maintenance ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1297 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-263
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
Additional Checks •
Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16
volts.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the reference circuit can cause an engine
miss condition. The scan tool can usually detect EMI by monitoring the engine
speed. A sudden increase in speed with little change in actual engine speed change
indicates that EMI is present. If a problem exists, check routing of high voltage
components, such as fuel injection solenoid wiring, near the sensor circuits.
Surges/Chuggles
Checks Action
DIFINITION:The engine has a power variation under a steady throttle or cruise. The vehicle seems to speed up and slow down
with no change in the accelerator pedal.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1299 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-265
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
Additional Checks •
Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16
volts.
• Inspect the EGR system operating correctly.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. (A/T only)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1301 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-267
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intercooler.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
• Inspect for a worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor
wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Inspect for turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve
inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1303 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-269
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intercooler.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
• Inspect for a worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor
wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Inspect for turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve
inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1350 of 6020

EXHAUST SYSTEM 6F – 17
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
Make the necessary adjustments, repairs, and part replacements if excessive wear or damage is discovered during
inspection.
Turbocharger pressure check
1. Remove the hose between the waste gate and the
compressor outlet pipe.
2. Connect the pressure gauge. To compressor outlet pipe.
3. Start the engine and gradually increase the engine speed (the vehicle must be stationary with no load
applied to the engine).
4. Check to see that turbocharger pressure rises to approximately 141.3 Kpa (1060 mmHg).
Pressure Gauge : 5-8840-0075-0
150RY00030
Waste gate operation check
1. Remove the hose between the waste gate and the compressor outlet pipe.
2. Connect the pressure gauge. To waste gate actuator.
3. Check to see that the rod begins to move when a pressure of approximately 118 Kpa (885 mmHg) is
applied to the waste gate.
Note:
Do not apply a pressure greater than 150Kpa (1125
mmHg) to the waste gate during this check.
150RY00031
Unit Inspection (Remove Turbo. from engine)
Check to see the pressure required to move the control
rod 2 mm is within the limits shown below.
Kpa/mmHg
4JH1TC 134.8/1011
4JA1TC 147.7/1108
150RY00032
Contact the “ISUZU MOTORS LIMITED” Dealer service
department or “IHI SERVICE FACILITY” for major repairs
and maintenance.
Important wheel shaft end play and bearing clearance
standards and limits are included below for your reference.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1363 of 6020

ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6A-3
ISUZU DIESEL ENGINE (4JK1/4JJ1)
Service Precautions
Matters that require attention in terms of
maintenance
To prevent damage to the engine and ensure reliabilit
y
of its performance, pay attention to the following in
maintaining the engine:
• W hen lifting up or supporting the engine, do not
apply a jack on the oil pan.
W hen taking down the engine on the ground, do not make the bearing surface of the oil pan touch
the ground directly. Use a wooden frame, fo
r
example, to support the engine with the engine
foot and the flywheel housing.
Because there is only a small clearance between the oil pan and the oil pump strainer, it can
damage the oil pan and the oil strainer.
• W hen the air duct or air cleaner is removed, cove
r
the air intake opening to prevent foreign matter
from getting into the cylinder. If it gets
contaminated, it can considerably damage the
cylinder and others while the engine is operating.
• W hen maintaining the engine, never fail to remove
the battery earth cable. If not, it may damage the
wire harness or electrical parts. If you need
electricity on for the purpose of inspection, fo
r
instance, watch out for short circuits and others.
•
Apply engine oil to the sliding contact surfaces of
the engine before reassembling it. This ensures
adequate lubrication when the engine is first
started.
• W hen valve train parts, pistons, piston rings,
connecting rods, connecting rod bearings o
r
crankshaft journal bearings are removed, put them
in order and keep them.
• W hen installing them, put them back in the same
location they were removed from.
• Gaskets, oil seals, O-rings, etc. must be replaced
with new ones when the engine is reassembled.
•
As for parts where a liquid gasket is used, remove
an old liquid gasket completely and clean it up
thoroughly so that no oil, water or dust is clinging
to them. Then, apply the designated liquid gasket
to each place anew before assembly.
• Surfaces covered with liquid gasket must be
assembled within 5 minutes of gasket application.
If more than 5 minutes has elapsed, remove the
existing liquid gasket and apply a new liquid
gasket.
• W hen assembling or installing parts, fasten them
with the prescribed tightening torque so that the
y
are installed properly.
Matters that require attention in specifically dealing
with this engine.
