engine JEEP CJ 1953 Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: CJ, Model: JEEP CJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 75 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
SUBJEC
GENERAL
.... . . Dl-1 Oil Pump Cl(
ENGINE DESCRIPTION
D1-2
Engine
Mounts Dl-3
ENGINE REMOVAL
Dl-4
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Dl-5
Alternator
and Fan Belt Dl-11
Camshaft
.... Dl-26
Cooling Fan and Water Pump.
......
.Dl-12
Crankshaft
Front Oil Seal .Dl-21
Crankshaft
Pulley D1-17
Crankshaft
Vibration Damper Dl-18
Cylinder
Head Assembly Dl-24
Distributor
Dl-9
Exhaust
Manifold .Dl-8
Flywheel
Dl-28
Flywheel
Housing and
Clutch
Dl-27
Fuel
Pump. ... . .Dl-10
Intake
Manifold and
Carburetor
Assembly.
.............
.Dl-7
Main
Bearing and Crankshaft. Dl-32 Mounting Engine on Engine Stand. . . . .Dl-6
Oil
Dipstick. Dl-16
Oil
Filter
Dl-13
Oil
Pan.. ...
.......
.Dl-29
Oil
Pressure Sending Unit Dl-15
Oil
Pump Dl-19
Oil
Pump Intake Pipe and Screen Dl-30
Piston and Rod Assembly. Dl-31
Push
Rod and Valve
Lifter.
.Dl-25
Rocker
Arm Cover Dl-23
Starter
Motor Dl-14
Timing
Chain
and Sprocket Dl-22
Timing
Chain
Cover Dl-20
ENGINE CLEANING, INSPECTION AND REPAIR
. . ... .Dl-33
Camshaft
Cleaning and Inspection Dl-55
Connecting Rod Bearing Inspection
and
Fitting .Dl-49
Crankshaft
Cleaning Dl-38
Crankshaft
Inspection and Repair Dl-39
Crankshaft
Main Bearing Cleaning
and
Inspection Dl-41
Crankshaft
Main Bearings. Dl-40
Crankshaft
Pulley Inspection. Dl-70
Crankshaft
Vibration Damper Inspection. D1-69
Cylinder
Block .Dl-34
Cylinder
Block Cleaning Dl-35
Cylinder
Block Inspection Dl-36
Cylinder
Block Repair. .Dl-37
Cylinder
Head and Valve Repair .Dl-63
Cylinder
Head and Valve Cleaning
and
Inspection.. . .Dl-62
Flywheel
Cleaning and Inspection Dl-52
Flywheel
Housing Cleaning
and
Inspection Dl-54
Hydraulic
Valve
Lifter
Leakdown Test. .Dl-57
Main
Bearing Fitting or
Shim
Stock Dl-42, Dl-43
Oil
Pan Cleaning and Inspection .Dl-51
PAR.
and
Inspection. .... .Dl-68
Oil
Pump Intake and Screen Cleaning. . .Dl-50
Piston and Rod Assembly.
...........
.Dl-48
Piston and Rod Cleaning and Inspection.D1-45
Piston and Rod Disassembly Dl-44
Piston Fitting Dl-46
Piston Ring Fitting. .Dl-47
Ring
Gear
Replacement. .Dl-53
Rocker
Arm Assembly. Dl-60
Rocker
Arm Cleaning and Inspection. . .Dl-59
Rocker
Arm Cover Cleaning
and
Inspection D1-65
Rocker
Arm Disassembly .Dl-58
Timing
Chain
and Sprocket Inspection. . .Dl-66
Timing
Chain
Cover Cleaning
and
Inspection.. . Dl-67
Valve
Installation D1-64
Valve
Lifter
and Push Rod
Cleaning
and Inspection. . Dl-56
Valve
Removal Dl-61
ENGINE REASSEMBLY
Dl-71
Alternator
and Fan Belt Dl-96
Camshaft
Dl-80
Clutch
and Flywheel Housing Dl-79
Cooling Fan.. . .Dl-95
Crankshaft
End Play Check. . Dl-74
Crankshaft
Front Oil Seal Dl-85
Crankshaft
Pulley Dl-89
Crankshaft
Vibration Damper Dl-88
Cylinder
Block and Crankshaft
Rear
Oil Seals Dl-72
Cylinder
Head Assembly .Dl-82
Distributor
Dl-99
Exhaust
Manifold Dl-98
Flywheel
.Dl-78
Fuel
Pump.. .. . Dl-97
Intake
Manifold and Carburetor Assembly Dl-101
Main
Bearing and
Crankshaft
Installation
.
Dl-73
Oil
Filter
Dl-93
Oil
Level
Dipstick Dl-90
Oil
Pan Dl-77
Oil
Pressure Sending Unit Dl-91
Oil
Pump.. .Dl-87
Oil
Pump Intake and Screen Assembly. .Dl-76
Piston and Rod Installation Dl-75
Rocker
Arm Cover. Dl-83
Spark
Plugs.. Dl-100
Starter
Motor Dl-92
Timing
Chain
and Sprocket.
..........
.Dl-84
Timing
Chain
Cover Dl-86
Valve
Lifter
and Push Rod Dl-81
Water
Pump. Dl-94
ENGINE INSTALLATION
Dl-102
FINAL
IN-VEHICLE
ADJUSTMENTS.
