DTC CHECK ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 4396 of 6020

7A2-112 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
D3: Gearshift Point is Low or High at All Points
D4: Gearshift Point is Low or High at Limited Area
D5: No Kick-down
E1: No Gearshift
Checks Action
Definition: • Gearshift point is deviated from the shift speed chart.
• Gear is not shifted up properly, even though the vehicle is accelerating.
• Gear is not shifted immediately and enough acceleration cannot be obtained, even though the accelerator pedal is being stepped on.
Diagnosis Hints • Inspect the output shaft speed (OSS) sensor for faulty operation.
• Incorrect accelerator pedal position signal is suspected. Observe the Accelerator Pedal Position (APP). APP parameter should change linearly
from 0 to 99 or 100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
Checks Action
Definition:
The engine speeds up but the vehicle speed does not increase when the accelerator pedal is being stepped on at starting.
Diagnosis Hints Incorrect accelerator pedal position signal is suspected. Observe the
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP). APP parameter should change linearly from
0 to 99 or 100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
Checks Action
Definition: • Gear is fixed, such as no gearshift from 1st to 2nd, 2nd to 3rd, and 3rd to 4th.
• Sometimes the gear is shifted, and sometimes it is not possible.
Diagnosis Hints • Fixing at same gear speed, a signal error from the accelerator pedal
position (APP) sensor or trouble in the transmission main unit are
suspected.
• Slipping of the clutch is suspected. Gear ratio error DTC might be set.
Transmission Range Switch & Selector Lever
Cable Checks Inspect the transmission range switch and selector lever cable for misadjusting
or disordering. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for the following conditions. If the transmission
fluid is extremely blacked, contaminated or smells burnt, slipping of clutch is
suspected.
• Low quantity
• Contamination
•Smell
Line Pressure Checks Inspect the line pressure in forward ranges for a possible dropped pressure.
Refer to Line Pressure Test in Test Instruction section.
Stall Speed Checks Inspect the stall speed in forward ranges. Refer to Stall Test in Test Instruction
section.
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking shift solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Clutch and Brake Checks Inspect the low clutch, high clutch or low & reverse brake for slipping.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4399 of 6020

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-115
F3: Noise or Vibration Occurs During in R, D, 3, 2 or L Range
F4: Engine Brake Does Not Apply in L Range
F5: Engine Stalls Before Vehicle Stops from Running
G1: Vehicle Moves in P Range or Parking is Not Disengaged in Other Than P Range
Diagnosis Hints The same causes as in category No. “C1 - C8: Engine Race Up (Slipping)”
are suspected. When the condition of No. C1 - C8 grows worse, No. F2
results.
Checks Action
Definition:
Noise or vibration occurs in the vicinity of the transmission during running.
Diagnosis Hints Cause other than transmission is suspected. Reproduce the running
condition using a lift up, chassis dynamo, etc. to investigate the origin of the
noise and vibration.
Additional Checks • Inspect the differential gear noise.
• Inspect the propeller shaft noise.
• Inspect the tires for unbalanced or poor uniformity.
Checks
Action
Checks Action
Definition:
The engine brake does not apply, allowing the vehicle to run freely when the accelerator pedal is released at low speed in L
range.
Diagnosis Hints • Slipping of the clutch is suspected. Gear ratio error DTC might be set.
Line Pressure Checks Inspect the line pressure in forward ranges for a possible dropped pressure.
Refer to Line Pressure Test in Test Instruction section.
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking shift solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On- Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Clutch and Brake Checks Inspect the low & reverse brake for slipping.
Sensor Checks Inspect the input shaft speed (ISS) sensor and output shaft speed (OSS)
sensor for faulty operation.
Checks Action
Definition:
The engine stalls simultaneously with the vehicle when the brake pedal is stepped on to stop the vehicle during running.
Diagnosis Hints The same causes as in category No. “B5: Engine Stalls When Selector Lever
is Changed from N to R, D, 3, 2 or L Range” is suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
Vehicle moves even though it stops on a slope and P range is selected.
Vehicle does not move even though a position other than P range is selected, and the accelerator pedal is being stepped on.
Diagnosis Hints If the vehicle moves in N range, refer to category No. “B1: Vehicle Runs in
N Range”.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4402 of 6020

7A2-118 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
J1: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Breather
J2: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Engine and Converter Housing
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Converter Housing and Transmission Case
J4: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Transmission Case and Extension Housing
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Oil Pan
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Manual Shaft Oil Seal
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Oil Cooler Pipe Joint
Z1: Transmission Overheat
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for the following conditions. If the transmission
fluid is extremely blacked, contaminated or smells burnt, slipping of clutch is
suspected.
