Heating JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1301 of 2199
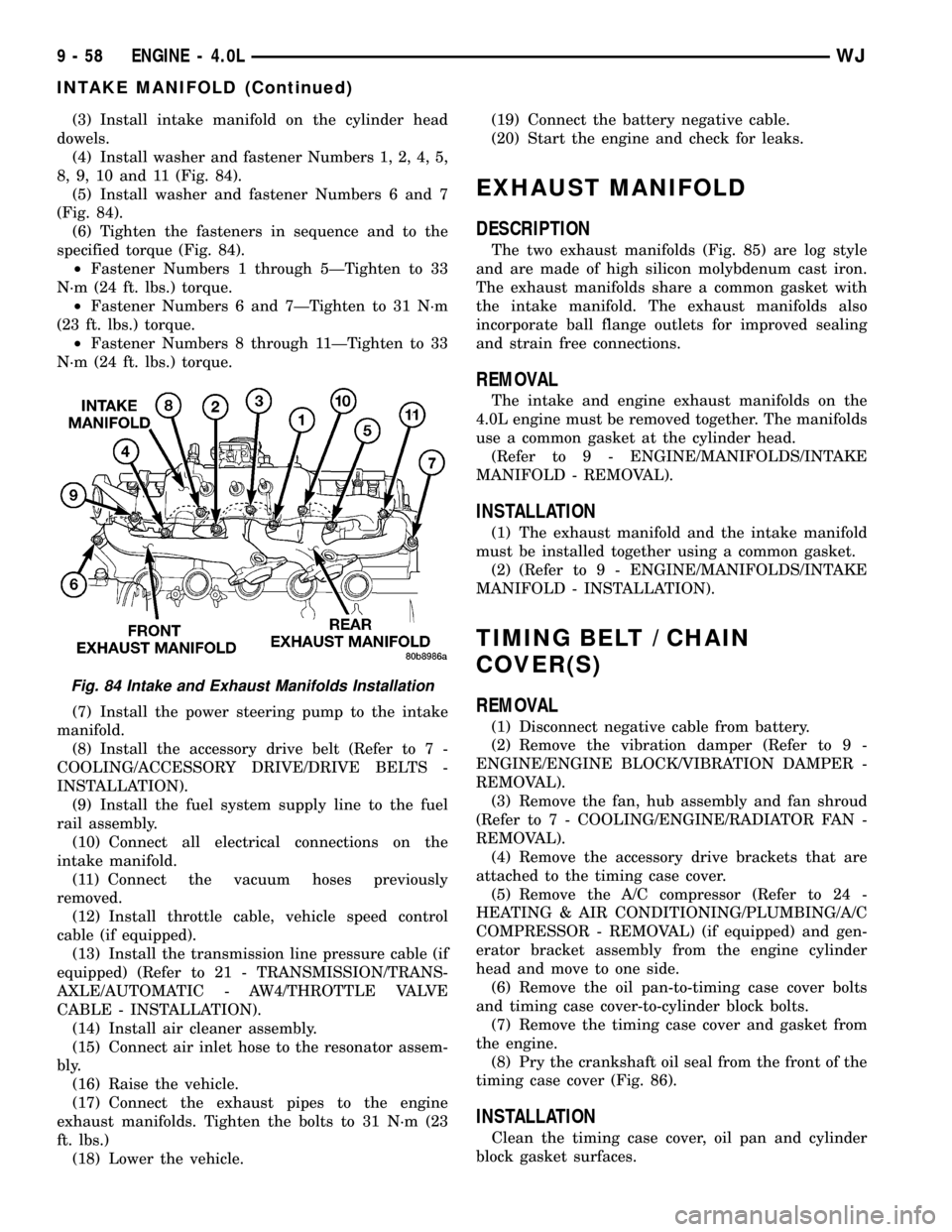
(3) Install intake manifold on the cylinder head
dowels.
(4) Install washer and fastener Numbers 1, 2, 4, 5,
8, 9, 10 and 11 (Fig. 84).
(5) Install washer and fastener Numbers 6 and 7
(Fig. 84).
(6) Tighten the fasteners in sequence and to the
specified torque (Fig. 84).
