Radio JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 301 of 2199

(2) Press firmly and evenly on the remote radio
switch until each of the switch snap features is fully
engaged in the mounting hole of the steering wheel
rear trim cover.
(3) Reconnect the steering wheel wire harness con-
nector to the connector receptacle of the remote radio
switch.
(4) Install the speed control switch onto the steer-
ing wheel. Refer to Electrical, Speed Control for the
procedures.
(5) Install the driver side airbag onto the steering
wheel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION) for the proce-
dures.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
SPEAKER
DESCRIPTION
STANDARD
The standard equipment speaker system includes
speakers in six locations. One 6.4 centimeter (2.50
inch) diameter tweeter is installed on each end of the
instrument panel top pad. One 15.2 by 22.9 centime-
ter (6 by 9 inch) full-range speaker is located in each
front door. There is also one full-range 16.5 centime-
ter (6.5 inch) diameter full-range speaker located in
each rear door.
PREMIUM
The optional premium speaker system features six
Infinity model speakers in six locations. Each of the
standard speakers is replaced with Infinity model
speakers. One 6.4 centimeter (2.50 inch) diameter
Infinity tweeter is installed on each end of the
instrument panel top pad. One 15.2 by 22.9 centime-
ter (6 by 9 inch) Infinity woofer is located in each
front door. There is also one full-range 16.5 centime-
ter (6.5 inch) diameter Infinity full-range speaker
located in each rear door. The premium speaker sys-
tem also includes an additional Infinity power ampli-
fier. The total available power of the premium
speaker system is about 180 watts.
OPERATION
STANDARD
Each of the two tweeters and four full-range speak-
ers used in the standard speaker system is driven by
the amplifier that is integral to the factory-installed
radio receiver. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring infor-
mation includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and
connector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
PREMIUM
The six Infinity speakers used in the premium
speaker system are all driven by the radio receiver
through an Infinity power amplifier. For complete cir-
cuit diagrams, refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring
diagrams, proper wire and connector repair proce-
dures, details of wire harness routing and retention,
connector pin-out information and location views for
the various wire harness connectors, splices and
grounds.
Fig. 17 Remote Radio Switches Remove/Install
1 - STEERING WHEEL
2 - SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
3 - SCREW
4 - DRIVER SIDE AIRBAG MODULE
5 - REMOTE RADIO SWITCH
6 - REAR TRIM COVER
8A - 22 AUDIOWJ
REMOTE SWITCHES (Continued)
Page 302 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPEAKER
Any diagnosis of the Audio system should
begin with the use of the DRB IIItdiagnostic
tool. For information on the use of the DRB
IIIt, refer to the appropriate Diagnostic Service
Manual.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, SEAT BELT TENSIONER, SIDE
AIRBAG, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
CAUTION: The speaker output of the radio is a
ªfloating groundº system. Do not allow any speaker
lead to short to ground, as damage to the radio
may result.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Turn the radio receiver on. Adjust the balance and
fader controls to check the performance of each indi-
vidual speaker. Note the speaker locations that are
not performing correctly. Go to Step 2.
(2) Turn the radio receiver off. Turn the ignition
switch to the Off position. Disconnect and isolate the
battery negative cable. Remove the radio receiver
from the instrument panel. If the vehicle is equipped
with the Infinity speaker package, also disconnect
the wire harness connectors at the power amplifier.
Check both the speaker feed (+) circuit and return (±)
circuit cavities for the inoperative speaker location(s)
at the radio receiver wire harness connectors for con-
tinuity to ground. In each case, there should be no
continuity. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the
shorted speaker feed (+) and/or return (±) circuit(s) to
the speaker as required.
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with the Infinity
speaker package, go to Step 6. If the vehicle is
equipped with the standard speaker system, check
the resistance between the speaker feed (+) circuit
and return (±) circuit cavities of the radio receiverwire harness connectors for the inoperative speaker
location(s). The meter should read between 2 and 3
ohms (speaker resistance). If OK, go to Step 4. If not
OK, go to Step 5.
