heater LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DEFENDER, Model: LAND ROVER DEFENDER 1999Pages: 667, PDF Size: 8.76 MB
Page 254 of 667

19 - FUEL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPONENT LOCATION 1...................................................................................
DESCRIPTION 2.....................................................................................................
FUEL PUMP AND FUEL GAUGE SENDER 3........................................................
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR 5........................................................................
INJECTORS 7.........................................................................................................
FUEL FILTER 9.......................................................................................................
WATER SENSOR 10..............................................................................................
OPERATION 11......................................................................................................
ADJUSTMENT
HEATER PLUG TEST 1..........................................................................................
FUEL SYSTEM - BLEED 1.....................................................................................
FUEL TANK - DRAIN 2...........................................................................................
REPAIR
ELEMENT - AIR FILTER 1......................................................................................
SENSOR - FUEL TEMPERATURE 1......................................................................
SWITCH - INERTIA - FUEL CUT OFF 2.................................................................
SENSOR - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) 2....................................................................
SENSOR - COMBINED MAP AND IAT 3................................................................
SENSOR - AMBIENT AIR PRESSURE (AAP) 3.....................................................
ELEMENT - FUEL FILTER 4...................................................................................
COOLER - FUEL 4..................................................................................................
TURBOCHARGER 5...............................................................................................
FILTER ASSEMBLY - AIR 6...................................................................................
INJECTOR - SET 7.................................................................................................
HEATER PLUGS - SET 9.......................................................................................
INTERCOOLER 9...................................................................................................
