Oil JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: LIBERTY, Model: JEEP LIBERTY 2002 KJ / 1.GPages: 1803, PDF Size: 62.3 MB
Page 263 of 1803
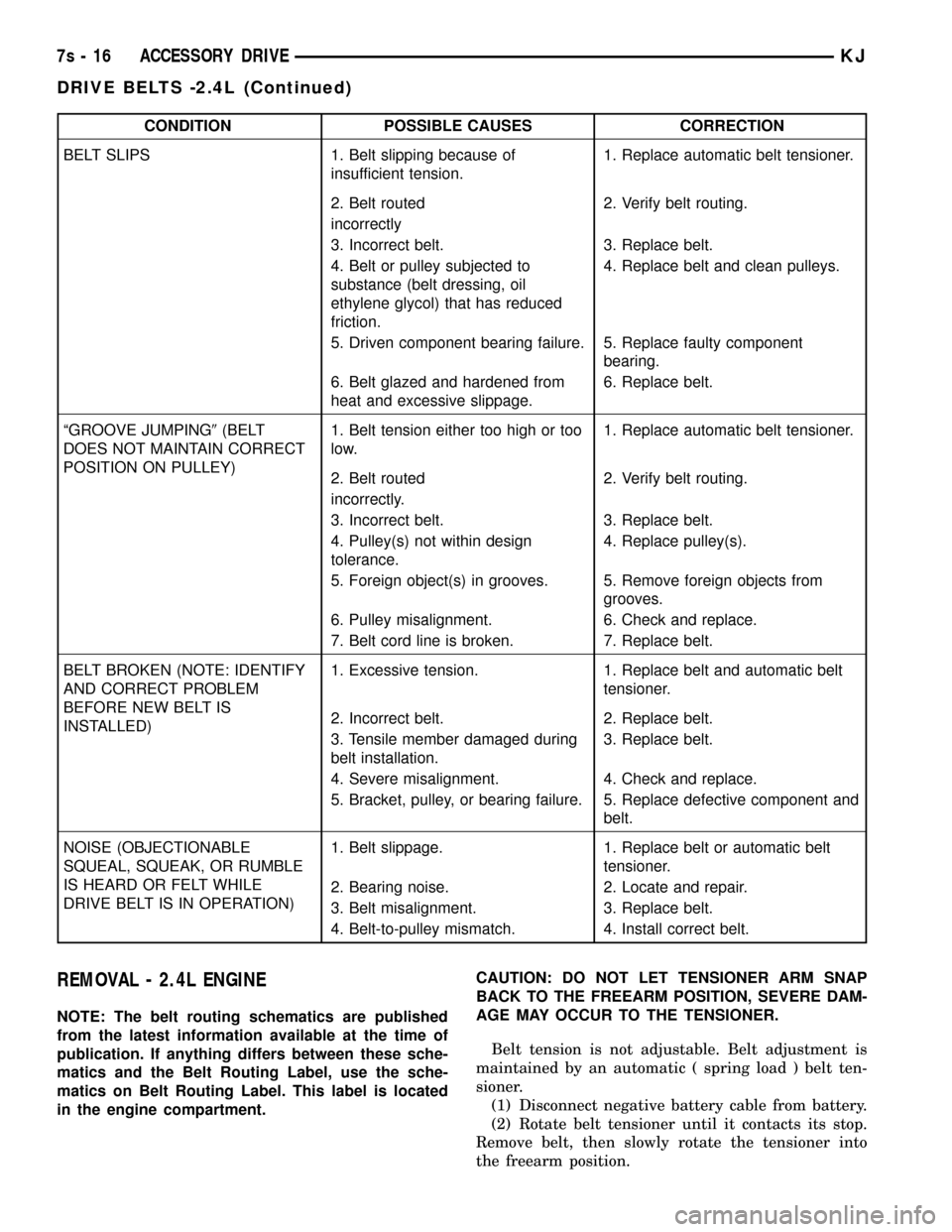
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BELT SLIPS 1. Belt slipping because of
insufficient tension.1. Replace automatic belt tensioner.
2. Belt routed 2. Verify belt routing.
incorrectly
3. Incorrect belt. 3. Replace belt.
4. Belt or pulley subjected to
substance (belt dressing, oil
ethylene glycol) that has reduced
friction.4. Replace belt and clean pulleys.
