engine ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3582 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–58
Engine Oil Level and Temperature Sensor
Level sensor type ....................................... Magnetic reed switch
Temperature sensor type .......................... Negative temperature
................................................................... coefficient thermistor
Engine Oil Temperature Vs Resistance
Temperature °C Resistance – Ohms ( Ω)
0 7570 – 8000
20 2351 – 2649
30 2225 – 2375
40 1118 – 1231
50 1050 – 1150
80 380 – 470
100 270 – 290
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Valve
Type .............................................................................. Solenoid
Resistance @ 20°C...................................................... 24 – 28 Ω
Operating voltage................................................... 12.0 – 16.0 V
Engine Firing Order ..................................................................... 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Fuel Injector
Type .............................................................................. Solenoid
Fuel Injector Resistance @ 20°C ........................... 11.4 – 12.6 Ω
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) – Four wire
Type ...................................................... Four wire, planar sensor
Operating range (greater than 360°C) .................. 10 – 1000 mV
Closed loop operating range ................................. 300 – 600 mV
Heater resistance @ 20°C ....................................... 8.0 – 10.0 Ω
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) – Six W ire
Type ....................................... Six wire, wide band planar sensor
Heater resistance @ 20°C ....................................... 8.0 – 10.0 Ω
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Type .......................................................... Negative temperature
.................................................................. Coefficient thermistor
Intake Air Temperature Vs Resistance
Temperature °C Resistance – Ohms ( Ω)
-40 35140 – 43760
-20 12660 – 15120
-10 7943 – 9307
0 5119 – 5892
20 2290 – 2551
25 1900 –2100
40 1096 –1238
60 565 – 654
80 312 – 370
100 184 – 222
120 114 –141
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3583 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–59
Intake Air Temperature Vs Resistance
Temperature °C Resistance – Ohms (Ω)
140 74 –93
Knock Sensor
Type ........................................................ Piezo ceramic element
Mass Air Flow Sensor
Type ......................................................Hot film air-mass sensor
Spark Plug
Type ....................................................................................J gap
Gap ........................................................................ 1.1 – 1.2 mm
Adjustment ........................................................... No adjustment
Throttle Position Sensor 1
Type .....................................................Three wire potentiometer
Closed throttle ................................................. Less than 1.25 V
Wide open throttle ...............................................5.0 V maximum
Throttle Position Sensor 2
Type .....................................................Three wire potentiometer
Closed throttle ................................................. Less than 1.25 V
Wide open throttle ...............................................5.0 V maximum
