Dtc JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 2037 of 3039

Exterior Lighting - Headlamps
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation Published: 11-Jul-2014
For a detailed description of the exterior lighting system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the
workshop manual. REFER to: (417-01 Exterior Lighting)
Exterior Lighting (Description and Operation), Exterior Lighting (Description and Operation), Exterior Lighting (Description and Operation).
Safety Information
WARNINGS:
The Xenon Headlamp system generates up to 28,000 volts. Make sure that the headlamps are switched off before
working on the system. Failure to follow this instruction may lead to fatality.
The following safety precautions must be followed when working on the Xenon Headlamp system:
DO NOT attempt any procedures on the Xenon Headlamps or circuits when the system is energized.
Handling of the xenon bulb must be performed using suitable protective equipment, e.g. gloves and goggles. The glass
part of the bulb must not be touched.
Only operate the lamp in a mounted condition in the reflector.
All safety procedures and precautions must be followed to prevent personal injury.
CAUTION: Xenon bulbs must be disposed of as hazardous waste.
There are instructions on the correct procedures for Xenon Headlamp System repairs in the manual, refer to section 100-00 -
General Information, Standard Workshop Practices of the workshop manual.
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage.
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Low beam lamp(s)
inoperative
Bulb failure
Fuse(s) blown
Circuit fault
Lighting control switch
fault
Left-hand steering
column multifunction
switch fault Check the bulb and fuse condition (see visual inspection). Check the
headlamp circuits. Check the lighting control switch function. Check the
left-hand steering column multifunction switch operation. Refer to the
electrical guides. Check for DTCs indicating a headlamp or related circuit
fault. High beam lamp(s)
inoperative Electrical
Headlamp Leveling Module (HLM)
Bulb(s)
Photocell(s)
Ballast
Wiring harness/electrical connectors
Fuse(s) Visual Inspection
Page 2038 of 3039
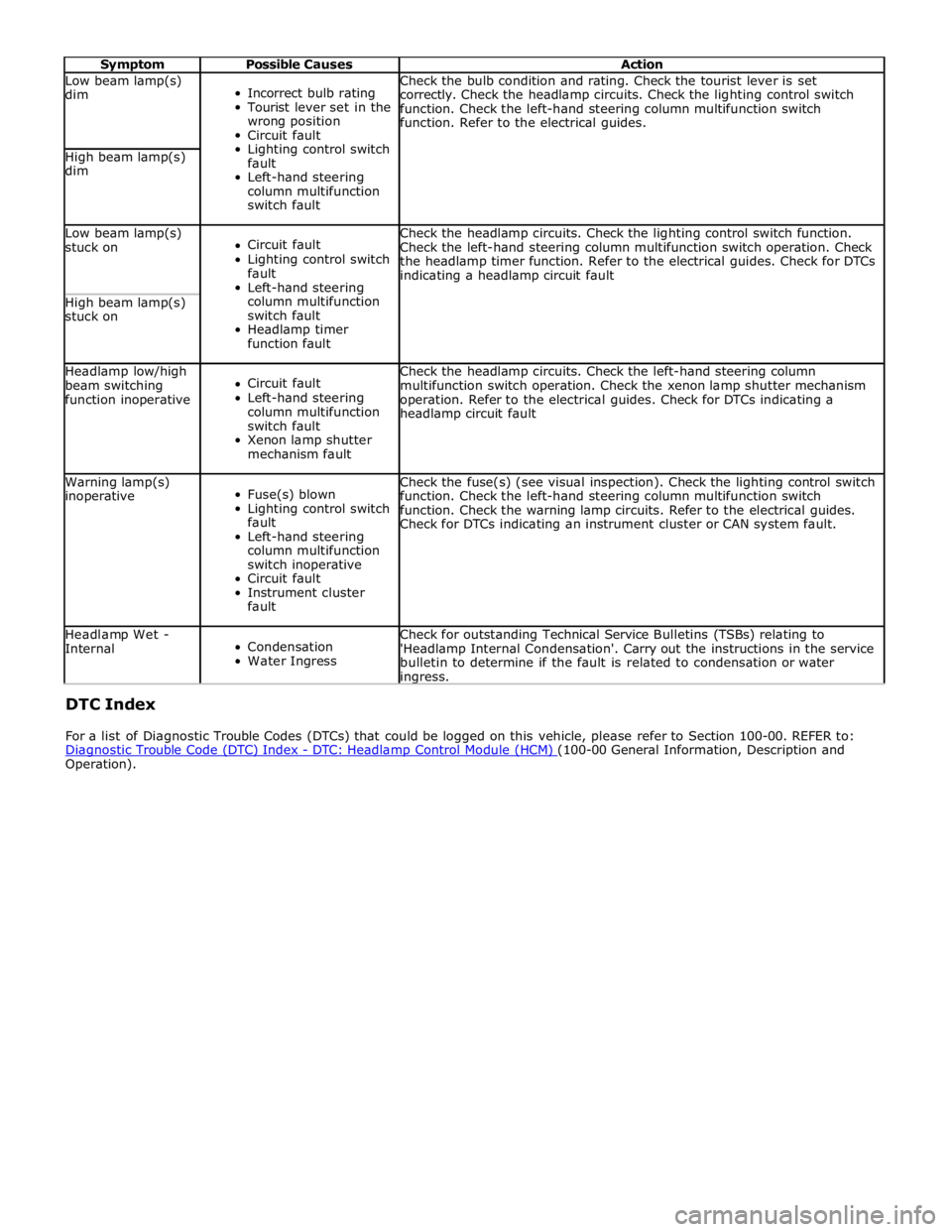
Symptom Possible Causes Action Low beam lamp(s)
dim
Incorrect bulb rating
Tourist lever set in the
wrong position
Circuit fault
Lighting control switch
fault
Left-hand steering
column multifunction
switch fault Check the bulb condition and rating. Check the tourist lever is set
correctly. Check the headlamp circuits. Check the lighting control switch
function. Check the left-hand steering column multifunction switch
function. Refer to the electrical guides. High beam lamp(s)
dim Low beam lamp(s)
stuck on
Circuit fault
Lighting control switch
fault
Left-hand steering
column multifunction
switch fault
Headlamp timer
function fault Check the headlamp circuits. Check the lighting control switch function.
Check the left-hand steering column multifunction switch operation. Check
the headlamp timer function. Refer to the electrical guides. Check for DTCs
indicating a headlamp circuit fault High beam lamp(s)
stuck on Headlamp low/high
beam switching
function inoperative
Circuit fault
Left-hand steering
column multifunction
switch fault
Xenon lamp shutter
mechanism fault Check the headlamp circuits. Check the left-hand steering column
multifunction switch operation. Check the xenon lamp shutter mechanism
operation. Refer to the electrical guides. Check for DTCs indicating a
headlamp circuit fault Warning lamp(s)
inoperative
Fuse(s) blown
