Throttle JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 696 of 3039
a decrease in engine torque. At the same time the ABS module will control the HCU to apply brake pressure to the relevant wheels to correct the understeer.
Electronic Brake Prefill (Vehicles With ACC Only)
Electronic brake prefill (Bosch ESP®plus8.1), senses any rapid throttle lift off, activating a small brake hydraulic pressure
build-up of approximately 3 to 5 bar (43.5 to 72.5 lbf/in²) in anticipation of the brakes being applied.
This application produces a quicker brake pedal response and consequently slightly shorter stopping distances. The system
supports vehicles with ACC (adaptive cruise control).
When the ABS module detects rapid throttle lift off (from the signals received from the ECM over the high speed CAN bus), it controls the HCU to apply a low brake pressure to assist in a quicker brake application.
Brake Vacuum Assist (3.0L Vehicles Only)
Operation of Brake Vacuum Assist generally occurs at the beginning of an ignition cycle when brake booster vacuum levels are
low; refer to Brake Booster Vacuum sensor, below.
Brake vacuum assist operation will be recognized by the driver experiencing a vibrating brake pedal and slight modulator noise.
This will be similar to that experienced when ABS system is operating.
As the engine warms up, Brake Vacuum Assist operation will become less frequent. However, it can be become more active
when vacuum levels are low due to driving at high-altitudes, or during frequent heavy-braking.
Noise levels during Brake Vacuum Assist may vary with initial system activity being the loudest observed. In some
circumstances initial activity may be interpreted as a 'thump' noise, particularly if there is no immediate and significant Brake
Vacuum Assist functionality.
In this circumstance system behavior is normal and should not be a cause for fault investigation.
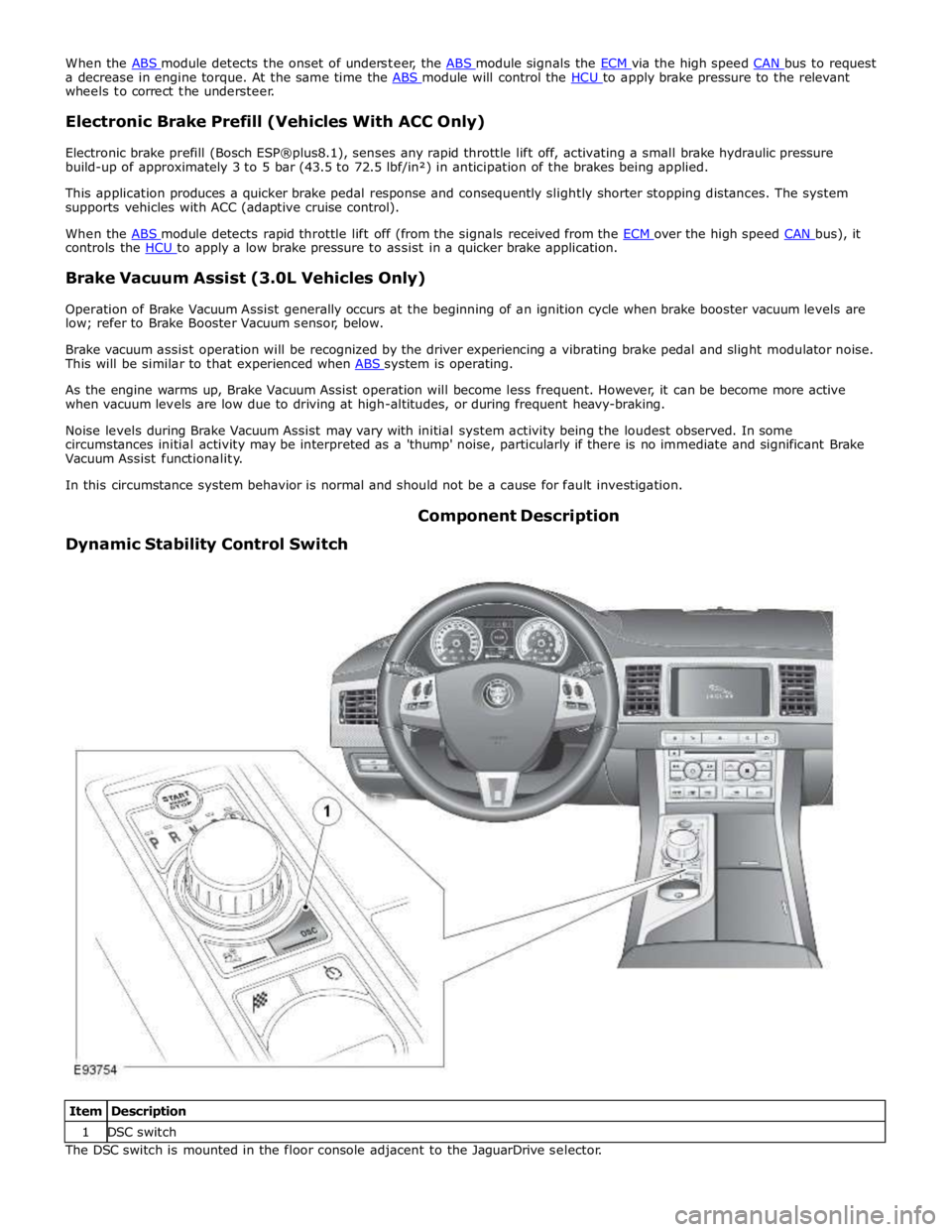
Dynamic Stability Control Switch Component Description
Item Description 1 DSC switch The DSC switch is mounted in the floor console adjacent to the JaguarDrive selector.
Page 816 of 3039

9. WEAK VALVE SPRINGS: When the needle oscillation becomes more violent as engine RPM is increased, weak valve
springs are indicated. The reading at idle could be relatively steady.
10. LATE VALVE TIMING: A steady but low reading could be caused by late valve timing.
11.
IGNITION TIMING RETARDED: Retarded ignition timing will produce a steady but somewhat low reading.