Holes or clearances in the fuel system, which serve as
a passage of fuel, including the inside of the injector,
are made with extreme precision. For this reason, the
y
are highly sensitive to foreign matter and, if it gets in, it
can lead to an accident on the road, for instance; thus,
make sure that foreign matter is prevented from getting
in.
W hen servicing the fuel system, every precaution must
be taken to prevent the entry of foreign material into the
system.
• Before beginning the service procedure, wash the
fuel line and the surrounding area.
• Perform the service procedures with clean hands.
Do not wear work gloves.
• Immediately after removing the fuel hose and/o
r
fuel pipe, carefully tape vinyl bags over the
exposed ends of the hose or pipe.
• If parts are to be replaced (fuel hose, fuel pipe,
etc.) do not open the new part packaging until
installation.
Work procedure
• The fuel opening must be quickly sealed when
removing the fuel pipe, injection pipe, fuel injector,
fuel supply pump, and fuel rail.
• The eyebolts and gasket must be stored in a clean
parts box with a lid to prevent adhesion of foreign
matter.
• Fuel leakage could cause fires. Therefore, afte
r
finishing the work, wipe off the fuel that has leaked
out and make sure there is no fuel leakage afte
r
starting the engine.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1528 of 6020
ENGINE COOLING (4JK1/4JJ1) 6B-5
Radiator
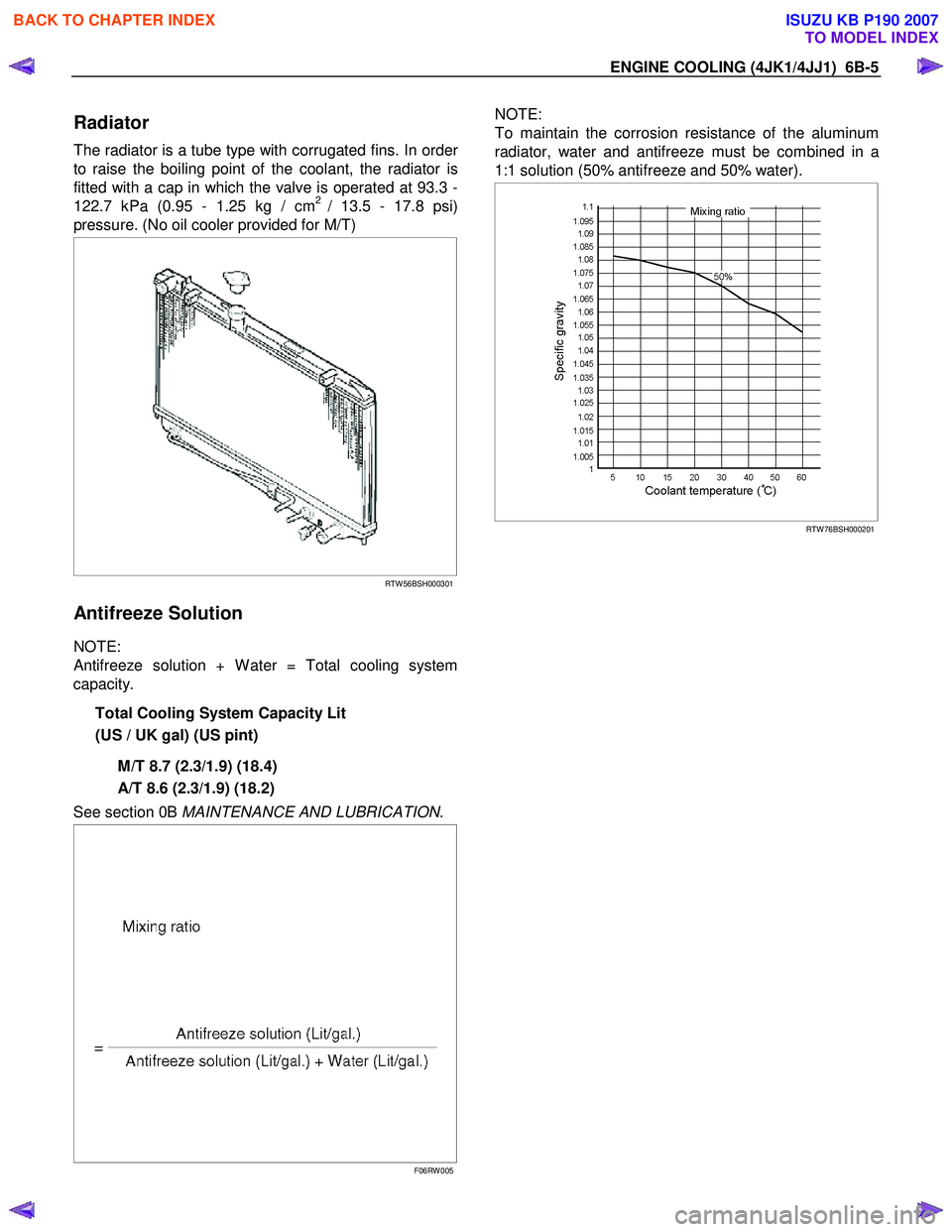
The radiator is a tube type with corrugated fins. In order
to raise the boiling point of the coolant, the radiator is
fitted with a cap in which the valve is operated at 93.3 -
122.7 kPa (0.95 - 1.25 kg / cm
2 / 13.5 - 17.8 psi)
pressure. (No oil cooler provided for M/T)
RTW 56BSH000301
Antifreeze Solution
NOTE:
Antifreeze solution + W ater = Total cooling system
capacity.
