fuse JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1261 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Starting System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Starting System - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
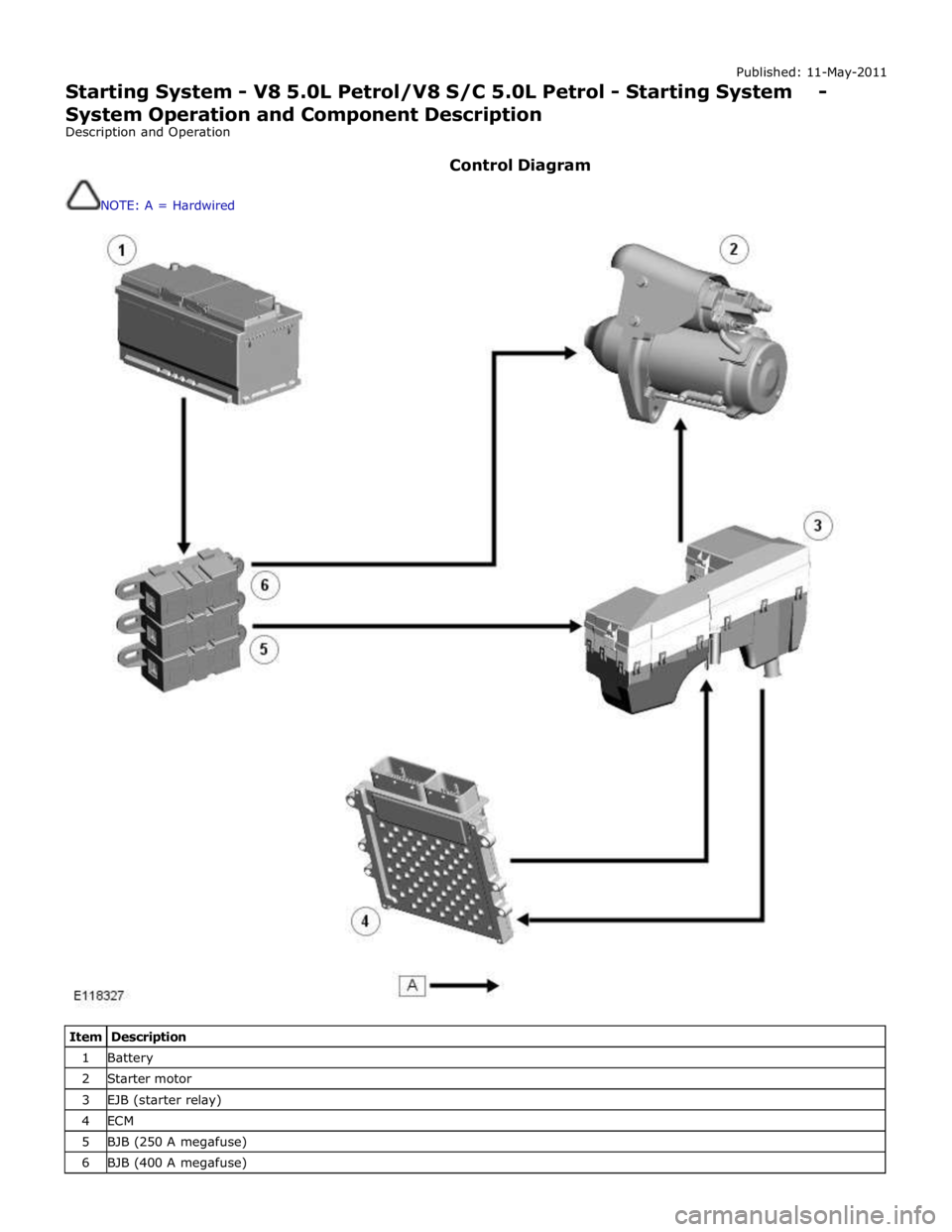
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired
Item Description 1 Battery 2 Starter motor 3 EJB (starter relay) 4 ECM 5 BJB (250 A megafuse) 6 BJB (400 A megafuse)
Page 1262 of 3039

When the ECM receives a crank request, it energizes the starter relay in the EJB (engine junction box). The energized starter relay supplies 12 V power (fed via the 250 A megafuse in the BJB (battery junction box)) to energize the pull-in coil of the
starter solenoid. Once activated, the pull-in coil engages the solenoid plunger, which engages the pinion with the ring gear.
The plunger then closes the solenoid circuit, feeding power from the 400 A megafuse in the BJB to the starter motor.
