reset ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2946 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–169
Page 6A1–169
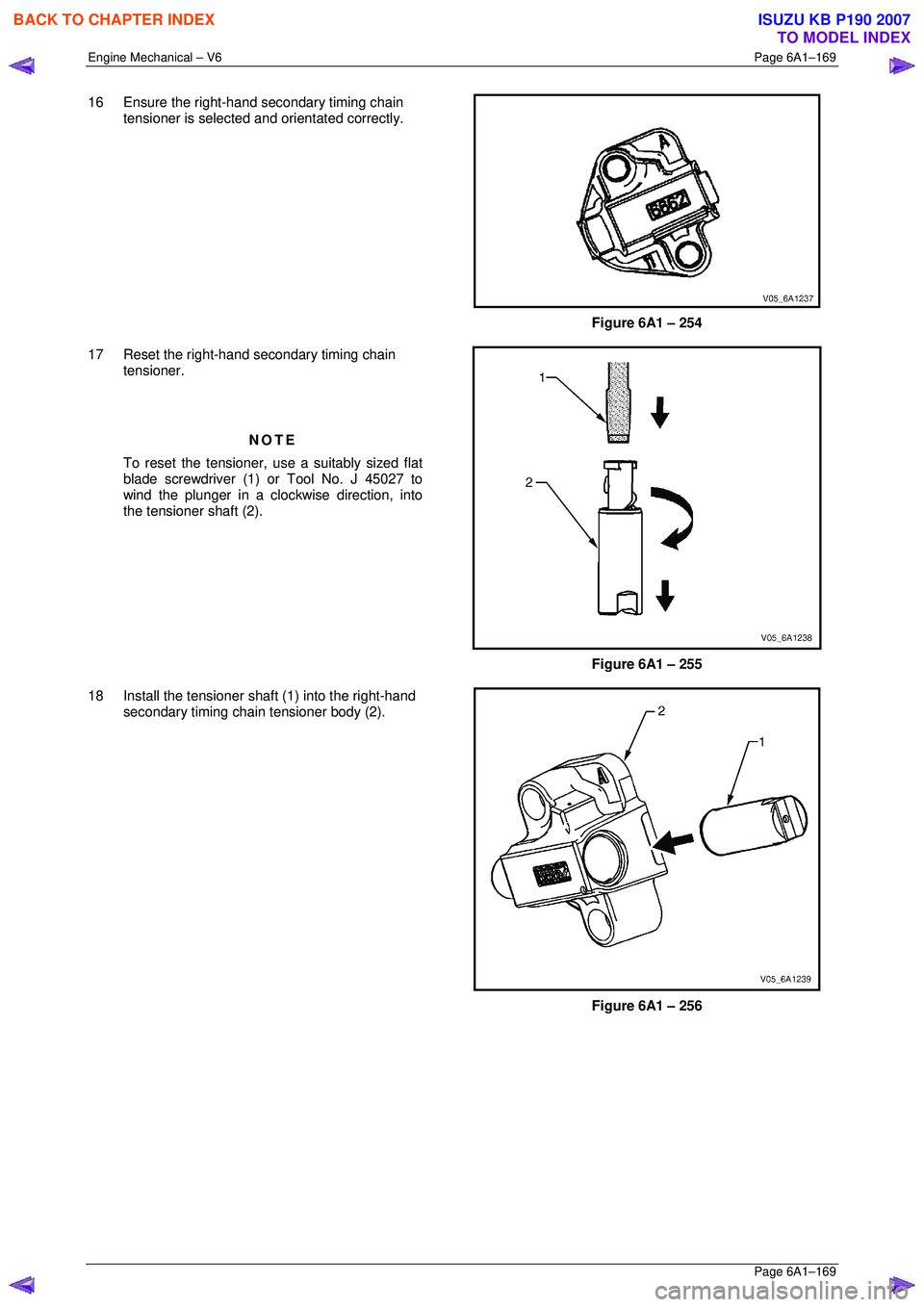
16 Ensure the right-hand secondary timing chain
tensioner is selected and orientated correctly.
Figure 6A1 – 254
17 Reset the right-hand secondary timing chain tensioner.
NOTE
To reset the tensioner, use a suitably sized flat
blade screwdriver (1) or Tool No. J 45027 to
wind the plunger in a clockwise direction, into
the tensioner shaft (2).
Figure 6A1 – 255
18 Install the tensioner s haft (1) into the right-hand
secondary timing chain tensioner body (2).
