checking oil ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 86 of 6020

1-52 HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING
Checking and Adjusting for Used Compressor
(1) Perform Oil return operation.
(Refer to "Oil Return Operation" in this section.)
(2) Discharge refrigerant and remove the compressor.
(3) Drain the compressor oil and measure the extracted oil with
a measuring cylinder.
(4) Check the compressor oil for contamination.
(Refer to "Contamination of Compressor Oil" in this section.)
(5) Adjust oil level following the procedure below.
Type Collected Amount Charging Amount
more than 90 cm3
(2.53 lmp fl oz) same as collected
amount
less than 90 cm3
(2.53 lmp fl oz) 90 cm3
(2.53 lmp fl oz) CR-14
(6) Install the compressor, then evacuate, charge and perform
oil return operation.
(7) Check system operation.
When it is impossible to perform oil return operation, the
compressor oil should be checked in the following order:
(1) Discharge refrigerant and remove the compressor.
(2) Drain the compressor oil and measure the extracted oil with a measuring cylinder.
(3) Check the oil for contamination.
(4) If more than 90 cm
3 (2.53 lmp fl oz) for CR-14 type is
extracted from the compressor, supply same amount of oil
to the compressor to be installed.
If the amount of oil extracted is less than 90 cm
3 (2.53 lmp
fl oz) for CR-14 type recheck the compressor oil in the
following order:
(5) Supply 90 cm
3 (2.53 lmp fl oz) for CR-14 type oil to the
compressor and install it onto the vehicle.
(6) Perform oil return operation.
(7) Remove the compressor and recheck the amount of oil.
(8) Adjust the compressor oil.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 87 of 6020

HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1-53
Checking and Adjusting for Compressor
Replacement
180 cm3 (5.07 lmp fl oz) of oil is charged in compressor
(service parts). So it is necessary to drain the proper amount
of oil from the new compressor.
1) Perform oil return operation.
2) Discharge refrigerant and remove the compressor.
3) Drain the compressor oil and measure the extracted oil.
4) Check the compressor oil for contamination.
5) Adjust oil level as required.
Amount of oil drained
From used compressor Draining amount of oil
From new compressor
less than
90 cm
3 (2.53 lmp fl oz) Some as drained
amount
more than
90 cm
3 (2.53 lmp fl oz) 90 cm
3 (2.53 lmp fl oz)
6) Evacuate, charge and perform oil return operation.
7) Check system operation.
CONTAMINATION OF COMPRESSOR OIL
Unlike engine oil, no cleaning agent is added to the
compressor oil. Even is the compressor runs for a long period
of time (approximately 1 season), the oil never becomes
contaminated as long as there is nothing wrong with the
compressor or its method of use.
Inspect the extracted oil for any of the following
conditions:
• The capacity of the oil has increased.
• The oil has changed color to red.
• Foreign substances, metal powder, etc., are present in the
oil.
If any of these conditions exists, compressor oil is
contaminated. Whenever contaminated compressor oil is
discovered, the receiver/drier must be replaced.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 88 of 6020

1-54 HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING
OIL RETURN OPERATION
There is close affinity between the oil and the refrigerant.
During normal operation, part of the oil recirculates with the
refrigerant in the system.
W hen checking the amount of oil in the system, or replacing
any component of the system, the compressor must be run in
advance for oil return operation. The procedure is as follows:
1) Open the all doors and engine hood.
2) Start the engine and A/C switch is "ON" and Set the fan control knob at its highest position.
3) Run the compressor for more than 20 minutes between 800 and 1,000 rpm in order to operate the system.
4) Stop the engine.
REPLACEMENT OF COMPONENT PARTS
W hen replacing system component parts, supply the following
amount of oil to the component parts to be installed.
Component parts to be installed Amount of oil
Evaporator 50 cm3 (1.41 lmp fl oz)
Condenser 30 cm3 (0.84 lmp fl oz)
Receiver/drier 30 cm3 (0.84 lmp fl oz)
Refrigerant line (One piece) 10 cm3 (0.28 lmp fl oz)
Refrigeration oil must be replenished if more than two parts
are removed at the same time. After installing these
components, check compressor oil.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 269 of 6020

3B-8 POWER-ASSISTED STEERING SYSTEM
6. Fully close the shutoff valve. Record the highest
pressures.
