fuses ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 129 of 6020
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1-95
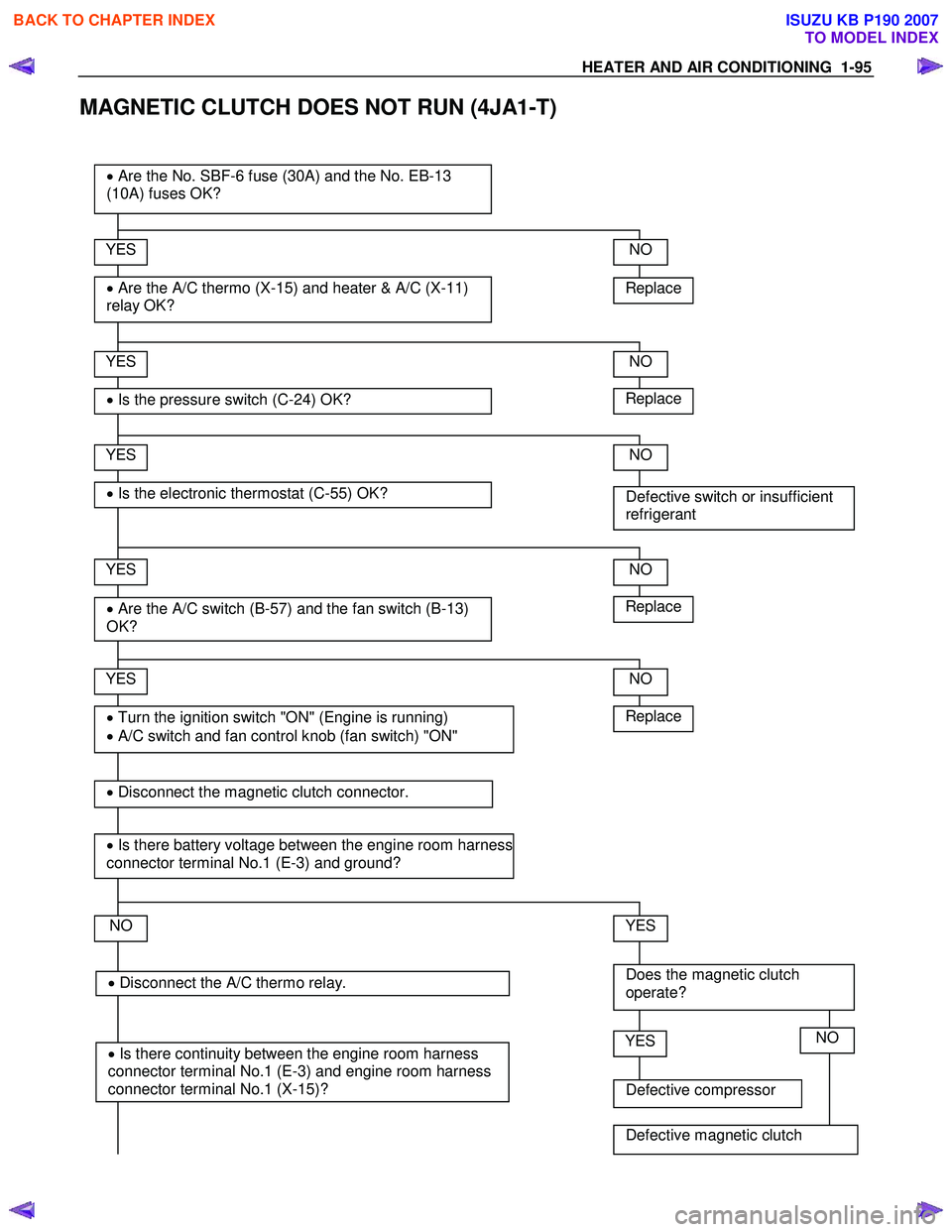
MAGNETIC CLUTCH DOES NOT RUN (4JA1-T)
Replace
YES
• Are the A/C thermo (X-15) and heater & A/C (X-11)
relay OK?