• Low quantity
• Contamination
• Smell
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking TCC solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On- Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Sensor Checks Inspect the TFT sensor. Use the Temperature vs. Resistance table to test
the TFT sensor at various temperature levels to evaluate the possibility of a
skewed sensor.
Checks
Action
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid leaks from breather.
Diagnosis Hints Transmission fluid quantity is excessively high.
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid leaks between engine and converter housing.
Transmission fluid leaks between converter housing and transmission case.
Transmission fluid leaks between transmission case and extension housing.
Transmission fluid leaks from oil pan.
Transmission fluid leaks from manual shaft oil seal.
Transmission fluid leaks from oil cooler pipe joint.
Diagnosis Hints Faulty oil seal or contact surface is suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
Smells burnt or smoke from transmission.
Diagnosis Hints • Transmission fluid quantity is excessively high.
• Slipping of the clutch is suspected. Gear ratio error DTC might be set.
• Clogged oil cooler.
• Faulty operation of oil pump.
• Faulty torque converter clutch (TCC) piston.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4409 of 6020

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-125
Road Test
Road Test Procedure
*1: Shifting at high vehicle speed, the transmission may
hold the gear position until vehicle speed gets down to
prevent engine overruning.
Notice: Perform this test at the normal transmission
fluid temperature between 50 to 80 °C (122 to 176 °F).
Drive the vehicle on level ground so as not to change to
up slope mode and down slope mode.
1. D range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the D range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3, 3 to 4 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown
in the shift speed chart.
• Also check to see that downshift is made from 4 to 3, 3 to 2 and 2 to 1 point is within the limits shown
in the shift speed chart.
2. 3 range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the 3 range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the
shift speed chart.
• While running in the 3 range, does not upshift from 3 to 4.
3. 2 range road test in normal mode. • Select into the 2 range and hold the accelerator
pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2 upshift should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the shift speed chart.
• While running in the 2 range, does not upshift from 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not operate.
4. L range road test in normal mode.
• While running in the L range, does not upshift from 1 to 2, 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not
operate.
5. R range road test. • Select into the R range and check for slipping.
6. P range road test. • Stop the vehicle on a grade and release the park brake after selecting into the P range. Then check
to see that the parking lock pawl holds the vehicle
in place.