・ If the pressure recorded is within 9800-10300 kPa
(100-105 kg/cm
2/1422-1493psi), the pump is
functioning within its specifications.
・ If the pressure recorded is higher than 10300 kPa
(105 kg/cm
2/1493psi), the valve in the pump is
defective.
・ If the pressure recorded is lower than 9800 kPa
(100 kg/cm
2/1422psi), the valve or the rotating
assembly in the pump is defective.
7. If the pump pressures are within specifications, leave the valve open and turn (or have someone
else turn) the steering wheel fully in both directions.
Record the highest pressures and compare with the
maximum pump pressure recorded in step 6. If this
pressure cannot be built up at either side of the
power steering unit, the power steering unit is
leaking internally and must be replaced.
8. Shut the engine off, remove the testing gauge.
9. Reconnect the pressure hose, check the fluid level and make the needed repairs.
10. If the problem still exists, the steering and front suspension must be thoroughly examined.
Maintenance
The hydraulic system should be kept clean, the fluid
level in the reservoir should be checked at regula
r
intervals and fluid added when required. Refer to
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants in General
Information section for the type of fluid to be used and
the intervals for filling.
If the system contains some dirt, flush it as described in
this section. If it is exceptionally dirty, the pump must be
completely disassembled before further usage. (The
steering unit cannot be disassembled.)
All tubes, hoses, and fittings should be inspected for
leakage at regular intervals. Fittings must be tight. Make
sure the clips, clamps and supporting tubes and hoses
are in place and properly secured.
Power steering hoses and lines must not be twisted,
kinked or tightly bent. Air in the system will cause
spongy action and noisy operation. W hen a hose is
disconnected or when fluid is lost, for any reason, the
system must be bled after refilling. Refer to Bleeding the
Power Steering System in this section.
・ Inspect gear for looseness or damage.
・ Inspect hoses to insure they are not touching an
y
other parts of the vehicle.
・ Inspect fluid level and fill to the proper level.
Fluid Level
1. Run the engine until the power steering fluid
reaches normal operating temperature, about 55 °
C (130 °F), then shut the engine off.
2. Check the level of fluid in the reservoir.
3. If the fluid level is low, add power steering fluid as
specified in General Information to the proper level
and install the receiver cap.
4. W hen checking the fluid level after the steering system has been serviced, air must be bled from
the system. Refer to Bleeding the Power Steering
System in this section.
Bleeding the Power Steering System
W hen a power steering pump or unit has been installed,
or an oil line has been disconnected, the air that has
entered the system must be bled out before the vehicle
is operated. If air is allowed to remain in the powe
r
steering fluid system, noisy and unsatisfactory operation
of the system may result.
Bleeding Procedure
W hen bleeding the system, and any time fluid is added
to the power steering system, be sure to use only powe
r
steering fluid as specified in General Information.
1. Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level and let the fluid settle for at least two minutes.
2. Start the engine and let it run for a few seconds. Do not turn the steering wheel. Then turn the engine
off.
3. Add fluid if necessary.
4. Repeat the above procedure until the fluid level remains constant after running the engine.
5. Raise and support the front end of the vehicle so that the wheels are off the ground.
6. Start the engine. Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left, lightly contacting the wheel stops.
7. Add power steering fluid if necessary.
8. Lower the vehicle, set the steering wheel at the straight forward position after turning it to its full
steer positions 2 or 3 times, and stop the engine.
9. Check the fluid level and refill as required.
10. If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehicle to settle for a few minutes, then repeat the above
procedure.
Flushing the Power Steering System
1. Raise and support the front end of the vehicle off
the ground until the wheels are free to turn.
2. Remove the fluid return line at the pump inlet connector and plug the connector port on the pump.
Direct the line toward a large container to catch the
draining fluid.