²Fastener Numbers 1 through 5ÐTighten to 33
N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Fastener Numbers 6 and 7ÐTighten to 31 N´m
(23 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Fastener Numbers 8 through 11ÐTighten to 33
N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the power steering pump to the intake
manifold.
(8) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the fuel system supply line to the fuel
rail assembly.
(10) Connect all electrical connections on the
intake manifold.
(11) Connect the vacuum hoses previously
removed.
(12) Install throttle cable, vehicle speed control
cable (if equipped).
(13) Install the transmission line pressure cable (if
equipped) (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - AW4/THROTTLE VALVE
CABLE - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install air cleaner assembly.
(15) Connect air inlet hose to the resonator assem-
bly.
(16) Raise the vehicle.
(17) Connect the exhaust pipes to the engine
exhaust manifolds. Tighten the bolts to 31 N´m (23
ft. lbs.)
(18) Lower the vehicle.(19) Connect the battery negative cable.
(20) Start the engine and check for leaks.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The two exhaust manifolds (Fig. 85) are log style
and are made of high silicon molybdenum cast iron.
The exhaust manifolds share a common gasket with
the intake manifold. The exhaust manifolds also
incorporate ball flange outlets for improved sealing
and strain free connections.
REMOVAL
The intake and engine exhaust manifolds on the
4.0L engine must be removed together. The manifolds
use a common gasket at the cylinder head.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
(1) The exhaust manifold and the intake manifold
must be installed together using a common gasket.
(2) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION).
TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the vibration damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the fan, hub assembly and fan shroud
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the accessory drive brackets that are
attached to the timing case cover.
(5) Remove the A/C compressor (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL) (if equipped) and gen-
erator bracket assembly from the engine cylinder
head and move to one side.
(6) Remove the oil pan-to-timing case cover bolts
and timing case cover-to-cylinder block bolts.
(7) Remove the timing case cover and gasket from
the engine.
(8) Pry the crankshaft oil seal from the front of the
timing case cover (Fig. 86).
INSTALLATION
Clean the timing case cover, oil pan and cylinder
block gasket surfaces.
Fig. 84 Intake and Exhaust Manifolds Installation
9 - 58 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1302 of 2199

(1) Install a new crankshaft oil seal in the timing
case cover. The open end of the seal should be toward
the inside of the cover. Support the cover at the seal
area while installing the seal. Force it into position
with Seal Installation Tool 6139.
(2) Position the gasket on the cylinder block.
(3) Position the timing case cover on the oil pan
gasket and the cylinder block.
(4) Insert Timing Case Cover Alignment and Seal
Installation Tool 6139 in the crankshaft opening in
the cover (Fig. 87).
(5) Install the timing case cover-to-cylinder block
and the oil pan-to-timing case cover bolts.
(6) Tighten the 1/4 inch cover-to-block bolts to 7
N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the 5/16 inch front
cover-to-block bolts to 22 N´m (192 in. lbs.) torque.
Tighten the oil pan-to-cover 1/4 inch bolts to 9.5 N´m
(84 in. lbs.) torque.(7) Remove the cover alignment tool.
(8) Apply a light film of engine oil on the vibration
damper hub contact surface of the seal.
(9) Apply MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant to the keyway in the crankshaft and insert the
key. With the key inserted in the keyway in the
crankshaft, install the vibration damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the A/C compressor (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - INSTALLATION) (if equipped) and
generator bracket assembly.
(11) Install the engine fan, hub assembly and
shroud (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FAN - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install the serpentine drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(13) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 85 EXHAUST MANIFOLDS 4.0L ENGINE
Fig. 86 Timing Case Cover Components
1 - TIMING CASE COVER
2 - OIL SLINGER
3 - CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL
4 - VIBRATION DAMPER PULLEYFig. 87 Timing Case Cover Alignment
1 - TIMING CASE COVER ALIGNMENT AND SEAL
INSTALLATION TOOL
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 59
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) (Continued)
Page 1317 of 2199
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
(10) Install generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install A/C condenser (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C CON-
DENSER - INSTALLATION).
