JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 1181 of 1784

(8) Check fluid condition. Fluid should be dark to
light red in color and free of dirt or debris.
(9) If fluid is discolored or smells burned but trans-
mission operation was OK, check cooler flow, flush
cooler and lines and change fluid and filter. Then
road test again to confirm proper operation.
(10) If fluid is black or dark brown, burned/turned
to sludge, contains large quantities of metal or fric-
tion material particles, transmission will need over-
haul. Especially if problems were evident during
road test and preliminary diagnosis. Fluid cooler
should also be flow tested and flushed if necessary.
EFFECTS OF INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn
the fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid causing
the same conditions that occur with a low level.
In either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating,
oxidation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve, clutch and servo operation. Foaming also
causes fluid expansion which can result in fluid over-
flow from the transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid
overflow can easily be mistaken for a leak if inspec-
tion is not careful.
TRANSMISSION THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
ADJUSTMENT
Throttle cable adjustment is important to proper
operation. This adjustment positions the throttle
valve which controls shift speed, quality and part
throttle downshift sensitivity.
If cable adjustment setting is too short, early shifts
and slippage between shifts may occur. If the setting
is too long, shifts may be delayed and part throttle
downshifts may be very sensitive. Refer to the In-Ve-
hicle Service section for adjustment procedure.
GEARSHIFT LINKAGE
Gearshift linkage adjustment is important because
it positions the valve body manual valve. Incorrect
adjustment will cause creeping in Neutral, prema-
ture clutch wear, delayed engagement in any gear, or
a no-start in Park or Neutral position.
Proper operation of the neutral start switch will
provide a quick check of linkage adjustment. Refer to
the In-Vehicle Service section for adjustment proce-
dure.
ROAD TEST
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and all
linkage adjustments have been checked and adjusted
if necessary.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow an accurate
analysis of transmission operation.Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for slippage and shift variations. Note whether the
shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed, early, or if part
throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Watch closely for slippage or engine flare which
usually indicates clutch, band or overrunning clutch
problems. If the condition is advanced, an overhaul
may be necessary to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart (Fig. 3) provides a basis for analyzing road
test results.
ANALYZING THE ROAD TEST
Refer to the Clutch and Band Application chart
(Fig. 3) and note which elements are in use in the
various gear ranges.
The rear clutch is applied in all forward ranges (D,
2, 1). The overrunning clutch is applied in first gear
(D and 2 range only). The rear band is applied in 1
and R range only.
For example: If slippage occurs in first gear in D
and 2 range but not in 1 range, the overrunning
clutch is slipping. Similarly, if slippage occurs in any
two forward gears, the rear clutch is slipping.
Applying the same method of analysis, note that
both clutches are applied in D range third gear only.
If the transmission slips in third gear, either the
front clutch or the rear clutch is slipping. By select-
ing another gear which does not use one of these
units, the slipping clutch can be determined.
Although road test analysis will help determine
the slipping unit, the actual cause of a malfunction
may not be determined until hydraulic and air pres-
sure tests are performed. Practically any condition
Fig. 3 Clutch And Band Application Chart
21 - 70 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1182 of 1784

can be caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or stick-
ing valves. Unless the problem is an obvious one, do
not remove and disassemble the transmission until
hydraulic and air pressure tests have been per-
formed.
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST
Hydraulic test pressures range from a low of one
psi (6.895 kPa) governor pressure, to 300 psi (2068.5
kPa) at the rear servo pressure port in reverse.
Use 100 psi Pressure Gauge C-3292 to check pres-
sure at the accumulator, front servo, governor and
fluid cooler line. Use 300 psi Gauge C-3293 to check
pressure at the rear servo. The 300 psi gauge can be
used at any other port when more than one gauge is
required for testing.
PRESSURE TEST PORT LOCATIONS
There are pressure test ports at the accumulator,
front servo, rear servo and governor.
Line pressure is checked at the accumulator port
on the right side of the case (Fig. 4). The front servo
release pressure port is at the right side of the case
just behind the filler tube opening (Fig. 4).
The rear servo pressure port is at the right rear of
the transmission case (Fig. 5).
On4x2models, the governor pressure port is at
the left side of case at the transmission rear (Fig. 5).
