cooling ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3511 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–233
APP Sensor 2 (Accelerator Pedal Position) V 0.47 0.47
TP Sensor 1 (Throttle Position) V 0.73 0.57
TP Sensor 2 (Throttle Position) V 4.27 4.43
TP Sensor 1 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position) V 0.53 0.53
TP Sensor 2 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position) V 4.49 4.49
Electronic Throttle Control Learn Counter Counts 11 11
Brake Lamp Switch Inactive / Active Inactive Inactive
Brake Switch Signal Status Valid / Invalid Valid Valid
Initial Brake Apply Signal Inactive / Active Inactive Inactive
Engine Speed RPM 0 598
Desired Engine Idle Speed RPM 680 600
Coolant Temperature
°C 38 96
Intake Air Temperature
°C 32 29
Mass Air Flow Sensor
V 1.0 1.1
Mass Air Flow g/s 0.00 3.11
Barometric Pressure kPa 102 102
Barometric Pressure V 4.88 4.88
Engine Load % 100 20
Volumetric Efficiency % 99 14
Ignition Accessory Signal Off / On On On
Ignition On Signal Off / On On On
Engine Control Ignition Relay Off / On On On
Engine Control Ignition Relay Feedback V 11.7 14.0
DTC Set This Ignition No DTC / DTC Set No DTC No DTC
Vehicle Speed km/h 0 0
Engine Runtime h:m:s 00:00:00 00:16:25
(1) Automatic Transmission Only (2) Manual Transmission Only
Cooling/HVAC Data
Tech 2 Display Units Displayed Ignition On Engine Running
Coolant Temperature
°C 37 100
Cooling Fan
Off / On Off Off
Intake Air Temperature
°C 32 30
A/C Request
No / Yes No No
A/C Relay (Air Conditioning) Off / On Off Off
A/C Pressure Sensor (Air Conditioning) V 1.0 1.5
A/C Pressure Sensor (Air Conditioning) kPa 732.55 1121.25
A/C Cutoff Mode (Air Conditioning) Inactive / Pressure /
Max. Acceleration / Active Inactive Inactive
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3518 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–240
Cruise Control Switch: This parameter displays the state of the cruise control on/off switch input to the control module.
Cruise Control Disengagement Reason: The parameter displays which of a possible 28 causes for the cruise control
to disengage.
CC Disengagement 1 – 8 History (Cruise Control): The parameter displays the last 8 cruise control disengages in
order from 1 to 8, with 8 being the most recent. There are about 28 possible causes for the cruise control to disengage.
Cruise Resume/Acceleration Switch: This parameter displays the state of the cruise control resume/accel switch
position input to the ECM.
Cruise Set / Coast Switch: This parameter displays the state of the cruise controls set/decel. switch position input to
the ECM.
Cycles of Misfire: This parameter displays the number of misfire tests during 200 engine revolutions.
Cylinder 1 – 6 Injector Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fuel injector control circuit. The
parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the fuel injector control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. This
parameter displays ‘Undefined Status’ until the control circuit has been commanded ‘On’.
Dec. Fuel Cutoff (Deceleration): This parameter displays the status of the ECM operating mode, used to turn off the
fuel injectors and the evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge valve during certain deceleration conditions.
Desired Engine Idle Speed: This parameter displays the desired engine idle speed as commanded by the ECM.
Desired Throttle Position: This parameter displays the desired throttle position (TP) angle commanded by the ECM.
Distance Since DTC Cleared: This parameter displays the distance (km) travelled since any diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) has been cleared from the ECM memory.
DTC Set This Ignition: This parameter displays Yes if a DTC set on the current ignition cycle.
ECM Immobilized: This parameter displays ‘Yes’ when an internal control module reset occurs. Tech 2 will display ‘No’
under normal operating conditions.
Electronic Throttle Control Learn Counter: W hen the ECM performs a throttle body relearn procedure, the throttle
plate is commanded to move from the rest position (7% open) to full closed (0%), then to around 10% open.
At the start of this procedure, the Tech 2 ‘TAC Learn Counter’ parameter should display 0, then count up to 11 after the
procedure is completed. If the counter did not start at 0 or if the counter did not end at 11, a fault has occurred and a
DTC should set.
Engine Control Ignition Relay: This parameter displays the state of the control circuit for control module power relay
as commanded by the ECM.
Engine Control Ignition Relay Feedback: This parameter displays the voltage available at the engine control ignition
relay pin of the control module.