Lighting control switch
fault
Left-hand steering
column multifunction
switch inoperative
Circuit fault
Instrument cluster
fault Check the fuse(s) (see visual inspection). Check the lighting control switch
function. Check the left-hand steering column multifunction switch
function. Check the warning lamp circuits. Refer to the electrical guides.
Check for DTCs indicating an instrument cluster or CAN system fault. Headlamp Wet -
Internal
Condensation
Water Ingress Check for outstanding Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) relating to
'Headlamp Internal Condensation'. Carry out the instructions in the service
bulletin to determine if the fault is related to condensation or water ingress. DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00. REFER to:
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Headlamp Control Module (HCM) (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Page 2063 of 3039

Interior Lighting - Interior Lighting
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation Published: 11-May-2011
For a detailed description of the interior lighting system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
workshop manual. REFER to: (417-02 Interior Lighting)
Interior Lighting (Description and Operation), Interior Lighting (Description and Operation), Interior Lighting (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Bulbs
Fuses/relays (refer to electrical guide)
Wiring harness
Correct engagement of electrical connectors
Loose or corroded connections
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
CAUTION: When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit, part
number 3548-1358-00
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only five digit codes. Match the five digits from the scan
tool to the first five digits of the seven digit code listed to identify the fault (the last two digits give extra information read by
the manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal places and
with a current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads into account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B116511
Left Front
Puddle Lamp
Output
Left front puddle lamp
control circuit - short to
ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and test left front puddle
lamp control circuit for short to ground
Page 2064 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Cause Action B116515
Left Front
Puddle Lamp
Output
Left front puddle lamp
control circuit - short to
power, open circuit Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test left front puddle lamp control circuit
for short to power, open circuit B116611
Right Front
Puddle Lamp
Output
Right front puddle lamp
control circuit - short to
ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and test right front
puddle lamp control circuit for short to ground B116615
Right Front
Puddle Lamp
Output
Right front puddle lamp
control circuit - short to
power, open circuit Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test right front puddle lamp control circuit
for short to power, open circuit B111E11
Boot/Trunk
Lamps
Luggage compartment lamp
control circuit - short to
ground Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check luggage compartment lamp control
circuit for short to ground B111E15
Boot/Trunk
Lamps
Luggage compartment lamp
control circuit - short to
power, open circuit Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check luggage compartment lamp control
circuit for short to power, open circuit B112412
Lamp Fade
Control
Interior lamp fade control