3. W hile running the engine at idle, fill the reservoi
r
with new power steering fluid. Turn the steering
wheel in both directions. Do not contact or hold the
steering wheel to the wheel stops. This will cause
the pump to go to pressure relief mode, which ma
y
cause a sudden fluid overflow at the reservoir.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 585 of 6020
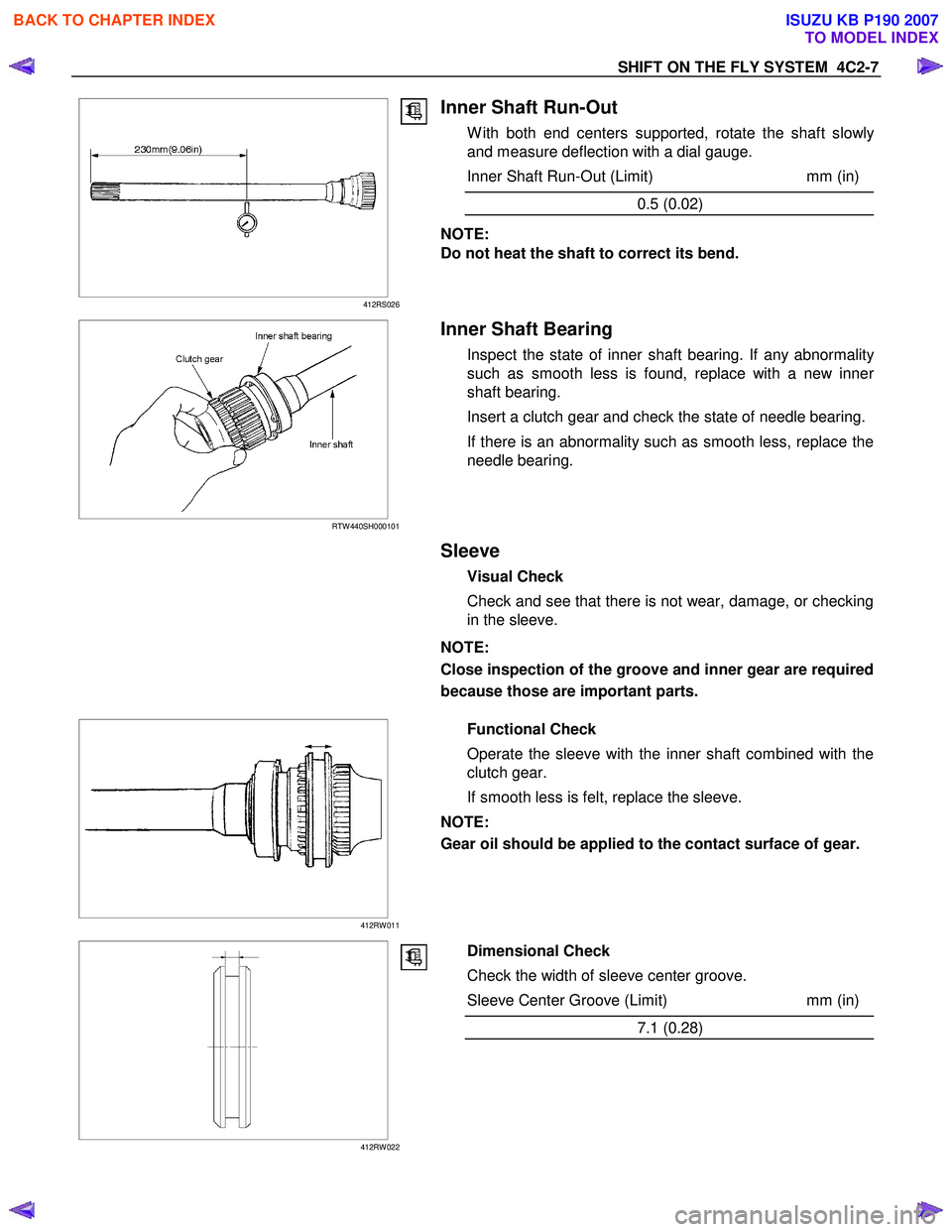
SHIFT ON THE FLY SYSTEM 4C2-7
412RS026
Inner Shaft Run-Out
W ith both end centers supported, rotate the shaft slowly
and measure deflection with a dial gauge.
Inner Shaft Run-Out (Limit) mm (in)
0.5 (0.02)
NOTE:
Do not heat the shaft to correct its bend.
