IMMOBILISER ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 2388 of 6020
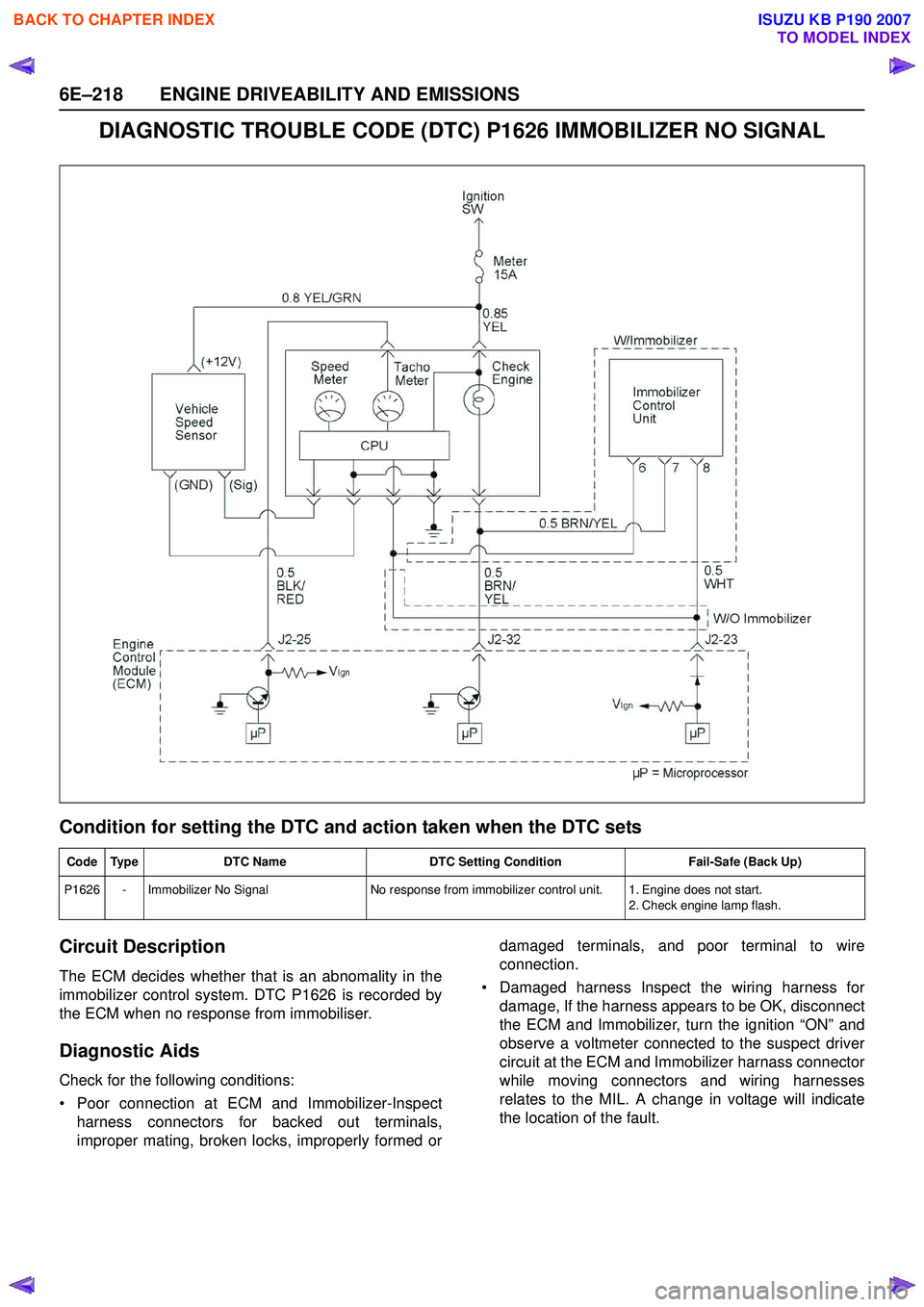
6E–218 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1626 IMMOBILIZER NO SIGNAL
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The ECM decides whether that is an abnomality in the
immobilizer control system. DTC P1626 is recorded by
the ECM when no response from immobiliser.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
• Poor connection at ECM and Immobilizer-Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire
connection.
