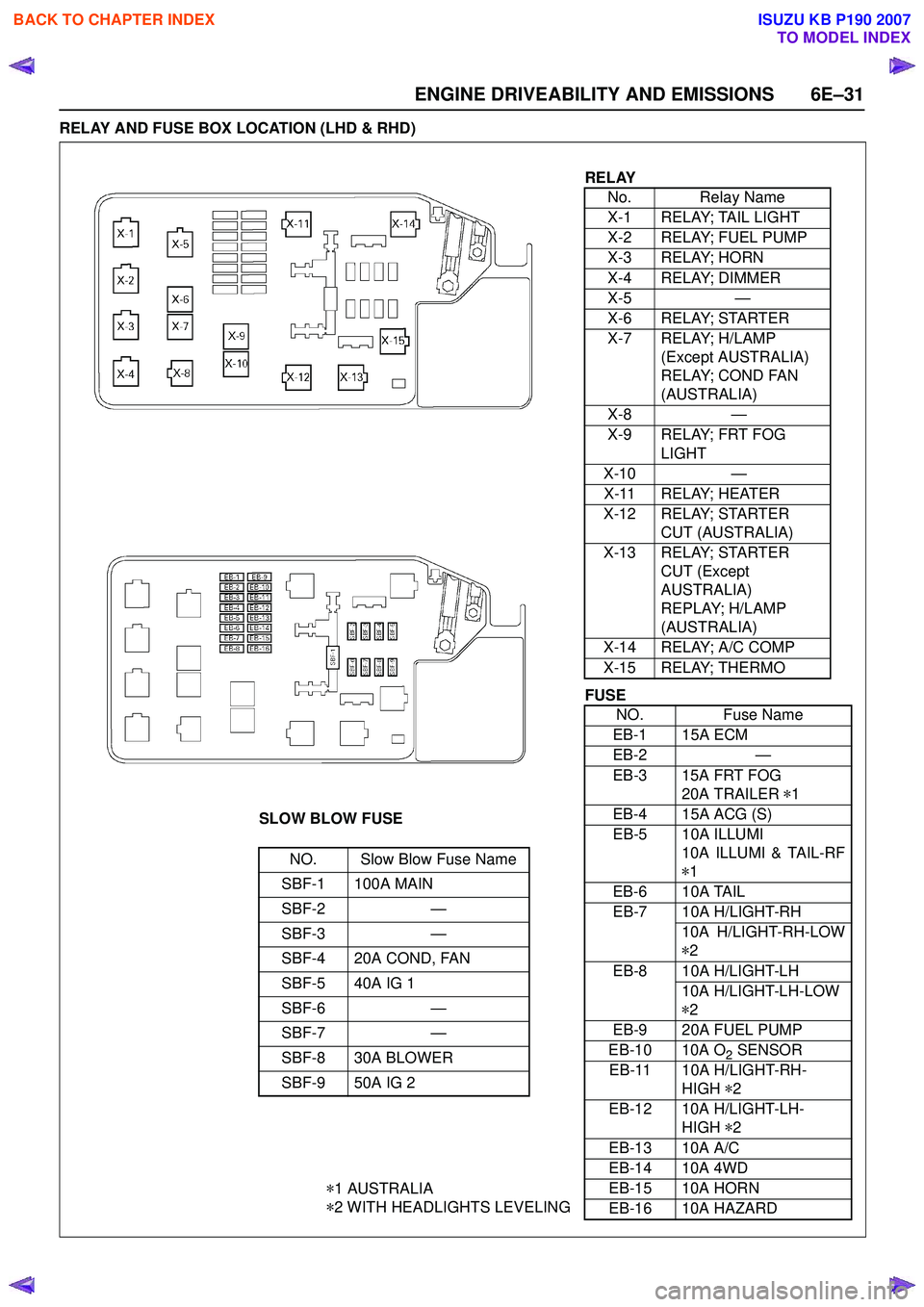
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–31
RELAY AND FUSE BOX LOCATION (LHD & RHD)
RELAYNo. Relay Name
X-1 RELAY; TAIL LIGHT
X-2 RELAY; FUEL PUMP
X-3 RELAY; HORN
X-4 RELAY; DIMMER
X-5 —
X-6 RELAY; STARTER
X-7 RELAY; H/LAMP (Except AUSTRALIA)
RELAY; COND FAN
(AUSTRALIA)
X-8 —
X-9 RELAY; FRT FOG LIGHT
X-10 —
X-11 RELAY; HEATER
X-12 RELAY; STARTER CUT (AUSTRALIA)
X-13 RELAY; STARTER CUT (Except
AUSTRALIA)
REPLAY; H/LAMP
(AUSTRALIA)
X-14 RELAY; A/C COMP
X-15 RELAY; THERMO
SLOW BLOW FUSE
NO. Slow Blow Fuse Name
SBF-1 100A MAIN
SBF-2 —
SBF-3 —
SBF-4 20A COND, FAN
SBF-5 40A IG 1
SBF-6 —
SBF-7 —
SBF-8 30A BLOWER
SBF-9 50A IG 2
* 1 AUSTRALIA
* 2 WITH HEADLIGHTS LEVELING
FUSE
NO. Fuse Name
EB-1 15A ECM
EB-2 —
EB-3 15A FRT FOG 20A TRAILER *1
EB-4 15A ACG (S)
EB-5 10A ILLUMI 10A ILLUMI & TAIL-RF
* 1
EB-6 10A TAIL
EB-7 10A H/LIGHT-RH 10A H/LIGHT-RH-LOW
* 2
EB-8 10A H/LIGHT-LH 10A H/LIGHT-LH-LOW
* 2
EB-9 20A FUEL PUMP
EB-10 10A O
2 SENSOR
EB-11 10A H/LIGHT-RH- HIGH *2
EB-12 10A H/LIGHT-LH- HIGH *2
EB-13 10A A/C
EB-14 10A 4WD
EB-15 10A HORN
EB-16 10A HAZARD
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2224 of 6020
6E–54 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ELECTRIC
IGNITION SYSTEM
The engine use two ignition coils, one per two cylinders.
A two wire connector provides a battery voltage primary
supply through the ignition fuse.
The ignition control spark timing is the ECM’s method of
controlling the spark advance and the ignition dwell.
The ignition control spark advance and the ignition dwell
are calculated by the ECM using the following inputs.
• Engine speed
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
• Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
• Throttle position sensor
• Vehicle speed sensor
• ECM and ignition system supply voltage
Ignition coil works to generate only the secondary
