alternator JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1997, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.GPages: 227, PDF Size: 7.2 MB
Page 7 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
Roadside repairs0•7
When jump-starting a car using a
booster battery, observe the following
precautions:
4Before connecting the booster
battery, make sure that the ignition
is switched off.
4Ensure that all electrical equipment
(lights, heater, wipers, etc) is
switched off.
4Take note of any special precautions
printed on the battery case.4Make sure that the booster battery
is the same voltage as the
discharged one in the vehicle.
4If the battery is being jump-started
from the battery in another vehicle,
the two vehicles MUST NOT TOUCH
each other.
4Make sure that the transmission is in
neutral (or PARK, in the case of
automatic transmission).
Jump starting will get you
out of trouble, but you must
correct whatever made the
battery go flat in the first
place. There are three possibilities:
1) The battery has been drained by
repeated attempts to start, or by
leaving the lights on.
2) The charging system is not working
properly (alternator drivebelt slack or
broken, alternator wiring fault or
alternator itself faulty).
3) The battery itself is at fault (electrolyte
low, or battery worn out).
Connect one end of the red jump lead
to the positive (+) terminal of the flat
batteryConnect the other end of the red lead
to the positive (+) terminal of the
booster batteryConnect one end of the black jump lead
to the negative (-) terminal of the
booster battery
Connect the other end of the black
jump lead to a bolt or bracket on the
engine block, well away from the
battery, on the vehicle to be started
123
4
Make sure that the jump leads will not
come into contact with the fan,
drivebelts or other moving parts of the
engine5
Start the engine using the booster
battery, then with the engine running at
idle speed, disconnect the jump leads
in the reverse order of connection6
Jump starting
Page 21 of 227
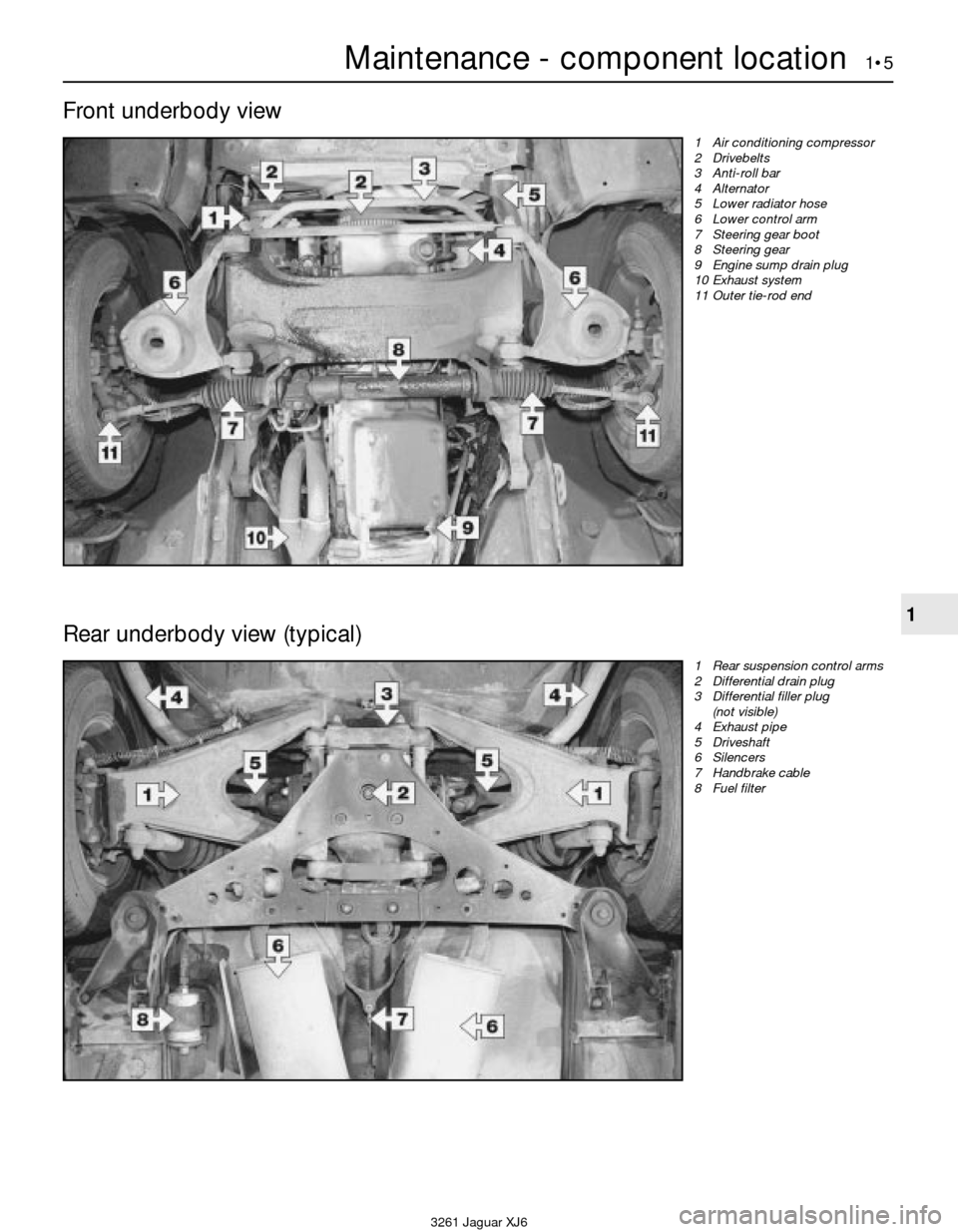
Maintenance - component location 1•5
1
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Front underbody view
1 Air conditioning compressor
2 Drivebelts
3 Anti-roll bar
4 Alternator
5 Lower radiator hose
6 Lower control arm
7 Steering gear boot
8 Steering gear
9 Engine sump drain plug
10 Exhaust system
11 Outer tie-rod end
Rear underbody view (typical)
1 Rear suspension control arms
2 Differential drain plug
3 Differential filler plug
(not visible)
4 Exhaust pipe
5 Driveshaft
6 Silencers
7 Handbrake cable
8 Fuel filter
Page 32 of 227
20 Crankcase ventilation
system check
1
Refer to Chapter 6.