12.
INSUFFICIENT SPARK PLUG GAP: When spark plugs are gapped too close, a regular, small pulsation of the needle can
occur.
13. INTAKE LEAK: A low, steady reading can be caused by an intake manifold or throttle body gasket leak.
14.
BLOWN HEAD GASKET: A regular drop of fair magnitude can be caused by a blown head gasket or warped cylinder head
to cylinder block surface.
15.
RESTRICTED EXHAUST SYSTEM: When the engine is first started and is idled, the reading may be normal, but as the
engine RPM is increased, the back pressure caused by a clogged muffler, kinked tail pipe or other concerns will cause
the needle to slowly drop to 0 kPa (0 in-Hg). The needle then may slowly rise. Excessive exhaust clogging will cause
the needle to drop to a low point even if the engine is only idling.
When vacuum leaks are indicated, search out and correct the cause. Excess air leaking into the system will upset the fuel
mixture and cause concerns such as rough idle, missing on acceleration or burned valves. If the leak exists in an accessory
such as the power brake booster, the unit will not function correctly. Always repair vacuum leaks.
Engine Oil Pressure Check
NOTE: Prior to checking the engine oil pressure, a road test of 6 miles (10 kilometres), must be carried out. Do not
attempt to attain engine normal operating temperature by allowing the engine to idle.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable. Refer to section 414-00 - Charging System - General Information of the workshop
manual
2. WARNINGS:
The spilling of hot engine oil is unavoidable during this procedure, care must be taken to prevent scalding.
Wear protective gloves.
Remove the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
3. Install the oil filter element into special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451)
4. Install the special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451) to the engine. Torque: 25 Nm
5. Install the special tool (Oil pressure testing gauge, 303-871) and tighten the union
6. Connect the battery ground cable
7. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
8. Start and run the engine
9. Note the oil pressure readings with the engine running at idle and 3500 RPM
10.
Turn off the engine
11.
Disconnect the battery ground cable
12. Remove the special tools
1. Clean the components
13.
Install the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
14.
