engine ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 3654 of 6020
Battery Page 6D1-3–14
4 Service Operations
4.1 Battery
Remove
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems. Refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before
disconnecting the battery.
1 Read and obey the safety precautions for working with batteries, refer to 2 Safety Precautions.
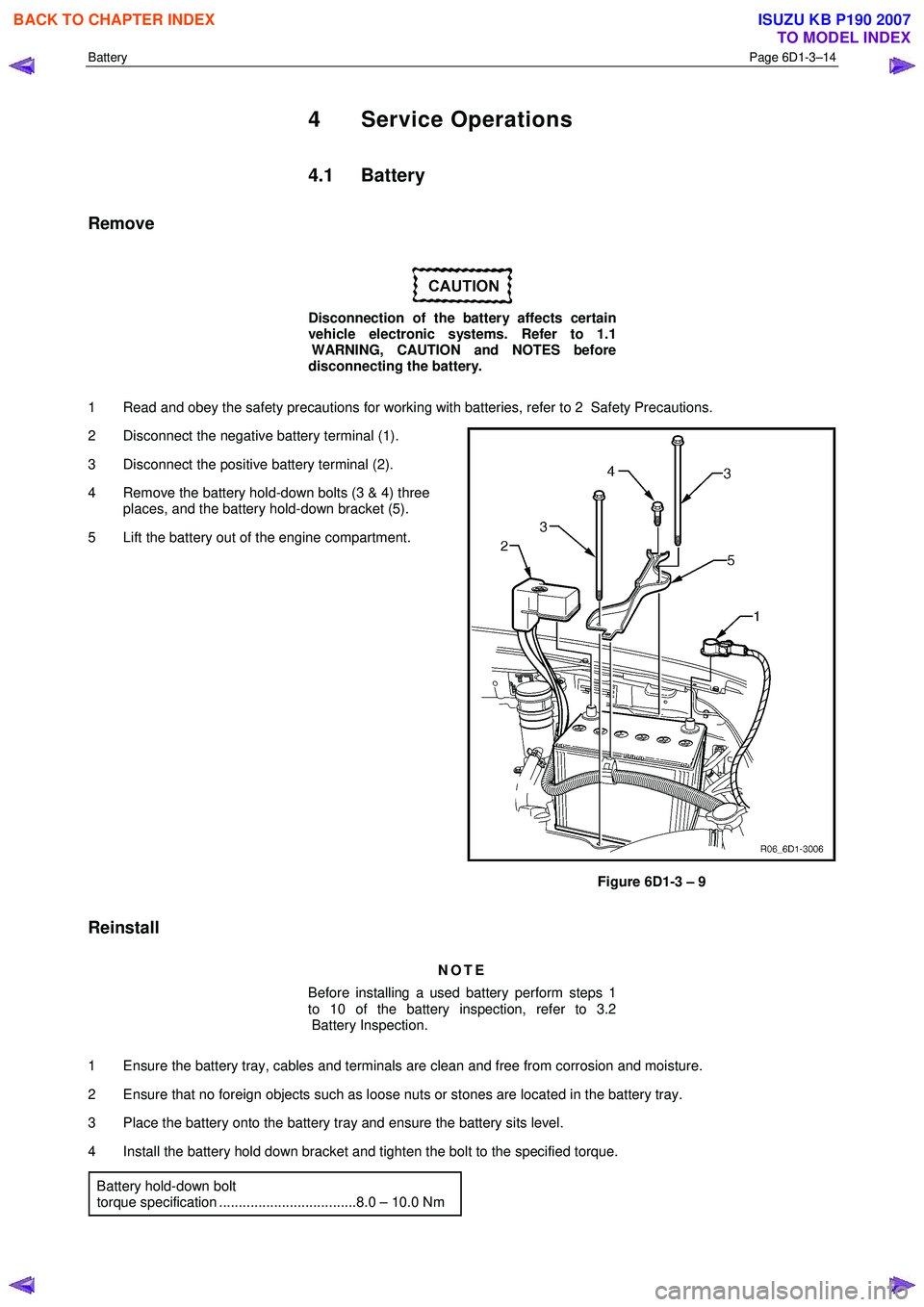
2 Disconnect the negative battery terminal (1).
3 Disconnect the positive battery terminal (2).
4 Remove the battery hold-down bolts (3 & 4) three places, and the battery hold-down bracket (5).
5 Lift the battery out of the engine compartment.
Figure 6D1-3 – 9
Reinstall
NOTE
Before installing a used battery perform steps 1
to 10 of the battery inspection, refer to 3.2
Battery Inspection.
