ESP JAGUAR X308 1998 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1998, Model line: X308, Model: JAGUAR X308 1998 2.GPages: 2490, PDF Size: 69.81 MB
Page 488 of 2490
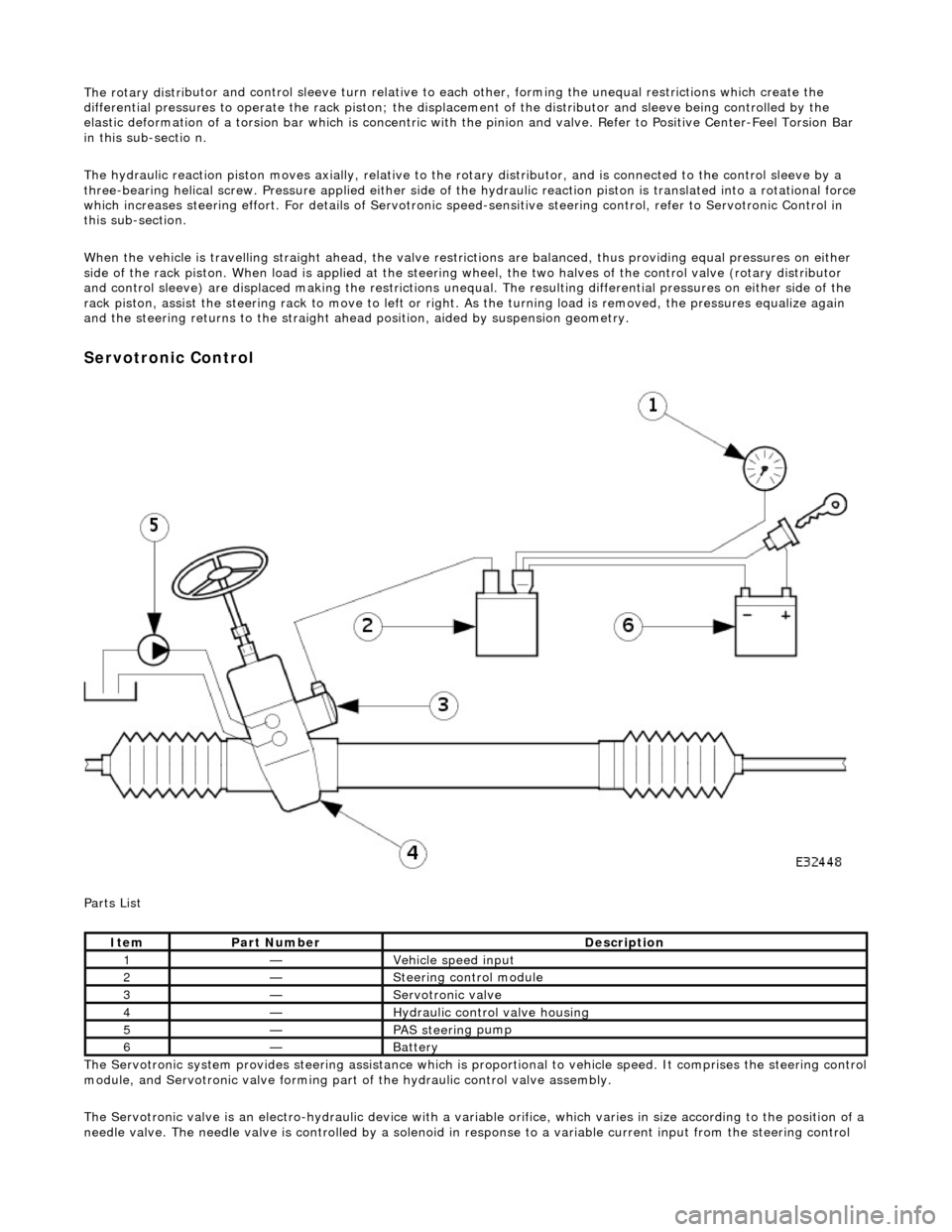
The rotary distri
butor and control sleeve turn relative to ea
ch other, forming the unequal restrictions which create the
differential pressures to operat e the rack piston; the displacement of the di stributor and sleeve being controlled by the
elastic deformation of a torsion bar which is concentric with the pinion and valve. Refer to Positive Center-Feel Torsion Bar
in this sub-sectio n.