(4) Install a known good radio receiver. Connect
the battery negative cable. Turn the ignition switch
to the On position. Turn on the radio receiver and
test the speaker operation. If OK, replace the faulty
radio receiver. If not OK, turn the radio receiver off,
turn the ignition switch to the Off position, discon-
nect and isolate the battery negative cable, remove
the test radio receiver, and go to Step 5.
(5) Disconnect the wire harness connector at the
inoperative speaker. Check for continuity between
the speaker feed (+) circuit cavities of the radio
receiver wire harness connector and the speaker wire
harness connector. Repeat the check between the
speaker return (±) circuit cavities of the radio
receiver wire harness connector and the speaker wire
harness connector. In each case, there should be con-
tinuity. If OK, replace the faulty speaker. If not OK,
repair the open speaker feed (+) and/or return (±) cir-
cuit(s) as required.
(6) For each inoperative speaker location, check for
continuity between the speaker feed (+) circuit cavi-
ties of the radio receiver wire harness connectors and
the power amplifier wire harness connectors. Repeat
the check for each inoperative speaker location
between the speaker return (±) circuit cavities of the
radio receiver wire harness connectors and the power
amplifier wire harness connectors. In each case,
there should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 7. If not
OK, repair the open speaker feed (+) and/or return
(±) circuit(s) as required.
(7) Check for continuity between the two ground
circuit cavities of the power amplifier wire harness
connector and a good ground. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, go to Step 8. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit(s) to ground as required.
(8) Check the fused B(+) fuse for the power ampli-
fier in the junction block. If OK, go to Step 9. If not
OK, repair the shorted circuit or component as
required and replace the faulty fuse.
(9) Install the radio receiver. Connect the battery
negative cable. Check for battery voltage at the fused
B(+) fuse for the power amplifier in the junction
block. If OK, go to Step 10. If not OK, repair the
open fused B(+) circuit to the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) fuse as required.
(10) Check for battery voltage at the two fused
B(+) circuit cavities of the power amplifier wire har-
ness connector. If OK, go to Step 11. If not OK, repair
the open fused B(+) circuit(s) to the power amplifier
fuse in the junction block as required.
(11) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Turn the radio receiver on. Check for battery voltage
WJAUDIO 8A - 23
SPEAKER (Continued)
Page 303 of 2199

at the enable signal to amplifier circuit cavity of the
power amplifier wire harness connector. If OK, go to
Step 12. If not OK, repair the open enable signal to
amplifier circuit to the radio receiver as required.
(12) Turn the radio receiver off. Turn the ignition
switch to the Off position. Disconnect and isolate the
battery negative cable. For each inoperative speaker
location, check both the amplified feed (+) circuit and
the amplified return (±) circuit cavities of the power
amplifier wire harness connectors for continuity to
ground. In each case there should be no continuity. If
OK, go to Step 13. If not OK, repair the shorted
amplified feed (+) and/or amplified return (±) cir-
cuit(s) to the speaker as required.
(13) For each inoperative speaker location, check
the resistance between the amplified feed (+) circuit
and the amplified return (±) circuit cavities of the
power amplifier wire harness connectors. The meter
should read between 2 and 3 ohms (speaker resis-
tance). If OK, replace the faulty power amplifier. If
not OK, go to Step 14.
(14) Disconnect the speaker wire harness connec-
tor at the inoperative speaker. Check for continuity
between the amplified feed (+) circuit cavities of the
speaker wire harness connector and the power ampli-
fier wire harness connector. Repeat the check
between the amplified return (±) circuit cavities of
the speaker wire harness connector and the power
amplifier wire harness connector. In each case there
should be continuity. If OK, replace the faulty
speaker. If not OK, repair the open amplified feed (+)
and/or amplified return (±) circuit(s) as required.
