air bleeding JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1997, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.GPages: 227, PDF Size: 7.2 MB
Page 123 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
9
Chapter 9
Braking system
General
Brake fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Minimum brake pad thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc minimum permissible thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cast into disc
Parallelism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch) maximum
Runout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.102 mm (0.004 inch) maximum
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Brake servo mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Caliper bolts (front and rear) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 to 40 23 to 29
Caliper bracket bolts
Front bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102 to 128 75 to 94
Rear bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 to 62 40 to 45
Master cylinder-to-brake servo nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 28 16 to 20
Wheel nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Specifications Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Brake fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake hoses and lines - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Brake hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Brake light switch - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Brake servo - general information, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 7Disc brake caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Disc brake pads - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Handbrake cable - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Handbrake cables - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Handbrake shoes - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Master cylinder - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
9•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
1 General information
All models covered by this manual are
equipped with hydraulically operated front
and rear disc brake systems. Both front and
rear brakes are self adjusting.
Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system is divided into
two separate circuits. The master cylinder has
separate reservoirs for the two circuits, and, in
the event of a leak or failure in one hydraulic
circuit, the other circuit will remain operative.
All models are equipped with an Anti-lock
Braking System (ABS).
Brake servo
A hydraulic brake servo system is used on
all models covered by this manual. Thissystem uses hydraulic pressure from an
engine-driven pump on models equipped with
a power hydraulic system, and an electric
pump on models without the power hydraulic
system.
Handbrake
The handbrake lever operates the rear
brakes through cable actuation. It’s activated
by a lever mounted in the centre console. The
handbrake assembly uses a pair of brake
shoes located inside the rear hub/brake disc.
Brake pad wear warning system
The brake pad wear warning system turns
on a red light in the instrument cluster when
the brake pads have worn down to the point
at which they must be replaced. Do NOT
ignore this reminder. If you don’t renew the
pads shortly after the brake pad wear warning
light comes on, the brake discs will be
damaged.The wear sensors are attached to the brake
pads. Once the pads wear down to the point
at which they’re flush with the sensor, the disc
grinds away the side of the sensor facing the
disc, the wire inside the sensor is broken, the
circuit is opened and the red light on the
instrument panel comes on.
Always check the sensor(s) when replacing
the pads. If you change the pads before the
warning light comes on, the sensor(s) may still
be good; once the light has come on, renew
the sensor.
Service
After completing any operation involving
dismantling of any part of the brake system,
always test drive the vehicle to check for
proper braking performance before resuming
normal driving. When testing the brakes,
perform the tests on a clean, dry, flat surface.
Conditions other than these can lead to
inaccurate test results.
Page 128 of 227
Refitting
8Place the disc on the hub and refit the disc
retaining screw. Tighten the screw securely.
9Refit the caliper mounting bracket, using a
new safety wire on the mounting bolts.
10Refit the brake pads and caliper (see
Section 3). Tighten all fasteners to the torque
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
11Refit the wheel and wheel nuts, then lower
the vehicle to the ground. Tighten the wheel
nuts to the specified torque (see Chapter 1
Specifications). Depress the brake pedal a
few times to bring the brake pads into contact
with the disc.
12Adjust the handbrake shoes, if necessary.
13Check the operation of the brakes
carefully, if possible before driving the vehicle
on public roads.
6 Master cylinder- removal,
overhaul and refitting
3
Note:Although master cylinder parts and
rebuild kits are available for most models, we
recommend replacing the master cylinder with
a new or remanufactured unit, if possible.
Removal
1The master cylinder is connected to the
brake servo, which is attached to the pedal
box, in front of the bulkhead on the driver’s
side of the engine compartment.
2Remove as much fluid as you can from the
reservoir with a syringe.
3Place rags under the line fittings and
prepare caps or plastic bags to cover the
ends of the lines once they are disconnected.
Caution: Brake fluid will damage paint.
Cover all body parts and be careful not to
spill fluid during this procedure.
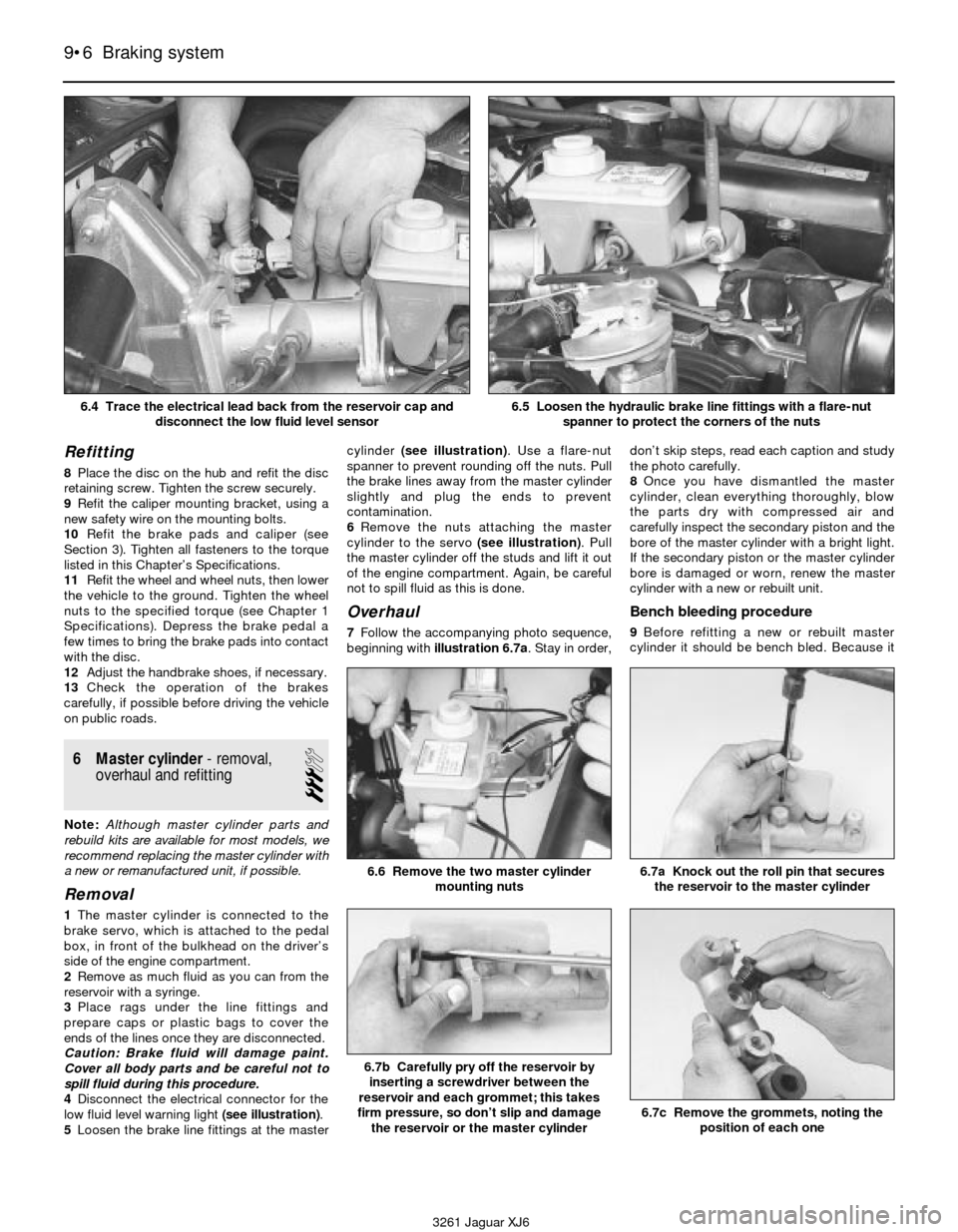
4Disconnect the electrical connector for the
low fluid level warning light (see illustration).