D1-103
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
Dl-104
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
. .Dl-105 75
Page 76 of 376
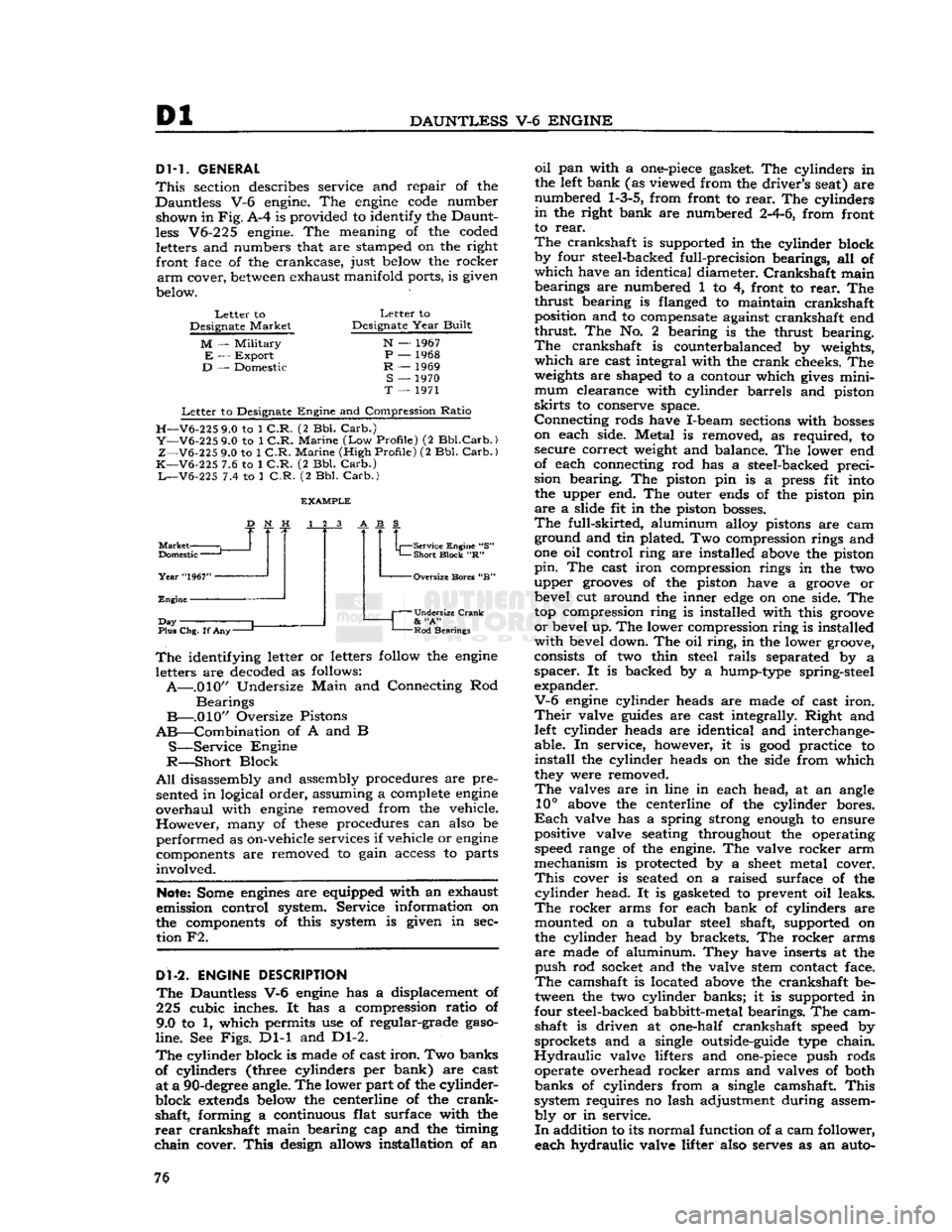
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
DM.
GENERAL
This
section describes service and repair of the
Dauntless V-6 engine. The
engine
code
number shown in
Fig.
A-4 is provided to identify the Daunt
less
V6-225 engine. The meaning of the coded letters and numbers that are stamped on the right front face of the crankcase, just below the rocker
arm
cover,
between
exhaust manifold ports, is given
below.
Letter
to
Designate
Market
M
—
Military
E
—
Export
D
— Domestic
Letter
to
Designate
Year
Built
N
— 1967
P
— 1968
R
— 1969
S
— 1970
T
— 1971
Letter
to Designate
Engine
and Compression
Ratio
H—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
Y—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
Marine
(Low
Profile)
(2
Bbl.Carb.)
Z—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
Marine
(High
Profile)
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
K—V6-225
7.6 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
L—V6-225
7.4 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
Market
Domestic
—
Year
"1967"
Engine
J
Day
Plus Chg. If
Any-
Service Engine "S"
Short
Block
"R" -Oversize Bores "B"
Undersize Crank
&
"A"
Rod
Bearings
The
identifying letter or letters follow the
engine
letters are decoded as follows:
A—.010"
Undersize
Main
and Connecting Rod
Bearings
B—.010"
Oversize Pistons
AB—Combination
of A and B
S—Service
Engine
R—Short
Block
All
disassembly and assembly procedures are pre sented in logical order, assuming a complete
engine
overhaul
with
engine
removed from the vehicle.
However,
many of
these
procedures can also be
performed as on-vehicle services if vehicle or
engine
components are removed to gain access to parts
involved.
Note:
Some
engines
are equipped with an exhaust
emission control system. Service information on
the components of this system is given in sec tion F2.
Dl-2.
ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
The
Dauntless V-6
engine
has a displacement of
225 cubic inches. It has a compression ratio of
9.0 to 1, which permits use of regular-grade
gaso
line.
See
Figs.
Dl-1 and Dl-2.
The
cylinder block is made of cast
iron.
Two banks
of cylinders (three cylinders per bank) are cast at a
90-degree
angle. The lower part of the cylinder-
block
extends
below the centerline of the
crank
shaft, forming a continuous flat surface with the
rear
crankshaft main bearing cap and the timing
chain
cover.
This
design allows installation of an
oil
pan with a
one-piece
gasket. The cylinders in
the left bank (as viewed from the driver's seat) are
numbered
1-3-5,
from front to
rear.
The cylinders
in
the right bank are numbered
2-4-6,
from front
to
rear.
The
crankshaft is supported in the cylinder block
by four steel-backed full-precision bearings, all of
which
have an identical diameter.
Crankshaft
main bearings are numbered 1 to 4, front to
rear.
The
thrust
bearing is flanged to maintain crankshaft position and to compensate against crankshaft end
thrust
The No. 2 bearing is the thrust bearing.
The
crankshaft is counterbalanced by weights,
which
are cast integral with the
crank
cheeks. The
weights
are shaped to a contour which
gives
mini
mum
clearance with cylinder barrels and piston
skirts
to conserve space.
Connecting
rods have I-beam sections with
bosses
on each side. Metal is removed, as required, to secure correct weight and balance. The lower end
of each connecting rod has a steel-backed preci
sion bearing. The piston pin is a press fit into the upper end. The outer ends of the piston pin
are
a slide fit in the piston
bosses.
The
full-skirted, aluminum alloy pistons are cam ground and tin plated. Two compression rings and
one oil control ring are installed above the piston
pin.
The cast iron compression rings in the two
upper
grooves
of the piston have a
groove
or bevel cut around the inner
edge
on one side. The
top compression ring is installed with this
groove
or
bevel up. The lower compression ring is installed
with
bevel down. The oil
ring,
in the lower groove,
consists of two thin steel
rails
separated by a
spacer.
It is backed by a hump-type spring-steel
expander.
V-6
engine
cylinder heads are made of cast
iron.
Their
valve
guides
are cast integrally. Right and left cylinder heads are identical and interchange
able. In service, however, it is
good
practice to
install
the cylinder heads on the side from which
they were removed.
The
valves are in line in each head, at an angle
10°
above the centerline of the cylinder bores.
Each
valve has a spring strong enough to ensure
positive valve seating throughout the operating speed range of the engine. The valve rocker arm
mechanism is protected by a
sheet
metal cover.
This
cover is seated on a raised surface of the
cylinder
head. It is gasketed to prevent oil leaks.
The
rocker arms for each bank of cylinders are mounted on a tubular steel shaft, supported on
the cylinder head by brackets. The rocker arms
are
made of aluminum. They have inserts at the
push
rod socket and the valve stem contact face.
The
camshaft is located above the crankshaft be
tween the two cylinder banks; it is supported in
four steel-backed babbitt-metal bearings. The cam shaft is driven at one-half crankshaft speed by
sprockets and a single outside-guide type chain.
Hydraulic
valve lifters and
one-piece
push rods operate overhead rocker arms and valves of both
banks
of cylinders from a single camshaft.
This
system requires no lash adjustment during assem
bly
or in service.