Diagnosis 1. If there is no 1 to 2 upshift.• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
2. If there is no 2 to 3 upshift.
• Faulty operation of high clutch
• Faulty operation of high clutch hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of high clutch solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
3. If there is no 3 to 4 upshift.
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
4. If there is no lock up in 2nd, 3rd and 4th. • Faulty operation of torque converter clutch (TCC) piston
• Faulty operation of lock up hydraulic circuit
• Sticking of TCC solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. I1: No Lock-up
5. If there is no reverse. • Faulty operation of reverse clutch
• Faulty operation of reverse clutch hydraulic circuits
• Faulty operation of low & reverse brake hydraulic circuits
Selector lever
position GearshiftSelected gear
position
P
R
N
D
3
2
L 1st
2nd 3rd4th1st
2nd 3rd
4th(*1) 1st
2nd
3rd(*1) 4th(*1) 1st
2nd(*1) 3rd(*1)4th(*1)
Reverse
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4436 of 6020
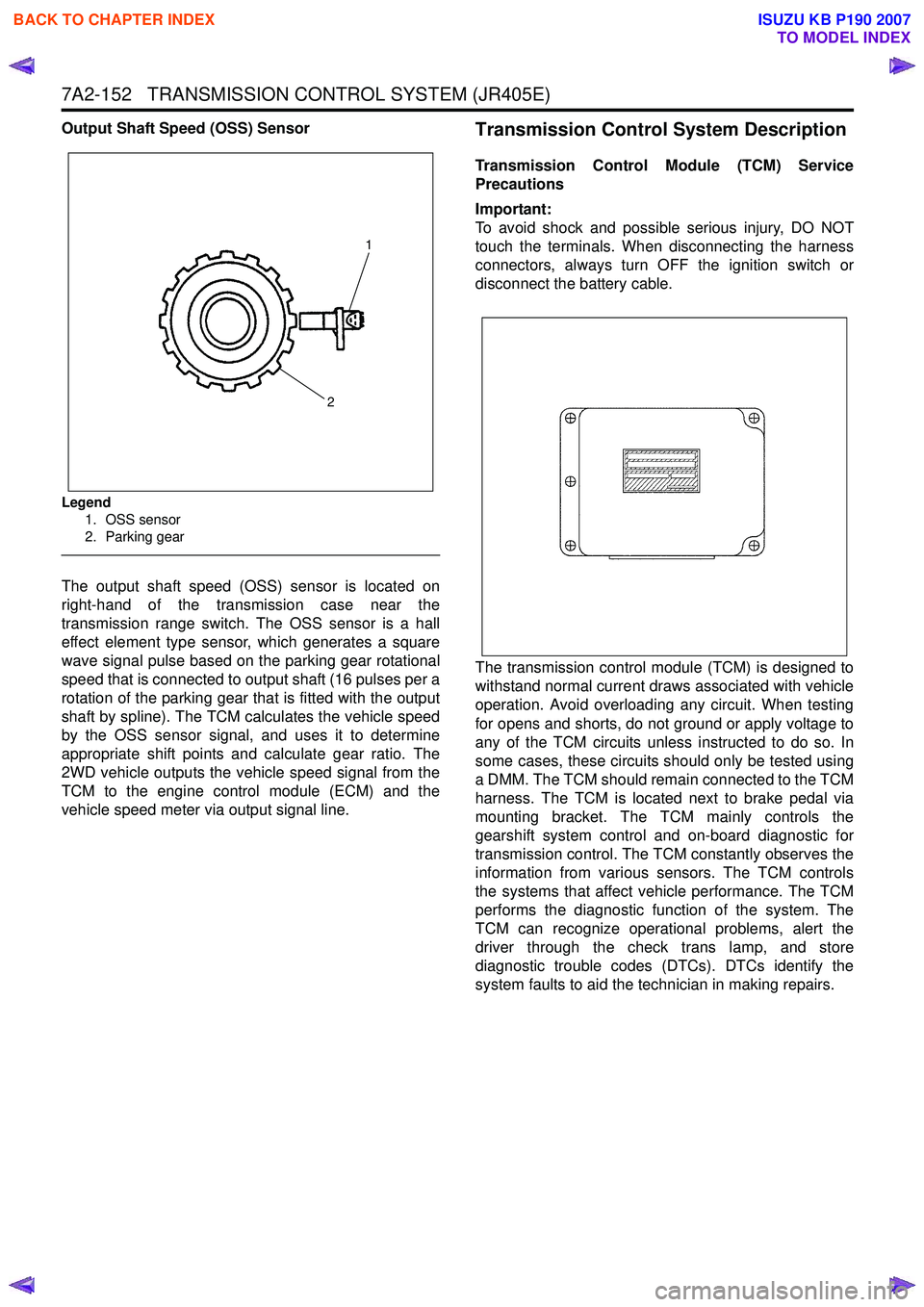
7A2-152 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Output Shaft Speed (OSS) Sensor
Legend1. OSS sensor
2. Parking gear
The output shaft speed (OSS) sensor is located on
right-hand of the transmission case near the
transmission range switch. The OSS sensor is a hall
effect element type sensor, which generates a square
wave signal pulse based on the parking gear rotational
speed that is connected to output shaft (16 pulses per a
rotation of the parking gear that is fitted with the output
shaft by spline). The TCM calculates the vehicle speed
by the OSS sensor signal, and uses it to determine
appropriate shift points and calculate gear ratio. The
2WD vehicle outputs the vehicle speed signal from the
TCM to the engine control module (ECM) and the
vehicle speed meter via output signal line.
Transmission Control System Description
Transmission Control Module (TCM) Service
Precautions
Important:
To avoid shock and possible serious injury, DO NOT
touch the terminals. When disconnecting the harness
connectors, always turn OFF the ignition switch or
disconnect the battery cable.
The transmission control module (TCM) is designed to
withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle
operation. Avoid overloading any circuit. When testing
for opens and shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to
any of the TCM circuits unless instructed to do so. In
some cases, these circuits should only be tested using
a DMM. The TCM should remain connected to the TCM
harness. The TCM is located next to brake pedal via
mounting bracket. The TCM mainly controls the
gearshift system control and on-board diagnostic for
transmission control. The TCM constantly observes the
information from various sensors. The TCM controls
the systems that affect vehicle performance. The TCM
performs the diagnostic function of the system. The
TCM can recognize operational problems, alert the
driver through the check trans lamp, and store
diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the
system faults to aid the technician in making repairs.