5Loosen the brake line fittings at the mastercylinder (see illustration). Use a flare-nut
spanner to prevent rounding off the nuts. Pull
the brake lines away from the master cylinder
slightly and plug the ends to prevent
contamination.
6Remove the nuts attaching the master
cylinder to the servo (see illustration). Pull
the master cylinder off the studs and lift it out
of the engine compartment. Again, be careful
not to spill fluid as this is done.
Overhaul
7Follow the accompanying photo sequence,
beginning with illustration 6.7a. Stay in order,don’t skip steps, read each caption and study
the photo carefully.
8Once you have dismantled the master
cylinder, clean everything thoroughly, blow
the parts dry with compressed air and
carefully inspect the secondary piston and the
bore of the master cylinder with a bright light.
If the secondary piston or the master cylinder
bore is damaged or worn, renew the master
cylinder with a new or rebuilt unit.
Bench bleeding procedure
9Before refitting a new or rebuilt master
cylinder it should be bench bled. Because it
9•6 Braking system
6.7a Knock out the roll pin that secures
the reservoir to the master cylinder
6.7b Carefully pry off the reservoir by
inserting a screwdriver between the
reservoir and each grommet; this takes
firm pressure, so don’t slip and damage
the reservoir or the master cylinder
6.7c Remove the grommets, noting the
position of each one
6.6 Remove the two master cylinder
mounting nuts
3261 Jaguar XJ6 6.4 Trace the electrical lead back from the reservoir cap and
disconnect the low fluid level sensor
6.5 Loosen the hydraulic brake line fittings with a flare-nut
spanner to protect the corners of the nuts
Page 130 of 227

will be necessary to apply pressure to the
master cylinder piston and, at the same time,
control flow from the brake line outlets, it is
recommended that the master cylinder be
mounted in a vice. Use caution not to clamp
the vice too tightly, or the master cylinder
body might crack.
10Insert threaded plugs into the brake line
outlet holes and snug them down so that
there will be no air leakage past them, but not
so tight that they cannot be easily loosened.
11Fill the reservoir with brake fluid of the
recommended type (see Recommended
lubricants and fluidsin Chapter 1).
12Remove one plug and push the piston
assembly into the master cylinder bore to
expel the air from the master cylinder. A large
Phillips screwdriver can be used to push on
the piston assembly.
13To prevent air from being drawn back into
the master cylinder, the plug must be
replaced and tightened before releasing the
pressure on the piston assembly.
14Repeat the procedure until only brake
fluid is expelled from the brake line outlet
hole. When only brake fluid is expelled, repeat
the procedure with the other outlet hole and
plug. Be sure to keep the master cylinder
reservoir filled with brake fluid to prevent the
introduction of air into the system.
15Since high pressure is not involved in the
bench bleeding procedure, an alternative to
the removal and renewal of the plugs witheach stroke of the piston assembly is
available. Before pushing in on the piston
assembly, remove the plug as described inStep 12. Before releasing the piston, however,
instead of replacing the plug, simply put your
finger tightly over the hole to keep air from
9•8 Braking system
6.7m Apply some clean brake fluid to the
secondary piston and refit it with the slot
oriented with the stopper pin hole, so that
the stopper pin will go through the slot6.7n Apply a coat of clean brake fluid to
the primary piston and refit it into the bore6.7o Using the same technique as in
illustration 6.7f, depress the pistons and
refit the stopper pin
6.7p Refit the end plate as shown, with the
bend in the plate flange aligned with the
groove in the master cylinder flange6.7q Using a hammer and punch, stake
the end plate as shown (there’s a dimple in
the side of the plate for this purpose)6.7r Refit the grommets
3261 Jaguar XJ6
6.7s Align the reservoir pipes with the
grommets as shown . . .