1 Ensure the battery tray, cables and terminals are clean and free from corrosion and moisture.
2 Ensure that no foreign objects such as loose nuts or stones are located in the battery tray.
3 Place the battery onto the battery tray and ensure the battery sits level.
4 Install the battery hold down bracket and tighten the bolt to the specified torque. Battery hold-down bolt
torque specification ...................................8.0 – 10.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3657 of 6020
Battery Page 6D1-3–17
4 Turn off the ignition, lights and all other electrical loads.
5 Check the battery filler caps on both batteries are tight.
6 Place a wet cloth over the battery filler caps of each battery.
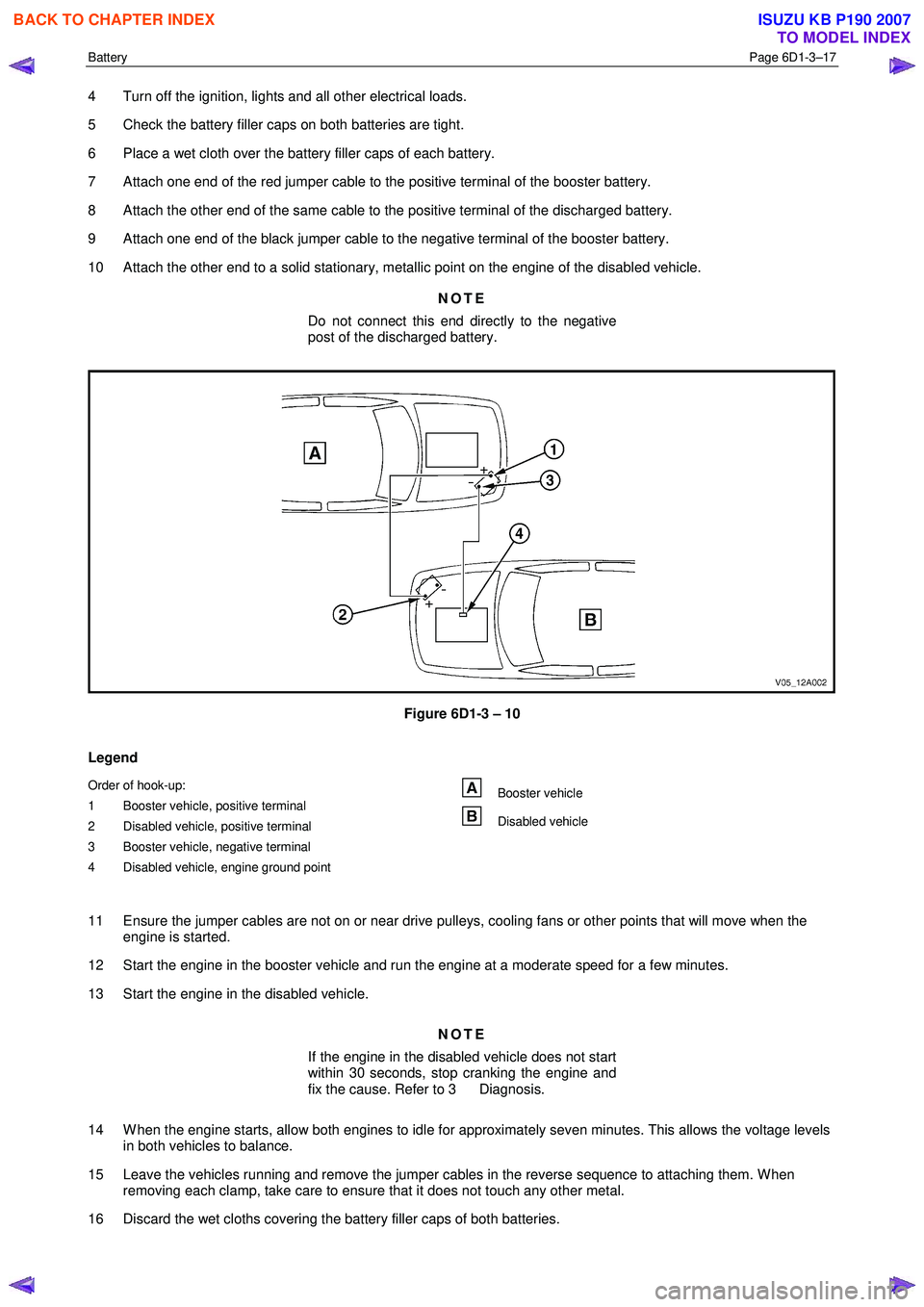
7 Attach one end of the red jumper cable to the positive terminal of the booster battery.
8 Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal of the discharged battery.