21 Drivebelt check and renewal
2
Check
1The drivebelts, or V-belts as they are
sometimes called, are located at the front of
the engine and play an important role in the
overall operation of the vehicle and its
components. Due to their function and
material make-up, the belts are prone to
failure after a period of time and should be
inspected and adjusted periodically to prevent
major engine damage.
2The number of belts used on a particular
vehicle depends on the accessories installed.
The main belt transmits power from the
crankshaft to the water pump, alternator and
the power steering pump. The second belt
transmits power from the crankshaft to the air
conditioning compressor.
3With the engine off, open the bonnet and
locate the drivebelts. With a flashlight, check
each belt for separation of the adhesive
rubber on both sides of the core, core
separation from the belt side, a severed core,
separation of the ribs from the adhesive
rubber, cracking or separation of the ribs, and
torn or worn ribs or cracks in the inner ridges
of the ribs (see illustrations). Also check for
fraying and glazing, which gives the belt a
shiny appearance. Both sides of the belt
should be inspected, which means you will
have to twist the belt to check the underside.
Use your fingers to feel the belt where you
can’t see it. If any of the above conditions are
evident, replace the belt (go to paragraph 7).
4Check the belt tension by pushing firmly on
the belt with your thumb at a distance halfway
between the pulleys and note how far the beltcan be pushed (deflected). Measure this
deflection with a ruler (see illustration). As a
rule of thumb, if the distance from pulley
centre-to- pulley centre is between 7 and
11 inches, the belt should deflect 1/4-inch. If
the belt travels between pulleys spaced 12 to
16 inches apart, the belt should deflect
1/2-inch for a V-belt or 1/4-inch for a
serpentine belt.
Adjustment
5There are two belt tensioning mechanisms.
The first one adjusts the air conditioning
compressor belt, which is accessible from
underneath the car. The second tensioning
mechanism is above the alternator - it adjusts
the tension on the main belt (the water pump,
alternator and power steering pump belt).
6The air conditioning compressor and the
alternator each have a belt tensioning
mechanism and pivot bolt(s) which must be
loosened slightly to enable you to move the
component (see illustrations).
7After the bolts have been loosened, belt
tension can be adjusted by either loosening or
tightening the locknuts on the belt tensioning
adjustment rod (see illustration 21.6a and b).
Move the component away from the engine totighten the belt or toward the engine to loosen
the belt.
8Measure the belt tension using the method
described in paragraph 4. Repeat this
procedure until the drivebelt is adjusted
properly.
Renewal
9To replace a belt, loosen the drivebelt
adjustment rod and pivot bolt as described
above, slip the belt off the crankshaft pulley
and remove it. If you are replacing the