Connect the battery ground cable
15. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1109 of 3039

1 Engine vent hose 2 Throttle 3 Coolant expansion tank 4 Bleed point 5 Throttle body heater hose 6 Engine oil cooler 7 Engine block heater (110 V version shown) or drain plug 8 Coolant supply/expansion hose 9 Outlet tube 10 Radiator upper hose 11 Supercharger cooling system connecting hose 12 Auxiliary radiator supply hose 13 Auxiliary radiator return hose 14 Auxiliary radiator 15 Transmission fluid cooler supply and return hoses 16 Transmission fluid cooler 17 Heater core supply and return hoses 18 Heater manifold 19 Radiator lower hose 20 Cooling fan 21 Thermostat 22 Coolant pump 23 Radiator
Page 1111 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Engine Cooling - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Cooling - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
The engine cooling system maintains the engine within an optimum temperature range under changing ambient and engine
operating conditions. The system is a pressurized expansion tank system with continuous bleeds to separate air from the
coolant and prevent the formation of air locks. The engine cooling system also provides:
Heating for:
- The passenger compartment. For additional information, refer to 412-01 Climate Control.
- The throttle body.
Cooling for:
- The engine oil cooler. For additional information, refer to 303-01F Engine - 5.0L, Vehicles With: Supercharger or
303-01E Engine - 5.0L, Vehicles Without: Supercharger.
- The transmission fluid cooler. For additional information, refer to 307-02B Transmission/Transaxle Cooling -
5.0L/3.0L Diesel.
The primary components of the engine cooling system are the:
Coolant pump.
Thermostat.
Radiator.
Auxiliary radiator (SC (supercharger) vehicles only).
Cooling fan.
Expansion tank.
Engine oil cooler.
Outlet tube and heater manifold.
Connecting hoses and pipes.
Page 1113 of 3039
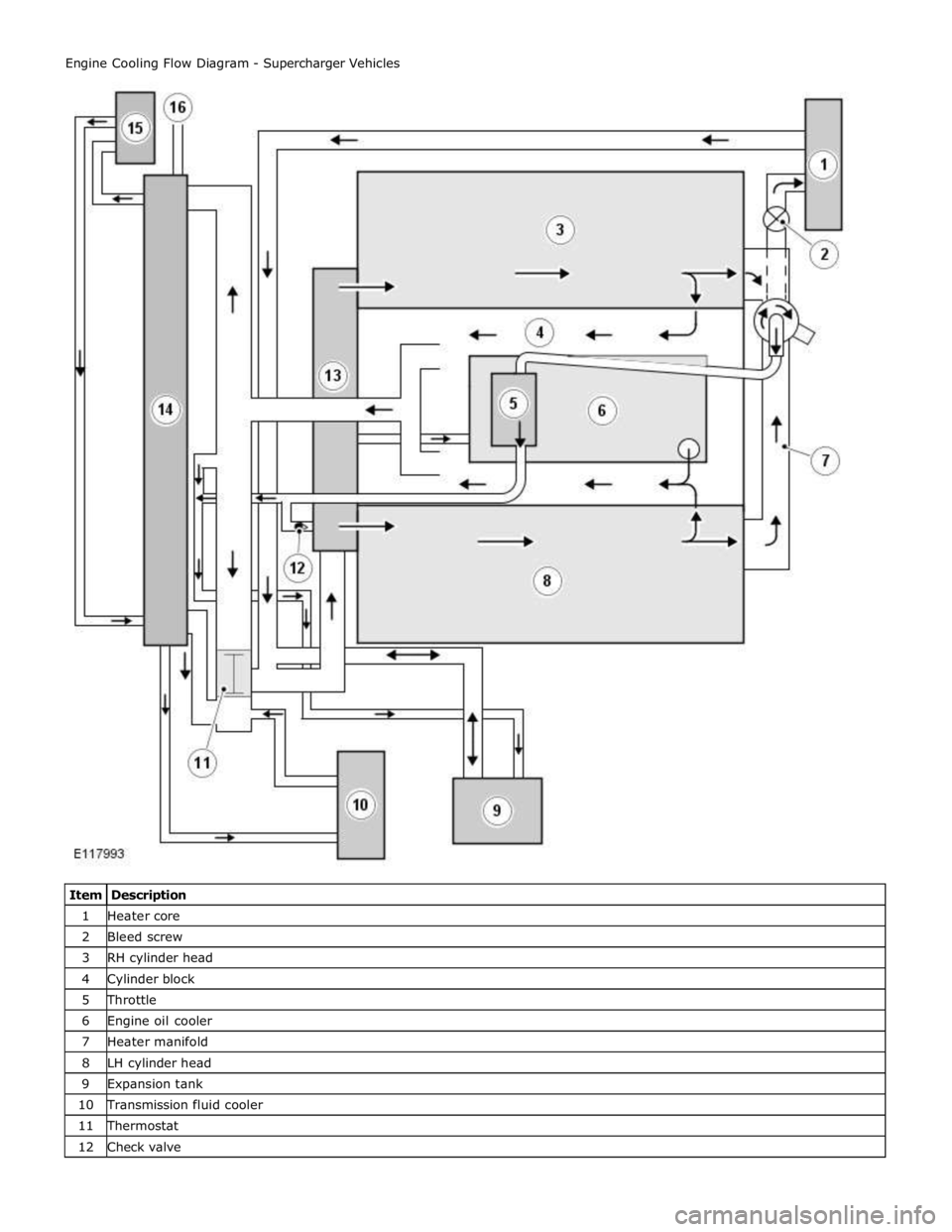
1 Heater core 2 Bleed screw 3 RH cylinder head 4 Cylinder block 5 Throttle 6 Engine oil cooler 7 Heater manifold 8 LH cylinder head 9 Expansion tank 10 Transmission fluid cooler 11 Thermostat 12 Check valve
Page 1114 of 3039
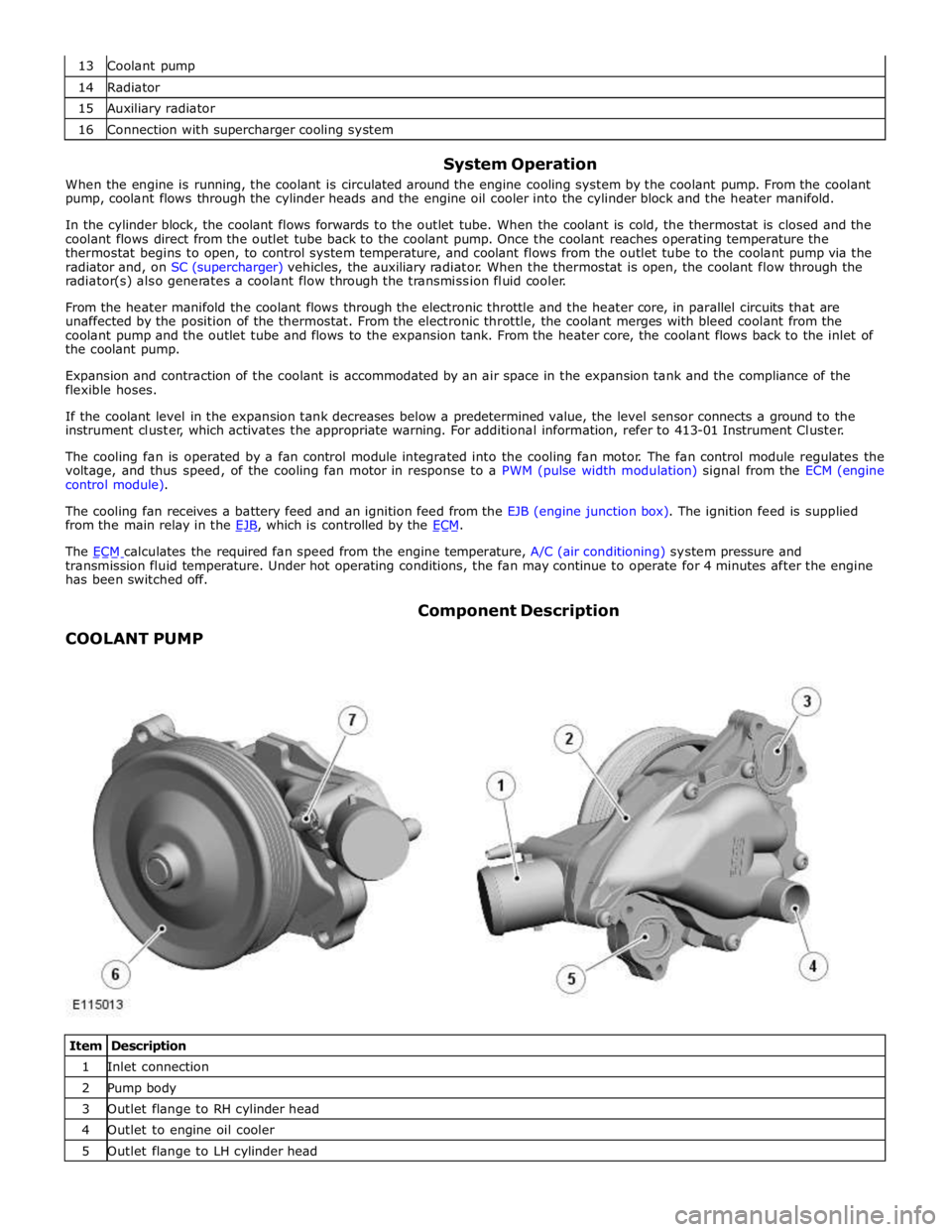
14 Radiator 15 Auxiliary radiator 16 Connection with supercharger cooling system
System Operation
When the engine is running, the coolant is circulated around the engine cooling system by the coolant pump. From the coolant
pump, coolant flows through the cylinder heads and the engine oil cooler into the cylinder block and the heater manifold.