Figure 6A1 – 256
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2954 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–177
Page 6A1–177
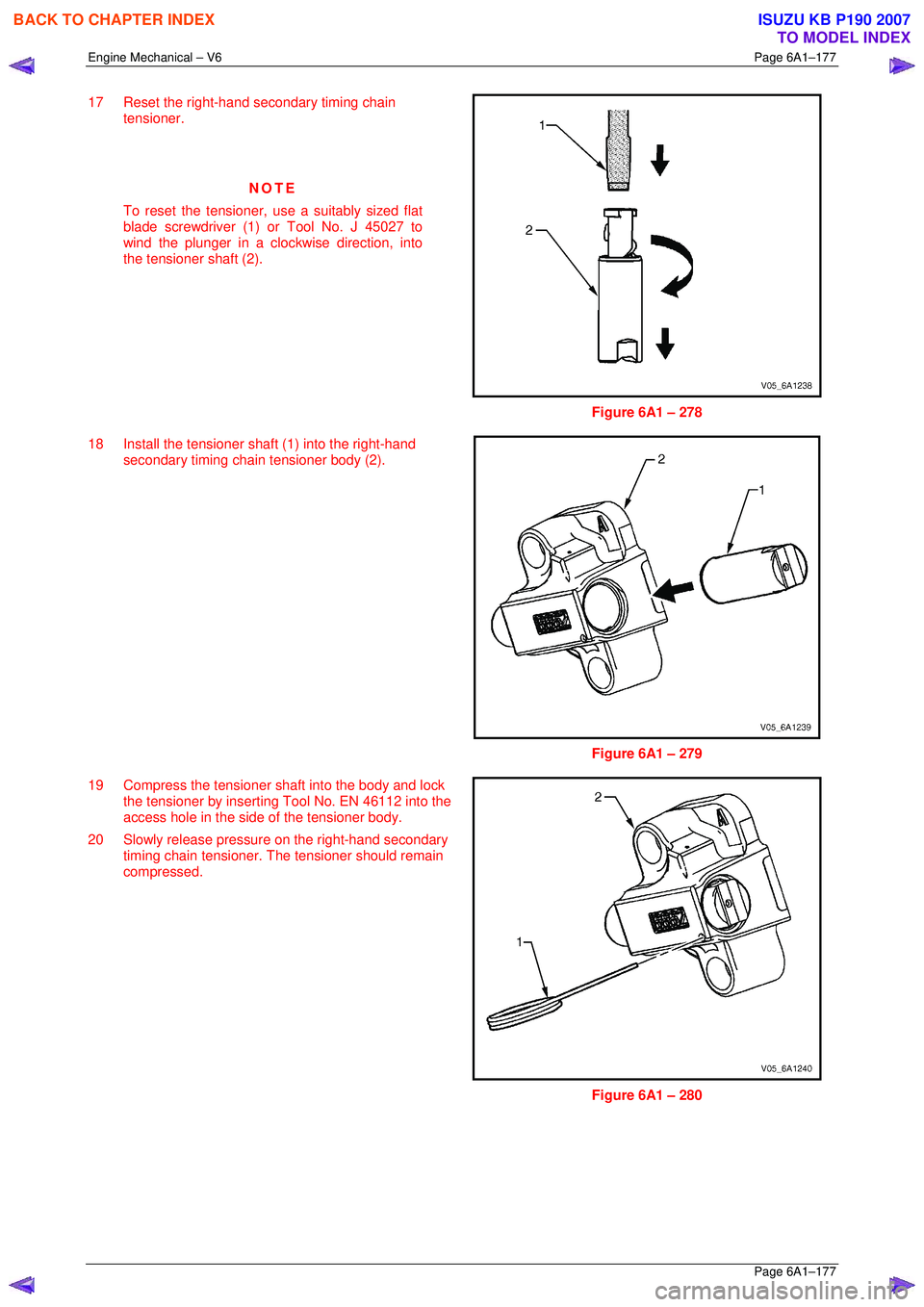
17 Reset the right-hand secondary timing chain
tensioner.
NOTE
To reset the tensioner, use a suitably sized flat
blade screwdriver (1) or Tool No. J 45027 to
wind the plunger in a clockwise direction, into
the tensioner shaft (2).
Figure 6A1 – 278
18 Install the tensioner s haft (1) into the right-hand
secondary timing chain tensioner body (2).
Figure 6A1 – 279
19 Compress the tensioner shaft into the body and lock the tensioner by inserting Tool No. EN 46112 into the
access hole in the side of the tensioner body.