In
addition to its normal function of a cam follower,
each hydraulic valve lifter also serves as an auto- 76
Page 77 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
©©©©©©©©©
12697
FIG.
Dl-1—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE, SIDE SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Fan
Blade
2—
Fan
Spacer
3—Fan
Pulley
4—
Water
Pump 5—
Timing
Chain
Cover
6—
Camshaft
Sprocket
7—
Thermostat
Bypass Hose
8—
Thermostat
Housing
9—
Thermostat
10—
Carburetor
11—
Intake
Manifold
12—
Rocker
Arm Cover 13—
Cylinder
Block 14—
Push
Rod
15—
Camshaft
16—
Flywheel
17—
Clutch
Pressure Plate
18—
Clutch
Driven Plate
19—
Clutch
Pilot Bearing
20—
Oil
Seal Packing
21—
Rear
Main
Bearing Shell
22— Connecting Rods
23—
Rear
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
24—
Oil
Screen
25—
Oil
Screen Pipe and Housing
26—
Oil
Pan 27—
Front
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
28—
Crankshaft
29—
Front
Main
Bearing Shell
30—
Timing
Chain
31—
Crankshaft
Sprocket
32—
Oil
Slinger
33—
Oil
Shedder 34 Oil Shedder Packing
35—
-Woodruff
Key
36—
"Vibration
Damper
37—
Crankshaft
Pulley
38—
Fan
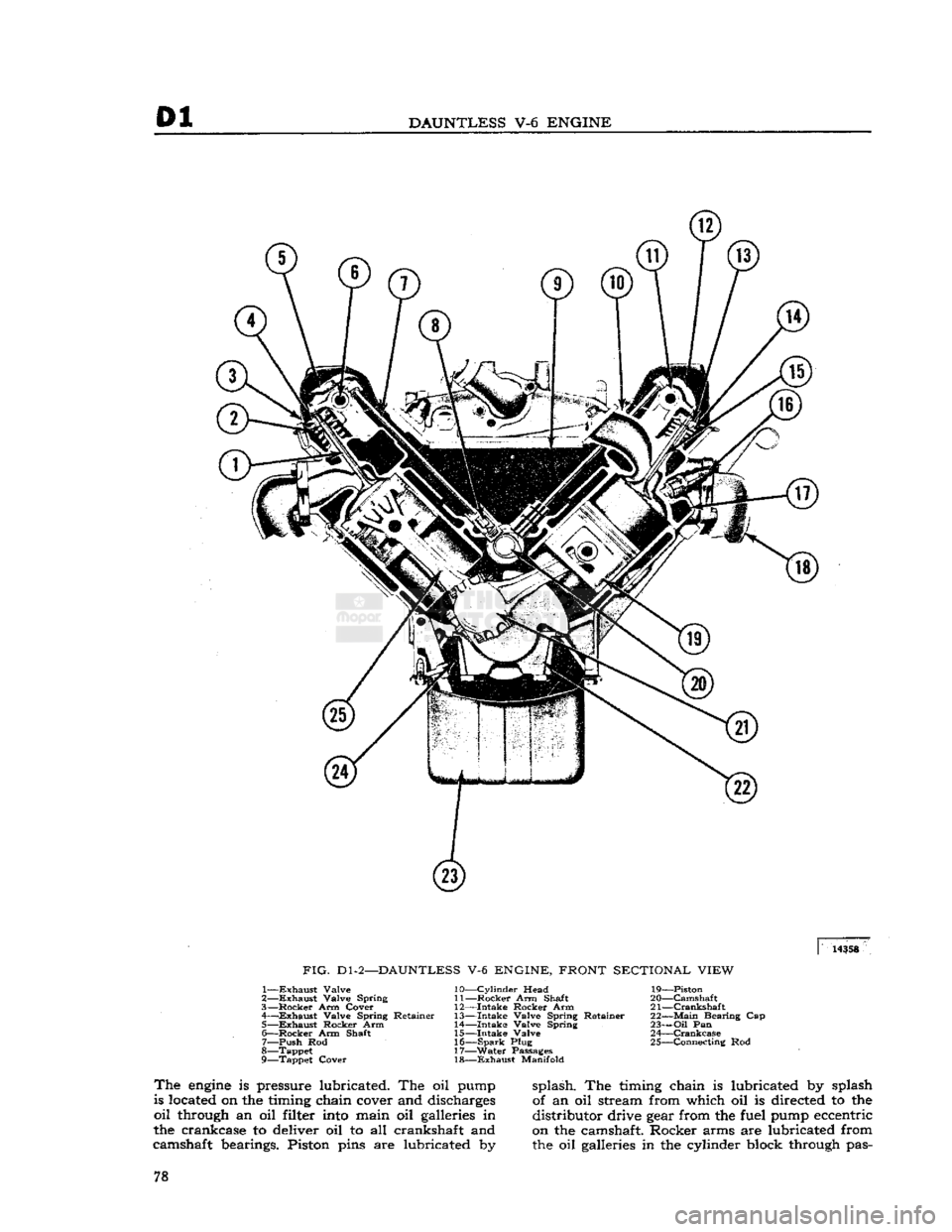
Belt matic adjuster, to prevent lash in the valve operat
ing linkage. Hydraulic valve lifters also provide
a
cushion of oil to absorb operating shocks. As shown in Fig. Dl-3, all parts of a hydraulic lifter
are
housed in the body, which is the cam follower.
At
the beginning of valve operation, the valve lifter body rests on the camshaft base circle.
Plunger
spring tension prevents lash clearances in the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft forces the valve lifter body up
ward,
both oil in the lower chamber and check
ball
spring
tension firmly seat the check ball against the plunger to prevent appreciable
loss
of oil from
the lower chamber. Oil pressure forces the plunger
upward,
with the body, to operate the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft rotates to closed-valve position, the valve spring forces the linkage and lifter down
ward.
When the
engine
valve seats, the linkage
parts
and plunger stop, but the plunger spring forces
the body downward .002" to .003"
[0,050
a
0,076
mm.] until it again rests on the camshaft base
circle.
Oil pressure then forces the check ball away
from
its seat and allows passage of oil past the check ball into the lower chamber.
This
replaces
the slight amount of oil lost by leakage. During
the valve opening and closing operation, a very
slight amount of oil escapes
between
plunger and body, and returns to the crankcase.
