KIA CARNIVAL 2007 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: KIA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: CARNIVAL, Model: KIA CARNIVAL 2007Pages: 1575, PDF Size: 44.86 MB
Page 1231 of 1575

1.The aim of this function is to receive the key fob signal and decode it. There are 8 different data included in the
radio frequency frame sent by the RKE to the IPM module:
a. Central door lock
b. Central door unlock
c. Panic function
d. Driver door window close (long press on RKE lock button)
e. Driver door window open (long press on RKE unlock button)
f. Left sliding door open/close
g. Right sliding door open/close
h. Power tailgate open/close
2. Each vehicle can have at most 2 associated key fobs. The key fob is physically separated from the key itself
(separate device).
3. Input/Output Definition and Characteristics
Central Lock/unlock
1.Central locking/unlocking logic is controlled by IPM. Locking/Unlocking inputs are located in ADM, DDM
(Lock/Unlock switch, door knobs, door key cylinder) and in IPM (RKE receiver).
2. Locking/Unlocking actuators are located in ADM for passenger door, DDM for driver door and RAM for sliding doors
and tailgate.
There are 5 ways of operating central lock/unlock:
a. With Key RKE
b. With Door Lock/Unlock switches located on ADM/DDM
c. With Door Lock Monitoring switches located on the passenger/driver door
d. With Door/Tailgate Key Cylinder Lock/Unlock switches located on the tailgate or passenger/driver door.
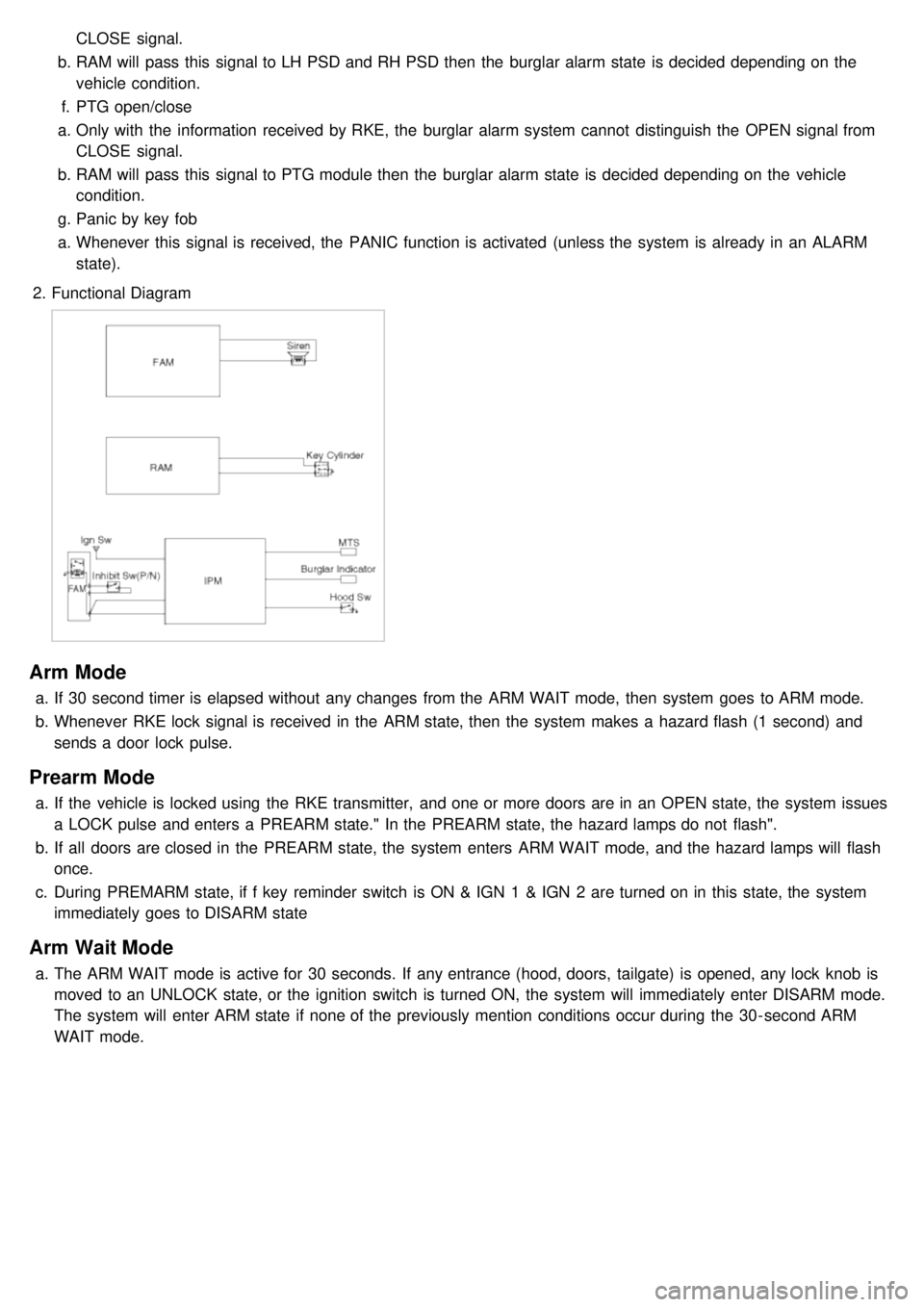
3. Functional Diagram
Page 1232 of 1575