alternator/power steering pump belt, you’ll
have to remove the air conditioning
1•16Every 15 000 miles or 12 months
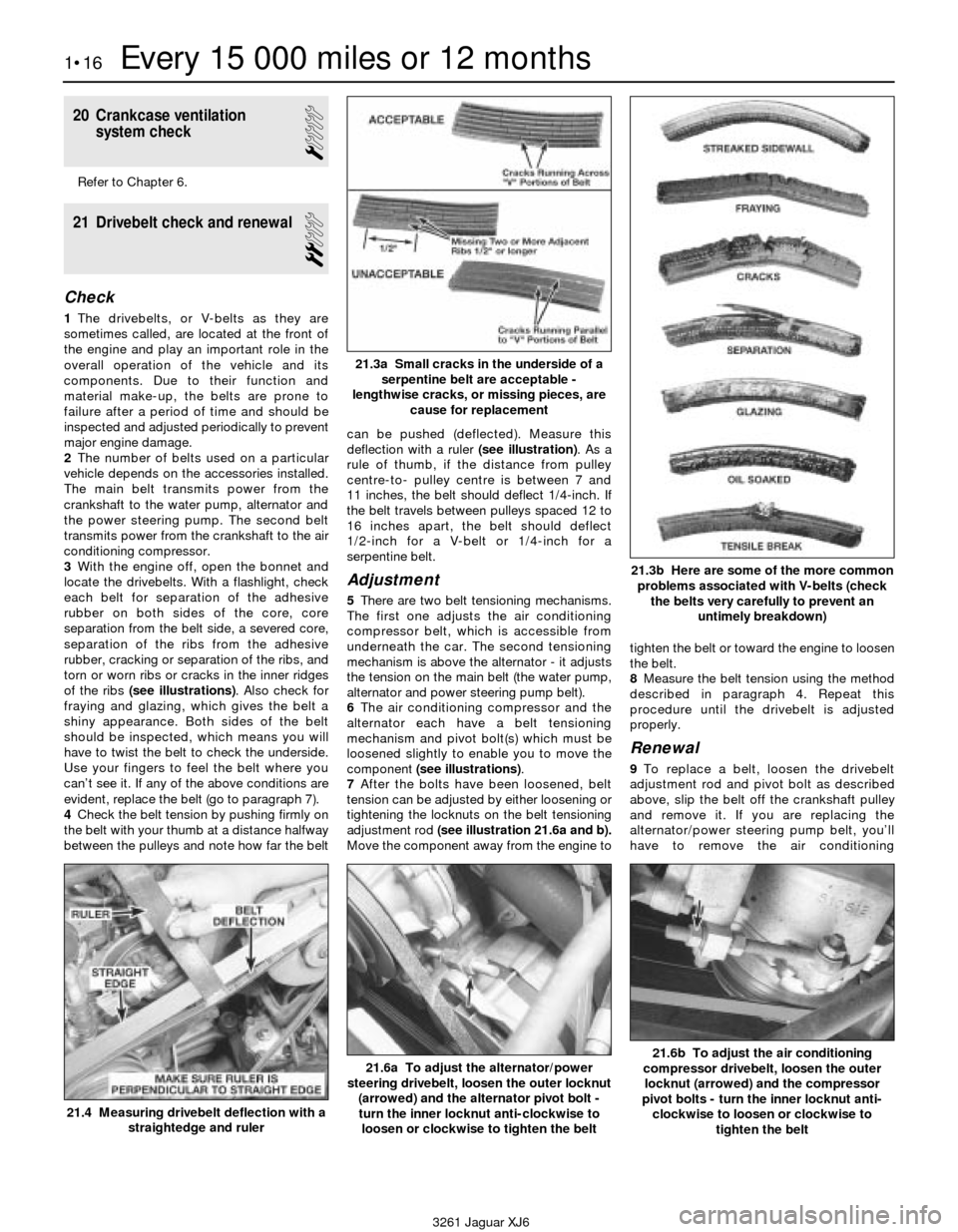
21.3a Small cracks in the underside of a
serpentine belt are acceptable -
lengthwise cracks, or missing pieces, are
cause for replacement
21.3b Here are some of the more common
problems associated with V-belts (check
the belts very carefully to prevent an
untimely breakdown)
21.4 Measuring drivebelt deflection with a
straightedge and ruler
21.6a To adjust the alternator/power
steering drivebelt, loosen the outer locknut
(arrowed) and the alternator pivot bolt -
turn the inner locknut anti-clockwise to
loosen or clockwise to tighten the belt21.6b To adjust the air conditioning
compressor drivebelt, loosen the outer
locknut (arrowed) and the compressor
pivot bolts - turn the inner locknut anti-
clockwise to loosen or clockwise to
tighten the belt
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 39 of 227
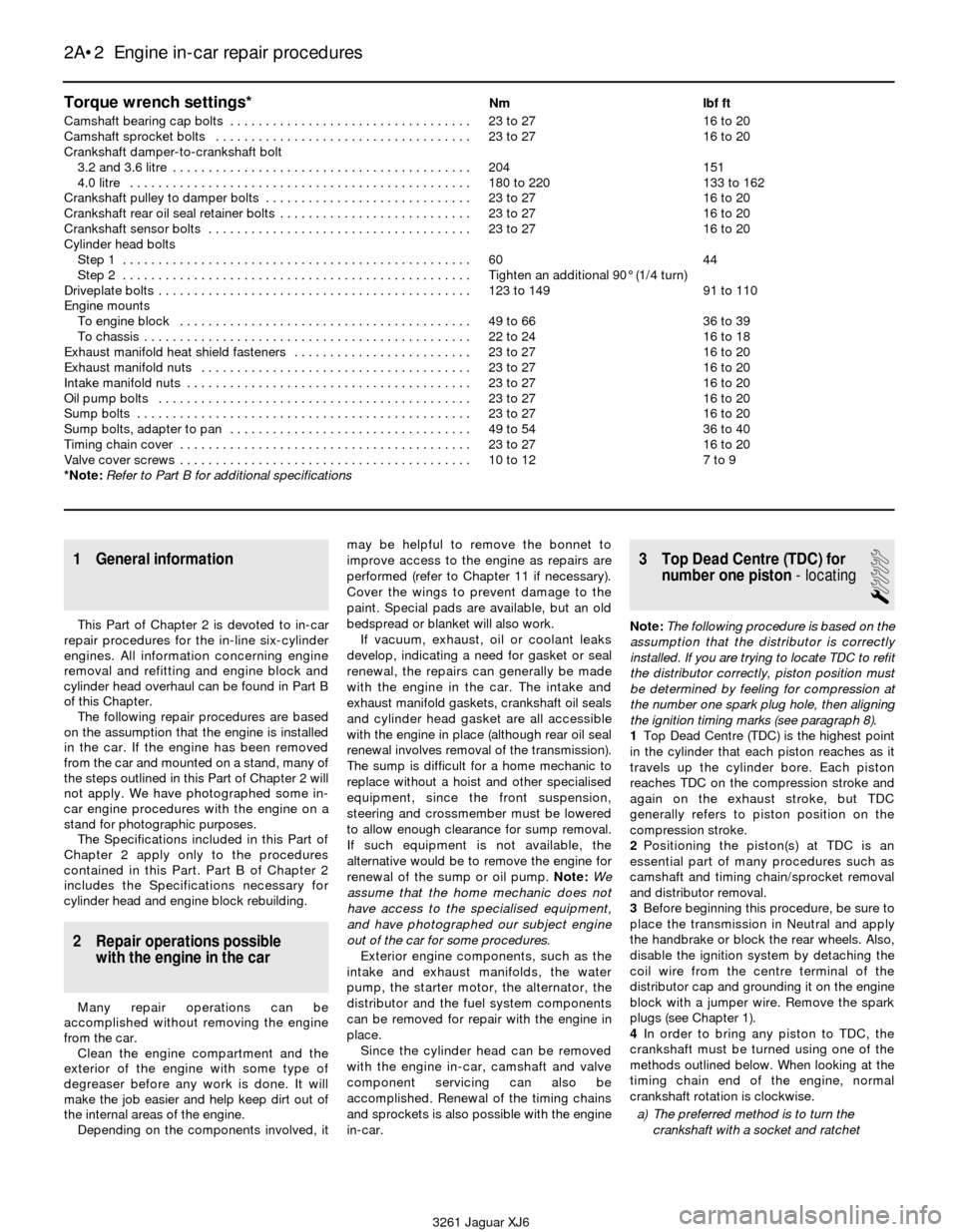
Torque wrench settings*Nm lbf ft
Camshaft bearing cap bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Camshaft sprocket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Crankshaft damper-to-crankshaft bolt
3.2 and 3.6 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204 151
4.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180 to 220 133 to 162
Crankshaft pulley to damper bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Crankshaft rear oil seal retainer bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Crankshaft sensor bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Cylinder head bolts
Step 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60 44
Step 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Tighten an additional 90° (1/4 turn)
Driveplate bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123 to 149 91 to 110
Engine mounts
To engine block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 to 66 36 to 39
To chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 24 16 to 18
Exhaust manifold heat shield fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Exhaust manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Intake manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Oil pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Sump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Sump bolts, adapter to pan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 to 54 36 to 40
Timing chain cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 to 27 16 to 20
Valve cover screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 to 12 7 to 9
*Note:Refer to Part B for additional specifications
2A•2 Engine in-car repair procedures
3261 Jaguar XJ6
1 General information
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to in-car
repair procedures for the in-line six-cylinder
engines. All information concerning engine
removal and refitting and engine block and
cylinder head overhaul can be found in Part B
of this Chapter.