Engine Load: This parameter displays the calculated engine load in percent based on inputs to the control module from
various engine sensors.
Engine Oil Life Remaining: This parameter displays the percentage of engine oil life remaining. The controller
calculates the engine oil life by monitoring engine load, collant temperature and engine speed.
Engine Oil Pressure: This parameter displays the oil pressure in kPa from the ECM, developed from the engine oil
pressure (EOP) sensor input.
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor: This parameter displays ‘High’ if the engine oil pressure is within the correct range. If the
ECM detects that the engine oil pressure is not within the correct range, Tech 2 will display ‘Low’.
Engine Runtime: This parameter displays the time elapsed since the engine was started.
Engine Speed: This parameter displays the speed of the engine crankshaft rotation from information received from the
CKP sensor. If there is a CKP sensor DTC, the ECM calculates the engine speed from one of the camshaft position
(CMP) sensors.
EVAP Purge Solenoid (Evaporative Emission): This parameter displays the on-time or duty cycle of the EVAP
canister purge solenoid commanded by the ECM. Zero percent indicates no purge. One hundred percent indicates full
purge.
EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve Circuit Status (Evaporative Emission): This parameter displays the state of the EVAP
purge solenoid control circuit. The parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the EVAP purge solenoid control circuit is open, shorted
to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter displays ‘Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been established as
‘OK’.
Cooling Fan Relay: This parameter displays the control module commanded state of the fan relay control circuit.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3519 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–241
Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fan relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the fan relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter displays
‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Level: This parameter displays the amount of fuel in the fuel tank in litres, as calculated by the ECM from data
received from the fuel level sensor.
Fuel Level Sensor: This parameter displays the voltage received from the fuel level sensor in the fuel tank, by the ECM.
Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fuel pump relay control circuit. The
parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the fuel pump relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The
parameter displays ‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Pump Relay: This parameter displays the ECM commanded state of the fuel pump relay control circuit.
Fuel Trim Learn: This parameter displays ‘Enabled’ when conditions are appropriate for enabling long term fuel trim
corrections. This indicates that the long term fuel trim is adapting continuing amounts of short term fuel trim. If Tech 2
displays ‘Disabled’, then long term fuel trim will not respond to changes in short term fuel trim.
Ignition Accessory Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the
ignition ‘ACC’ terminal, X1-4 of the ignition switch.
Ignition On Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the ignition ‘IGN’
terminal X1-3 of the ignition switch.
Initial Brake Apply Signal: This parameter displays the status of the brake lamp switch. Before the cruise control can
be activated, this switch contact must be open circuit when the brake pedal is pressed.
Injection Time Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the amount of fuel injector On-time or pulse width as
commanded by the ECM.
Intake Air Temperature: This parameter displays the temperature of the air entering the air induction system based on
input to the ECM from the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor.
Knock Sensor Signal (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameters displays the voltage input to the control module from the
knock sensor (KS).
Knock Retard: This parameter indicates the amount of spark advance in crankshaft degrees, that the ECM removes
from the ignition control (IC) spark advance in response to the signal from the knock sensors.
Knock Retard Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the knock retard as commanded by the ECM for cylinders 1-6.
Each cylinder is controlled individually based on both knock sensor signal inputs.
Loop Status B1S1 / B2S1 (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the state of the fuel control system
as commanded by the ECM. ‘Closed’ Loop operation indicates that the ECM is controlling the fuel delivery based on the
oxygen sensors input signal. In ‘Open’ Loop operation the ECM ignores the oxygen sensor input signal and bases the
amount of fuel to be delivered on other sensor inputs.
LTFT Idle/Deceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for idle and deceleration conditions.
LTFT Cruise/Acceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for cruise and acceleration conditions.
Malfunction Indicator (MI): This parameter displays the commanded (‘On, ‘Off’ or ‘Flashing’) state of the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) control circuit by the ECM.
Malfunction Indicator (MI) Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the MIL control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the MIL control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. This parameter displays
‘Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Mass Air Flow: This parameter displays the measured quantity (g/s) of air flowing into the engine during all operating
conditions.
Mass Air Flow Sensor: This parameter displays the signal voltage from the mass air flow (MAF) sensor to the ECM.
Misfire Current Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 200 counts. This parameter displays the number of
misfires that have been detected during the last 200 cylinder firing events. The counters may normally display some
activity, but the activity should be nearly equal for all of the cylinders, and in low numbers.