voltage be receiving the primary voltage from ECM.
The primary voltage is generated at the coil driver
located in the ECM. The coil driver generate the primary
voltage based on the crankshaft position signal. In
accordance with the crankshaft position signal, ignition
coil driver determines the adequate ignition timing and
also cylinder number to ignite.
Ignition timing is determined the coolant temperature,
intake air temperature, engine speed, engine load,
knock sensor signal, etc.
Spark Plug
Although worn or dirty spark plugs may give satisfactory
operation at idling speed, they frequently fail at higher
engine speeds. Faulty spark plugs may cause poor fuel
economy, power loss, loss of speed, hard starting and
generally poor engine performance. Follow the
scheduled maintenance service recommendations to
ensure satisfactory spark plug performance. Refer to
Maintenance and Lubrication .
Normal spark plug operation will result in brown to
grayish-tan deposits appearing on the insulator portion
of the spark plug. A small amount of red-brown, yellow,
and white powdery material may also be present on the
insulator tip around the center electrode. These
deposits are normal combustion by-products of fuels
and lubricating oils with additives. Some electrode wear
will also occur. Engines which are not running properly
are often referred to as “misfiring.” This means the
ignition spark is not igniting the air/fuel mixture at the
proper time. While other ignition and fuel system causes
must also be considered, possible causes include
ignition system conditions which allow the spark voltage
to reach ground in some other manner than by jumping
across the air gap at the tip of the spark plug, leaving
the air/fuel mixture unburned. Misfiring may also occur
when the tip of the spark plug becomes overheated and
ignites the mixture before the spark jumps. This is
referred to as “pre-ignition.”