6.7u Refit the reservoir roll pin . . .6.7v . . . and tap it into place
6.7t . . . and squeeze the reservoir and
master cylinder together; make sure the
reservoir is fully seated
Page 131 of 227
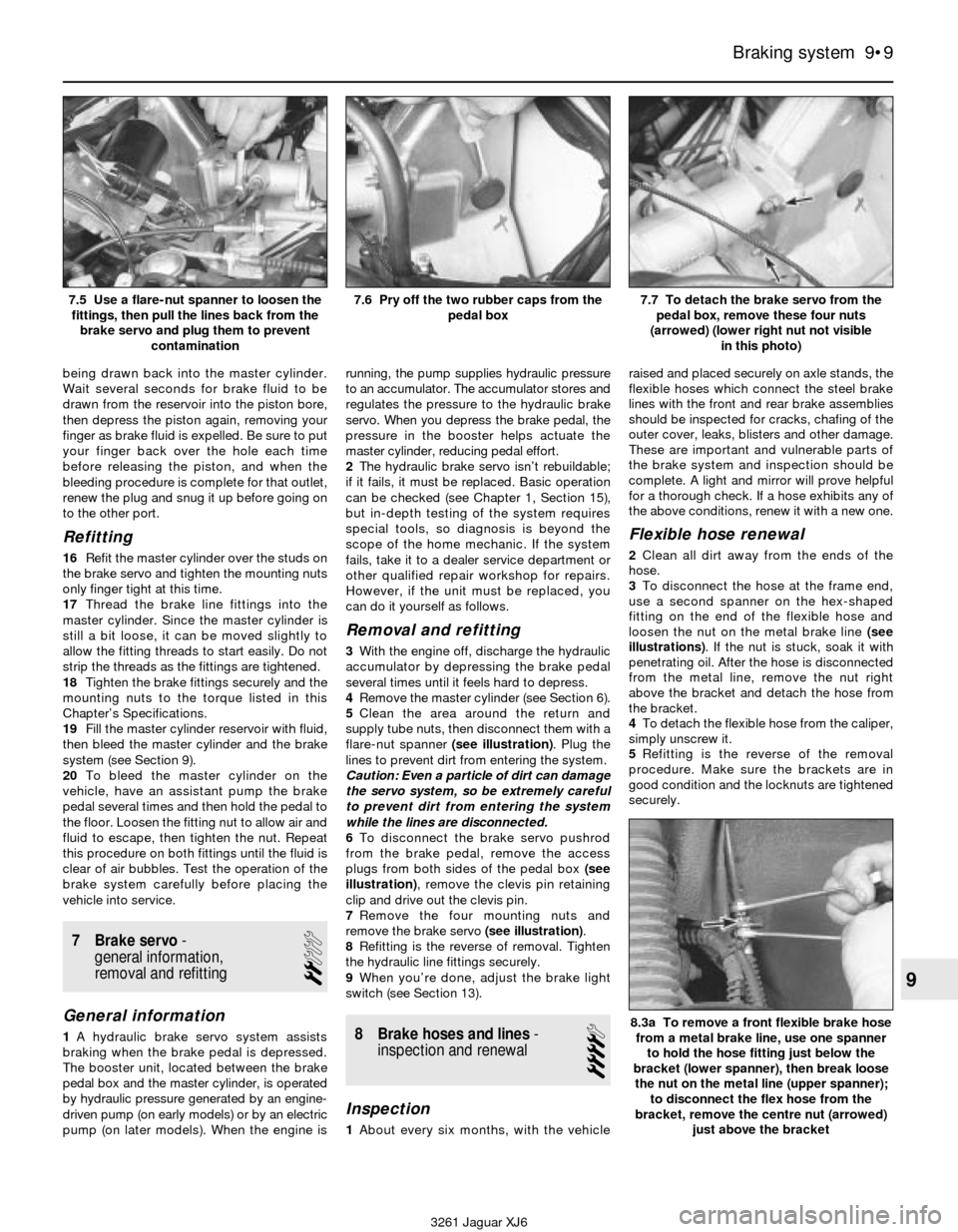
being drawn back into the master cylinder.
Wait several seconds for brake fluid to be
drawn from the reservoir into the piston bore,
then depress the piston again, removing your
finger as brake fluid is expelled. Be sure to put
your finger back over the hole each time
before releasing the piston, and when the
bleeding procedure is complete for that outlet,
renew the plug and snug it up before going on
to the other port.
Refitting
16Refit the master cylinder over the studs on
the brake servo and tighten the mounting nuts
only finger tight at this time.
17Thread the brake line fittings into the
master cylinder. Since the master cylinder is
still a bit loose, it can be moved slightly to
allow the fitting threads to start easily. Do not
strip the threads as the fittings are tightened.
18Tighten the brake fittings securely and the
mounting nuts to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
19Fill the master cylinder reservoir with fluid,
then bleed the master cylinder and the brake
system (see Section 9).
20To bleed the master cylinder on the
vehicle, have an assistant pump the brake
pedal several times and then hold the pedal to
the floor. Loosen the fitting nut to allow air and
fluid to escape, then tighten the nut. Repeat
this procedure on both fittings until the fluid is
clear of air bubbles. Test the operation of the
brake system carefully before placing the
vehicle into service.
7 Brake servo-
general information,
removal and refitting
2
General information
1A hydraulic brake servo system assists
braking when the brake pedal is depressed.
The booster unit, located between the brake
pedal box and the master cylinder, is operated
by hydraulic pressure generated by an engine-
driven pump (on early models) or by an electric
pump (on later models). When the engine isrunning, the pump supplies hydraulic pressure
to an accumulator. The accumulator stores and
regulates the pressure to the hydraulic brake
servo. When you depress the brake pedal, the
pressure in the booster helps actuate the
master cylinder, reducing pedal effort.
2The hydraulic brake servo isn’t rebuildable;
if it fails, it must be replaced. Basic operation
can be checked (see Chapter 1, Section 15),
but in-depth testing of the system requires
special tools, so diagnosis is beyond the
scope of the home mechanic. If the system
fails, take it to a dealer service department or
other qualified repair workshop for repairs.
However, if the unit must be replaced, you
can do it yourself as follows.
Removal and refitting
3With the engine off, discharge the hydraulic
accumulator by depressing the brake pedal
several times until it feels hard to depress.
4Remove the master cylinder (see Section 6).
5Clean the area around the return and
supply tube nuts, then disconnect them with a
flare-nut spanner (see illustration). Plug the
lines to prevent dirt from entering the system.
Caution: Even a particle of dirt can damage
the servo system, so be extremely careful
to prevent dirt from entering the system
while the lines are disconnected.
6To disconnect the brake servo pushrod
from the brake pedal, remove the access
plugs from both sides of the pedal box (see
illustration), remove the clevis pin retaining
clip and drive out the clevis pin.
7Remove the four mounting nuts and
remove the brake servo (see illustration).
8Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the hydraulic line fittings securely.
9When you’re done, adjust the brake light
switch (see Section 13).