5. Driven component bearing failure. 5. Replace faulty component
bearing.
6. Belt glazed and hardened from
heat and excessive slippage.6. Replace belt.
ªGROOVE JUMPING9(BELT
DOES NOT MAINTAIN CORRECT
POSITION ON PULLEY)1. Belt tension either too high or too
low.1. Replace automatic belt tensioner.
2. Belt routed 2. Verify belt routing.
incorrectly.
3. Incorrect belt. 3. Replace belt.
4. Pulley(s) not within design
tolerance.4. Replace pulley(s).
5. Foreign object(s) in grooves. 5. Remove foreign objects from
grooves.
6. Pulley misalignment. 6. Check and replace.
7. Belt cord line is broken. 7. Replace belt.
BELT BROKEN (NOTE: IDENTIFY
AND CORRECT PROBLEM
BEFORE NEW BELT IS
INSTALLED)1. Excessive tension. 1. Replace belt and automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Incorrect belt. 2. Replace belt.
3. Tensile member damaged during
belt installation.3. Replace belt.
4. Severe misalignment. 4. Check and replace.
5. Bracket, pulley, or bearing failure. 5. Replace defective component and
belt.
NOISE (OBJECTIONABLE
SQUEAL, SQUEAK, OR RUMBLE
IS HEARD OR FELT WHILE
DRIVE BELT IS IN OPERATION)1. Belt slippage. 1. Replace belt or automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Bearing noise. 2. Locate and repair.
3. Belt misalignment. 3. Replace belt.
4. Belt-to-pulley mismatch. 4. Install correct belt.
REMOVAL - 2.4L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.CAUTION: DO NOT LET TENSIONER ARM SNAP
BACK TO THE FREEARM POSITION, SEVERE DAM-
AGE MAY OCCUR TO THE TENSIONER.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Rotate belt tensioner until it contacts its stop.
Remove belt, then slowly rotate the tensioner into
the freearm position.
7s - 16 ACCESSORY DRIVEKJ
DRIVE BELTS -2.4L (Continued)
Page 266 of 1803

CAUTION: MoparTAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (MS-9769) may not be
mixed with any other type of antifreeze. Mixing of
coolants other than specified (non-HOAT or other
HOAT), may result in engine damage that may not
be covered under the new vehicle warranty, and
decreased corrosion protection.
COOLANT PERFORMANCE
The required ethylene-glycol (antifreeze) and water
mixture depends upon climate and vehicle operating
conditions. The coolant performance of various mix-
tures follows:
Pure Water-Water can absorb more heat than a
mixture of water and ethylene-glycol. This is for pur-
pose of heat transfer only. Water also freezes at a
higher temperature and allows corrosion.
100 percent Ethylene-Glycol-The corrosion
inhibiting additives in ethylene-glycol need the pres-
ence of water to dissolve. Without water, additives
form deposits in system. These act as insulation
causing temperature to rise to as high as 149ÉC
(300ÉF). This temperature is hot enough to melt plas-
tic and soften solder. The increased temperature can
result in engine detonation. In addition, 100 percent
ethylene-glycol freezes at -22ÉC (-8ÉF).
50/50 Ethylene-Glycol and Water-Is the recom-
mended mixture, it provides protection against freez-
ing to -37ÉC (-34ÉF). The antifreeze concentration
must alwaysbe a minimum of 44 percent, year-
round in all climates. If percentage is lower, engine
parts may be eroded by cavitation. Maximum protec-
tion against freezing is provided with a 68 percent
antifreeze concentration, which prevents freezing
down to -67.7ÉC (-90ÉF). A higher percentage will
freeze at a warmer temperature. Also, a higher per-
centage of antifreeze can cause the engine to over-
heat because specific heat of antifreeze is lower than
that of water.
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.
COOLANT SELECTION AND ADDITIVES
The use of aluminum cylinder blocks, cylinder
heads and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. Only MopartAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (glycol base coolant with
corrosion inhibitors called HOAT, for Hybrid Organic
Additive Technology) is recommended. This coolant
offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when
mixed with 50% distilled water to obtain to obtain a
freeze point of -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If it loses color or
becomes contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with
fresh properly mixed coolant solution.CAUTION: Do not use coolant additives that are
claimed to improve engine cooling.