Spark plugs may also misfire due to fouling, excessive
gap, or a cracked or broken insulator. If misfiring occurs before the recommended replacement interval, locate
and correct the cause.
Carbon fouling of the spark plug is indicated by dry,
black carbon (soot) deposits on the portion of the spark
plug in the cylinder. Excessive idling and slow speeds
under light engine loads can keep the spark plug
temperatures so low that these deposits are not burned
off. Very rich fuel mixtures or poor ignition system output
may also be the cause. Refer to DTC P1167.
Oil fouling of the spark plug is indicated by wet oily
deposits on the portion of the spark plug in the cylinder,
usually with little electrode wear. This may be caused by
oil during break-in of new or newly overhauled engines.
Deposit fouling of the spark plug occurs when the
normal red-brown, yellow or white deposits of
combustion by-products become sufficient to cause
misfiring. In some cases, these deposits may melt and
form a shiny glaze on the insulator around the center
electrode. If the fouling is found in only one or two
cylinders, valve stem clearances or intake valve seals
may be allowing excess lubricating oil to enter the
cylinder, particularly if the deposits are heavier on the
side of the spark plug facing the intake valve.
Excessive gap means that the air space between the
center and the side electrodes at the bottom of the
spark plug is too wide for consistent firing. This may be
due to improper gap adjustment or to excessive wear of
the electrode during use. A check of the gap size and
comparison to the gap specified for the vehicle in
Maintenance and Lubrication will tell if the gap is too
wide. A spark plug gap that is too small may cause an
unstable idle condition. Excessive gap wear can be an
indication of continuous operation at high speeds or
with engine loads, causing the spark to run too hot.
Another possible cause is an excessively lean fuel
mixture.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2235 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–65
Step 3: Simulate the symptom and isolate the
problem
Simulate the symptom and isolate the system by
reproducing all possible conditions suggested in Step 1
while monitoring suspected circuits/components/
systems to isolate the problem symptom. Begin with the
most logical circuit/component.
Isolate the circuit by dividing the suspect system into
simpler circuits. Next, confine the problem into a smaller
area of the system. Begin at the most logical point (or
point of easiest access) and thoroughly check the
isolated circuit for the fault, using basic circuit tests.
Hints
You can isolate a circuit by:
• Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to separate one part of the circuit from another
• If only component fails to operate, begin testing the component
• If a number of components do not operate, begin test at areas of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches, main connectors or major
components)
• Substitute a known good part from the parts department or the vehicle system
• Try the suspect part in a known good vehicle
See Symptom Simulation Tests on the next page for
problem simulation procedures. Refer to service manual
sections 6E and 8A for information about intermittent
diagnosis. Follow procedures for basic circuit testing in
service manual section 8A.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
• Service manual
• Bulletins
• Digital multimeter (with a MIN/MAX feature)
• Tech II and Tech II upload function
• Circuit testing tools (including connector kits/ harnesses and jumper wires)
• Experience
• Intermittent problem solving simulation methods
• Customer complaint check sheet
Symptom Simulation Tests
1. Vibration
This method is useful when the customer complaint
analysis indicates that the problem occurs when the
vehicle/system undergoes some form of vibration.
For connectors and wire harness, slightly shake
vertically and horizontally. Inspect the connector joint
and body for damage. Also, tapping lightly along a
suspected circuit may be helpful. For parts and sensors, apply slight vibration to the part
with a light tap of the finger while monitoring the system
for a malfunction.
2. Heat
This method is important when the complaint suggests
that the problem occurs in a heated environment. Apply
moderate heat to the component with a hair drier or
similar tool while monitoring the system for a
malfunction.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid overheating
the component.
3. Water and Moisture
This method may be used when the complaint suggests
that the malfunction occurs on a rainy day or under
conditions of high humidity. In this case, apply water in a
light spray on the vehicle to duplicate the problem.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid directly
exposing electrical connections to water.
4. Electrical loads
This method involves turning systems ON (such as the
blower, lights or rear window defogger) to create a load
on the vehicle electrical system at the same time you
are monitoring the suspect circuit/component.