The hydraulic reaction piston moves axially, relative to th e rotary distributor, and is connected to the control sleeve by a
three-bearing helical screw. Pressure applied either side of the hydraulic reaction piston is translated into a rotational force
which increases steering effort. For detail s of Servotronic speed-sensitive steering control, refer to Servotronic Control in
this sub-section.
When the vehicle is travelling straight ah ead, the valve restrictions are balanced, thus providing equal pressures on either
side of the rack piston. When load is a pplied at the steering wheel, the two halves of the control valve (rotary distributor
and control sleeve) are displaced making the restrictions unequa l. The resulting differential pressures on either side of the
rack piston, assist the steering rack to mo ve to left or right. As the turning load is removed, the pressures equalize again
and the steering return s to the straight ahead position , aided by suspension geometry.
Serv
otronic Control
P a
rts List
The Servotronic system provides steering assistance which is pr oportional to vehicle speed. It comprises the steering control
module, and Servotronic valve forming part of the hydraulic control valve assembly.
The Servotronic valve is an electro-hydrauli c device with a variable orifice, which varies in size according to the position of a
needle valve. The needle valve is controlled by a solenoid in response to a variable current input from the steering control
Ite
m
Part
Number
Descr
iption
1—Vehi
cl
e speed input
2—Steeri
ng control
module
3—Servotronic valve
4—Hydraulic
control valve housing
5—PAS stee
rin
g pump
6—Batt
ery
Page 489 of 2490
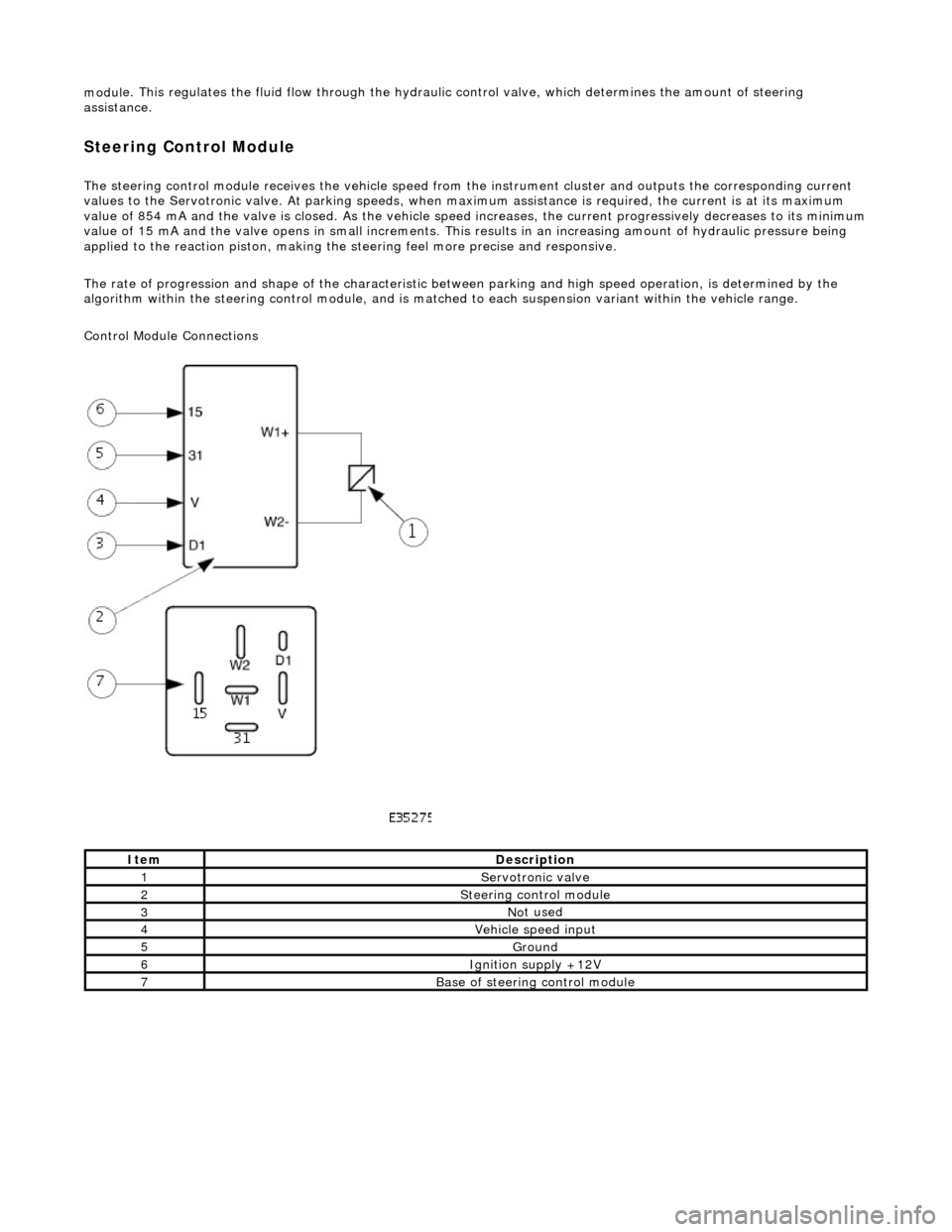
modul
e. This regulates the fluid flow
through the hydraulic control valve, wh ich determines the amount of steering
assistance.