• Damaged harness Inspect the wiring harness for damage, If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the ECM and Immobilizer, turn the ignition “ON” and
observe a voltmeter connected to the suspect driver
circuit at the ECM and Immobilizer harnass connector
while moving connectors and wiring harnesses
relates to the MIL. A change in voltage will indicate
the location of the fault.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P1626 - Immobilizer No Signal No response from immobilizer control unit. 1. Engine does not start.
2. Check engine lamp flash.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3244 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–2
3.9 Serial Data Communication System ................................................................................................................... 17
3.10 Self Diagnostics System ..................................................................................................................................... 17
3.11 Service Programming System ..................................................................................................... ....................... 17
3.12 Immobiliser System ............................................................................................................................................. 18
4 Component Description and Operation ............................................................................................ .19
4.1 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor ....................................................................................................................... 19
4.2 Brake Pedal Switch Assembly ............................................................................................................................ 19
Stop Lamp and Initial Brake Apply Switch ....................................................................................... ................. 19
Stop Lamp Switch ............................................................................................................................................ 19
Initial Brake Apply Switch ..................................................................................................... ............................ 19
4.3 Barometric Pressure Sensor..................................................................................................... .......................... 20
4.4 Camshaft Position Sensor .................................................................................................................................. 20
4.5 Crankshaft Position Sensor ................................................................................................................................ 21
4.6 Clutch Pedal Switch Assembly – Manual Vehicles Only ............................................................................ ...... 22
4.7 Engine Control Module........................................................................................................................................ 22
4.8 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor .............................................................................................. ................... 23
4.9 Electric Cooling Fans .......................................................................................................................................... 23
4.10 Engine Oil Level and Temperature Sensor ........................................................................................ ................ 24
Engine Oil Temperature Sensor ......................................................................................................................... 24
Engine Oil Level Sensor ...................................................................................................................................... 25
4.11 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor..................................................................................................... ........................... 25
4.12 Fuel Injectors........................................................................................................................................................ 26
4.13 Fuel Rail Assembly ............................................................................................................. ................................. 27
4.14 Heated Oxygen Sensors .......................................................................................................... ............................ 27
LSF 4.2 Two-step Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors .................................................................................. ......... 27
LSU 4.2 Wide-band Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors ................................................................................. ....... 29
4.15 Ignition Coil and Spark Plug ............................................................................................................................... 31
4.16 Intake Air Temperature Sensor .................................................................................................. ......................... 32
4.17 Knock Sensor ....................................................................................................................................................... 32
4.18 Mass Air Flow Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................... 33
Air Intake System ................................................................................................................................................. 33
Mass Air Flow Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................... 33
Construction ..................................................................................................................................................... 34
Operation ......................................................................................................................................................... 34
5 Abbreviations and Glossary of Terms ............................................................................................ ...35
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3254 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–12
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
The ECM monitors the battery voltage circuit to ensure the voltage available to the engine management system stays
within the specified range. A low system voltage changes the voltage across the fuel injectors, which affects the fuel
injector flow rate. In addition, a low system voltage fault condition may cause other engine management system
components to malfunction.
The ECM switches to battery voltage correction mode when the ECM detects a low battery voltage fault condition. W hile
in battery voltage correction mode, the ECM performs the following functions to compensate for the low system voltage:
• Increases the injector on-time to maintain the correct amount of fuel being delivered, and
• Increases the idle speed to increase the generator output.
Limp Mode
The programming in the ECM software allows the engine to run in a back-up fuel strategy or limp mode when the ECM
fails to receive signal inputs from critical sensors or when a critical engine management fault condition exists.