Misfire History Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 65,535 counts. The misfire history counters display the total
level of misfire that has been detected on each cylinder. The misfire history counters will not update or show any activity
until a misfire DTC P0300 has become active. The misfire history counters will update every 200 cylinder firing events.
Oil Level: W hen the ECM receives information from the engine oil level switch, where the engine oil level is within
preset parameters, Tech 2 will display ‘Normal’. If not within preset parameters, the display will show ‘Low’.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3522 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–244
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’.
Cooling Fan (PWM)
Take care that no-one can access the engine
compartment during these tests!
This test allows the Technician to turn the cooling fan on in increments to its maximum speed.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’ Air conditioning is ‘Off’..
Alternator L Terminal
This test allows the Technician to turn ‘On’ and ‘Off’, the commanded state of the voltage regulator in the alternator. ‘On’
displays a commanded state of 99%, while ‘Off’ displays a commanded state of 0%.
Precondition: Engine running.
EVAP Purge Solenoid
This test allows the Technician to control the EVAP purge solenoid valve. The normal commanded state is ‘0%’. The
system will increase or decrease the amount of purge by changing the duty cycle of the purge valve in 10% increments
within a range of 0 – 100%. The system will remain in the commanded state until cancelled by Tech 2.
NOTE
The EVAP Purge Solenoid Command parameter
may not change states when using this output
control.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’.
Engine Speed Control
Other DTCs may set when the Engine Speed
Control function is used. Disregard those
DTCs that set under this condition.
Allows the increase / decrease of the engine speed in 20 – 30 rpm increments from the base idle speed, up to 1,600
rpm.
NOTE
If the engine coolant temperature is below the
prescribed minimum, a message to that effect is
displayed and access to engine speed control is
blocked.
Preconditions: Engine running, engine temperature above 80 °C, transmission in Park or Neutral.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3540 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–16
2.6 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Remove
To avoid serious personal injury, never
remove the engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor when the engine is hot. Allow the
engine to cool to ambient temperature (less
than 50 °
°°
°
C) before performing this procedure.
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
To avoid serious personal injury, never
remove the coolant filler cap when the engine
is hot. Allow the engine to cool to ambient
temperature (less than 50 °
°°
°
C) before
performing this procedure.
2 Allow the engine to cool to ambient temperature less than 50 °C, and slowly remove coolant filler cap located on the
coolant outlet housing.
3 Drain approximately two litres of coolant into a suitable container, refer to 6B1 – Engine Cooling – V6.