(13) Connect radiator lower hose at the thermostat
housing.
(14) Connect the transmission oil cooler lines to
the radiator.
(15) Install A/C compressor. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
(16) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION) and radiator fan (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(17) Install breathers, then connect tube to both
crankcase breathers (Fig. 5).
(18) Connect throttle and speed control cables.
(19) Install throttle body resonator assembly and
inlet hose.
(20) Raise vehicle.
(21) Connect two ground straps on the lower left
hand side of the engine and one ground strap on the
lower right side.
(22) Install torque converter bolts.
(23) Connect crankshaft position sensor (Fig. 4).
(24) Install starter.
(25) Install rubber splash shield.
CAUTION: The structural cover requires a specific
torque sequence. Failure to follow this sequence
may cause severe damage to the cover.
(26) Install structural cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(27) Install exhaust crossover pipe.
(28) Install engine block heater power cable, If
equipped.
(29) Lower vehicle.
(30) Check and fill engine oil (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES - SPECIFI-
CATIONS).
(31) Recharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(32) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(33) Connect the battery negative cable.
(34) Start engine and check for leaks.SPECIFICATIONS
4.7L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Engine Type 90É SOHC V-8 16-Valve
Displacement 4.7 Liters / 4701cc
(287 Cubic Inches)
Bore 93.0 mm (3.66 in.)
Stroke 86.5 mm (3.40 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.0:1
Horsepower 235 BHP @ 4800 RPM
Torque 295 LB-FT @ 3200 RPM
Lead Cylinder #1 Left Bank
Firing Order 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
CYLINDER BLOCK
Cylinder Block Cast Iron
Bore Diameter 93.010 .0075 mm
(3.6619 0.0003 in.)
Out of Round (MAX) 0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Taper (MAX) 0.051 mm (0.002 in.)
PISTONS
Material Aluminum Alloy
Diameter 92.975 mm (3.6605 in.)
Weight 367.5 grams (12.96 oz)
Ring Groove Diameter
No. 1 83.73 - 83.97 mm
(3.296 - 3.269 in.)
No. 2 82.833 - 83.033 mm
(3.261 - 3.310 in.)
No. 3 83.88 - 84.08 mm
(3.302 - 3.310 in.)
PISTON PINS
Type Pressed Fit
Clearance In Piston 0.010 - 0.019 mm
(0.0004 - 0.0008 in.)
Diameter 24.013 - 24.016 mm
(0.9454 - 0.9456 in.)
9 - 74 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1328 of 2199

(3) Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes
before restarting. Repeat this several times after
engine has reached normal operating temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the
oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with
debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the left side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove accessory drive belt. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(9) Remove the power steering pump and set
aside.
(10) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper tim-
ing mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark (Fig.
9).
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 85
CYLINDER HEAD - LEFT (Continued)
Page 1340 of 2199

(5) Using special tool 8516 press downward on the
valve spring, install rocker arm (Fig. 28).
(6) Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
The valve springs are made from high strength
chrome silicon steel. The springs are common for
intake and exhaust applications. The valve spring
seat is integral with the valve stem seal, which is a
positive type seal to control lubrication.
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION
The valve stem seals are made of rubber and incor-
porate an integral steel valve spring seat. The inte-
gral garter spring maintains consistent lubrication
control to the valve stems.
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder heads are made of an aluminum alloy.
The cylinder head features two valves per cylinder
with pressed in powdered metal valve guides. The
cylinder heads also provide enclosures for the timing
chain drain, necessitating unique left and right cylin-
der heads.
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and
are pressed into the cylinder head. The guides are
not replaceable or serviceable, and valve guide ream-
ing is not recommended. If the guides are worn
beyond acceptable limits, replace the cylinder heads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
Fig. 28 Rocker ArmÐRemoval
1 - CAMSHAFT
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8516
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 97
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1401 of 2199
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER 4.0L
ENGINE
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove spark plug wires from
plugs or by any other means short out cylinders.