The ECM switches to limp mode to enable the vehicle to be driven until service operations can be performed.
Engine Protection Mode
Engine protection mode is engaged to protect engine components from friction damage in the event of an engine over-
temperature condition being detected by the ECM.
W hen the ECM is in engine protection mode, fuel injectors are systematically disabled and re-activated. The injectors
that have been shut down allow the air being drawn into the engine to assist with engine cooling.
Clear Flood Mode
If the engine is flooded with fuel during starting and will not start, the clear flood mode can be manually selected by
depressing the accelerator pedal to wide open throttle (W OT). In this mode, the ECM will completely disable the fuel
injectors, and will maintain this state during engine cranking as long as the ECM detects a W OT condition with engine
speed less than 1,000 rpm.
3.3 Ignition Control System
The electronic ignition system provides a spark to ignite the compressed air / fuel mixture at the correct time. The ECM
maintains correct spark timing and dwell for all engine operating conditions. The ECM calculates the optimum spark
parameters from information received from the various sensors and triggers the appropriate ignition module / coil to fire
the spark plug.
3.4 Starter Motor Operation
The engine control module controls the activation of the start relay in response to inputs from:
• Ignition switch,
• Battery,
• Immobiliser system, and
• Automatic transmission gear selector position / clutch pedal position switch for vehicles with manual transmissions.
3.5 Throttle Actuator Control System
Description
The throttle actuator control (TAC) system is used to improve emissions, fuel economy and driveability. The TAC system
eliminates the mechanical link between the accelerator pedal and the throttle plate and eliminates the need for a cruise
control module and idle air control motor. The TAC system comprises of:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3259 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–17
3.9 Serial Data Communication System
The engine control module (ECM) communicates directly with the following control units using the General Motors local
area network (GM LAN) serial data communication protocol:
• Transmission control module (TCM) (if fitted)
• Powertrain interface module (PIM)
The immobiliser control unit (ICU) communicates directly with the PIM using Keyword 2000 serial data communication
protocol. Refer to 11A Immobiliser for further information
As the GM LAN serial data communication protocol is not compatible with the Keyword 2000 serial data communication
protocol, a powertrain interface module (PIM) is integrated to the serial data communication system to perform the
following tasks (Refer to 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6):
• Translate the GM LAN serial data transmitted by the ECM into a Keyword 2000 serial data that can be received
and recognised by the ICU.
• Translate the cruise control switch, automatic transmission power mode switch and 3
rd start switch signal into a GM
LAN serial data that can be received and recognised by the ECM.
3.10 Self Diagnostics System
The ECM constantly performs self-diagnostic tests on the engine management system. W hen the ECM detects a
malfunction, it also stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC). A stored DTC will identify the problem area(s) and is
designed to assist the technician in rectifying the fault. In addition, DTCs are classified as either Current or History DTC.
Depending on the type of DTC set, the ECM may turn on the
malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) to warn the driver there
is a fault in the Engine Management System.
Figure 6C1-1 – 12
3.11 Service Programming System
The ECM has an Electronically erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM) where the software and
calibration information required to operate the engine management system are stored.
The ECM features a service programming system (SPS) to flash program the EEPROM in the ECM with the latest ECM
software to provide optimum performance, driveability and emissions control or to program a new ECM.
Flash programming refers to the SPS used to transfer (or download) ECM data from a computer terminal to the vehicle’s
ECM. The system is designed so the vehicle verification procedures are required to eliminate EEPROM tampering that
could increase engine emission levels.
There are three main flash programming techniques:
1 Direct programming (pass through). This is where the vehicle’s data link connector (DLC) is connected directly to a computer terminal. On screen directions are then followed for downloading.
2 Remote Programming. Reprogramming information is downloaded from a computer terminal to Tech 2. Tech 2 is then connected to the vehicle’s DLC. On screen directions are then followed for downloading.