On4x4transmissions, the test port is in the driver
side of the adapter housing (Fig. 6).
PRESSURE TEST PROCEDURE
Connect a tachometer to the engine. Position the
tachometer so it can be observed from under the ve-
hicle. Raise the vehicle on hoist that will allow the
wheels to rotate freely.
Test One-Transmission In 1 Range
This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion, and condition of the rear clutch and rear
servo circuits. Use 300 psi Test Gauge C-3293 for
this test
(1) Connect test gauges to line pressure and rear
servo ports (Figs. 4-6).Be sure pressure test gauge
is connected to rear servo port.
(2) Disconnect throttle and gearshift rods at trans-
mission.
(3) Start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(4) Move valve body selector lever forward into 1
range.
(5) Read pressures on both gauges as transmission
throttle lever is moved from full forward to full rear-
ward position.
(6) Line pressure should be 54-60 psi (372-414
kPa) with throttle lever forward and gradually in-
crease to 90-96 psi (620-662 kPa) as lever is moved
rearward.
(7) Rear servo pressure should be same as line
pressure within 3 psi.
Test Two-Transmission In 2 Range
This test checks pump output and pressure
regulation. Use 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292 for
this test.
(1) Connect test gauge to line pressure port (Fig.
4).
(2) Start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(3) Move valve body selector lever one detent rear-
ward from full forward position. This is 2 range.
(4) Move transmission throttle lever from full for-
ward to full rearward position and read pressure at
both gauges.
Fig. 4 Front Servo And Line Pressure Test Ports
Fig. 5 Rear Servo And Governor Pressure Test
Ports (4 x 2 Transmission)
Fig. 6 Governor Pressure Test Port (4 x 4
Transmission)
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 71
Page 1183 of 1784

(5) Line pressure should be 54-60 psi (372-414
kPa) with throttle lever forward and gradually in-
crease to 90-96 psi (620-662 kPa) as lever is moved
rearward.
Test Three-Transmission In D Range
This test checks pressure regulation and con-
dition of the front and rear clutch circuits.
Both test gauges are required for this test.
(1) Connect one test gauge to line pressure port
and other gauge to front servo pressure port (Fig. 4).
Either gauge can be used at either port.
(2) Start and run engine at 1600 rpm.
(3) Move selector lever two detents rearward from
full forward position. This is D range.
(4) Read pressures on both gauges as transmission
throttle lever is moved from full forward to full rear-
ward position.
(5) Line pressure should be 54-60 psi (372-414
kPa) with throttle lever forward and gradually in-
crease as lever is moved rearward.
(6) Front servo is pressurized only in D range and
should be same as line pressure within 3 psi (21
kPa), up to downshift point.
Test Four-Transmission In Reverse
This test checks pump output, pressure regu-
lation and the front clutch and rear servo cir-
cuits. Use 300 psi Pressure Test Gauge C-3293
for this test.
(1) Connect pressure test gauge to rear servo port
(Fig. 5).
(2) Start and run engine at 1600 rpm for test.
(3) Move valve body selector lever four detents
rearward from full forward position. This is Reverse
range.
(4) Move throttle lever all way forward then all the
way rearward and note gauge readings.
(5) Pressure should be 145 - 175 psi (1000-1207
kPa) with lever forward and increase to 230 - 280 psi
(1586-1931 kPa) as lever is moved rearward.
Test Five-Governor Pressure
This test checks governor operation by mea-
suring governor pressure response to changes
in engine speed. It is usually not necessary to
check governor operation unless shift speeds
are incorrect or if the transmission will not
shift up or down. Use 100 psi Pressure Test
Gauge C-3292 for this test.
(1) Connect test gauge to governor pressure port
(Figs. 5 and 6).
(2) Move selector lever to D range.
(3) Apply service brakes. Start and run engine at
curb idle speed and note pressure. At idle and with
wheels stopped, pressure should be zero to 1-1/2 psi
maximum. If pressure exceeds this figure, governor
valve or weights are sticking open.(4) Slowly increase engine speed and observe
speedometer and pressure test gauge. Governor pres-
sure should increase in proportion to vehicle speed
(approximately 1 psi for every 1 mph shown on
speedometer).