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT
ETHYLENE-GLYCOL MIXTURES
CAUTION: Richer antifreeze mixtures cannot be
measured with normal field equipment and can
cause problems associated with 100 percent ethyl-
ene-glycol.
The required ethylene-glycol (antifreeze) and water
mixture depends upon the climate and vehicle oper-
ating conditions. The recommended mixture of 50/50
ethylene-glycol and water will provide protection
against freezing to -37 deg. C (-35 deg. F). The anti-
freeze concentrationmust alwaysbe a minimum of
44 percent, year-round in all climates.If percentage
is lower than 44 percent, engine parts may be
eroded by cavitation, and cooling system com-
ponents may be severely damaged by corrosion.
Maximum protection against freezing is provided
with a 68 percent antifreeze concentration, which
prevents freezing down to -67.7 deg. C (-90 deg. F). A
higher percentage will freeze at a warmer tempera-
ture. Also, a higher percentage of antifreeze can
cause the engine to overheat because the specific
heat of antifreeze is lower than that of water.
Use of 100 percent ethylene-glycol will cause for-
mation of additive deposits in the system, as the cor-
rosion inhibitive additives in ethylene-glycol require
the presence of water to dissolve. The deposits act as
insulation, causing temperatures to rise to as high as
149 deg. C (300) deg. F). This temperature is hot
enough to melt plastic and soften solder. The
increased temperature can result in engine detona-
tion. In addition, 100 percent ethylene-glycol freezes
at 22 deg. C (-8 deg. F ).
PROPYLENE-GLYCOL MIXTURES
It's overall effective temperature range is smaller
than that of ethylene-glycol. The freeze point of 50/50
propylene-glycol and water is -32 deg. C (-26 deg. F).
5 deg. C higher than ethylene-glycol's freeze point.
The boiling point (protection against summer boil-
over) of propylene-glycol is 125 deg. C (257 deg. F )
at 96.5 kPa (14 psi), compared to 128 deg. C (263
deg. F) for ethylene-glycol. Use of propylene-glycol
can result in boil-over or freeze-up on a cooling sys-
tem designed for ethylene-glycol. Propylene glycol
also has poorer heat transfer characteristics than
ethylene glycol. This can increase cylinder head tem-
peratures under certain conditions.
KJENGINE7s-19
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 267 of 1803

Propylene-glycol/ethylene-glycol Mixtures can
cause the destabilization of various corrosion inhibi-
tors, causing damage to the various cooling system
components. Also, once ethylene-glycol and propy-
lene-glycol based coolants are mixed in the vehicle,
conventional methods of determining freeze point will
not be accurate. Both the refractive index and spe-
cific gravity differ between ethylene glycol and propy-
lene glycol.
OPERATION
Coolant flows through the engine block absorbing
the heat from the engine, then flows to the radiator
where the cooling fins in the radiator transfers the
heat from the coolant to the atmosphere. During cold
weather the ethylene-glycol coolant prevents water
present in the cooling system from freezing within
temperatures indicated by mixture ratio of coolant to
water.
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS
CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION
This system works along with the radiator pres-
sure cap. This is done by using thermal expansion
and contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant
free of trapped air. It provides:
²A volume for coolant expansion and contraction.
²A convenient and safe method for checking/ad-
justing coolant level at atmospheric pressure. This is
done without removing the radiator pressure cap.
²Some reserve coolant to the radiator to cover
minor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-
ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and
returned to a proper level in the radiator.
The coolant reservoir/overflow system has a radia-
tor mounted pressurized cap, an overflow tube, and a
plastic coolant reservoir/overflow tank, mounted to
the right side of the cowl. It is mounted to the cowl
with two nuts on top, and a slide bracket on the bot-
tom.
OPERATION
The pressure chamber keeps the coolant free of
trapped air, provides a volume for expansion and con-
traction, and provides a convenient and safe method
for checking and adjusting coolant level at atmo-
spheric pressure. It also provides some reserve cool-
ant to cover minor leaks, evaporation or boiling
losses. The overflow chamber allows coolant recovery
in case of an overheat.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER - 2.4L
DESCRIPTION
The block heater is operated by ordinary house
current (110 Volt A.C.) through a power cord and con-
nector located in the engine compartment. The
heater is mounted in a core hole (in place of a core
hole plug) in the engine block, with the heating ele-
ment immersed in coolant.