The following repair procedures are based
on the assumption that the engine is installed
in the car. If the engine has been removed
from the car and mounted on a stand, many of
the steps outlined in this Part of Chapter 2 will
not apply. We have photographed some in-
car engine procedures with the engine on a
stand for photographic purposes.
The Specifications included in this Part of
Chapter 2 apply only to the procedures
contained in this Part. Part B of Chapter 2
includes the Specifications necessary for
cylinder head and engine block rebuilding.
2 Repair operations possible
with the engine in the car
Many repair operations can be
accomplished without removing the engine
from the car.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier and help keep dirt out of
the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, itmay be helpful to remove the bonnet to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (refer to Chapter 11 if necessary).
Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint. Special pads are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for gasket or seal
renewal, the repairs can generally be made
with the engine in the car. The intake and
exhaust manifold gaskets, crankshaft oil seals
and cylinder head gasket are all accessible
with the engine in place (although rear oil seal
renewal involves removal of the transmission).
The sump is difficult for a home mechanic to
replace without a hoist and other specialised
equipment, since the front suspension,
steering and crossmember must be lowered
to allow enough clearance for sump removal.
If such equipment is not available, the
alternative would be to remove the engine for
renewal of the sump or oil pump. Note:We
assume that the home mechanic does not
have access to the specialised equipment,
and have photographed our subject engine
out of the car for some procedures.
Exterior engine components, such as the
intake and exhaust manifolds, the water
pump, the starter motor, the alternator, the
distributor and the fuel system components
can be removed for repair with the engine in
place.
Since the cylinder head can be removed
with the engine in-car, camshaft and valve
component servicing can also be
accomplished. Renewal of the timing chains
and sprockets is also possible with the engine
in-car.
3 Top Dead Centre (TDC) for
number one piston- locating
1
Note:The following procedure is based on the
assumption that the distributor is correctly
installed. If you are trying to locate TDC to refit
the distributor correctly, piston position must
be determined by feeling for compression at
the number one spark plug hole, then aligning
the ignition timing marks (see paragraph 8).
1Top Dead Centre (TDC) is the highest point
in the cylinder that each piston reaches as it
travels up the cylinder bore. Each piston
reaches TDC on the compression stroke and
again on the exhaust stroke, but TDC
generally refers to piston position on the
compression stroke.
2Positioning the piston(s) at TDC is an
essential part of many procedures such as
camshaft and timing chain/sprocket removal
and distributor removal.
3Before beginning this procedure, be sure to
place the transmission in Neutral and apply
the handbrake or block the rear wheels. Also,
disable the ignition system by detaching the
coil wire from the centre terminal of the
distributor cap and grounding it on the engine
block with a jumper wire. Remove the spark
plugs (see Chapter 1).
4In order to bring any piston to TDC, the
crankshaft must be turned using one of the
methods outlined below. When looking at the
timing chain end of the engine, normal
crankshaft rotation is clockwise.
a) The preferred method is to turn the
crankshaft with a socket and ratchet
Page 57 of 227

Engine block
Deck warpage limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.076 mm (0.003 inch)
Cylinder bore diameter
Standard
Size group A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90.990 to 91.003 mm (3.5823 to 3.5828 inches)
Size group B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91.005 to 91.018 mm (3.5829 to 3.5834 inches)
Oversize
0.25 mm (0.010 inch) OS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91.259 to 91.272 mm (3.5929 to 3.5934 inches)
0.50 mm (0.020 inch) OS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91.513 to 91.526 mm (3.6029 to 3.6034 inches)
Pistons and rings
Piston-to-bore clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.017 to 0.043 mm (0.0007 to 0.0017 inch)
Piston ring end gap
No.1 (top) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 to 0.66 mm (0.016 to 0.026 inch)
No.2 (middle) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.40 to 0.66 mm (0.016 to 0.026 inch)
Oil ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.30 to 0.55 mm (0.012 to 0.022 inch)
Piston ring groove clearance
No. 1 (top) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.040 to 0.076 mm (0.0016 to 0.0030 inch)
No. 2 (middle) compression ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.040 to 0.076 mm (0.0016 to 0.0030 inch)
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Main bearing cap bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136 to 142 100 to 105
Connecting rod cap nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 to 60 37 to 44
* Note:Refer to Part A for additional torque specifications.
2B•2 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
3261 Jaguar XJ6
1 General information
Included in this portion of Chapter 2 are the
general overhaul procedures for the cylinder
head and internal engine components.
The information ranges from advice
concerning preparation for an overhaul and
the purchase of replacement parts to detailed,
step-by-step procedures covering removal
and refitting of internal engine components
and the inspection of parts.
The following Sections have been written
based on the assumption that the engine has
been removed from the vehicle. For
information concerning in-vehicle engine
repair, as well as removal and refitting of the
external components necessary for the
overhaul, see Part A of this Chapter.
The Specifications included in this Part are
only those necessary for the inspection and
overhaul procedures which follow. Refer to
Part A for additional Specifications.
2 Engine overhaul-
general information
It’s not always easy to determine when, or if,
an engine should be completely overhauled,
as a number of factors must be considered.