Steering Control Module
The steering control
module re
ceives the vehicle speed from the instrument cluster and outputs the corresponding current
values to the Servot ronic valve. At parking speeds, wh en maximum assistance is required , the current is at its maximum
value of 854 mA and the valve is closed. As the vehicle speed increases, the current progressively decreases to its minimum
value of 15 mA and the valve opens in sma ll increments. This results in an increasing amount of hydraulic pressure being
applied to the reaction piston, making the steering feel more precise and responsive.
The rate of progression and shape of the characteristic between parking and high speed operation, is determined by the
algorithm within the steering control module, and is matched to each suspension variant within the vehicle range.
Control Module Connections
It
em
De
scription
1Servotronic valve
2Steeri
ng control module
3No
t used
4Vehi
cle speed input
5Ground
6Ignition su
pply +12V
7Base of
steering control module
Page 505 of 2490
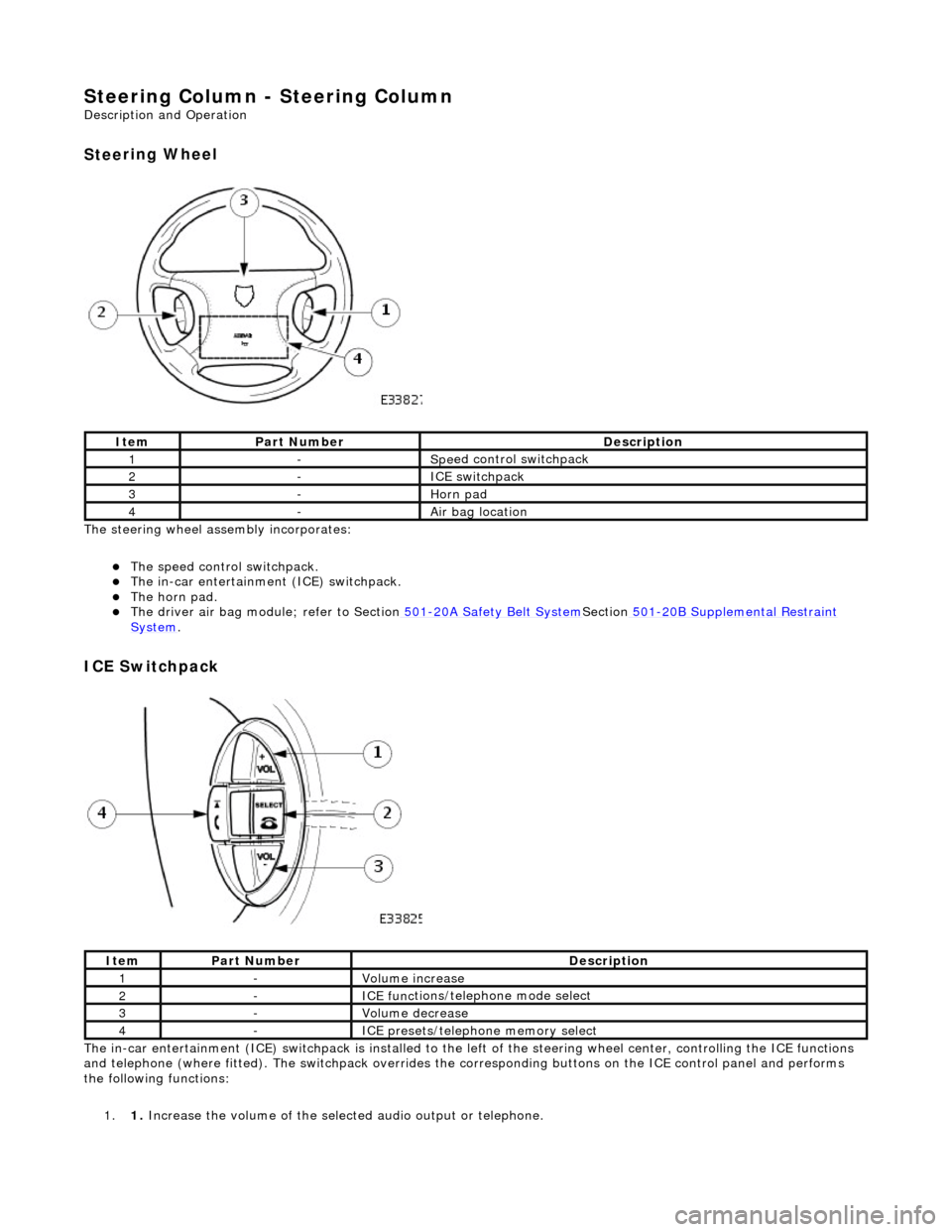
Steering Column - Steering Column
Description an
d Operation
Stee
ring Wheel
T
he steering wheel assembly incorporates:
The s
peed control switchpack.
The i
n-car entertainment (ICE) switchpack.
The h
orn pad.
The driver ai
r bag module; refer to Section
501
-20A Safety Belt
System
Sectio
n
501
-2
0B Supplemental Restraint
Sy
stem
.
I
CE Switchpack
The
in-car entertainment (ICE) switchpack is installed to the le
ft of the steering wheel center, controlling the ICE functions
and telephone (where fitted). The switchpack overrides the corresponding bu ttons on the ICE control panel and performs
the following functions:
1. 1. Increase the volume of the select ed audio output or telephone.
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1-Spe
ed control switchpack
2-I
CE switchpack
3-Horn pad
4-Air bag lo
cation
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1-Vol
ume increase
2-ICE func
tions/teleph
one mode select
3-Volum
e decrease