Page 1263 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Starting System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Starting System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the starting system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section of the
workshop manual. REFER to: (303-06C Starting System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Starting System (Description and Operation), Starting System (Description and Operation), Starting System (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical and electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Gear selector lever cable adjustment (vehicles with automatic
transmission)
Starter motor
Engine (turns freely)
Battery
Fuses
Starter relay
Wiring harness(es)
Damaged, loose or corroded
connectors
Ignition switch
Generator
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action The engine does
not crank (starter
motor does not
turn)
Gear selector not in P or N
position (vehicles with
automatic transmission)
Battery
Starter relay
Invalid key code received by
Central Junction Box (CJB)
Harness/Connectors
Starter motor
Ignition switch
Generator
Transmission Control Module
(TCM)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Engine seized Make sure the gear selector is in the P or N position and correctly
adjusted. Check the battery condition and state of charge. Check for
DTCs indicating an immobilizer fault. Check the starter motor relay,
ignition switch and generator circuits. Refer to the electrical guides.
Check for TCM and ECM DTCs. Check that the engine turns freely. The engine does
not crank (starter
motor does turn)
Starter motor installation
Starter motor
Flywheel/Drive plate ring
gear Check the starter motor installation (fasteners tight, starter motor
square to engine, etc). Check the flywheel/drive plate ring gear teeth
for damage, foreign objects, etc. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1265 of 3039

Starting System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Starting
System Vehicles With: Smart Key
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation Published: 06-Apr-2013
For a detailed description of the starting system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the workshop
manual.
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Steering column
Brake pedal
Smart key
Steering Wheel
Fuses
Harnesses and connectors
Warning lamp operation
Smart key operation
Engine start operation
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) and refer to the DTC Index.
5. Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSM's which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as needed.
CAUTIONS:
Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not guarantee
confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit, part number
3548-1358-00
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If diagnostic trouble codes are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent
concern may be the cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
Symptom Chart
Symptom - Message Displayed Symptom - Possible Cause Action Smart key not found - Refer to handbook Ignition mode fails to switch on GO to Pinpoint Test A.
Page 1273 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Engine Ignition - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Ignition - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
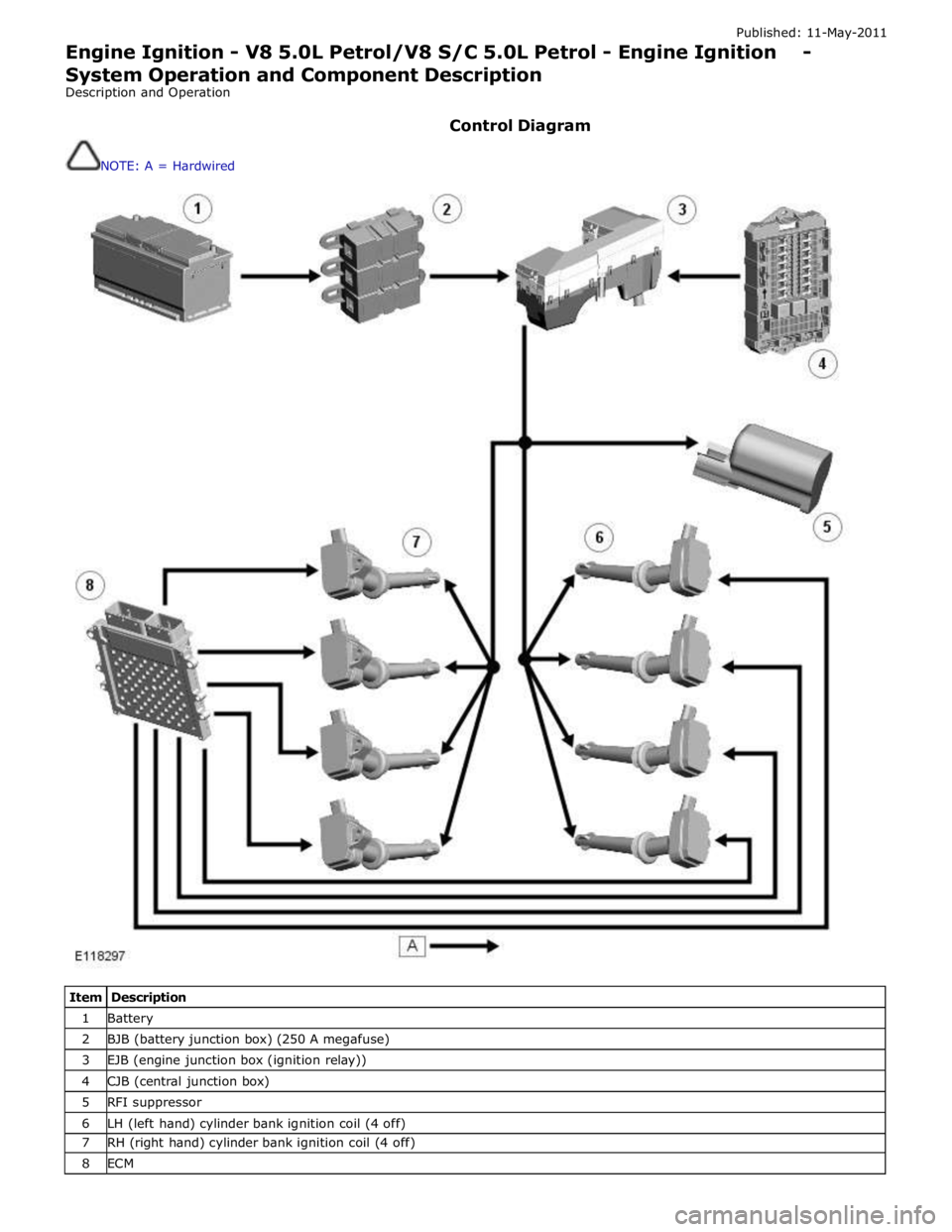
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired
Item Description 1 Battery 2 BJB (battery junction box) (250 A megafuse) 3 EJB (engine junction box (ignition relay)) 4 CJB (central junction box) 5 RFI suppressor 6 LH (left hand) cylinder bank ignition coil (4 off) 7 RH (right hand) cylinder bank ignition coil (4 off) 8 ECM
Page 1274 of 3039
GENERAL System Operation
The ignition coils are supplied with electrical power from the battery via a 250 A megafuse in the BJB (battery junction box)
and the ignition relay in the EJB (engine junction box). The control signal for the ignition relay is supplied by the CJB (central
junction box).