20 Slowly release pressure on the right-hand secondary timing chain tensioner. The tensioner should remain
compressed.
Figure 6A1 – 280
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2963 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–186
Page 6A1–186
3.18 Camshaft Sprocket – Excluding MY06
Update
CAUTION
Setting the camshaft timing is required
whenever the camshaft drive system is
disturbed to ensure the relationship between
any chain and sprocket is not lost. Even when
only one sprocket is involved, multiple
crankshaft rotations will not produce
conditions where correct timing can be
confirmed.
If required, follow the Left-hand Secondary
Camshaft Chain Components reinstallation
procedure to reset the camshaft timing.
Remove
Right-hand Side
1 Remove the right-hand ca mshaft cover, refer to 3.12 Camshaft Cover.
2 Remove the camshaft position sensors, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – Service Operations.
3 Remove the camshaft position actuator solenoids, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations .
4 Remove the crankshaft bal ancer assembly, refer to 3.13 Crankshaft Balancer Assembly .
5 Install the crankshaft rotation socket Tool No. EN-46111 onto the crankshaft.
6 Rotate the crankshaft until the camshafts are in a neutral low tension position. The camshaft flats will be
parallel with the camshaft cover rail (1).
Figure 6A1 – 298
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2970 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–193
Page 6A1–193
3.19 Camshaft Sprocket – MY06 Update
CAUTION
Setting the camshaft timing is required
whenever the camshaft drive system is
disturbed to ensure the relationship between
any chain and sprocket is not lost. Even when
only one sprocket is involved, multiple
crankshaft rotations will not produce
conditions where correct timing can be
confirmed.
If required, follow the Left-hand Secondary
Camshaft Chain Components reinstallation
procedure to reset the camshaft timing.
Remove
Right-hand Side
1 Remove the right-hand camshaft cover, refer to 3.12 Camshaft Cover.
2 Remove the camshaft position sensors, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – Service Operations.
3 Remove the camshaft position actuator solenoids, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations .
4 Remove the crankshaft bal ancer assembly, refer to 3.13 Crankshaft Balancer Assembly .
5 Install the crankshaft rotation socket Tool No. EN-46111 onto the crankshaft.
6 Rotate the crankshaft until the camshafts are in a neutral low tension position. The camshaft flats will be
parallel with the camshaft cover rail (1).
Figure 6A1 – 312
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3134 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–357
Page 6A1–357
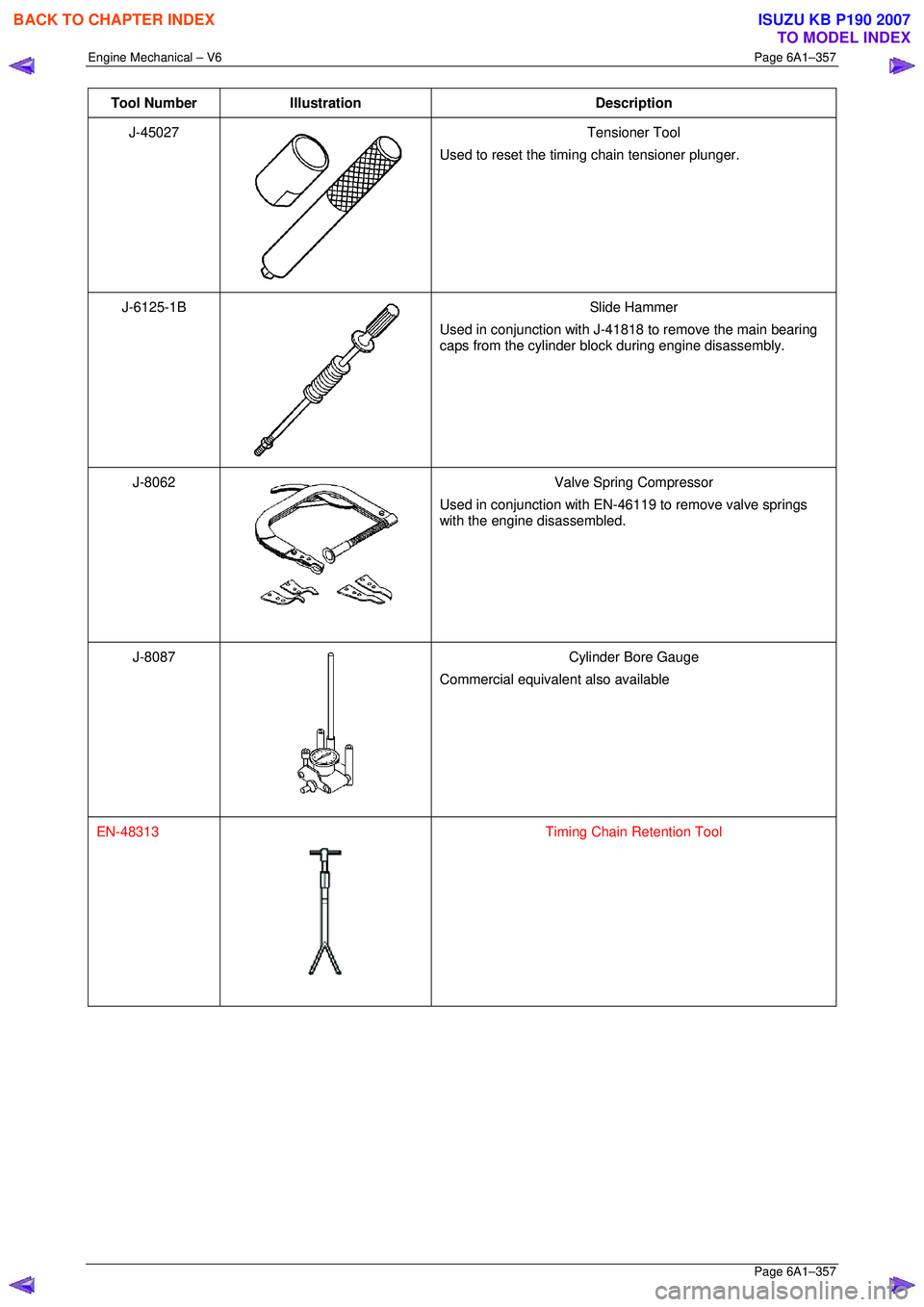
Tool Number Illustration Description
J-45027
Tensioner Tool
Used to reset the timing chain tensioner plunger.
J-6125-1B
Slide Hammer
Used in conjunction with J-41818 to remove the main bearing
caps from the cylinder block during engine disassembly.
J-8062
Valve Spring Compressor
Used in conjunction with EN-46119 to remove valve springs
with the engine disassembled.