REMOVAL
REAR DOOR SPEAKER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the trim panel from the rear door.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/DOORS - REAR/TRIM PANEL -
REMOVAL) for the procedures.
(3) Remove the three screws that secure the
speaker to the rear door inner panel (Fig. 18).
(4) Disconnect the rear door wire harness connec-
tor from the speaker connector receptacle.
(5) Remove the speaker from the rear door inner
panel.
INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.(2) Remove the top cover from the instrument
panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the speaker wire harness connector
(Fig. 19).
(4) Remove the two screws that secure the speaker
to the top of the instrument panel.
(5) Remove the speaker from the top of instrument
panel.
FRONT DOOR SPEAKER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the trim panel from the front door.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/DOOR - FRONT/TRIM PANEL -
REMOVAL) for the procedures.
(3) Remove the four screws that secure the
speaker to the front door inner panel (Fig. 20).
(4) Disconnect the front door wire harness connec-
tor from the speaker connector receptacle.
(5) Remove the speaker from the front door inner
panel.
Fig. 18 Rear Door Speaker Remove/Install
1 - PLASTIC NUT (3)
2 - REAR DOOR
3 - REAR DOOR SPEAKER
4 - REAR DOOR WIRE HARNESS
5 - SCREW (3)
8A - 24 AUDIOWJ
SPEAKER (Continued)
Page 313 of 2199

BCM programming then performs those tasks and
provides features through both PCI data bus commu-
nication with other electronic modules and hard
wired outputs to a number of relays. These relays
provide the BCM with the ability to control numer-
ous high current accessory systems in the vehicle.
The BCM circuitry operates on battery current
received through fuses in the Junction Block (JB) on a
non-switched fused B(+) circuit, a fused ignition switch
output (start-run) circuit, and a fused ignition switch
output (run-accessory) circuit. This arrangement allows
the BCM to provide some features regardless of the
ignition switch position. The BCM circuitry is grounded
through the chassis beneath the center console.
The BCM monitors its own internal circuitry as
well as many of its input and output circuits, and
will store a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. These DTCs
can be retrieved and diagnosed using a DRBIIItscan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
HARD WIRED INPUTS
The hard wired inputs to the BCM include the fol-
lowing:
²A/C switch signal
²Ambient temperature sensor signal
²Body control module flash enable
²Coolant level switch sense
²Door ajar switch sense (two circuits - one left
rear, and one right rear)
²Driver seat heater switch mux
²Fog lamp switch sense
²Fused B(+)
²Fused ignition switch output (run-acc)
²Fused ignition switch output (st-run)
²Ground (five circuits - two Z1, and three Z2)
²Hazard switch sense
²Headlamp switch mux
²High beam switch sense
²Hood ajar switch sense (export)
²Key-in ignition switch sense
²Liftgate ajar switch sense
²Liftgate courtesy disable
²Liftgate flip-up ajar switch sense
²Panel lamps dimmer signal
²Park lamp relay output
²Passenger seat heater switch mux
²PCI bus
²Radio control mux
²Rear window defogger switch sense
²Seat belt switch sense
²Ultralight sensor signal
²Washer fluid switch sense
²Washer pump switch sense
²Windshield wiper switch mux
²Wiper park switch sense
MESSAGING
The BCM uses the following messages received
from other electronic modules over the PCI data bus:
²Accessory Delay Control (DDM/PDM)
²Battery Temperature (PCM)
²Chime Request (EMIC, EVIC, SKIM)
²Cylinder Lock Switch Status (DDM)
²Door Ajar Status/Front Doors (DDM/PDM)
²Door Lock Status (DDM/PDM)
²Engine Model (PCM)
²Engine RPM (PCM)
²Engine Temperature (PCM)
²English/Metric Default (EMIC)
²Fuel Tank Level (PCM)
²Fuel Used/Injector Pulses (PCM)
²Panic Control (PDM)
²Programmable Features Preferences/Audible &
Optical Chirps/Headlamp Delay (EVIC)
²RKE Status (PDM)
²Vehicle Identification Number (PCM)
²Vehicle Speed (PCM)
The BCM provides the following messages to other
electronic modules over the PCI data bus:
²A/C Switch Status (PCM)