Failure of the catalytic converter can occur due to a
temperature increase caused by unburned fuel
passing through the converter.The stainless steel catalytic converter body is
designed to last the life of the vehicle. Excessive heat
can result in bulging or other distortion, but exces-
sive heat will not be the fault of the converter. If
unburned fuel enters the converter, overheating may
occur. If a converter is heat-damaged, correct the
cause of the damage at the same time the converter
is replaced. Also, inspect all other components of the
exhaust system for heat damage.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid con-
taminating the catalyst core.
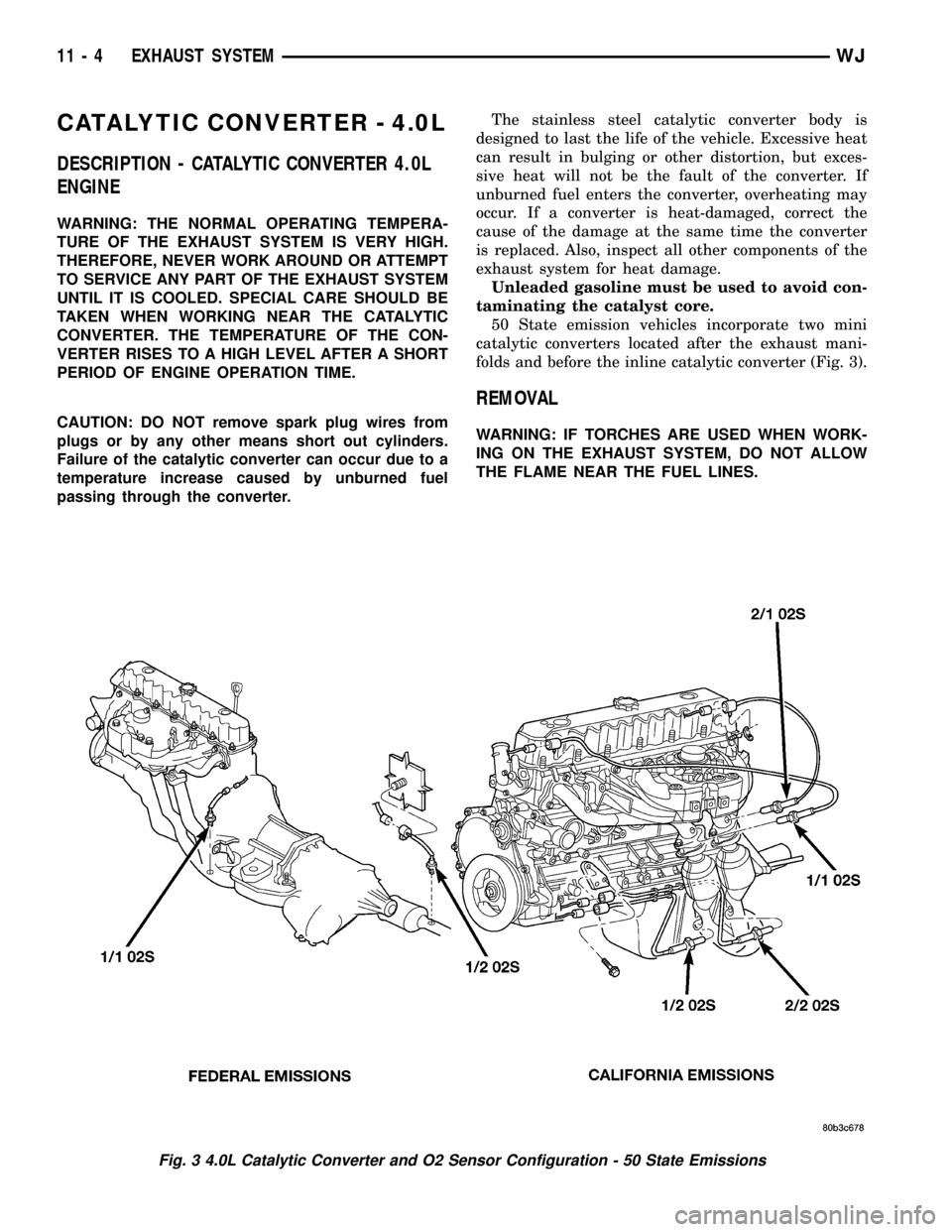
50 State emission vehicles incorporate two mini
catalytic converters located after the exhaust mani-
folds and before the inline catalytic converter (Fig. 3).