This
slight
loss
of oil (leak-down) is beneficial. It provides a
gradual
change of oil in the valve lifter; fresh oil
enters the lower chamber at the end of each cycle
of operation. 77
Page 78 of 376
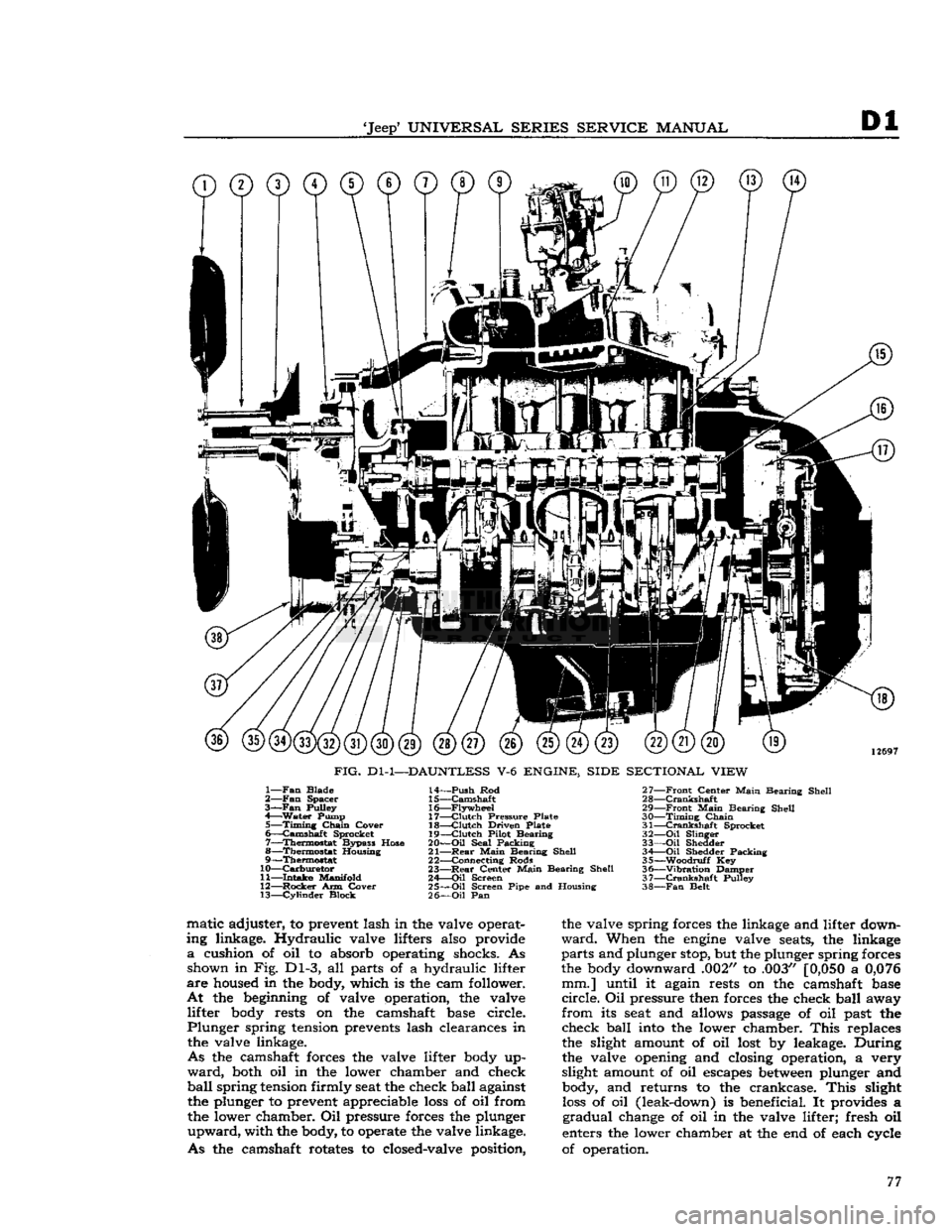
01
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
14358
FIG.
Dl-2—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE, FRONT SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Exhaust
Valve
2—
Exhaust
Valve Spring
3—
Rocker
Arm Cover
4—
—Exhaust
Valve Spring Retainer 5—
Exhaust
Rocker Arm
6—
Rocker
Arm Shaft 7— push Rod
8— Tappet
9— Tappet Cover 10—
Cylinder
Head
11—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
12—
Intake
Rocker Arm
13—
Intake
Valve Spring Retainer
14—
Intake
Valve Spring
15—
Intake
Valve 16—
Spark
Plug
17—
Water
Passages 18—
Exhaust
Manifold 19— Piston
20—
Camshaft
21—
Crankshaft
22—
Main
Bearing Cap
23—
Oil
Pan
24—
Crankcase
25— Connecting Rod
The
engine
is pressure lubricated. The oil pump
is located on the timing chain cover and discharges
oil
through an oil filter
into
main oil galleries in
the crankcase to deliver oil to all crankshaft and
camshaft bearings. Piston pins are lubricated by- splash. The timing chain is lubricated by splash
of an oil stream from which oil is directed to the
distributor drive gear from the fuel pump eccentric
on the camshaft. Rocker arms are lubricated from
the oil galleries in the cylinder block through pas- 78
Page 79 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
12710
FIG.
D1
-3—HYDRAULIC VALVE
LIFTER
ASSEMBLY, CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Snap
Ring
6—Ball Retainer
2— Rod
Seat
7—Plunger Spring
3—
Oil
Inlets
8—Lifter
Body
4—
Plunger
9—Bronzed
Cap
5— Feed
Hole
sages
in the block and cylinder head.
The
water cooled system is pressurized to provide efficient
engine
cooling. It consists of a centrifugal-
type water pump, mounted on the timing chain cover, and is driven by the
engine
fan pulley. The
pump provides coolant flow equally to both
cylin
der banks under control of a thermostat. Coolant
flow is around the cylinders and through the
cylinder
head to dispel the heat of combustion in
the engine.
Dl-3.
Engine Mounts
The
engine-transmission unit is mounted to the chassis at three points by rubber pads. The two
front mounts are bolted to the
engine
cylinder
block and the frame members. These mounts sup port most of the
engine
weight, and absorb
vibra
tion which would otherwise be caused by changes
in
engine
output torque. The single
rear
mount is
placed
between
the transmission and the trans mission support. It supports part of the engine'
and
transmission weight, and locates the
rear
of
the
engine
with respect to the centerline of the
vehicle.
Dl-4. ENGINE REMOVAL
To
remove the
engine
from the vehicle follow the
procedurers listed below:
a.
Remove hood. b. Disconnect battery cables from battery and
engine. c. Remove air cleaner.
d.
Drain
coolant from radiator and engine.
e.
Drain
engine
oil.
f. Disconnect alternator wiring harness from con nector at regulator.
cj.
Disconnect the fuel evaporative purge line con nected to the
P.C.V.
valve.
h.
Disconnect upper and lower radiator
hoses
from
the engine.
i.
Remove right and left radiator support
bars,
j.
Remove radiator from the vehicle.
k.
Disconnect
engine
wiring harnesses from con
nectors located on
engine
firewall.
I.
On
engines
equipped with exhaust emission con
trol,
remove the air pump, air distribution manifold,
and
anti-backfire (gulp) valve. See Section F2 for
procedure.
m.
Disconnect battery cable and wiring from en
gine
starter assembly.
n.
Remove
engine
starter assembly from engine,
o.
Disconnect
engine
fuel
hoses
from fuel lines at
right
frame
rail,
p. Plug fuel lines.
q.
Disconnect choke cable from carburetor and cable support bracket mounted on engine,
r.
Disconnect exhaust pipes from right and left
engine
manifolds.
s. Place
jack
under transmission and support trans
mission weight.
f. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to front motor mounts.
u.
Attach suitable sling to
engine
lifting
eyes
and,
using hoist, support
engine
weight.
v. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to flywheel housing.
w. Raise
engine
slightly and slide
engine
forward
to remove transmission main shaft from clutch plate spline.