POTENTIOMETER - THROTTLE 10......................................................................
PUMP - FUEL 10.....................................................................................................
REGULATOR - FUEL PRESSURE 11....................................................................
FUEL TANK 12.......................................................................................................
NECK - FUEL TANK FILLER 14.............................................................................
ProCarManuals.com
Page 258 of 667
FUEL SYSTEM
3
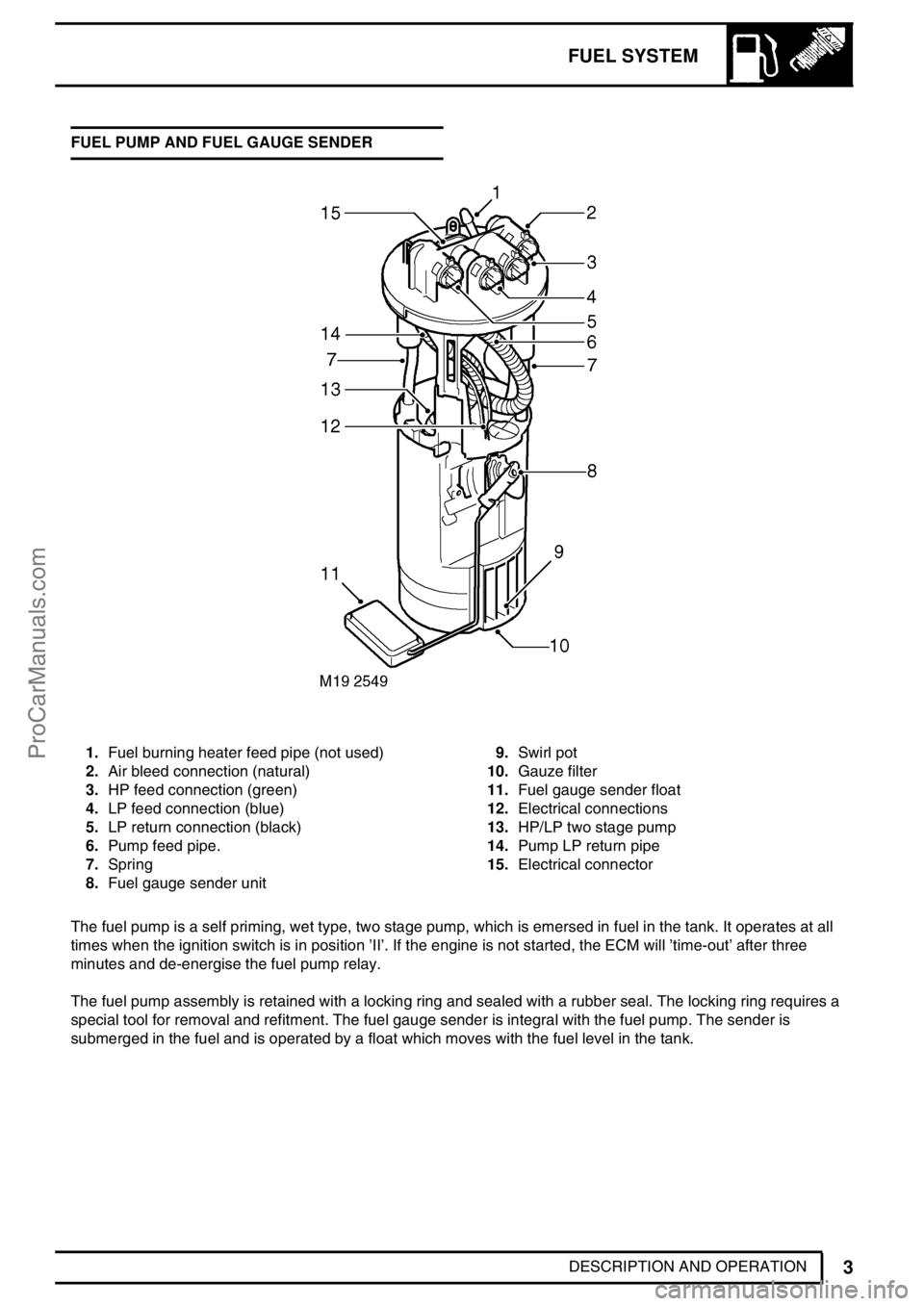
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION FUEL PUMP AND FUEL GAUGE SENDER
1.Fuel burning heater feed pipe (not used)
2.Air bleed connection (natural)
3.HP feed connection (green)
4.LP feed connection (blue)
5.LP return connection (black)
6.Pump feed pipe.
7.Spring
8.Fuel gauge sender unit9.Swirl pot
10.Gauze filter
11.Fuel gauge sender float
12.Electrical connections
13.HP/LP two stage pump
14.Pump LP return pipe
15.Electrical connector
The fuel pump is a self priming, wet type, two stage pump, which is emersed in fuel in the tank. It operates at all
times when the ignition switch is in position’II’. If the engine is not started, the ECM will’time-out’after three
minutes and de-energise the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump assembly is retained with a locking ring and sealed with a rubber seal. The locking ring requires a
special tool for removal and refitment. The fuel gauge sender is integral with the fuel pump. The sender is
submerged in the fuel and is operated by a float which moves with the fuel level in the tank.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 268 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
1
ADJUSTMENT HEATER PLUG TEST
Service repair no - 19.90.20.01
Check
1. Test out of engine
2.Remove heater plug.See Repair.
3.UsingLRT-12-511,connect RED lead to battery
’+’positive and the BLACK lead to battery’-’
negative.
4.Position heater plug into tester and retain with
spring loaded bar.
5.Connect YELLOW lead to heater plug terminal.
6.Press red button on tester and note ammeter
reading. Keep button depressed, heater plug tip
should start to glow after 5 seconds
CAUTION: The heater plug tip must glow
first, if it fails to do so, replace heater plug.
7.The ammeter reading should show an initial
current draw of 25 amps, which should fall to 12
amps after 20 seconds.
8.Refit heater plug.See Repair.FUEL SYSTEM - BLEED
Service repair no - 19.50.07
Fuel Purging Procedure
1.If the vehicle runs out of fuel, or the fuel level is
so low that the fuel system draws air into the fuel
rail, the fuel rail will need to be purged before the
engine will start. This can be achieved by
following a set procedure. The process does not
require the use of any specialist equipment and
can be performed by the driver of the vehicle.