Total Cooling System Capacity Lit
(US / UK gal) (US pint)
M/T 8.7 (2.3/1.9) (18.4)
A/T 8.6 (2.3/1.9) (18.2)
See section 0B MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION .
F06RW 005
NOTE:
To maintain the corrosion resistance of the aluminum
radiator, water and antifreeze must be combined in a
1:1 solution (50% antifreeze and 50% water).
RTW 76BSH000201
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1615 of 6020
ENGINE ELECTRICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6D-27
Magnetic Switch
The following tests must be performed with the starter
motor fully assembled.
The yoke lead wire must be disconnected from the “M”
terminal.
To prevent coil burning, complete each test as quickl
y
as possible (within three to five seconds).
Temporarily connect the solenoid switch between the
clutch and the housing and run the following test.
Complete each test within three to five seconds.
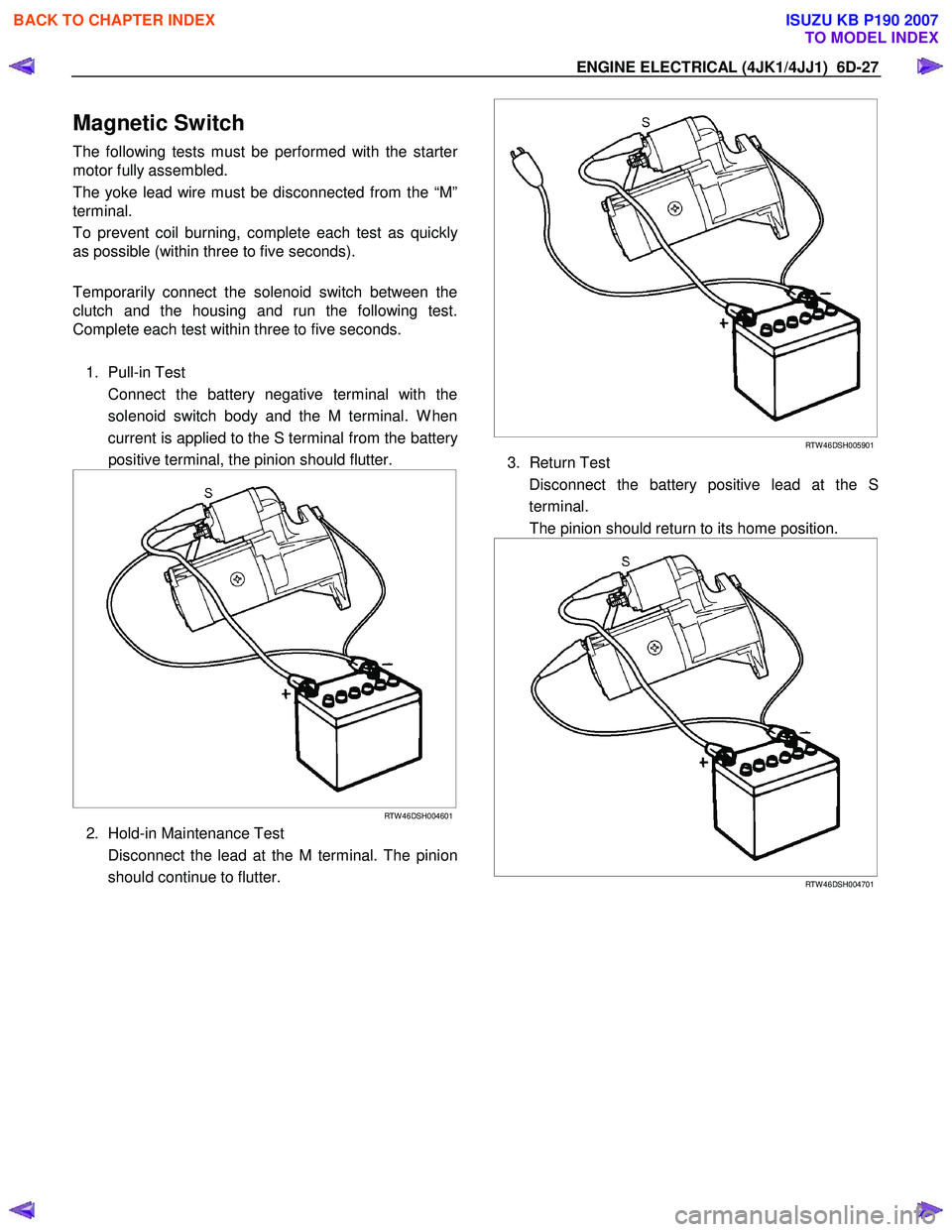
1. Pull-in Test
Connect the battery negative terminal with the solenoid switch body and the M terminal. W hen
current is applied to the S terminal from the batter
y
positive terminal, the pinion should flutter.