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF TORCHES ARE USED WHEN WORK-
ING ON THE EXHAUST SYSTEM, DO NOT ALLOW
THE FLAME NEAR THE FUEL LINES.
Fig. 3 4.0L Catalytic Converter and O2 Sensor Configuration - 50 State Emissions
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMWJ
Page 1402 of 2199

(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove nuts from the catalytic converter and
exhaust pipe flange connection (Fig. 4).
(4) Loosen exhaust clamp from the catalytic con-
verter and muffler connection (Fig. 4).
(5) Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring (Fig. 4).
(6) Heat the catalytic converter to muffler connec-
tion with a torch until the metal becomes cherry red.
(7) While the metal is still cherry red, twist the
catalytic converter back and forth to separate it from
the exhaust pipe and the muffler (Fig. 5).
INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the catalytic converter onto the
exhaust pipe flange connection (Fig. 4). Tighten the
nuts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the muffler onto the catalytic converter
until the alignment tab is inserted into the align-
ment slot.
(3) Install the exhaust clamp at the muffler and
catalytic converter connection (Fig. 4). Tighten the
clamp nuts to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect oxygen sensor wiring (Fig. 4).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks
and exhaust system contact with the body panels.
Adjust the alignment, if needed.
Fig. 4 Exhaust Pipe-to-Catalytic Converter-to-Muffler
Connection
1 - EXHAUST CLAMP ASSEMBLY
2 - OXYGEN SENSOR
3 - MUFFLER
4 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
5 - EXHAUST PIPE WITH FLANGE JOINT
6 - NUTS (3)
Fig. 5 Catalytic ConverterÐRemoval
1 - EXHAUST PIPE WITH FLANGE
2 - NUTS (3)
3 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
WJEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 5
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1403 of 2199
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove spark plug wires from
plugs or by any other means short out cylinders.
Failure of the catalytic converter can occur due to a
temperature increase caused by unburned fuel
passing through the converter.The stainless steel catalytic converter body is
designed to last the life of the vehicle. Excessive heat
can result in bulging or other distortion, but exces-
sive heat will not be the fault of the converter. If
unburned fuel enters the converter, overheating may
occur. If a converter is heat-damaged, correct the