5e. Vehicle Operates as Designed
This condition refers to instances where a system
operating as designed is perceived to be unsatisfactory
or undesirable. In general, this is due to:
• A lack of understanding by the customer
• A conflict between customer expectations and vehicle design intent
• A system performance that is unacceptable to the customer
What you should do
You can verify that a system is operating as designed
by:
• Reviewing service manual functional/diagnostic checks
• Examining bulletins and other service information for supplementary information
• Compare system operation to an identical vehicle
If the condition is due to a customer misunderstanding
or a conflict between customer expectation and system
operation, you should explain the system operation to
the customer.
If the complaint is due to a case of unsatisfactory
system performance, you should contact Technical
Assistance for the latest information.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the diagnostic process:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2264 of 6020
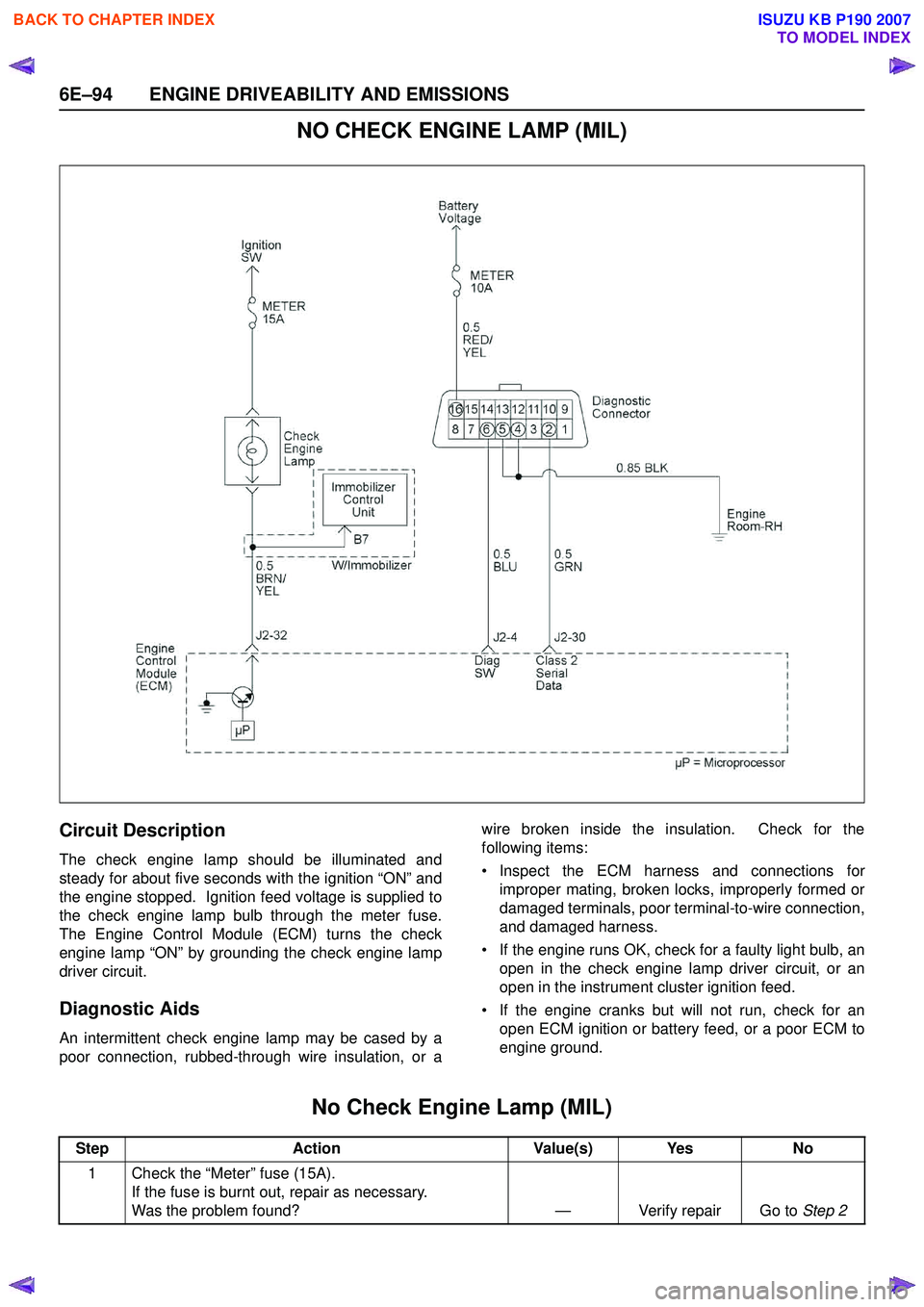
6E–94 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
NO CHECK ENGINE LAMP (MIL)
Circuit Description
The check engine lamp should be illuminated and
steady for about five seconds with the ignition “ON” and
the engine stopped. Ignition feed voltage is supplied to
the check engine lamp bulb through the meter fuse.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) turns the check
engine lamp “ON” by grounding the check engine lamp
driver circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent check engine lamp may be cased by a
poor connection, rubbed-through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside the insulation. Check for the
following items:
• Inspect the ECM harness and connections for improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal-to-wire connection,
and damaged harness.