(5) Governor pressure rise should be smooth and
drop back to 0 to 1-1/2 psi when throttle is closed
and wheels are stopped.
(6) Compare results of pressure tests with analysis
chart (Fig. 7).
CONVERTER STALL TEST
Stall testing involves determining maximum engine
rpm obtainable at full throttle with the rear wheels
locked and the transmission in D range. This test
checks the holding ability of the converter overrun-
ning clutch and both of the transmission clutches.
When stall testing is completed, refer to the Stall
Speed Specifications chart and Stall Speed Diagnosis
guides.
WARNING: NEVER ALLOW ANYONE TO STAND IN
FRONT OF THE VEHICLE DURING A STALL TEST.
ALWAYS BLOCK THE FRONT WHEELS AND APPLY
THE SERVICE AND PARKING BRAKES DURING THE
TEST.
Fig. 7 Pressure Test Analysis Chart
21 - 72 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1184 of 1784

STALL TEST PROCEDURE
(1) Connect tachometer to engine.
(2) Check and adjust transmission fluid level.
(3) Start and run engine until transmission fluid
reaches normal operating temperature.
(4) Block front wheels.
(5) Fully apply service and parking brakes.
(6) Open throttle completely for no more than five
seconds and record maximum engine rpm registered
on tachometer.
CAUTION: Stall testing causes a rapid increase in
transmission fluid temperature. Do not hold the
throttle open any longer than five seconds. If more
than one stall test is required, run the engine at
1000 rpm with the transmission in Neutral for at
least 20 seconds to cool the fluid.
(7) If engine speed exceeds maximum shown in
stall speed chart, release accelerator immediately.
This indicates that transmission clutch slippage is
occurring.
(8) Shift transmission into Neutral. Run engine for
20 seconds to cool fluid. Then stop engine, shift
transmission into Park and release brakes.
(9) Stall speeds should be in 1700-2000 rpm range.
(10) Refer to Stall Test Diagnosis.
STALL TEST DIAGNOSIS
Stall Speed Too High
If the stall speed exceeds specifications by more
than 200 rpm, transmission clutch slippage is indi-
cated.
Stall Speed Too Low
Low stall speeds with a properly tuned engine in-
dicate a torque converter overrunning clutch prob-
lem. The condition should be confirmed by road
testing prior to converter replacement.
The converter overrunning clutch is slipping when
stall speeds are 250 to 350 rpm below specified min-
imum. And when the vehicle operates properly at
highway speeds but has poor low speed acceleration.
Stall Speed Normal
If stall speeds are normal but abnormal throttle
opening is required to maintain highway speeds, the
converter overrunning clutch is seized and the torque
converter must be replaced.
Converter Noise During Test
A whining noise caused by fluid flow is normal
during a stall test. However, loud metallic noises in-
dicate a damaged converter. To confirm that noise is
originating from the converter, operate the vehicle at
light throttle in Drive and Neutral on a hoist and lis-
ten for noise coming from the converter housing.
AIR PRESSURE TEST
Air pressure testing can be used to check clutch
and band operation with the transmission either in
the vehicle, or on the work bench as a final check af-
ter overhaul.
Air pressure testing requires that the oil pan and
valve body be removed from the transmission.
The servo and clutch apply passages are shown in
Figure 8.
Air Test Procedure
(1) Place one or two fingers on the clutch housing
and apply air pressure through front clutch apply
passage (Fig. 8). Piston movement can be felt and a
soft thud heard as the clutch applies.
(2) Place one or two fingers on the clutch housing
and apply air pressure through rear clutch apply pas-
sage (Fig. 8). Piston movement can be felt and a soft
thud heard as the clutch applies.
(3) Apply air pressure to the front servo apply pas-
sage. The servo rod should extend and cause the
band to tighten around the drum. Spring tension
should release the servo when air pressure is re-
moved.
(4) Apply air pressure to the rear servo apply pas-
sage. The servo rod should extend and cause the
band to tighten around the drum. Spring tension
should release the servo when air pressure is re-
moved.
CONVERTER HOUSING LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Two items must be established when diagnosing
leaks from the converter housing area. First, it must
be verified that a leak condition actually exists. And
second, the true source of the leak must be deter-
mined.