8 Brake hoses and lines-
inspection and renewal
4
Inspection
1About every six months, with the vehicleraised and placed securely on axle stands, the
flexible hoses which connect the steel brake
lines with the front and rear brake assemblies
should be inspected for cracks, chafing of the
outer cover, leaks, blisters and other damage.
These are important and vulnerable parts of
the brake system and inspection should be
complete. A light and mirror will prove helpful
for a thorough check. If a hose exhibits any of
the above conditions, renew it with a new one.
Flexible hose renewal
2Clean all dirt away from the ends of the
hose.
3To disconnect the hose at the frame end,
use a second spanner on the hex-shaped
fitting on the end of the flexible hose and
loosen the nut on the metal brake line (see
illustrations). If the nut is stuck, soak it with
penetrating oil. After the hose is disconnected
from the metal line, remove the nut right
above the bracket and detach the hose from
the bracket.
4To detach the flexible hose from the caliper,
simply unscrew it.
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Make sure the brackets are in
good condition and the locknuts are tightened
securely.
Braking system 9•9
9
7.5 Use a flare-nut spanner to loosen the
fittings, then pull the lines back from the
brake servo and plug them to prevent
contamination7.6 Pry off the two rubber caps from the
pedal box7.7 To detach the brake servo from the
pedal box, remove these four nuts
(arrowed) (lower right nut not visible
in this photo)
8.3a To remove a front flexible brake hose
from a metal brake line, use one spanner
to hold the hose fitting just below the
bracket (lower spanner), then break loose
the nut on the metal line (upper spanner);
to disconnect the flex hose from the
bracket, remove the centre nut (arrowed)
just above the bracket
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 132 of 227
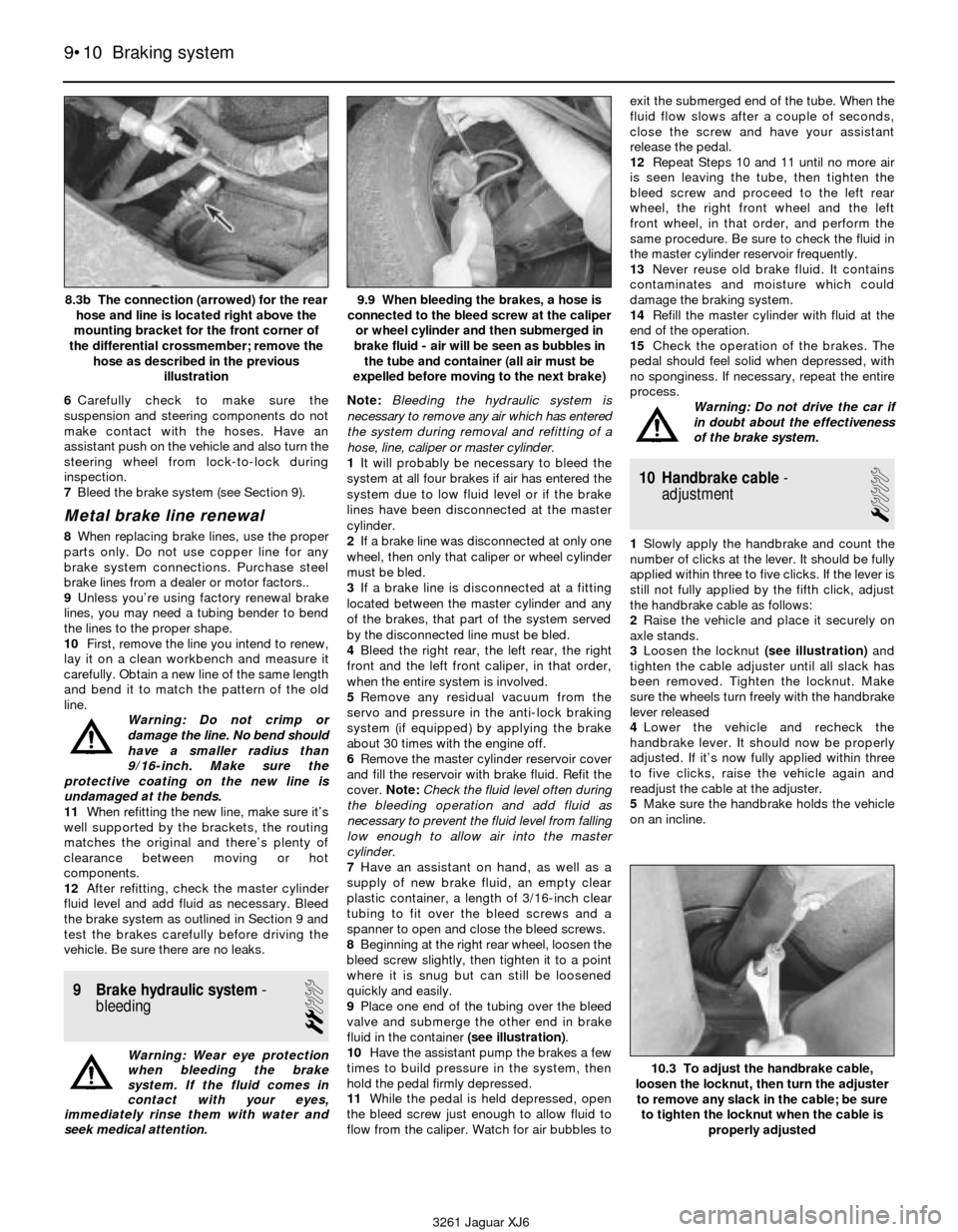
6Carefully check to make sure the
suspension and steering components do not
make contact with the hoses. Have an
assistant push on the vehicle and also turn the
steering wheel from lock-to-lock during
inspection.
7Bleed the brake system (see Section 9).
Metal brake line renewal
8When replacing brake lines, use the proper
parts only. Do not use copper line for any
brake system connections. Purchase steel
brake lines from a dealer or motor factors..
9Unless you’re using factory renewal brake
lines, you may need a tubing bender to bend
the lines to the proper shape.
10First, remove the line you intend to renew,
lay it on a clean workbench and measure it
carefully. Obtain a new line of the same length
and bend it to match the pattern of the old
line.
Warning: Do not crimp or
damage the line. No bend should
have a smaller radius than
9/16-inch. Make sure the
protective coating on the new line is
undamaged at the bends.