In the cylinder block, the coolant flows forwards to the outlet tube. When the coolant is cold, the thermostat is closed and the
coolant flows direct from the outlet tube back to the coolant pump. Once the coolant reaches operating temperature the
thermostat begins to open, to control system temperature, and coolant flows from the outlet tube to the coolant pump via the
radiator and, on SC (supercharger) vehicles, the auxiliary radiator. When the thermostat is open, the coolant flow through the
radiator(s) also generates a coolant flow through the transmission fluid cooler.
From the heater manifold the coolant flows through the electronic throttle and the heater core, in parallel circuits that are
unaffected by the position of the thermostat. From the electronic throttle, the coolant merges with bleed coolant from the
coolant pump and the outlet tube and flows to the expansion tank. From the heater core, the coolant flows back to the inlet of
the coolant pump.
Expansion and contraction of the coolant is accommodated by an air space in the expansion tank and the compliance of the
flexible hoses.
If the coolant level in the expansion tank decreases below a predetermined value, the level sensor connects a ground to the
instrument cluster, which activates the appropriate warning. For additional information, refer to 413-01 Instrument Cluster.
The cooling fan is operated by a fan control module integrated into the cooling fan motor. The fan control module regulates the
voltage, and thus speed, of the cooling fan motor in response to a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal from the ECM (engine
control module).
The cooling fan receives a battery feed and an ignition feed from the EJB (engine junction box). The ignition feed is supplied
from the main relay in the EJB, which is controlled by the ECM.
The ECM calculates the required fan speed from the engine temperature, A/C (air conditioning) system pressure and transmission fluid temperature. Under hot operating conditions, the fan may continue to operate for 4 minutes after the engine