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3584 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–60
4 Assembly Lubricants
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor O-ring ........................................... Engine Oil
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor .................................................... Engine Oil
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Valve
Quick Connect Fitting ........................................................................ Engine Oil
Fuel Feed Hose Quick Connect Fitting .............................................. Engine Oil
Fuel Injector Seals............................................................................. Engine Oil
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) – All .............................. Anti-seize Compound
Ignition Coil Boot .......................................................................Talcum Powder
Ignition Coil Sealing Rubber .............................................................. Engine Oil
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3585 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–61
5 Torque Specifications
Fuel Rail Attaching Bolt ............................................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Support Bracket
Attaching Nut ............................................................................... 8.5 – 11.5 Nm
Air Cleaner Lower Housing Attaching Bolt................................. 18.0 – 22.0 Nm
Barometric Pressure Sensor Attaching Bolt ................................ 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Camshaft Position Sensor Attaching Bolt .................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Crankshaft Position Sensor Attaching Bolt .................................. 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor ................................................... 22.0 Nm
Engine Control Module Attaching Bolt ......................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Ground Terminal Attaching Screw.......................................................... 4.5 Nm
Engine Control Module Bracket Assembly
Attaching bolt (6mm Bolt) ............................................................ 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Engine Control Module Bracket Assembly
Attaching bolt (8mm Bolt) .......................................................... 20.0 – 25.0 Nm
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor ...................................................... 12.0 – 14.0 Nm
Heated Oxygen Sensor ............................................................. 40.0 – 50.0 Nm
Ignition Coil Attaching Bolt........................................................... 7.0 – 11.0 Nm
Air Intake Duct Retaining Clamp ................................................... 1.5 – 2.5 Nm
Knock Sensor Attaching Bolt ..................................................... 21.0 – 25.0 Nm
Mass Air Flow Sensor Attaching Nut ............................................. 1.8 – 2.2 Nm
Spark Plug ................................................................................. 16.0 – 20.0 Nm
Throttle Body Assembly Attaching Bolt........................................ 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3586 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–62
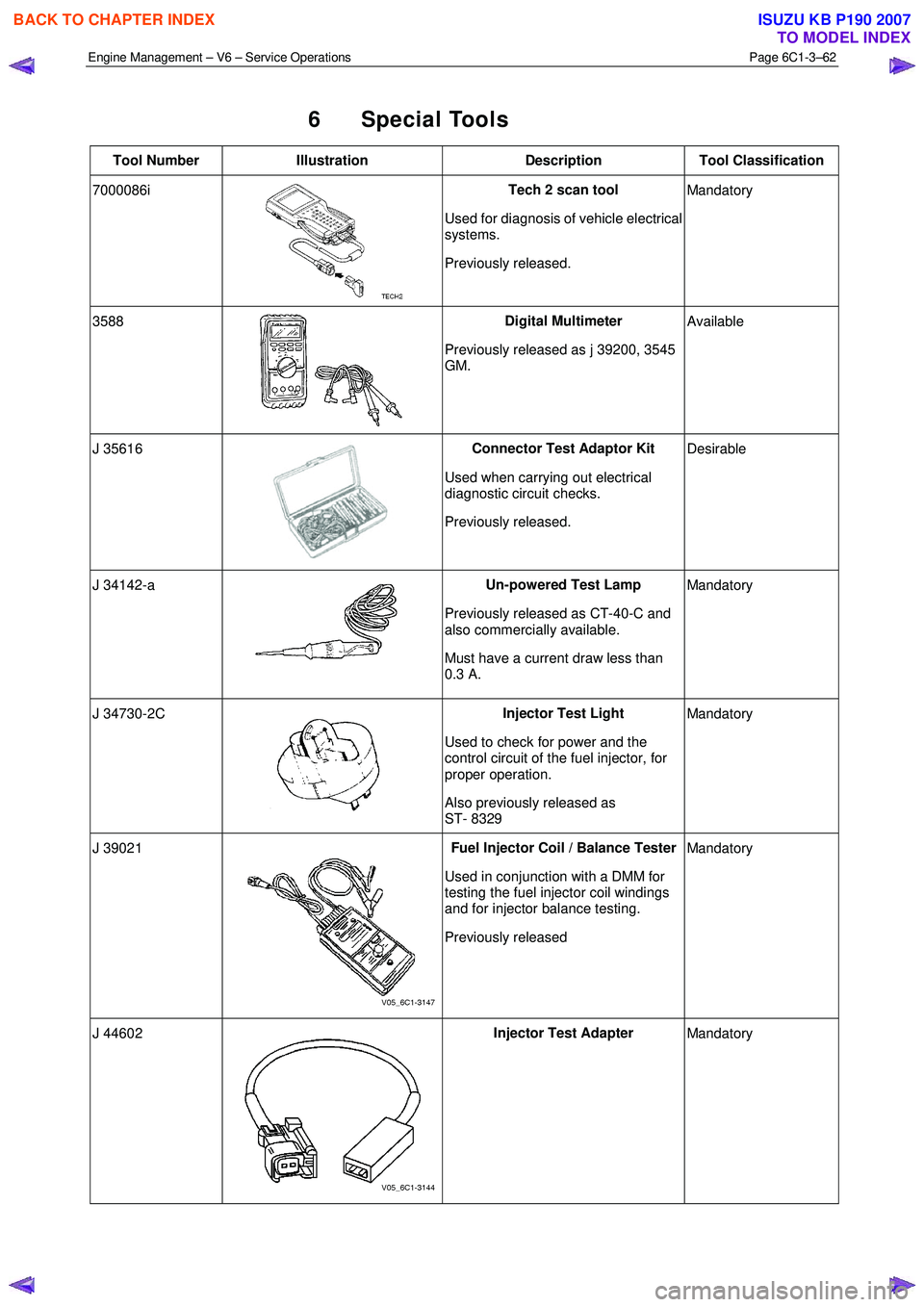
6 Special Tools
Tool Number Illustration Description Tool Classification
7000086i
Tech 2 scan tool
Used for diagnosis of vehicle electrical
systems.