4-ICE pres
ets/telephone memory select
Page 516 of 2490

IGNITION.
All circuits, except the star
ter motor, are activated. The key rema ins in this position when driving.
Position 'III'
START. The starter operates for as long as the key is held in this position, ag ainst spring pressure. If the engine fails to
start, the key must be returned to position 'I' befo re another start is attempted.
Lighting Switch
The li
ghting switch is on the left-h
and side of the steering column and controls the following functions.
Direction Indicators
The direction in
dicators:
Operate
when the ignition switch is in position II.
Are operat
ed by movi
ng the switch stalk up or down until it latches in position, to in
dicate a right or left turn
respectively.
Can be o p
erated while the switch stalk is held against
spring pressure before reaching the latch position.
Cancel
automatically upon completion of a turn, the
column switch returning to the center position.
An audible ticking and a flashing green warning lamp on the in strument cluster indicate that the direction indicators are
Ite
m
De
scr
iption
1D
i
rection indicator LH or RH position
2All lamps OFF
3Side
lamps ON
4Headlamps ON
5Headlamps AUT O
(where fitted)
6He
adlam
p main beam position
7Mai
n
beam flash position
8M
e
ssage center function button
Page 527 of 2490

E
ngine Management System Components
Electronic Throt
tle
The
electronic throttle assembly, in resp
onse to signals from both the driver and the ECM, adjusts idle speed, sets the
throttle valve to the position requested by the driver's accelerator / throttle pedal, cruise and traction control, power
limitation and catalyst warm-up.
Mass
Air Flow Meter
The sensor i
s located in the air flow mete
r assembly and outputs an analogue voltag e to the ECM. This sensor measures air
flow into the engine inlet system and is calibrated to measure kg / hour.
In
take Air Temperature
Th
e intake air temperature sensor is loca
ted in the air flow meter assembly and outputs an analogue voltage to the ECM.