RTW 440SH000101
Inner Shaft Bearing
Inspect the state of inner shaft bearing. If any abnormality
such as smooth less is found, replace with a new inner
shaft bearing.
Insert a clutch gear and check the state of needle bearing.
If there is an abnormality such as smooth less, replace the
needle bearing.
Sleeve
Visual Check
Check and see that there is not wear, damage, or checking
in the sleeve.
NOTE:
Close inspection of the groove and inner gear are required
because those are important parts.
412RW 011
Functional Check
Operate the sleeve with the inner shaft combined with the
clutch gear.
If smooth less is felt, replace the sleeve.
NOTE:
Gear oil should be applied to the contact surface of gear.
412RW 022
Dimensional Check
Check the width of sleeve center groove.
Sleeve Center Groove (Limit) mm (in)
7.1 (0.28)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1556 of 6020
FUEL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6C-15
The fuel system consists of many tiny holes and spaces
that allow the movement of fuel from one place to
another. These holes and spaces are milled to
extremely high precision. This is especially true of the
fuel injector.
The fuel injector is very sensitive to foreign material.
Foreign material will result in fuel system breakdown.
Exercise great care not to allow the entry of foreign
material into the fuel system or fuel injector during the
removal and installation procedure.
Note: To avoid electric shock;
Set the switch to the 'OFF' position and disconnect the
negative battery cable before checking or repairing the
fuel injector, wiring or/and connectors.
Removal
1. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to the removal procedure for the cylinde
r
head cover in this manual.
Remove the attachment bolt of the engine oil gauge
guide tube.
2. Loosen the fuel injector clamp fixing bolts and
remove the fuel injector.
If the fuel injector is difficult to remove, use the remover. Use a screwdriver to force the fuel
injector clamp off the fuel injector.
Note: Do not remove the fuel injector sleeve.
Note: Cover the areas exposed during parts removal to
prevent the entry of foreign material into the fuel
system.
3. Mark each fuel injector with the number of the cylinder from which it was removed. Store the fuel
injector in a safe place. Position the fuel injector so
that the nozzle is protected.
Note: Do not tamper with the electromagnetic portion of
the fuel injector. Reduced electromagnetic function will
result in injector failure.
Note: After replacement of the fuel injector, perform the