Previously released. Mandatory
3588
Digital Multimeter
Previously released as j 39200, 3545
GM. Available
J 35616
Connector Test Adaptor Kit
Used when carrying out electrical
diagnostic circuit checks.
Previously released. Desirable
J 34142-a
Un-powered Test Lamp
Previously released as CT-40-C and
also commercially available.
Must have a current draw less than
0.3 A. Mandatory
J 34730-2C
Injector Test Light
Used to check for power and the
control circuit of the fuel injector, for
proper operation.
Also previously released as
ST- 8329 Mandatory
J 39021 Fuel Injector Coil / Balance Tester
Used in conjunction with a DMM for
testing the fuel injector coil windings
and for injector balance testing.
Previously released Mandatory
J 44602 Injector Test Adapter
Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3587 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–63
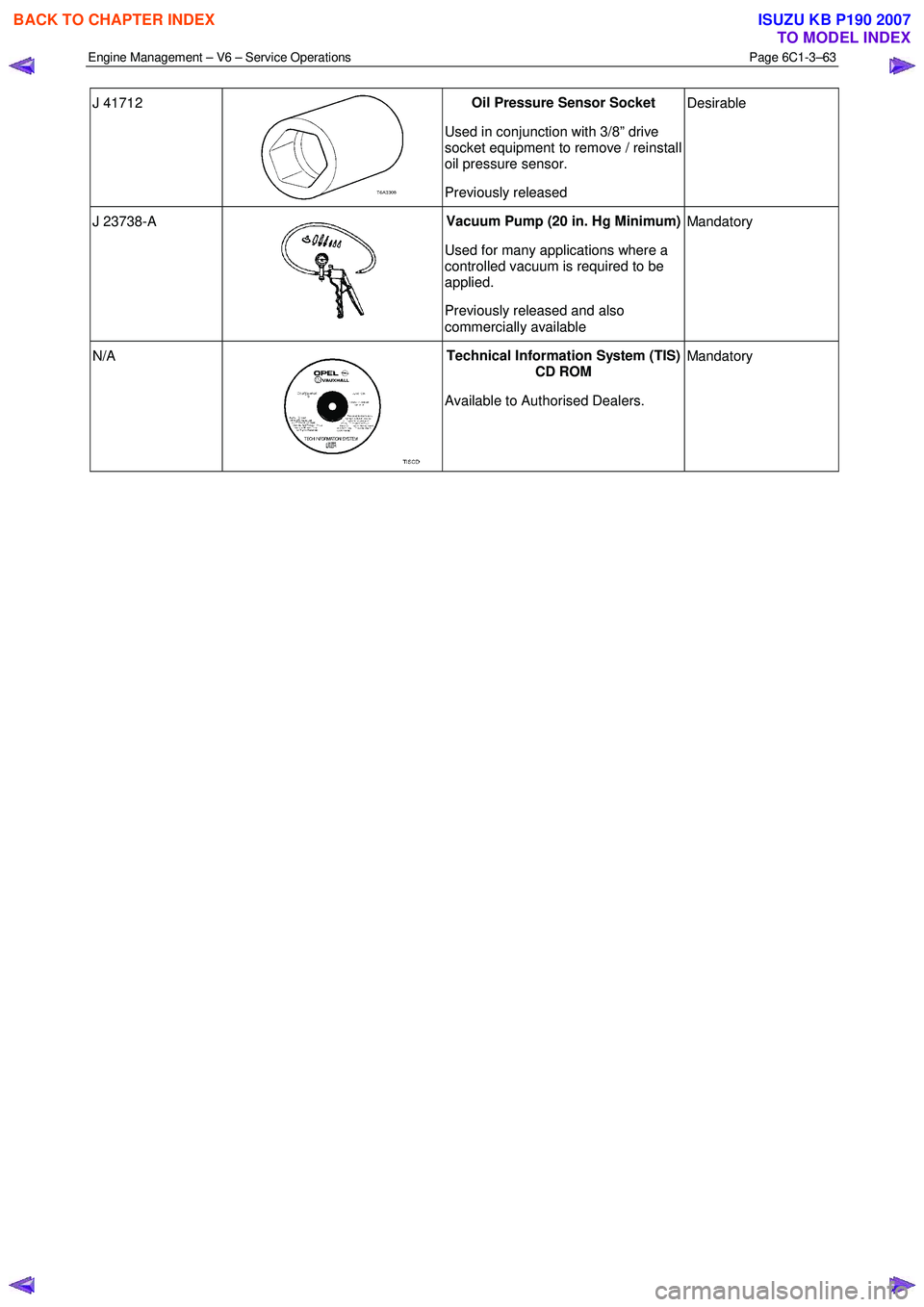
J 41712
Oil Pressure Sensor Socket
Used in conjunction with 3/8” drive
socket equipment to remove / reinstall
oil pressure sensor.
Previously released Desirable
J 23738-A
Vacuum Pump (20 in. Hg Minimum)
Used for many applications where a
controlled vacuum is required to be
applied.
Previously released and also
commercially available Mandatory
N/A
Technical Information System (TIS)
CD ROM
Available to Authorised Dealers. Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3590 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-3
1 General Information
1.1 Components
Generator
The Mitsubishi generator can be identified visually by its two lower and one upper mounting lugs.
It is mounted to the lower right-hand side of the engine block. It is driven by the same drive belt that drives other engine
ancillaries and requires no periodic drive belt adjustment.