11When refitting the new line, make sure it’s
well supported by the brackets, the routing
matches the original and there’s plenty of
clearance between moving or hot
components.
12After refitting, check the master cylinder
fluid level and add fluid as necessary. Bleed
the brake system as outlined in Section 9 and
test the brakes carefully before driving the
vehicle. Be sure there are no leaks.
9 Brake hydraulic system-
bleeding
2
Warning: Wear eye protection
when bleeding the brake
system. If the fluid comes in
contact with your eyes,
immediately rinse them with water and
seek medical attention.Note:Bleeding the hydraulic system is
necessary to remove any air which has entered
the system during removal and refitting of a
hose, line, caliper or master cylinder.
1It will probably be necessary to bleed the
system at all four brakes if air has entered the
system due to low fluid level or if the brake
lines have been disconnected at the master
cylinder.
2If a brake line was disconnected at only one
wheel, then only that caliper or wheel cylinder
must be bled.
3If a brake line is disconnected at a fitting
located between the master cylinder and any
of the brakes, that part of the system served
by the disconnected line must be bled.
4Bleed the right rear, the left rear, the right
front and the left front caliper, in that order,
when the entire system is involved.
5Remove any residual vacuum from the
servo and pressure in the anti-lock braking
system (if equipped) by applying the brake
about 30 times with the engine off.
6Remove the master cylinder reservoir cover
and fill the reservoir with brake fluid. Refit the
cover. Note:Check the fluid level often during
the bleeding operation and add fluid as
necessary to prevent the fluid level from falling
low enough to allow air into the master
cylinder.
7Have an assistant on hand, as well as a
supply of new brake fluid, an empty clear
plastic container, a length of 3/16-inch clear
tubing to fit over the bleed screws and a
spanner to open and close the bleed screws.
8Beginning at the right rear wheel, loosen the
bleed screw slightly, then tighten it to a point
where it is snug but can still be loosened
quickly and easily.
9Place one end of the tubing over the bleed
valve and submerge the other end in brake
fluid in the container (see illustration).
10Have the assistant pump the brakes a few
times to build pressure in the system, then
hold the pedal firmly depressed.
11While the pedal is held depressed, open
the bleed screw just enough to allow fluid to
flow from the caliper. Watch for air bubbles toexit the submerged end of the tube. When the
fluid flow slows after a couple of seconds,
close the screw and have your assistant
release the pedal.
12Repeat Steps 10 and 11 until no more air
is seen leaving the tube, then tighten the
bleed screw and proceed to the left rear
wheel, the right front wheel and the left
front wheel, in that order, and perform the
same procedure. Be sure to check the fluid in
the master cylinder reservoir frequently.
13Never reuse old brake fluid. It contains
contaminates and moisture which could
damage the braking system.
14Refill the master cylinder with fluid at the
end of the operation.
15Check the operation of the brakes. The
pedal should feel solid when depressed, with
no sponginess. If necessary, repeat the entire
process.
Warning: Do not drive the car if
in doubt about the effectiveness
of the brake system.
10 Handbrake cable-
adjustment
1
1Slowly apply the handbrake and count the
number of clicks at the lever. It should be fully
applied within three to five clicks. If the lever is
still not fully applied by the fifth click, adjust
the handbrake cable as follows:
2Raise the vehicle and place it securely on
axle stands.
3Loosen the locknut (see illustration)and
tighten the cable adjuster until all slack has
been removed. Tighten the locknut. Make
sure the wheels turn freely with the handbrake
lever released
4Lower the vehicle and recheck the
handbrake lever. It should now be properly
adjusted. If it’s now fully applied within three
to five clicks, raise the vehicle again and
readjust the cable at the adjuster.
5Make sure the handbrake holds the vehicle
on an incline.
9•10 Braking system
8.3b The connection (arrowed) for the rear
hose and line is located right above the
mounting bracket for the front corner of
the differential crossmember; remove the
hose as described in the previous
illustration9.9 When bleeding the brakes, a hose is
connected to the bleed screw at the caliper
or wheel cylinder and then submerged in
brake fluid - air will be seen as bubbles in
the tube and container (all air must be
expelled before moving to the next brake)
10.3 To adjust the handbrake cable,
loosen the locknut, then turn the adjuster
to remove any slack in the cable; be sure
to tighten the locknut when the cable is
properly adjusted
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 137 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
10
Chapter 10
Suspension and steering systems
General
Power steering fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Front suspension
Balljoints
Retaining bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 to 62 41 to 45
Ball stud nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 to 68 35 to 50
Lower control arm
Spring pan bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 to 34 19 to 25
Pivot nuts/bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 to 68 32 to 50
Shock absorber
Lower nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61 to 68 45 to 50
Upper nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 to 43 26 to 31
Anti-roll bar
Bushing bracket bolts
Upper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 28 16 to 20
