engine ISUZU TROOPER 1998 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TROOPER, Model: ISUZU TROOPER 1998Pages: 3573, PDF Size: 60.36 MB
Page 1586 of 3573
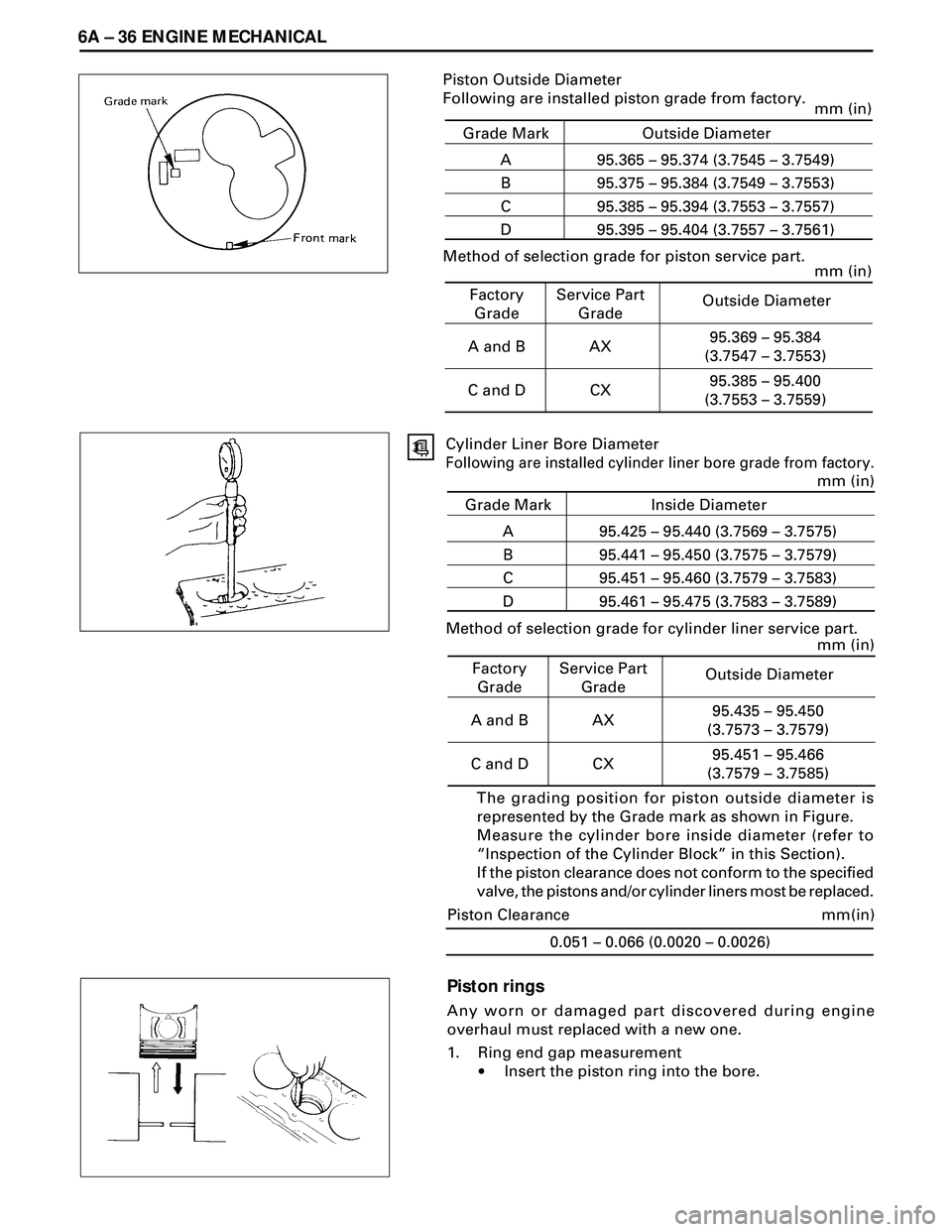
6A Ð 36 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Piston rings
Any worn or damaged part discovered during engine
overhaul must replaced with a new one.
1. Ring end gap measurement
·Insert the piston ring into the bore. Grade Mark Piston Outside Diameter
Following are installed piston grade from factory.