RTW 46DSH004601
2. Hold-in Maintenance Test
Disconnect the lead at the M terminal. The pinion should continue to flutter.
RTW 46DSH005901
3. Return Test
Disconnect the battery positive lead at the S terminal.
The pinion should return to its home position.
RTW 46DSH004701
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2013 of 6020
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE) 6-13
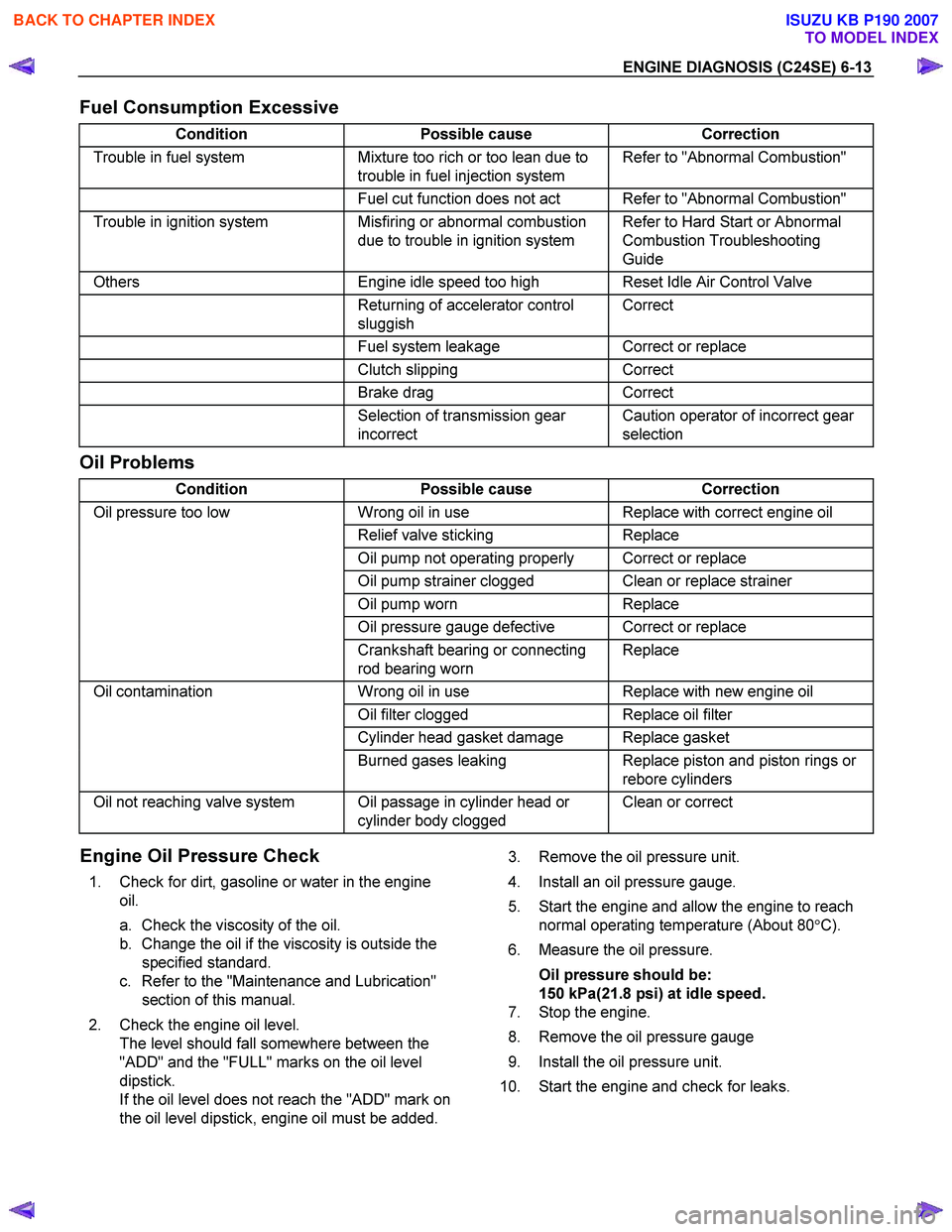
Fuel Consumption Excessive
Condition Possible cause Correction
Trouble in fuel system Mixture too rich or too lean due to
trouble in fuel injection system Refer to "Abnormal Combustion"
Fuel cut function does not act Refer to "Abnormal Combustion"
Trouble in ignition system Misfiring or abnormal combustion
due to trouble in ignition system Refer to Hard Start or Abnormal
Combustion Troubleshooting
Guide
Others Engine idle speed too high Reset Idle Air Control Valve
Returning of accelerator control
sluggish Correct
Fuel system leakage Correct or replace
Clutch slipping Correct
Brake drag Correct
Selection of transmission gear
incorrect Caution operator of incorrect gear
selection
Oil Problems
Condition Possible cause Correction
Oil pressure too low Wrong oil in use Replace with correct engine oil
Relief valve sticking Replace
Oil pump not operating properly Correct or replace
Oil pump strainer clogged Clean or replace strainer
Oil pump worn Replace
Oil pressure gauge defective Correct or replace
Crankshaft bearing or connecting
rod bearing worn Replace
Oil contamination
Wrong oil in use Replace with new engine oil
Oil filter clogged Replace oil filter
Cylinder head gasket damage Replace gasket
Burned gases leaking Replace piston and piston rings or
rebore cylinders
Oil not reaching valve system Oil passage in cylinder head or cylinder body clogged Clean or correct
Engine Oil Pressure Check
1. Check for dirt, gasoline or water in the engine
oil.
a. Check the viscosity of the oil.
b. Change the oil if the viscosity is outside the specified standard.