cause of the damage at the same time the converter
is replaced. Also, inspect all other components of the
exhaust system for heat damage.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid con-
taminating the catalyst core.
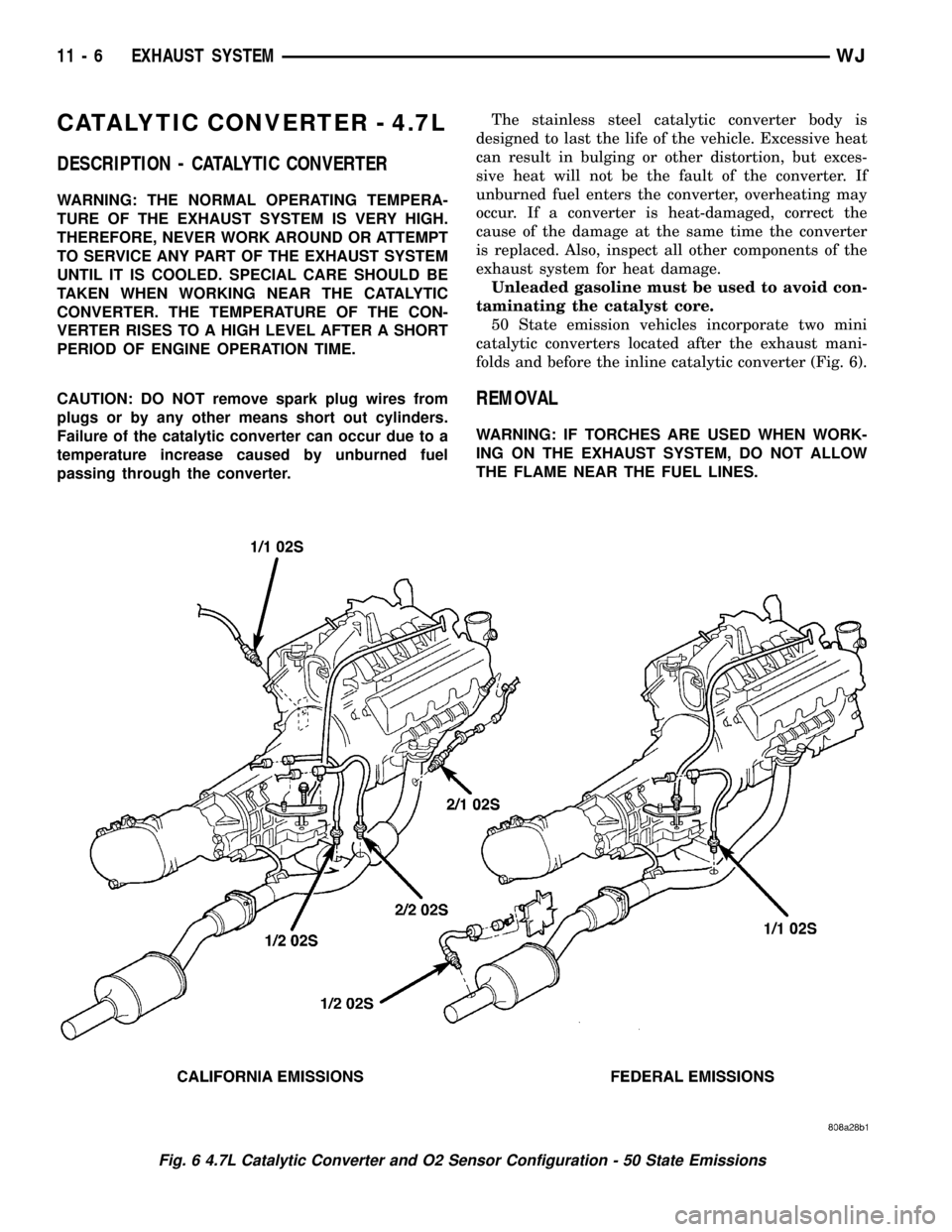
50 State emission vehicles incorporate two mini
catalytic converters located after the exhaust mani-
folds and before the inline catalytic converter (Fig. 6).
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF TORCHES ARE USED WHEN WORK-
ING ON THE EXHAUST SYSTEM, DO NOT ALLOW
THE FLAME NEAR THE FUEL LINES.
Fig. 6 4.7L Catalytic Converter and O2 Sensor Configuration - 50 State Emissions
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMWJ
Page 1404 of 2199

(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove nuts from the catalytic converter and
exhaust pipe flange connection (Fig. 7).
(4) Loosen exhaust clamp from the catalytic con-
verter and muffler connection (Fig. 7).
(5) Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring (Fig. 7).
(6) Heat the catalytic converter to muffler connec-
tion with a torch until the metal becomes cherry red.
(7) While the metal is still cherry red, twist the
catalytic converter back and forth to separate it from
the muffler (Fig. 8).
INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the catalytic converter onto the
exhaust pipe flange connection (Fig. 7). Tighten the
nuts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the muffler onto the catalytic converter
until the alignment tab is inserted into the align-
ment slot.
(3) Install the exhaust clamp at the muffler and
catalytic converter connection (Fig. 7). Tighten the
clamp nuts to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect oxygen sensor wiring (Fig. 7).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks
and exhaust system contact with the body panels.
Adjust the alignment, if needed.
Fig. 7 Exhaust Pipe-to-Catalytic Converter-to-Muffler
Connection
1 - EXHAUST CLAMP ASSEMBLY
2 - OXYGEN SENSOR
3 - MUFFLER
4 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
5 - EXHAUST PIPE WITH FLANGE JOINT
6 - NUTS (3)
Fig. 8 Catalytic ConverterÐRemoval
1 - EXHAUST PIPE WITH FLANGE
2 - NUTS (3)
3 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
WJEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 7
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1469 of 2199

The other two heater elements (downstream sen-
sors 1/2 and 2/2) are controlled by the downstream
heater relay through output signals from the PCM.