Note:
Engine and transmission must be raised
slightly to release the main shaft from the clutch
plate while sliding the
engine
forward.
x. When
engine
is free of transmission shaft raise
engine
and remove from vehicle,
y. Place
engine
on suitable blocking or
engine
stand and remove sling from engine.
Dl-5.
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Engine
disassembly is presented in the sequence to be followed when the
engine
is to be completely
overhauled after removal from the vehicle. Some of the operations of the procedure are also applicable separately with the
engine
in the vehicle,
provided that wherever necessary the part of the
engine
to be worked on is first made accessible by removal of
engine
accessories or other parts.
When
the disassembly operations are performed
with
the
engine
out of the vehicle, it is assumed,
in
this procedure, that all of the accessories have
been removed
prior
to starting the disassembly and
the oil has been drained.
Page 80 of 376
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
In
addition to the instructions covering operations
for disassembling the
engine
out of the vehicle, special instructions are given to cover different
operations required when disassembly is
done
with
the
engine
installed.
During
disassembly operations, the
engine
should be mounted in a suitable
engine
repair stand.
Where
practicable, modify or adapt an existing re
pair
stand as necessary to accommodate the
engine.
If
an
engine
repair stand is not used, take care to
perform
disassembly operations in a manner that
will
protect personnel against an accident and the
engine
and its parts against damage.
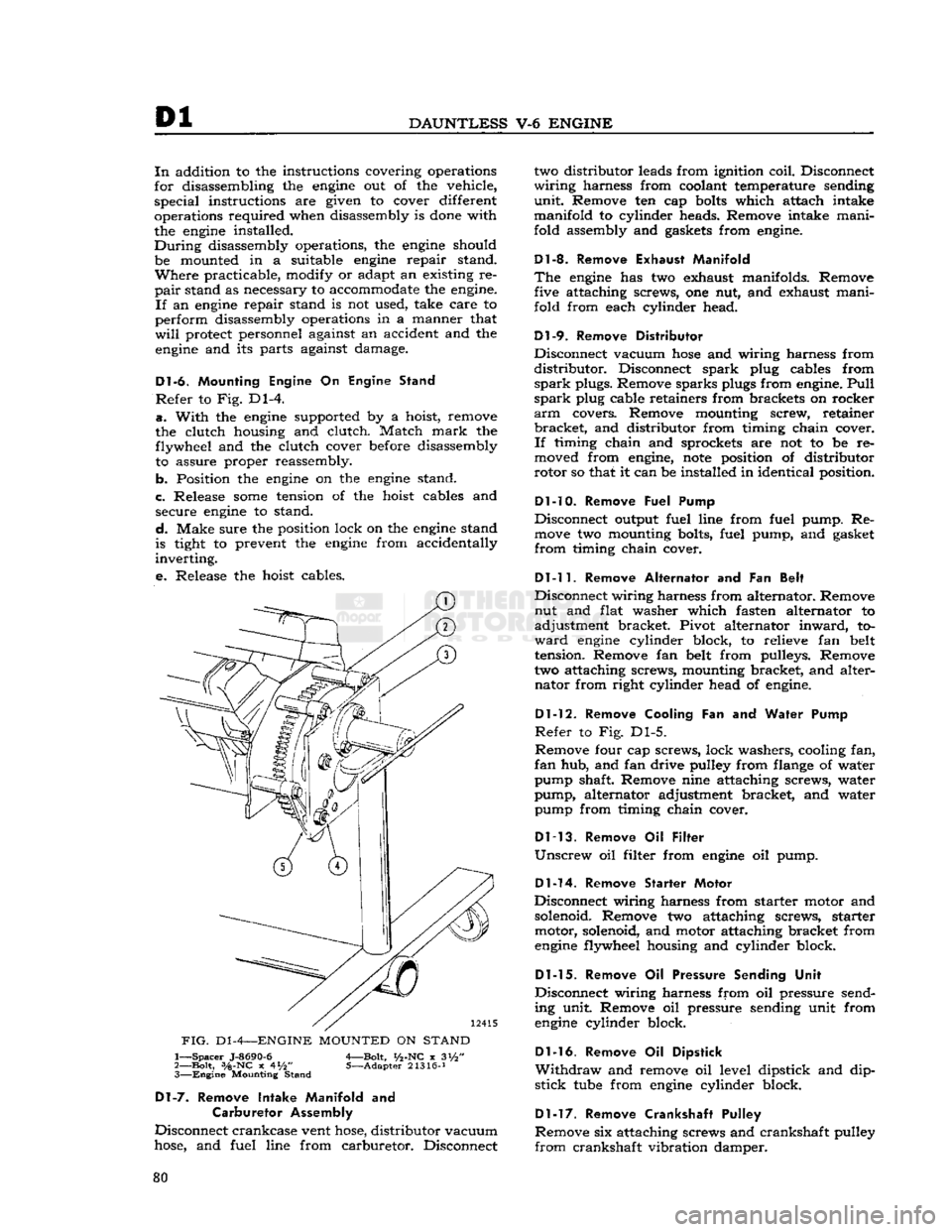
Dl-6.
Mounting Engine
On
Engine Stand
Refer
to Fig. Dl-4.
a.
With
the
engine
supported by a hoist, remove
the clutch housing and clutch. Match
mark
the flywheel and the clutch cover before disassembly to assure proper reassembly.
b. Position the
engine
on the
engine
stand.
c. Release
some
tension of the hoist cables and secure
engine
to stand.
d.
Make sure the position lock on the
engine
stand
is tight to prevent the
engine
from accidentally
inverting.
e.
Release the hoist cables.
FIG.
D1
-4—ENGINE
MOUNTED
ON
STAND
1—
Spacer
J-8690-6
A—Bolt,
i/2-NC
x 3i/2"
2—
Bolt,
3/a-NC
x 4*/2" 5—Adapter 21316-J 3—
Engine
Mounting Stand
Dl-7.
Remove Intake Manifold
and
Carburetor Assembly
Disconnect crankcase vent
hose,
distributor vacuum
hose,
and fuel line from carburetor. Disconnect two distributor leads from ignition coil. Disconnect
wiring
harness from coolant temperature sending
unit.
Remove ten cap
bolts
which attach intake
manifold to cylinder heads. Remove intake mani
fold assembly and gaskets from
engine.
Dl-8. Remove Exhaust Manifold
The
engine
has two exhaust manifolds. Remove five attaching screws, one nut, and exhaust mani
fold from each cylinder head.
Dl-9.
Remove Distributor
Disconnect vacuum
hose
and wiring harness from
distributor.
Disconnect spark plug cables from
spark
plugs. Remove sparks plugs from
engine.
Pull
spark
plug cable retainers from brackets on rocker
arm
covers. Remove mounting screw, retainer
bracket,
and distributor from timing chain cover.
If
timing chain and sprockets are not to be re
moved from
engine,
note
position of distributor
rotor so that it can be installed in identical position.
Dl-10. Remove
Fuel Pump
Disconnect output fuel line from fuel pump. Re
move
two mounting bolts, fuel pump, and gasket
from
timing chain cover.