following procedure.
• All fuel injectors are replaced:
Remove the fuel injector ID code label on the cylinder head cover.
• Any fuel injector(s) is replaced:
Black out the replaced cylinder of the fuel injecto
r
ID code on the fuel injector ID code label with a
marking pen or equivalent.
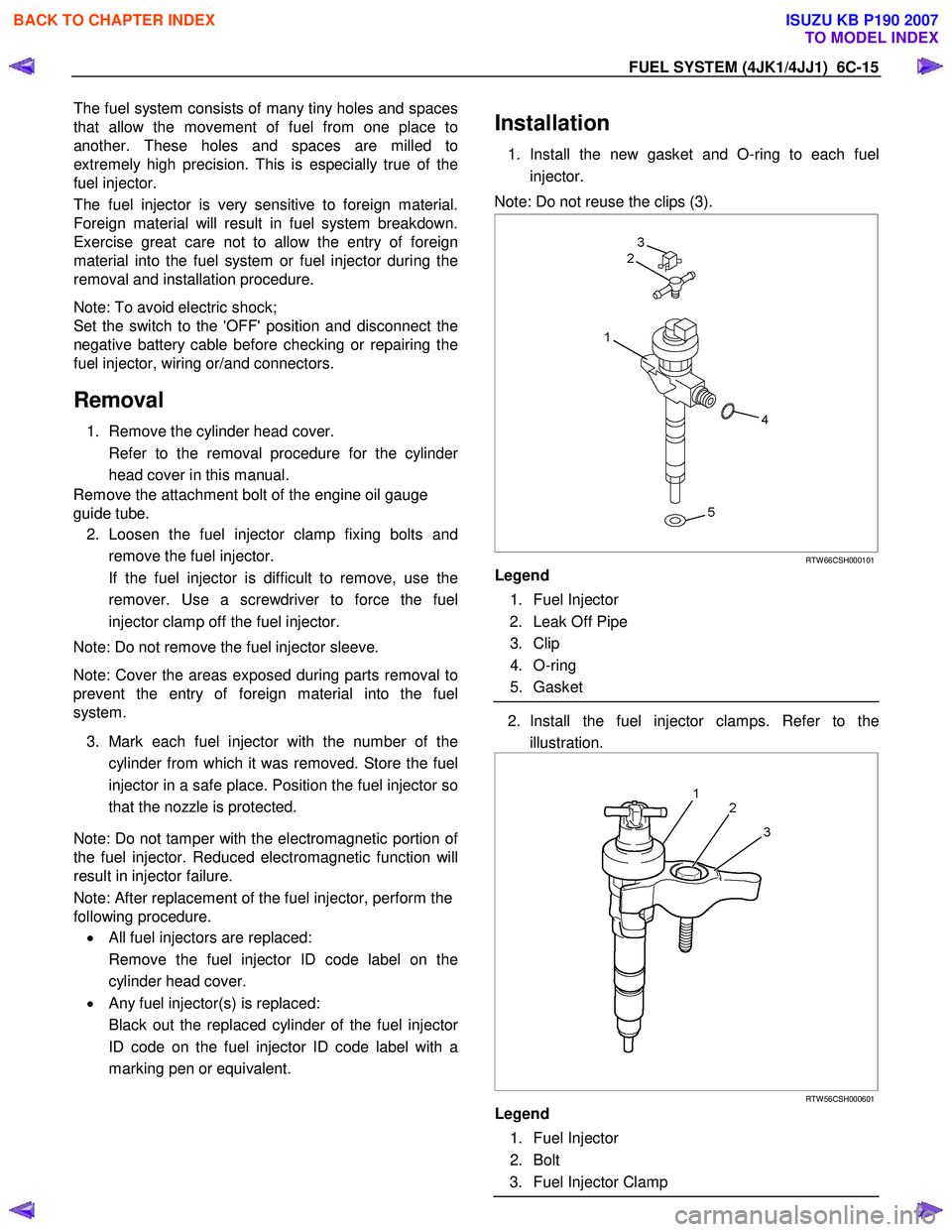
Installation
1. Install the new gasket and O-ring to each fuel
injector.
Note: Do not reuse the clips (3).
RTW 66CSH000101
Legend
1. Fuel Injector
2. Leak Off Pipe
3. Clip
4. O-ring
5. Gasket
2. Install the fuel injector clamps. Refer to the
illustration.
RTW 56CSH000601
Legend
1. Fuel Injector
2. Bolt
3. Fuel Injector Clamp
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1590 of 6020

6D-2 ENGINE ELECTRICAL (4JK1/4JJ1)
Charging System
Servicing Cautions
• Battery polarity is important. If the battery cables
are reversed, the generator diodes will be
destroyed.
• Do not remove the battery cables or the charging
circuit wiring when the engine is running.
• Confirm that the terminal wires are connected to
the proper terminals by checking the terminal
numbers (the number on the terminal wire and the
terminal must be the same).
• Disconnect the battery negative cable (-) before
inspecting the generator.
• Do not open or close the battery relay switch when
the engine is running.
• Disconnect the battery negative cable (-) when
using external equipment (Quick-Charge) to
charge the battery.
• W hen steam cleaning or washing the engine, do
not allow steam or water to come in direct contact
with the battery and other electrical system
components.
• Be sure to read the item on belt tension
adjustment before beginning the procedure.
Important Generator Components
and Function
• The generator used on 4JK1 engine cannot be
disassembled.
• The generator uses a built-in solid-state IC voltage
regulator. The regulator and other important
components together with their connections are
shown in the illustration.
• The voltage regulator is installed to the rear cove
r
assembly of the generator together with the brush
holder and the rectifier. The generator requires no
additional voltage regulation.
• 9 diodes are connected to the stator coil to convert
AC to DC. The DC voltage is delivered to the
generator output terminal.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2447 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–277
SPARK PLUG CABLES
The cable contains a synthetic conductor which is easily
damaged. Never stretch or kink the cable. Disconnect
the cable from spark plug and the ignition coil.