9 Attach one end of the black jumper cable to the negative terminal of the booster battery.
10 Attach the other end to a solid stationary, metallic point on the engine of the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
Do not connect this end directly to the negative
post of the discharged battery.
Figure 6D1-3 – 10
Legend
Order of hook-up:
1 Booster vehicle, positive terminal
2 Disabled vehicle, positive terminal
3 Booster vehicle, negative terminal
4 Disabled vehicle, engine ground point Booster vehicle
Disabled vehicle
11 Ensure the jumper cables are not on or near drive pulleys, cooling fans or other points that will move when the engine is started.
12 Start the engine in the booster vehicle and run the engine at a moderate speed for a few minutes.
13 Start the engine in the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
If the engine in the disabled vehicle does not start
within 30 seconds, stop cranking the engine and
fix the cause. Refer to 3 Diagnosis.
14 W hen the engine starts, allow both engines to idle for approximately seven minutes. This allows the voltage levels in both vehicles to balance.
15 Leave the vehicles running and remove the jumper cables in the reverse sequence to attaching them. W hen removing each clamp, take care to ensure that it does not touch any other metal.
16 Discard the wet cloths covering the battery filler caps of both batteries.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3662 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–1
6E1
Powertrain Interface Module – V6
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to 1.2 Warning
Caution and Notes for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and / or property damage.
1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ...................6
1.1 General Description ............................................................................................................ ................................... 6
Serial Data Communication .................................................................................................................................. 6
Serial Data Layout.................................................................................................................................................. 8
1.2 Warning Caution and Notes .................................................................................................................................. 8
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements ............................................................................. .... 8
2 Component Location............................................................................................................................10
2.1 Engine Compartment............................................................................................................. .............................. 10
2.2 Interior................................................................................................................................................................... 11
3 Component Description and Operation ............................................................................................ .12
3.1 Powertrain Interface Module ............................................................................................................................... 12
3.2 Powertrain Interface Module Gateway Components ................................................................................. ....... 13
Engine Control Module........................................................................................................................................ 13
Immobiliser Control Unit ..................................................................................................................................... 13
Automatic Transmission Control Module .......................................................................................... ................ 13
3.3 Powertrain Interface Module Direct Input Switches.............................................................................. ............ 14
Cruise Control Switch.......................................................................................................................................... 14
Power Mode Switch – Automatic Transmission..................................................................................... ........... 14
3rd Start Switch – Automatic Transmission ....................................................................................................... 14
4 Diagnostics ...........................................................................................................................................15
4.1 Diagnostic General Descriptions................................................................................................ ........................ 15
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Tables........................................................................................... ................... 15
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) ...................................................................................................................... 15
Tech 2 PIM Diagnostic Tests............................................................................................................................... 16
5 GM LAN Serial Communication Circuit ............................................................................................ ..17
6 Wiring Diagram and Connector Chart ................................................................................................18
6.1 Wiring Diagrams .................................................................................................................................................. 18
6.2 Connector Chart................................................................................................................................................... 20
6.3 Connector Information .......................................................................................................... .............................. 21
PIM Connector Pin Specifications ............................................................................................... ....................... 21
7 Diagnostics Starting Point ..................................................................................................................24
7.1 Diagnostic Requirements, Precautions and Preliminary Checks .................................................................... 24
Basic Knowledge Required ................................................................................................................................. 24
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required ................................................................................................ ....................... 24
Diagnostic Precautions ....................................................................................................................................... 24
Preliminary Checks.............................................................................................................................................. 25
7.2 Diagnostic System Check ........................................................................................................ ........................... 25
7.3 Powertrain Interface Module – Module Communication Check Failure Diagnostic Table............................. 27
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3663 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–2
8 Intermittent Fault Conditions ..............................................................................................................29
8.1 Intermittent Conditions Diagnostic Table ....................................................................................... ................... 29
Description ........................................................................................................................................................... 29
Diagnostic Table .................................................................................................................................................. 29
9 DTC Tables ............................................................................................................................................31