Dl-11.
Remove Alternator
and Fan
Belt
Disconnect wiring harness from alternator. Remove nut and flat washer which fasten alternator to
adjustment bracket. Pivot alternator
inward,
to
ward
engine
cylinder block, to relieve fan belt
tension. Remove fan belt from pulleys. Remove
two attaching screws, mounting bracket, and alter nator from right cylinder head of
engine.
Dl-12.
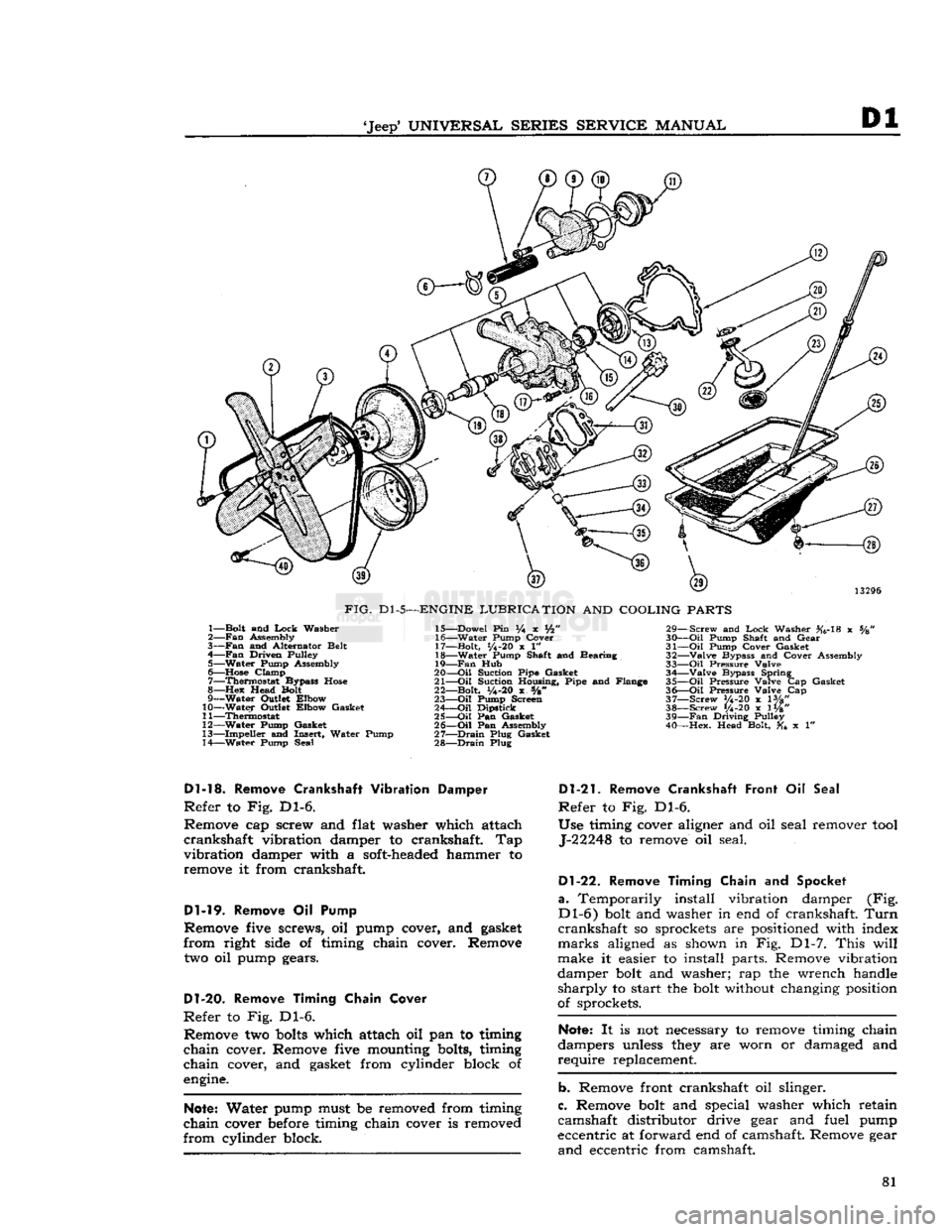
Remove Cooling
Fan and
Water Pump
Refer
to Fig. Dl-5.
Remove four cap screws, lock washers, cooling fan,
fan
hub, and fan drive pulley from flange of water
pump shaft. Remove nine attaching screws, water
pump, alternator adjustment bracket, and water pump from timing chain cover.
Dl-13.
Remove
Oil
Filter
Unscrew
oil filter from
engine
oil pump.
Dl-14.
Remove Starter Motor
Disconnect wiring harness from starter motor and
solenoid. Remove two attaching screws, starter motor, solenoid, and motor attaching bracket from
engine
flywheel housing and cylinder block.
Dl-15.
Remove
Oil
Pressure Sending Unit
Disconnect wiring harness from oil pressure send
ing unit. Remove oil pressure sending unit from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-16.
Remove
Oil
Dipstick
Withdraw
and remove oil level dipstick and dip
stick
tube
from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-17.
Remove Crankshaft Pulley
Remove six attaching screws and crankshaft pulley
from
crankshaft vibration damper. 80
Page 81 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
13296
FIG.
Dl-5—ENGINE
LUBRICATION
AND
COOLING
PARTS
1— Bolt and
Lock
Washer
2—
Fan
Assembly
3—
Fan
and Alternator Belt
4—
Fan
Driven Pulley 5— Water Pump Assembly
6—
Hose
Clamp 7— Thermostat Bypass
Hose
8—Hex
Head Bolt
9— Water Outlet Elbow
10— Water Outlet Elbow Gasket
11— Thermostat
12— Water Pump Gasket
13— Impeller and Insert, Water Pump
14— Water Pump Seal 15— Dowel Pin % x Vfc"
16— Water Pump Cover
17— Bolt,
1/4-20
x 1"
18— Water Pump Shaft and Bearing
19—
Fan
Hub
20—
-Oil
Suction Pipe Gasket
21—
Oil
Suction Housing, Pipe and Flange
22— Bolt,
y4-20
x s/8"
23—
Oil
Pump Screen
24—
Oil
Dipstick
25—
Oil
Pan Gasket
26—
Oil
Pan Assembly
27—
Drain
Plug Gasket
28—
Drain
Plug 29— Screw and
Lock
Washer #6-18 x %
30—
Oil
Pump Shaft and Gear
31—
Oil
Pump Cover Gasket
32— Valve Bypass and Cover Assembly
33—
Oil
Pressure Valve 34— Valve Bypass Spring
35—
Oil
Pressure Valve Cap Gasket
36—
Oil
Pressure Valve Cap
37— Screw V4-20 x lVg"
38— Screw 1/4-20 x 1W' 39—
Fan
Driving Pulley
40— Hex. Head Bolt, x 1"
Dl-13.