3 Off-board Programming. The off-board programming method is used when a re-programmable ECM must be programmed while it is removed from the vehicle. For example, an independent repair facility may find it necessary
to replace a faulty ECM. On flash programming equipped vehicles, the replacement ECM must be programmed
with data for the specific vehicle identification number (VIN) or the vehicle may not operate properly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3260 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–18
3.12 Immobiliser System
The vehicle incorporates an immobiliser system. After the ignition switch is turned to the ON position, and the powertrain
interface module (PIM) has authenticated the immobiliser control unit (ICU), the PIM sends an encrypted security code to
the engine control module (ECM). The ECM compares the received security code with its own security code, and if it is
valid, the ECM enables the vehicle to be started. For further information and diagnosis of the immobiliser system, refer to
11A Immobiliser.
For further information on the PIM, refer to 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3299 of 6020
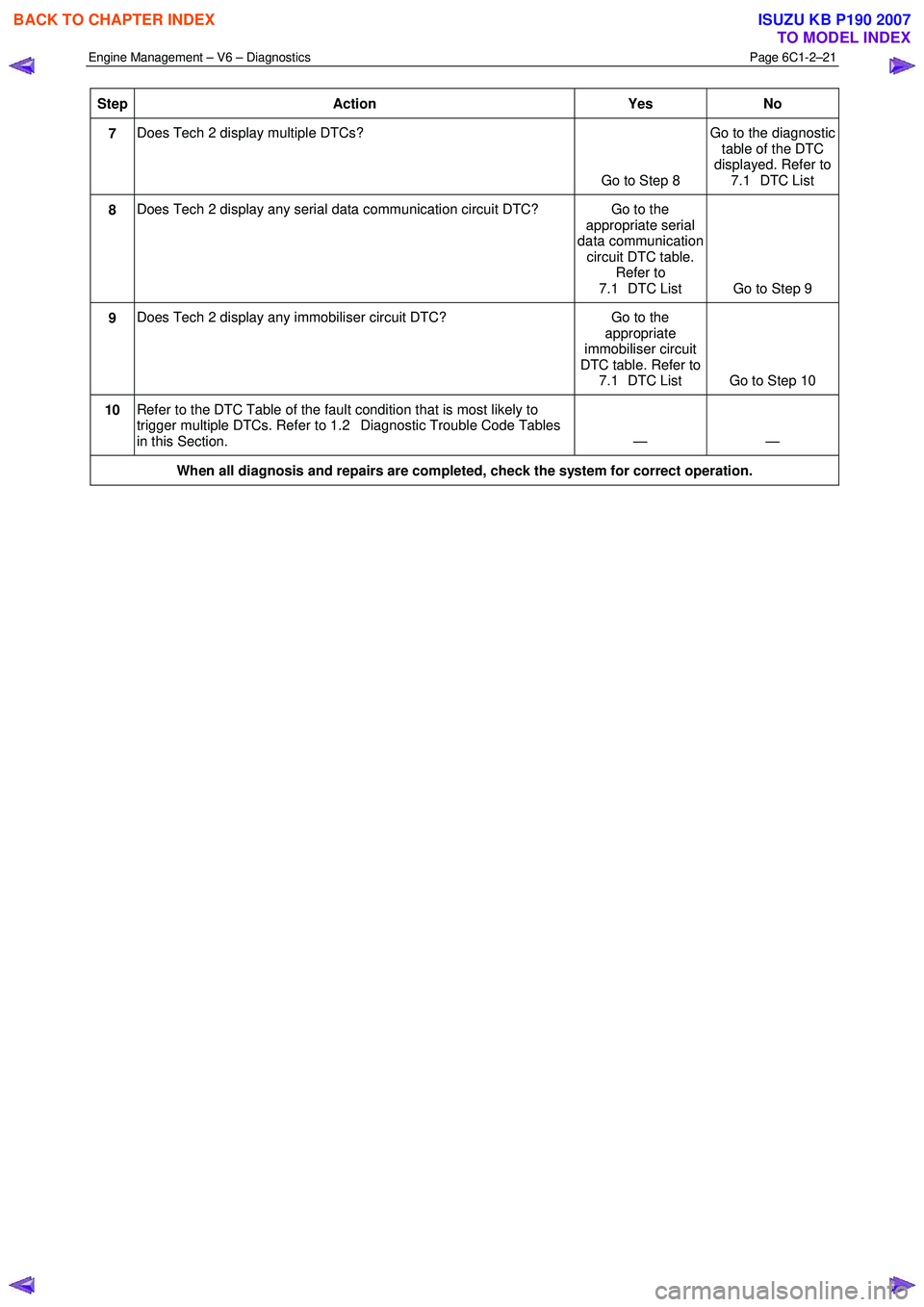
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–21
Step Action Yes No
