check engine JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1253 of 2199

FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gaskets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1)
Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light scuff-
ing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes will
clean up a bore and maintain the required limits.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60
strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
9 - 10 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1254 of 2199

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 40É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 4).CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Mark the hinge locations on the hood panel for
alignment reference during installation. Remove the
engine compartment lamp. Remove the hood.
(3) Remove the radiator drain cock and radiator
cap to drain the coolant. DO NOT waste usable cool-
ant. If the solution is clean, drain the coolant into a
clean container for reuse.
(4) Remove the upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
(5) Remove the lower radiator hose.
(6) Remove upper radiator support retaining bolts
and remove radiator support.
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
Fig. 4 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 11
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1264 of 2199

CLEANING
Thoroughly clean the engine cylinder head and cyl-
inder block mating surfaces. Clean the intake and
engine exhaust manifold and engine cylinder head
mating surfaces. Remove all gasket material and car-
bon.
Check to ensure that no coolant or foreign material
has fallen into the tappet bore area.
Remove the carbon deposits from the combustion
chambers and top of the pistons.
INSPECTION
Use a straightedge and feeler gauge to check the
flatness of the engine cylinder head and block mating
surfaces.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
in or out of the vehicle.
The engine cylinder head gasket is a composition
gasket. The gasket is to be installed DRY.DO NOT
use a gasket sealing compound on the gasket.
If the engine cylinder head is to be replaced and
the original valves used, measure the valve stem
diameter. Only standard size valves can be used with
a service replacement engine cylinder head unless
the replacement head valve stem guide bores are
reamed to accommodate oversize valve stems.
Remove all carbon buildup and reface the valves.
(1) Remove the shop towels from the cylinder
bores. Coat the bores with clean engine oil.
(2) Position the engine cylinder head gasket (with
the numbers facing up) using the alignment dowels
in the cylinder block, to position the gasket.
CAUTION: Engine cylinder head bolts should be
reused only once. Replace the head bolts if they
were used before or if they have a paint dab on the
top of the bolt.
(3) With bolt No.14 held in place (tape around
bolt), install the engine cylinder head over the same
dowels used to locate the gasket. Remove the tape
from bolt No.14.
(4) Coat the threads of stud bolt No.11 with Loc-
tite 592 sealant, or equivalent.
(5) Tighten the engine cylinder head bolts in
sequence according to the following procedure (Fig.
10).
CAUTION: During the final tightening sequence,
bolt No.11 will be tightened to a lower torque than
the rest of the bolts. DO NOT overtighten bolt
No.11.(a) Tighten all bolts in sequence (1 through 14)
to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
(b) Tighten all bolts in sequence (1 through 14)
to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(c) Check all bolts to verify they are set to 61
N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Tighten bolts in sequence:
²Bolts 1 through 10 to 149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.)
torque.
²Bolt 11 to 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Bolts 12 through 14 to 149 N´m (110 ft. lbs.)
torque.
CYLINDER HEAD BOLTS
POSITION DESCRIPTION
1,4,5,12,13 1/2 in.-13 BOLT
8,9 1/2 in.-13 BOLT WITH DOWEL
POINT
2,3,6,7,10,11,14 1/2 in.-13 WITH 7/16 in.-14 STUD
END
All bolts are 12 point drives for rocker cover clearance
(e) Check all bolts in sequence to verify the cor-
rect torque.
(f) If not already done, clean and mark each bolt
with a dab of paint after tightening. Should you
encounter bolts which were painted in an earlier
service operation, replace them.
(6) Install the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG - INSTAL-
LATION).
(7) Connect the temperature sending unit wire
connector.
(8) Install the ignition coil rail (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/COIL RAIL -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the intake and exhaust manifolds (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the fuel line.
(11) Attach the power steering pump and bracket.
Fig. 10 Engine Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening
Sequence
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 21
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1269 of 2199