Fig. 8 Air Pressure Test Passages
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 73
Page 1185 of 1784
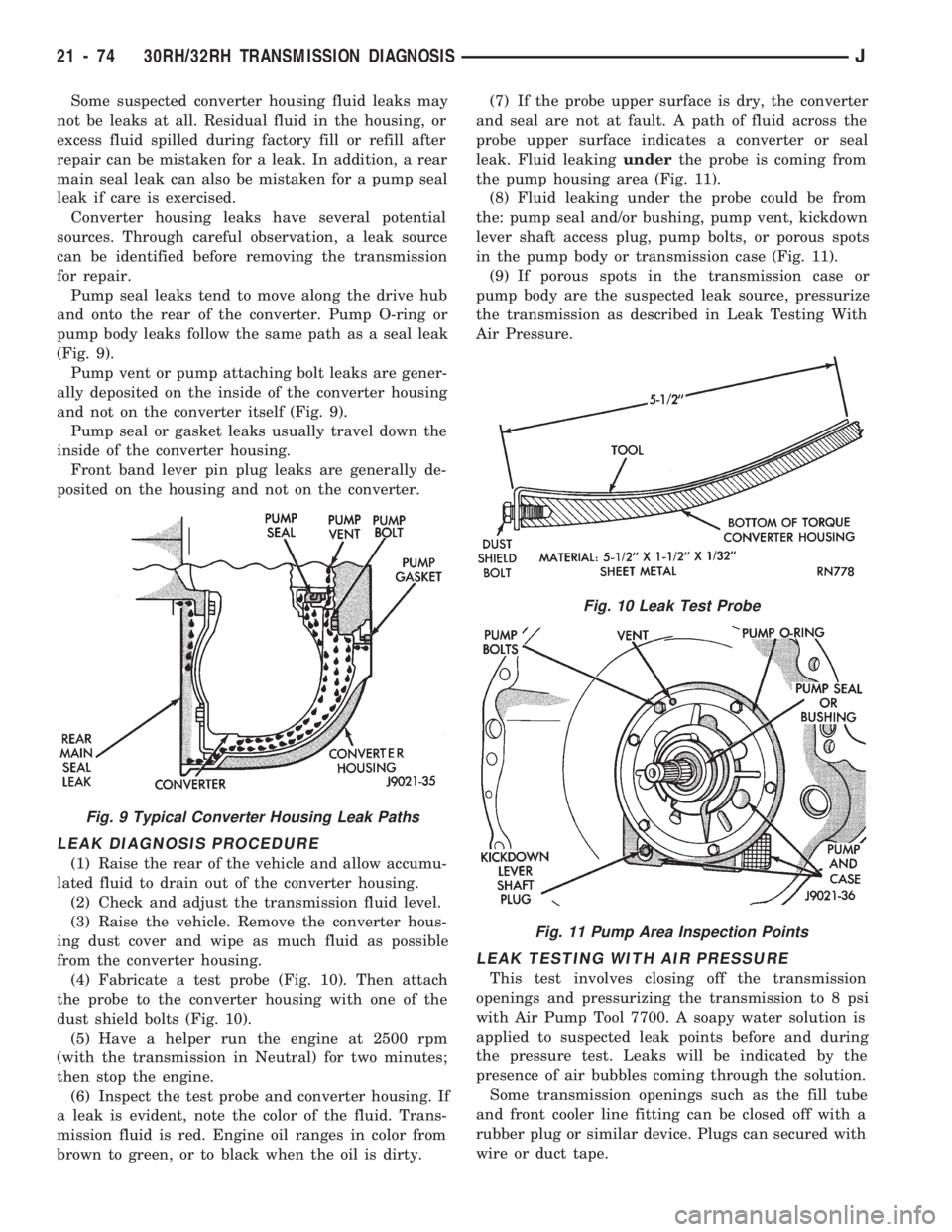
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. Residual fluid in the housing, or
excess fluid spilled during factory fill or refill after
repair can be mistaken for a leak. In addition, a rear
main seal leak can also be mistaken for a pump seal
leak if care is exercised.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter. Pump O-ring or
pump body leaks follow the same path as a seal leak
(Fig. 9).
Pump vent or pump attaching bolt leaks are gener-
ally deposited on the inside of the converter housing
and not on the converter itself (Fig. 9).