7 Does Tech 2 display multiple DTCs?
Go to Step 8 Go to the diagnostic
table of the DTC
displayed. Refer to 7.1 DTC List
8 Does Tech 2 display any serial data communication circuit DTC? Go to the
appropriate serial
data communication circuit DTC table. Refer to
7.1 DTC List Go to Step 9
9 Does Tech 2 display any immobiliser circuit DTC? Go to the
appropriate
immobiliser circuit
DTC table. Refer to 7.1 DTC List Go to Step 10
10 Refer to the DTC Table of the fault condition that is most likely to
trigger multiple DTCs. Refer to 1.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables
in this Section. — —
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3301 of 6020
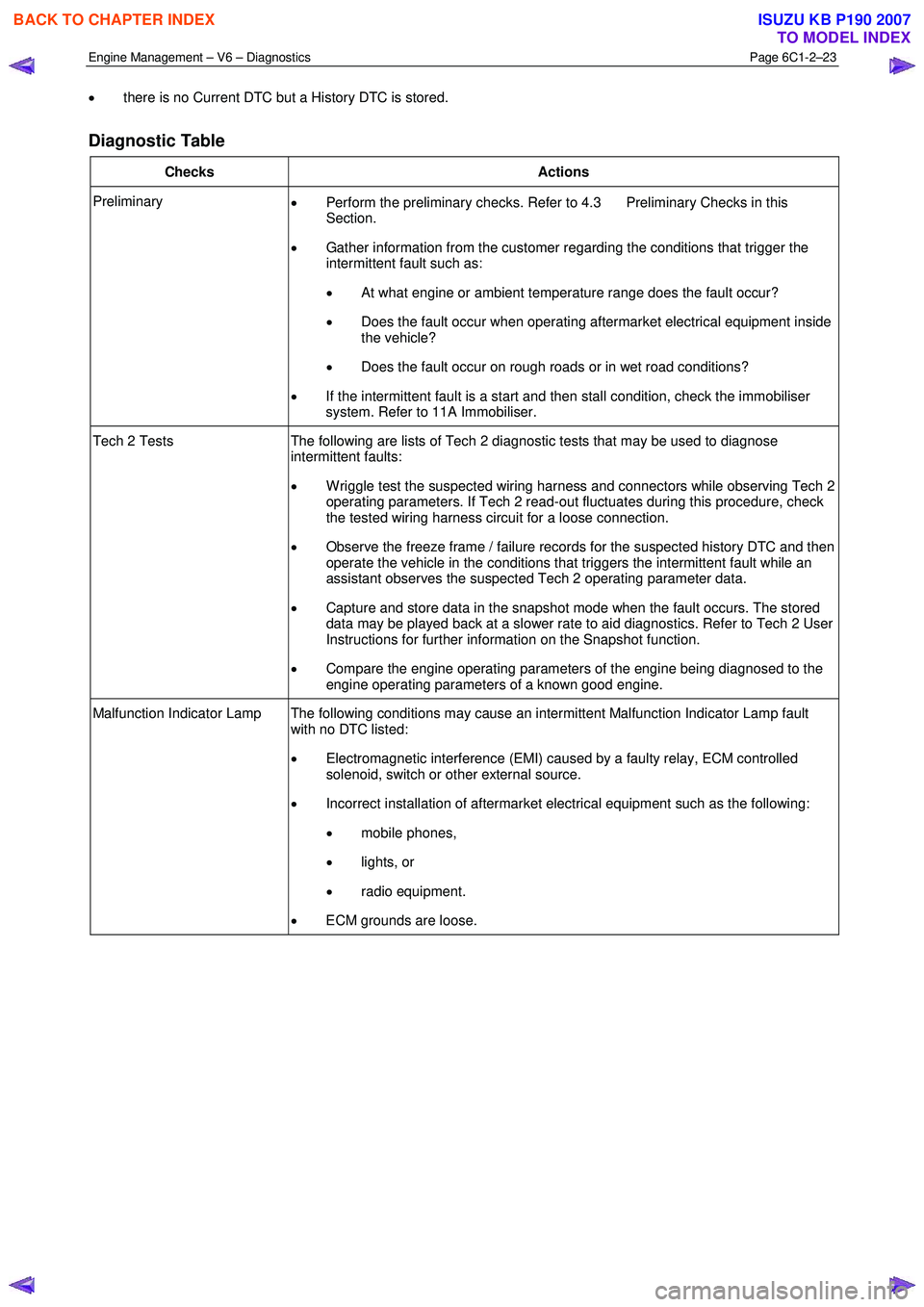
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–23
• there is no Current DTC but a History DTC is stored.
Diagnostic Table
Checks Actions
Preliminary
• Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Gather information from the customer regarding the conditions that trigger the
intermittent fault such as:
• At what engine or ambient temperature range does the fault occur?
• Does the fault occur when operating aftermarket electrical equipment inside
the vehicle?
• Does the fault occur on rough roads or in wet road conditions?
• If the intermittent fault is a start and then stall condition, check the immobiliser
system. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Tech 2 Tests The following are lists of Tech 2 diagnostic tests that may be used to diagnose
intermittent faults:
• W riggle test the suspected wiring harness and connectors while observing Tech 2
operating parameters. If Tech 2 read-out fluctuates during this procedure, check
the tested wiring harness circuit for a loose connection.
• Observe the freeze frame / failure records for the suspected history DTC and then
operate the vehicle in the conditions that triggers the intermittent fault while an
assistant observes the suspected Tech 2 operating parameter data.
• Capture and store data in the snapshot mode when the fault occurs. The stored
data may be played back at a slower rate to aid diagnostics. Refer to Tech 2 User
Instructions for further information on the Snapshot function.
• Compare the engine operating parameters of the engine being diagnosed to the
engine operating parameters of a known good engine.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp The following conditions may cause an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp fault with no DTC listed:
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid, switch or other external source.