Remove
Crankshaft
Vibration Damper
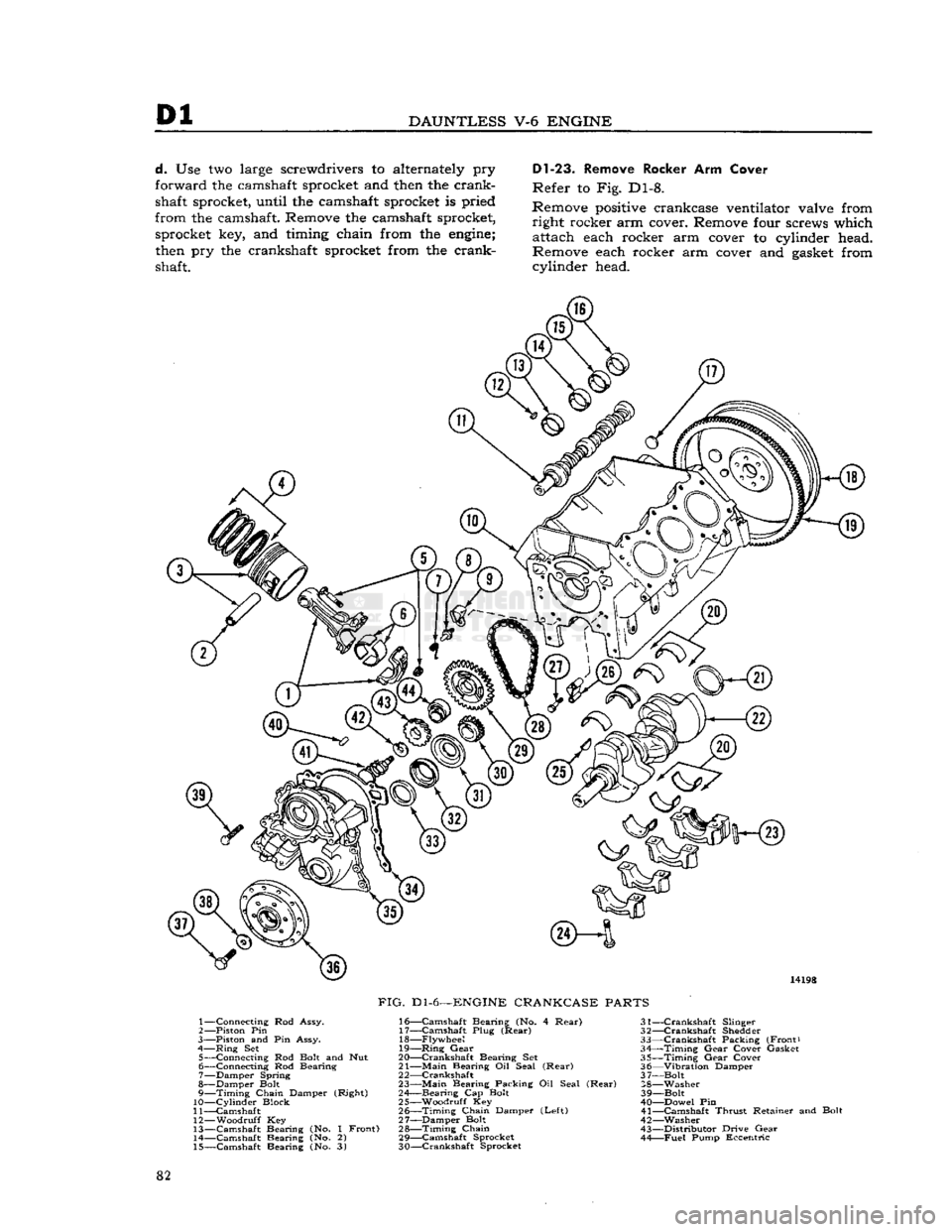
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
Remove cap screw and flat washer which attach
crankshaft
vibration damper to crankshaft. Tap
vibration
damper with a soft-headed hammer to remove it from crankshaft.
Dl-19.
Remove Oil Pump
Remove five screws, oil pump cover, and gasket
from
right side of timing chain cover. Remove
two oil pump gears.
D1-20.
Remove Timing Chain Cover
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6. Remove two
bolts
which attach oil pan to timing
chain
cover. Remove five mounting bolts, timing
chain
cover, and gasket from cylinder block of
engine.
Note:
Water pump must be removed from timing
chain
cover before timing chain cover is removed
from
cylinder block.
Dl-21.
Remove Crankshaft Front
Oil
Seal
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
Use timing cover aligner and oil seal remover
tool
J-22248 to remove oil seal.
Dl-22.
Remove Timing Chain
and
Spocket
a.
Temporarily install vibration damper (Fig.
Dl-6)
bolt and washer in end of crankshaft.
Turn
crankshaft
so sprockets are positioned with index
marks
aligned as shown in Fig. Dl-7.
This
will
make it easier to install parts. Remove vibration
damper bolt and washer; rap the wrench handle
sharply
to start the bolt without changing position
of sprockets.
Note:
It is not necessary to remove timing chain
dampers unless they are worn or damaged and
require
replacement.
b. Remove front crankshaft oil slinger.
c. Remove bolt and special washer which retain
camshaft distributor drive gear and fuel pump
eccentric at forward end of camshaft. Remove gear
and
eccentric from camshaft. 81
Page 82 of 376
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
d.
Use two large screwdrivers to alternately pry
forward the camshaft sprocket and
then
the crank
shaft sprocket, until the camshaft sprocket is pried
from the camshaft. Remove the camshaft sprocket, sprocket key, and timing chain from the
engine;
then
pry the crankshaft sprocket from the crankshaft.
Dl-23.
Remove Rocker Arm Cover
Refer to Fig. Dl-8.
Remove
positive
crankcase ventilator valve from right rocker arm cover. Remove four screws which attach each rocker arm cover to cylinder head.
Remove each rocker arm cover and
gasket
from cylinder head. 14198
FIG.
Dl-6—ENGINE
CRANKCASE
PARTS
1— Connecting Rod Assy.
2— —Piston Pin
3—
Piston and Pin Assy.
4—
Ring
Set 5— Connecting Rod
Bolt
and Nut
6— Connecting Rod Bearing
7— Damper Spring
8— Damper
Bolt
9—
Timing
Chain Damper (Right)
10—
Cylinder
Block
11— Camshaft
12—
Woodruff
Key
13— Camshaft Bearing (No. 1 Front) 14— Camshaft Bearing (No. 2)
15— Camshaft Bearing (No. 3) 16—
Camshaft
Bearing (No. 4
Rear)
31-
17—
Camshaft
Plug
(Rear)
32-18—
Flywheel
33-
19—
Ring
Gear
34-
20— Crankshaft Bearing Set 35-
21—
Main
Bearing Oil Seal
(Rear)
36-
2 2—Crankshaft 3 7-
23—
Main
Bearing Packing Oil Seal
(Rear)
28-
24— Bearing Cap
Bolt
39-
25— Woodruff Key 40-
26—
Timing
Chain Damper
(Left)
41-
27— Damper Bolt 42- 28—
Timing
Chain
43-
29—
Camshaft
Sprocket 44-
30— Crankshaft Sprocket
—Crankshaft
Slinger
—Crankshaft
Shedder
—Crankshaft
Packing (Front)
—Timing
Gear
Cover Gasket
—Timing
Gear
Cover
—Vibration
Damper
-Bolt
-Washer
-Bolt
—Dowel Pin
-Camshaft
Thrust
Retainer and Bolt
—Washer
-Distributor
Drive
Gear
—Fuel
Pump Eccentric
82
Page 83 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
14028
j
FIG.