• Are the No. SBF-6 fuse (30A) and the No. EB-13
(10A) fuses OK?
YES
• Is the pressure switch (C-24) OK?
YES
• Are the A/C switch (B-57) and the fan switch (B-13)
OK?
NO
YES
• Turn the ignition switch "ON" (Engine is running)
• A/C switch and fan control knob (fan switch) "ON"
NO
Replace
NO
Defective switch or insufficient
refrigerant
NO
NO
Does the magnetic clutch
operate?
YES
Replace
• Disconnect the magnetic clutch connector.
• Is there battery voltage between the engine room harness
connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and ground?
Defective compressor
YESNO
Defective magnetic clutch
• Is the electronic thermostat (C-55) OK?
YES
Replace
NO
• Disconnect the A/C thermo relay.
• Is there continuity between the engine room harness
connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and engine room harness
connector terminal No.1 (X-15)?
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 134 of 6020
1-100 HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING
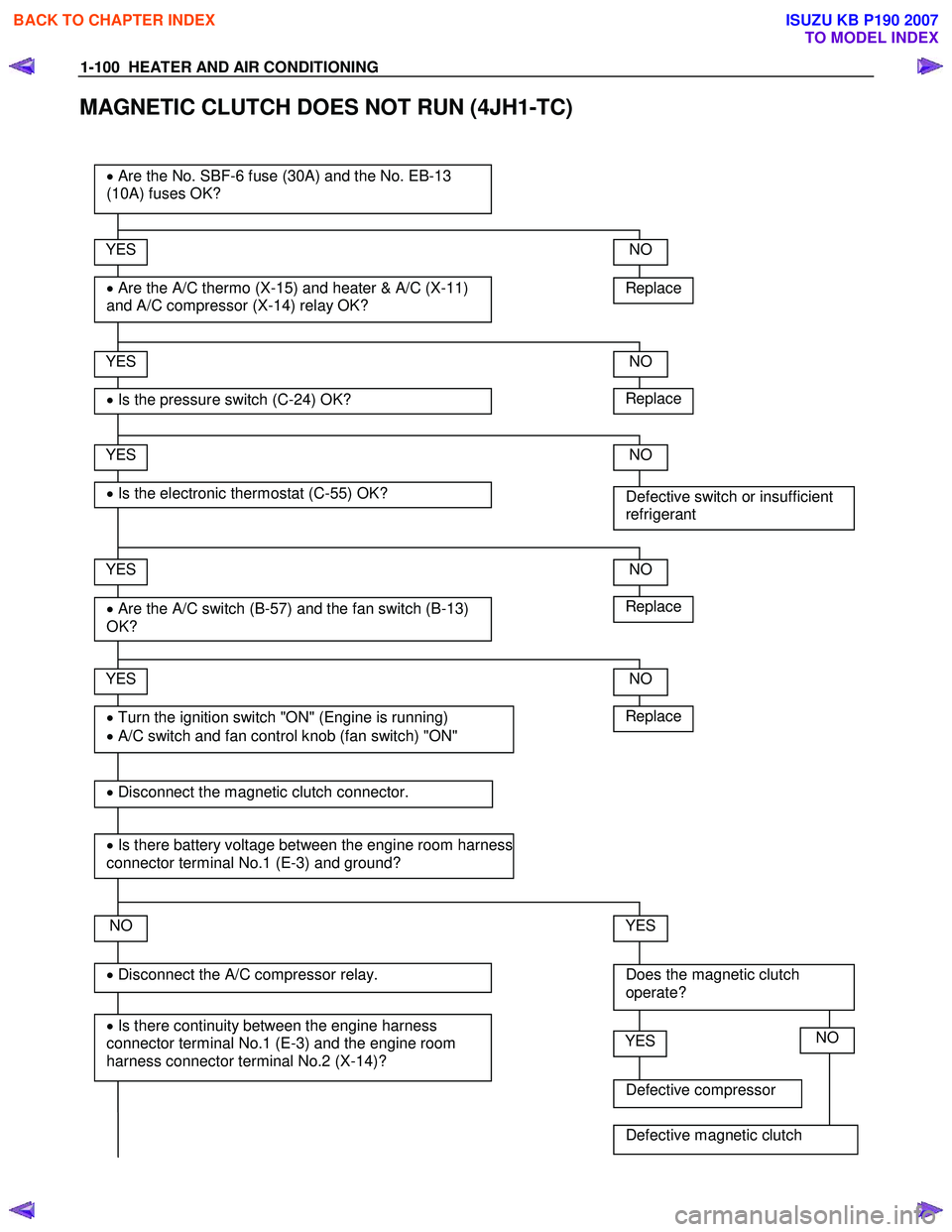
MAGNETIC CLUTCH DOES NOT RUN (4JH1-TC)
Replace
YES
• Are the A/C thermo (X-15) and heater & A/C (X-11)
and A/C compressor (X-14) relay OK?