The ECM will substitute a default value eq ual to 50°C should this sensor fail.
Fuel Injectors
The eigh
t bottom fed fuel injectors are located in the fuel rails. Th
e fuel injectors are electromagnetic solenoid valves
controlled by the ECM. The pulse time for the injector combined with the fuel pr essure determines the volume of fuel
injected to the manifold.
Fue
l Delivery
The fu
el pump provides fuel to the fuel rail where the circulat
ing pressure is controlled by a pressure regulator valve; excess
fuel is returned to the fuel tank.
The pressure regulator valve is controlled by manifold depression so that fuel delivery pressure is maintained at
approximately 3 bar above manifold pressure.
Fuel Pump
Relay
The ECM controls thi
s component for normal
engine running. The security system may disable this relay via communication
with the ECM.
Fuel Lev
el Sensing
The tank fuel
is measured by the fuel le
vel sensor . This signal is used by the ECM as an in put to certain diagnostics.
Eva
porative Valve
Excess vapour
formed in the fuel tank is
absorbed into the evaporative emission pu rge control canister. While the engine is
running, the fuel absorbed in the canister is gradually purged back into the engine. The rate of purging is governed by
engine operating conditions and vapour concentration level. Operating conditions which affect the purge rate are:
2—Purge
valve
3—Engine
torque reduction
4—E
lectronic throttle assembly
5—Coo
ling fans
6—Ignition amplifier driver
7—Engine overspeed
8—Cli
mate control compressor clutch
9—O
BDII information (J1962, CAN, ISO)
10—F
uel pump relay
11—Heat
ed oxygen sensor
12—Vari
able valve timing
13—MIL sw
itching
ECM Out
puts
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Exhaus
t gas recirculation
Page 528 of 2490

Speed an
d load
Coo
l
ant temperature
Ti
me el
apsed from start up
Cl
osed l
oop fuelling
Determination of the vapour concentration is made by stepped opening of the EVAP valve and subsequent monitoring of the
fuelling correction. This function is performed prior to purging, so that at the onse t of purging the EVAP valve can be set to
the optimum position. Should the ECM be unable to determine the concentration before purging, a default value is
employed, which is then modified whilst purging is in progress.
When the purging process is operational th e ECM modifies the basic fuelling calculation to maintain the correct air / fuel
ratio.
Purging is inhibited during fuel cut-off and stability / traction control intervention.
Coolant Temperature Sen
sor
Th
e
sensor outputs a voltage to the ECM which decreases as temperature increases.
Cooling Fans
In response to engi
ne coolant temperat
u
re and climate control system demand, the ECM will energize the cooling fans.
Climate Control Compressor
The E
C
M will allow the compressor clutch to be engaged if th
e engine temperature and load demand are normal. Should the
driver require maximum engine powe r or the coolant temperature be high, the request will be denied.
Cranking Signal
The ECM reacts to a signal fr
om th
e Body Processor Module (BPM) when the starter motor relay is energi
zed. This signal is
used to trigger starting, fu el and ignition strategies.
Engine Speed and Cranksh
aft Position
Engine
speed and cran
k position are moni
tored by a sensor which is mounted on the cylinder block (flywheel housing)
behind the crankshaft drive plat e. It indicates rotational speed to the ECM in the form of 12 pulses per crank revolution.
Engine speed is used for synchronization of fuel an d ignition systems, as well as other functions.
Camshaft Position
The ca
mshaft position sensor is mounted at
the rear of Bank 2 cylinder head on the inlet side and provides one signal every
720 degrees of crankshaft rotation. The signal, in conjunction with the signal from the crankshaft position sensor, indicates
to the ECM that the piston of cylinder 1A is approaching TDC on the compression stroke.
Variable Valve
Timing (Where Fitted)
By energi
si
ng a solenoid to allow the pass
age of pressurized oil on each of the inle t camshaft drives, the ECM can vary by a
single stepped amount, the relati ve timing of the inlet valves.
Ign
ition
Ignit
i
on spark is produced by
individual on-plug coil units.
There are two ignition amplifiers; module #1 drives coils 1A, 2B, 3B and 4A, whilst module #2 drives coils 1B, 2A, 3A and
4B. The ECM controls the amplifiers.