(5) Position the valve spring and retainer on the
engine cylinder head and compress the valve spring
with Valve Spring Compressor Tool MD-998772A.
(6) Install the valve locks and release the tool.
(7) Tap the valve spring from side to side with a
hammer to ensure that the spring is properly seated
at the engine cylinder head. Also tap the top of the
retainer to seat the valve locks.
(8) Install the engine cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The rocker arms are made of stamped steel and
have a operational ratio of 1.6:1 (Fig. 21).
OPERATION
When the push rods are forced upward by the cam-
shaft lobes the push rod presses upward on the
rocker arms, the rocker arms pivot, forcing down-
ward pressure on the valves forcing the valves to
move downward and off from their seats.
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be done with the engine
in or out of the vehicle.
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Check for rocker arm bridges which are caus-
ing misalignment of the rocker arm to valve tip area.
(3) Remove the capscrews at each bridge and pivot
assembly (Fig. 22). Alternately loosen the capscrews
one turn at a time to avoid damaging the bridges.
(4) Remove the bridges, pivots and corresponding
pairs of rocker arms (Fig. 22). Place them on a bench
in the same order as removed.
(5) Remove the push rods and place them on a
bench in the same order as removed.
CLEANING
Clean all the components with cleaning solvent.
Use compressed air to blow out the oil passages in
the rocker arms and push rods.
Fig. 20 Valve and Valve Components
1 - VALVE LOCKS (3±BEAD)
2 - RETAINER
3 - VALVE STEM OIL SEAL
4 - INTAKE VALVE
5 - EXHAUST VALVE
6 - VALVE SPRING
Fig. 21 Rocker ArmsÐTypical
1 - CAPSCREWS
2 - BRIDGE
3 - PIVOT ASSEMBLY
4 - PUSH RODS
5 - ROCKER ARMS
9 - 26 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1276 of 2199