4 Disconnect the wiring harness connector (1) from the ECT sensor (2).
Figure 6C1-3 – 12
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3541 of 6020
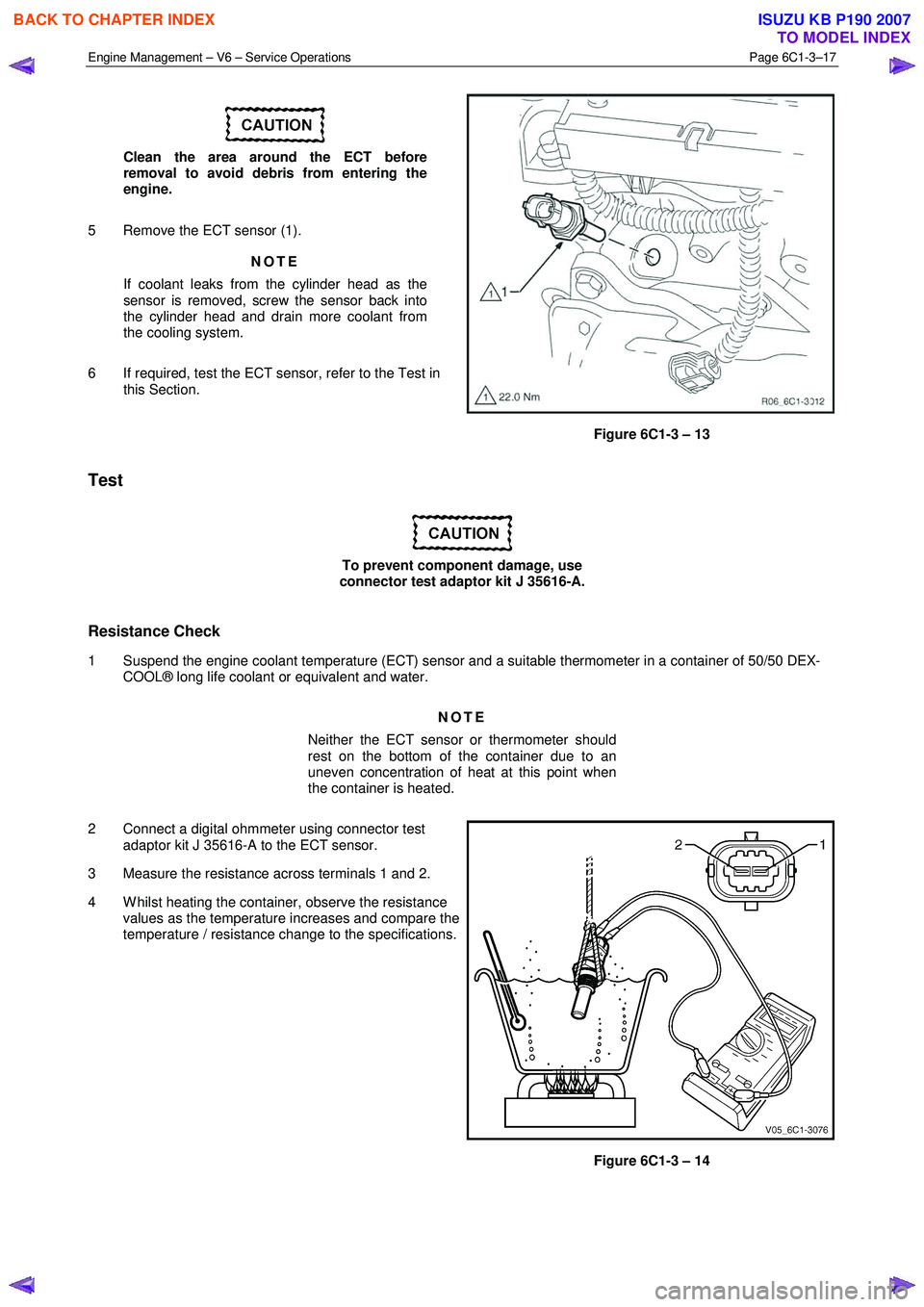
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–17
Clean the area around the ECT before
removal to avoid debris from entering the
engine.
5 Remove the ECT sensor (1). NOTE
If coolant leaks from the cylinder head as the
sensor is removed, screw the sensor back into
the cylinder head and drain more coolant from
the cooling system.
6 If required, test the ECT sensor, refer to the Test in this Section.
Figure 6C1-3 – 13
Test
To prevent component damage, use
connector test adaptor kit J 35616-A.
Resistance Check
1 Suspend the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and a suitable thermometer in a container of 50/50 DEX- COOL® long life coolant or equivalent and water.
NOTE
Neither the ECT sensor or thermometer should
rest on the bottom of the container due to an
uneven concentration of heat at this point when
the container is heated.
2 Connect a digital ohmmeter using connector test adaptor kit J 35616-A to the ECT sensor.
3 Measure the resistance across terminals 1 and 2.
4 W hilst heating the container, observe the resistance values as the temperature increases and compare the
temperature / resistance change to the specifications.
Figure 6C1-3 – 14
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3542 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–18
5 If the resistance is not within specifications, replace
the ECT sensor.
Engine Coolant Temperature Vs Resistance
Temperature °C Resistance – Ohms (
Ω)
-40 40490 – 50136
-20 14096 – 16827
-10 8642 – 10152
0 5466 – 6326
20 2351 – 2649
25 1941 – 2173
40 1118 – 1231
60 573 – 618
80 313 – 332
100 182 – 191
120 109 – 116
140 68 – 74
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following:
1 Tighten the ECT sensor to the correct torque specification.
Engine coolant temperature sensor
torque specification ............................................22.0 Nm
2 Refill the cooling system, refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
3 Road test the vehicle and check for correct operation, taking particular note there is no coolant leakage.
2.7 Engine Control Module
Service of the engine control module (ECM) should normally consist of either replacement or ECM programming. If the
diagnostic procedures call for the ECM to be replaced, it should be first checked to ensure it is the correct part. If it is,
replace the faulty ECM.
Do not touch the ECM connector pins as
electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage may
result.
When removing or reinstalling the ECM wiring
harness connector/s, ensure the ignition
switch is in the OFF position and the battery
has been disconnected. Failure to do so may
result in damage to the ECM and / or
associated componentry.
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems. Refer to 6D1-3
Battery - V6 before disconnecting the battery.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3576 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–52
Oil Fouled (3)
W et, oily deposits with minor electrode wear possibly due to oil leaking past worn piston rings.
