change key battery ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1310 of 6020

6E-276 Engine Control System (4JH1)
1. Connect the scan tool to the vehicle DLC, with theengine and the scan tool OFF.
2. Turn ON the scan tool.
3. Select Diagnostic > appropriate vehicle identification > Powertrain > 4JH1-TC >
Programming > Program VIN.
4. Input correct VIN reading from stamped VIN o
r
affixed VIN plate on the vehicle.
Select Lock ECU and lock the programmed VIN.
Service Programming System (SPS)
Description
The service programming system (SPS) allows a
technician to program a control module through the data
link connector (DLC). The information transfer circuit that
is used at the DLC is the same serial data circuit used be
the scan tool for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes
(DTCs), displaying data, clearing DTCs etc. This
procedure offers the ability to install software/calibrations
matched to a particular vehicle.
Most control modules have two types of memory. The
software/calibrations reside in the flash memory. The two
types of memory are listed below: • Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Onl
y
Memory (EEPROM).
This type of memory allows selected portions o
f
memory to be programmed while other portions
remain unchanged.
Certain learned values reside in the EEPROM, such as:
- The vehicle identification number (VIN)
- The software/calibrations identification numbers
- The control module security information
• Flash Read Only Memory-Flash Memory
Flash memory has increased memory storage capacity. During programming, all information within
this type of memory is erased, and then replaced
with entirely new information.
Service Programming Methods
The two methods of programming an engine control
module (ECM) are listed below: • Remote Programming
• Pass Thru Programming
For information on programming an ECM using one o
f
the methods listed above, refer to Service Programming
System (SPS) (Remote Procedure) or Service
Programming System (SPS) (Pass-Thru Procedure).
Before Programming a Control Module
Important:
DO NOT program an existing ECM with the identical
software/calibration package. This procedure is not a
short cut to correct the driveability condition. This is an
ineffective repair. An ECM should only be programmed
when the following occurs: • W hen a service procedure instructs you to replace
the ECM. W hen the ECM from another vehicle is
installed, VIN must be changed. And change
vehicle information as necessary such as type o
f
transmission.
• An updated software/calibrations is released.
Ensure that the following conditions are met before
programming an ECM: • The scan tool PCMCIA card is programmed with
the latest software.
• The TIS 2000 is installed with the latest software.
• The hardware key is plugged into the compute
r
port.
• Vehicle system voltage:
- There are no charging system concerns. All charging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the ECM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts bu
t
less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the ECM.
-
A battery charger is NOT connected to the
vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage o
r
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or ECM damage.
- Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF o
r
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The
scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position o
f
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure:
- The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1949 of 6020