has been switched off.
COOLANT PUMP Component Description
Item Description 1 Inlet connection 2 Pump body 3 Outlet flange to RH cylinder head 4 Outlet to engine oil cooler 5 Outlet flange to LH cylinder head
Page 1121 of 3039
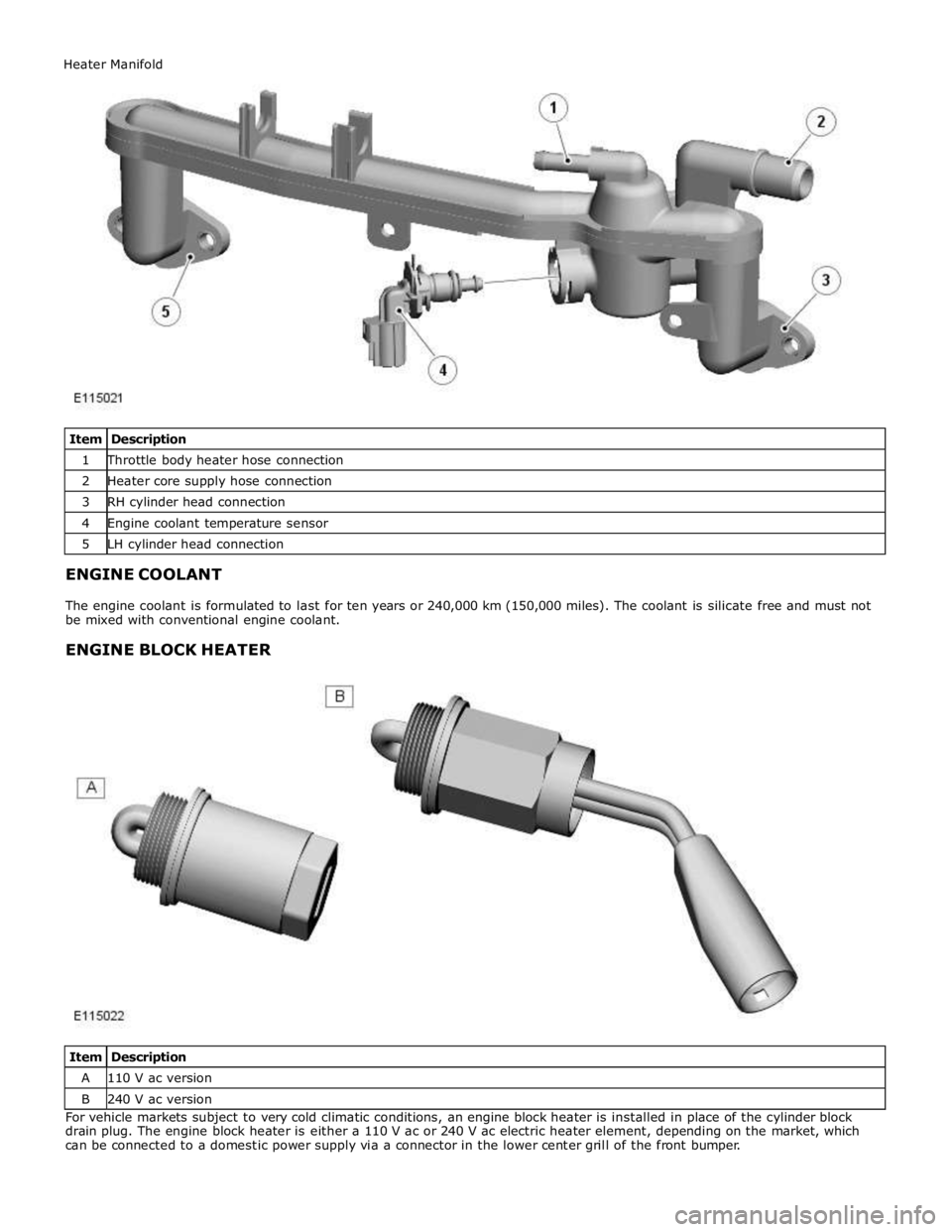
1 Throttle body heater hose connection 2 Heater core supply hose connection 3 RH cylinder head connection 4 Engine coolant temperature sensor 5 LH cylinder head connection
ENGINE COOLANT
The engine coolant is formulated to last for ten years or 240,000 km (150,000 miles). The coolant is silicate free and must not
be mixed with conventional engine coolant.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
Item Description A 110 V ac version B 240 V ac version For vehicle markets subject to very cold climatic conditions, an engine block heater is installed in place of the cylinder block
drain plug. The engine block heater is either a 110 V ac or 240 V ac electric heater element, depending on the market, which
can be connected to a domestic power supply via a connector in the lower center grill of the front bumper. Heater Manifold
Page 1177 of 3039

Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol -
WARNINGS: Published: 11-May-2011
Do not smoke or carry lighted tobacco or open flame of any type when working on or near any fuel related components.
Highly flammable vapors are always present and may ignite. Failure to follow these instructions may result in personal injury.
Before any work is carried out on the fuel system, ground the vehicle to earth and maintain the ground connection until
the work is complete.
CAUTION: Before disconnecting or removing components, make sure the area around the joint faces and connections are
clean. Plug open connections to prevent contamination.
NOTE: Tighten the fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line unions and fuel rail crossover pipe unions as it is instructed
in service manual.