Page 550 of 2490
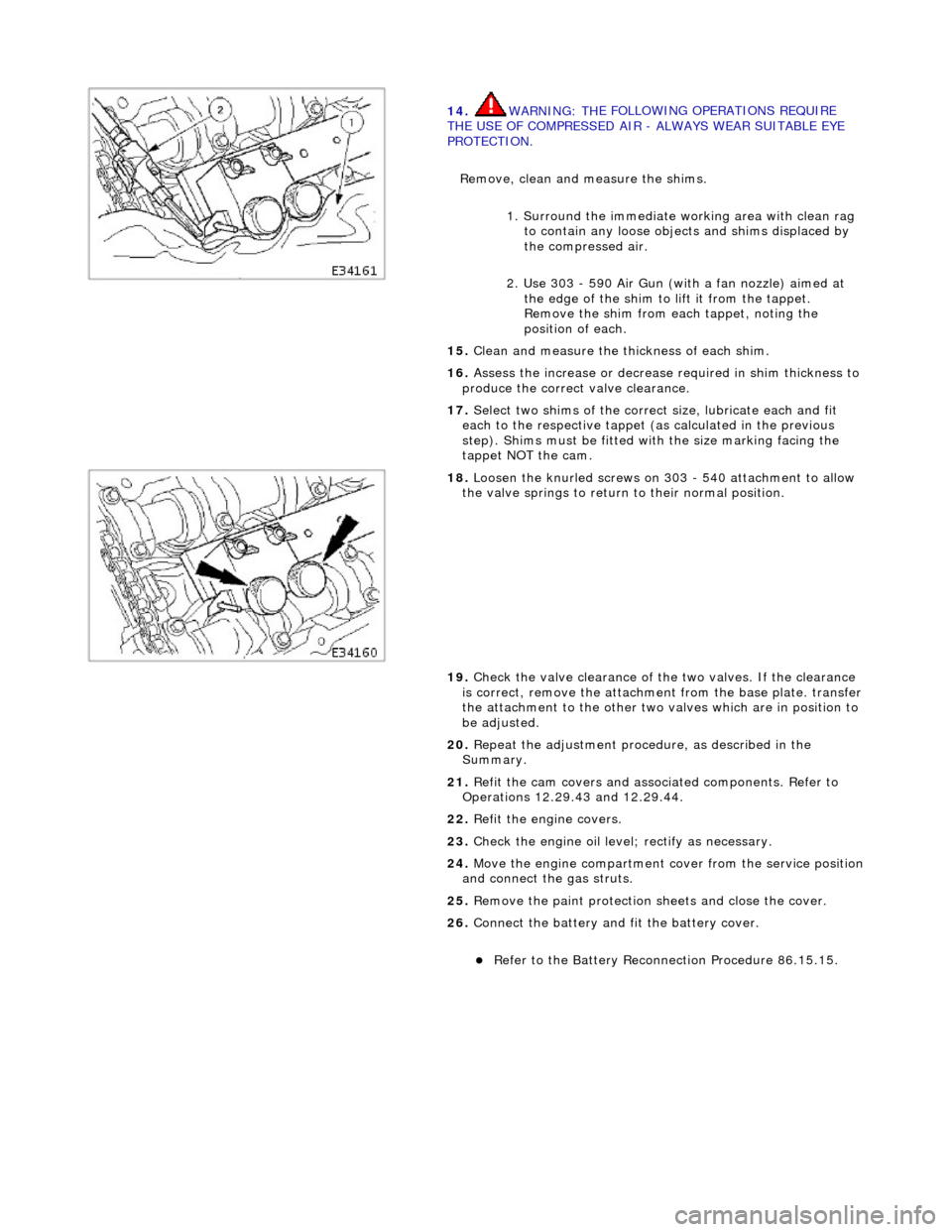
14
. WARNING: TH
E FOLLOWING OPERATIONS REQUIRE
THE USE OF COMPRESSED AIR - ALWAYS WEAR SUITABLE EYE
PROTECTION.
Remove, clean and measure the shims.
1. Surround the immediate wo rking area with clean rag
to contain any loose objects and shims displaced by
the compressed air.
2. Use 303 - 590 Air Gun (with a fan nozzle) aimed at the edge of the shim to lift it from the tappet.
Remove the shim from each tappet, noting the
position of each.