The process is as follows:
2.Switch off ignition and wait 15 seconds.
3.Turn ignition key to position 2 and wait 3
minutes, (this ensures that the fuel system
purges all the air from the fuel rail within the
cylinder head).
4.Depress the throttle pedal to more than 90% of
its total travel, (to the throttle stop).
5.Crank the engine keeping the throttle pedal
depressed.
NOTE: This operation is controlled by the
ECM and it is important that the purging
operation is not carried out on a vehicle
that has not run out of fuel. If it is carried out
unnecessarily it can lead to the engine flooding
and failing to start.
This operation will be cancelled:
6.As soon as engine speed exceeds 600 rev/min.
7.The driver allows the throttle pedal to close to a
position less than 90% of its travel.
8.The ignition key is released from the start
position.
NOTE: The engine must not be cranked for
more than 30 seconds in any one period.
9.Repeat the above procedure if the engine fails to
start.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 278 of 667

FUEL SYSTEM
9
REPAIR HEATER PLUGS - SET
Service repair no - 19.60.31
Remove
1.Remove 3 bolts and remove engine acoustic
cover.
2.Remove battery cover.
3.Disconnect battery negative lead.
4.Disconnect 4 heater plug leads.
5.Loosen and remove 4 heater plugs.
Refit
6.Throughly clean heater plugs and seating area
in cylinder head.
7.Apply a suitable anti-seize compound to threads
of heater plugs.
8.Fit heater plugs and tighten to16 Nm (12 lbf. ft)
.
9.Connect heater plug leads.
10.Fit engine acoustic cover.
11.Reconnect battery negative lead.
12.Fit battery cover.INTERCOOLER
Service repair no - 19.42.15
Remove
1.Remove radiator.See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair.
2.Release clip and remove air hose from
intercooler.
Refit
3.Position air hose to intercooler and secure with
clip.
4.Fit radiator.See COOLING SYSTEM, Repair.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 290 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
NOTE: Inset A shows differences for Pre
EU3 models
1.Pressure cap
2.Overflow pipe
3.Heater return hose
4.Heater matrix
5.Heater inlet hose
6.Oil cooler return pipe - EU3 models
7.Connecting hose
8.Oil cooler housing assembly
9.Heater inlet pipe
10.Connecting hose
11.Outlet housing
12.Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
13.Bleed screw
14.Radiator top hose
15.Radiator - upper
16.Intercooler
17.Gearbox oil cooler
18.Radiator - lower
19.Viscous fan
20.Drain plug
21.Connecting hose
22.Fuel cooler feed hose
23.Radiator bottom hose
24.Thermostat housing
25.Connecting hose
26.Coolant pump feed pipe
27.Coolant by-pass pipe
28.Radiator bleed pipe
29.Connecting hose
30.Coolant pump
31.Fuel cooler
32.Heater/expansion tank return hose
33.Expansion tank
34.EGR Cooler - EU3 models
35.Connecting hose - EU3 models
36.Connecting hose - EU3 models
37.Hose - EGR Cooler to oil cooler return pipe -
EU3 models
38.Radiator lower feed hose - Pre EU3 models
39.Oil cooler return pipe - Pre EU3 models
ProCarManuals.com
Page 292 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION A - EU 3 Models
B- Pre EU3 Models
GENERAL
The cooling system used on the Diesel engine is a pressure relief by-pass type system which allows coolant to
circulate around the engine block and heater circuit when the thermostat is closed. With coolant not passing
through the by-pass or the radiator promotes faster heater warm-up which in turn improves passenger comfort.
A coolant pump is mounted on a casting behind the PAS pump and is driven from the PAS pump at crankshaft
speed by the auxiliary drive belt. The pump mounting casting connects with passages in the cylinder block and
pumps coolant from the radiator through the cylinder block.