²Ambient Temperature Data (AZC/EVIC/PCM)
²Average/Instantaneous Fuel Economy (EVIC)
²Country Code (EMIC)
²Courtesy Lamp Status (DDM/PDM)
²Distance To Empty (EVIC)
²Elapsed Ignition On Timer (EVIC)
²English/Metric Status (EMIC)
²Front & Rear Door Ajar Status (EVIC)
²Front & Rear Fog Lamp Status (EMIC)
²Heated Seat Switch Status (HSM/MHSM)
²High Beam Status (EMIC)
²Ignition Off Timer (EVIC)
²Ignition Switch Position (DDM/PDM)
²Key-In Ignition Status (DDM/PDM)
²Low Beam Status (EMIC)
²Panel Lamp Status (AZC/EMIC/Radio)
²Rear Window Defogger Relay Status (DDM/
PDM)
²Remote Radio Switch Status (Radio)
²Seatbelt Status (EMIC/MHSM/MSM)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BODY CONTROL
MODULE
The hard wired inputs to and outputs from the
Body Control Module (BCM) may be diagnosed and
tested using conventional diagnostic tools and proce-
dures. Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
Conventional diagnostic methods may not prove
conclusive in the diagnosis of the BCM. In order to
obtain conclusive testing of the BCM, the Program-
mable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work and all of the electronic modules that provide
8E - 4 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 316 of 2199

faults arenoterased if the battery is disconnected.
(Fig. 4)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove negative battery cable from the bat-
tery.
(2) Remove air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - REMOVAL) OR (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
REMOVAL).
(3) Release CAB harness connector and remove
connector (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove pump motor connector.
(5) Remove CAB mounting bolts (Fig. 6) and
remove the CAB from the HCU.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the CAB onto the HCU and tighten
mounting bolts to 1.8 N´m (16 in. lbs.).
(2) Install pump motor connector.
(3) Install CAB harness connector and push down
connector release.
(4) Install air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - INSTALLATION) OR (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install negative battery cable to the battery.
DATA LINK CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
The data link connector (DLC) is located at the
lower edge of the instrument panel near the steering
column.
OPERATION - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
The 16±way DLC links the DRBIIItscan tool or
the Mopar Diagnostic System (MDS) with the Power-
train Control Module (PCM).
DOOR MODULE
DESCRIPTION
A door module is concealed behind the trim panel
of each front door (Fig. 7).The module on the driver
side is referred to as the Driver Door Module (DDM),
while the module on the passenger side is the Pas-
senger Door Module (PDM). Each door module
houses both the front power lock and power window
switches. In addition to the power window and power
lock switches for its own door, the DDM also houses
individual switches for each passenger door power
window, a power window lockout switch, the power
mirror switch, and the power foldaway mirror switch
for export vehicles.
The DDM and PDM each utilize integrated cir-
cuitry and information carried on the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus network
along with many hard wired inputs to monitor many
sensor and switch inputs throughout the vehicle. The
PDM also receives inputs through an integral Radio
Fig. 5 CAB Connector Release
1 - CONNECTOR RELEASE
2 - CAB
Fig. 6 CAB Mounting Bolts
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 7
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (Continued)
Page 318 of 2199

lamp flash features), Unlock with the optional RKE
unlock, and Panic Mode functions. The optional RKE
features are programmable.
²Switch Illumination- Each door module pro-
vides control of the power window and power lock
switch illumination for the front and rear doors on
the same side of the vehicle. The DDM provides con-
trol of the power mirror switch illumination.
²Window Lockout- The DDM monitors and
transmits the status of its integral window lockout
switch to provide the power window lockout feature
and coordinate power window switch knob illumina-
tion.