Outside Diameter
Factory
GradeService Part
GradeOutside Diameter A
B
C
D95.365 – 95.374 (3.7545 – 3.7549)
95.375 – 95.384 (3.7549 – 3.7553)
95.385 – 95.394 (3.7553 – 3.7557)
95.395 – 95.404 (3.7557 – 3.7561)
95.369 – 95.384
(3.7547 – 3.7553)
95.385 – 95.400
(3.7553 – 3.7559) A and B
C and DAX
CX
mm (in)
Method of selection grade for piston service part.mm (in)
Grade Mark Inside Diameter
A
B
C
D95.425 – 95.440 (3.7569 – 3.7575)
95.441 – 95.450 (3.7575 – 3.7579)
95.451 – 95.460 (3.7579 – 3.7583)
95.461 – 95.475 (3.7583 – 3.7589)
Cylinder Liner Bore Diameter
Following are installed cylinder liner bore grade from factory.
Factory
GradeService Part
GradeOutside Diameter
95.435 – 95.450
(3.7573 – 3.7579)
95.451 – 95.466
(3.7579 – 3.7585) A and B
C and DAX
CXmm (in)
Method of selection grade for cylinder liner service part.
mm (in)
The grading position for piston outside diameter is
represented by the Grade mark as shown in Figure.
Measure the cylinder bore inside diameter (refer to
ÒInspection of the Cylinder BlockÓ in this Section).
If the piston clearance does not conform to the specified
valve, the pistons and/or cylinder liners most be replaced.
0.051 – 0.066 (0.0020 – 0.0026)
mm(in) Piston Clearance
Page 1587 of 3573
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A Ð 37
·Push the ring by the piston, at a right angle to the
wall, into the point at which the cylinder bore
diameter is the smallest.
·Measure the ring end gap.
Standard
Compression
ringLimit
1st/2nd0.20-0.35
(0.0079-0.0138)
1.5
(0.0591)
0.10-0.30
(0.0039-0.0118) Oil ringmm(in)
2. Measure the clearance between the piston ring groove
and the piston ring with a feeler gauge. If the piston ring
groove/piston ring clearance exceeds the specified limit,
the piston must be replaced.
Standard
Compression
ringLimit
Top 0.05-0.09
(0.0020-0.0035)
2nd 0.05-0.09
(0.0020-0.0035)
0.15
(0.0059)
0.03-0.07
(0.0012-0.0028) Oil ringmm(in)
Piston pin
Visually inspect the piston pin for cracks, flaws, and other
damage and replace if necessary.
1. Use a micrometer to measure the piston pin outside
diameter in both directions at three different
positions. If the measurement exceed the specified
limit, the piston pin must be replaced.
Standard
Piston pin outside
diameterLimit
33.995-34.000
(1.3384-1.3386)
33.970
(1.3374)
mm (in)
2. Measure the inside diameter of the connecting rod
small end. If the clearance between the small end
and pin does not conform to the specified value, the
connecting rod or bushing and pin must be replaced.
Standard
Limit
0.008 ~ 0.020
(0.0003 ~ 0.0008)0.05
(0.0020)
Clearancemm (in)
Page 1588 of 3573
6A Ð 38 ENGINE MECHANICAL
NOTE:
Align the bushing with the connecting rod oil port.
After installing a new bushing, finish the bushing bore
with a pin hole grinder. 3. Insert the piston pin into the piston and rotate it. If
the pin rotates smoothly with no backlash, the
clearance is normal. If there is backlash or
roughness, measure the clearance. If the clearance
exceeds the specified limit, the piston and the piston
pin must be replaced.
Standard Limit
0.002 ~ 0.015
(0.00008 ~ 0.0006)0.04
(0.0016) Clearancemm (in)
Bushing replacement
Removal: Use a suitable bar and bench press or
hammer.
Installation: Use a suitable bar and bench press.
Connecting rods
1. Check the connecting rod alignment with a
connecting rod aligner.
If either the bend or the twist exceeds the specified
limit, the connecting rod must be replaced.
2. Measure the connecting rod thrust clearance.
Use a feeler gauge to measure the thrust clearance at
the big end of the connecting rod.
If the clearance exceeds the specified limit, the
connecting rod must be replaced.
Standard Limit
0.230 (0.0091) 0.350 (0.0138)mm (in)
Limit
Bend per 100 (3.937)
Twist per 100 (3.937)mm (in)
0.20 (0.0079)
0.15 (0.0059)Standard
0.08 (0.0031) or less
0.05 (0.0020) or less
Page 1589 of 3573
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A Ð 39
3. Measure the oil clearance between the connecting
rod and the crankshaft by:
1) Remove the connecting rod cap nuts and the rod
caps.