A viscous fan is attached to an idler pulley at the front of the engine. The fan is attached to a threaded spigot on
the pulley with a right hand threaded nut. The fan draws air through the radiator to assist in cooling when the
vehicle is stationary. The fan rotational speed is controlled relative to the running temperature of the engine by a
thermostatic valve regulated by a bi-metallic coil.
The cooling system uses a 50/50 mix of anti-freeze and water.
Thermostat Housing
A plastic thermostat housing is located behind the radiator. The housing has three connections which locate the
radiator bottom hose, top hose and coolant pump feed pipe. The housing contains a wax element thermostat and
a spring loaded by-pass flow valve.
Thermostat - Main valve
The thermostat is used to maintain the coolant at the optimum temperature for efficient combustion and to aid
engine warm-up. The thermostat is closed at temperatures below approximately 82°C (179°F). When the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 82°C the thermostat starts to open and is fully open at approximately 96°C
(204°F). In this condition the full flow of coolant is directed through the radiator.
The thermostat is exposed to 90% hot coolant from the engine on one side and 10% cold coolant returning from
the radiator bottom hose on the other side.
Hot coolant from the engine passes from the by-pass pipe through four sensing holes in the flow valve into a tube
surrounding 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant returning from the radiator, cooled by the ambient
air, conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area.
In cold ambient temperatures, the engine temperature is raised approximately 10°C (50°F) to compensate for the
heat loss of 10% exposure to the cold coolant returning from the radiator bottom hose.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 293 of 667

26COOLING SYSTEM
6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION By-pass flow valve
The by-pass flow valve is held closed by a light spring. It operates to further aid heater warm-up. When the main
valve is closed and the engine speed is below 1500 rev/min, the coolant pump does not produce sufficient flow
and pressure to open the valve. In this condition the valve prevents coolant circulating through the by-pass circuit
and forces the coolant through the heater matrix only. This provides a higher flow of warm coolant through the
heater matrix to improve passenger comfort in cold conditions.
When the engine speed increases above 1500 rev/min the coolant pump produces a greater flow and pressure
than the heater circuit can take. The pressure acts on the flow valve and overcomes the valve spring pressure,
opening the valve and limiting the pressure in the heater circuit. The valve modulates to provide maximum coolant
flow through the heater matrix and yet allowing excess coolant to flow into the by-pass circuit to provide the
engines cooling needs at higher engine rev/min.
Outlet Housing
A cast aluminium outlet housing is attached to the cylinder head with three bolts and sealed with a gasket. Coolant
leaves the engine through the outlet housing and is directed through a hose to the heater matrix, the radiator or
the by-pass circuit.
An Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is installed in a threaded port on the side of the outlet housing. The
sensor monitors coolant temperature emerging from the engine and sends signals to the Engine Control Module
(ECM) for engine management and temperature gauge operation.
Expansion Tank
The expansion tank is located in the engine compartment. The tank is made from moulded plastic and attached to
brackets on the right hand inner wing. A maximum coolant when cold level is moulded onto the tank.
Excess coolant created by heat expansion is returned to the expansion tank from the radiator bleed pipe at the top
of the radiator. An outlet pipe is connected into the coolant pump feed hose and replaces the coolant displaced by
heat expansion into the system when the engine is cool.
The expansion tank is fitted with a sealed pressure cap. The cap contains a pressure relief valve which opens to
allow excessive pressure and coolant to vent through the overflow pipe. The relief valve is open at a pressure of
1.4 bar (20 lbf.in) and above.
Heater Matrix
The heater matrix is fitted in the heater assembly inside the passenger compartment. Two pipes pass through the
bulkhead into the engine compartment and provide coolant flow to and from the matrix. The pipes from the
bulkhead are connected to the matrix, sealed with’O’rings and clamped with circular rings.
The matrix is constructed from aluminium with two end tanks interconnected with tubes. Aluminium fins are
located between the tubes and conduct heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes. Air from the heater
assembly is warmed as it passes through the matrix fins. The warm air is then distributed in to the passenger
compartment as required.