• If the engine runs OK, check for a faulty light bulb, an open in the check engine lamp driver circuit, or an
open in the instrument cluster ignition feed.
• If the engine cranks but will not run, check for an open ECM ignition or battery feed, or a poor ECM to
engine ground.
No Check Engine Lamp (MIL)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Check the “Meter” fuse (15A). If the fuse is burnt out, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 2
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2279 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–109
• The fuel injector(s).
4. Fuel pressure that drops off during acceleration, cruise, or hard cornering may case a lean condition.
A lean condition can cause a loss of power, surging,
or misfire. A lean condition can be diagnosed using a
Tech 2 Scan Tool.
Following are applicable to the vehicle with
closed Loop System:
If an extremely lean condition occurs, the oxygen
sensor(s) will stop toggling. The oxygen sensor
output voltage(s) will drop below 500 mV. Also, the
fuel injector pulse width will increase.
Important: Make sure the fuel system is not
operating in the “Fuel Cut-Off Mode.”
When the engine is at idle, the manifold pressure is
low (high vacuum). This low pressure (high vacuum)
is applied to the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm.
The low pressure (high vacuum) will offset the
pressure being applied to the fuel pressure regulator
diaphragm by the spring inside the fuel pressure
regulator. When this happens, the result is lower fuel
pressure. The fuel pressure at idle will vary slightly
as the barometric pressure changes, but the fuel
pressure at idle should always be less than the fuel
pressure noted in step 2 with the engine OFF.
16.Check the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation in order to
determine if that particular fuel injector is leaking. If
checking the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation does not
determine that a particular fuel injector is leaking,
use the following procedure:
• Remove the fuel rail, but leave the fuel lines and injectors connected to the fuel rail. Refer to Fuel
Rail Assembly in On-Vehicle Service .
• Lift the fuel rail just enough to leave the fuel injector nozzles in the fuel injector ports.
Caution: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury that may result from fuel
spraying on the engine, verify that the fuel rail is
positioned over the fuel injector ports and verify
that the fuel injector retaining clips are intact.
• Pressurize the fuel system by connecting a 20 amp fused jumper between B+ and the fuel
pump relay connector.
• Visually and physically inspect the fuel injector nozzles for leaks.
17.A rich condition may result from the fuel pressure being above 376 kPa (55 psi). A rich condition may
cause a 45 to set. Driveability conditions associated with rich conditions can include hard starting
(followed by black smoke) and a strong sulfur smell
in the exhaust.
20.This test determines if the high fuel pressure is due to a restricted fuel return line or if the high fuel
pressure is due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
21.A lean condition may result from fuel pressure below 333 kPa (48 psi). A lean condition may cause a 44 to
set. Driveability conditions associated with lean
conditions can include hard starting (when the
engine is cold), hesitation, poor driveability, lack of
power, surging, and misfiring.
22.Restricting the fuel return line causes the fuel pressure to rise above the regulated fuel pressure.