Key Reminder Unlock
1.Key reminder door unlock does not take into account the lock/unlock commands from RKE, key cylinder or door
lock switches. It only takes into account the state of the door lock monitoring switch, key reminder switch and door
open status in order to proceed with the unlock sequence or not.
2. Functional Diagram
Remote Keyless Entry Panic
1.Working Conditions
RKE panic function is only active when the key is out of key cylinder.
Once started, panic operation is not stopped when ignition key is inserted, ignition is ACC, RUN or START, or
door is opened or closed.
2. Functional Diagram
Page 1233 of 1575

Horn
1.Working Conditions
Required key positions:
a. At any position of the key in the cylinder for the horn stalk activation,
b. At Key out from the key cylinder for the horn lock activation or for panic activation.
2. Functional Diagram
Burglar Alarm Function
Burglar Alarm
1.Basic Concept
a. The following functions are related to the RKE and burglar alarm systems..
a. Door locking
b. Door unlocking
c. PSD open/close (both for left and right)
d. PTG open/close
e. Panic
b. If IGN key is inserted into the key cylinder, the RKE transmitter functions are inoperative..
c. Door locking by RKE signal:
a. Whenever this signal is received, door LOCK pulse is always issued.
b. Hazard lamp flashes one time for 1 second depending on the burglar alarm state.
c. This signal will make the system possible to enter into the ARM state (or PREARM state depending on the
vehicle condition).
d. Door unlocking by RKE signal.
a. Whenever this signal is received, door UNLOCK pulse is always issued.
b. Hazard lamp flashes two times whenever the key fob unlock signal is received.
c. This signal will make the system possible to enter into the DISARM or 30sec DELAY state depending on
Condition A is true or not.
e. LH or RH PSD open/close by RKE signal.
a. Only with the information received by RKE, the burglar alarm system cannot distinguish the OPEN signal from
CLOSE signal.
Page 1234 of 1575
CLOSE signal.
b. RAM will pass this signal to LH PSD and RH PSD then the burglar alarm state is decided depending on the
vehicle condition.
f. PTG open/close
a. Only with the information received by RKE, the burglar alarm system cannot distinguish the OPEN signal from
CLOSE signal.
b. RAM will pass this signal to PTG module then the burglar alarm state is decided depending on the vehicle
condition.
g. Panic by key fob
a. Whenever this signal is received, the PANIC function is activated (unless the system is already in an ALARM
state).
2. Functional Diagram
Arm Mode
a.If 30 second timer is elapsed without any changes from the ARM WAIT mode, then system goes to ARM mode.
b. Whenever RKE lock signal is received in the ARM state, then the system makes a hazard flash (1 second) and
sends a door lock pulse.
Prearm Mode
a.If the vehicle is locked using the RKE transmitter, and one or more doors are in an OPEN state, the system issues
a LOCK pulse and enters a PREARM state." In the PREARM state, the hazard lamps do not flash".
b. If all doors are closed in the PREARM state, the system enters ARM WAIT mode, and the hazard lamps will flash
once.
c. During PREMARM state, if f key reminder switch is ON & IGN 1 & IGN 2 are turned on in this state, the system
immediately goes to DISARM state
Arm Wait Mode
a.The ARM WAIT mode is active for 30 seconds. If any entrance (hood, doors, tailgate) is opened, any lock knob is
moved to an UNLOCK state, or the ignition switch is turned ON, the system will immediately enter DISARM mode.
The system will enter ARM state if none of the previously mention conditions occur during the 30- second ARM
WAIT mode.
Page 1235 of 1575