CAUTION: The power cord must be secured in its
retainer clips, and not positioned so it could con-
tact linkages or exhaust manifolds and become
damaged.
OPERATION
The block heater element is submerged in the cool-
ing system's coolant. When electrical power (110 volt
A.C.) is applied to the element, it creates heat. This
heat is transferred to the engine coolant. This pro-
vides easier engine starting and faster warm-up
when vehicle is operated in areas having extremely
low temperatures.
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Detach power cord plug from heater.
(4) Loosen screw in center of heater. Remove
heater assembly.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Thoroughly clean core hole and heater seat.
(2) Insert heater assembly (Fig. 1) with element
loop positionedupward.
(3) With heater seated, tighten center screw
securely to assure a positive seal.
CAUTION: To prevent damage, the power cord must
be secured in it's retaining clips, and not positioned
so it could contact linkages or exhaust manifold.
(4) Connect power cord to heater.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
7s - 20 ENGINEKJ
COOLANT (Continued)
Page 272 of 1803

RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION
The cooling system cap is located on the coolant
pressure bottle. The cap construction includes; stain-
less steel swivel top, rubber seals and retainer, main
spring, and a spring loaded valve (Fig. 9).
OPERATION
The pressure cap allows the cooling system to oper-
ate at higher than atmospheric pressure which raises
the coolant boiling point, thus allowing increased
radiator cooling capacity. The pressure cap releases
pressure at some point within a range of 110 kPa
14 kPa (16 psi 2 psi).
A spring-loaded vent valve in the center of the cap
allows the system to pressurize and depressurize
without creating a vacuum. If the valve is stuck
open, coolant will escape to the overflow hose. There
is also a gasket in the cap to seal to the top of the
filler neck.
CAUTION: Use only the pressure cap specified for
this vehicle. Use of other pressure caps can lead to
coolant loss and overheating.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP
Remove cap from radiator. Be sure that sealing
surfaces are clean. Moisten rubber gasket with water
and install the cap on pressure tester (tool 7700 or
an equivalent) (Fig. 10).Operate the tester pump and observe the gauge
pointer at its highest point. The cap release pressure
should be 124 to 145 kPa (18 to 21 psi). The cap is
satisfactory when the pressure holds steady. It is also
good if it holds pressure within the 124 to 145 kPa
(18 to 21 psi) range for 30 seconds or more. If the
pointer drops quickly, replace the cap.
CAUTION: Radiator pressure testing tools are very
sensitive to small air leaks, which will not cause
cooling system problems. A pressure cap that does
not have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to tool. Turn tool upside
down and recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap
needs replacement.
CLEANING
Clean the radiator pressure cap using a mild soap
and water only.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the pressure valve gasket on the
cap. Replace cap if the gasket is swollen, torn or
worn. Inspect the area around radiator filler neck for
white deposits that indicate a leaking cap.
Fig. 9 PRESSURE CAP
1 - MAIN SPRING
2 - GASKET RETAINER
3 - STAINLESS STEEL SWIVEL TOP
4 - RUBBER SEALS
5 - SPRING LOADED VALVE
6 - COOLANT PRESSURE BOTTLE
7 - FILLER NECK
8 - OVERFLOW NIPPLEFig. 10 Pressure Testing Radiator Pressure Cap -
Typical
1 - PRESSURE CAP
2 - TYPICAL COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
KJENGINE7s-25
Page 277 of 1803

TRANSMISSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANS COOLER
DESCRIPTION.........................30STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING
COOLERS AND TUBES.................30
TRANS COOLER
DESCRIPTION
An internal high capacity/high efficiency cooler is
used on all vehicles, these coolers are an oil-to-cool-
ant type, which consists of plates mounted in the
radiator outlet tank.Because the internal oil cooler is
so efficient, no auxiliary oil cooler is offered. The
cooler is not serviceable separately from the radiator.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUSHING
COOLERS AND TUBES
When a transmission failure has contaminated the
fluid, the oil cooler(s) must be flushed. The torque
converter must also be replaced. This will insure that
metal particles or sludged oil are not later trans-
ferred back into the reconditioned (or replaced) trans-
mission.
The only recommended procedure for flushing cool-
ers and lines is to use Tool 6906-B Cooler Flusher.