Command the fuel pump ON with the scan tool. The
fuel pressure should rise above 376 kPa (55 psi) as
the fuel return line becomes partially closed.
NOTE: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 414
kPa (60 psi). Fuel pressure in excess of 414 kPa (60
psi) may damage the fuel pressure regulator. Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
• It is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure before connecting a fuel pressure gauge.
Refer to Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure,
below.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before
disconnecting, to catch any fuel that may leak
out. Place the towel in an approved container
when the disconnect is completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Located on the intake manifold which is at the top right part of the engine.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Pressure Gauge Installation
1. Remove the fuel pressure fitting cap.
2. Install fuel pressure gauge 5-8840-0378-0 to the fuel feed line located on the upper right side of the
engine.
3. Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2373 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–203
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0562 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0562 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Monitor the “Ignition Voltage” in the data display.
3. Load the electrical system by turning on the headlights, etc..
Does the Tech 2 indicate enough ignition voltage? 10 - 14.5V Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5 Using the DVM and check the battery voltage at the battery terminal.
Does the tester indicate enough battery voltage?
10 - 14.5V Go to Step 6Check the
charging
system, charge or replace the battery
6 Check for poor/faulty connection at the ECM connector. If a poor/faulty connection is found, repair
as necessary.
Was the problem found?
— Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 Check for poor/faulty connection of the ECM ground at the inlet manifold. If a poor/faulty connection is
found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found?
— Verify repair Go to Step 8
8 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
16
2
17
12
C-56(J2)
E-60(J1)
E-72
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2375 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–205
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0563 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0563 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Monitor the “Ignition Voltage” in the data display.
3. Load the electrical system by turning on the headlights, etc..
Does the Tech 2 indicate correct ignition voltage? Less than 16V Go to Step 5Check the
charging
system and Go to Step 5
5 Is the battery jamp start cable incorrectly connecting? —Ve r if y
procedure Go to Step 6
6 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2387 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–217
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1625 ECM SYSTEM RESET
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) monitors unexpected
ECM reset. This will not turn on MIL light on, only
records code DTC P1625.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the follwing conditions:
• P1625 alone stored does not need diagnosis. Clear DTC code.
NOTE: DTC P1625 is a DTC to record a ECM reset
history. If DTC P1625 is not reset and no engine
abnormality occurs after learing the DTC, no farther
diagnostic procedures are required.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1625 ECM System Reset
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P1625 B ECM System Reset ECM reset has occurred other than “On”. Engine control disabled.
StepAction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to
On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P1625 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P1625 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 Is the Immobilizer function programmed in the ECM? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2402 of 6020

6E–232 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Before using this section, perform the “On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” and verify all of the
following items:
• The engine control module (ECM) and malfunction indicator lamp (MIL = Check Engine Lamp) are
operating correctly.
• There are no Diagnostic Trouble Code(s) stored.
• Tech 2 data is within normal operating range. Refer to Typical Scan Data Values.
• Verify the customer complaint and locate the correct symptom in the table of contents. Perform the
procedure included in the symptom chart.
VISUAL/PHYSICAL CHECK
Several of the symptom procedures call for a careful
visual/physical check. This can lead to correcting a
problem without further checks and can save valuable
time. This check should include the following items:
• ECM grounds for cleanliness, tightness and proper location.
• Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper connection, shown on the “Emission Control System
Schematics”. Check thoroughly for any type of leak or
restriction.
• Air intake ducts for collapsed or damaged areas.
• Air leaks at throttle body mounting area, manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor and intake manifold
sealing surfaces.
• Ignition wires for cracking, harness, and carbon tracking.
• Wiring for proper connections, pinches and cuts.
INTERMITTENT
Important: An intermittent problem may or may not turn
on the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) or store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code. Do NOT use the Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) charts for intermittent problems.
The fault must be present to locate the problem.
Most intermittent problems are cased by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical
check for the following conditions.
• Poor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not fully seated in the connector (backed out).
• Improperly formed or damaged terminal.
• All connector terminals in the problem circuit should be carefully checked for proper contact tension.