• Are the No. SBF-6 fuse (30A) and the No. EB-13
(10A) fuses OK?
YES
• Is the pressure switch (C-24) OK?
YES
• Are the A/C switch (B-57) and the fan switch (B-13)
OK?
NO
YES
• Is there continuity between the engine harness
connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and the engine room
harness connector terminal No.2 (X-14)?
• Disconnect the A/C compressor relay.
• Turn the ignition switch "ON" (Engine is running)
• A/C switch and fan control knob (fan switch) "ON"
NO
Replace
NO
Defective switch or insufficient
refrigerant
NO
NO
Does the magnetic clutch
operate?
YES
Replace
• Disconnect the magnetic clutch connector.
• Is there battery voltage between the engine room harness
connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and ground?
Defective compressor
YESNO
Defective magnetic clutch
• Is the electronic thermostat (C-55) OK?
YES
Replace
NO
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 139 of 6020

HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1-105
MAGNETIC CLUTCH DOES NOT RUN (4JJ1-TC Standard Output, 4JJ1-TC
High Output, 4JK1-TC High Output RHD MODEL)
Replace
YES
• Are the A/C thermo (X-15), heater & A/C (X-11) and
A/C compressor (X-14) relay OK?
• Are the No. SBF-6 fuse (30A) and the No. EB-13
(10A) fuses OK?
YES
• Is the pressure switch (C-24) OK?
YES
• Are the A/C switch (B-57) and the fan switch (B-13)
OK?
NO
YES
• Is there continuity between the engine harness
connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and the engine room
harness connector terminal No.2 (X-14)?
• Disconnect the A/C compressor relay.
• Turn the ignition switch "ON" (Engine is running)
• A/C switch and fan control knob (fan switch) "ON"
NO
Replace
NO
Defective switch or insufficient
refrigerant
NO
NO
Does the magnetic clutch
operate?
YES
Replace
• Disconnect the magnetic clutch connector.
• Is there battery voltage between the engine room
harness connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and ground?
Defective compressor
YESNO
Defective magnetic clutch
• Is the electronic thermostat (C-55) OK?
YES
Replace
NO
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 144 of 6020

1-110 HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING
MAGNETIC CLUTCH DOES NOT RUN (4JJ1-TC Standard Output, 4JJ1-TC
High Output, 4JK1-TC High Output LHD MODEL)
Replace
YES
• Are the A/C thermo (X-15), heater & A/C (X-11) and
A/C compressor (X-14) relay OK?
• Are the No. SBF-6 fuse (30A) and the No. EB-13
(10A) fuses OK?
YES
• Is the pressure switch (C-24) OK?
YES
• Are the A/C switch (B-57) and the fan switch (B-13)
OK?
NO
YES
• Is there continuity between the engine harness
connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and the engine room
harness connector terminal No.2 (X-14)?
• Disconnect the A/C compressor relay.