Arrange the removed rod caps in the cylinder
number order.
2) Clean the rod bearings and the crankshaft pins.
3) Carefully check the rod bearings.
If even one bearing is found to be damaged or
badly worn, the entire bearing assembly must be
replaced as a set. Reinstall the bearings in their
original positions.
Apply plastigage to the crank pin.
4) Reinstall the rod caps to their original positions.
5) Tighten the cap nuts in 2 steps, using angular
tightening method as shown in the following
specifications.
NOTE:
Do not allow the crankshaft to rotate.
N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
45¡ ~ 60¡ 1st step 2nd step
29 (3.0/22)
6) Remove the rod caps.
7) Measure the width of the plastigage and determine
the oil clearance. If the oil clearance exceeds the
limit, replace the rod bearings as a set.
8) Clean the plastigage from the bearings and the
crankshaft pins.
REASSEMBLY
10. Connecting Rod
9. Piston
8. Piston Pin
·Apply a coat of engine oil to the piston pin and the
piston pin hole.
7. Piston Pin Snap Ring
·Apply a thin coat of engine oil to the piston pin.
Try to insert the piston pin into the piston pin hole
with normal finger pressure.
Weigh each piston and connecting rod assembly.
Select piston and connecting rod combinations so
that the weight variation of the different assemblies
is held within the specified limits.
Variance in weight
after assemblyLess than 3
(0.1058)g (oz)
Standard Limit
0.029 (0.0011) – 0.083 (0.0033) 0.100 (0.0039)
mm (in)
NOTE:
When changing piston/connecting rod combinations, do
not change the piston/piston pin combination.
Page 1590 of 3573
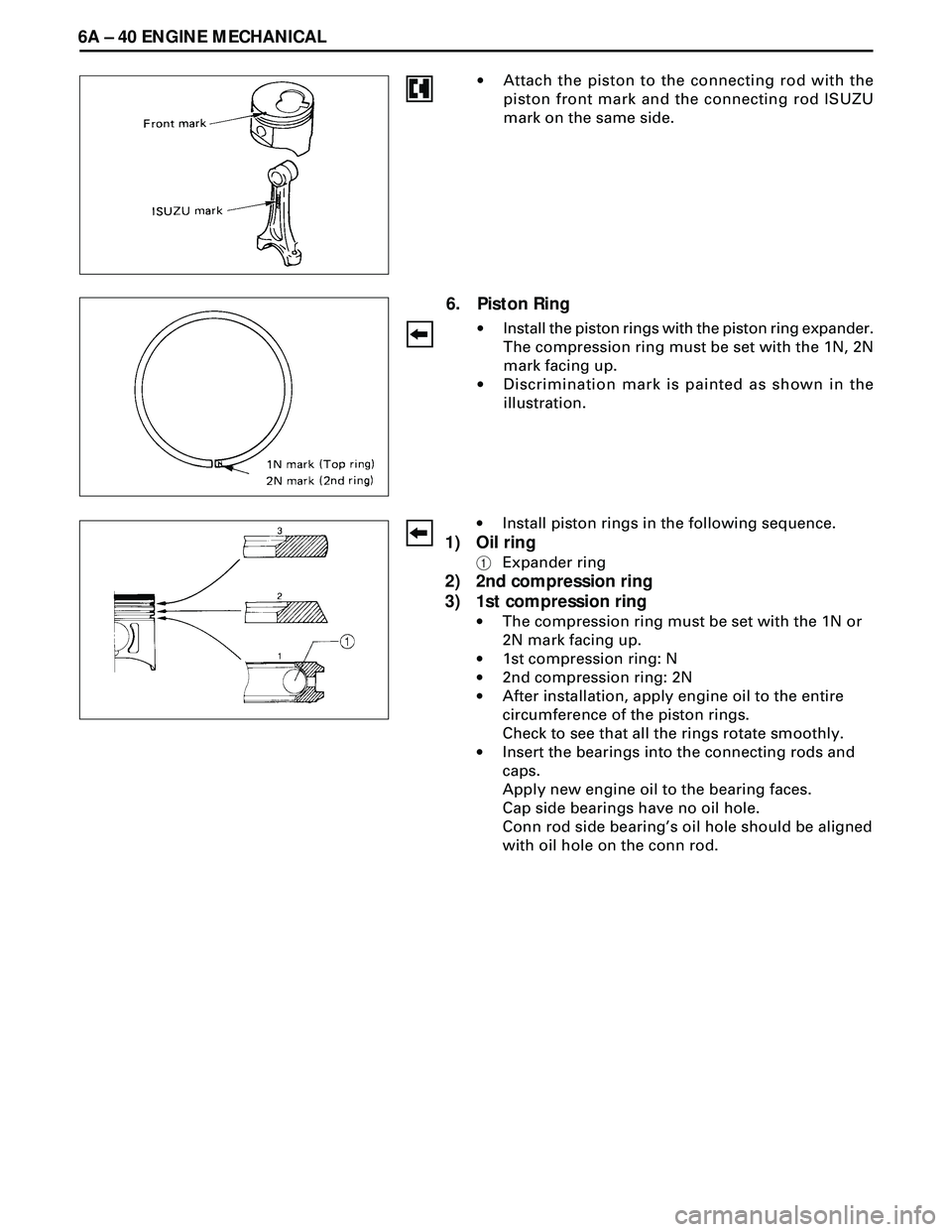
6A Ð 40 ENGINE MECHANICAL
6. Piston Ring
·Install the piston rings with the piston ring expander.