15 . Cl
ean and measure the thickness of each shim.
16. Assess the increase or decrease required in shim thickness to
produce the correct valve clearance.
17. Select two shims of the correct size, lubricate each and fit
each to the respective tappet (as calculated in the previous
step). Shims must be fitted with the size marking facing the
tappet NOT the cam.
18 . Loos
en the knurled screws on 303 - 540 attachment to allow
the valve springs to return to their normal position.
19. Check the valve clearance of the two valves. If the clearance
is correct, remove the attachment from the base plate. transfer
the attachment to the other two valves which are in position to
be adjusted.
20. Repeat the adjustment procedure, as described in the
Summary.
21. Refit the cam covers and associated components. Refer to
Operations 12.29.43 and 12.29.44.
22. Refit the engine covers.
23. Check the engine oil level; rectify as necessary.
24. Move the engine compartment cover from the service position
and connect the gas struts.
25. Remove the paint protection sheets and close the cover.
26. Connect the battery and fit the battery cover.
Refe
r to the Battery Reconnection Procedure 86.15.15.
Page 571 of 2490

I
nstallation
32
.
Clean and inspect all relevant components.
1. F
it the sprockets to the crankshaft.
Th
e teeth of the A-Bank and the B-Bank sprockets on the
crankshaft must be out of phas e with each other. If they
are in-phase after fitting, remove the A-Bank sprocket,
turn it on its vertical axis and refit it.
2. F
it the chain tensioning tool 303 - 532 to the exhaust camshaft
sprocket, B-Bank.
Re
position the sprocket (and
the VVT unit) for the most
advantageous position for use of the tool.
R
emove the tool.
3. R
efit the primary timing chain, B-Bank.
1. Fit the primary chain over the crankshaft sprocket and the VVT unit sprocket. There must be no slack on
the drive side of the primary chain and the VVT unit
must not be rotate d on the camshaft.
Sl
ide the VVT and exhaust sprocket fully rearwards onto
the respective camshafts.
4. Fit the primary chain tensioner blade.
1. Position the tensioner blade to the cylinder block.
Page 581 of 2490
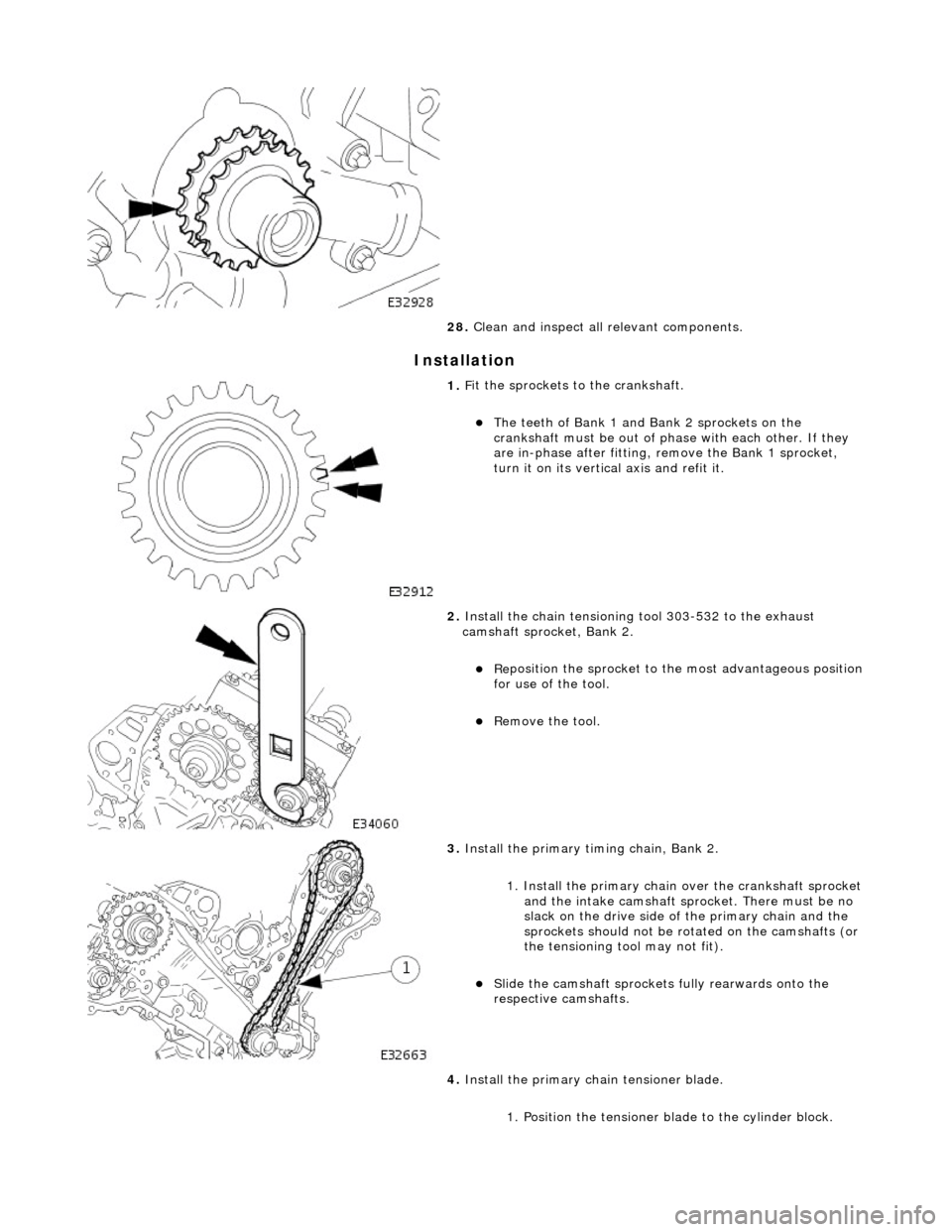
I
nstallation
28
.
Clean and inspect all relevant components.
1. F
it the sprockets to the crankshaft.
The teeth
of Bank 1 and Bank 2 sprockets on the
crankshaft must be out of phas e with each other. If they