T1 : 0.5 sec
T2 : 1.0 ± 0.1 sec
Disarm Mode
a.If RKE unlock signal is received, then UNLOCK output is issued together with the flashing of hazard lamp (two
times) and the system enters into the DISARM condition.
b. When entering into DISARM from ALARM state, current alarm will be cancelled and burglar alarm relay drive
output is turned off.
c. When RKE unlock signal is received again in the DISARM state, UNLOCK output is issued again and hazard lamp
is flashed also (two times).
Alarm Mode
a.If one or more of entrances are opened in the ARM or REARM state, then Burglar alarm relay drive output is
turned ON in order to inhibit the start condition, and hazard lamp and siren are activated for once of 27 seconds
duration.
b. Siren output and hazard lamp should be synchronized to get the same output period.
c. Even though all the doors are closed during alarm, alarm continues to operate it for the remaining time.
d. When there is a new attack (with one of the entrance is still open) in the vehicle after completing the alarm output,
alarm should not be started again.
T1 : 27 sec ( - 0, +3sec)
T2 : 0.5 ± 0.1 sec
After Alarm State
a.If ALARM cycle is elapsed, the system goes into AFTER ALARM state.
b. During this state,
a. Burglar alarm relay drive output maintains ON.
b. Siren and hazard lamp output are stopped.
c. If another entry is opened during the AFTER ALARM state, the burglar alarm relay drive output remains ON, but
the siren will not be re- activated.
Rearm State
a.If all entrances are is closed during AFTER ALARM state, the system goes into REARM state.
Page 1236 of 1575

Battery Removal
a.If the battery is removed with the system in the ARM state, the system will be placed into the ARM state upon
battery reconnect.
b. The ALARM state will be re- activated if the battery is disconnected, then reconnected, with the system in an
ALARM state.
c. If the battery is disconnected and reconnected with the system in AFTER ALARM state, the alarm will be re-
activated.
d. The system will enter DISARM mode if the battery is disconnected during the ALARM WAIT state.
Panic
a.If RKE PANIC signal is received, Siren output and hazard lamp operate for 27 seconds and the system return to
the previous state as soon as the PANIC function finishes.
b. The PANIC function will be stopped if any RKE signal is received during PANIC activation..
c. If Key reminder switch is ON during PANIC function is operating, PANIC is stopped immediately.
d. If the system goes to ALARM mode during PANIC function is operating, PANIC is stopped immediately and then
ALARM function should be activated.
e. During ALARM state;
If RKE PANIC signal is received, ALARM mode is maintained and PANIC function should be ignored. ALARM has
higher priority than PANIC function.
f. During AFTER_ALARM state;
If RKE PANIC signal is received, AFTR_ALARM mode is maintained and PANIC function should be activated.
Safe & Rescue Mode
The goal of those modes is to be able to cope with failures that may happen on some of the most critical
functionalities (for the driver security) of the system.
Safe Mode
The safe mode is entered in case of system problems such as:
a. Incoherent inputs on monitored signals. In this case, safe mode is the debouncing time before the inputs are
considered INVALID. Note that today, we have no way to detect if the rain/light sensor is in working operation or
not. It means that a driver action will be required in case of failure of this sensor;
b. Loss of the CAN frame containing the monitored signal:
c. Loss of the CAN network: CAN goes to BUS OFF state, safe mode is the time necessary for detecting the BUS
OFF state.
In all cases, the action in safe mode is to maintain the previous state of the system (for lighting and wiping). The list of
monitored signals is the same as in rescue mode
Exiting Safe Mode
The software safe mode is exited and the module goes back to the normal mode when: a. On IPM, hardware inputs return to a coherent state;
b. The lost CAN signal comes back while timeout has not elapsed;
c. The CAN network returns to a normal state without reaching BUS OFF state.
Software safe mode is also exited when the software rescue mode is entered (problem does not disappear).
Hardware safe mode is exited and the module goes back to normal mode if the internal problem disappears (watchdog
is properly triggered again). If the problem stays, hardware safe mode is exited to enter hardware rescue mode.
Rescue Modes
The rescue mode consists in activating some safety functions when IGN2 = ON: a. Switch on the low beams (FAM), park lamps (FAM), tail lamps (RAM) and cluster backlighting (IPM);
b. Unlock of all the doors when the rescue mode is entered with IGN2 = ON
c. Front wipers do not need to be turned on by software in rescue mode because wipers can be turned on by
manually setting the MF switch to low speed. The FAM software must keep the same state as before entering the
rescue mode.
d. When IGN2 = OFF, low beams, park/tail lamps and cluster backlighting are turned off.
Entering Rescue Modes
Page 1237 of 1575