The compression ring must be set with the 1N, 2N
mark facing up.
·Discrimination mark is painted as shown in the
illustration. ·Attach the piston to the connecting rod with the
piston front mark and the connecting rod ISUZU
mark on the same side.
·Install piston rings in the following sequence.
1) Oil ring
1Expander ring
2) 2nd compression ring
3) 1st compression ring
·The compression ring must be set with the 1N or
2N mark facing up.
·1st compression ring: N
·2nd compression ring: 2N
·After installation, apply engine oil to the entire
circumference of the piston rings.
Check to see that all the rings rotate smoothly.
·Insert the bearings into the connecting rods and
caps.
Apply new engine oil to the bearing faces.
Cap side bearings have no oil hole.
Conn rod side bearingÕs oil hole should be aligned
with oil hole on the conn rod.
Page 1591 of 3573
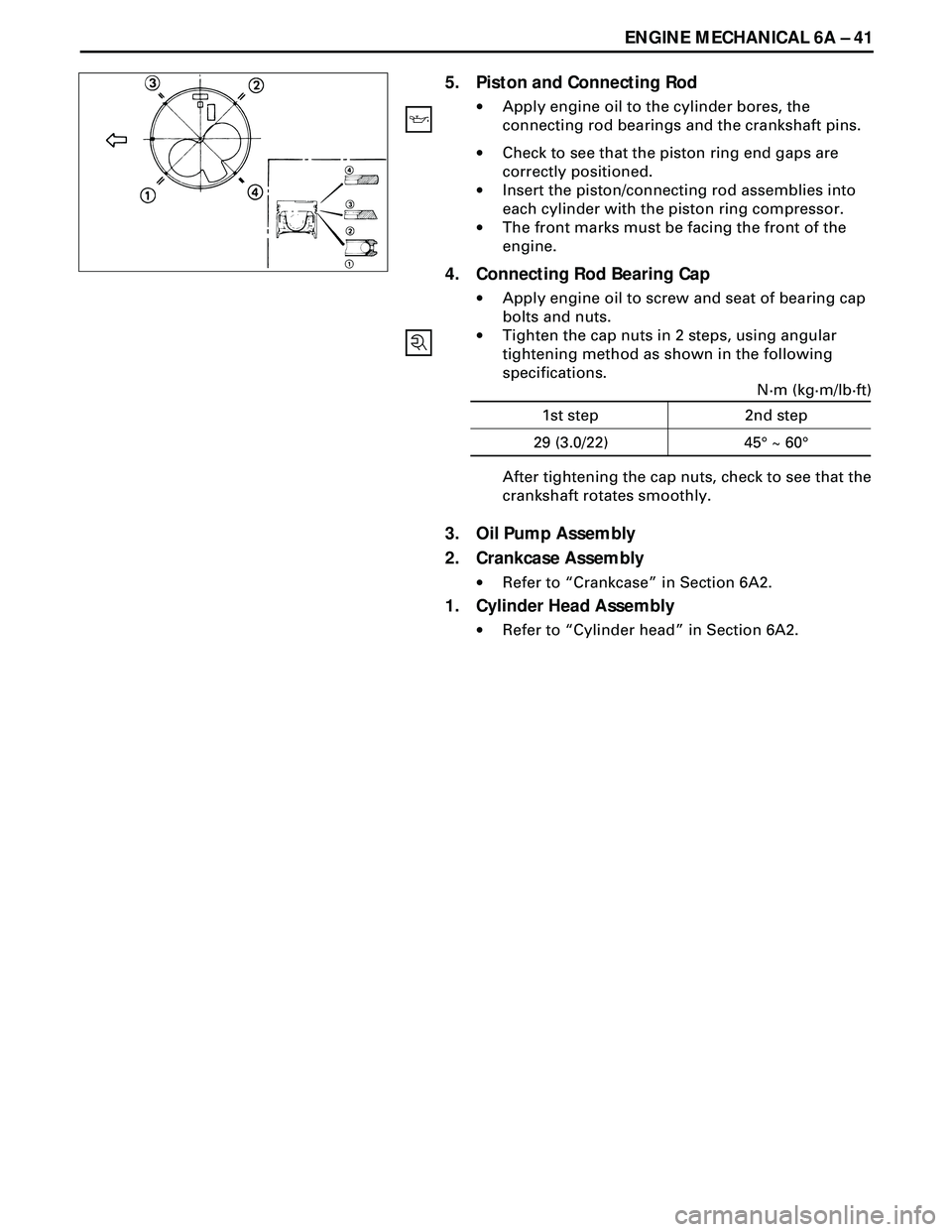
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A Ð 41
5. Piston and Connecting Rod
·Apply engine oil to the cylinder bores, the
connecting rod bearings and the crankshaft pins.
·Check to see that the piston ring end gaps are