are in-phase after fitting, remove the Bank 1 sprocket,
turn it on its vertical axis and refit it.
2. Inst
all the chain tensioning
tool 303-532 to the exhaust
camshaft sprocket, Bank 2.
Re
position the sprocket to the most advantageous position
for use of the tool.
R
emove the tool.
3. Install th
e primary timi
ng chain, Bank 2.
1. Install the primary chain over the crankshaft sprocket and the intake camshaft sp rocket. There must be no
slack on the drive side of the primary chain and the
sprockets should not be rotated on the camshafts (or
the tensioning tool may not fit).
Sli
de the camshaft sprocket
s fully rearwards onto the
respective camshafts.
4. Install the primary ch ain tensioner blade.
1. Position the tensioner blade to the cylinder block.
Page 622 of 2490

2. In
stall the camshaft caps to their respective locations (inlet 0 to 4
and exhaust 5 to 9 from the front) and in the correct orientation
(arrow to front of engine).
3. Install and tighten the cap securing bolts. Tighten evenly, in stages, to 10 Nm.
19. Install the camshaft locking tool 303 - 530, align the camshafts as
necessary.
20 . Install the chain guide
.
The
c
hain guide must be installed so that the slotted hole is towards
the top, and the rais ed shoulder to the cylinder block.
1. Install the chain guide to the block and locate it onto the upper retaining pin.
2. Install the retaining bolt and tighten it to 12 Nm.
21. P
ush the secondary chain tensioner piston into the body to provide
clearance for installing the chain.
1. Insert a thin rigid wire through the hole in the end of the tensioner
piston to displace the ball from the non-return valve seat.
2. With the wire in position, press the piston fully into the tensioner body.
Rem
ove the wire.
22 . Ins
tall the secondary chain tensioner to the engine.
1. Fully seat the tensioner to the cylinder head.
2. Install the two bolts which secure the tensioner and tighten to 12 Nm.
23 . N
OTE: Assemble the VVT unit, the exhaust camshaft sprocket and the
secondary chain, in preparation for installing to the engine.
Install the VVT unit to the engine.
1. Install the above assembly to the camshafts with the chain correctly positioned over the tensioner; VVT unit to the inlet and
the sprocket to the exhaust.
2. Install, but do not tighten, each bolt which secures the VVT unit and the exhaust sprocket to the camshafts.
24. Install the chain tensioning tool 303 - 532 to the exhaust camshaft
sprocket.