The door modules are serviced only as complete
units. Many of the features in the vehicle controlled
or supported by the door modules are programmable
using either the Electronic Vehicle Information Cen-
ter (EVIC) user interface, or the DRBIIItscan tool. If
a door module is damaged or faulty, the entire door
module unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The microprocessor-based DDM and PDM hard-
ware and software monitors integral and hard wired
external switch inputs as well as those resources it
shares with other electronic modules in the vehicle
through its communication over the PCI data bus
network. The internal programming and all of these
inputs allow the DDM or PDM microprocessor to
determine the tasks it needs to perform and their
priorities, as well as both the standard and optional
features that it should provide.
The DDM and PDM are powered by a fused bat-
tery circuit so that they can operate regardless of the
ignition switch position. The DDM and PDM cir-
cuitry is grounded to the chassis beneath the front
seat.
The DDM and PDM can be diagnosed using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information.
HARD WIRED INPUTS
The hard wired inputs to the door modules include
the following:
²Door ajar switch sense
²Driver door key cylinder switch sense (DDM)
²Fused B(+)
²Ground
²Memory switch mux (DDM)
²Mirror horizontal position signal
²Mirror vertical position signal
²PCI bus
HARD WIRED OUTPUTS
The hard wired outputs of the door modules
include the following:
²Courtesy lamp driver
²Courtesy lamp ground
²Diagnostic out (DDM)
²Door/liftgate lock driver
²Door/liftgate unlock driver
²Door switch illumination (rear power window)
²Front window driver (down)
²Front window driver (up)
²Memory set indicator driver (DDM)
²Memory switch return (DDM)
²Mirror common driver
²Mirror heater ground
²Mirror heater 12V supply
²Rear window driver (down)
²Rear window driver (up)
²Mirror horizontal driver
²Mirror sensor ground
²Mirror vertical driver
²PCI bus
²Switch illumination driver (memory - DDM)
MESSAGING
The door modules use the following messages
received from other electronic modules over the PCI
data bus:
²Accessory Delay Control (PDM)
²Courtesy Lamp Status (BCM)
²Door Ajar Status/Rear Doors (BCM)
²Door Lock Status (DDM/PDM)
²Ignition Switch Position (BCM)
²Key-In Ignition Status (BCM)
²Programmable Features Preferences/Auto Lock/
Auto Unlock/RKE Unlock Sequence/RKE Link to
Memory (EVIC)
²Memory Recall (DDM)
²Rear Window Defogger Relay Status (BCM)
²Vehicle Speed (PCM)
The door modules provide the following messages
to other electronic modules over the PCI data bus:
²Cylinder Lock Switch Status (BCM)
²Door Ajar Status/Front Doors (BCM/DDM/PDM)
²Door Lock Status (DDM/PDM)
²Memory Recall (PDM/MHSM/MSM/Radio)
²Memory Set Switch Status (PDM/MHSM/MSM/
Radio)
²Panic Control (BCM)
²Power Window Switch Status (PDM)
²RKE Status (BCM/DDM)
²Window Lockout Switch Status (PDM)
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 9
DOOR MODULE (Continued)
Page 326 of 2199

(2) If equipped, remove Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
(3) Remove coolant reserve/overflow tank.
(4) Remove cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(5) Carefully unplug three 32±way connectors at
PCM.
(6) Remove three PCM bracket-to-body mounting
nuts (Fig. 13).
(7) Remove PCM/PCM bracket assembly from
vehicle.
(8) Remove 3 PCM-to-PCM bracket bolts (screws)
(Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
USE THE DRBIIItSCAN TOOL TO REPRO-
GRAM THE NEW POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE (PCM) WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGI-
NAL IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND
THE VEHICLES ORIGINAL MILEAGE. IF THIS
STEP IS NOT DONE, A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODE (DTC) MAY BE SET.
The PCM is located on the cowl panel in right/rear
side of engine compartment (Fig. 12).
(1) Check pins in three 32±way electrical connec-
tors for damage. Repair as necessary.