6E-332 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
High Idle Speed
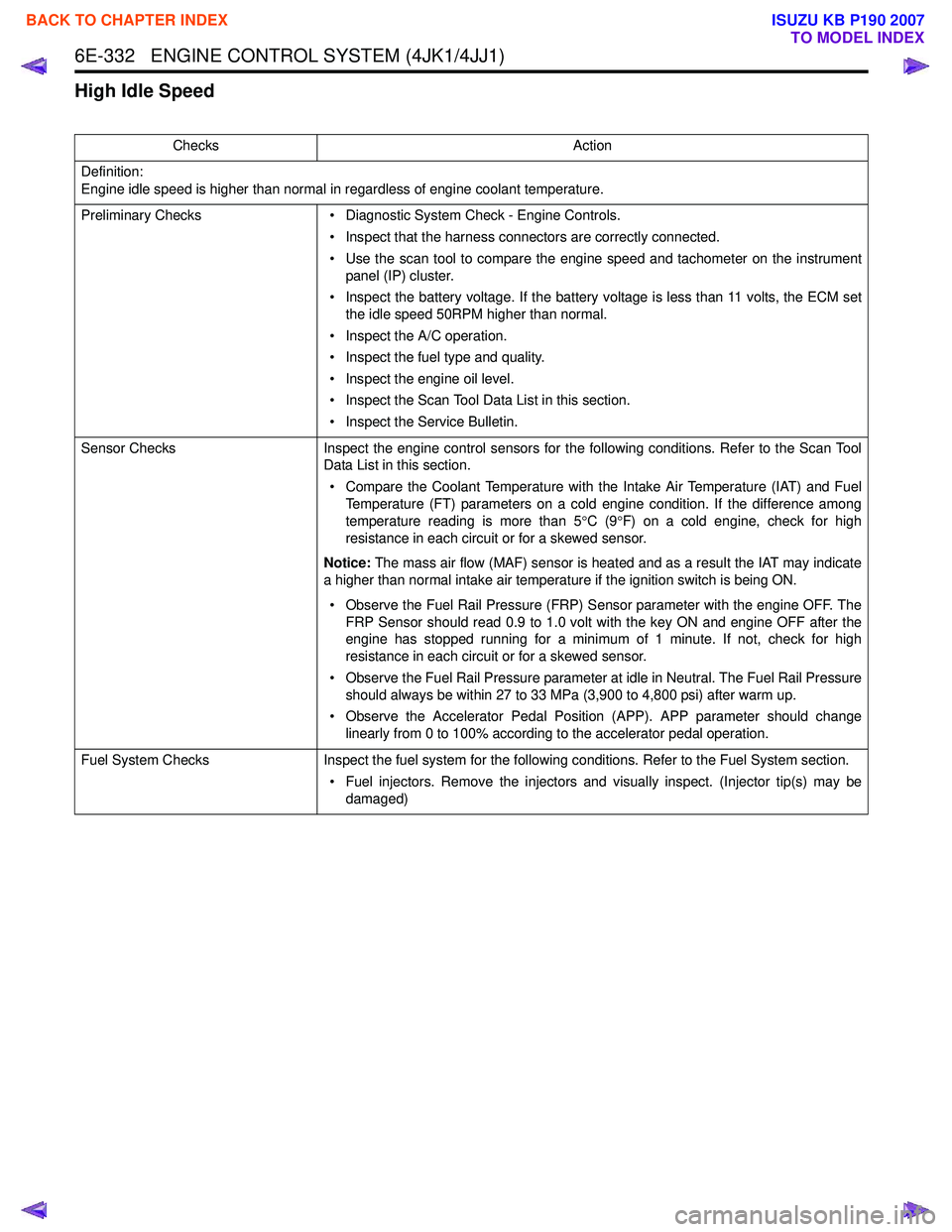
ChecksAction
Definition:
Engine idle speed is higher than normal in regardless of engine coolant temperature.
Preliminary Checks • Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Inspect that the harness connectors are correctly connected.
• Use the scan tool to compare the engine speed and tachometer on the instrument panel (IP) cluster.
• Inspect the battery voltage. If the battery voltage is less than 11 volts, the ECM set the idle speed 50RPM higher than normal.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the fuel type and quality.
• Inspect the engine oil level.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure parameter at idle in Neutral. The Fuel Rail Pressure should always be within 27 to 33 MPa (3,900 to 4,800 psi) after warm up.
• Observe the Accelerator Pedal Position (APP). APP parameter should change linearly from 0 to 100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect. (Injector tip(s) may be damaged)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1967 of 6020

6E-350 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
• The hardware key is plugged into the computerport.
• Vehicle system voltage: - There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the ECM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the ECM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or ECM damage.
- Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure: - The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
ECM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the ECM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the ECM. Performing the Remote Procedure
1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the ECM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the ECM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
d. If there is already stored in the scan tool, the existing data is displayed on the screen. The
scan tool asks user to keep existing data "Keep
Data" or "Continue" to request new vehicle
information from the ECM. If there is no data in
the scan tool, it will immediately start vehicle
identification.
e. Select the vehicle description by following the on-screen instructions based on stamped VIN
or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle.
f. During obtaining information, the scan tool is receiving information from all modules at the
same time. But only ECM information is
displayed on the screen.
g. Turn OFF all accessories and press "Okay".
h. Verify that the correct VIN is displayed on the scan tool. If the VIN is incorrect or no VIN,
record the correct VIN.
2. Turn OFF the ignition.
3. Turn OFF the scan tool and disconnect from the vehicle.
4. Transfer the data from the terminal to the scan tool using the following procedure:
Notice: The TIS supports service programming with
the Tech 2 scan tool only.
a. Connect the scan tool to the terminal.
b. Launch the TIS application.
c. Select the Service Programming System at the main screen.
d. Highlight the following information on the Select Diagnostic Tool and Programming Process
screen, then click "Next".
• Select Diagnostic Tool - Tech 2
• Select Programming Process - Identify whether an existing ECM is being
reprogrammed or an ECM is being replaced
with a new one
• Select ECU Location - Vehicle
e. Verify the connections on the Preparing for Communication screen, then click "Next".
f. Verify the VIN on the Validate Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) screen, then click
"Next".