The ECM (engine control module) sends a separate signal to each ignition coil to trigger the power stage switching. The ECM calculates the dwell time from the battery voltage and engine speed, to ensure a constant energy level is produced in the
secondary coil each time the power stage is switched. This ensures sufficient spark energy is available without excessive
primary current flow, which avoids overheating and damage to the ignition coils.
The ECM calculates the ignition timing for individual cylinders from: Engine speed
Camshaft position
Engine load
Engine temperature
The knock control function
The shift control function
The idle speed control function.
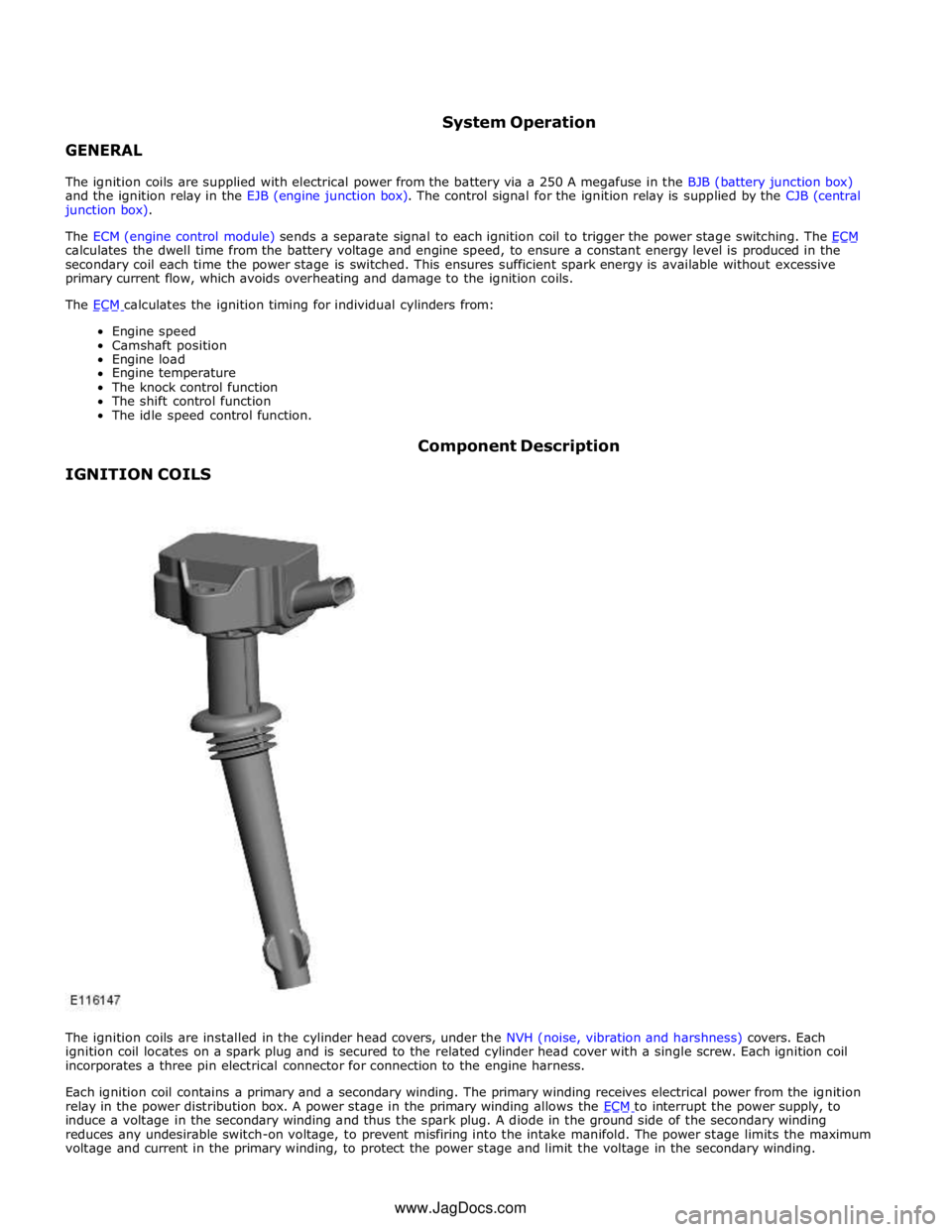
IGNITION COILS Component Description
The ignition coils are installed in the cylinder head covers, under the NVH (noise, vibration and harshness) covers. Each
ignition coil locates on a spark plug and is secured to the related cylinder head cover with a single screw. Each ignition coil
incorporates a three pin electrical connector for connection to the engine harness.