Pump seal or gasket leaks usually travel down the
inside of the converter housing.
Front band lever pin plug leaks are generally de-
posited on the housing and not on the converter.
LEAK DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle and allow accumu-
lated fluid to drain out of the converter housing.
(2) Check and adjust the transmission fluid level.
(3) Raise the vehicle. Remove the converter hous-
ing dust cover and wipe as much fluid as possible
from the converter housing.
(4) Fabricate a test probe (Fig. 10). Then attach
the probe to the converter housing with one of the
dust shield bolts (Fig. 10).
(5) Have a helper run the engine at 2500 rpm
(with the transmission in Neutral) for two minutes;
then stop the engine.
(6) Inspect the test probe and converter housing. If
a leak is evident, note the color of the fluid. Trans-
mission fluid is red. Engine oil ranges in color from
brown to green, or to black when the oil is dirty.(7) If the probe upper surface is dry, the converter
and seal are not at fault. A path of fluid across the
probe upper surface indicates a converter or seal
leak. Fluid leakingunderthe probe is coming from
the pump housing area (Fig. 11).
(8) Fluid leaking under the probe could be from
the: pump seal and/or bushing, pump vent, kickdown
lever shaft access plug, pump bolts, or porous spots
in the pump body or transmission case (Fig. 11).
(9) If porous spots in the transmission case or
pump body are the suspected leak source, pressurize
the transmission as described in Leak Testing With
Air Pressure.
LEAK TESTING WITH AIR PRESSURE
This test involves closing off the transmission
openings and pressurizing the transmission to 8 psi
with Air Pump Tool 7700. A soapy water solution is
applied to suspected leak points before and during
the pressure test. Leaks will be indicated by the
presence of air bubbles coming through the solution.
Some transmission openings such as the fill tube
and front cooler line fitting can be closed off with a
rubber plug or similar device. Plugs can secured with
wire or duct tape.
Fig. 9 Typical Converter Housing Leak Paths
Fig. 10 Leak Test Probe
Fig. 11 Pump Area Inspection Points
21 - 74 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1186 of 1784
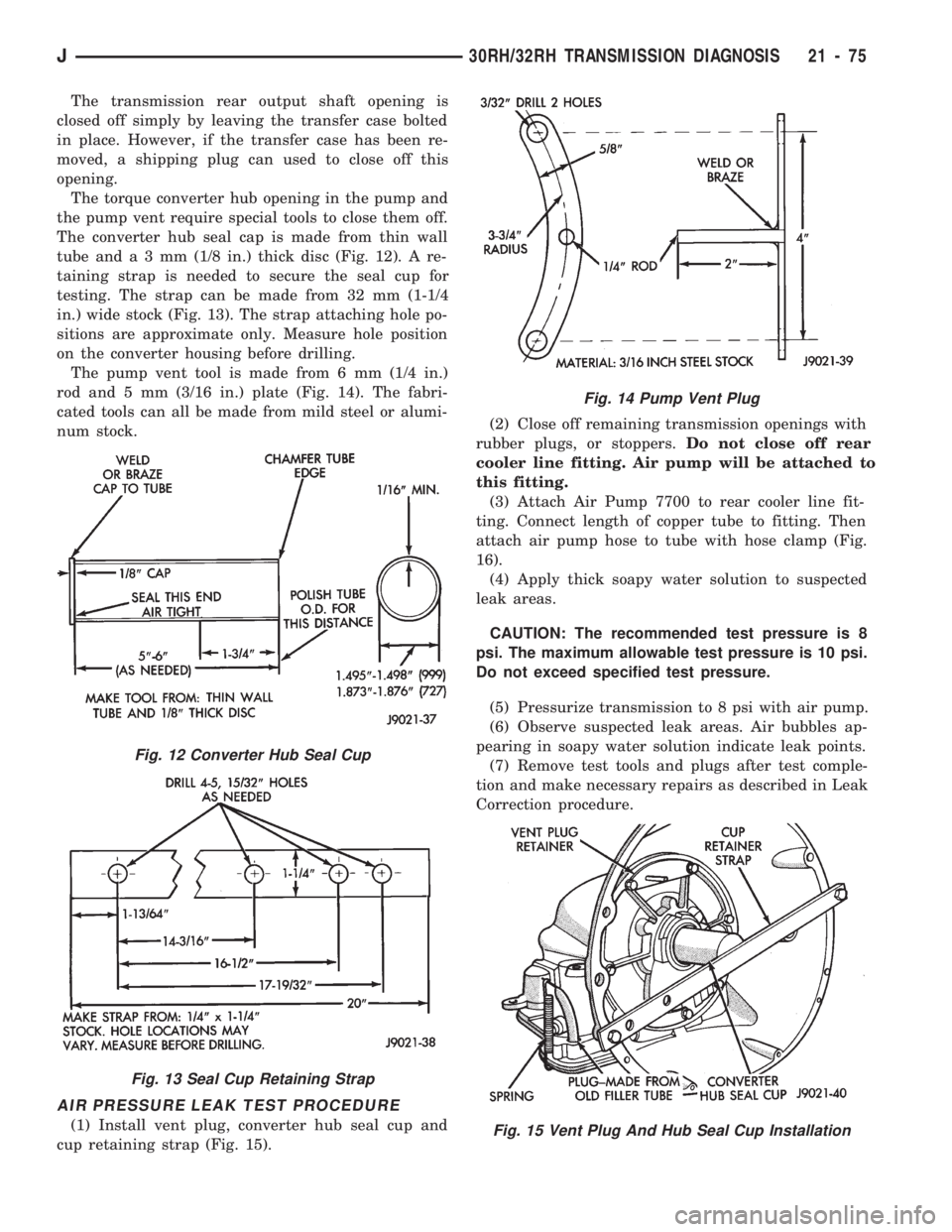
The transmission rear output shaft opening is
closed off simply by leaving the transfer case bolted
in place. However, if the transfer case has been re-