9.1 DTC C0550 – PIM Internal Fault ................................................................................................. ......................... 31
DTC Description ................................................................................................................................................... 31
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................... 31
Additional Information......................................................................................................... ................................ 31
Conditions for Running the DTC ................................................................................................. ....................... 31
Conditions for Setting the DTC........................................................................................................................... 31
Action Taken When the DTC Sets ................................................................................................. ..................... 31
Conditions for Clearing the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 31
Test Description ................................................................................................................................................... 31
DTC C0550 Diagnostic Table ..................................................................................................... ......................... 32
9.2 DTC U2100 – No Communication With CAN Bus (High Speed) ....................................................................... 32
DTC Description ................................................................................................................................................... 32
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................... 32
Additional Information......................................................................................................... ................................ 32
Conditions for Running the DTC ................................................................................................. ....................... 33
Conditions for Setting the DTC........................................................................................................................... 33
Action Taken When the DTC Sets ................................................................................................. ..................... 33
Conditions for Clearing the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 33
Test Description ................................................................................................................................................... 33
DTC U2100 Diagnostic Table ..................................................................................................... ......................... 33
9.3 DTC U2105 – CAN Bus No Communication With Engine Control Module ...................................................... 35
DTC Description ................................................................................................................................................... 35
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................... 35
Additional Information......................................................................................................... ................................ 35
Conditions for Running the DTC ................................................................................................. ....................... 35
Conditions for Setting the DTC........................................................................................................................... 35
Action Taken When the DTC Sets ................................................................................................. ..................... 35
Conditions for Clearing the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 36
Test Description ................................................................................................................................................... 36
DTC U2105 Diagnostic Table ..................................................................................................... ......................... 36
9.4 DTC U2106 – CAN Bus No Communication With Transmission Control Module........................................... 38
DTC Description ................................................................................................................................................... 38
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................... 38
Additional Information......................................................................................................... ................................ 38
Conditions for Running the DTC ................................................................................................. ....................... 38
Conditions for Setting the DTC........................................................................................................................... 38
Action Taken When the DTC Sets ................................................................................................. ..................... 38
Conditions for Clearing the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 38
Test Description ................................................................................................................................................... 38
DTC U2106 Diagnostic Table ..................................................................................................... ......................... 39
9.5 DTC B0565 – Coolant Temperature Gauge Circuit High Current ..................................................................... 40
9.6 DTC B0575 – Fuel Gauge Circuit High Current ................................................................................................. 40
9.7 DTC B3598 – Cruise Control Cancel Signal Malfunction........................................................................... ....... 41
DTC Description ................................................................................................................................................... 41
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................... 41
Additional Information......................................................................................................... ................................ 41
Conditions for Running the DTC ................................................................................................. ....................... 41
Conditions for Setting the DTC........................................................................................................................... 41
Action Taken When the DTC Sets ................................................................................................. ..................... 41
Conditions for Clearing the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 41
Test Description ................................................................................................................................................... 42
DTC B3628 Diagnostic Table ..................................................................................................... ......................... 42
9.8 DTC B3627 – Cruise Control Resume Signal Malfunction........................................................................... ..... 43
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3667 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–6
1 General Information
A powertrain interface module (PIM) is fitted that incorporates the following functionality:
• Communication protocol between the engine control module (ECM) and transmission control module (TCM) is
General Motors Local Area Network (GM LAN).
• Communication protocol between the PIM and immobiliser control unit is keyword 2000.
• ECM to PIM and PIM to immobiliser control unit (ICU) authentication for vehicle security.
• The following switches, where fitted, input directly into the PIM:
• Automatic transmission power mode switch.
• Automatic transmission 3
rd gear start switch.
• Cruise control switch.
1.1 General Description
Serial Data Communication
The various electronic control modules communicate with each other through the serial data bus. The ECM and TCM
communicate on the serial data bus using the GM LAN communication protocol. Figure 6E1 – 2 shows the serial data
layout.
NOTE
Serial data components shown in Figure 6E1 – 2
will vary depending on vehicle options.