(16) Install the serpentine drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
NOTE: During installation, lubricate the hydraulic
valve tappets and all valve components with
MoparTEngine Oil Supplement, or equivalent. TheMoparTEngine Oil Supplement, or equivalent must
remain with the engine oil for at least 1609 km
(1,000 miles). The oil supplement need not be
drained until the next scheduled oil change.
(17) Install the radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION).
(18) Check the ignition timing and adjust as nec-
essary.
(19) Install the grille and bumper, if removed.
(20) Connect negative cable to battery.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
Inspect the connecting rod bearings for scoring and
bent alignment tabs (Fig. 35) (Fig. 36). Check the
bearings for normal wear patterns, scoring, grooving,
fatigue and pitting (Fig. 37). Replace any bearing
that shows abnormal wear.
Inspect the connecting rod journals for signs of
scoring, nicks and burrs.
Misaligned or bent connecting rods can cause
abnormal wear on pistons, piston rings, cylinder
walls, connecting rod bearings and crankshaft con-
necting rod journals. If wear patterns or damage to
any of these components indicate the probability of a
misaligned connecting rod, inspect it for correct rod
alignment. Replace misaligned, bent or twisted con-
necting rods.
Fig. 33 Crankshaft / Camshaft Chain Drive
InstallationÐTypical
1 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
2 - TIMING MARKS
3 - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET
Fig. 34 Timing Case Cover Components
1 - TIMING CASE COVER
2 - OIL SLINGER
3 - CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL
4 - VIBRATION DAMPER PULLEY
Fig. 35 Connecting Rod Bearing Inspection
1 - UPPER BEARING HALF
2 - MATING EDGES
3 - GROOVES CAUSED BY ROD BOLTS SCRATCHING
JOURNAL DURING INSTALLATION
4 - WEAR PATTERN - ALWAYS GREATER ON UPPER BEARING
5 - LOWER BEARING HALF
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 33
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1278 of 2199
is needed to provide the correct clearance. Refer to
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING CHART .
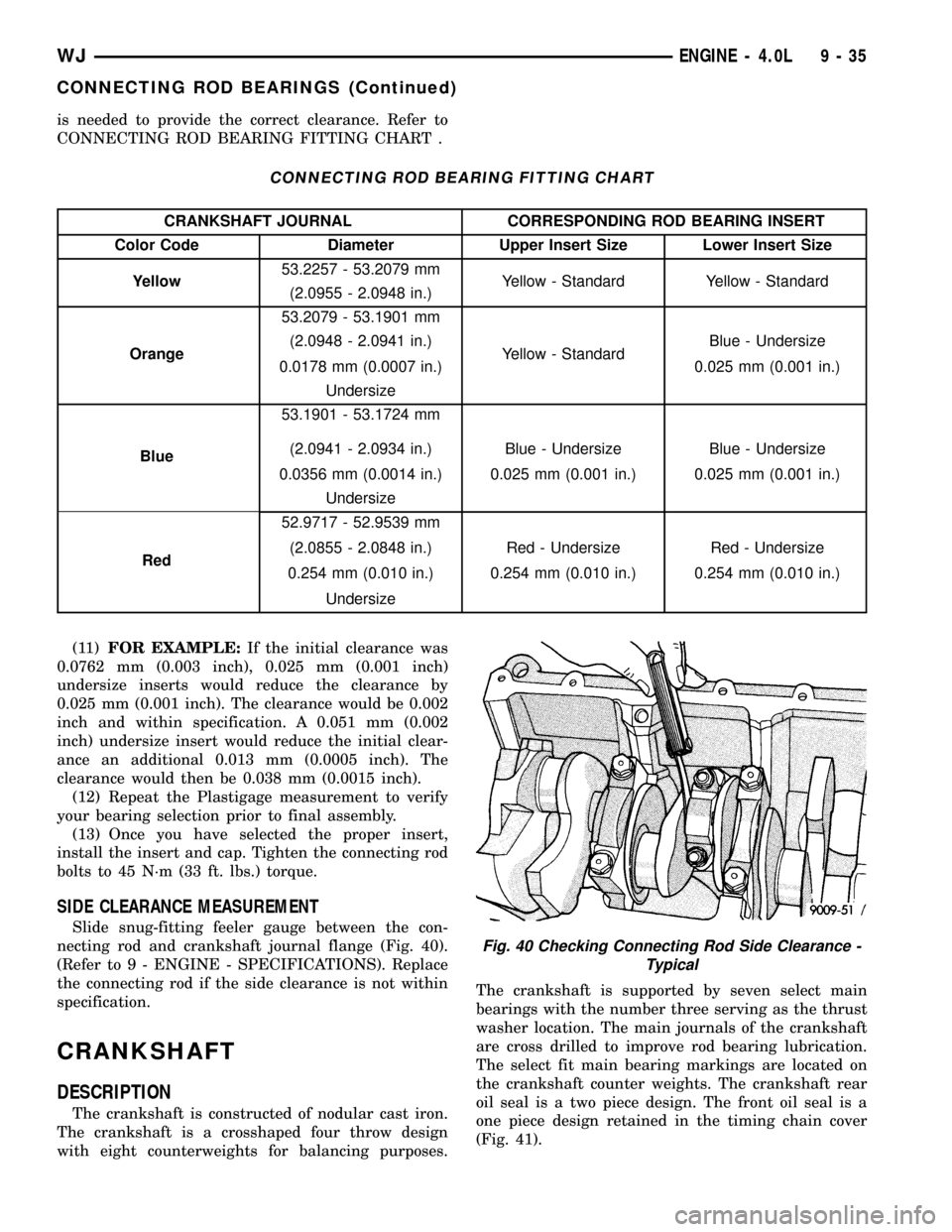
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING CHART
CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL CORRESPONDING ROD BEARING INSERT
Color Code Diameter Upper Insert Size Lower Insert Size
Yellow53.2257 - 53.2079 mm
Yellow - Standard Yellow - Standard
(2.0955 - 2.0948 in.)
Orange53.2079 - 53.1901 mm
Yellow - StandardBlue - Undersize (2.0948 - 2.0941 in.)
0.0178 mm (0.0007 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Blue53.1901 - 53.1724 mm
Blue - Undersize Blue - Undersize (2.0941 - 2.0934 in.)
0.0356 mm (0.0014 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Red52.9717 - 52.9539 mm
Red - Undersize Red - Undersize (2.0855 - 2.0848 in.)
0.254 mm (0.010 in.) 0.254 mm (0.010 in.) 0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
Undersize
(11)FOR EXAMPLE:If the initial clearance was
0.0762 mm (0.003 inch), 0.025 mm (0.001 inch)
undersize inserts would reduce the clearance by
0.025 mm (0.001 inch). The clearance would be 0.002
inch and within specification. A 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) undersize insert would reduce the initial clear-
ance an additional 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch). The
clearance would then be 0.038 mm (0.0015 inch).
(12) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
(13) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 45 N´m (33 ft. lbs.) torque.
SIDE CLEARANCE MEASUREMENT
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the con-
necting rod and crankshaft journal flange (Fig. 40).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Replace
the connecting rod if the side clearance is not within
specification.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is constructed of nodular cast iron.
The crankshaft is a crosshaped four throw design
with eight counterweights for balancing purposes.The crankshaft is supported by seven select main
bearings with the number three serving as the thrust
washer location. The main journals of the crankshaft
are cross drilled to improve rod bearing lubrication.
The select fit main bearing markings are located on
the crankshaft counter weights. The crankshaft rear
oil seal is a two piece design. The front oil seal is a
one piece design retained in the timing chain cover
(Fig. 41).
Fig. 40 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance -
Typical
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 35
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1279 of 2199

CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
FITTING BEARINGS (CRANKSHAFT INSTALLED)
The main bearing caps, numbered (front to rear)
from 1 through 7 have an arrow to indicate the for-
ward position. The upper main bearing inserts are
grooved to provide oil channels while the lower
inserts are smooth.
Each bearing insert pair is selectively fitted to its
respective journal to obtain the specified operating
clearance. In production, the select fit is obtained by
using various-sized color-coded bearing insert pairs
as listed in the Main Bearing Fitting Chart. The
bearing color code appears on the edge of the insert.
The size is not stamped on bearing inserts used
for engine production.
The main bearing journal size (diameter) is identi-
fied by a color-coded paint mark (Fig. 42)on the adja-
cent cheek or counterweight towards the rear of the
crankshaft (flange end). The rear main journal, is
identified by a color-coded paint mark on the crank-
shaft rear flange.
When required, upper and lower bearing inserts of
different sizes may be used as a pair. A standard size
insert is sometimes used in combination with a 0.025
mm (0.001 inch) undersize insert to reduce the clear-
ance by 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch).Never use a pair
of bearing inserts with greater than a 0.025 mm
(0.001 inch) difference in size. Refer to the
Bearing Insert Pair Chart.NOTE: When replacing inserts, the odd size inserts
must be either all on the top (in cylinder block) or
all on the bottom (in main bearing cap).
Once the bearings have been properly fitted, (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT
MAIN BEARINGS - INSTALLATION).
BEARING-TO-JOURNAL CLEARANCE (CRANKSHAFT
INSTALLED)
When using Plastigage, check only one bearing
clearance at a time.
Install the grooved main bearings into the cylinder
block and the non-grooved bearings into the bearing
caps.
Install the crankshaft into the upper bearings dry.
Place a strip of Plastigage across full width of the
crankshaft journal to be checked.
Install the bearing cap and tighten the bolts to 108
N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
NOTE: DO NOT rotate the crankshaft. This will
cause the Plastigage to shift, resulting in an inaccu-
rate reading. Plastigage must not be permitted to
crumble. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
Remove the bearing cap. Determine the amount of
clearance by measuring the width of the compressed
Plastigage with the scale on the Plastigage envelope
(Fig. 43). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS)
for the proper clearance.
Plastigage should indicate the same clearance
across the entire width of the insert. If clearance var-
ies, it may indicate a tapered journal or foreign
material trapped behind the insert.
If the specified clearance is indicated and there are
no abnormal wear patterns, replacement of the bear-
ing inserts is not necessary. Remove the Plastigage
from the crankshaft journal and bearing insert. Pro-
ceed to (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS -
INSTALLATION).
If the clearance exceeds specification, install a pair
of 0.025 mm (0.001 inch) undersize bearing inserts
and measure the clearance as described in the previ-
ous steps.
The clearance indicate with the 0.025 mm (0.001
inch) undersize insert pair installed will determine if
this insert size or some other combination will pro-
vide the specified clearance.FOR EXAMPLE:If the
clearance was 0.0762 mm (0.003 inch) originally, a
pair of 0.0254 mm (0.001 inch) undersize inserts
would reduce the clearance by 0.0254 mm (0.001
inch). The clearance would then be 0.0508 mm (0.002
inch) and within the specification. A 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) undersize bearing insert and a 0.0254 mm
(0.001 inch) undersize insert would reduce the origi-
Fig. 41 Crankshaft with Select Fit Marking Location
1 - 1/4º LETTERS
2 - (ROD)
3 - (MAIN)
9 - 36 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1283 of 2199