• Turn the ignition switch "ON" (Engine is running)
• A/C switch and fan control knob (fan switch) "ON"
NO
Replace
NO
Defective switch or insufficient
refrigerant
NO
NO
Does the magnetic clutch
operate?
YES
Replace
• Disconnect the magnetic clutch connector.
• Is there battery voltage between the engine room
harness connector terminal No.1 (E-3) and ground?
Defective compressor
YESNO
Defective magnetic clutch
• Is the electronic thermostat (C-55) OK?
YES
Replace
NO
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 149 of 6020

HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1-115
MAGNETIC CLUTCH DOES NOT RUN (C24SE)
Replace
YES
• Are the A/C thermo (X-15), heater & A/C (X-11)
and A/C compressor (X-14) relay OK?
• Are the No. SBF 8 fuse (30A) and the No. EB-13
(10A) fuses OK?
YES
• Is the pressure switch (C-24) OK?
YES
• Are the A/C switch (B-57) and the fan switch (B-13)
OK?
NO
YES
• Is there continuity between the engine harness
connector terminal No.1 (E-2) and the engine room
harness connector terminal No.2 (X-14)?
• Disconnect the A/C compressor relay.
• Turn the ignition switch "ON" (Engine is running)
• A/C switch and fan control knob (fan switch "ON")
NO
Replace
NO
Defective switch or insufficient
refrigerant
NO
NO
Does the magnetic clutch
operate?
YES
Replace
• Disconnect the magnetic clutch connector.
• Is there battery voltage between the engine room
harness connector terminal No.1 (E-2) and ground?
Defective compressor
YESNO
Defective magnetic clutch
• Is the electronic thermostat (C-55) OK?
Replace
NOYES
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 617 of 6020

5A-24 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Computer System Service Precautions
The Anti-lock Brake System and Electronic Brake-force
Distribution interfaces directly with the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) which is a control
computer that is similar in some regards to the Engine
Control Module. These modules are designed to
withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle
operation. However, care must be taken to avoid
overloading any of the EHCU circuits. In testing for
opens or shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to any
of the circuits unless instructed to do so by the
appropriate diagnostic procedure. These circuits should
only be tested with a high impedance multimeter
5-8840-0366-0 or special tools as described in this
section. Power should never be removed or applied to
any control module with the ignition in the “ON” position.
Before removing or connecting battery cables, fuses or
connectors, always turn the ignition switch to the “OFF”
position.
General Service Precautions
The following are general precautions which should be
observed when servicing and diagnosing the Anti-lock
Brake System and/or other vehicle systems. Failure to
observe these precautions may result in Anti-lock Brake
System and Electronic Brake-force Distribution
damage.
• If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle using an electric arc welder, the EHCU and valve
block connectors should be disconnected before the
welding operation begins.
• The EHCU and valve block connectors should never be connected or disconnected with the
ignition “ON”.
Note:
• If only rear wheels are rotated using jacks or drum tester, the system will diagnose a speed sensor
malfunction and the “ABS and Brake” warning lamp
will illuminate. But actually no trouble exists. W hen
the DTC is not detected and the ABS and BRAKE
warning lamp is on, “How to erase code” is
performed and an ABS and BRAKE warning lamp
are off.
If the battery has been discharged
The engine may stall if the battery has been completely
discharged and the engine is started via jumper cables.
This is because the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) and
Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD) System
requires a large quantity of electricity. In this case, wait
until the battery is recharged, or set the ABS and EBD
to a non-operative state by removing the fuse for the
ABS. After the battery has been recharged, stop the
engine and install the ABS fuse. Start the engine again,
and confirm that the ABS warning Lamp does not light.
Note on Intermittents
As with virtually any electronic system, it is difficult to
identify an intermittent failure. In such a case duplicating
the system malfunction during a test drive or a good
description of vehicle behavior from the customer may
be helpful in locating a “most likely” failed component or
circuit. The symptom diagnosis chart may also be
useful in isolating the failure. Most intermittent
problems are caused by faulty electrical connections or
wiring. W hen an intermittent failure is encountered,
check suspect circuits for:
• Suspected harness damage.