Bus
A bus is a physical circuit or circuits which provides a communication path between two or more control modules.
GM LAN Serial Data Bus
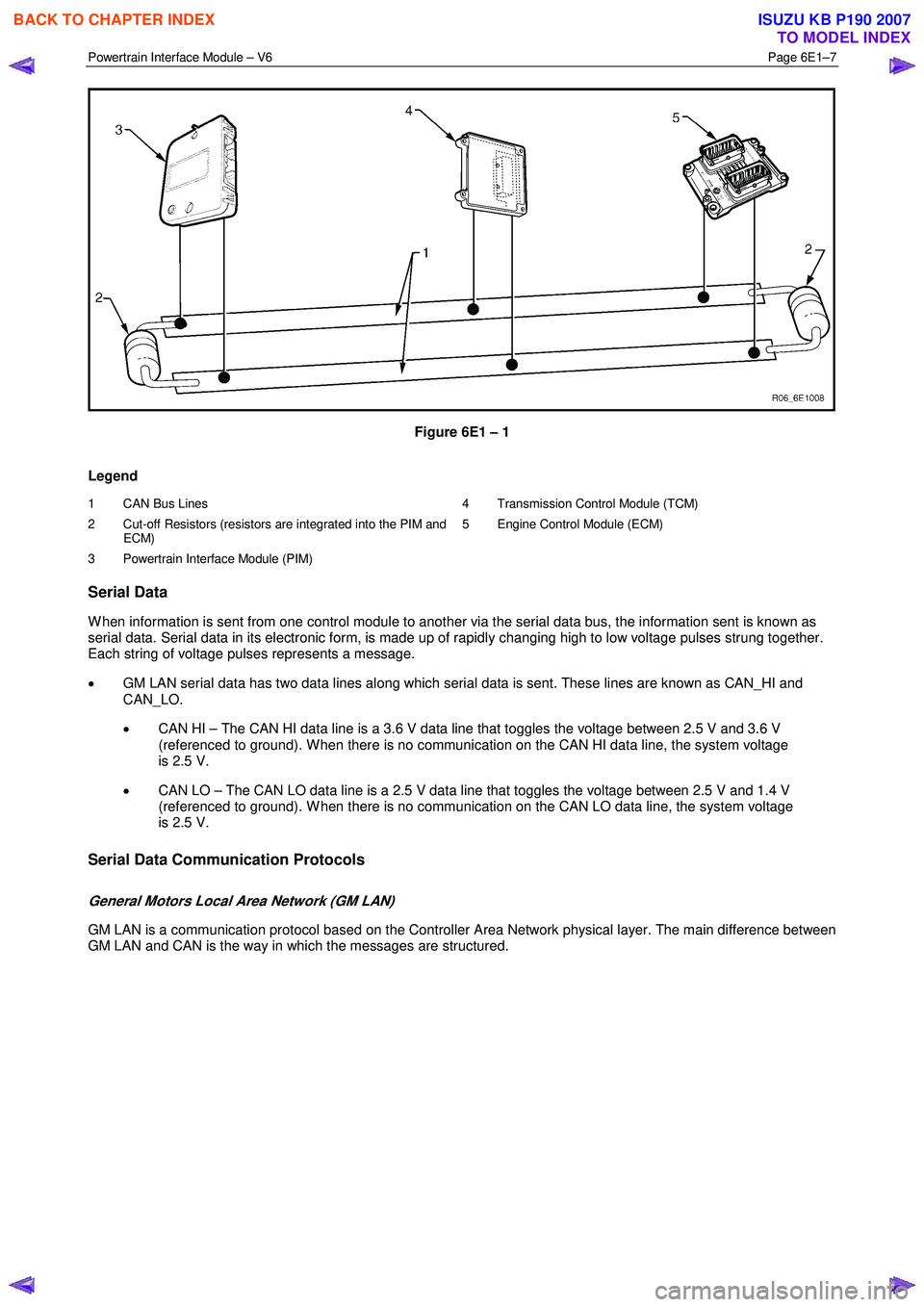
The GM LAN bus is a two wire circuit (1), refer to Figure 6E1 – 1. The GM LAN bus circuits are terminated with cut-off
resistors (2) which are located inside the two control modules at either end of the bus circuit. The purpose of these cut-off
resistors is to prevent data from returning as an echo after reaching the end of the GM LAN bus circuit.