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2219 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–49
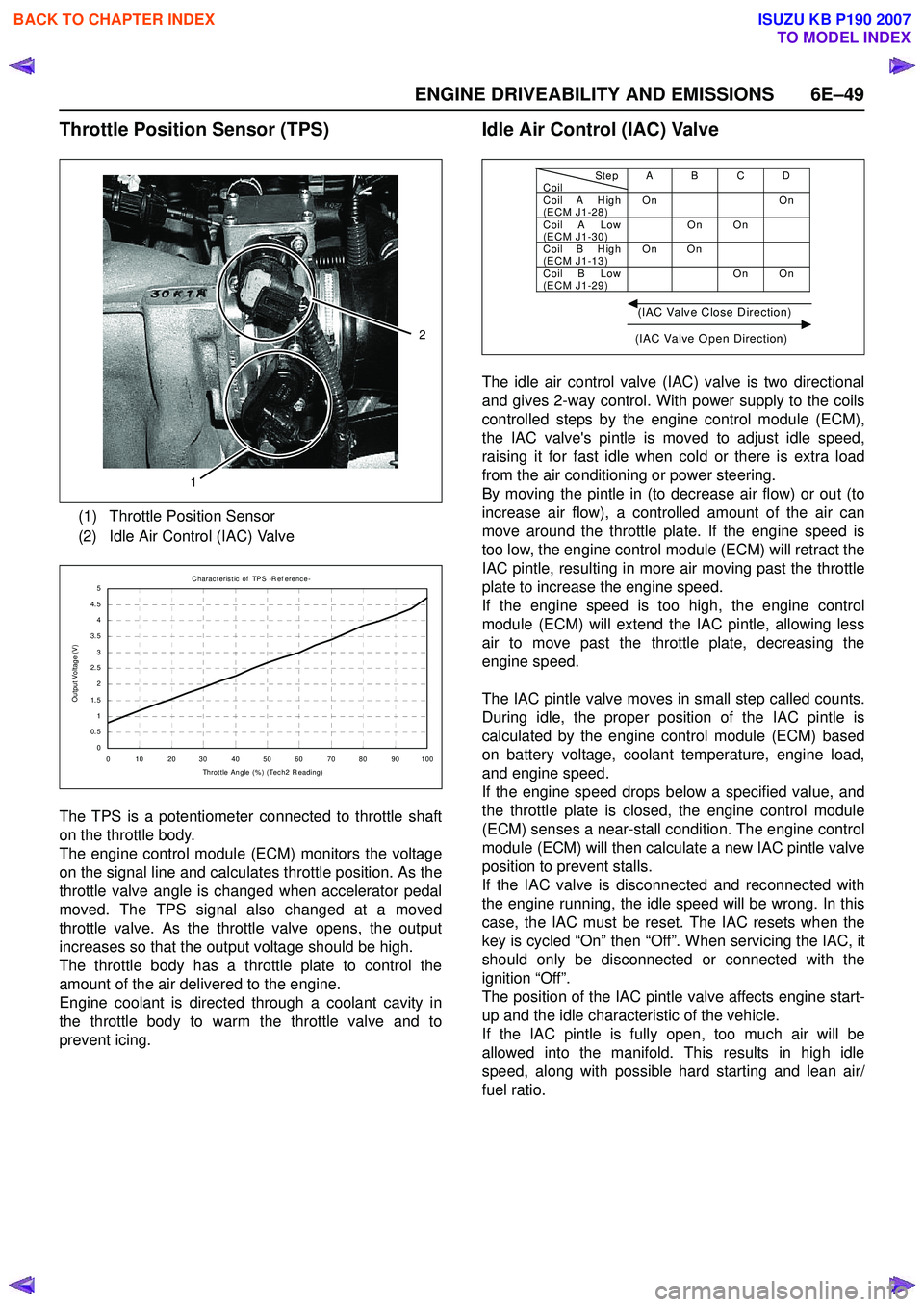
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS is a potentiometer connected to throttle shaft
on the throttle body.
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the voltage
on the signal line and calculates throttle position. As the
throttle valve angle is changed when accelerator pedal
moved. The TPS signal also changed at a moved
throttle valve. As the throttle valve opens, the output
increases so that the output voltage should be high.
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of the air delivered to the engine.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The idle air control valve (IAC) valve is two directional
and gives 2-way control. With power supply to the coils
controlled steps by the engine control module (ECM),
the IAC valve's pintle is moved to adjust idle speed,
raising it for fast idle when cold or there is extra load
from the air conditioning or power steering.