(2) Install PCM to its mounting bracket. Tighten
three mounting bolts to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install PCM/PCM bracket to body. Install 3
nuts and tighten 9 N´m (80 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install three 32±way connectors.(5) Install cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(6) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank.
(7) If equipped, install Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to reprogram new
PCM with vehicles original Identification Number
(VIN) and original vehicle mileage.
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) is the
primary component of the Sentry Key Immobilizer
System (SKIS) (Fig. 15). The SKIM is located in the
steering column, below the ignition lock cylinder
housing. The SKIM has an integral halo-like antenna
ring that extends from one side.
The SKIM cannot be adjusted or repaired. If faulty
or damaged, the entire SKIM unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) con-
tains a Radio Frequency (RF) transceiver and a
microprocessor. The SKIM transmits RF signals to,
and receives RF signals from the Sentry Key tran-
Fig. 14 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Mounting
Bracket
1 - PCM BRACKET
2 - PCM
3 - PCM-TO-BRACKET SCREWS (3)
Fig. 15 Sentry Key Immobilizer Module
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - SKIM
3 - MOUNTING SCREW
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 17
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 344 of 2199
STANDARD PROCEDURE - IGNITION-OFF
DRAW TEST
The term Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) identifies a nor-
mal condition where power is being drained from the
battery with the ignition switch in the Off position. A
normal vehicle electrical system will draw from five
to thirty-five milliamperes (0.005 to 0.035 ampere)
with the ignition switch in the Off position, and all
non-ignition controlled circuits in proper working
order. Up to thirty-five milliamperes are needed to
enable the memory functions for the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM), digital clock, electronically tuned
radio, and other modules which may vary with the
vehicle equipment.
A vehicle that has not been operated for approxi-
mately twenty days, may discharge the battery to an
inadequate level. When a vehicle will not be used for
twenty days or more (stored), remove the IOD fuse
from the Power Distribution Center (PDC). This will