1
2
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4438 of 6020
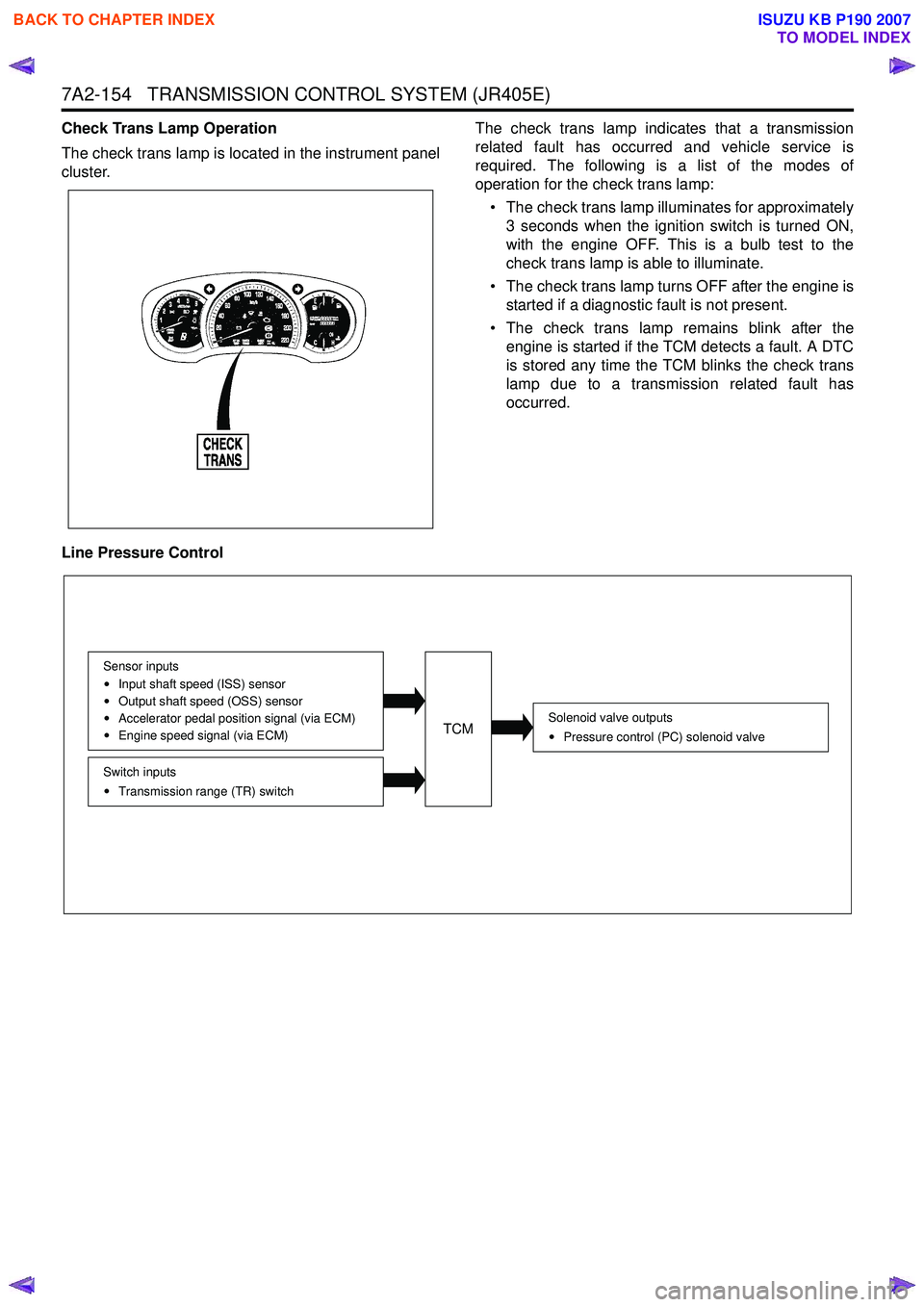
7A2-154 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Check Trans Lamp Operation
The check trans lamp is located in the instrument panel
cluster. The check trans lamp indicates that a transmission
related fault has occurred and vehicle service is
required. The following is a list of the modes of
operation for the check trans lamp:
• The check trans lamp illuminates for approximately 3 seconds when the ignition switch is turned ON,
with the engine OFF. This is a bulb test to the
check trans lamp is able to illuminate.
• The check trans lamp turns OFF after the engine is started if a diagnostic fault is not present.
• The check trans lamp remains blink after the engine is started if the TCM detects a fault. A DTC
is stored any time the TCM blinks the check trans
lamp due to a transmission related fault has
occurred.