By moving the pintle in (to decrease air flow) or out (to
increase air flow), a controlled amount of the air can
move around the throttle plate. If the engine speed is
too low, the engine control module (ECM) will retract the
IAC pintle, resulting in more air moving past the throttle
plate to increase the engine speed.
If the engine speed is too high, the engine control
module (ECM) will extend the IAC pintle, allowing less
air to move past the throttle plate, decreasing the
engine speed.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small step called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the engine control module (ECM) based
on battery voltage, coolant temperature, engine load,
and engine speed.
If the engine speed drops below a specified value, and
the throttle plate is closed, the engine control module
(ECM) senses a near-stall condition. The engine control
module (ECM) will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve
position to prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with
the engine running, the idle speed will be wrong. In this
case, the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the
key is cycled “On” then “Off”. When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “Off”.
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-
up and the idle characteristic of the vehicle.
If the IAC pintle is fully open, too much air will be
allowed into the manifold. This results in high idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and lean air/
fuel ratio.
(1) Throttle Position Sensor
(2) Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
1
2
C harac teris t ic of TPS -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5
1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
0 10 2030 405060 7080 90100 Throt t le Angle (% ) (Tec h2 R eading)
Output Voltage (V)
StepCoilAB CDCoil A H igh
(ECM J1-28) On On
Coil A Low
(ECM J1-30) On On
Coil B H igh
(ECM J1-13) On On
Coil B Low
(ECM J1-29) On On
(IAC Valve Close Direction)
(IAC Valve Open Direction)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4007 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (AW30–40LE) 7A2-41
• All of the following conditions are met.
- Device Control is not operating
- Disable Normal Communication Service is receiving enable
- DTC Clear is not operating
Condition For Setting The DTC
W hen the TCM detects following conditions at 20 times
continuously.
• Ignition voltage is less than 9 volts for 1 second o
r
more continuously. (DTC P0562)
• Ignition voltage is more than 18 volts for 1 second o
r
more continuously. (DTC P0563)
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• DTC stored.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the TCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warm-up cycles without a
failure reported.
•
After more than 1 second has elapsed after the
ignition key has been turned “ON”, short between
No.11 and No.4 (ground) of DLC (Data Link
Connector). Then, after 1 second, but within 6
seconds, discontinue shorting.
Diagnostic Aids
•
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
TCM. Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed
or damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal
tension as well. Also check for a chafed wire that
could short to bare metal or other wiring.
Inspect for a broken wire inside the insulation.
• W hen diagnosing for a possible intermittent short o
r
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
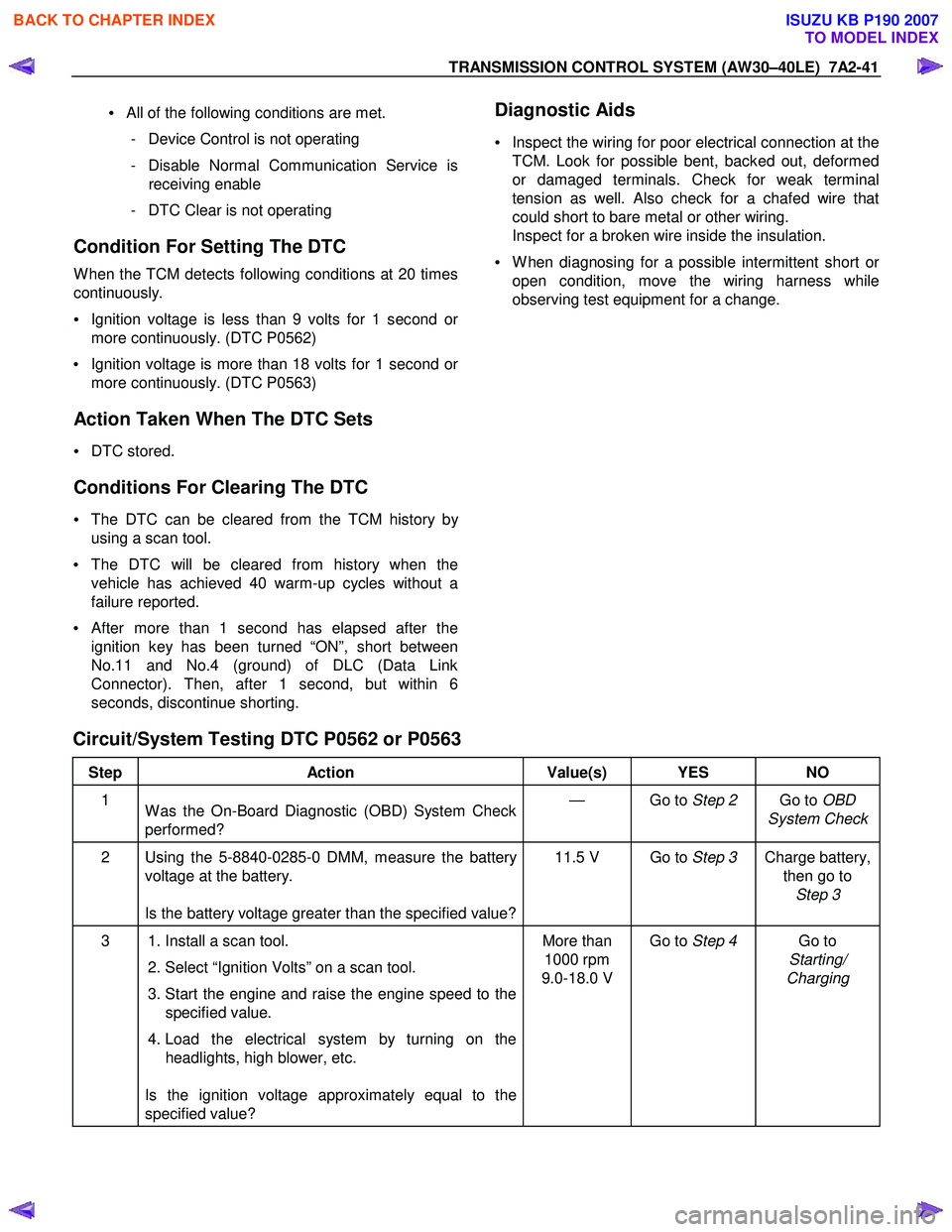
Circuit/System Testing DTC P0562 or P0563