WARNING: WEAR PROTECTIVE EYEWEAR THAT
MEETS THE REQUIREMENTS OF OSHA AND ANSI
Z87.1±1968. WEAR STANDARD INDUSTRIAL RUB-
BER GLOVES. KEEP LIGHTED CIGARETTES,
SPARKS, FLAMES, AND OTHER IGNITION
SOURCES AWAY FROM THE AREA TO PREVENT
THE IGNITION OF COMBUSTIBLE LIQUIDS AND
GASES. KEEP A CLASS (B) FIRE EXTINGUISHER IN
THE AREA WHERE THE FLUSHER WILL BE USED.
KEEP THE AREA WELL VENTILATED.DO NOT LET
FLUSHING SOLVENT COME IN CONTACT WITH
YOUR EYES OR SKIN: IF EYE CONTAMINATION
OCCURS, FLUSH EYES WITH WATER FOR 15 TO 20
SECONDS. REMOVE CONTAMINATED CLOTHING
AND WASH AFFECTED SKIN WITH SOAP AND
WATER. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION.
(1) Remove cover plate filler plug on Tool 6906-B.
Fill reservoir 1/2 to 3/4 full of fresh flushing solution.
Flushing solvents are petroleum based solutions gen-
erally used to clean automatic transmission compo-
nents.DO NOTuse solvents containing acids, water,
gasoline, or any other corrosive liquids.(2) Reinstall filler plug on Tool 6906-B.
(3) Verify pump power switch is turned OFF. Con-
nect red alligator clip to positive (+) battery post.
Connect black (-) alligator clip to a good ground.
(4) Disconnect the cooler lines at the transmission.
NOTE: When flushing transmission cooler and
lines, ALWAYS reverse flush.
NOTE: The converter drainback valve must be
removed and an appropriate replacement hose
installed to bridge the space between the transmis-
sion cooler line and the cooler fitting. Failure to
remove the drainback valve will prevent reverse
flushing the system. A suitable replacement hose
can be found in the adapter kit supplied with the
flushing tool.
(5) Connect the BLUE pressure line to the OUT-
LET (From) cooler line.
(6) Connect the CLEAR return line to the INLET
(To) cooler line
(7) Turn pump ON for two to three minutes to
flush cooler(s) and lines.
(8) Turn pump OFF.
(9) Disconnect CLEAR suction line from reservoir
at cover plate. Disconnect CLEAR return line at
cover plate, and place it in a drain pan.
(10) Turn pump ON for 30 seconds to purge flush-
ing solution from cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(11) Place CLEAR suction line into a one quart
container of MopartATF +4, type 9602, Automatic
Transmission Fluid.
(12) Turn pump ON until all transmission fluid is
removed from the one quart container and lines. This
purges any residual cleaning solvent from the trans-
mission cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(13) Disconnect alligator clips from battery. Recon-
nect flusher lines to cover plate, and remove flushing
adapters from cooler lines.
7s - 30 TRANSMISSIONKJ
Page 291 of 1803

speaker is installed on each end of the instrument
panel top pad. One 16.5 centimeter (6.5 inch) Pre-
mium woofer is located in each front door. There is
also one full-range 16.5 centimeter (6.5 inch) diame-
ter Premium full-range speaker located in each rear
door. The premium speaker system also includes a
power amplifier mounted to each front door speaker.
The total available power of the premium speaker
system is about 160 watts.
OPERATION
Two wires connected to each speaker, one feed cir-
cuit (+) and one return circuit (±), allow the audio
output signal electrical current to flow through the
voice coil. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
REMOVAL
FRONT DOOR
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the front door trim panel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOOR - FRONT/TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the speaker mounting screws (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove the speaker from the door and discon-
nect the wire harness connector.
INSTRUMENT PANEL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the A-pillar trim (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/A-PILLAR TRIM - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove instrument panel top cover (Refer to
23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL TOP COVER - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove speaker mounting screws (Fig. 17).
(5) Remove speaker and disconnect the wire har-
ness connector.
Fig. 16 FRONT DOOR SPEAKER
1 - FRONT DOOR SPEAKER
2 - MOUNTING SCREW
3 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
Fig. 17 INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER
2 - INSTRUMENT PANEL
8A - 14 AUDIOKJ
SPEAKER (Continued)
Page 296 of 1803

economy, and/or trip odometer data has been reset.