correctly positioned.
·Insert the piston/connecting rod assemblies into
each cylinder with the piston ring compressor.
·The front marks must be facing the front of the
engine.
4. Connecting Rod Bearing Cap
·Apply engine oil to screw and seat of bearing cap
bolts and nuts.
·Tighten the cap nuts in 2 steps, using angular
tightening method as shown in the following
specifications.
N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
45¡ ~ 60¡ 1st step 2nd step
29 (3.0/22)
After tightening the cap nuts, check to see that the
crankshaft rotates smoothly.
3. Oil Pump Assembly
2. Crankcase Assembly
·Refer to ÒCrankcaseÓ in Section 6A2.
1. Cylinder Head Assembly
·Refer to ÒCylinder headÓ in Section 6A2.
Page 1592 of 3573
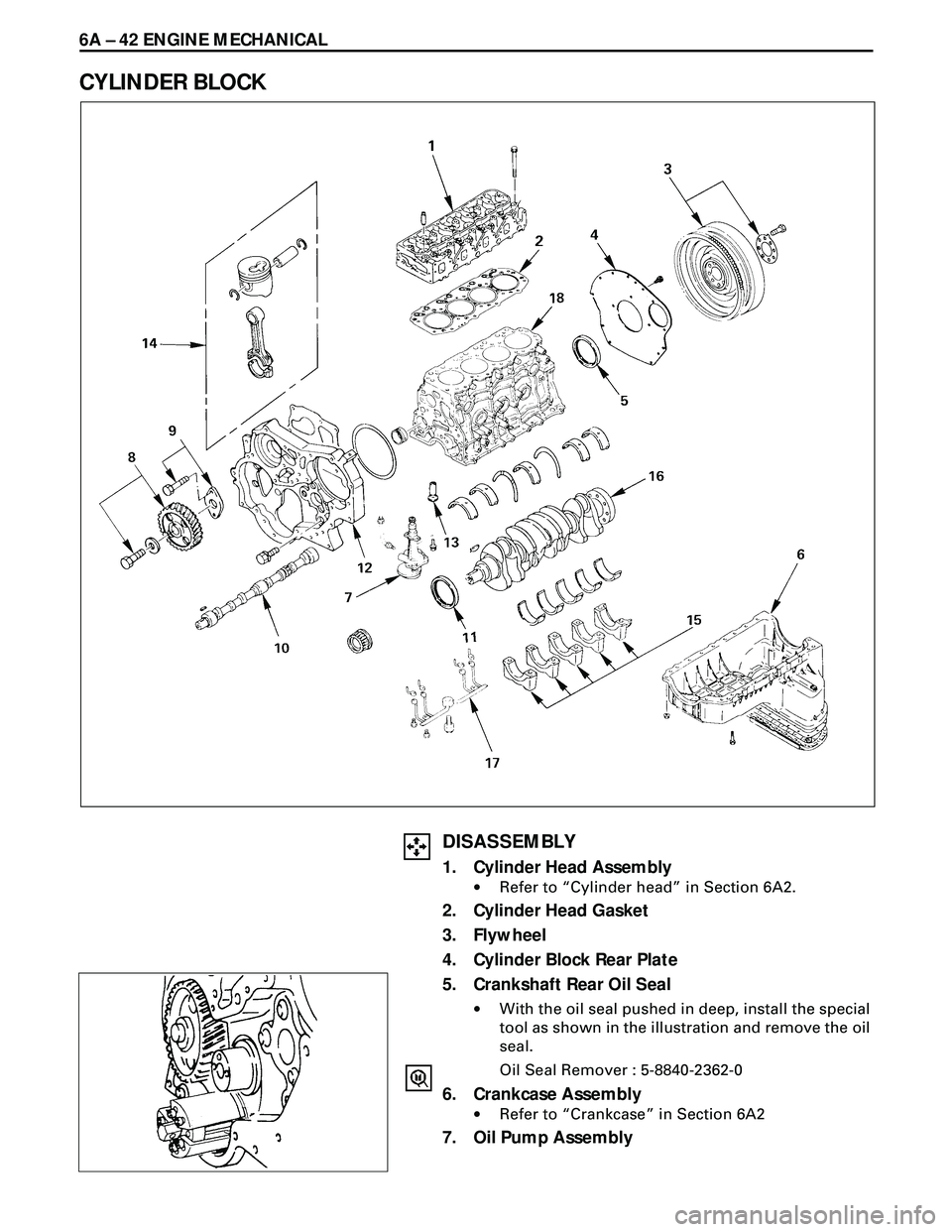
6A Ð 42 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CYLINDER BLOCK
DISASSEMBLY
1. Cylinder Head Assembly
·Refer to ÒCylinder headÓ in Section 6A2.
2. Cylinder Head Gasket
3. Flywheel
4. Cylinder Block Rear Plate
5. Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal
·With the oil seal pushed in deep, install the special