Step Action Value(s) YES NO
1
W as the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? — Go to
Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
2 Using the 5-8840-0285-0 DMM, measure the battery voltage at the battery.
Is the battery voltage greater than the specified value? 11.5 V Go to
Step 3 Charge battery,
then go to Step 3
3 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Select “Ignition Volts” on a scan tool.
3. Start the engine and raise the engine speed to the specified value.
4. Load the electrical system by turning on the headlights, high blower, etc.
Is the ignition voltage approximately equal to the
specified value? More than
1000 rpm
9.0-18.0 V Go to
Step 4 Go to
Starting/
Charging
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4424 of 6020

7A2-140 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
• Electrically Erasable Programmable Read OnlyMemory (EEPROM)
This type of memory allows selected portions of
memory to be programmed while other portions
remain unchanged.
Certain learned values reside in the EEPROM,
such as:
- The vehicle identification number (VIN)
- The software/ calibrations identification numbers
- The control module security information
• Flash Read Only Memory-Flash Memory
Flash memory has increased memory storage capacity.
During programming, all information within this type of
memory is erased, and then replaced with entirely new
information.
Service Programming Methods
The two methods of programming a TCM are listed
below:
• Remote Programming
• Pass Thru Programming
For information on programming a TCM using one of
the methods listed above, refer to Service
Programming System (SPS) (Remote Procedure) or
Service Programming System (SPS) (Pass-Thru
Procedure).
Before Programming a Control Module
Important: DO NOT program an existing TCM with the
identical software/ calibration package. This procedure
is not a short cut to correct the driveability condition.
This is an ineffective repair. An TCM should only be
programmed when the following occurs:
• When a service procedure instructs you to replace the TCM.
• An updated software/ calibrations is released.
Ensure that the following conditions are met before
programming a TCM:
• The scan tool PCMCIA card is programmed with the latest software.
• The TIS 2000 is installed with the latest software.
• The hardware key is plugged into the computer port.
• Vehicle system voltage:
- There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the TCM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the TCM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or TCM damage. - Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a
load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure:
- The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
TCM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the TCM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the TCM.
Performing the Remote Procedure 1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the TCM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the TCM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5517 of 6020

ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS 8A-579
Remote key
Remove Key Assembly
Replacing the battery in the remote control unit
Replace the battery as soon as the range of the remote control
starts to become reduced.
Open the underside of the remote control unit by removing the
battery cover with a screwdriver as shown in the illustration.
Replace the battery, ensuring that it is inserted correctly.