Breaking in a new or recently overhauled engine before the rings are fully seated may also result in this condition.
Deposit Fouling A (4)
Red brown, yellow and white coloured coatings on the insulator tip which are by-products of combustion. They come
from fuel and lubricating oil which generally contain additives. Most powdery deposits have no adverse effect on spark
plug operation, however, they may cause intermittent missing under severe operating conditions.
Deposit Fouling B (5)
Deposits similar to those identified in deposit fouling A (4). These are also by-products of combustion from fuel and
lubricating oil. Excessive valve stem clearances and / or defective intake valve seals allow too much oil to enter the
combustion chamber. The deposits will accumulate on the portion of the spark plug that projects into the chamber and
will be heaviest on the side facing the intake valve. If this condition is only detected in one or two cylinders, check the
valve stem seals.
Deposit Fouling C (6)
Most powdery deposits identified in deposit fouling A (4) have no adverse effect on the operation of the spark plug as
long as they remain powdery.
Under certain conditions of operation however, these deposits melt and form a shiny glaze coating on the insulator.
W hen hot, this acts as a good electrical conductor allowing the current to flow along the deposit instead of sparking
across the gap.
Detonation (7)
Commonly referred to as engine knock or pinging, detonation causes severe shocks inside the combustion chamber
causing damage to parts.
Pre-ignition (8)
Burnt or blistered insulator tip and badly eroded electrodes probably due to the excessive heat.
This is often caused by a cooling system blockage, sticking valves, improperly installed spark plugs or plugs that are the
wrong heat rating (too hot).
Sustained high speed with a heavy load can produce temperatures high enough to cause pre-ignition.
Heat Shock Failure (9)
A rapid increase in spark plug tip temperature under severe operating conditions can cause heat shock and result in
fractured insulators. This is a common cause of broken and cracked insulator tips.
Insufficient Installation Torque (10)
Poor contact between the spark plug and the cylinder head seat.
The lack of proper heat transfer that results from poor seat contact causes overheating of the spark plug. In many cases,
severe damage occurs. Dirty threads in the cylinder head can cause the plug to seize before it is seated.
Ensure the cylinder head and spark plug threads are free of deposits, burrs and scale before installation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3590 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-3
1 General Information
1.1 Components
Generator
The Mitsubishi generator can be identified visually by its two lower and one upper mounting lugs.
It is mounted to the lower right-hand side of the engine block. It is driven by the same drive belt that drives other engine
ancillaries and requires no periodic drive belt adjustment.
The generator has three phases, incorporating a rotor with six pole pairs fitted and two internal cooling fans; one on the
drive-end and one on the slip-ring end. The rotor is supported by ball bearings in both the drive and slip-ring end
housings. Surrounding the rotor is a stator, which has a three phase delta connected output winding construction on a
ring shaped lamination pack.
The output of the stator winding is rectified by eight diodes that are contained within the slip-ring end housing. Excitation
current is supplied to the rotor field coil via the voltage regulator, the brushes and slip-rings. The electronic voltage
regulator requires no adjustment in service.
The generator has four external connections (refer to Figure 6D1-1 1):
• Generator – Terminal P-9 to the battery positive terminal P-1 via fuse SBF1,
• Generator – E-4 pin 1 to the ECM connection E-60 pin 43 – regulator monitoring,
• Generator – E-4 pin 2 to the ECM connection E60 pin 21 – battery voltage sensing, and
• ground connection via the installation bolts.