Lower . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 to 30 18 to 22
Link nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 to 60 41 to 44
Upper control arm pivot nuts/bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61 to 75 45 to 55
Rear suspension
Carrier-to-control arm bolt/nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 to 80 51 to 59
Rear control arm-to-crossmember bolt/nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 105 62 to 77
Shock absorber/coil spring assembly
Lower shock-to-control arm bolt/nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160 to 200 118 to 147
Upper shock-to-body bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 28 16 to 20
Steering
Steering wheel-to-steering shaft nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 to 45 26 to 33
Steering shaft-to-steering gear pinion shaft U-joint pinch bolt . . . . . . . 19 to 24 14 to 17
Steering gear mounting bracket bolts/nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 to 29 19 to 21
Tie-rod end-to-steering knuckle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61 to 68 45 to 50 Anti-roll bar (front) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Balljoints - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Coil spring (front) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Control arm (rear) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Front wheel bearing - check, repack and adjustment . . See Chapter 1
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Hub and bearing (rear) - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Hub carrier (rear) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Lower control arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Power steering fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Power steering pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Power steering system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Self-levelling rear suspension system - general information . . . . . . . 2
Shock absorber (front) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4Shock absorber/coil spring (rear) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 10
Steering and suspension check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Steering gear - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Steering gear boots - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Steering knuckle - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Steering wheel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Suspension and steering checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Tie-rod ends - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Tyre and tyre pressure checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Tyre rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Upper control arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Wheel alignment - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Wheel bearing lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Wheels and tyres - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
10•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 147 of 227
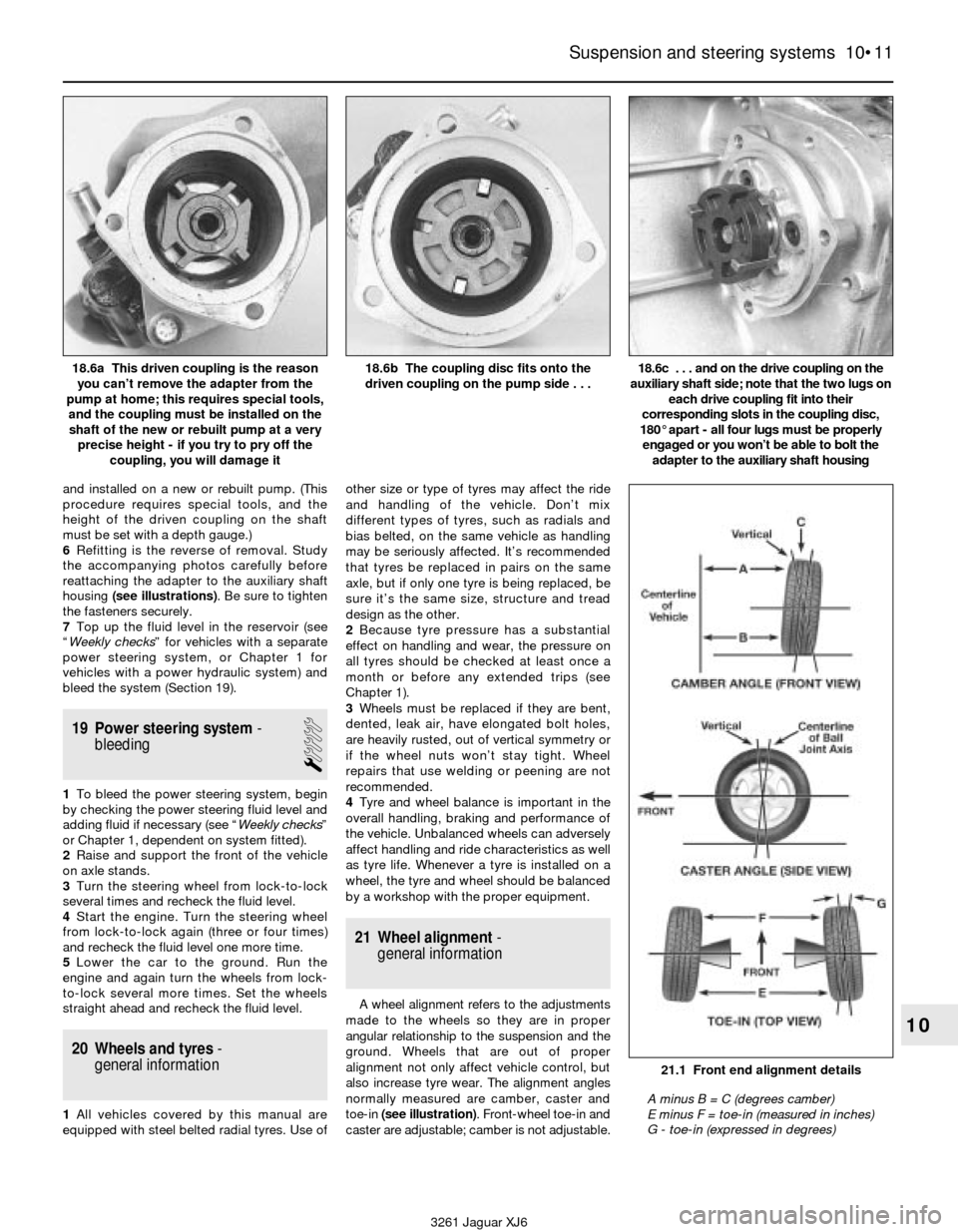
and installed on a new or rebuilt pump. (This
procedure requires special tools, and the
height of the driven coupling on the shaft
must be set with a depth gauge.)
6Refitting is the reverse of removal. Study
the accompanying photos carefully before
reattaching the adapter to the auxiliary shaft
housing (see illustrations). Be sure to tighten
the fasteners securely.
7Top up the fluid level in the reservoir (see
“Weekly checks” for vehicles with a separate
power steering system, or Chapter 1 for
vehicles with a power hydraulic system) and
bleed the system (Section 19).
19 Power steering system-
bleeding
1
1To bleed the power steering system, begin
by checking the power steering fluid level and
adding fluid if necessary (see “Weekly checks”
or Chapter 1, dependent on system fitted).
2Raise and support the front of the vehicle
on axle stands.
3Turn the steering wheel from lock-to-lock
several times and recheck the fluid level.
4Start the engine. Turn the steering wheel
from lock-to-lock again (three or four times)
and recheck the fluid level one more time.
5Lower the car to the ground. Run the
engine and again turn the wheels from lock-
to-lock several more times. Set the wheels
straight ahead and recheck the fluid level.
20 Wheels and tyres-
general information
1All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with steel belted radial tyres. Use ofother size or type of tyres may affect the ride
and handling of the vehicle. Don’t mix
different types of tyres, such as radials and
bias belted, on the same vehicle as handling
may be seriously affected. It’s recommended
that tyres be replaced in pairs on the same
axle, but if only one tyre is being replaced, be
sure it’s the same size, structure and tread
design as the other.
2Because tyre pressure has a substantial
effect on handling and wear, the pressure on
all tyres should be checked at least once a
month or before any extended trips (see
Chapter 1).
3Wheels must be replaced if they are bent,
dented, leak air, have elongated bolt holes,
are heavily rusted, out of vertical symmetry or
if the wheel nuts won’t stay tight. Wheel
repairs that use welding or peening are not
recommended.
4Tyre and wheel balance is important in the
overall handling, braking and performance of
the vehicle. Unbalanced wheels can adversely
affect handling and ride characteristics as well
as tyre life. Whenever a tyre is installed on a
wheel, the tyre and wheel should be balanced
by a workshop with the proper equipment.