Rescue mode is entered when some important CAN signal or hardware input are not available. Rescue mode is
entered when one of the following conditions is true:
IPMa. Timeout on CAN signal InhibitSwSts, to detect loss of CAN connection with FAM.
b. Timeout on CAN signal StopLpErrorSts, to detect loss of CAN connection with RAM.
c. MF Light Switch information is invalid: when the signals coming from MF Light Switch are not coherent for more
than 2 s, CAN signal ParkTailHeadLpCtrl is sent with INVALID value and rescue mode is entered.
d. Front Wiper MF Switch information is invalid: when the signals coming from Front Wiper MF Switch are not
coherent for more than 2 s, CAN signal FWiperCtrl is sent with INVALID value and rescue mode is entered.
e. CAN is in Bus Off state
RAM a. Timeout on CAN signal InhibitSwSts, to detect loss of CAN connection with FAM.
b. Timeout on CAN signal ParkTailHeadLpCtrl or FWiperCtrl, to detect loss of CAN connection with IPM.
c. ParkTailHeadLpCtrl = INVALID or unknown value
d. FWiperCtrl = INVALID or unknown value
e. CAN is in Bus Off state
FAM a. Timeout on CAN signal StopLpErrorSts, to detect loss of CAN connection with RAM
b. Timeout on CAN signal ParkTailHeadLpCtrl or FWiperCtrl, to detect loss of CAN connection with IPM
c. ParkTailHeadLpCtrl = INVALID or unknown value
d. FWiperCtrl = INVALID or unknown value
e. CAN is in Bus Off state
For all CAN signals, timeout duration is 2.5 times signal periodicity.
Page 1238 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSTICS WHEN USING DIAGNOSIS TOOL
1.The diagnosis tool supports quick diagnosis of supported body electrical systems through input/output monitoring.
and actuation testing.
2. To diagnose the BCM function, select the menu of model and body control module.
3.Select the module menu to diagnose.
4.The CURRENT DATA function is used to monitor input/output conditions.
Page 1239 of 1575

5.Use the ACTUATION TEST mode to force output devices to operate for testing purposes.
6.Use the "DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES" mode.
INSPECTION
1.The body network system consists of several ECUs that communicates via a CAN bus. The diagnostic tester is not
directly connected to the CAN bus, but utilises a one- wire communication line (K- line) that connects to a gateway
in the IPM ECU.
Page 1240 of 1575

2.The IPM communicates with the diagnostic tester directly. But other units operate self diagnostic, input/output
monitoring and actuator operation via the IPM using the CAN communication.
INPUT MONITORING
IPM (In- Panel Module)
No. Input switch Unit
1 IPM Node Availability PRESENT/NOT PRESENT
2 FAM Node Availability PRESENT/NOT PRESENT
3 RAM Node Availability PRESENT/NOT PRESENT
4 DDM Node Availability PRESENT/NOT PRESENT
5 ADM Node Availability PRESENT/NOT PRESENT
6 IMS Node Availability PRESENT/NOT PRESENT
7 CLU Node Availability PRESENT/NOT PRESENT
8 IPM Node Failure FAILURE/ O.K
9 FAM Node Failurey FAILURE/ O.K
10 RAM Node Failure FAILURE/ O.K
11 DDM Node Failure FAILURE/ O.K
12 ADM Node Failure FAILURE/ O.K
13 IMS Node Failure FAILURE/ O.K
14 CLU Node Failure FAILURE/ O.K
15 Auto Head lamp ON/OFF
16 Headlamp low beam ON/OFF
17 High beam ON/OFF