moved, a shipping plug can used to close off this
opening.
The torque converter hub opening in the pump and
the pump vent require special tools to close them off.
The converter hub seal cap is made from thin wall
tube anda3mm(1/8 in.) thick disc (Fig. 12). A re-
taining strap is needed to secure the seal cup for
testing. The strap can be made from 32 mm (1-1/4
in.) wide stock (Fig. 13). The strap attaching hole po-
sitions are approximate only. Measure hole position
on the converter housing before drilling.
The pump vent tool is made from 6 mm (1/4 in.)
rod and 5 mm (3/16 in.) plate (Fig. 14). The fabri-
cated tools can all be made from mild steel or alumi-
num stock.
AIR PRESSURE LEAK TEST PROCEDURE
(1) Install vent plug, converter hub seal cup and
cup retaining strap (Fig. 15).(2) Close off remaining transmission openings with
rubber plugs, or stoppers.Do not close off rear
cooler line fitting. Air pump will be attached to
this fitting.
(3) Attach Air Pump 7700 to rear cooler line fit-
ting. Connect length of copper tube to fitting. Then
attach air pump hose to tube with hose clamp (Fig.
16).
(4) Apply thick soapy water solution to suspected
leak areas.
CAUTION: The recommended test pressure is 8
psi. The maximum allowable test pressure is 10 psi.
Do not exceed specified test pressure.
(5) Pressurize transmission to 8 psi with air pump.
(6) Observe suspected leak areas. Air bubbles ap-
pearing in soapy water solution indicate leak points.
(7) Remove test tools and plugs after test comple-
tion and make necessary repairs as described in Leak
Correction procedure.
Fig. 12 Converter Hub Seal Cup
Fig. 13 Seal Cup Retaining Strap
Fig. 14 Pump Vent Plug
Fig. 15 Vent Plug And Hub Seal Cup Installation
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 75
Page 1187 of 1784

CONVERTER HOUSING AREA LEAK
CORRECTION
(1) Remove converter.
(2) Tighten front band adjusting screw until band
is tight around clutch retainer. This prevents
clutches from coming out when oil pump is removed.
(3) Remove oil pump and seal. Inspect pump hous-
ing drainback and vent holes for obstructions. Clear
holes with solvent and wire.(4) Inspect pump bushing and converter hub. If
bushing is scored, replace it. If converter hub is
scored, either polish it with crocus cloth or replace
converter if scoring is severe.
(5) Install new pump seal, O-ring, gasket, bushing.
Replace oil pump if cracked, porous or damaged in
any way.