D1-7—TIMING
CHAIN
AND
SPROCKET ALIGNMENT 1—
Camshaft Sprocket
2—
Crankshaft
3—Timing
Chain
Timing
Marks
Dl-24.
Remove
Cylinder
Head Assembly
a.
Unscrew, but do not remove, three
bolts
(Fig.
Dl-8)
which attach rocker
arm
assembly to cylinder
head.
Remove rocker arm assembly, with bolts,
from
cylinder head. See Section F2 for
engines
equipped with exhaust emission control.
b. Remove
eight
cylinder head bolts, cylinder head,
and
gasket from cylinder block.
Dl-25.
Remove Push Rod and Valve
Lifter
Refer
to Fig. Dl-8. Remove push rods and valve lifters from the
cylin
der
block.
Mark,
or otherwise identify, each valve
lifter
according to its cylinder and valve position.
Note:
If valve lifters are not to be serviced, cover
valve lifters and camshaft with a clean cloth to
protect them from dirt
Dl-26.
Remove Camshaft
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
Carefully
withdraw camshaft forward from bear
ing bores; avoid marring the bearing surfaces. Re
move
camshaft from cylinder block.
Dl-27.
Remove Flywheel Housing and
Clutch
a.
If flywheel housing and clutch was not pre
viously removed, remove six mounting
bolts
and
flywheel housing from cylinder block.
b.
Mark
clutch cover and flywheel to assure that
clutch
will
be installed in identical position when
engine
is assembled.
c. Remove six attaching screws and clutch assem
bly from flywheel.
D1-28. Remove Flywheel
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
Remove six attaching
bolts
and flywheel from
engine
crankshaft.
Dl-29.
Remove Oil Pan
Refer
to Fig. Dl-5.
To
gain access to oil pan mounting bolts, invert
the
engine.
Remove mounting bolts, oil pan, and gasket from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-30.
Remove Oil Pump Intake Pipe and Screen
Refer
to Fig. Dl-5.
Remove two attaching screws, and oil pump intake
pipe and screen assembly from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-31.
Remove Piston and
Connecting
Rod Assembly
a.
Examine the cylinder bores. If bores are worn
so that shoulder or ridges exist at the top of piston
ring
travel, remove the ridges with a ridge reamer.
FIG.
Dl-8-
-CYLINDER HEAD,
AND COVER
ROCKER
ARM
1—
—Right
Rocker
Arm
Cover
2—
Rocker
Arm
Cover
Bolt
3—
Gasket
4—
Bolt
5—
Baffle
6—
Left
Rocker
Arm
Cover
7—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
8—Plug
9—
Rocker
Arm Spring
10—
Cylinder
Head
11—
Head
Gasket
12—
Push
Rod
13—
Valve
Lifter
14—
Intake
Valve
15—
Exhaust
Valve
16—
Dowel
Pin
17—
Valve
Spring 18—
Valve
Spring Cap
19—
Valve
Spring Cap Key
20—
Cotter
Pin
21—
Rocker
Arm Shaft End Washer
22—
Rocker
Arm Shaft Spring
23—
Rocker
Arm
24—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
Bracket
25—
Bolt
83
Page 84 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
This
will
prevent damage to piston rings or
crack
ing piston lands during removal.
b. Use a silver pencil or quick-drying paint to mark
the cylinder number on all pistons, connecting rods,
and
caps. Starting at the front end of the crankcase,
the cylinders in the right bank are numbered 2-4-6
and
in the
left
bank are numbered
1-3-5.
c. Remove cap and lower connecting rod bearing
half
from No. 1 connecting rod.
d.
Push the piston and rod assembly away from
the crankshaft and remove it from top of cylinder bore. Then install cap and lower bearing half on
connecting rod.
e. Remove each connecting rod and piston as sembly as described in c and d, above.
FIG.
D1-9—CRANKSHAFT
MAIN
BEARING
CAPS
1—Thrust
Bearing
D1-32.
Remove
Main
Bearing and Crankshaft
a.
This
engine
has four crankshaft main bearings.
Front
to
rear,
they are numbered 1 to 4. Refer to
Fig.
Dl-9. With a silver pencil or quick-drying
paint, mark the bearing number on each main bearing cap.
b. Remove two
bolts
which secure first (front)
main
bearing cap to
engine
cylinder block. With
a
lifting bar, carefully pry the cap from the crank shaft and block. Be careful not to damage the cap,
block or crankshaft. Remove the bearing cap, with
lower main bearing half, from the cylinder block.
Keep
bearing half and cap
together.
Similarly, remove the next two main bearing caps with lower
main
bearing halves. To remove
rear
main bearing
cap,
use
rear
main bearing remover bolt W-323.
c. Remove the fabric seal from inside diameter of
fourth (rear) main bearing cap, and remove neo-
prene composition seal from outer surface of this
bearing cap. Discard both seals.
d.
Lift
and remove the crankshaft from
engine
cylinder
block. Do not remove upper main bearing
halves from block or lower main bearing halves
from
caps at this time. Mount main bearing caps
in
their original positions.
Dl-33.
ENGINE
CLEANING,
INSPECTION,
AND
REPAIR
The
cleaning, inspection, and repair procedures
detailed herein are recommended to be followed
when a
complete
engine
overhaul is to be made
with the
engine
out of the vehicle. These instruc
tions
can generally be applied individually with the
engine
in the vehicle. Wherever the procedure dif
fers due to the
engine
being in the vehicle, the necessary special instructions are provided. Inspec
tion and repair instructions are included to cover
the cylinder block, cylinder head, crankshaft and bearings, connecting rods and bearings, oil pump,
valves and tappets, pistons and rings, flywheel,
timing gears, and the camshaft and bearings. In
addition, fitting operations for
these
engine
com
ponents
are included.
D1-34.
Cylinder Block
The
cylinder block must be cleaned thoroughly, inspected, and repaired as necessary, as described
below.
Dl-35.
Cylinder Block Cleaning
Steam-clean the cylinder block, or clean it with
a
suitable cleaning solvent A scraper can be used
to remove
hard
deposits, but do not score machined
surfaces. Be certain that oil passages, valve cham
bers,
crankcase, and cylinder walls are free from sludge, dirt, and carbon deposits. After cleaning,
dry
the cylinder block carefully with compressed
air.
Dl-36.
Cylinder Block Inspection
a.
Inspect cylinder walls visually for scoring,
roughness, or ridges which indicate excessive wear.
Check
cylinder bores for taper and out-of-round
with an accurate cylinder
gauge.
Measure eact bore at top, middle and bottom, both parallel tc
and
at right
angles
to the centerline of the
engine
The
diameter of the cylinder bores at any poin
FIG.
Dl-10—MEASURING
CYLINDER
BORE
1—Telescope Gauge [90*
From
Piston Pin]
84