High mileage is not necessarily an indication
that an overhaul is needed, while low mileage
doesn’t preclude the need for an overhaul.
Frequency of servicing is probably the most
important consideration. An engine that’s had
regular and frequent oil and filter changes, as
well as other required maintenance, will most
likely give many thousands of miles of reliableservice. Conversely, a neglected engine may
require an overhaul very early in its life.
Excessive oil consumption is an indication
that piston rings, valve seals and/or valve
guides are in need of attention. Make sure that
oil leaks aren’t responsible before deciding
that the rings and/or guides are bad. Perform a
cylinder compression check to determine the
extent of the work required (see Section 4).
Also check the vacuum readings under various
conditions (see Section 3).
Check the oil pressure with a gauge
installed in place of the oil pressure sender
unit (see illustrations)and compare it to this
Chapter’s Specifications. If it’s extremely low,
the bearings and/or oil pump are probably
worn out.
Loss of power, rough running, knocking or
metallic engine noises, excessive valve train
noise and high fuel consumption rates may
also point to the need for an overhaul,
especially if they’re all present at the same
time. If a complete tune-up doesn’t remedy
the situation, major mechanical work is the
only solution.An engine overhaul involves restoring the
internal parts to the specifications of a new
engine. During an overhaul, the piston rings
are replaced and the cylinder walls are
reconditioned (rebored and/or honed). If a
rebore is done by an automotive machine
workshop, new oversize pistons will also be
installed. The main bearings, big-end bearings
and camshaft bearings are generally replaced
with new ones and, if necessary, the
crankshaft may be reground to restore the
journals. Generally, the valves are serviced as
well, since they’re usually in less-than-perfect
condition at this point. While the engine is
being overhauled, other components, such as
the distributor, starter and alternator, can be
rebuilt as well. The end result should be a like
new engine that will give many trouble free
miles. Note:Critical cooling system
components such as the hoses, drivebelts,
thermostat and water pump should be
replaced with new parts when an engine is
overhauled. The radiator should be checked
carefully to ensure that it isn’t clogged or
leaking (see Chapter 3).If you purchase a
2.4a The oil pressure sender unit (arrowed)
is located in the right front corner of the
engine block, near the oil filter2.4b The oil pressure can be checked by
removing the sender unit and refitting a
pressure gauge in its place
Page 61 of 227

incorporated throughout. The refitting of
manifolds and external parts is all that’s
necessary. Engines in this rebuilt form are
available from Jaguar dealers, and some
independent rebuilders.
Give careful thought to which alternative is
best for you and discuss the situation with
local automotive machine shops, auto parts
dealers and experienced rebuilders before
ordering or purchasing replacement parts.
8 Engine overhaul-
dismantling sequence
1It’s much easier to dismantle and work on
the engine if it’s mounted on a portable
engine stand. A stand can often be rented
quite cheaply from an equipment rental yard.
Before the engine is mounted on a stand, the
driveplate and rear oil seal retainer should be
removed from the engine.
2If a stand isn’t available, it’s possible to
dismantle the engine with it blocked up on the
floor. Be extra careful not to tip or drop the
engine when working without a stand.
3If you’re going to obtain a rebuilt engine, all
external components must come off first, to
be transferred to the replacement engine, just
as they will if you’re doing a complete engine
overhaul yourself. These include:
Alternator and brackets
Emissions control components
Distributor, spark plug leads and spark
plugs
Thermostat and housing cover
Water pump
EFI components
Intake/exhaust manifolds
Oil filter
Engine mounts
Driveplate
Transmission adapter plate
Note:When removing the external
components from the engine, pay close
attention to details that may be helpful or
important during refitting. Note the installed
position of gaskets, seals, spacers, pins,
brackets, washers, bolts and other small items.
4If you’re obtaining a short block, which
consists of the engine block, crankshaft,
pistons and connecting rods all assembled,
then the cylinder head, sump and oil pump will
have to be removed as well from your engine
so that your short-block can be turned in to
the rebuilder as a core. See Engine rebuilding
alternativesfor additional information
regarding the different possibilities to be
considered.
5If you’re planning a complete overhaul, the
engine must be dismantled and the internal
components removed in the following order:
Intake and exhaust manifolds
Valve cover
Upper timing chain and camshaft
sprocketsCamshafts
Timing chain cover
Cylinder head
Sump
Oil pump
Piston/connecting rod assemblies
Crankshaft rear oil seal retainer
Crankshaft and main bearings
6Before beginning the dismantling and
overhaul procedures, make sure the following
items are available. Also, refer to Section 21
for a list of tools and materials needed for
engine reassembly.
Common hand tools
Small cardboard boxes or plastic bags for
storing parts
Gasket scraper
Ridge reamer
Micrometers
Telescoping gauges
Dial indicator set
Valve spring compressor
Cylinder surfacing hone
Piston ring groove-cleaning tool
Electric drill motor
Tap and die set
Wire brushes
Oil gallery brushes
Cleaning solvent
Special Jaguar tools
Engine lifting brackets (18G 1465)
Timing damper simulator (18E 1436)
Camshaft TDC tool (18G 1433)
9 Cylinder head- dismantling
2
Note: New and rebuilt cylinder heads are
available from Jaguar and some independent
rebuilders. Due to the fact that some
specialised tools are necessary for the
dismantling and inspection procedures, and
replacement parts may not be readily
available, it may be more practical and
economical for the home mechanic to
purchase a replacement cylinder head rather
than taking the time to dismantle, inspect and
recondition the original.1Cylinder head dismantling involves removal
of the intake and exhaust valves and related
components. It’s assumed that the lifters and
camshafts have already been removed (see
Part A as needed).
2Before the valves are removed, arrange to
label and store them, along with their related
components, so they can be kept separate
and reinstalled in the same valve guides they
are removed from (see illustration).