• Poor mating of connector halves or terminals not fully seated in the connector body (backed out).
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Test Driving ABS Complaint Vehicles
If there has been an abnormality in the lighting pattern
of the “ABS” warning lamp, the fault can be located in
accordance with the “DIAGNOSIS BY “ABS” W ARNING
LAMP ILLUMINATION PATTERN”. Although such
problems can be detected by the driver as a vehicle
symptom, it is still necessary to perform a test drive
following the test procedure mentioned below, in order
to reproduce the symptom for problem diagnosis on a
symptom basis:
1. Start the engine and make sure that the “ABS” W /L
goes OFF. If the W /L remains ON, it means that
the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
Therefore, read the code and locate the fault.
Note: The DTC cannot be cleared if the vehicle speed
does not exceed about 10km/h (6mph) at DTC, even
though the repair operation is completed.
2. Start the vehicle and accelerate to about 30 km/h (19 mph) or more.
3. Slowly brake and stop the vehicle completely.
4. Then restart the vehicle and accelerate to about 40 km/h (25 mph) or more.
5. Brake at a time so as to actuate the ABS and stop the vehicle.
6. Be cautious of abnormality during the test. If the W /L is actuated while driving, read the DTC and
locate the fault.
7. If the abnormality is not reproduced by the test, make best efforts to reproduce the situation
reported by the customer.
8. If the abnormality has been detected, repair in accordance with the “SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS”.
Note:
• Be sure to perform a test drive on a wide, even road
with light traffic.
• If an abnormality is detected, be sure to suspend the test and start trouble diagnosis at once.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1034 of 6020
ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D – 33
PRE-HEATING SYSTEM
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
Make the necessary adjustments, repairs, and part replacement if excessive wear of damage is discovered during
inspection.
VISUAL CHECK
Check the main fuses and glow indicator for damage.
Replace the part(s) if required.
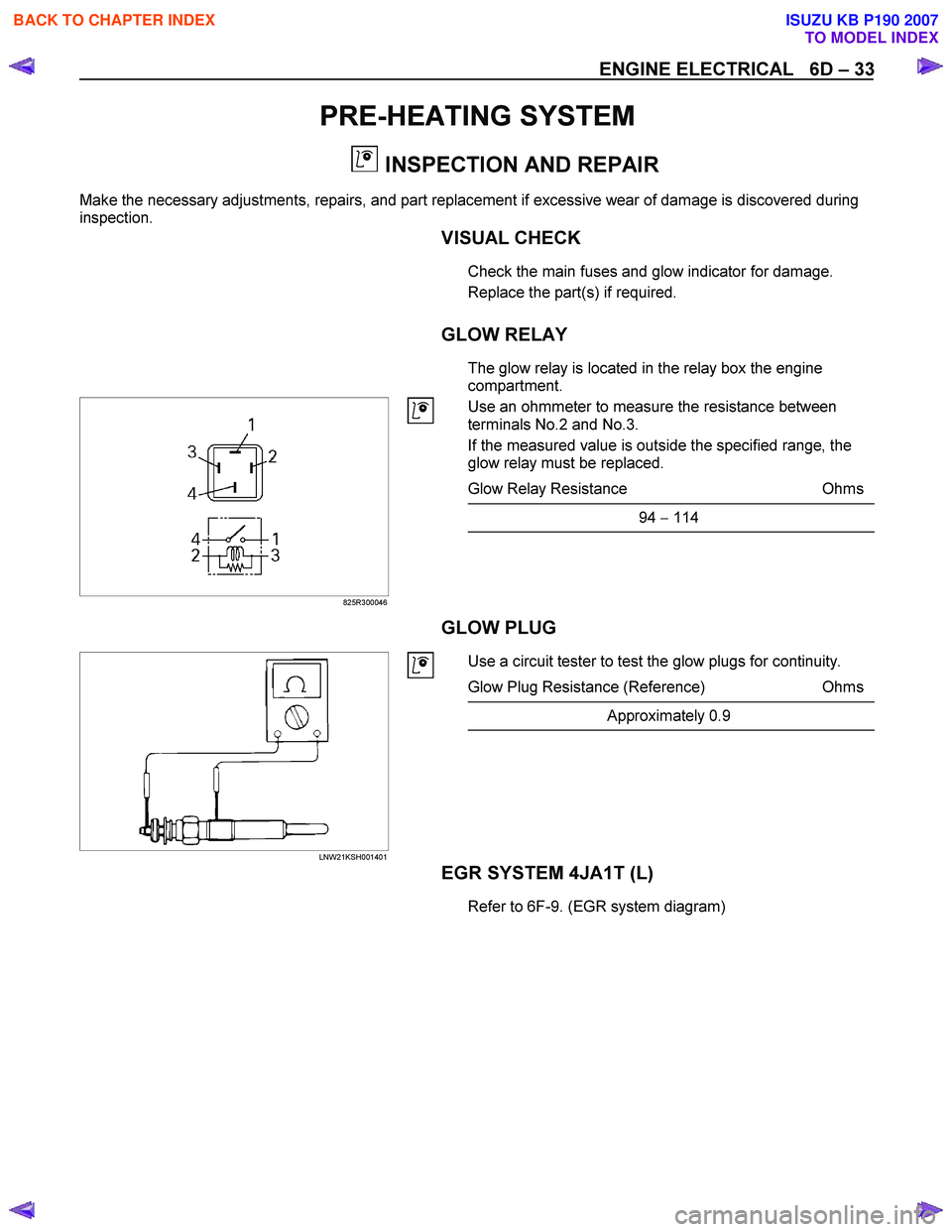
GLOW RELAY
The glow relay is located in the relay box the engine
compartment.
825R300046
Use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance between
terminals No.2 and No.3.
If the measured value is outside the specified range, the
glow relay must be replaced.