Line Pressure Control
Solenoid valve outputs Pressure control (PC) solenoid valve
Switch inputsTransmission range (TR) switch
Sensor inputs
Input shaft speed (ISS) sensor
Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
Accelerator pedal position signal (via ECM)
Engine speed signal (via ECM)TCM
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5522 of 6020

8A-584 ELECTRICAL-BODY AND CHASSIS
RTW 38DLH000101
Menu
The left table shows witch functions are used for the
available equipment versions.
NOTE: Marked items are not applied for keyless entry
system.
DTC
On OBD has three options available in the Tech-2
DTC mode to display the enhanced information
available.
• Read DTC Info Ordered By Priority.
• Read DTC Info As Stored By ECU.
• Clear DTC and Alarm Code Info.
Clear DTC Information
To clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), Use the
diagnostic scan tool “Clear DTC Information” function.
Tech-2 Data Display
The Tech-2 data values represent values that would
be seen on a normally-keyless entry system.
RTW 38DSH001601
Actuator Test
Unlock/Lock Test
Check whether opening and closing of a door lock
can be performed by operation of Tech-2.
1. Turn the key “OFF”.
2. Turn the key “ON”.
3. Check the display and test menu.
4. Operate the Tech-2.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5588 of 6020

Cruise Control – HFV6 Page 8C–10
Tech 2 Data List
The Tech 2 displays the status of certain cruise control system input parameters.
To view the data list:
1 Connect Tech 2 to the data link connector (DLC) and turn on the ignition.
2 On Tech 2 select Body / Powertrain Interface Module / Diagnostic Data Display / Data List .
Tech 2 Parameter Units Displayed Typical Display Values
Cruise Cancel Switch Inactive / Active Inactive
Cruise Resume Switch Off / Enabled Off
Cruise Set Switch Inactive / Active Inactive
Cruise Main Switch Inactive / Active Inactive
Cruise Control Set Lamp Off / On Off
Cruise Control On Lamp Off / On Off
3 On Tech 2 select Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display / Data List / Cruise Control Data.
Tech 2 Parameter Units Displayed Typical Display Values
Brake Lamp Switch Inactive / Active Inactive
Initial Brake Apply Sig Inactive / Active Inactive
Cruise Set / Decel Swit Inactive / Active Inactive
Cruise Resume / Accelerat Inactive / Active Inactive
Cruise Control Disengag Engine Speed / Brake Engine Speed
4 On Tech 2 select Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display / Data List / Engine Data 1.
Tech 2 Parameter Units Displayed Typical Display Values
Clutch Pedal Switch Inactive / Active Inactive
2.2 Diagnostic Systems Check
Diagnostic Systems Check
Refer to 2.3 Wiring Diagram to aid in the diagnosis of the cruise control system.
For the cruise control system to work effectively the following systems / components need to be serviceable:
Step Action Yes No
1 Is the fault specifically isolated to this system / module?
Go to Step 2 Go to 6E1
Powertrain Interface Module – V6
2 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Ignition ON, engine OFF.
3 On Tech 2 select Body / Powertrain Interface Module / Diagnostic Trouble
codes / Read DTCs’.
Are there any set DTC’s? Go to the
appropriate DTC table in 6E1
Powertrain Interface Module – V6. Go to Step 3
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5589 of 6020

Cruise Control – HFV6 Page 8C–11
Step Action Yes No
3 On Tech 2 select
Engine / V6 Engine / Diagnostic Trouble codes / Read DTCs’.
Are there any set DTC’s? Go to the
appropriate DTC table in 6C1-2 Engine
Management – V6 – Diagnostics Go to Step 4
4 Is the instrument cluster assembly functioning correctly? Go to 2.4
Cruise
Control Inoperative / Malfunctioning Refer to 8A
Electrical – Body
and Chassis.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5597 of 6020

Cruise Control – HFV6 Page 8C–19
Step Action Yes No
28 1 Disconnect the ECM connector C – 56.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector C – 56 pin 53 and ground.
3 W ith the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and press and release the clutch pedal.
• With the clutch pedal in the rest position, the multimeter
should display battery voltage
• W ith the clutch pedal pressed, the multimeter should
display 0 V
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 31 Check for a blown
fuse C-4.
Check for short to ground or open circuit
Repair as required (refer to Note 2).
Go to Step 32
29 Check all associated circuits and connectors for the following:
• Loose or damaged connections
• Intermittent faults.
Refer to the Wiring Diagrams in this Section and repair as required.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 32 —
30 Replace the PIM, refer to 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 32 —
31 Replace the ECM module, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 32 —
32 Operate the system in order to verify the repair.
Did you correct the condition? System OK Go to Step 1
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007