3Compress the springs on the first valve with
a spring compressor and remove the keepers
(see illustration). Carefully release the valve
spring compressor and remove the retainer,
the spring and the spring seat (if used). Note:
If your spring compressor does not have an
end (such as the one shown) with cut-outs on
the side, an adapter is available to use with a
standard spring compressor.
Caution: Be very careful not to nick or
otherwise damage the lifter bores when
compressing the valve springs.
4Pull the valve out of the cylinder head, then
remove the oil seal from the guide. If the valve
binds in the guide (won’t pull through), push it
back into the cylinder head and deburr the
area around the keeper groove with a fine file
or whetstone.
5Repeat the procedure for the remaining
valves. Remember to keep all the parts for
each valve together so they can be reinstalled
in the same locations.
6Once the valves and related components
have been removed and stored in an
organised manner, the cylinder head should
be thoroughly cleaned and inspected. If a
complete engine overhaul is being done,
finish the engine dismantling procedures
before beginning the cylinder head cleaning
and inspection process.
10 Cylinder head-
cleaning and inspection
2
1Thorough cleaning of the cylinder head(s)
and related valve train components, followed
by a detailed inspection, will enable you to
decide how much valve service work must be
2B•6 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
9.2 A small plastic bag, with an appropriate
label, can be used to store the valve train
components so they can be kept together
and reinstalled in the correct guide
3261 Jaguar XJ6
9.3 Compress the spring until the keepers
can be removed with a small magnetic
screwdriver or needle-nose pliers - use a
valve spring compressor with an adapter
(arrowed) to remove the keepers
Page 100 of 227

headlights or heated rear window and confirm
that the engine rpm decreases at first and
then increases. This check monitors the ISC
motor as it is signalled by the computer to
increase idle speed due to additional
amperage required from the charging system.
As the headlights draw current from the
charging system, the alternator will create
resistance on the belt as it works to produce
the additional energy. If the rpm does not
increase, check the ISC motor.
23Check for approximately 11.2 volts to the
ISC stepper motor (see illustrations).
Disconnect the ISC harness connector and
working on the harness side, check for
11.2 volts with the ignition key ON (engine not
running). Also, check the corresponding
terminals for the correct voltage amounts. If
the correct voltage does not exist, check the
wiring harness. Refer to the wiring diagrams
at the end of Chapter 12.24The ISC motor or stepper motor can be
checked for correct operation but a special tool
is required to activate the internal coils. Have
the stepper motor checked by a dealer service
department or other qualified repair workshop.
25Reconnect the ISC motor electrical
connector.
Renewal
26Detach the cable from the negative
terminal of the battery (see Cautionat the
beginning of this Section).
27Use a large open-end spanner and
unscrew the ISC motor from the housing (see
illustration).
28Refitting is the reverse of removal, but be
sure to use a new gasket.
Fuel rail and fuel injectors
Note:If there is a distinct knocking noise
coming from the dash when the engine is
idling, the fuel feed hose may have hardenedrestricting fuel flow and causing abnormal
sounds. Replace the fuel inlet (feed) hose with
a new part from the dealer parts department.
Check
29Refer to the fuel injection system checking
procedure (see Section 12).
Renewal
30Relieve the fuel pressure (see Section 2).
31Detach the cable from the negative
terminal of the battery (see Cautionat the
beginning of this Section).
32Disconnect the fuel injector wiring con-
nectors and set the injector wire harness aside.
33Detach the vacuum sensing hose from the
fuel pressure regulator.
34Disconnect the fuel lines from the fuel
pressure regulator and the fuel rail (see
illustration 3.6a)
35Remove the fuel rail mounting bolts (see
illustration).
4•12 Fuel and exhaust systems
3261 Jaguar XJ6 13.23a To check the ISC motor, turn the ignition key ON
(engine not running) and check for the proper voltage amounts
at the harness connector (1989 model shown)
13.23b Later models are equipped with a different shape
ISC connector but the voltage values should be the same
as the early style
13.27 Use a large open end spanner to remove the ISC motor
from the intake manifold13.35 Remove the fuel rail mounting bolts (arrowed) . . .
Page 103 of 227
3261 Jaguar XJ6
5
Chapter 5
Engine electrical systems
Ignition system
Ignition timing (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Not adjustable
Ignition coil resistance (at 68°F):
Primary resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.4 to 0.5 ohms
Secondary resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.0 to 6.5 k-ohms
Charging system
Charging voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.9 to 15.1 volts
Standard amperage:
No load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Less than 10 amps
Full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 amps or more Amplifier - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Alternator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Battery cables - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Battery check, maintenance and charging . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Battery - emergency jump starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Battery - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Charging system - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Charging system - general information and precautions . . . . . . . . . 10
CHECK ENGINE light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 6
Distributor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Drivebelt check, adjustment and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Ignition coil - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Ignition system - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Ignition system - general information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Spark plug lead, distributor cap and rotor check
and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Starter motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Starter motor - testing in vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Starter solenoid - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Starting system - general information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . 13
5•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
1 General information
The engine electrical systems include all
ignition, charging and starting components.
Because of their engine related functions,
these components are discussed separately
from chassis electrical devices such as the
fuses, relays, lights, etc. (which are included in
Chapter 12).
Always observe the following precautions
when working on the electrical systems:
a) Be extremely careful when servicing
engine electrical components. They are
easily damaged if checked, connected or
handled improperly.
b) Never leave the ignition switch on for long
periods of time (10 minutes maximum)
with the engine off.c) Don’t disconnect the battery cables while
the engine is running.
d) Maintain correct polarity when connecting
a battery cable from another vehicle
during jump starting.
e) Always disconnect the negative cable first
and hook it up last or the battery may be
shorted by the tool being used to loosen
the cable clamps.
It’s also a good idea to review the safety-
related information regarding the engine
electrical systems in the Safety first section
near the front of this manual before beginning
any operation included in this Chapter.
2 Battery-
emergency jump starting
1
See “Jump starting”in “Roadside repairs”
at the front of this Manual.