Glow Relay Resistance Ohms
94 − 114
GLOW PLUG
LNW21KSH001401
Use a circuit tester to test the glow plugs for continuity.
Glow Plug Resistance (Reference) Ohms
Approximately 0.9
EGR SYSTEM 4JA1T (L)
Refer to 6F-9. (EGR system diagram)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1291 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-257
Checks Action
Electrical Connections or W iring Poor electrical connections, terminal tension or wiring problems cause most intermittent. To perform the following inspections:
• Inspect for poor mating of the connector halves, or terminals improperly seated in the
connector body.
• Inspect for improperly formed or damaged terminals. Test for poor terminal tension.
• Inspect for poor terminal to wire connections including terminals crimped over
insulation. This requires removing the terminal from the connector body.
• Inspect for corrosion/water intrusion. Pierced or damaged insulation can allow
moisture to enter the wiring. The conductor can corrode inside the insulation, with
little visible evidence. Look for swollen and stiff sections of wire in the suspect
circuits.
• Inspect for wires that are broken inside the insulation.
• Inspect the harness for pinched, cut or rubbed through wiring.
• Ensure that the wiring does not come in contact with hot exhaust components.
Control Module Power and Grounds
Component Power and Grounds Poor power or ground connections can cause widely varying symptoms.
• Test all control module power supply circuits. Many vehicles have multiple circuits
supplying power to the control module. Other components in the system may have
separate power supply circuits that may also need to be tested. Inspect connections
at the module/component connectors, fuses, and any intermediate connections
between the power source and the module/component. A test lamp or a DMM may
indicate that voltage is present, but neither tests the ability of the circuit to carry
sufficient current. Ensure that the circuit can carry the current necessary to operate
the component.
• Test all control module ground and system ground circuits. The control module may
have multiple ground circuits. Other components in the system may have separate
grounds that may also need to be tested. Inspect grounds for clean and tight
connections at the grounding point. Inspect the connections at the component and in
splice packs, where applicable. Ensure that the circuit can carry the current
necessary to operate the component.