The CMTC uses internal programming, hard wired
inputs from the U.S./Metric and Reset switches, and
electronic messages received from the Body Control
Module (BCM) to determine the proper reset mes-
sages to send to the EMIC.
²Door Ajar Warning- The EMIC chime tone
generator will generate a single ªbong-likeº chime
tone when the ignition switch is in the On position,
and electronic messages are received over the PCI
data bus from the Body Control Module (BCM) indi-
cating that the status of any door ajar input has
changed from closed to not closed, and from the PCM
indicating that the vehicle is moving. The BCM uses
internal programming, and hard wired inputs from
the door ajar switches and the ignition switch to
determine the proper door ajar switch messages to
send to the EMIC. The PCM uses internal program-
ming and a hard wired vehicle speed pulse input
received from the BCM to determine the proper vehi-
cle distance messages to send to the EMIC.
²Electrical System Voltage Low or High
Warning- Each time the ignition switch is turned to
the On position, the EMIC chime tone generator will
generate a single ªbong-likeº chime tone the first
time an electronic message is received over the PCI
data bus from the PCM requesting ªChargingº indi-
cator illumination. This warning would indicate that
the monitored electrical system voltage is either too
low or too high. This warning will only occur once
during an ignition cycle. The PCM uses internal pro-
gramming and hard wired inputs from the electrical
and charging systems to determine the proper
ªChargingº indicator messages to send to the EMIC.
²Engine Coolant Temperature High Warning
- Each time the ignition switch is turned to the On
position, the EMIC chime tone generator will gener-
ate ªbong-likeº chime tones the first time an elec-
tronic message is received over the PCI data bus
from the PCM indicating that the engine coolant
temperature is too high. This chime will sound for
five consecutive single tones, unless an electronic
message is received from the PCM indicating that
the engine coolant temperature is not too high, or
unless the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion before the five single tones have completed. The
PCM uses internal programming and a hard wired
input from the engine coolant temperature sensor to
determine the proper engine coolant temperature
messages to send to the EMIC.
²Engine Oil Pressure Low Warning- Each
time the ignition switch is turned to the On position,
the EMIC chime tone generator will generate a sin-
gle ªbong-likeº chime tone the first time three
sequential sets of electronic messages are received
over the PCI data bus from the PCM indicating thatthe engine oil pressure is too low with the engine
running. The PCM uses internal programming and
hard wired inputs from the oil pressure sensor and
the crankshaft position sensor to determine the
proper oil pressure and engine speed messages to
send to the EMIC.
²Fasten Seat Belt Warning- Each time the
ignition switch is turned to the On position, the
EMIC chime tone generator will generate repetitive
ªbong-likeº chime tones at a slow rate the first time
an electronic message is received over the PCI data
bus from the ACM requesting ªSeatbeltº indicator
illumination. The ACM uses internal programming
and hard wired inputs from the driver side front seat
belt switch and the ignition switch to determine that
the driver side front seat belt is not fastened with
the ignition switch in the On position. These chimes
will continue to sound for a duration of about six sec-
onds each time the ignition switch is turned to the
On position, or until the driver side front seat belt is
fastened, whichever occurs first. This audible warn-
ing occurs independent of the visual warning pro-
vided by the EMIC ªSeatbeltº indicator.
²Gate Ajar Warning- The EMIC chime tone
generator will generate a single ªbong-likeº chime
tone when the ignition switch is in the On position,
and electronic messages are received over the PCI
data bus from the BCM indicating that the status of
the tailgate ajar input has changed from closed to
not closed, and from the PCM indicating that the
vehicle is moving. The BCM uses internal program-
ming, and hard wired inputs from the tailgate ajar
switch and the ignition switch to determine the
proper tailgate ajar switch messages to send to the
EMIC. The PCM uses internal programming and a
hard wired vehicle speed pulse input received from
the BCM to determine the proper vehicle distance
messages to send to the EMIC.
²Glass Ajar Warning- The EMIC chime tone
generator will generate a single ªbong-likeº chime
tone when the ignition switch is in the On position,
and electronic messages are received over the PCI
data bus from the BCM indicating that the status of
the rear flip-up glass ajar input has changed from
closed to not closed, and from the PCM indicating
that the vehicle is moving. The BCM uses internal
programming, and hard wired inputs from the flip-up
glass ajar switch and the ignition switch to deter-
mine the proper flip-up glass ajar switch messages to
send to the EMIC. The PCM uses internal program-
ming and a hard wired vehicle speed pulse input
received from the BCM to determine the proper vehi-
cle distance messages to send to the EMIC.