INSPECTION
Wipe the inserts clean and inspect for abnormal
wear patterns and for metal or other foreign material
imbedded in the lining. Normal main bearing insert
wear patterns are illustrated (Fig. 47). In general the
lower bearing half will have a heaver wear pattern.
NOTE: If any of the crankshaft journals are scored,
remove the engine for crankshaft repair.
Inspect the back of the inserts for fractures, scrap-
ings or irregular wear patterns.
Inspect the upper insert locking tabs for damage.
Replace all damaged or worn bearing inserts.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the bearing surface of each insert
with engine oil.
(2) Loosen all the main bearing caps. Install the
main bearing upper inserts.
(3) Install the lower bearing inserts into the main
bearing caps.
(4) On the rear main cap, apply MopartGasket
Maker sealer on both sides of cylinder block as
shown in (Fig. 48). The dab of sealer should be 3 mm
(0.125 in.) in diameter.
(5) Apply MopartGasket Maker on the rear bear-
ing cap. The bead should be 2.3 mm (0.09 in.) in
diameter. DO NOT apply sealer to the lip of the seal.
(6) Install the main bearing cap(s) and lower
insert(s).
(7) Tighten the bolts of caps 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, and 7 to
54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque. Now tighten these bolts to
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque. Finally, tighten these
bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque.(8) Push the crankshaft forward and backward.
Load the crankshaft front or rear and tighten cap
bolt No.3 to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque. Then tighten
to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque and finally tighten to
108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Rotate the crankshaft after tightening each
main bearing cap to ensure the crankshaft rotates
freely.
(10) Check crankshaft end play. Crankshaft end
play is controlled by the thrust bearing which is
flange and installed at the No.2 main bearing posi-
tion.
(a) Attach a magnetic base dial indicator to the
cylinder block at either the front or rear of the
engine.
(b) Position the dial indicator rod so that it is
parallel to the center line of the crankshaft.
(c) Pry the crankshaft forward, position the dial
indicator to zero.
(d) Pry the crankshaft forward and backward.
Note the dial indicator readings. End play is the
difference between the high and low measurements
(Fig. 49). Correct end play is 0.038-0.165 mm
(0.0015-0.0065 inch). The desired specifications are
0.051-0.064 mm (0.002-0.0025 inch).
Fig. 47 Main Bearing Wear Patterns
1 - UPPER INSERT
2 - NO WEAR IN THIS AREA
3 - LOW AREA IN BEARING LINING
4 - LOWER INSERT
Fig. 48 Location of Sealer
1-DOWEL
2-SEALER LOCATIONS
3-CYLINDER BLOCK
4-HALFWAY BETWEEN
5-REAR FACE OF CYLINDER BLOCK
6-3mm (0.125 in.)
9 - 40 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1294 of 2199

crankshaft is drilled internally to pass oil from the
main bearing journals (except number 4 main bear-
ing journal) to the connecting rod journals. Each con-
necting rod bearing cap has a small squirt hole, oil
passes through the squirt hole and is thrown off as
the rod rotates. This oil throwoff lubricates the cam-
shaft lobes, distributor drive gear, cylinder walls, and
piston pins.
The hydraulic valve tappets receive oil directly
from the main oil gallery. Oil is provided to the cam-
shaft bearing through galleries. The front camshaft
bearing journal passes oil through the camshaft
sprocket to the timing chain. Oil drains back to the
oil pan under the number one main bearing cap.
The oil supply for the rocker arms and bridged
pivot assemblies is provided by the hydraulic valve
tappets which pass oil through hollow push rods to a
hole in the corresponding rocker arm. Oil from the
rocker arm lubricates the valve train components,
then passes down through the push rod guide holes
in the cylinder head past the valve tappet area, and
returns to the oil pan (Fig. 73).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Disconnect connector and remove oil pressure
sending unit.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292 or equivalent. Start engine and record pres-
sure. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for
the correct pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.If the oil leak source is not pos-itively identified at this time, proceed with the air
leak detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the CCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the CCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service informa-
tion procedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS .
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the CCV valve and breather cap hose.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 51
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1296 of 2199

(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
SERVICE
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug if
damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Replace engine oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(8) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type of engine oil (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAIN-
TENANCE/FLUID TYPES - DESCRIPTION) and
amount of engine oil (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(9) Install oil fill cap.
(10) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(11) Stop engine and inspect oil level. Refer to
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION .
USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL
Care should be exercised when disposing used
engine oil after it has been drained from a vehicle
engine.
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
The engine oil level indicator (Dipstick) is located
at the right rear of the 4.0L engine. Inspect engine
oil level approximately every 800 kilometers (500
miles). Unless the engine has exhibited loss of oil
pressure, run the engine for about five minutes
before checking oil level. Checking engine oil level on
a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick (Fig. 74).
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading (Fig. 74).
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Do not use oil filter with metric threads.
The proper oil filter has SAE type 3/4 X 16 threads.
An oil filter with metric threads can result in oil
leaks and engine failure.
Fig. 74 Engine Oil DipstickÐ4.0L Engine
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - ADD
3 - SAFE
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 53
LUBRICATION (Continued)