Temperature Sensitivity • An intermittent condition may occur when a component/connection reaches normal
operating temperature. The condition may occur only when the
component/connection is cold, or only when the component/connection is hot.
• If the intermittent is related to heat, review the data for a relationship with the
following: - High ambient temperatures
- Under hood/engine generated heat
- Circuit generated heat due to a poor connection, or high electrical load
- Higher than normal load conditions, towing, etc.
• If the intermittent is related to cold, review the data for the following:
- Low ambient temperatures–In extremely low temperatures, ice may form in a connection or component. Test for water intrusion.
- The condition only occurs on a cold start.
- The condition goes away when the vehicle warms up.
• Information from the customer may help to determine if the trouble follows a pattern
that is temperature related.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1617 of 6020

ENGINE ELECTRICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6D-29
Pre-Heating System
Inspection and Repair
Make the necessary adjustments, repairs, and part
replacement if excessive wear of damage is discovered
during inspection.
Visual Check
Check the main fuses and glow indicator for damage.
Replace the part(s) if required.
Glow Relay
The glow relay is located in the relay box the engine
compartment.
Use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance between
terminals No.2 and No.3.
If the measured value is outside the specified range, the
glow relay must be replaced.
Glow Relay Resistance Ohms
94 - 114
825R300046
Glow Plug
Use a circuit tester to test the glow plugs for continuity.
Glow Plug Resistance (Reference) Ohms
Approximately 0.9
LNW 21KSH001401
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1942 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-325
Intermittent Conditions
ChecksAction
Definition:
The problem is not currently present but is indicated in DTC History.
OR
There is a customer complaint, but the symptom cannot currently be duplicated, if the problem is not DTC related.
Preliminary Checks • Refer to Symptoms - Engine Controls before starting.
Harness/ Connector Many intermittent open or shorted circuits are affected by harness/ connector
movement that is caused by vibration, engine torque, bumps/ rough pavement, etc.
Test for this type of condition by performing the applicable procedure from the following
list:
• Move related connectors and wiring while monitoring the appropriate scan tool data.
• Move related connectors and wiring with the component commanded ON, and OFF, with the scan tool. Observe the component operation.
• With the engine running, move related connectors and wiring while monitoring engine operation.
If harness or connector movement affects the data displayed, component/ system
operation, or engine operation, inspect and repair the harness/ connections as
necessary.
Electrical Connections or Wiring Poor electrical connections, terminal tension or wiring problems cause most intermittent. To perform the following inspections:
• Poor mating of the connector halves, or terminals improperly seated in the connector body.
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals. Test for poor terminal tension.
• Poor terminal to wire connections including terminals crimped over insulation. This requires removing the terminal from the connector body.
• Corrosion/ water intrusion. Pierced or damaged insulation can allow moisture to enter the wiring. The conductor can corrode inside the insulation, with little visible
evidence. Look for swollen and stiff sections of wire in the suspect circuits.
• Wires that are broken inside the insulation.
• Harness for pinched, cut or rubbed through wiring.
• Ensure that the wiring does not come in contact with hot exhaust components.
Control Module Power and Grounds
Component Power and Grounds Poor power or ground connections can cause widely varying symptoms.
• Test all control module power supply circuits. Many vehicles have multiple circuits supplying power to the control module. Other components in the system may have
separate power supply circuits that may also need to be tested. Inspect connections
at the module/ component connectors, fuses, and any intermediate connections
between the power source and the module/ component. A test lamp or a DMM may
indicate that voltage is present, but neither tests the ability of the circuit to carry
sufficient current. Ensure that the circuit can carry the current necessary to operate
the component.
• Test all control module ground and system ground circuits. The control module may have multiple ground circuits. Other components in the system may have separate
grounds that may also need to be tested. Inspect grounds for clean and tight
connections at the grounding point. Inspect the connections at the component and
in splice packs, where applicable. Ensure that the circuit can carry the current
necessary to operate the component.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007