3 Battery- removal and refitting
1
1Disconnect the negative terminal, then the
positive terminal from the battery. On 1989 to
1992 models, the battery is located in the
engine compartment on the passenger side
bulkhead and on 1993 and 1994 models, it is
located in the boot.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
2Remove the battery hold-down clamp.
3Lift out the battery. Be careful, it’s heavy.
4While the battery is out, inspect the carrier
(tray) for corrosion.
5If you are replacing the battery, make sure
that you get one that’s identical, with the
Page 107 of 227
Refitting
7Insert the distributor into the engine in
exactly the same relationship to the block that
it was in when removed.
8If the distributor does not seat completely,
recheck the alignment marks between the
distributor base and the block to verify that
the distributor is in the same position it was in
before removal. Also check the rotor to see if
it’s aligned with the mark you made on the
edge of the distributor base.
9Refit the distributor hold-down bolt(s).
10The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
10 Charging system- general
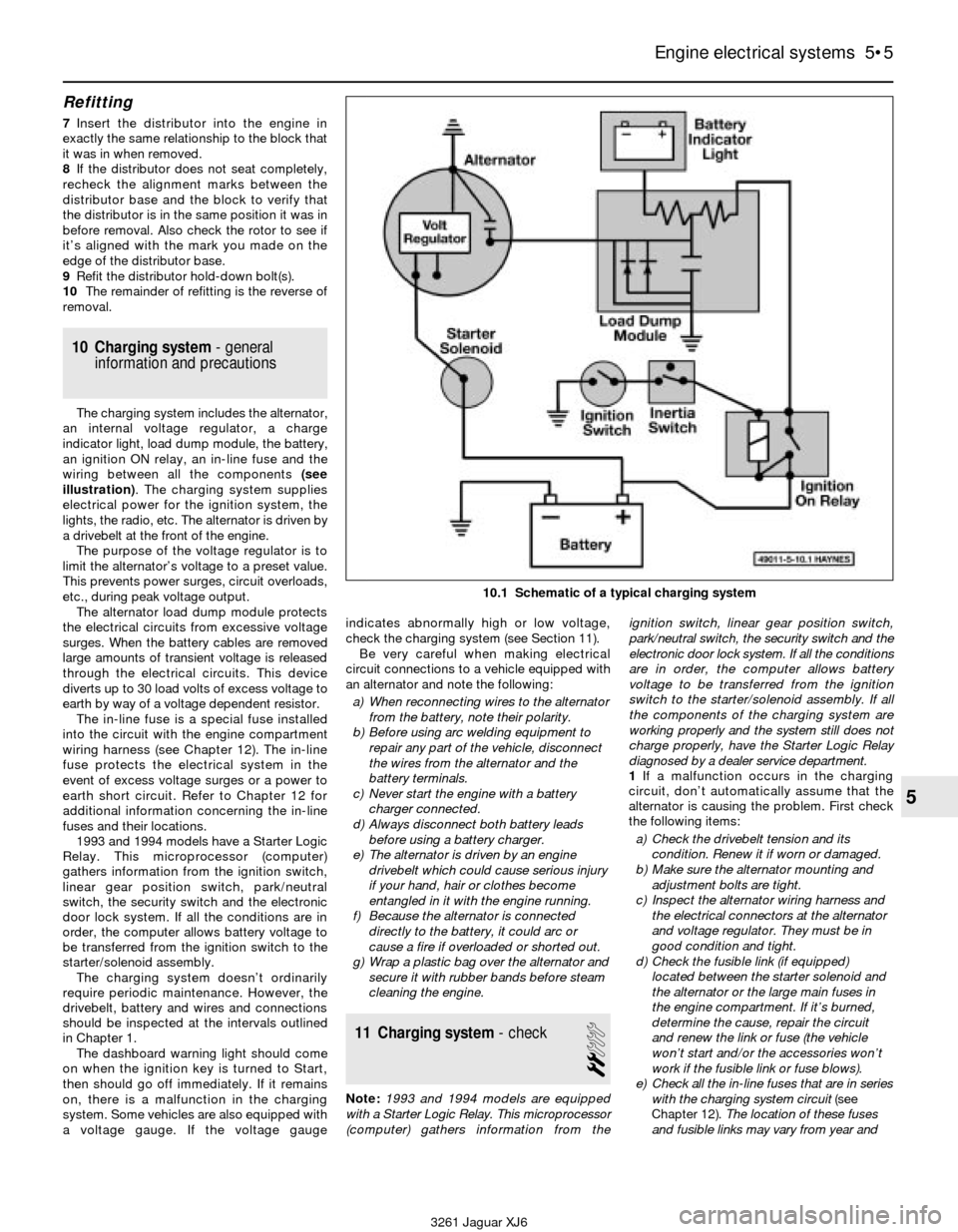
information and precautions
The charging system includes the alternator,
an internal voltage regulator, a charge
indicator light, load dump module, the battery,
an ignition ON relay, an in-line fuse and the
wiring between all the components (see
illustration). The charging system supplies
electrical power for the ignition system, the
lights, the radio, etc. The alternator is driven by
a drivebelt at the front of the engine.
The purpose of the voltage regulator is to
limit the alternator’s voltage to a preset value.
This prevents power surges, circuit overloads,
etc., during peak voltage output.
The alternator load dump module protects
the electrical circuits from excessive voltage
surges. When the battery cables are removed
large amounts of transient voltage is released
through the electrical circuits. This device
diverts up to 30 load volts of excess voltage to
earth by way of a voltage dependent resistor.
The in-line fuse is a special fuse installed
into the circuit with the engine compartment
wiring harness (see Chapter 12). The in-line
fuse protects the electrical system in the
event of excess voltage surges or a power to
earth short circuit. Refer to Chapter 12 for
additional information concerning the in-line
fuses and their locations.