c. Refer to the "Maintenance and Lubrication" section of this manual.
2. Check the engine oil level. The level should fall somewhere between the
"ADD" and the "FULL" marks on the oil level
dipstick.
If the oil level does not reach the "ADD" mark on
the oil level dipstick, engine oil must be added.
3. Remove the oil pressure unit.
4. Install an oil pressure gauge.
5. Start the engine and allow the engine to reach normal operating temperature (About 80 °C).
6. Measure the oil pressure.
Oil pressure should be:
150 kPa(21.8 psi) at idle speed.
7. Stop the engine.
8. Remove the oil pressure gauge
9. Install the oil pressure unit.
10. Start the engine and check for leaks.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2124 of 6020

6C-6 ENGINE FUEL (C24SE)
Fuel Filter
Inspection
1. Replace the fuel filter if the fuel leaks from fuel filter
body or if the fuel filter body itself is damaged.
2. Replace the filter if it is clogged with dirt o
r
sediment.
Installation
1. Install the filter to holder from fuel tank front side.
NOTE: Attend direction of fuel filter. (1) to engine side
(2) to fuel tank side.
NOTE: Verify to hang holder hook to fuel filter.
RTW 36CSH000301
2. Connect the quick connector from the fuel tube to
the fuel filter.
NOTE: Pull of the left checker into the fuel pipe.
NOTE: Refer to “Fuel Tube/Quick Connector Fittings” in
this section when performing any repairs.
3. Tighten fuel filler cap until at least one click are heard.
4. Connect the battery ground cable.
Inspection
After installation, start engine and check for fuel
leakage.
In–Tank Fuel Filter
The filter is located on the lower end of fuel pickup tube
in the fuel tank. It prevents dirt from entering the fuel
pipe and also stops water unless the filter is completel
y
submerged in the water. It is a selfcleaning type, not
requiring scheduled maintenance. Excess water and
sediment in the tank restricts fuel supply to the engine,
resulting in engine stoppage. In such a case, the tank
must be cleaned thoroughly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007