The generator has three phases, incorporating a rotor with six pole pairs fitted and two internal cooling fans; one on the
drive-end and one on the slip-ring end. The rotor is supported by ball bearings in both the drive and slip-ring end
housings. Surrounding the rotor is a stator, which has a three phase delta connected output winding construction on a
ring shaped lamination pack.
The output of the stator winding is rectified by eight diodes that are contained within the slip-ring end housing. Excitation
current is supplied to the rotor field coil via the voltage regulator, the brushes and slip-rings. The electronic voltage
regulator requires no adjustment in service.
The generator has four external connections (refer to Figure 6D1-1 1):
• Generator – Terminal P-9 to the battery positive terminal P-1 via fuse SBF1,
• Generator – E-4 pin 1 to the ECM connection E-60 pin 43 – regulator monitoring,
• Generator – E-4 pin 2 to the ECM connection E60 pin 21 – battery voltage sensing, and
• ground connection via the installation bolts.
Generator Types
The vehicle is fitted with a 120 amp generator.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3592 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-5
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
1.3 System Operation
Operation
W ith the ignition switch in the ON position and the engine at rest, current is supplied via the regulator to generator
connector E-4 pin 1 and to the engine control module ECM connector E-60 pin 43. This initiates current flow (within the
regulator) from the generator connection P-9, to the brushes and rotor winding, to ‘excite’ the circuit.
The current in the rotor winding creates magnetic fields between adjacent rotor poles.