NOTE
• For illustration purposes, the cut-off resistors
are shown outside of the control modules.
• The two control modules with the cut-off
resistors are the PIM and the ECM.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3668 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–7
Figure 6E1 – 1
Legend
1 CAN Bus Lines
2 Cut-off Resistors (resistors are integrated into the PIM and ECM)
3 Powertrain Interface Module (PIM) 4 Transmission Control Module (TCM)
5 Engine Control Module (ECM)
Serial Data
W hen information is sent from one control module to another via the serial data bus, the information sent is known as
serial data. Serial data in its electronic form, is made up of rapidly changing high to low voltage pulses strung together.
Each string of voltage pulses represents a message.
• GM LAN serial data has two data lines along which serial data is sent. These lines are known as CAN_HI and
CAN_LO.
• CAN HI – The CAN HI data line is a 3.6 V data line that toggles the voltage between 2.5 V and 3.6 V
(referenced to ground). W hen there is no communication on the CAN HI data line, the system voltage
is 2.5 V.
• CAN LO – The CAN LO data line is a 2.5 V data line that toggles the voltage between 2.5 V and 1.4 V
(referenced to ground). W hen there is no communication on the CAN LO data line, the system voltage
is 2.5 V.
Serial Data Communication Protocols
General Motors Local Area Network (GM LAN)
GM LAN is a communication protocol based on the Controller Area Network physical layer. The main difference between
GM LAN and CAN is the way in which the messages are structured.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3669 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–8
Serial Data Layout
Figure 6E1 – 2
Legend
1 Powertrain Interface Module (PIM)
2 Transmission Control Module (TCM)
3 Engine Control Module (ECM)
4 Immobiliser Control Unit (ICU)
5 Data Link Connector
A GM LAN Serial Data Circuit
B Keyword 2000 Serial Data Circuit
NOTE
Serial data Components shown in Figure 6E1 – 2
will vary depending on vehicle options.
1.2 Warning Caution and Notes
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
GM HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these
instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. GM HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to
diagnose and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard
to the technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3671 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–10
2 Component Location
2.1 Engine Compartment
Figure 6E1 – 3
Legend
1 Engine Control Module (ECM) 2 Vehicle Acceleration Sensor
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3673 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–12
3 Component Description and