²Head/Park/Fog Lights-On Warning- The
EMIC chime tone generator will generate repetitive
ªbong-likeº chime tones at a fast rate when the igni-
KJCHIME/BUZZER 8B - 3
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 312 of 1803

²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
²Oxygen (O2S) sensors
Based on these inputs, the following occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then adjust
the injector pulse width by turning the ground circuit
to each individual injector on and off.
²The PCM monitors the O2S sensor input and
adjusts air-fuel ratio. It also adjusts engine idle
speed through the idle air control (IAC) motor.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil(s) on and off.
²The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch
through the clutch relay. This happens if A/C has
been selected by the vehicle operator and requested
by the A/C thermostat.
ACCELERATION MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. The PCM recognizes
an abrupt increase in throttle position or MAP pres-
sure as a demand for increased engine output and
vehicle acceleration. The PCM increases injector
pulse width in response to increased throttle opening.
DECELERATION MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this
is an Open Loop mode. During hard deceleration, the
PCM receives the following inputs.
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Park/neutral switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
²Vehicle speed
If the vehicle is under hard deceleration with the
proper rpm and closed throttle conditions, the PCM
will ignore the oxygen sensor input signal. The PCM
will enter a fuel cut-off strategy in which it will not
supply a ground to the injectors. If a hard decelera-
tion does not exist, the PCM will determine the
proper injector pulse width and continue injection.Based on the above inputs, the PCM will adjust
engine idle speed through the idle air control (IAC)
motor.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil on and off.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. During wide open
throttle operation, the PCM receives the following
inputs.
²Battery voltage
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal
During wide open throttle conditions, the following
occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
ASD relay via the PCM. The PCM will then control
the injection sequence and injector pulse width by
turning the ground circuit to each individual injector
on and off. The PCM ignores the oxygen sensor input
signal and provides a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel. This is done by adjusting injector pulse
width.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil(s) on and off.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When ignition switch is turned to OFF position,
the PCM stops operating the injectors, ignition coil,
ASD relay and fuel pump relay.
DESCRIPTION - 5 VOLT SUPPLIES
Two different Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
five volt supply circuits are used; primary and sec-
ondary.
DESCRIPTION - IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE
This circuit ties the ignition switch to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM).
DESCRIPTION - POWER GROUNDS
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has 2 main
grounds. Both of these grounds are referred to as
power grounds. All of the high-current, noisy, electri-
cal devices are connected to these grounds as well as
all of the sensor returns. The sensor return comes
into the sensor return circuit, passes through noise
suppression, and is then connected to the power
ground.
The power ground is used to control ground cir-
cuits for the following PCM loads:
²Generator field winding
KJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 13
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 313 of 1803

²Fuel injectors
²Ignition coil(s)
²Certain relays/solenoids
²Certain sensors
DESCRIPTION - SENSOR RETURN
The Sensor Return circuits are internal to the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM).
Sensor Return provides a low±noise ground refer-
ence for all engine control system sensors. Refer to
Power Grounds for more information.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM
The PCM operates the fuel system. The PCM is a
pre-programmed, triple microprocessor digital com-
puter. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain
transmission features, speed control, air conditioning
compressor clutch engagement and idle speed. The
PCM can adapt its programming to meet changing
operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to as Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) Outputs. The sensors and switches that pro-
vide inputs to the PCM are considered Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) Inputs.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based upon
inputs it receives from sensors that react to: engine
rpm, manifold absolute pressure, engine coolant tem-
perature, throttle position, transmission gear selec-
tion (automatic transmission), vehicle speed, power
steering pump pressure, and the brake switch.
The PCM adjusts idle speed based on inputs it
receives from sensors that react to: throttle position,
vehicle speed, transmission gear selection, engine
coolant temperature and from inputs it receives from
the air conditioning clutch switch and brake switch.