tool as shown in the illustration and remove the oil
seal.
Oil Seal Remover : 5-8840-2362-0
6. Crankcase Assembly
·Refer to ÒCrankcaseÓ in Section 6A2
7. Oil Pump Assembly
Page 1593 of 3573

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A Ð 43
8. Camshaft Timing Gear
9. Camshaft Thrust Plate
10. Camshaft
11. Crankshaft Front Oil Seal
·With the oil seal pushed in deep, install the special
tool as shown in the illustration and remove the oil
seal.
Oil Seal Remover : 5-8840-2362-0
12. Timing Gear Case
13. Tappet
14. Piston Assembly
15. Main Bearing Cap Assembly
16. Crankshaft
17. Piston Cooling Oil Pipe
18. Cylinder Block
Page 1594 of 3573
6A Ð 44 ENGINE MECHANICAL
INSPECTION REPAIR
Make the necessary adjustments, repairs, and part replacements if excessive wear or damage is discovered
during inspection.
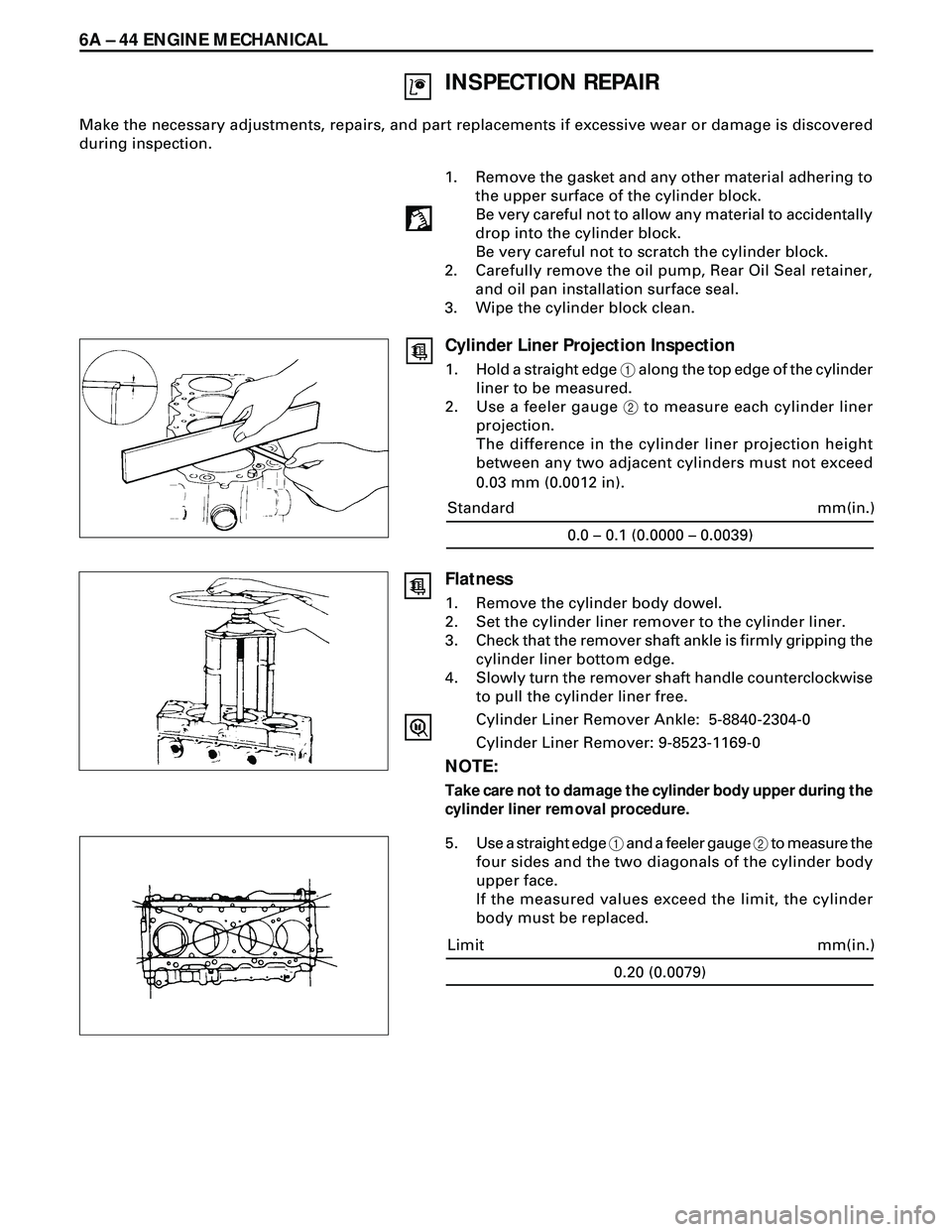
1. Remove the gasket and any other material adhering to
the upper surface of the cylinder block.
Be very careful not to allow any material to accidentally
drop into the cylinder block.
Be very careful not to scratch the cylinder block.
2. Carefully remove the oil pump, Rear Oil Seal retainer,
and oil pan installation surface seal.
3. Wipe the cylinder block clean.
Cylinder Liner Projection Inspection
1. Hold a straight edge 1 along the top edge of the cylinder
liner to be measured.
2. Use a feeler gauge 2 to measure each cylinder liner
projection.
The difference in the cylinder liner projection height
between any two adjacent cylinders must not exceed
0.03 mm (0.0012 in).
0.0 – 0.1 (0.0000 – 0.0039)
mm(in.) Standard
Flatness
1. Remove the cylinder body dowel.
2. Set the cylinder liner remover to the cylinder liner.
3. Check that the remover shaft ankle is firmly gripping the
cylinder liner bottom edge.
4. Slowly turn the remover shaft handle counterclockwise
to pull the cylinder liner free.
Cylinder Liner Remover Ankle: 5-8840-2304-0
Cylinder Liner Remover: 9-8523-1169-0
NOTE:
Take care not to damage the cylinder body upper during the
cylinder liner removal procedure.
5. Use a straight edge 1 and a feeler gauge 2 to measure the
four sides and the two diagonals of the cylinder body
upper face.
If the measured values exceed the limit, the cylinder
body must be replaced.