(6) Loosen kickdown lever pin plug two turns. Ap-
ply Permatex No. 2 or equivalent to plug threads and
tighten plug to 17 Nzm (150 in-lbs) torque.
(7) Adjust front band.
(8) Lubricate pump seal and converter hub with
transmission fluid or petroleum jelly and install con-
verter.
(9) Install transmission.
(10) Install converter housing dust shield and
lower vehicle.DIAGNOSIS GUIDES AND CHARTS
The diagnosis charts provide additional reference
for transmission diagnosis.
The hydraulic flow charts outline fluid flow and hy-
draulic circuitry. Circuit operation is provided for all
gear ranges. Normal working pressures are also sup-
plied for each of the various gear ranges.
Fig. 16 Pressurizing Transmission
21 - 76 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1188 of 1784

30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 77
Page 1189 of 1784
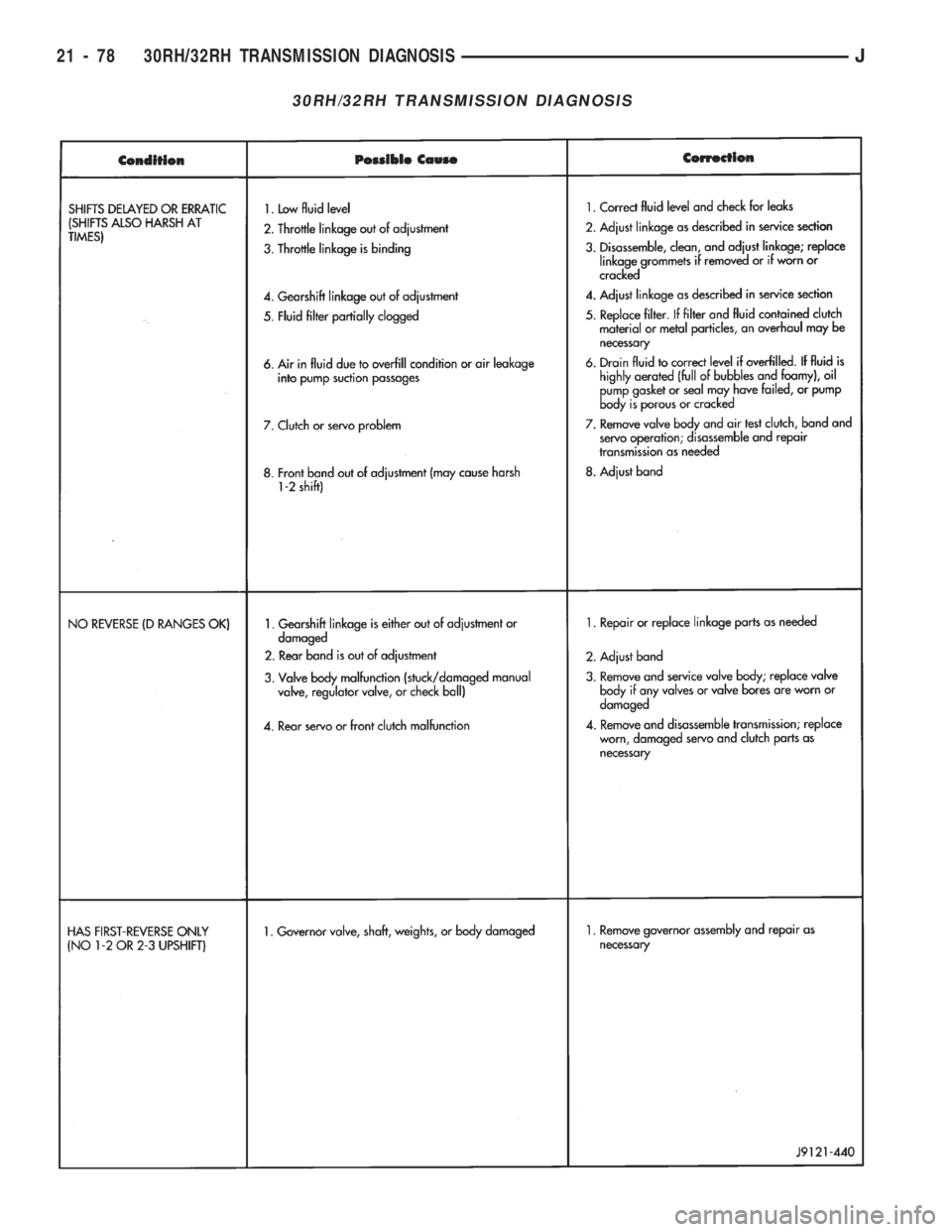
30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
21 - 78 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1190 of 1784
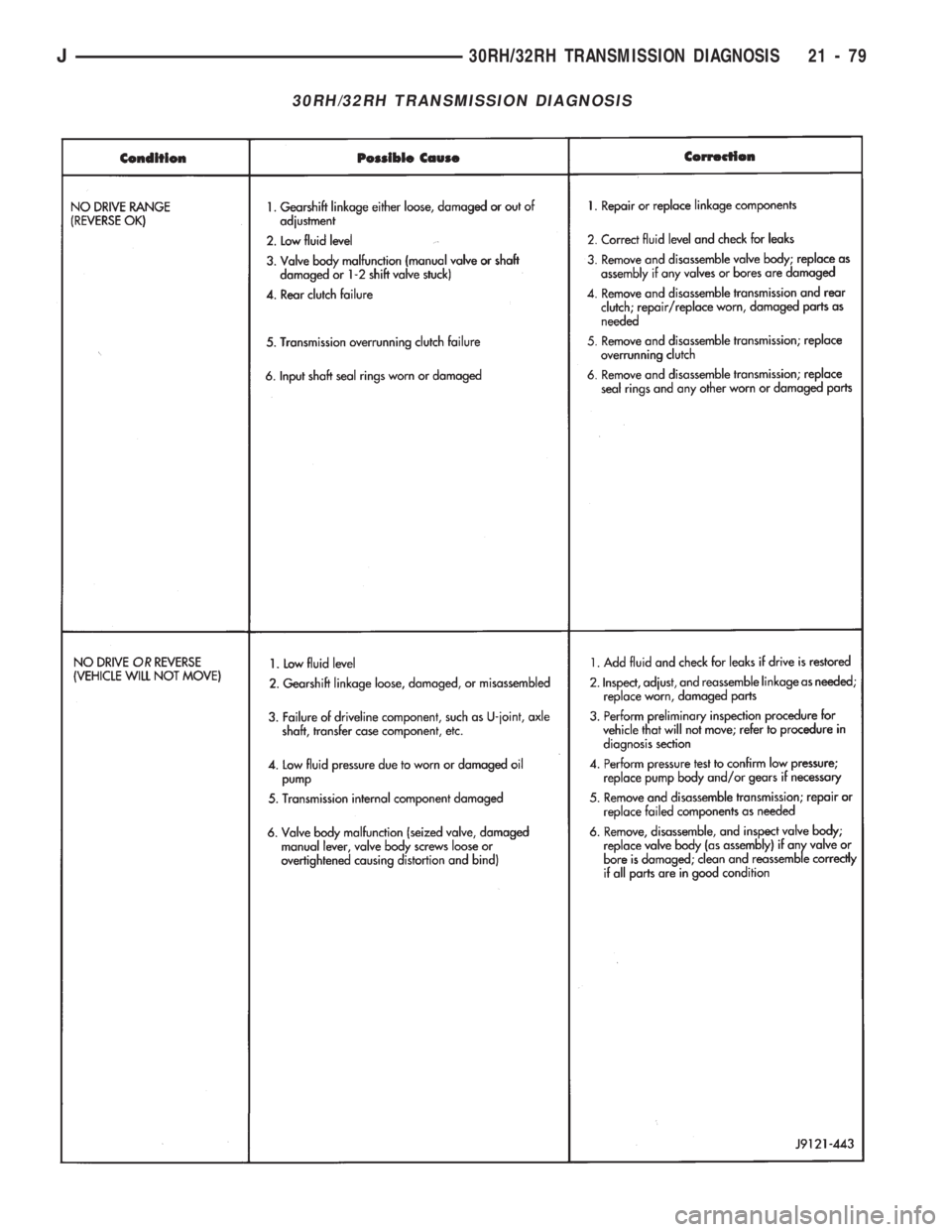
30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 79