Based on inputs that it receives, the PCM adjusts
ignition coil dwell. The PCM also adjusts the gener-
ator charge rate through control of the generator
field and provides speed control operation.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²A/C request (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C select (if equipped with factory A/C)
²A/C pressure transducer
²Auto shutdown (ASD) sense
²Battery temperature
²Battery voltage
²Brake switch²J1850 bus (+) circuits
²J1850 bus (-) circuits
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Fuel level (through J1850 circuitry)
²Generator (battery voltage) output
²Ignition circuit sense (ignition switch in on/off/
crank/run position)
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Knock sensors (2 on 3.7L engine)
²Leak detection pump (switch) sense (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Oil pressure
²Oxygen sensors
²Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only)
²Power ground
²Power steering pressure switch
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Speed control multiplexed single wire input
²Throttle position sensor
²Transfer case switch (4WD range position)
²Vehicle speed sensor
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²A/C clutch relay
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay
²J1850 bus (+/-) circuits for: speedometer, voltme-
ter, fuel gauge, oil pressure gauge/lamp, engine temp.
gauge and speed control warn. lamp
²Clutch pedal position switch override relay
²Data link connection for DRB scan tool
²EGR valve control solenoid (if equipped)
²EVAP canister purge solenoid
²Five volt sensor supply (primary)
²Five volt sensor supply (secondary)
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel pump relay
²Generator field driver (-)
²Generator field driver (+)
²Idle air control (IAC) motor
²Ignition coil(s)
²Leak detection pump (if equipped)
²Malfunction indicator lamp (Check engine lamp).
Driven through J1850 circuits.
²Oxygen sensor heater relays
²Oxygen sensors (pulse width modulated)
²Radiator cooling fan relay (pulse width modu-
lated)
²Speed control vacuum solenoid
²Speed control vent solenoid
²Tachometer (if equipped). Driven through J1850
circuits.
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESKJ
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 314 of 1803

²Transmission convertor clutch circuit. Driven
through J1850 circuits.
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLIES
Primary 5±volt supply:
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor.
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor.
²supplies a reference voltage for the Manifold
Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
²supplies a reference voltage for the Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS) sensor.
Secondary 5±volt supply:
²supplies the required 5 volt power source to the
oil pressure sensor.
²supplies the required 5 volt power source for the
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) (if equipped).
²supplies the 5 volt power source to the transmis-
sion pressure sensor (certain automatic transmis-
sions).
OPERATION - IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSE
The ignition circuit sense input tells the PCM the
ignition switch has energized the ignition circuit.
Battery voltage is also supplied to the PCM
through the ignition switch when the ignition is in
the RUN or START position. This is referred to as
the9ignition sense9circuit and is used to9wake up9
the PCM. Voltage on the ignition input can be as low
as 6 volts and the PCM will still function. Voltage is
supplied to this circuit to power the PCM's 8-volt reg-
ulator and to allow the PCM to perform fuel, ignition
and emissions control functions.
REMOVAL
USE THE DRB SCAN TOOL TO REPROGRAM
THE NEW POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(PCM) WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGINAL IDEN-
TIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND THE VEHI-
CLES ORIGINAL MILEAGE. IF THIS STEP IS
NOT DONE, A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
(DTC) MAY BE SET.
The PCM is located in the engine compartment
near the battery (Fig. 9).
To avoid possible voltage spike damage to the
PCM, ignition key must be off, and negative battery
cable must be disconnected before unplugging PCM
connectors.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(3) Carefully unplug the three 32±way connectors
from PCM.
(4) Remove three PCM mounting bolts and remove
PCM from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
USE THE DRB SCAN TOOL TO REPROGRAM
THE NEW POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(PCM) WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGINAL IDEN-
TIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND THE VEHI-
CLES ORIGINAL MILEAGE. IF THIS STEP IS
NOT DONE, A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
(DTC) MAY BE SET.
(1) Install PCM and 3 mounting bolts to vehicle.
(2) Tighten bolts. Refer to torque specifications.
(3) Check pin connectors in the PCM and the three
32±way connectors for corrosion or damage. Also, the
pin heights in connectors should all be same. Repair
as necessary before installing connectors.
(4) Install three 32±way connectors.
(5) Install cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(6) Install battery cable.
(7) Use the DRB scan tool to reprogram new PCM
with vehicles original Identification Number (VIN)
and original vehicle mileage.
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) is the
primary component of the Sentry Key Immobilizer
System (SKIS) (Fig. 10). The SKIM is located on the
right side of the steering column, below the ignition
Fig. 9 PCM REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - PCM
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
3 - 32-WAY CONNECTORS
KJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 15
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)