The original equipment cables and the ignition coil are
marked to show correct location of the cables. If spark
plug cables or the ignition coil are replaced previously,
before cables are removed from the ignition coil, mark
the cables and the coil so they can be reconnected in
the same position.
Inspection
NOTE: Never puncture the spark plug cable’s insulation
with a needle or the pointed end of a probe into the
cable. An increase in resistance would be created which
would cause the cable to become defective.
1. If the cable has broken or cracked insulation, it must be replaced.
2. If the terminals are corroded or loose, the cable must be replaced.
3. Check that the cable resistance does not exceed specified value.
#1 cylinder: 3.50k Ω - 5.24k Ω
#2 cylinder: 2.89k Ω - 4.33k Ω
#3 cylinder: 2.49k Ω - 3.73k Ω
#4 cylinder: 2.22k Ω - 3.32k Ω
EMISSION CONTROL ; *
**
*
CO ADJUSTER (W/
O CATALYSTIC CONVERTER)
* CO : Carbon monoxide
Location
Under the leht-hand side of the front sheet.
Removal Procedure 1. Remove the left-hand side of the front sheet. Refer to Sec.10 CAB “Front Sheet”.
2. Disconnect the CO adjuster connector.
3. Remove the CO adjuster.
Installation Procedure 1. Connect the CO adjuster connector.
2. Install the left-hand side of the front sheet. Refer to Sec.10 CAB “Front Sheet”.
3. Check and adjust CO concentration.
Checking procedure 1. Operate the engine at normal temperature.
2. Turn all accessories switch OFF.
3. Place the select lever in the “N” range.
4. Start the engine at idle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3765 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–5
Clean and Inspect
Do not use solvents on neoprene seals,
composition faced clutch plates or thrust
washers as damage to parts may occur.
After complete disassembly of a component, wash all metal parts in a clean solvent and dry with compressed air. Blow
oil passages out and check to make sure they are not obstructed, small passages should be checked with tag wire. All
parts should be inspected to determine if replacement is required.
Pay particular attention to the following:
• Inspect linkage and pivot points for excessive wear.
• Bearing and thrust surfaces of all parts should be checked for excessive wear and scoring.
• Check for broken seal rings, damaged ring lands and damaged threads.
• Inspect seals for damage.
• Mating surfaces of castings should be checked for burrs. Irregularities may be removed by lapping the surface with
emery paper laid on a flat surface, such as a piece of plate glass.
• Castings should be checked for cracks and porosity.
1.3 7C2 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
Electrical Diagnosis
For transmissions fitted to V6 engines, the electrical diagnosis is in this Section. A new electrical circuit and control
module has been introduced for automatic transmissions fitted to the V6 engines.
1.4 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis
Information contained in 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis will assist in the
diagnosis of the mechanical and hydraulic components in the 4L60E automatic transmission, while the transmission
remains installed on the vehicle.
Examples of the type of diagnostic information contained within this section are:
• transmission functional test,
• line pressure information,
• transmission fluid diagnosis,
• symptom diagnosis and
• shift speed charts.