W ith the engine running, the rotor spins, the stator windings cut through this field and induce voltage. As the engine
speed is increased, this induced voltage increases. Current then flows through the three-phase diode bridge in the
rectifier to convert the AC voltage to DC. This is supplied to the generator connector P-9 output and then to the battery
terminal via fuse SBF1.
The regulator monitors the voltage to the battery. W hen this voltage reaches approximately 14.5 V, the regulator opens
the circuit through the rotor winding, causing the generator output voltage to drop. W hen the regulator senses a voltage
below a preset voltage, the regulator closes the circuit through the rotor winding and voltage to the battery again
increases. This cycle repeats very rapidly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3594 of 6020
Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-7
2 Diagnosis
2.1 Diagnostic General Information
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required
Use of incorrect electrical circuit diagnostic
tools when performing the generator
diagnostic procedures could result in
incorrect diagnostic results or damage to
components.
The following electrical circuit testing tools are required to perform the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Section:
• digital multimeter with 10 mega ohms impedance, and
• connector test adapter kit Tool No. KM609.
For further information on the use of these tools, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
2.2 Tech 2 Data List
The Tech 2 displays the status of certain charging system parameters.
To view the data list:
1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 On Tech 2 select: Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display / Data List / Electrical/Theft Data .
Tech 2 Parameter Units Displayed Typical Display Values
Alternator L Terminal D Percentage Various
2.3 Diagnostic Systems Check
Step Action Yes No
1 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Ignition ON, engine OFF.
3 On Tech 2 select: Engine / V6 Engine / Diagnostic Trouble codes / Read
DTC’s.
Are there any set DTC’s? Go to the
appropriate DTC table in 6C1-2 Engine
Management – V6 – Diagnostics. Refer to 2.5
Charging
System Inoperative / Malfunctioning
Reference to following information will assist when diagnosing charging circuit faults:
• for battery testing, refer to 6D1-3 Battery – V6,
• for wiring diagram details, refer to Figure 6D1-1 2, and
• for electrical component locations, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3597 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-10
3 Minor Service Operations
3.1 Safety Precautions
Observe the following precautions. Failure to observe these precautions will result in serious damage to the generator.
• Only use the generator and voltage regulator in a negative ground system.
• Always refer to 1.2 W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before disconnecting the battery.
• W hen installing a battery, fit the positive (+) cable to the battery before fitting the negative cable.
• W hen a slave battery is used for starting purposes, ensure that both batteries are connected in parallel. That is,
positive terminals connected and negative terminals connected.
• Only use jumper leads that have surge protection.
• Disconnect both battery cables when charging the battery. This isolates the generator from the battery and from
the external charging equipment.
• Do not operate the generator within an open circuit or without a battery in the circuit.
• Do not disconnect the battery while the generator is running.
• Do not attempt to polarise the generator.
• Do not connect generator connector E-4 pin 1 to 12 V (the battery or ignition circuits).
• Some battery powered timing lights can produce high transient voltages when connected or disconnected.
Only disconnect or connect timing lights when the engine is switched off.
Ensure the generator connector E-4 pin 1 has
a maximum sinking current of 50mA.
3.2 Maintenance
Regular Checks
Check the following at regular intervals:
• generator terminals – for corrosion and loose connections,
• wiring – for continuity and damaged insulation,
• mounting bolts – for tightness,
• drive belt – for alignment and wear, and
• drive pulley – for damage and warping.
NOTE
The drive-belt adjustment for the engine
ancillaries (i.e. generator and water pump) is
provided by a spring-loaded tensioner. Therefore,
the drive belt does not require manual
adjustment.
Lubrication
High tolerance bearings are used in this generator. If the bearings are removed during the generator disassembly, new
bearings must be installed to restore the generator to original specification. The ball bearings supporting the rotor shaft
are pre-lubricated and sealed. Do not attempt to lubricate these during servicing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007