• Poor terminal-to-wire connection. This requires removing the terminal form the connector body to
check.
• Ignition coils shorted to ground and arcing at ignition wires or plugs. • MIL (Check Engine Lamp) wire to ECM shorted to
ground.
• Poor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams.
Road test the vehicle with a Digital Multimeter
connected to a suspected circuit. An abnormal voltage
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a fault in the circuit being monitored.
Using Tech 2 to help detect intermittent conditions. The
Tech 2 has several features that can be used to located
an intermittent condition.
An intermittent MIL (Check Engine Lamp) with no stored
Diagnostic Trouble Code may be caused by the
following:
• Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at ignition wires or plugs.
• MIL (Check Engine Lamp) wire to ECM short to ground.
• Poor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams.
Check for improper installation of electrical options such
as light, cellular phones, etc. Check all wires from ECM
to the ignition control module for poor connections.
Check for an open diode across the A/C compressor
clutch and check for other open diodes (refer to wiring
diagrams in Electrical Diagnosis).
If problem has not been found, refer to ECM connector
symptom tables.
• Check the “Broadcast Code” of the ECM, and compare it with the latest Isuzu service bulletins and/
or Isuzu EEPROM reprogramming equipment to
determine if an update to the ECM’s reprogrammable
memory has been released.
To check the “Broadcast Code”, connect the Tech 2,
then look for “ID info.” then select “Broadcast Code”.
This should display a 4 character code, such as “XBYA”
(example only).
This identifies the contents of the reprogrammable
software and calibration contained in the ECM.
If the “Broadcast Code” is not the most current
available, it is advisable to reprogram the ECM’s
EEPROM memory, which may either help identify a
hard-to find problem or may fix the problem.
The Service Programming System (SPS) will not allow
incorrect software programming or incorrect calibration
changes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2404 of 6020

6E–234 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
12 Visually/physically inspect the secondary ignitionwires. Check for the following conditions:
• Verify that all ignition wire resistance are less than the specified value.
• Verify that ignition wires are correctly routed to eliminate cross-fitting.
• Verify that ignition wires are not arcing to ground. Spraying the secondary ignition wires with a light
mist of water may help locate an intermittent
problem.
Was a problem found? #1 cyl. 4.4k
Ω
#2 cyl. 3.6k Ω
#3 cyl. 3.1k Ω
#4 cyl. 2.8k ΩVerify repair Go to Step 13
13 1. Disconnect the spark plug high tension cable from No.1 spark plug.
2. Install a spark tester at the end of the disconnected ignition coil.
3. Clip the spark tester to a good ground.
4. Observe the spark tester while the engine is cranking.
Was a crisp blue spark observed? (Only one or two
sparks followed by no result is considered the same
as “No Spark”.) — Go to Step 21Go to Step 14
14 1. Disconnect the ignition coil harness connector. 2. Check for an open or short circuit between theignition coil and the ECM.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 1. Ignition “On”. 2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) check the ignitionwire coil at the ignition coil harness connector.
Was the voltage equal to the specified value? Battery
voltage Go to Step 16Verify repair
16 1. Ignition “Off”. 2. With DVM, check for an open in the ground wire atthe ignition coil harness connector.
Was the ground wire OK? — Go to Step 17Verify repair
17 Replace the ignition coil, verify the repair. Attempt to start the engine.
Is there still a problem? — Go to Step 18Verify repair
18 Use an ohmmeter to check the ignition coil primary winding resistance.
Was the primary winding resistance approximately
equal to the specified value? 0.8-18kΩGo to Step 19 Go to Step 20
19 Use an ohmmeter to check the ignition coil secondary winding resistance.
Was the primary winding resistance hear around the
to the specified value? 2.5kΩ Go to Step 21 Go to Step 20
20 Replace the ignition coil. — Verify repair —
21 1. Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders. 2. Visually inspect the spark plug electrodes.
3. Replace any spark plugs with loose or missing electrodes or cracked insulators.
Did your inspection reveal any spark plugs exhibiting
excessive fouling? —Correct the
fouling
condition Go to Step 22
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007