1.5 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing
Information in 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing covers transmission fluid level checking, as
well as specific information for servicing some components while the transmission remains installed on the vehicle. This
Section also covers the transmission removal and reinstallation to the vehicle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3785 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–25
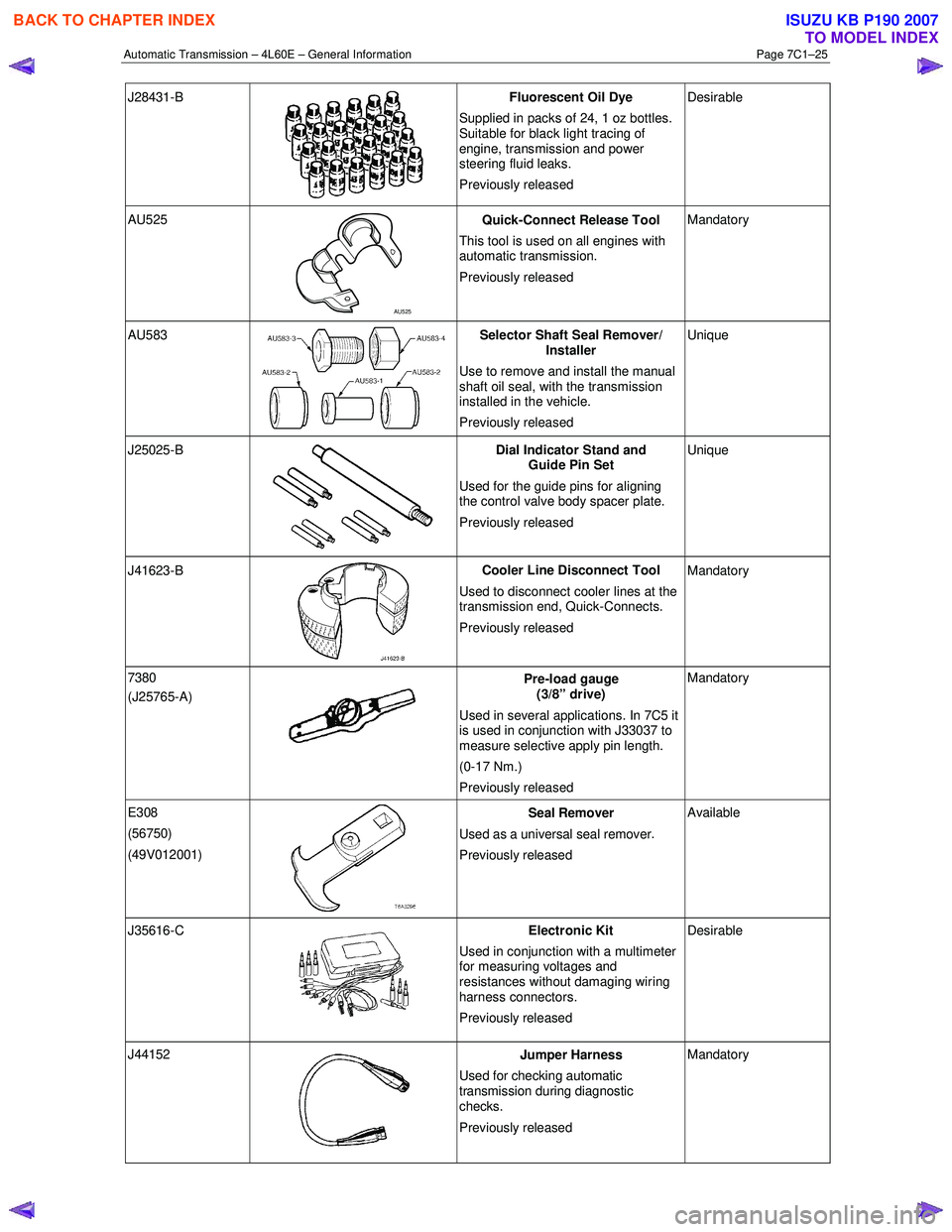
J28431-B
Fluorescent Oil Dye
Supplied in packs of 24, 1 oz bottles.
Suitable for black light tracing of
engine, transmission and power
steering fluid leaks.
Previously released Desirable
AU525
AU525 Quick-Connect Release Tool
This tool is used on all engines with
automatic transmission.
Previously released Mandatory
AU583 Selector Shaft Seal Remover/
Installer
Use to remove and install the manual
shaft oil seal, with the transmission
installed in the vehicle.
Previously released Unique
J25025-B
Dial Indicator Stand and
Guide Pin Set
Used for the guide pins for aligning
the control valve body spacer plate.
Previously released Unique
J41623-B
Cooler Line Disconnect Tool
Used to disconnect cooler lines at the
transmission end, Quick-Connects.
Previously released Mandatory
7380
(J25765-A)
Pre-load gauge
(3/8” drive)
Used in several applications. In 7C5 it
is used in conjunction with J33037 to
measure selective apply pin length.
(0-17 Nm.)
Previously released Mandatory
E308
(56750)
(49V012001)
Seal Remover
Used as a universal seal remover .
Previously released Available
J35616-C
Electronic Kit
Used in conjunction with a multimeter
for measuring voltages and
resistances without damaging wiring
harness connectors.
Previously released Desirable
J44152
Jumper Harness
Used for checking automatic
transmission during diagnostic
checks.
Previously released Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007