J-8087
Cylinder Bore Gauge
Commercial equivalent also available
EN-48313
Timing Chain Retention Tool
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3325 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–47
6.7 Throttle Body Relearn
A throttle body relearn procedure is performed in one of two ways:
• Engine Control Module initiated throttle body relearn, or
• Tech 2 initiated throttle body relearn.
Engine Control Module Throttle Body Relearn
The engine control module (ECM) will automatically perform a throttle body relearn procedure if either of the following
conditions exist:
• The battery has been disconnected, or
• The ignition switch is in the ON position for greater than 29 seconds, and the following conditions are met:
− Engine speed is less than 40 rpm,
− Vehicle speed is 0 km/h,
− Engine coolant temperature is 5 – 60°C,
− Intake air temperature is 5 – 60°C,
− Accelerator pedal position sensor angle is less than 14.9%, and
− Ignition voltage is greater than 10 V.
Tech 2 Throttle Body Relearn
To perform a throttle body relearn using Tech 2, complete the following procedure:
NOTE
Tech 2 will not initiate a throttle body relearn if
the engine is running.
1 Connect Tech 2 to the data link connector (DLC) and turn the ignition on.
2 On Tech 2 select Engine / Programming / Throttle Body Relearn.
3 W hen Tech 2 displays ‘Do you really want to Reset?’, press the ‘Yes’ soft key.
4 W hen Tech 2 displays ‘Programming Completed’, and the electronic throttle control value displayed by Tech 2 is ‘11’, press the ‘Confirm’ soft key to return to the Tech 2 Programming screen.
5 The throttle body relearn is now complete.
6.8 Electronic Ignition (EI) System Diagnosis
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls the ignition coils by pulsing the ignition control (IC) circuits, which triggers an
ignition coil and fires the spark plug. The ECM controls the sequencing and the timing of each ignition coil. The ignition
system consist of the following components:
• The six ignition coils
• The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
• The four camshaft position (CMP) sensors
• The ECM
The ignition coils use the following circuits:
• An IC circuit
• An ignition 1 voltage circuit
• Two ground circuits
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3383 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–105
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses information from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the camshaft position
(CMP) sensor to determine when an engine misfire is occurring. By monitoring variations in the crankshaft rotation
speed for each cylinder, the ECM is able to detect individual misfire events. A misfire rate that is high enough can cause
3-way catalytic converter damage. The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will flash ON and OFF when the conditions for
catalytic converter damage are preset. DTCs P0301 – P0306 correspond to cylinders 1 to 6. If the ECM is able to
determine that a specific cylinder is misfiring, the DTC for that cylinder sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0335, P0336, or P0338 are not set.