Replace the battery cover so that it engages audibly. The
battery change must be performed within 3 minutes, otherwise
the remote control will have to be reprogrammed. Make sure
that you dispose of old batteries in accordance with
environmental protection regulations.
604RW 055
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5958 of 6020

11B-4 ANTITHEFT SYSTEM
Transmitter (into remote key) power
The transmitted power is less than 10 m W .
Battery life time for transmitter power
The minimum life time of battery is 2 years with 15
lock/unlock cycles per day.
W hile the battery is changed, the data retention will be
at least 3 minutes without pressing a button.
Super lock
(Mechanical anti-theft locking system)
To Lock:
All doors must be closed; press the lock button on the
remote control unit again within 10 seconds after
locking or turn key in driver's door lock towards rear of
vehicle again within 10 seconds after locking, then turn
it back to the vertical position and remove.
Lock buttons on all doors are positioned such that doors
cannot be opened.
To unlock:
Press unlock button on remote key or turn key in
driver's door lock towards front of vehicle, then turn it
back to the vertical position and remove. If the key is
used, antitheft alarm sound operate which continues
until ignition switch turn ON. If a problem is found, open
the driver door as necessary.
No proper transmitter is available, what
should be done for the system?
W hen any proper transmitter is not available, a new
transmitter should be programmed. Up to 5 transmitters
can be provided with a scan tool (Tech-2) and by proper
procedure.
In addition to the absence of proper transmitter, it may
happen particular secret code to the particular vehicle is
missing. ln this case, the secret code must be provided
by your organization.
Otherwise transmitter cannot be programmed in any
way.
lf the essential for a scan tool (Tech-2) for programming
and proper software for Tech-2 are not available, there
is no permanent way to fix system. Temporary replace
with new ACU, new ICU and new transmitter without
any secret code can make the system be deactivated,
but it does not last long. Such a replacement does not
solve any condition. Even after replacement, the system
is activated automatically in short time and then no
operation of the vehicle can be made in any way.
Tech-2 should be provided in your organization.
• Security code management
Your organization must keep security codes for all
vehicles as confidential data. Once the security codes
are lost, anybody who have the security code can
access antitheft system. Your organization has
responsibility of any missing vehicles caused by stolen
security code.
• Essential tool (Scan tool: Tech-2)
Your dealership must have Tech-2, and Tech-2 updated
software for immobilizer system.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5990 of 6020

11B-36 ANTITHEFT SYSTEM
Diagnosis
Diagnostic procedure
• Once the cause of DTC is repaired or gone,
engine can be operated normally, and present
DTC becomes history code.
• History code is canceled by no repeat failure on 25
consequence ignition key on afterward.
• History code cannot be canceled by batter
y
connector disconnected.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
IMPORTANT: Do not clear DTCs unless directed to do
so by the service information provided for each
diagnostic procedure. W hen DTCs are cleared, the
Failure Record data which may help diagnose an
intermittent fault will also be erased from memory.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with immobilizer system
diagnostic. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records for the DTC which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC (s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail Records.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic test
associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on immobilizer systems. Failure to follow these
steps could result in unnecessary repairs.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by the following:
• Poor connections.
• Miss routed harness.
• Rubbed through wire insulation.
• Broken wire inside the insulation.
Check for the following conditions:
• Poor connection at ACU-Inspect harness
connectors for backed out terminals, imprope
r
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire
connection.
• Damaged harness-Inspect the wiring harness fo
r
damage.
If the harness appears to be OK, observe the data
display on the Tech2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the switch or actuator.
A change in the display will indicate the location of
the fault.
If DTC cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Failure Records data can be useful
in determined vehicle mileage since the DTC was
last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently, performing the DTC Diagnostic
Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
NOTE: Breakage of antitheft fuse does not operate
antitheft system. Check LED lamp flashes at this time.
Check the Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI)
• Location of vehicle check
Move the vehicle to a new location and perform
the check again.
• Non-OEM Parts.
Switch is “OFF” or remove the Non-OEM parts and
perform the check again.
• Other
Remove the accessory and another key from key.
Check the other items.
• Battery voltage is low.
• Antitheft programming functions.
Must be programmed antitheft system.
• Registration for security code, antitheft control unit
parts number.
• Key switch operation.
Antitheft system may detect a history DTC by the
timing of ON-OFF of a key switch.
• Active the antitheft system.
• Keyless entry system is malfunction.
• Immobilizer system is malfunction.
Check the operation
Check the operation "Lock / unlock" by using transmitter
(key) on the vehicle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007