reduce battery discharging.Excessive IOD can be caused by:
²Electrical items left on.
²Faulty or improperly adjusted switches.
²Faulty or shorted electronic modules and compo-
nents.
²An internally shorted generator.
²Intermittent shorts in the wiring.
If the IOD is over thirty-five milliamperes, the
problem must be found and corrected before replac-
ing a battery. In most cases, the battery can be
charged and returned to service after the excessive
IOD condition has been corrected.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are off.
Turn off all lamps, remove the ignition key, and close
all doors. If the vehicle is equipped with an illumi-
nated entry system or an electronically tuned radio,
allow the electronic timer function of these systems
to automatically shut off (time out). This may take
up to three minutes. See the Electronic Module Igni-
tion-Off Draw Table for more information.
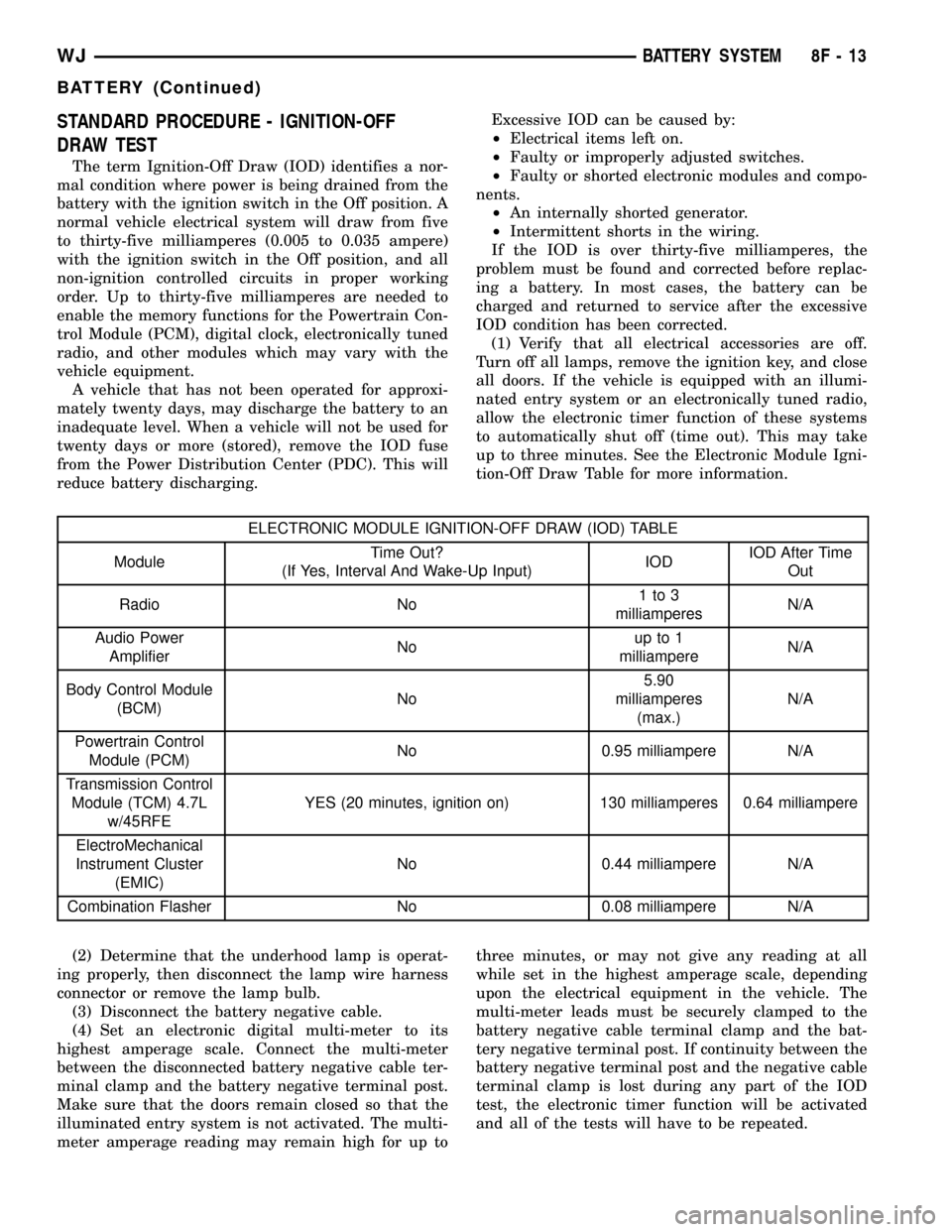
ELECTRONIC MODULE IGNITION-OFF DRAW (IOD) TABLE
ModuleTime Out?
(If Yes, Interval And Wake-Up Input)IODIOD After Time
Out
Radio No1to3
milliamperesN/A
Audio Power
AmplifierNoup to 1
milliampereN/A
Body Control Module
(BCM)No5.90
milliamperes
(max.)N/A
Powertrain Control
Module (PCM)No 0.95 milliampere N/A
Transmission Control
Module (TCM) 4.7L
w/45RFEYES (20 minutes, ignition on) 130 milliamperes 0.64 milliampere
ElectroMechanical
Instrument Cluster
(EMIC)No 0.44 milliampere N/A
Combination Flasher No 0.08 milliampere N/A
(2) Determine that the underhood lamp is operat-
ing properly, then disconnect the lamp wire harness
connector or remove the lamp bulb.
(3) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(4) Set an electronic digital multi-meter to its
highest amperage scale. Connect the multi-meter
between the disconnected battery negative cable ter-
minal clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
Make sure that the doors remain closed so that the
illuminated entry system is not activated. The multi-
meter amperage reading may remain high for up tothree minutes, or may not give any reading at all
while set in the highest amperage scale, depending
upon the electrical equipment in the vehicle. The
multi-meter leads must be securely clamped to the
battery negative cable terminal clamp and the bat-
tery negative terminal post. If continuity between the
battery negative terminal post and the negative cable
terminal clamp is lost during any part of the IOD
test, the electronic timer function will be activated
and all of the tests will have to be repeated.
WJBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 13
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 377 of 2199

(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the rear glass heating grid and to the fuse in the
junction block that feeds the rear window defogger
switch LED indicator. There should be continuity
between the cavity for relay terminal 87 and the rear
glass heating grid and the rear window defogger
switch LED indicator at all times. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, repair the open rear window defogger
relay output circuit as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is connected to bat-
tery voltage and should be hot at all times. Check for
battery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 86. If
OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open fused
B(+) circuit to the PDC fuse as required.
(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. This terminal is pro-
vided with ground by the Body Control Module
(BCM) rear window defogger timer and logic circuitry
to energize the defogger relay. There should be conti-
nuity to the rear window defogger relay control cir-
cuit cavity of the 22-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the BCM. If OK, use a DRB
scan tool and refer to the Appropriate Diagnostic
Information to test the BCM. If not OK, repair the
open rear window defogger relay control circuit as
required.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the steering column opening cover
from the instrument panel. Refer to Instrument
Panel System for the procedures.
(3) The rear window defogger relay is located on
the right side of the combination flasher in the junc-
tion block (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove the rear window defogger relay from
the junction block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the rear window defogger relay in the
proper receptacle in the junction block.
(2) Align the rear window defogger relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the junction block recep-
tacle.
(3) Push in firmly on the rear window defogger
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the junction block receptacle.
(4) Install the steering column opening cover onto
the instrument panel. Refer to Instrument Panel Sys-
tem for the procedures.
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The rear window defogger switch is integral to the
a/c heater control, which is located in the instrument
panel center stack below the radio receiver. This
momentary switch provides a hard wired ground sig-
nal to the Body Control Module (BCM) each time it is
depressed. A Light Emitting Diode (LED) in the push
button for the rear window defogger switch illumi-
nates to indicate when the rear window defogger sys-
tem is turned on.
The rear window defogger switch and the rear win-
dow defogger switch LED indicator cannot be
Fig. 5 JUNCTION BLOCK
1 - COMBINATION FLASHER
2 - JUNCTION BLOCK
8G - 6 HEATED GLASSWJ
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER RELAY (Continued)
Page 410 of 2199

IGNITION COIL CAPACITOR
DESCRIPTION
Two coil capacitors are used. One of them is
located near the center of, and on the left side of the
intake manifold (Fig. 20). The other capacitor is
located near the center of, and on the right side of
the intake manifold.
OPERATION
The 2 coil capacitors are used to prevent high-volt-
age spikes from interfering with the operation of cer-
tain powertrain sensors. They are also used to help
prevent radio interference.
REMOVAL
Two coil capacitors are used. One of them is
located near the center of, and on the left side of the
intake manifold (Fig. 21). The other capacitor is
located near the center of, and on the right side of
the intake manifold.
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at coil capacitor
(Fig. 21).
(2) Remove mounting nut.
(3) Remove capacitor from mounting stud.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position capacitor to manifold mounting stud.(2) Install nut and tighten to 8 N´m (70 in. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to capacitor (Fig.
21).
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
4.7L High-Output Engine
The 2 knock sensors are bolted into the cylinder
block under the intake manifold.
OPERATION
4.7L High-Output Engine
Two knock sensors are used on the 4.7L V-8 engine
if equipped with the high-output package; one for
each cylinder bank. When the knock sensor detects a
knock in one of the cylinders on the corresponding
bank, it sends an input signal to the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). In response, the PCM retards
ignition timing for all cylinders by a scheduled
amount.
Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage
(signal) to the PCM while the engine operates. As the
intensity of the crystal's vibration increases, the
knock sensor output voltage also increases.
Fig. 20 Coil Capacitor (Left Side Shown)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - COIL CAPACITOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
Fig. 21 Coil Capacitor (Left Side Shown)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - COIL CAPACITOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
WJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 13