21 Wheel alignment-
general information
A wheel alignment refers to the adjustments
made to the wheels so they are in proper
angular relationship to the suspension and the
ground. Wheels that are out of proper
alignment not only affect vehicle control, but
also increase tyre wear. The alignment angles
normally measured are camber, caster and
toe-in (see illustration). Front-wheel toe-in and
caster are adjustable; camber is not adjustable.
Suspension and steering systems 10•11
10
3261 Jaguar XJ6 18.6a This driven coupling is the reason
you can’t remove the adapter from the
pump at home; this requires special tools,
and the coupling must be installed on the
shaft of the new or rebuilt pump at a very
precise height - if you try to pry off the
coupling, you will damage it
18.6b The coupling disc fits onto the
driven coupling on the pump side . . .18.6c . . . and on the drive coupling on the
auxiliary shaft side; note that the two lugs on
each drive coupling fit into their
corresponding slots in the coupling disc,
180° apart - all four lugs must be properly
engaged or you won’t be able to bolt the
adapter to the auxiliary shaft housing
21.1 Front end alignment details
A minus B = C (degrees camber)
E minus F = toe-in (measured in inches)
G - toe-in (expressed in degrees)
Page 207 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
REF•6Tools and working facilities
Introduction
A selection of good tools is a fundamental
requirement for anyone contemplating the
maintenance and repair of a motor vehicle.
For the owner who does not possess any,
their purchase will prove a considerable
expense, offsetting some of the savings made
by doing-it-yourself. However, provided that
the tools purchased meet the relevant national
safety standards and are of good quality, they
will last for many years and prove an
extremely worthwhile investment.
To help the average owner to decide which
tools are needed to carry out the various tasks
detailed in this manual, we have compiled
three lists of tools under the following
headings: Maintenance and minor repair,
Repair and overhaul, and Special. Newcomers
to practical mechanics should start off with
the Maintenance and minor repairtool kit, and
confine themselves to the simpler jobs around
the vehicle. Then, as confidence and
experience grow, more difficult tasks can be
undertaken, with extra tools being purchased
as, and when, they are needed. In this way, a
Maintenance and minor repairtool kit can be
built up into a Repair and overhaultool kit over
a considerable period of time, without any
major cash outlays. The experienced do-it-
yourselfer will have a tool kit good enough for
most repair and overhaul procedures, and will
add tools from the Specialcategory when it is
felt that the expense is justified by the amount
of use to which these tools will be put.
Maintenance
and minor repair tool kit
The tools given in this list should be
considered as a minimum requirement if
routine maintenance, servicing and minor
repair operations are to be undertaken. We
recommend the purchase of combination
spanners (ring one end, open-ended the
other); although more expensive than open-
ended ones, they do give the advantages of
both types of spanner.
MCombination spanners:
Metric - 8 to 19 mm inclusive
MAdjustable spanner - 35 mm jaw (approx.)
MSpark plug spanner (with rubber insert) -
petrol models
MSpark plug gap adjustment tool - petrol
models
MSet of feeler blades
MBrake bleed nipple spanner
MScrewdrivers:
Flat blade - 100 mm long x 6 mm dia
Cross blade - 100 mm long x 6 mm dia
MCombination pliers
MHacksaw (junior)
MTyre pump
MTyre pressure gauge
MOil can
MOil filter removal tool
MFine emery cloth
MWire brush (small)
MFunnel (medium size)
Repair and overhaul tool kit
These tools are virtually essential for
anyone undertaking any major repairs to a
motor vehicle, and are additional to those
given in the Maintenance and minor repairlist.
Included in this list is a comprehensive set of
sockets. Although these are expensive, they
will be found invaluable as they are so
versatile - particularly if various drives are
included in the set. We recommend the half-
inch square-drive type, as this can be used
with most proprietary torque wrenches.
The tools in this list will sometimes need to
be supplemented by tools from the Speciallist:
MSockets (or box spanners) to cover range in
previous list (including Torx sockets)
MReversible ratchet drive (for use with
sockets)
MExtension piece, 250 mm (for use with
sockets)
MUniversal joint (for use with sockets)
MTorque wrench (for use with sockets)
MSelf-locking grips
MBall pein hammer
MSoft-faced mallet (plastic/aluminium or
rubber)
MScrewdrivers:
Flat blade - long & sturdy, short (chubby),
and narrow (electrician’s) types
Cross blade – Long & sturdy, and short
(chubby) types
MPliers:
Long-nosed
Side cutters (electrician’s)
Circlip (internal and external)
MCold chisel - 25 mm
MScriber
MScraper
MCentre-punch
MPin punch
MHacksaw
MBrake hose clamp
MBrake/clutch bleeding kit
MSelection of twist drills
MSteel rule/straight-edge
MAllen keys (inc. splined/Torx type)
MSelection of files
MWire brush
MAxle stands
MJack (strong trolley or hydraulic type)
MLight with extension lead
Sockets and reversible ratchet drive
Clutch plate alignment setPiston ring compressorSpline bit set
Valve spring compressor
Page 209 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
REF•8MOT test checks
This is a guide to getting your vehicle through the MOT test.
Obviously it will not be possible to examine the vehicle to the same
standard as the professional MOT tester. However, working through
the following checks will enable you to identify any problem areas
before submitting the vehicle for the test.
Where a testable component is in borderline condition, the tester
has discretion in deciding whether to pass or fail it. The basis of such
discretion is whether the tester would be happy for a close relative or
friend to use the vehicle with the component in that condition. If the
vehicle presented is clean and evidently well cared for, the tester may
be more inclined to pass a borderline component than if the vehicle is
scruffy and apparently neglected.
It has only been possible to summarise the test requirements here,
based on the regulations in force at the time of printing. Test standards
are becoming increasingly stringent, although there are some
exemptions for older vehicles. For full details obtain a copy of the Haynes
publication Pass the MOT! (available from stockists of Haynes manuals).
An assistant will be needed to help carry out some of these checks.
The checks have been sub-divided into four categories, as follows:
HandbrakeMTest the operation of the handbrake.
Excessive travel (too many clicks) indicates
incorrect brake or cable adjustment.
MCheck that the handbrake cannot be
released by tapping the lever sideways. Check
the security of the lever mountings.