• The engine speed is between 400 – 7,000 rpm and steady.
• The delivered torque signal is more than 10 percent at idle with the transmission in neutral.
• The delivered torque signal is between 10 – 30 percent with the transmission in drive.
• The intake air temperature (IAT) is more than –30° C.
• The engine run time is more than 45 seconds.
• The fuel level is more than 12 percent.
• The torque management is not active.
• DTCs P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305, and P0306 run continuously when the above conditions exist for at
least 1,000 engine revolutions.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects a crankshaft rotation speed variation indicating a single cylinder misfire rate sufficient to cause
emissions levels to exceed mandated standards.
• The condition exists for more than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The control module activates the MIL on the second ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic
fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the
second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after four consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission
related diagnostic.
• Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Additional Information
• A misfire DTC could be caused by an excessive vibration from sources other than the engine. Check for the
following possible sources:
− Tyre or wheel out of round or balance
− Variable thickness brake rotor or drum
− Drive shaft not balanced
− Certain rough road conditions
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3418 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–140
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM), the powertrain interface module (PIM) and the immobiliser control unit (ICU) are
integral parts of the vehicle immobiliser system. The immobiliser system authenticates the security code programmed
into each of these modules to prevent unauthorised vehicle operation. This authentication process includes the following
steps:
1 At predetermined situations, the ICU sends a security code to the PIM.
2 W hen the ignition is switched ON, the PIM receives and compares this security code from the ICU against the security code programmed into the PIM.
3 Once the PIM receives the correct security code from the ICU, it sends a security code to the ECM.
4 The ECM receives and compares this security code from the PIM against the security code programmed into the ECM.
5 The authentication process is complete once the ECM receives the correct security code from the PIM within the specified time frame.
6 The ECM allows normal vehicle operation.
NOTE
If any of these authentication processes fail, the
vehicle will not start and DTCs will set. For further
information on the immobiliser system, refer to
11A Immobiliser.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Conditions for running the DTC are:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
P0513
The ECM receives an incorrect response from the PIM during the immobiliser authentication process.
P0633
An attempt is made to start the engine before the immobiliser function has been programmed into a new PIM.
P1629
The ECM has not received a fuel enable password from the ICU.
P1632
The ECM receives an incorrect response from the PIM during the immobiliser authentication process.
P1677
An attempt is made to start the vehicle after the ECM was reset.
P1678
The ECM does not receive a valid response from the PIM when an attempt is made to start the engine.
P1679
The ECM receives a message from the PIM stating that it can't authenticate to the ICU.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3443 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–165
Step Action Yes
No
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0850 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.43 DTC P1648
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P1648 – W rong Security Code Entered.
Circuit Description
Tech 2 is used to program the engine control module (ECM). Before any programming, a security code must be entered
into Tech 2. The ECM will check if the code entered is correct before continuing. If the security code is incorrect, DTC
P1648 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Conditions for running the DTC are:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
An incorrect security code is entered into Tech 2 when attempting to program the ECM.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
W hen the DTC sets, the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is not displayed.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The immobiliser security code is a Type ‘C’ DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type ‘C’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘C’ DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management –V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6 – Service Operations for details on resetting the ECM.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3444 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–166
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
4 This step tests the ECM ground circuits and supply voltage.
DTC P1648 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
NOTE
Do not attempt to perform any Tech 2 function that
requires the ECM security code to be entered.
Does DTC P1648 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3 Using Tech 2, attempt a programming function that requires the ECM
security code to be entered. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6
– Service Operations for details on resetting the ECM.
Has the programming function been successfully performed? System OK Go to Step 4
4 1 Test all ECM ground circuits for a high resistance or an open
circuit fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis
for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
2 Test the ECM ignition supply voltage circuit for a high resistance, open circuit or short to ground fault condition. Refer
to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical
fault diagnosis.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6 – Service
Operations for details on replacing the ECM.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
Does DTC P1648 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
7.44 DTC P1668, P2500 or P2501
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P1668 – Generator L Terminal Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P2500 – Generator L Terminal Low Voltage
• DTC P2501 – Generator L Terminal High Voltage
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007