1993 and 1994 models have a Starter Logic
Relay. This microprocessor (computer)
gathers information from the ignition switch,
linear gear position switch, park/neutral
switch, the security switch and the electronic
door lock system. If all the conditions are in
order, the computer allows battery voltage to
be transferred from the ignition switch to the
starter/solenoid assembly.
The charging system doesn’t ordinarily
require periodic maintenance. However, the
drivebelt, battery and wires and connections
should be inspected at the intervals outlined
in Chapter 1.
The dashboard warning light should come
on when the ignition key is turned to Start,
then should go off immediately. If it remains
on, there is a malfunction in the charging
system. Some vehicles are also equipped with
a voltage gauge. If the voltage gaugeindicates abnormally high or low voltage,
check the charging system (see Section 11).
Be very careful when making electrical
circuit connections to a vehicle equipped with
an alternator and note the following:
a) When reconnecting wires to the alternator
from the battery, note their polarity.
b) Before using arc welding equipment to
repair any part of the vehicle, disconnect
the wires from the alternator and the
battery terminals.
c) Never start the engine with a battery
charger connected.
d) Always disconnect both battery leads
before using a battery charger.
e) The alternator is driven by an engine
drivebelt which could cause serious injury
if your hand, hair or clothes become
entangled in it with the engine running.
f) Because the alternator is connected
directly to the battery, it could arc or
cause a fire if overloaded or shorted out.
g) Wrap a plastic bag over the alternator and
secure it with rubber bands before steam
cleaning the engine.
11 Charging system- check
2
Note:1993 and 1994 models are equipped
with a Starter Logic Relay. This microprocessor
(computer) gathers information from theignition switch, linear gear position switch,
park/neutral switch, the security switch and the
electronic door lock system. If all the conditions
are in order, the computer allows battery
voltage to be transferred from the ignition
switch to the starter/solenoid assembly. If all
the components of the charging system are
working properly and the system still does not
charge properly, have the Starter Logic Relay
diagnosed by a dealer service department.
1If a malfunction occurs in the charging
circuit, don’t automatically assume that the
alternator is causing the problem. First check
the following items:
a) Check the drivebelt tension and its
condition. Renew it if worn or damaged.
b) Make sure the alternator mounting and
adjustment bolts are tight.
c) Inspect the alternator wiring harness and
the electrical connectors at the alternator
and voltage regulator. They must be in
good condition and tight.
d) Check the fusible link (if equipped)
located between the starter solenoid and
the alternator or the large main fuses in
the engine compartment. If it’s burned,
determine the cause, repair the circuit
and renew the link or fuse (the vehicle
won’t start and/or the accessories won’t
work if the fusible link or fuse blows).
e) Check all the in-line fuses that are in series
with the charging system circuit (see
Chapter 12).The location of these fuses
and fusible links may vary from year and
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
10.1 Schematic of a typical charging system
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 108 of 227

model but the designations are the same.
Refer to the wiring diagrams at the end of
Chapter 12.
f) Start the engine and check the alternator
for abnormal noises (a shrieking or
squealing sound indicates a bad bushing).
g) Check the specific gravity of the battery
electrolyte. If it’s low, charge the battery
(doesn’t apply to maintenance free
batteries).
h) Make sure that the battery is fully charged
(one bad cell in a battery can cause
overcharging by the alternator).
i) Disconnect the battery cables (negative
first, then positive). Caution:If the stereo
in your vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have the
correct activation code before
disconnecting the battery. Inspect the
battery posts and the cable clamps for
corrosion. Clean them thoroughly if
necessary (see Chapter 1). Reconnect the
positive cable, then the negative cable.
2Using a voltmeter, check the battery
voltage with the engine off. It should be
approximately 12 volts (see illustration).
3Start the engine and check the battery
voltage again. It should now be approximately
13.5 to 15.1 volts.
4Turn on the headlights. The voltage should
drop and then come back up, if the charging
system is working properly.
5If the voltage reading is greater than the
specified charging voltage, renew the
alternator.
6If you have an ammeter, connect it up to the
charging system according to its maker’s
instructions. If you don’t have a professional-
type ammeter, you can also use an inductive-
type current indicator. This device is
inexpensive, readily available at car accessory
outlets and accurate enough to perform simple
amperage checks like the following test.7With the engine running at 2000 rpm, check
the reading on the ammeter with all
accessories and lights off (no load), then again
with the high-beam headlights on and the
heater blower switch turned to the HI position
(full load). Compare your readings to the
standard amperage listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
8If the ammeter reading is less than standard
amperage, repair or renew the alternator.
9If the alternator is working but the charging
system still does function properly, check the
operation of the load dump module (see
illustration). Have this component checked at
a dealer service department.
12 Alternator-
removal and refitting
2
1Detach the cable from the negative terminal
of the battery.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.2Detach the electrical connectors from the
alternator.
3Loosen the alternator adjustment and pivot
bolts (see illustration) and detach the
drivebelt.
4Remove the adjustment and pivot bolts
(see illustration)from the alternator
adjustment bracket.
5If you are replacing the alternator, take the
old alternator with you when purchasing a
replacement unit. Make sure that the
new/rebuilt unit is identical to the old
alternator. Look at the terminals - they should
be the same in number, size and locations as
the terminals on the old alternator. Finally,
look at the identification markings - they will
be stamped in the housing or printed on a tag
or plaque affixed to the housing. Make sure
that these numbers are the same on both
alternators.
6Many new/rebuilt alternators do not have
a pulley installed, so you may have to switch
the pulley from the old unit to the new/rebuilt
one. When buying an alternator, find out the
policy regarding refitting of pulleys - some
shops will perform this service free of charge.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5•6 Engine electrical systems
12.3 Loosen the lock bolt and back-off
the adjustment bolt (arrowed) to remove
the drivebelt12.4 Remove the pivot bolt and nut
3261 Jaguar XJ6 11.2 Connect the probes of a voltmeter to the battery terminals
and observe battery voltage with the engine OFF
and then with the engine running
11.9 The load dump module is located on the bulkhead
next to the MAF sensor