Footbrake
MDepress the brake pedal and check that it
does not creep down to the floor, indicating a
master cylinder fault. Release the pedal, wait
a few seconds, then depress it again. If the
pedal travels nearly to the floor before firm
resistance is felt, brake adjustment or repair is
necessary. If the pedal feels spongy, there is
air in the hydraulic system which must be
removed by bleeding.MCheck that the brake pedal is secure and in
good condition. Check also for signs of fluid
leaks on the pedal, floor or carpets, which
would indicate failed seals in the brake master
cylinder.
MCheck the servo unit (when applicable) by
operating the brake pedal several times, then
keeping the pedal depressed and starting the
engine. As the engine starts, the pedal will
move down slightly. If not, the vacuum hose or
the servo itself may be faulty.
Steering wheel and column
MExamine the steering wheel for fractures or
looseness of the hub, spokes or rim.
MMove the steering wheel from side to side
and then up and down. Check that the
steering wheel is not loose on the column,
indicating wear or a loose retaining nut.
Continue moving the steering wheel as before,
but also turn it slightly from left to right.
MCheck that the steering wheel is not loose
on the column, and that there is no abnormalmovement of the steering wheel, indicating
wear in the column support bearings or
couplings.
Windscreen and mirrors
MThe windscreen must be free of cracks or
other significant damage within the driver’s
field of view. (Small stone chips are
acceptable.) Rear view mirrors must be
secure, intact, and capable of being adjusted.
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S SEAT
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S
SEAT2Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
ON THE GROUND3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
RAISED AND THE
WHEELS FREE TO
TURN4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S
EXHAUST EMISSION
SYSTEM
Page 219 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
REF•18Glossary of technical terms
A
ABS (Anti-lock brake system)A system,
usually electronically controlled, that senses
incipient wheel lockup during braking and
relieves hydraulic pressure at wheels that are
about to skid.
Air bag An inflatable bag hidden in the
steering wheel (driver’s side) or the dash or
glovebox (passenger side). In a head-on
collision, the bags inflate, preventing the
driver and front passenger from being thrown
forward into the steering wheel or windscreen.
Air cleanerA metal or plastic housing,
containing a filter element, which removes
dust and dirt from the air being drawn into the
engine.
Air filter elementThe actual filter in an air
cleaner system, usually manufactured from
pleated paper and requiring renewal at regular
intervals.
Allen keyA hexagonal wrench which fits into
a recessed hexagonal hole.
Alligator clipA long-nosed spring-loaded
metal clip with meshing teeth. Used to make
temporary electrical connections.
AlternatorA component in the electrical
system which converts mechanical energy
from a drivebelt into electrical energy to
charge the battery and to operate the starting
system, ignition system and electrical
accessories.
Ampere (amp)A unit of measurement for the
flow of electric current. One amp is the
amount of current produced by one volt
acting through a resistance of one ohm.
Anaerobic sealerA substance used to
prevent bolts and screws from loosening.
Anaerobic means that it does not require
oxygen for activation. The Loctite brand is
widely used.
AntifreezeA substance (usually ethylene
glycol) mixed with water, and added to a
vehicle’s cooling system, to prevent freezing
of the coolant in winter. Antifreeze also
contains chemicals to inhibit corrosion and
the formation of rust and other deposits that
would tend to clog the radiator and coolant
passages and reduce cooling efficiency.
Anti-seize compoundA coating that
reduces the risk of seizing on fasteners that
are subjected to high temperatures, such as
exhaust manifold bolts and nuts.
AsbestosA natural fibrous mineral with great
heat resistance, commonly used in the
composition of brake friction materials.Asbestos is a health hazard and the dust
created by brake systems should never be
inhaled or ingested.
AxleA shaft on which a wheel revolves, or
which revolves with a wheel. Also, a solid
beam that connects the two wheels at one
end of the vehicle. An axle which also
transmits power to the wheels is known as a
live axle.
AxleshaftA single rotating shaft, on either
side of the differential, which delivers power
from the final drive assembly to the drive
wheels. Also called a driveshaft or a halfshaft.
BBall bearingAn anti-friction bearing
consisting of a hardened inner and outer race
with hardened steel balls between two races.
BearingThe curved surface on a shaft or in a
bore, or the part assembled into either, that
permits relative motion between them with
minimum wear and friction.
Big-end bearingThe bearing in the end of
the connecting rod that’s attached to the
crankshaft.
Bleed nippleA valve on a brake wheel
cylinder, caliper or other hydraulic component
that is opened to purge the hydraulic system
of air. Also called a bleed screw.
Brake bleedingProcedure for removing air
from lines of a hydraulic brake system.
Brake discThe component of a disc brake
that rotates with the wheels.Brake drumThe component of a drum brake
that rotates with the wheels.
Brake liningsThe friction material which
contacts the brake disc or drum to retard the
vehicle’s speed. The linings are bonded or
riveted to the brake pads or shoes.
Brake padsThe replaceable friction pads
that pinch the brake disc when the brakes are
applied. Brake pads consist of a friction
material bonded or riveted to a rigid backing
plate.
Brake shoeThe crescent-shaped carrier to
which the brake linings are mounted and
which forces the lining against the rotating
drum during braking.
Braking systemsFor more information on
braking systems, consult the Haynes
Automotive Brake Manual.
Breaker barA long socket wrench handle
providing greater leverage.
BulkheadThe insulated partition between
the engine and the passenger compartment.
CCaliperThe non-rotating part of a disc-brake
assembly that straddles the disc and carries
the brake pads. The caliper also contains the
hydraulic components that cause the pads to
pinch the disc when the brakes are applied. A
caliper is also a measuring tool that can be set
to measure inside or outside dimensions of an
object.
CamshaftA rotating shaft on which a series
of cam lobes operate the valve mechanisms.
The camshaft may be driven by gears, by
sprockets and chain or by sprockets and a
belt.
CanisterA container in an evaporative
emission control system; contains activated
charcoal granules to trap vapours from the
fuel system.
CarburettorA device which mixes fuel with
air in the proper proportions to provide a
desired power output from a spark ignition
internal combustion engine.
CastellatedResembling the parapets along
the top of a castle wall. For example, a
castellated balljoint stud nut.
CastorIn wheel alignment, the backward or
forward tilt of the steering axis. Castor is
positive when the steering axis is inclined
rearward at the top.
Canister
Brake bleeding
Bearing
Air filter