0.20 (0.0079)
mm(in.) Limit
Page 1595 of 3573
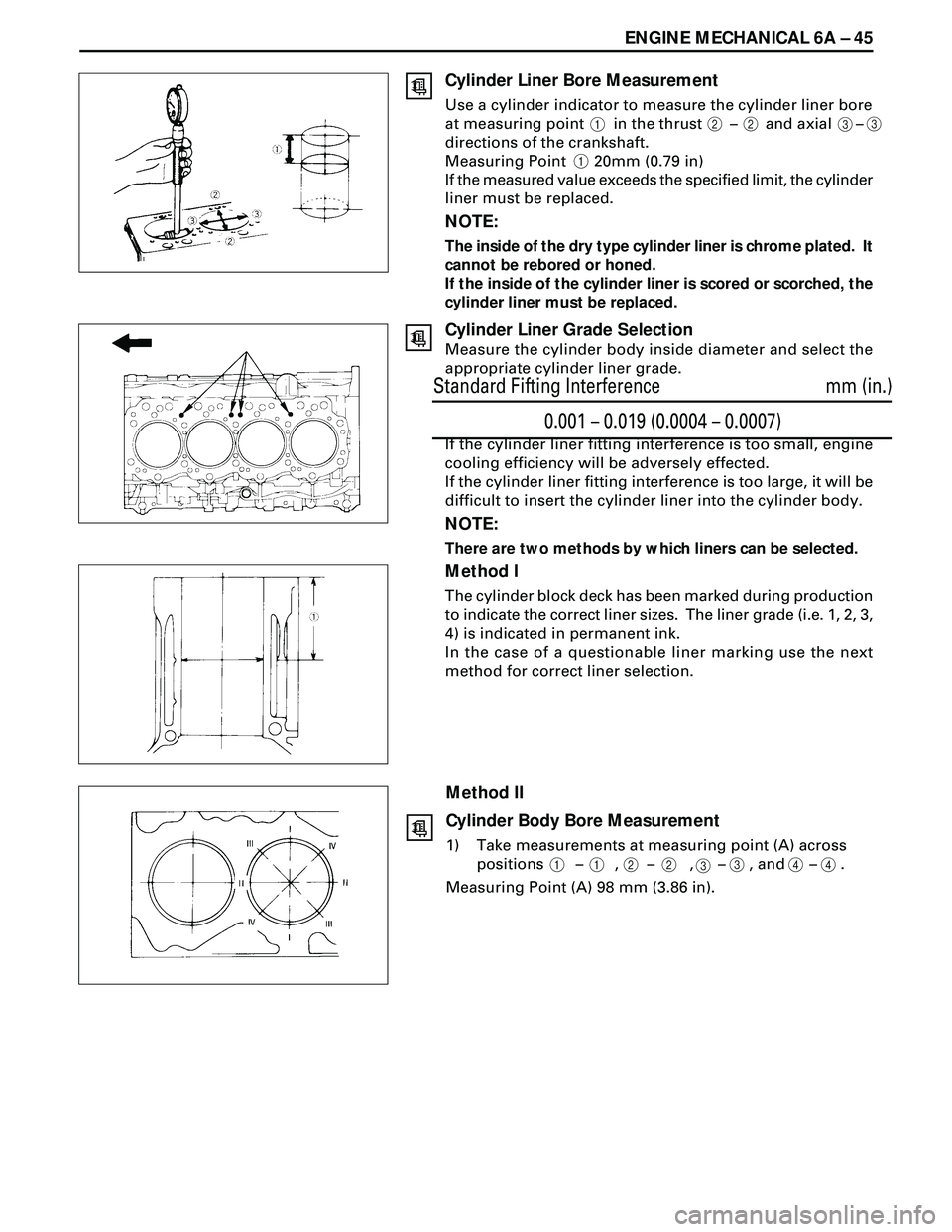
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A Ð 45
Cylinder Liner Bore Measurement
Use a cylinder indicator to measure the cylinder liner bore
at measuring point in the thrust Ð and axial Ð
directions of the crankshaft.
Measuring Point 20mm (0.79 in)
If the measured value exceeds the specified limit, the cylinder
liner must be replaced.
NOTE:
The inside of the dry type cylinder liner is chrome plated. It
cannot be rebored or honed.
If the inside of the cylinder liner is scored or scorched, the
cylinder liner must be replaced.
Cylinder Liner Grade Selection
Measure the cylinder body inside diameter and select the
appropriate cylinder liner grade.
If the cylinder liner fitting interference is too small, engine
cooling efficiency will be adversely effected.
If the cylinder liner fitting interference is too large, it will be
difficult to insert the cylinder liner into the cylinder body.
NOTE:
There are two methods by which liners can be selected.
Method I
The cylinder block deck has been marked during production
to indicate the correct liner sizes. The liner grade (i.e. 1, 2, 3,
4) is indicated in permanent ink.
In the case of a questionable liner marking use the next
method for correct liner selection.
Method II
Cylinder Body Bore Measurement
1) Take measurements at measuring point (A) across
positions Ð , Ð , Ð , and Ð .
Measuring Point (A) 98 mm (3.86 in).
12233
1
112
2334
4
0.001 – 0.019 (0.0004 – 0.0007)
mm (in.) Standard Fifting Interference