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• ECM grounds are loose.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3304 of 6020
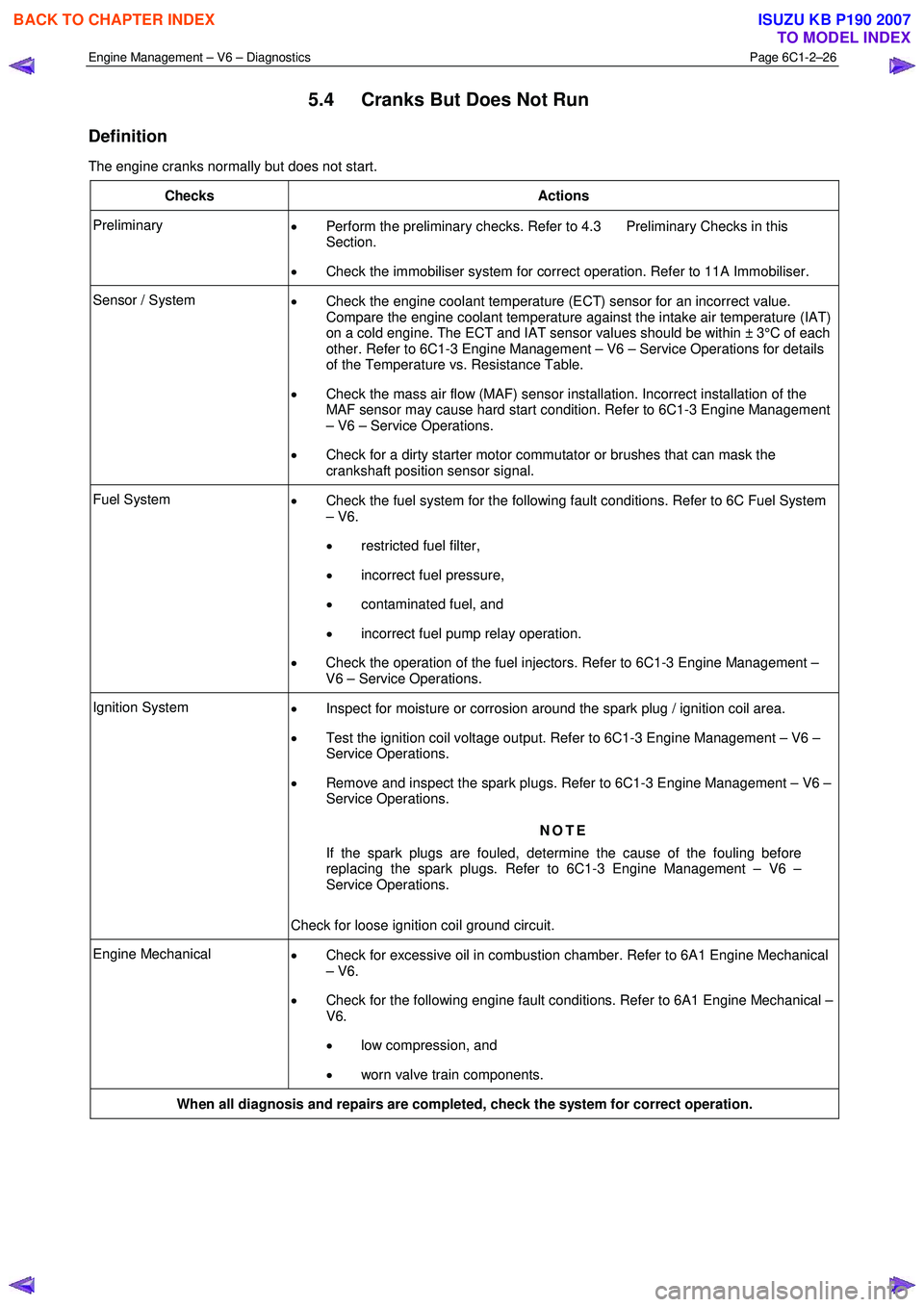
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–26
5.4 Cranks But Does Not Run
Definition
The engine cranks normally but does not start.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the immobiliser system for correct operation. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Sensor / System
• Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for an incorrect value.
Compare the engine coolant temperature against the intake air temperature (IAT)
on a cold engine. The ECT and IAT sensor values should be within ± 3°C of each
other. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for details
of the Temperature vs. Resistance Table.
• Check the mass air flow (MAF) sensor installation. Incorrect installation of the
MAF sensor may cause hard start condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check for a dirty starter motor commutator or brushes that can mask the
crankshaft position sensor signal.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure,
• contaminated fuel, and
• incorrect fuel pump relay operation.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical • Check for excessive oil in combustion chamber. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical
– V6.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3307 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–29
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this Section.
Fuel System Inspect the injectors for leaking condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Engine Cooling System • Check for engine overheating. Refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
• Check the engine thermostat for proper operation and correct heat range. Refer to
6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical • Check for build up of carbon deposit in the combustion chamber, which may
cause hot spots and increased compression ratio. Refer to 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Using Tech 2, check for incorrect engine idle speed.