Generator Types
The vehicle is fitted with a 120 amp generator.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3657 of 6020
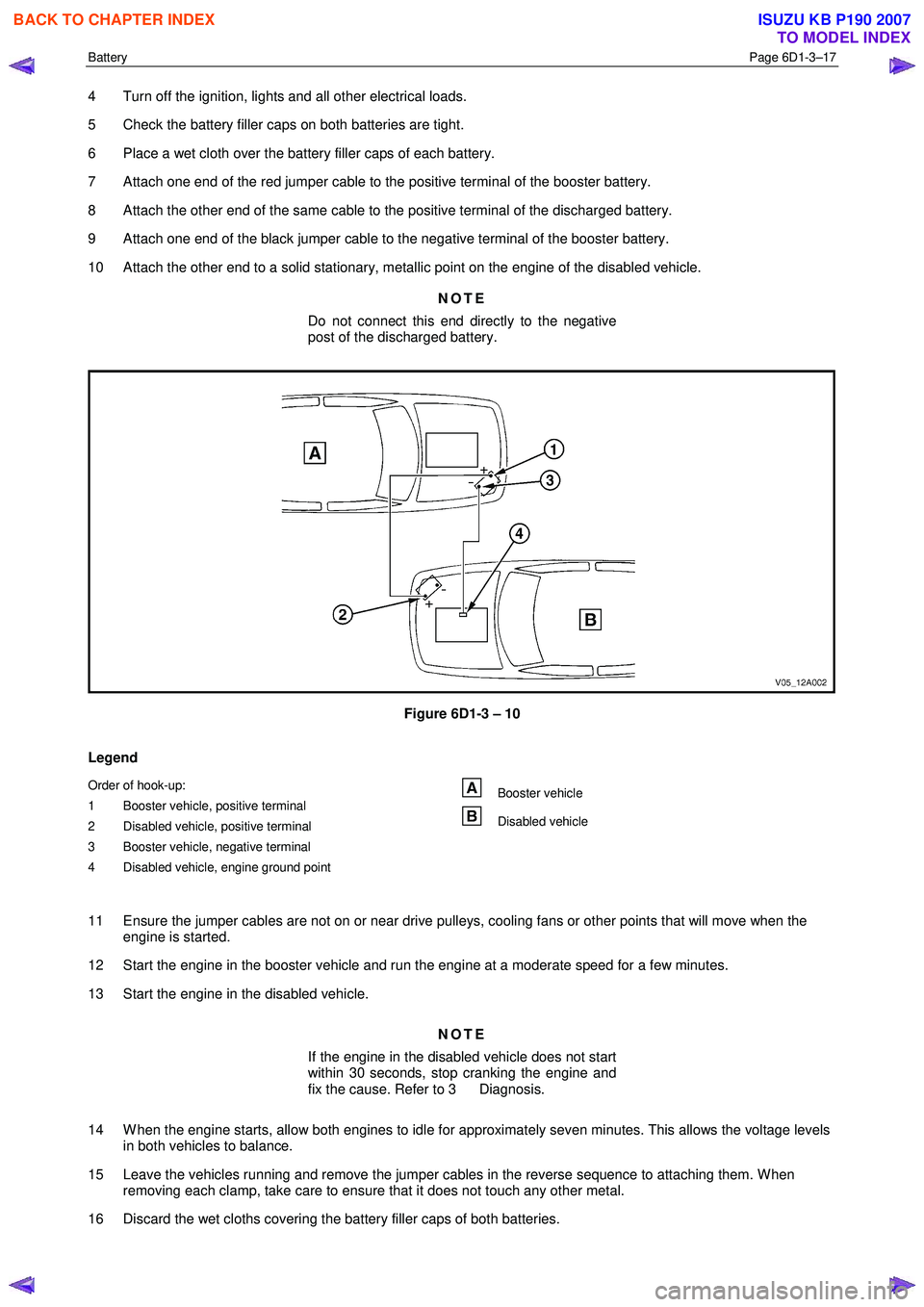
Battery Page 6D1-3–17
4 Turn off the ignition, lights and all other electrical loads.
5 Check the battery filler caps on both batteries are tight.
6 Place a wet cloth over the battery filler caps of each battery.
7 Attach one end of the red jumper cable to the positive terminal of the booster battery.
8 Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal of the discharged battery.
9 Attach one end of the black jumper cable to the negative terminal of the booster battery.
10 Attach the other end to a solid stationary, metallic point on the engine of the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
Do not connect this end directly to the negative
post of the discharged battery.
Figure 6D1-3 – 10
Legend
Order of hook-up:
1 Booster vehicle, positive terminal
2 Disabled vehicle, positive terminal
3 Booster vehicle, negative terminal
4 Disabled vehicle, engine ground point Booster vehicle
Disabled vehicle
11 Ensure the jumper cables are not on or near drive pulleys, cooling fans or other points that will move when the engine is started.
12 Start the engine in the booster vehicle and run the engine at a moderate speed for a few minutes.
13 Start the engine in the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
If the engine in the disabled vehicle does not start
within 30 seconds, stop cranking the engine and
fix the cause. Refer to 3 Diagnosis.
14 W hen the engine starts, allow both engines to idle for approximately seven minutes. This allows the voltage levels in both vehicles to balance.
15 Leave the vehicles running and remove the jumper cables in the reverse sequence to attaching them. W hen removing each clamp, take care to ensure that it does not touch any other metal.
16 Discard the wet cloths covering the battery filler caps of both batteries.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007