Operation
3.1 Powertrain Interface Module
The powertrain interface module (PIM) is located behind the
right-hand lower hinge pillar trim.
Figure 6E1 – 5
The PIM performs the following functions:
• The PIM acts as the communication gateway between the GM LAN communications protocol and keyword 2000
protocol.
• The PIM converts analogue signals from the cruise control switches into digital serial data.
• The PIM upon inputs received from the engine control module (ECM), transmission control module (TCM) and
immobiliser control unit (ICU) controls the operation of the following instruments and warning lamps:
• Speedometer
• Tachometer
• Check Transmission Lamp
• 3
rd Gear Start Lamp
• Power Mode Switch Lamp
• Automatic Transmission Oil Temp Lamp
• Cruise Set Lamp
• Oil Pressure Lamp
• Service Vehicle Soon (SVS) Lamp
• Charge W arning Lamp
• PRNDL Lamps
• The PIM is responsible for authenticating the immobiliser control unit (ICU) prior to the engine control module
(ECM) authenticating the PIM. If any of these authentication processes fail, the vehicle will not start. For further
information on the immobiliser system, refer to 11A Immobiliser System.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3674 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–13
3.2 Powertrain Interface Module Gateway
Components
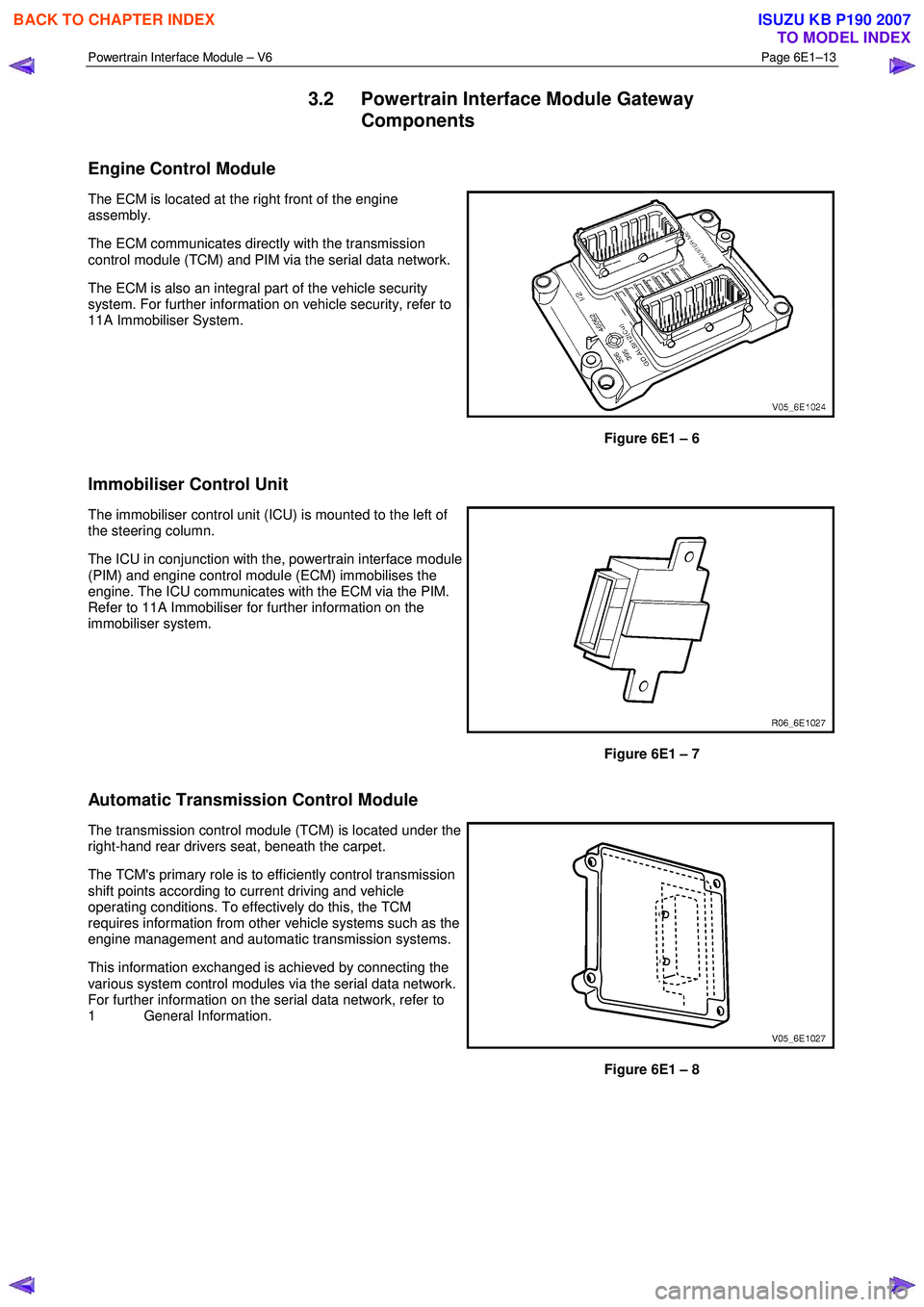
Engine Control Module
The ECM is located at the right front of the engine
assembly.
The ECM communicates directly with the transmission
control module (TCM) and PIM via the serial data network.
The ECM is also an integral part of the vehicle security
system. For further information on vehicle security, refer to
11A Immobiliser System.
Figure 6E1 – 6
Immobiliser Control Unit
The immobiliser control unit (ICU) is mounted to the left of
the steering column.
The ICU in conjunction with the, powertrain interface module
(PIM) and engine control module (ECM) immobilises the
engine. The ICU communicates with the ECM via the PIM.
Refer to 11A Immobiliser for further information on the
immobiliser system.
Figure 6E1 – 7
Automatic Transmission Control Module
The transmission control module (TCM) is located under the
right-hand rear drivers seat, beneath the carpet.
The TCM's primary role is to efficiently control transmission
shift points according to current driving and vehicle
operating conditions. To effectively do this, the TCM
requires information from other vehicle systems such as the
engine management and automatic transmission systems.
This information exchanged is achieved by connecting the
various system control modules via the serial data network.
For further information on the serial data network, refer to
1 General Information.
Figure 6E1 – 8
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007