Additional
• If the engine continues to run after the ignition is switched off but the engine runs
normally, check the following:
• ignition switch operation,
• voltage feedback from alternator L terminal to ignition switch, and
• sticking ignition control relay.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.8 Hard Start
Definition
The engine cranks normally but takes longer to start than usual. As soon as the engine runs, the engine may stall
immediately.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the immobiliser system for correct operation. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Sensor / System
• Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for an incorrect value.
Compare the engine coolant temperature against the intake air temperature (IAT)
on a cold engine. The ECT and IAT sensor values should be within ± 3°C of each
other. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for details
of the Temperature vs. Resistance Table.
• Check the mass air flow (MAF) sensor installation. Incorrect installation of the
MAF sensor may cause hard start condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Test the resistance of the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor. The CKP sensor
resistance must be within 700 – 1,200 Ω at all temperatures.
• Check for dirty starter motor commutator or brushes that can mask the crankshaft
position sensor signal.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3334 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–56
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0522 Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage Low 7.31 DTC P0521, P0522 or P0523
P0523 Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage High 7.31 DTC P0521, P0522 or P0523
P0532 A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage Low 7.32 DTC P0532 or P0533
P0533 A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage High 7.32 DTC P0532 or P0533
P0560 System Voltage Malfunction 7.33 DTC P0560, P0562 or P0563
P0562 System Voltage Low Voltage 7.33 DTC P0560, P0562 or P0563
P0563 System Voltage High Voltage 7.33 DTC P0560, P0562 or P0563
P0571 Cruise Control Brake Switch Circuit 7.28 DTC P0504 or P0571
P0601 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0602 Program Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0604 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0606 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0615 Starter Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.35 DTC P0615, P0616 or P0617
P0616 Starter Relay Circuit Low Voltage 7.35 DTC P0615, P0616 or P0617
P0617 Starter Relay Circuit High Voltage 7.35 DTC P0615, P0616 or P0617
P0625 Alternator F Terminal Low Voltage 7.36 DTC P0625 or P0626
P0626 Alternator F Terminal High Voltage 7.36 DTC P0625 or P0626
P0627 Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.37 DTC P0627, P0628 or P0629
P0628 Fuel Pump Relay Voltage Low 7.37 DTC P0627, P0628 or P0629
P0629 Fuel Pump Relay Voltage High 7.37 DTC P0627, P0628 or P0629
P0633 Immobiliser Function Not Programmed 7.30 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 or P1679
P0638 Commanded Versus Actual Throttle Position Correlation 7.29 DTC P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100, P2101, P2119 or P2176
P0645 A/C Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.38 DTC P0645, P0646 or P0647
P0646 A/C Relay Voltage Low 7.38 DTC P0645, P0646 or P0647
P0647 A/C Relay Voltage High 7.38 DTC P0645, P0646 or P0647
P0685 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.39 DTC P0685, P0686 or P0687
P0686 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Low Voltage 7.39 DTC P0685, P0686 or P0687
P0687 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit High Voltage 7.39 DTC P0685, P0686 or P0687
P0691 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit Low Voltage 7.26 DTC P0480, P0691 or P0692
P0692 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit High Voltage 7.26 DTC P0480, P0691 or P0692
P0700 Malfunction Indicator (MI) Request from Transmission
Control Module (TCM) 7.40 DTC P0700
P0704 Clutch Switch Input Circuit Malfunction
7.41 DTC P0704
P0850 Park / Neutral Signal Circuit Incorrect Signal 7.42 DTC P0850
P1258 Engine Coolant Over Temperature – Protection Mode
Active 7.8 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 or
P1258
P1551 Throttle Control Lower Position Not Reached during Learning Mode 7.29 DTC P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551,
P2100, P2101, P2119 or P2176
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007