Each ignition coil contains a primary and a secondary winding. The primary winding receives electrical power from the ignition
relay in the power distribution box. A power stage in the primary winding allows the ECM to interrupt the power supply, to induce a voltage in the secondary winding and thus the spark plug. A diode in the ground side of the secondary winding
reduces any undesirable switch-on voltage, to prevent misfiring into the intake manifold. The power stage limits the maximum
voltage and current in the primary winding, to protect the power stage and limit the voltage in the secondary winding. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1276 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Engine Ignition - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Ignition
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the engine ignition system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section
of the workshop manual. REFER to: (303-07B Engine Ignition - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Engine Ignition (Description and Operation), Engine Ignition (Description and Operation), Engine Ignition (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical and electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Engine oil level
Cooling system coolant level
Fuel level
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valves
Fuses
Wiring harness
Loose or corroded electrical connectors
Ignition coils
Sensor(s)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Engine cranks, but does not
fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine control Ensure the engine breather system is free from restriction
and is correctly installed. Check for ignition system, fuel
system and electronic engine control DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine cranks and fires, but
will not start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
HT short to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for
cracks/damage
Ignition system Check for evaporative emissions, fuel system and ignition
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index Difficult cold start
Engine coolant level/anti-
freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve stuck open
Fuel pump
Purge valve Check the engine coolant level and condition. Ensure the
battery is in a fully charged and serviceable condition.
Check for electronic engine controls, engine emissions, fuel
system and evaporative emissions system related DTCs
and refer to the relevant DTC Index
Page 1283 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Engine Emission Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Emission
Control
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the engine emission control system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section of the workshop manual. REFER to: (303-08C Engine Emission Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Engine Emission Control (Description and Operation), Engine Emission Control (Description and Operation), Engine Emission Control (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Exhaust gas recirculation system
Breather hoses
Positive crankcase ventilation valve
Fuel level
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Throttle body
Fuses
Loose or corroded electrical connectors
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve
Engine Control Module (ECM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Difficult to
start cold
Battery
Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve stuck open
Fuel system
Evaporative emissions purge
valve For battery information, CKP sensor, fuel system and purge valve tests,
refer to relevant workshop manual section. Check the EGR valve. Engine stalls
soon after
start
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Engine Control Module (ECM)
relay
MAF sensor
Ignition system
Air filter restricted
Air leakage
Fuel lines Check the engine breather hoses, PCV, etc. Check the Engine Control
Module (ECM) relay operation. For MAF sensor, ignition system tests, air
intake and fuel line information, refer to relevant workshop manual
section. Poor throttle
response
APP sensor malfunction
TP sensors
ECT sensor
MAF sensor
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event Air
leakage For APP, TP, ECT, MAF sensor tests, intake system checks and
transmission information, refer to relevant workshop manual section.
Check the breather system hoses, PCV, etc.
Page 1288 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired
Item Description 1 Battery 2 BJB (battery junction box) (250 A megafuse) 3 EJB (engine junction box) (EMS high current relay) 4 Tuning valve 5 ECM (engine control module)
Page 1349 of 3039

Published: 03-Jun-2014
Evaporative Emissions - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Evaporative
Emissions
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the Evaporative Emissions system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the
workshop manual.
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Fuel filler cap and seal
Fuel filler neck
Fuel pipes
Fuel tank
Evaporative emissions canister
Purge valve
Fuses
Wiring harnesses and connectors
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Purge valve
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index
5. Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Difficulty in filling
fuel tank
Restriction in the vapour line between the fuel tank and the
carbon canister outlet/atmospheric port
Check for
restrictions/damage Fuel smell
System leak
Purge valve inoperative
Check for leaks
Check the purge valve
operation DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.