circuit - short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check interior lamp
fade control circuit for short to power B113C12
Hazard Switch
Illumination
Hazard switch illumination
control circuit - short to
power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check hazard switch
illumination control circuit for short to power B1A8596
Ambient Light
Sensor
Light sensor internal
electronic failure Check and install a new sensor as required U201012
Switch
Illumination
Switch/interior illumination
PWM supply circuit - short to
power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check switch/interior
illumination PWM supply circuit for short to power U201014
Switch
Illumination
Switch/interior illumination
PWM supply circuit - short to
ground, open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check switch/interior
illumination PWM supply circuit for short to ground, open circuit
Page 2075 of 3039
Module Communications Network - Communications Network
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation Published: 25-Nov-2013
For a detailed description of the Communications Network, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
workshop manual. REFER to: (418-00 Module Communications Network)
Communications Network (Description and Operation),
Communications Network (Description and Operation), Communications Network (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTIONS:
Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not guarantee
confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
Electronic modules are sensitive to static electrical charges. If exposed to these charges, damage may result.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index
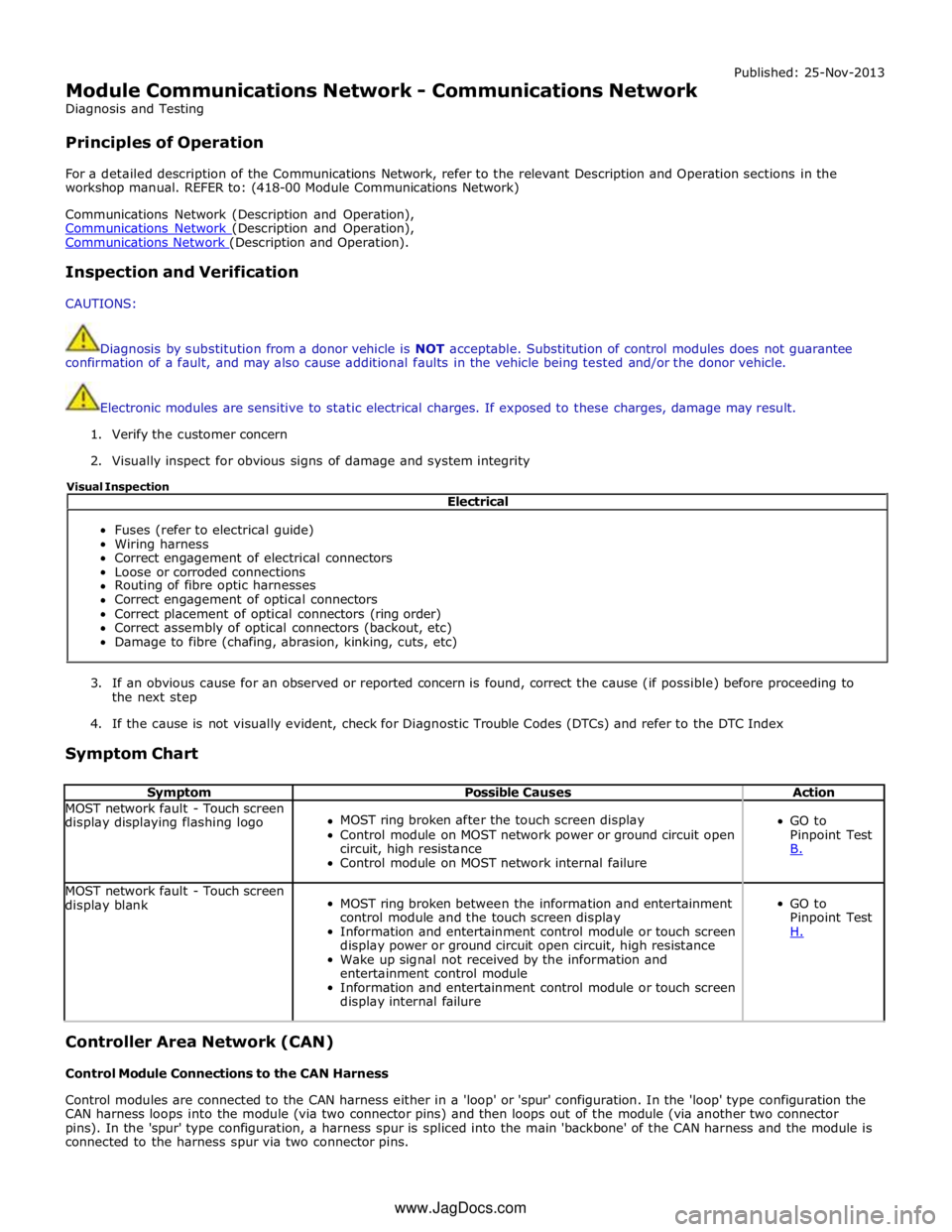
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action MOST network fault - Touch screen
display displaying flashing logo
MOST ring broken after the touch screen display
Control module on MOST network power or ground circuit open
circuit, high resistance
Control module on MOST network internal failure
GO to
Pinpoint Test
B. MOST network fault - Touch screen
display blank
MOST ring broken between the information and entertainment
control module and the touch screen display
Information and entertainment control module or touch screen
display power or ground circuit open circuit, high resistance
Wake up signal not received by the information and
entertainment control module
Information and entertainment control module or touch screen
display internal failure
GO to
Pinpoint Test
H. Controller Area Network (CAN)
Control Module Connections to the CAN Harness
Control modules are connected to the CAN harness either in a 'loop' or 'spur' configuration. In the 'loop' type configuration the
CAN harness loops into the module (via two connector pins) and then loops out of the module (via another two connector
pins). In the 'spur' type configuration, a harness spur is spliced into the main 'backbone' of the CAN harness and the module is
connected to the harness spur via two connector pins. Electrical
Fuses (refer to electrical guide)
Wiring harness
Correct engagement of electrical connectors
Loose or corroded connections
Routing of fibre optic harnesses
Correct engagement of optical connectors
Correct placement of optical connectors (ring order)
Correct assembly of optical connectors (backout, etc)
Damage to fibre (chafing, abrasion, kinking, cuts, etc) Visual Inspection
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2076 of 3039

CAN Harness Architecture
For a detailed description of the CAN Networks and architecture, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the
Workshop Manual.
CAN Network Integrity Tests
If a control module is suspected of non-communication, the Network Integrity test application available on the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system can be used to confirm if communication is possible between the control modules on the vehicle
and the manufacturer approved diagnostic system (via the J1962 diagnostic connector ). The results from the test can be used
to determine if either a single module or multiple modules are failing to communicate.
CAN Terminating Modules
If the Network Integrity test indicates that one or more module on one of the CAN networks (HS or MS) are failing to
communicate, there are several checks that can be made. The first step is to identify if both of the CAN terminating modules
on each individual CAN Bus are communicating. If both CAN terminating modules for each individual CAN Bus are
communicating (identified via the Network Integrity test), then it can be confirmed that the main 'backbone' of the CAN
harness is complete. The main 'backbone' of the CAN harness consists of all the modules connected to the CAN harness via a
'loop' configuration and also includes the two terminating modules.
Communication with both CAN terminating modules via the Network Integrity test confirms the physical integrity of the main
'backbone' of the CAN harness (and the harness spur to the J1962 diagnostic connector). This means that there is no
requirement to check the resistance of the CAN Network. This is because the standard check for 60 ohms across the CAN High
and CAN Low lines will not provide any additional information regarding the physical condition of the CAN harness, beyond
what has already been determined from the Network Integrity test.
Non-Communication of a Terminating Module
If a Network Integrity test reveals a terminating module is failing to communicate it can indicate a break in the main
'backbone' of the CAN harness. The first checks should always be to confirm the power and ground supplies to the
non-communicating module are correct. Providing these are correct, the resistance between the CAN High and CAN Low lines at
the J1962 connector can be checked to determine the integrity of the main 'backbone' of the CAN harness. After disconnecting
the battery a reading of 120 ohms would indicate an open circuit in the main 'backbone' of the CAN harness. Alternatively, a
reading of 60 ohms would indicate that there is no open circuit fault with the main 'backbone' of the CAN harness.
It is worth noting that even if one of the terminating modules is disconnected from the CAN harness, communications between
the modules still connected may still be possible. Therefore communication between the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system and the connected modules may also be possible.
Locating CAN Harness Open Circuits
In the case where multiple modules, including a terminating module, are failing to communicate, having first confirmed the
power and ground supplies are correct, the approximate location of the open circuit can be identified from analysis of the
Network Integrity test results and reference to the relevant CAN network circuit diagrams. For example, if an open circuit
existed in a certain position on the CAN harness, any module positioned on the Network between the J1962 connector and the
open circuit should return a response during the Network Integrity test. No responses would be returned from any modules
past the open circuit fault in the Network.
CAN Harness 'Spur' Type Configuration Circuits
If, after the initial checks (Network Integrity test using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system, and power and ground
supplies to the module have been checked and confirmed as correct), a module that is connected to the CAN harness via a
'spur' type configuration is suspected of not communicating, then the physical integrity of the CAN harness 'spur' can be
checked.
This is most easily undertaken by individually checking the continuity of the CAN High and CAN Low lines between the
non-communicating module connector (with the module disconnected) and the J1962 diagnostic connector.
'Lost Communications' DTCs
As well as the methods described so far in this document, which can be used to determine the location of an open circuit in
the CAN harness, 'Lost Communications' DTCs can also be used for this purpose. Lost communication DTCs mean that a
module is not receiving CAN information from another module.
For example, if a global DTC read were to be carried out, only DTCs stored in the modules that the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system could communicate with would be displayed. If there was an open circuit fault in a certain position on the
CAN harness, the modules that could display DTCs would all be prior to the open circuit on the Network, and these modules
should display 'Lost Communications' DTCs with all the modules located on the Network past the open circuit fault.
'Bus off' DTCs
The references to bus and its condition refer to the network concerned and the modules on that network.
If a module logs a 'Bus Off' DTC, it means that the module has detected CAN transmission errors and has disabled it's own
CAN transmissions and disconnected itself from the network in an attempt to allow the rest of the network to function. At this
point the 'Bus Off' DTC is set. A common cause of 'Bus Off' DTCs can be a short circuit in the CAN network.
Page 2083 of 3039
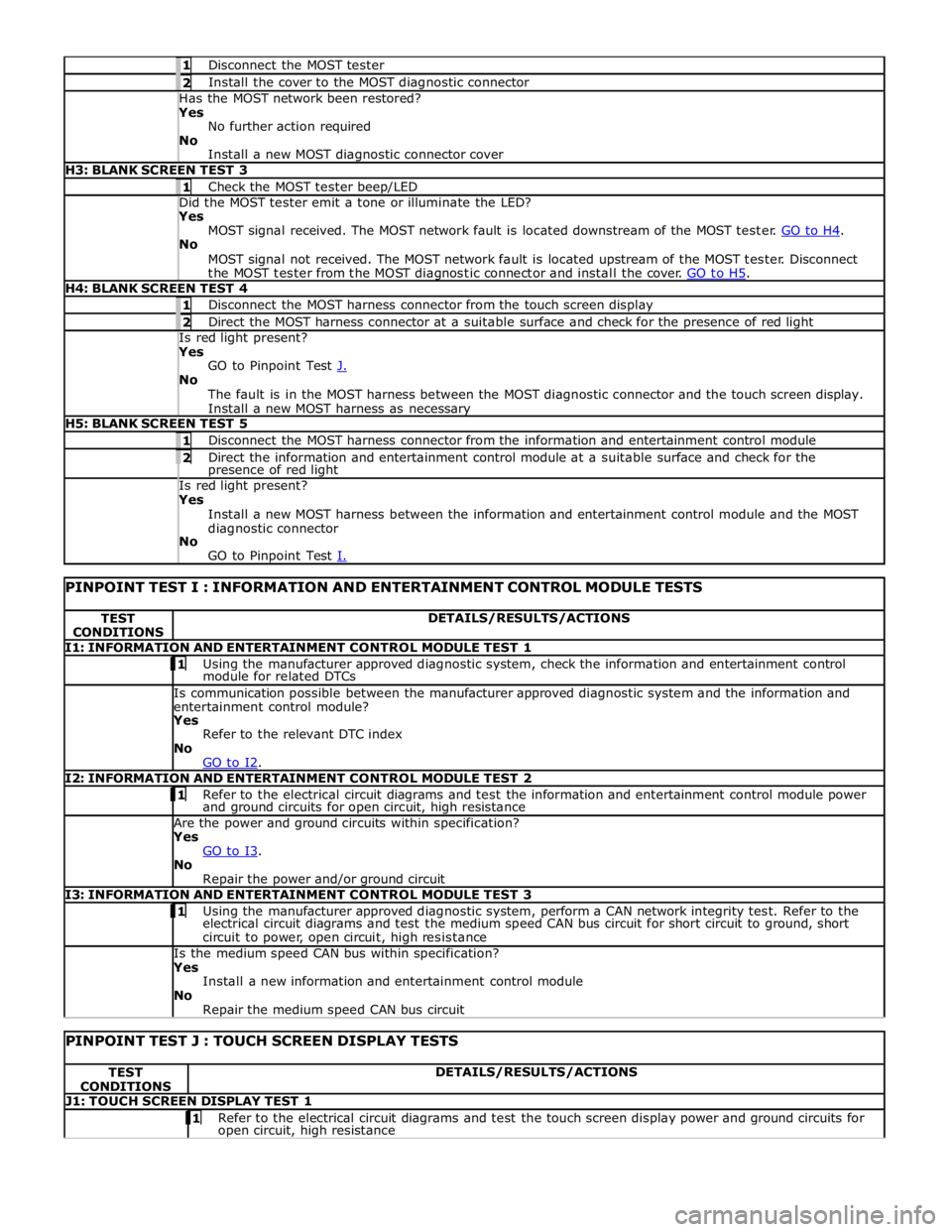
1 Disconnect the MOST tester 2 Install the cover to the MOST diagnostic connector Has the MOST network been restored? Yes
No further action required
No
Install a new MOST diagnostic connector cover H3: BLANK SCREEN TEST 3 1 Check the MOST tester beep/LED Did the MOST tester emit a tone or illuminate the LED? Yes
MOST signal received. The MOST network fault is located downstream of the MOST tester. GO to H4. No
MOST signal not received. The MOST network fault is located upstream of the MOST tester. Disconnect
the MOST tester from the MOST diagnostic connector and install the cover. GO to H5. H4: BLANK SCREEN TEST 4 1 Disconnect the MOST harness connector from the touch screen display 2 Direct the MOST harness connector at a suitable surface and check for the presence of red light Is red light present? Yes
GO to Pinpoint Test J. No
The fault is in the MOST harness between the MOST diagnostic connector and the touch screen display.
Install a new MOST harness as necessary H5: BLANK SCREEN TEST 5 1 Disconnect the MOST harness connector from the information and entertainment control module 2 Direct the information and entertainment control module at a suitable surface and check for the presence of red light Is red light present? Yes
Install a new MOST harness between the information and entertainment control module and the MOST
diagnostic connector
No
GO to Pinpoint Test I.
PINPOINT TEST I : INFORMATION AND ENTERTAINMENT CONTROL MODULE TESTS TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS I1: INFORMATION AND ENTERTAINMENT CONTROL MODULE TEST 1 1 Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system, check the information and entertainment control module for related DTCs Is communication possible between the manufacturer approved diagnostic system and the information and
entertainment control module? Yes
Refer to the relevant DTC index
No
GO to I2. I2: INFORMATION AND ENTERTAINMENT CONTROL MODULE TEST 2 1 Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and test the information and entertainment control module power and ground circuits for open circuit, high resistance Are the power and ground circuits within specification? Yes
GO to I3. No
Repair the power and/or ground circuit I3: INFORMATION AND ENTERTAINMENT CONTROL MODULE TEST 3 1 Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system, perform a CAN network integrity test. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and test the medium speed CAN bus circuit for short circuit to ground, short
circuit to power, open circuit, high resistance Is the medium speed CAN bus within specification? Yes
Install a new information and entertainment control module
No
Repair the medium speed CAN bus circuit
PINPOINT TEST J : TOUCH SCREEN DISPLAY TESTS TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS J1: TOUCH SCREEN DISPLAY TEST 1 1 Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and test the touch screen display power and ground circuits for open circuit, high resistance
Page 2084 of 3039

Are the power and ground circuits within specification?
Yes
GO to J2. No
Repair the power and/or ground circuit J2: TOUCH SCREEN DISPLAY TEST 2 1 Reconnect the MOST harness to the touch screen display 2 Check the touch screen display for indication of a MOST network fault Has the MOST network been restored?
Yes
Tests inconclusive. Repeat the tests from beginning. GO to Pinpoint Test B. No
Install a new touch screen display DTC Index
Central Junction Box (CJB)
CAUTIONS:
Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not guarantee
confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit, part number
3548-1358-00
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If diagnostic trouble codes are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent
concern may be the cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
Where an 'on demand self-test' is referred to, this can be accessed via the 'diagnostic trouble code monitor' tab on the
manufacturers approved diagnostic system
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B00D511
Restraint System
Passenger Disable
Indicator
PAD lamp supply circuit - short
to ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check PAD
lamp supply circuit for short to ground B00D512
Restraint System
Passenger Disable
Indicator
PAD lamp supply circuit - short
to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check PAD
lamp supply circuit for short to power B00D513
Restraint System
Passenger Disable
Indicator
PAD lamp supply circuit - open
circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check PAD
lamp supply circuit for open circuit
Page 2085 of 3039
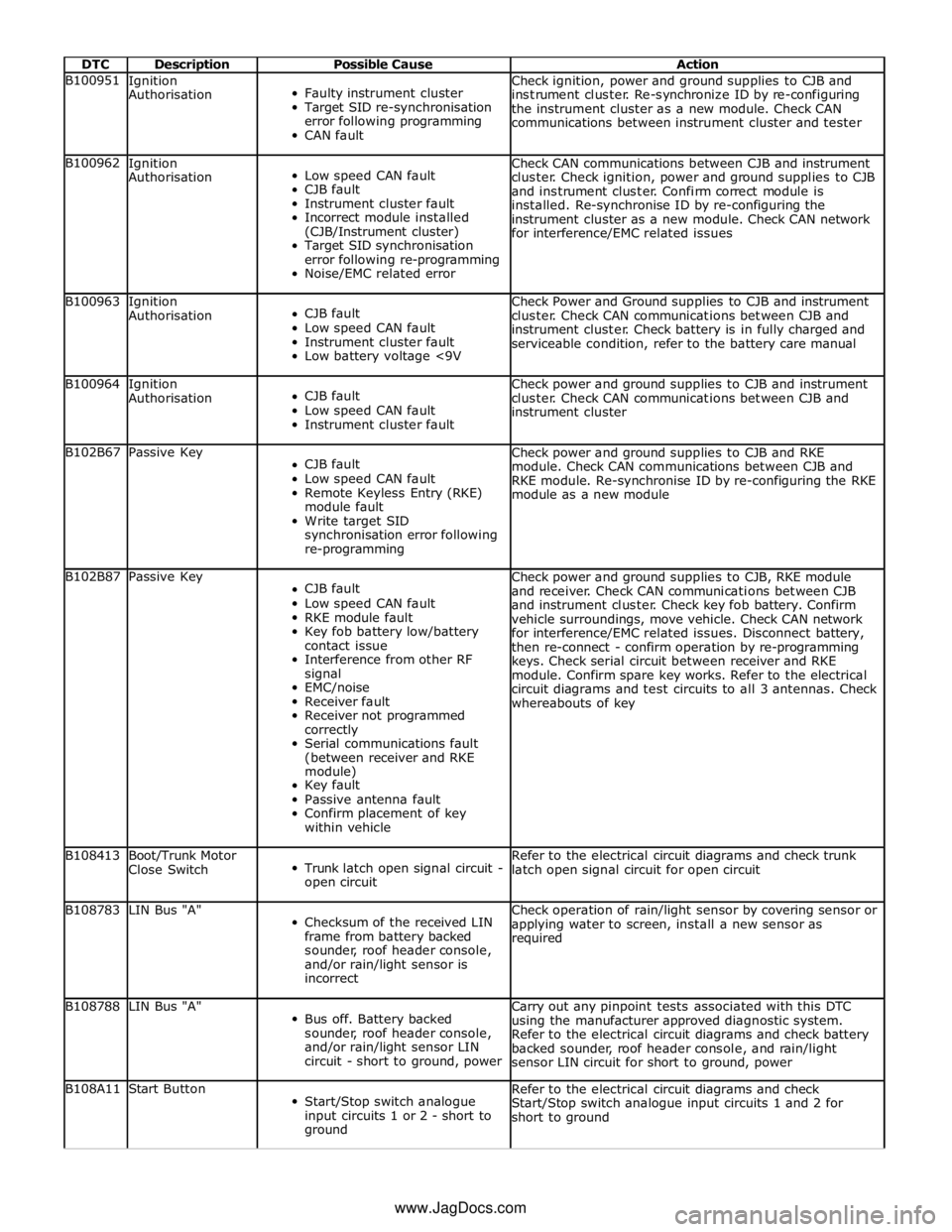
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B100951
Ignition
Authorisation
Faulty instrument cluster
Target SID re-synchronisation
error following programming
CAN fault Check ignition, power and ground supplies to CJB and
instrument cluster. Re-synchronize ID by re-configuring
the instrument cluster as a new module. Check CAN
communications between instrument cluster and tester B100962
Ignition
Authorisation
Low speed CAN fault
CJB fault
Instrument cluster fault
Incorrect module installed
(CJB/Instrument cluster)
Target SID synchronisation
error following re-programming
Noise/EMC related error Check CAN communications between CJB and instrument
cluster. Check ignition, power and ground supplies to CJB
and instrument cluster. Confirm correct module is
installed. Re-synchronise ID by re-configuring the
instrument cluster as a new module. Check CAN network
for interference/EMC related issues B100963
Ignition
Authorisation
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault
Low battery voltage <9V Check Power and Ground supplies to CJB and instrument
cluster. Check CAN communications between CJB and
instrument cluster. Check battery is in fully charged and
serviceable condition, refer to the battery care manual B100964
Ignition
Authorisation
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault Check power and ground supplies to CJB and instrument
cluster. Check CAN communications between CJB and
instrument cluster B102B67 Passive Key
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
module fault
Write target SID
synchronisation error following
re-programming Check power and ground supplies to CJB and RKE
module. Check CAN communications between CJB and
RKE module. Re-synchronise ID by re-configuring the RKE
module as a new module B102B87 Passive Key
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
RKE module fault
Key fob battery low/battery
contact issue
Interference from other RF
signal
EMC/noise
Receiver fault
Receiver not programmed
correctly
Serial communications fault
(between receiver and RKE
module)
Key fault
Passive antenna fault
Confirm placement of key
within vehicle Check power and ground supplies to CJB, RKE module
and receiver. Check CAN communications between CJB
and instrument cluster. Check key fob battery. Confirm
vehicle surroundings, move vehicle. Check CAN network
for interference/EMC related issues. Disconnect battery,
then re-connect - confirm operation by re-programming
keys. Check serial circuit between receiver and RKE
module. Confirm spare key works. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test circuits to all 3 antennas. Check
whereabouts of key B108413
Boot/Trunk Motor
Close Switch
Trunk latch open signal circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check trunk
latch open signal circuit for open circuit B108783 LIN Bus "A"
Checksum of the received LIN
frame from battery backed
sounder, roof header console,
and/or rain/light sensor is
incorrect Check operation of rain/light sensor by covering sensor or
applying water to screen, install a new sensor as
required B108788 LIN Bus "A"
Bus off. Battery backed
sounder, roof header console,
and/or rain/light sensor LIN
circuit - short to ground, power Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check battery
backed sounder, roof header console, and rain/light
sensor LIN circuit for short to ground, power B108A11 Start Button
Start/Stop switch analogue
input circuits 1 or 2 - short to
ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
Start/Stop switch analogue input circuits 1 and 2 for
short to ground www.JagDocs.com
Page 2086 of 3039
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B108A12 Start Button
Start/Stop switch analogue
input circuits 1 or 2 - short to
power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
Start/Stop switch analogue input circuits 1 and 2 for
short to power B109512 Wiper On/Off Relay
Wiper On/Off relay control
circuit - short to power Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check wiper
On/Off relay control circuit for short to power B109514 Wiper On/Off Relay
Wiper On/Off relay control
circuit - short to ground, open
circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check wiper
On/Off relay control circuit for short to ground, open
circuit B109612
Wiper High/Low
Relay
Wiper Fast/Slow relay control
circuit - short to power Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check wiper
Fast/Slow relay control circuit for short to power B109614
Wiper High/Low
Relay
Wiper Fast/Slow relay control
circuit - short to ground, open
circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check wiper
Fast/Slow relay control circuit for short to ground, open
circuit B109712
Heated Windshield
Relay
Heated windshield relay control
circuit - short to power Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check heated
windshield relay control circuit for short to power B109714
Heated Windshield
Relay
Heated windshield relay control
circuit - short to ground, open
circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check heated
windshield relay control circuit for short to ground, open
circuit B10A612 Main Light Switch
Master light switch signal from
roof header console circuit -
short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check master
light switch signal from roof header console circuit for
short to power B10A623 Main Light Switch
Master light switch signal from
roof header console signal
stuck low. Switch is read as ON
for too long a time Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check master
light switch signal from roof header console for short to
ground B10AD09 Rain Sensor
Component failures Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Suspect the rain/light sensor, check and install a new
sensor as required B10AD11 Rain Sensor
Rain/light sensor power circuit -
short to ground Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check rain/light sensor power circuit for short to ground B10AD96 Rain Sensor
Component internal failure Suspect the rain/light sensor, check and install a new
sensor as required B10E511
PCM Wake-up
Signal
ECM wake-up signal circuit -
short to ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check ECM
wake-up signal circuit for short to ground B10E512
PCM Wake-up
Signal
ECM wake-up signal circuit -
short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check ECM
wake-up signal circuit for short to power B10E513
PCM Wake-up
Signal
ECM wake-up signal circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check ECM
wake-up signal circuit for open circuit B10F111 Key In Switch
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - short to ground Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check keyless
vehicle module, key IN status circuit for short to ground B10F112 Key In Switch
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check keyless
vehicle module, key IN status circuit for short to power B10F113 Key In Switch
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check keyless
vehicle module, key IN status circuit for open circuit