To avoid a large simultaneous current surge, power
is delayed to the 2 downstream heater elements by
the PCM for approximately 2 seconds.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
O2S SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Oxygen Sensors (O2S) are attached to, and
protrude into the vehicle exhaust system. Depending
on the emission package, the vehicle may use a total
of either 2 or 4 sensors.
Federal Emissions Package:Two sensors are
used: upstream (referred to as 1/1) and downstream
(referred to as 1/2). With this emission package, the
upstream sensor (1/1) is located just before the main
catalytic convertor. The downstream sensor (1/2) is
located just after the main catalytic convertor.
4.7L V-8 With California Emissions Package:
On this emissions package, 4 sensors are used: 2
upstream (referred to as 1/1 and 2/1) and 2 down-
stream (referred to as 1/2 and 2/2). With this emis-
sion package, the right upstream sensor (2/1) is
located in the right exhaust downpipe just before the
mini-catalytic convertor. The left upstream sensor
(1/1) is located in the left exhaust downpipe just
before the mini-catalytic convertor. The right down-
stream sensor (2/2) is located in the right exhaust
downpipe just after the mini-catalytic convertor, and
before the main catalytic convertor. The left down-
stream sensor (1/2) is located in the left exhaust
downpipe just after the mini-catalytic convertor, and
before the main catalytic convertor.
4.0L 6±Cylinder With California Emissions
Package:On this emissions package, 4 sensors are
used: 2 upstream (referred to as 1/1 and 2/1) and 2
downstream (referred to as 1/2 and 2/2). With this
emission package, the rear/upper upstream sensor
(2/1) is located in the exhaust downpipe just beforethe rear mini-catalytic convertor. The front/upper
upstream sensor (1/1) is located in the exhaust down-
pipe just before the front mini-catalytic convertor.
The rear/lower downstream sensor (2/2) is located in
the exhaust downpipe just after the rear mini-cata-
lytic convertor, and before the main catalytic conver-
tor. The front/lower downstream sensor (1/2) is
located in the exhaust downpipe just after the front
mini-catalytic convertor, and before the main cata-
lytic convertor.
OPERATION
An O2 sensor is a galvanic battery that provides
the PCM with a voltage signal (0-1 volt) inversely
proportional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
In other words, if the oxygen content is low, the volt-
age output is high; if the oxygen content is high the
output voltage is low. The PCM uses this information
to adjust injector pulse-width to achieve the
14.7±to±1 air/fuel ratio necessary for proper engine
operation and to control emissions.
The O2 sensor must have a source of oxygen from
outside of the exhaust stream for comparison. Cur-
rent O2 sensors receive their fresh oxygen (outside
air) supply through the O2 sensor case housing.
Four wires (circuits) are used on each O2 sensor: a
12±volt feed circuit for the sensor heating element; a
ground circuit for the heater element; a low-noise
sensor return circuit to the PCM, and an input cir-
cuit from the sensor back to the PCM to detect sen-
sor operation.
Oxygen Sensor Heaters/Heater Relays:
Depending on the emissions package, the heating ele-
ments within the sensors will be supplied voltage
from either the ASD relay, or 2 separate oxygen sen-
sor relays. Refer to Wiring Diagrams to determine
which relays are used.
The O2 sensor uses a Positive Thermal Co-efficient
(PTC) heater element. As temperature increases,
resistance increases. At ambient temperatures
around 70ÉF, the resistance of the heating element is
approximately 4.5 ohms on 4.0L engines. It is
approximately 13.5 ohms on the 4.7L engine. As the
sensor's temperature increases, resistance in the
heater element increases. This allows the heater to
maintain the optimum operating temperature of
approximately 930É-1100ÉF (500É-600É C). Although
the sensors operate the same, there are physical dif-
ferences, due to the environment that they operate
in, that keep them from being interchangeable.
Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all
times allows the system to enter into closed loop
operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain
in closed loop operation during periods of extended
idle.
14 - 50 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
O2S HEATER RELAY (Continued)