Description Nm lb-ft lb-in Ignition coil-on-plugs retaining bolts 7 - 62 Spark plugs 20 15 - Fuel rail retaining bolt Stage 1 - 20 Stage 2 - 30 Stage 1 - 15 Stage 2 - 22 - Fuel rail crossover pipe unions 21 15 - Fuel rail crossover pipe retaining bolts 12 9 - Fuel pressure regulator 33 24 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line unions 21 15 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line M8 bolt 25 18 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line M6 bolt 11 8 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line M5 nut 6 - 53 Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line shield M10 bolt 29 21 - Fuel rail high-pressure fuel pump fuel line shield M6 bolt 11 8 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump torx bolts 12 9 - Throttle body retaining bolts 10 7 - Accessory drive belt idler pulley retaining bolts 25 18 - Steering gear retaining bolts 100 74 - Steering column lower universal joint assembly bolts 35 26 - Coolant expansion tank retaining bolt 10 7 - Engine compartment brace retaining bolts 45 33 - www.JagDocs.com
Page 1187 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Fuel Charging and Controls
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the fuel charging and controls system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and
Operation section of the workshop manual. REFER to:
Fuel Charging and Controls (303-04D Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Fuel Charging and Controls (303-04D Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Fuel Charging and Controls (303-04D Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Fuel Charging and Controls (303-04E Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Fuel Charging and Controls (303-04E Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Fuel Charging and Controls (303-04E Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Fuel level
Fuel leaks
Damaged fuel lines
Damaged push connect fittings
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Throttle body
Damaged fuel tank filler pipe cap
Damaged fuel tank filler pipe
Fuses
Loose or corroded electrical connectors
Harnesses
Sensor(s)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Engine cranks, but does not
fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine control Ensure the engine breather system is free from restriction
and is correctly installed. Check for ignition system, fuel
system and electronic engine control DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine cranks and fires, but
will not start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
HT short to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for
cracks/damage
Ignition system Check for evaporative emissions, fuel system and ignition
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index Difficult cold start
Engine coolant level/anti-
freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve stuck open
Fuel pump Check the engine coolant level and condition. Ensure the
battery is in a fully charged and serviceable condition.
Check for electronic engine controls, engine emissions, fuel
system and evaporative emissions system related DTCs
and refer to the relevant DTC Index www.JagDocs.com
Page 1188 of 3039

Symptom Possible Causes Action Purge valve
Difficult hot start
Injector leak
Electronic engine control
Purge valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck open Check for injector leak, install new injector as required.
Check for electronic engine controls, evaporative emissions,
fuel system, ignition system and engine emission system
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index Difficult to start after hot
soak (vehicle standing,
engine off, after engine has
reached operating
temperature)
Injector leak
Electronic engine control
Purge valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck open Check for injector leak, install new injector as required.
Check for electronic engine controls, evaporative emissions,
fuel system, ignition system and engine emission system
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index Engine stalls soon after start
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
ECM relay
Electronic engine control
Ignition system
Air intake system restricted
Air leakage
Fuel lines Ensure the engine breather system is free from restriction
and is correctly installed. Check for electronic engine
control, ignition system and fuel system related DTCs and
refer to the relevant DTC Index. Check for blockage in air
filter element and air intake system. Check for air leakage
in air intake system Engine hesitates/poor
acceleration
Fuel pressure, fuel pump,
fuel lines
Injector leak
Air leakage
Electronic engine control
Throttle motor
Restricted accelerator pedal
travel (carpet, etc)
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck open
Transmission malfunction Check for fuel system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index. Check for injector leak, install new
injector as required. Check for air leakage in air intake
system. Ensure accelerator pedal is free from restriction.
Check for electronic engine controls, ignition, engine
emission system and transmission related DTCs and refer
to the relevant DTC Index Engine backfires
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Sticking variable camshaft
timing (VCT) hub Check for fuel system failures. Check for air leakage in
intake air system. Check for electronic engine controls,
ignition system and VCT system related DTCs and refer to
the relevant DTC Index Engine surges
Fuel pump/lines
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor
Ignition system Check for fuel system failures. Check for electronic engine
controls, throttle system and ignition system related DTCs
and refer to the relevant DTC Index Engine detonates/knocks
Fuel pump/lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Sticking VCT hub Check for fuel system failures. Check for air leakage in
intake air system. Check for electronic engine controls and
VCT system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index No throttle response
Electronic engine controls
Throttle motor Check for electronic engine controls and throttle system
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index Poor throttle response
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Electronic engine control
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event Air
leakage Ensure the engine breather system is free from restriction
and is correctly installed. Check for electronic engine
controls, transmission and traction control related DTCs and
refer to the related DTC Index. Check for air leakage in
intake air system DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Engine Control Module (ECM), please refer to Section
303-14.
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing) / Electronic Engine Controls (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing).