warning JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 2595 of 3039

Safety Belt System - Safety Belt System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 13-Jun-2013
For a detailed description of the seatbelt system and operation, refer to the relevant description and operation section of the
workshop manual REFER to: (501-20A Safety Belt System)
Safety Belt System (Description and Operation), Safety Belt System (Description and Operation), Safety Belt System (Description and Operation).
Safety Information
WARNINGS:
To avoid accidental deployment the back-up power supply must be depleted before beginning any work on the SRS system
or its components. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury
Do not use a multimeter to probe an SRS module. It is possible for the power from the multimeter battery to trigger the
activation of the module. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury
NOTE: Do not to use a cellular phone or to have a cellular phone in close proximity when working on the SRS system or
components
Power supply depletion
Before beginning any work on the SRS system or related components:
1. Remove the ignition key
2. Disconnect the battery leads, ground first
3. Wait 2 minutes for the power circuit to discharge
There are comprehensive instructions on the correct procedures for SRS system repairs, refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines including pinpoint tests
1. Verify the customer concern by operating the seatbelt
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Check for the installation of non-standard accessories which may affect or
obstruct the function of the seatbelt system
Frayed or damaged webbing
Missing or damaged button stop
Pretensioner(s) Buckles/Stalks
Fuses
Wiring harness fault
Correct engagement of electrical
connectors
Loose or corroded connections
Warning lamp bulb(s)
Impact sensor(s)
Buckle sensor(s)
Pretensioner(s)
Belt tension sensor(s)
Restraints control module
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, carry out the test methods described below, alternatively check for diagnostic
trouble codes and refer to the relevant diagnostic trouble code index
Page 2611 of 3039

Published: 30-May-2012
Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
WARNING: All pyrotechnic devices are dangerous. Before performing any procedures on any pyrotechnic device, read all
information contained within the Standard Workshop Practices section of this manual.
Refer to: Standard Workshop Practices (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
The SRS (supplemental restraint system) provides additional protection for the vehicle occupants in certain impact conditions.
The system is controlled by the RCM (restraints control module), which is mounted beneath the floor console. The system
includes twin stage drivers and front passenger airbags.
The RCM receives inputs from various sensors around the vehicle and determines which, if any, airbags should be deployed.
The SRS features an occupant detection system. The occupant detection system comprises a mat fitted inside the front passenger seat. By monitoring the condition of the mat, the RCM can determine if the front passenger seat is occupied. It uses this information to determine which airbags to deploy in the event of an impact. This information is also used to illuminate the
safety belt instrument cluster warning lamp if the front passenger seat is occupied and the safety belt is not engaged.
North American Specification (NAS) vehicles also feature an occupant classification system. The occupant classification system
comprises a control module, pressure pad and safety belt tension sensor. The system can determine the size and weight of the
front seat passenger. This information is transmitted to the RCM over the high speed CAN (controller area network) bus. The RCM uses this information to help determine which airbags to deploy in the event of an impact.
Page 2615 of 3039
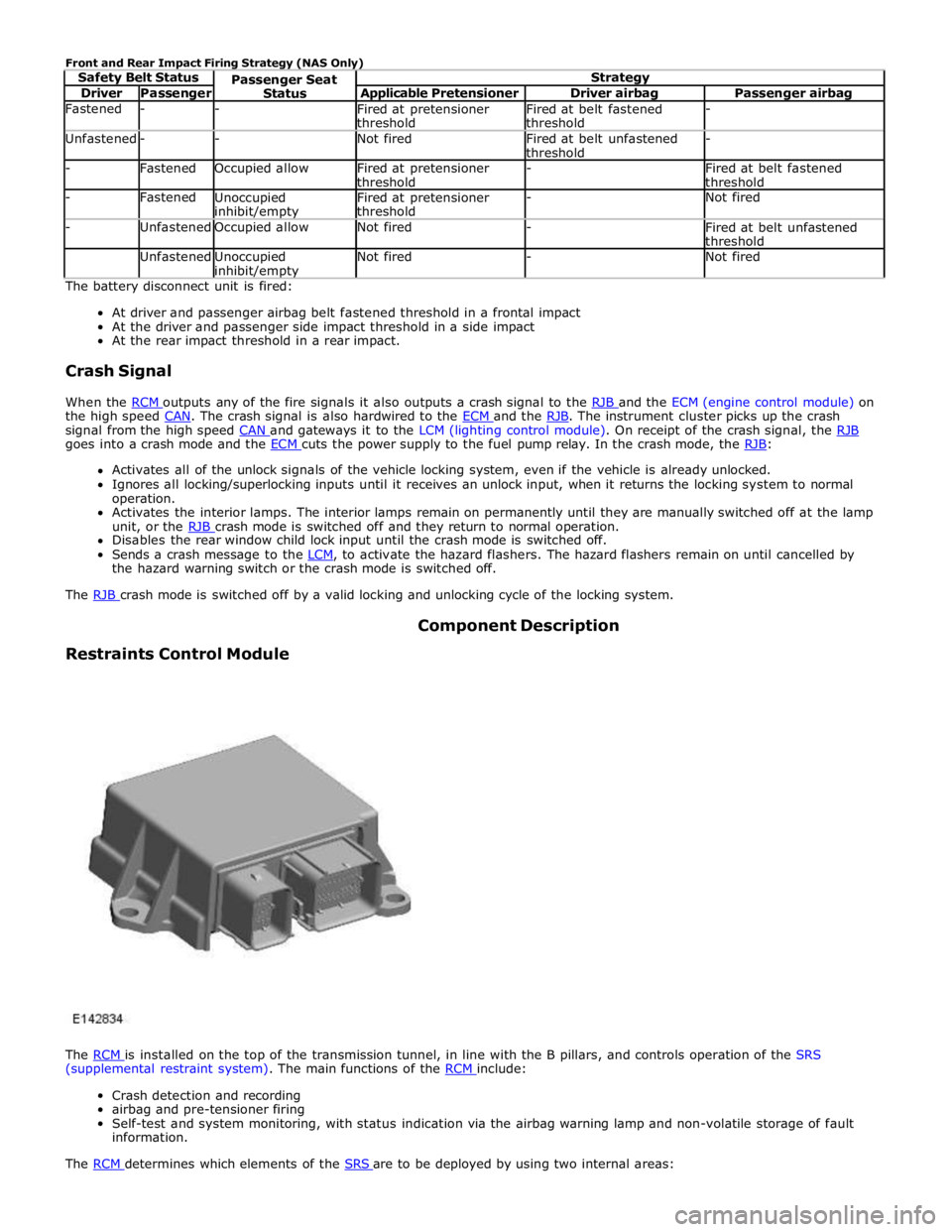
Driver Passenger Applicable Pretensioner Driver airbag Passenger airbag Fastened - -
Fired at pretensioner
threshold Fired at belt fastened
threshold - Unfastened - - Not fired
Fired at belt unfastened
threshold - - Fastened Occupied allow
Fired at pretensioner
threshold -
Fired at belt fastened
threshold - Fastened
Unoccupied inhibit/empty Fired at pretensioner
threshold - Not fired - Unfastened Occupied allow Not fired -
Fired at belt unfastened
threshold Unfastened
Unoccupied inhibit/empty Not fired - Not fired The battery disconnect unit is fired:
At driver and passenger airbag belt fastened threshold in a frontal impact
At the driver and passenger side impact threshold in a side impact
At the rear impact threshold in a rear impact.
Crash Signal
When the RCM outputs any of the fire signals it also outputs a crash signal to the RJB and the ECM (engine control module) on the high speed CAN. The crash signal is also hardwired to the ECM and the RJB. The instrument cluster picks up the crash signal from the high speed CAN and gateways it to the LCM (lighting control module). On receipt of the crash signal, the RJB goes into a crash mode and the ECM cuts the power supply to the fuel pump relay. In the crash mode, the RJB: Activates all of the unlock signals of the vehicle locking system, even if the vehicle is already unlocked.
Ignores all locking/superlocking inputs until it receives an unlock input, when it returns the locking system to normal
operation.
Activates the interior lamps. The interior lamps remain on permanently until they are manually switched off at the lamp
unit, or the RJB crash mode is switched off and they return to normal operation. Disables the rear window child lock input until the crash mode is switched off.
Sends a crash message to the LCM, to activate the hazard flashers. The hazard flashers remain on until cancelled by the hazard warning switch or the crash mode is switched off.
The RJB crash mode is switched off by a valid locking and unlocking cycle of the locking system.
Restraints Control Module Component Description
The RCM is installed on the top of the transmission tunnel, in line with the B pillars, and controls operation of the SRS (supplemental restraint system). The main functions of the RCM include:
Crash detection and recording
airbag and pre-tensioner firing
Self-test and system monitoring, with status indication via the airbag warning lamp and non-volatile storage of fault
information.
The RCM determines which elements of the SRS are to be deployed by using two internal areas:
Page 2616 of 3039
and the safety belt buckle sensor. Based on this data, the RCM decides which level of airbag module deployment is required and forwards the information to the second area, the deployment handler.
The deployment handler evaluates the status of the seat track position sensor and safety belt buckle sensors before a decision
is made about which restraints should finally be deployed.
Data from the side crash sensors is used by the RCM in conjunction with acceleration data from the RCM internal accelerometer to make a deployment decision. The RCM processes the acceleration data and subject to an impact being of high enough severity, decides whether the side airbag module should be deployed.
On board testing of the airbag modules, front safety belt pretensioner firing circuits, warning indicator circuits and module
status (the crash and side impact sensors perform basic self-tests) is performed by the RCM together with the storing of fault codes.
The RCM drives the SRS indicator on the instrument pack via a CAN signal. If the warning lamp fails, a fault code is recorded and a warning tone is sounded in place of the lamp if a further fault occurs. It also provides a temporary back-up power supply
to operate the airbag modules in the event that in crash conditions, the battery supply is lost. In the event of a crash, it
records certain data which can be accessed via the diagnostic connector.
A safing sensor in the RCM provides confirmation of an impact to verify if airbag and pretensioner activation is necessary. A roll-over sensor monitors the lateral attitude of the vehicle. Various firing strategies are employed by the RCM to ensure that during an accident only the appropriate airbags and pretensioners are fired. The firing strategy used also depends on the
inputs from the safety belt switches and the occupant monitoring system.
An energy reserve in the RCM ensures there is always a minimum of 150 milliseconds of stored energy available if the power supply from the ignition switch is disrupted during a crash. The stored energy is sufficient to produce firing signals for the
driver airbag, the passenger airbag and the safety belt pretensioners.
When the ignition is switched on, the RCM performs a self-test and then performs cyclical monitoring of the system. If a fault is detected the RCM stores a related fault code and illuminates the airbag warning indicator. The faults can be retrieved by the recommended Jaguar diagnostic tool over the CAN bus. If a fault that could cause a false fire signal is detected, the RCM disables the respective firing circuit, and keeps it disabled during a crash event.
Clock Spring
The clockspring is installed on the steering column to provide the electrical interface between the fixed wiring harness of the
steering column and the components that rotate with the steering wheel, i.e. the driver airbag, the horn and the steering
wheel switch packs.
The clockspring consists of a plastic cassette which incorporates an outer cover fixed to the steering column and an inner rotor
which turns with the steering wheel. Four securing lugs attach the cover to the multifunction switch on the steering column.
The rotor is keyed to the steering wheel by a drive peg. A lug on the underside of the rotor operates the self-cancelling feature
of the turn signal indicator switch. A ribbon lead, threaded on rollers in the rotor, links two connectors on the cover to two
connectors on the rotor. Link leads for the driver airbag are installed in one of the connectors on the rotor.
To prevent damage to the ribbon lead, both the steering and the clockspring must be centralized when removing and installing
the clockspring or the steering wheel. The clockspring is centralized when the drive peg is at six o'clock and 50 - 100% of a
yellow wheel is visible in the viewing window.
Replacement clocksprings are fitted with a stopper, which locks the cover to the rotor, in the central position. The stopper must
be broken off when the replacement clockspring is installed.
Page 2619 of 3039
provides the interface connection through which the side impact sensor communicates with the RCM using serial data messages. Acceleration is evaluated by the microchip and transmitted to the restraints control module, which then makes the
decision on whether or not to activate the airbags and pretensioners.
When the ignition is switched on, the RCM supplies power to the impact sensors, which perform a self-test. After satisfactory self tests the impact sensors continually output 'digital acceleration' messages to the restraints control module. If a fault is
detected the relevant impact sensor sends a fault message, instead of the digital acceleration message, to the restraints
control module. The RCM then stores a related fault code and illuminates the airbag warning indicator. Faults can be retrieved by the Jaguar approved diagnostic system from the RCM via the high speed CAN bus connection. www.JagDocs.com
Page 2621 of 3039

Operation of the airbag warning indicator is controlled by a high speed CAN bus message from the RCM to the instrument cluster. The RCM sends the signal to illuminate the airbag warning indicator if a fault is detected, and for approximately 6 seconds during the bulb check at the beginning of each ignition cycle.
Occupant Monitoring
There are two types of occupant monitoring:
In all markets except NAS & Australia, vehicles have an occupant detection sensor
In NAS markets, vehicles have an occupant classification system
For markets which have an occupant detection sensor, this has no interface with the restraints system and only provides the
belt reminder function.
For markets that have an occupant classification system, this provides the RCM with the occupancy status of the front passenger seat. The restraints control module uses this and the seat buckle status in the evaluation of the firing strategy for
the passenger front airbag, side airbag, and pretensioner.
Safety Belt Sensors
The buckle of each front safety belt incorporates a Hall effect sensor that provides a safety belt status signal to the RCM. The RCM broadcasts the status of the two front safety belts on the high speed CAN bus for use by the instrument cluster. In the event of a front impact the RCM will deploy the pretensioners provided the safety belt buckles are fastened. The safety belt buckle pretensioners have a lower deployment threshold than that required by the airbags. Hence it is possible during a minor
collision, which exceeds the deployment threshold and will deploy only the safety belt buckle pretensioners. Airbag Warning Indicator
Page 2624 of 3039

Published: 10-Jul-2014
Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the supplemental restraints system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section in the workshop manual. REFER to: (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System)
Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation), Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation), Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNING: TO AVOID ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY, THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY MUST
BE DEPLETED BEFORE REPAIRING OR REPLACING ANY AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) COMPONENTS. TO
DEPLETE THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY ENERGY, DISCONNECT THE BATTERY GROUND CABLE AND WAIT ONE MINUTE. FAILURE
TO FOLLOW THIS INSTRUCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Given the legal implications of a restraints system failure, harness repairs to Air Bag module circuits are not
acceptable. Where the text refers to "REPAIR the circuit", this will normally mean the replacement of a harness.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation). Electrical
Battery condition, state of charge
Make sure all electrical connector(s) are engaged correctly on the air bag circuits
Wiring harness
Air bag module(s)
Make sure the restraints control module (RCM) is correctly installed
Fuse(s)
Sensor(s)
Pretensioner(s)
Warning lamp bulb(s) Visual Inspection
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2625 of 3039

Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag Disposal
General Procedures
Deployed Air Bag Published: 11-May-2011
1. WARNING: Always wear safety glasses when repairing an air bag
supplemental restraint system (SRS) vehicle and when handling an air
bag module. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal
injury.
Deployed air bag modules are to be disposed of as special waste and
must comply with local environmental requirements, if in doubt, contact
Authority for disposal requirements.
2. NOTE: The storage, transportation, disposal, and/or recycling of air
bag module components must be carried out in accordance with all
applicable federal, state and local regulations including, but not limited
to, those governing building and fire codes, environmental protection,
occupational health and safety, and transportation.
Modules removed and deployed by Jaguar service are to be returned to
the importer for disposal.
Undeployed Air Bag — Inoperative
1. WARNING: Carry a live air bag module with the air bag and trim
cover or deployment door pointed away from your body. This will reduce
the risk of injury in the event of an accidental deployment. Failure to
follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
NOTE: All inoperative air bag modules have been placed on the
Mandatory Return List. All discolored or damaged air bag modules must
be treated the same as any inoperative live air bag being returned.
Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
Remove the inoperative driver air bag module or passenger air bag
module. For additional information Driver Air Bag Module or Passenger Air Bag Module in this section.
Remote Deployment Undeployed Air Bag — Scrapped Vehicle
1. WARNINGS:
Always wear safety glasses when repairing an air bag supplemental
restraint system (SRS) vehicle and when handling an air bag module.
Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
Carry a live air bag module with the air bag and trim cover or
deployment door pointed away from your body. This will reduce the risk
of injury in the event of an accidental deployment. Failure to follow this
instruction may result in personal injury.
Remote deployment is to be carried out outdoors with all personnel
at least 6.1 meters (20 feet) away to ensure personal safety. Due to the
loud report which occurs when the air bag is deployed, hearing protection
is required. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal
injury.
Page 2626 of 3039

Do not place the driver or passenger air bag module with the trim
cover or deployment door facing down, as the forces of the deploying air
bag can cause it to ricochet and cause personal injury. Failure to follow
this instruction may result in personal injury.
Equipment required: Universal deployment tool-Part N° 418-135 and 12V
Battery.
2. The deployment procedure should be carried out outdoors away from
other personnel.
3. Remove any loose debris from around air bag. Make sure that no
flammable liquids are present.
4. Disconnect the battery ground and positive cables.
5. Disconnect the relevant air bag module electrical connector.
6. Connect the appropriate adaptor lead to the restraint device.
7. Connect the deployment lead to the adaptor lead. Pass wire of the
deployment tool through window, close all doors, leave window with lead
for deployment tool open.
8. WARNING: Before proceeding, make sure precautions have been taken
to warn personnel of a possible loud noise upon activation. Do not allow
anybody to approach closer to restraint device than six meters. Failure
to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
Move as far from restraint device as possible and connect the tool clips
to a 12V vehicle battery.
9. WARNING: Do not handle the deployed device immediately after
activation - it may be hot. Allow the unit to cool for at least 20 minutes.
Cooling modules should be continuously monitored to make sure heat
does not create a fire with spilled liquids or other debris. Failure to
follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
Deploy the module by depressing both switches on the tool. If activation
does not occur, disconnect battery from tool and seek advise from Jaguar
Engineering and wait for further instructions.
10. Repeat procedure for all air bags in vehicle.
11. The vehicle is now to be scrapped in the normal manner with modules
installed.
Disposal of live air bag modules for all air bags, using tyres
1. Equipment required: Deployment tool 418-S135, Battery (12V), Safety
goggles to BS2092 grade 2, Rubber gloves to PrEN 374 class 2, Ear
protectors that have been measured to BS.EN 24869, Particulate
respirator to EN 149 grade FFP2S
2. The deployment procedure should be carried out outdoors, away from
other personnel.
3. Stack four scrap tyres, securing together with heavy gauge wire or cable.
Page 2627 of 3039

while disconnected from any electrical power source, connect deployment
harness and place air bag adaptor portion under tyre stack, ready for
connection to air bag.
4. WARNING: Power must not be connected during this step. Failure to
follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
CAUTION: Make sure the connector is not in contact with the
inflator or it will be damaged during the test.
Connect air bag to air bag connector, make sure the locking sleeve is
fully engaged. position the air bag with the cover facing upwards.
5. Make sure battery connections of deployment harness are ten meters
away from the tyre stack
6. Remove any loose from around the air bag . Make sure that no
flammable liquids are present.
7. WARNING: Before proceeding, make sure precautions have been taken
to warn personnel of a possible loud noise upon activation. Do not allow
anybody to approach closer to restraint device than six meters. Failure
to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
Move as far from restraint device as possible and connect the tool clips
to a 12V vehicle battery.
8. WARNING: Do not handle the deployed device immediately after
activation - it may be hot. Allow the unit to cool for at least 20 minutes.
Cooling modules should be continuously monitored to make sure heat
does not create a fire with spilled liquids or other debris. Failure to
follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
Deploy the module by depressing both switches on the tool. If activation
does not occur, disconnect battery from tool and seek advise from Jaguar
Engineering and wait for further instructions.
9. Allow the air bag to cool for at least 20 minutes. Cooling modules should
be continuously monitored to make sure heat generated a fire with
spilled liquids or other debris.
10. Remove the air bag from the tyre stack and seal in a plastic bag, ready
for disposal.
11. In the event of any problems or queries arising from this procedure,
contact Jaguar Engineering.