When the engine is running, coolant from the engine is constantly circulated through the heater matrix.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 294 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Radiator
The 44 row radiator is located at the front of the vehicle in the engine compartment. The cross flow type radiator is
manufactured from aluminium with moulded plastic end tanks interconnected with tubes. The bottom four rows are
separate from the upper radiator and form the lower radiator for the fuel cooler. Aluminium fins are located
between the tubes and conduct heat from the hot coolant flowing through the tubes, reducing the coolant
temperature as it flows through the radiator. Air intake from the front of the vehicle when moving carries the heat
away from the fins. When the vehicle is stationary, the viscous fan draws air through the radiator fins to prevent
the engine from overheating.
Two connections at the top of the radiator provide for the attachment of the top hose from the outlet housing and
bleed pipe to the expansion tank. Three connections at the bottom of the radiator allow for the attachment of the
bottom hose to the thermostat housing and the return hose from the oil cooler and the feed hose to the fuel cooler.
The bottom four rows of the lower radiator are dedicated to the fuel cooler. The upper of the two connections at
the bottom of the radiator receives coolant from the oil cooler. This is fed through the four rows of the lower
radiator in a dual pass and emerges at the lower connection. The dual pass lowers the coolant temperature by up
to 24°C before being passed to the fuel cooler. Two smaller radiators are located in front of the cooling radiator.
The upper radiator is the intercooler for the air intake system and the lower radiator provides cooling of the
gearbox oil.
Pipes and Hoses
The coolant circuit comprises flexible hoses and metal formed pipes which direct the coolant into and out of the
engine, radiator and heater matrix. Plastic pipes are used for the bleed and overflow pipes to the expansion tank.
A bleed screw is installed in the radiator top hose and is used to bleed air during system filling. A drain plug to
drain the heater and cylinder block circuit of coolant is located on the underside of the coolant pump feed pipe.
Oil Cooler
The oil cooler is located on the left hand side of the engine block behind the oil centrifuge and oil filter. Oil from the
oil pump is passed through a heat exchanger which is surrounded by coolant in a housing on the side of the
engine.
Full water pump flow is directed along the cooler housing which also distributes the flow evenly along the block
into three core holes for cylinder cooling. This cools the engine oil before it is passed into the engine. A small
percentage of the coolant from the oil cooler passes into a metal pipe behind the engine. It then flows into the
lower radiator via a hose.
Fuel Cooler
The fuel cooler is located on the right hand side of the engine and is attached to the inlet manifold. The cooler is
cylindrical in design and has a coolant feed connection at its forward end. A’T’connection at the rear of the cooler
provides a connection for the coolant return from the heater matrix and coolant return from the fuel cooler.
The’T’connection houses a thermostat which opens at approximately 82°C. This prevents the cooler operating in
cold climates. Two quick release couplings on the cooler allow for the connection of the fuel feed from the
pressure regulator and return to the fuel tank. A counter flow system is used within the cooler.
Fuel flows around a coolant jacket within the cooler and flows from the back to the front of the cooler. As the hot
fuel cools travelling slowly forwards it meets progressively colder coolant travelling in the opposite direction
maintaining a differential cooling effect.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 298 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION
Coolant Flow - Engine Warm Up
During warm up the coolant pump moves fluid through the cylinder block and it emerges from the outlet housing.
From the outlet housing, the warm coolant flow is prevented from flowing through the upper and lower radiators
because both thermostats are closed. The coolant is directed into the heater circuit.
Some coolant from the by-pass pipe can pass through small sensing holes in the flow valve. The warm coolant
enters a tube in the thermostat housing and surrounds 90% of the thermostat sensitive area. Cold coolant
returning from the radiator bottom hose conducts through 10% of the thermostat sensitive area. In cold ambient
temperatures the engine temperature can be raised by up to 10°C (50°F) to compensate for the heat loss of the
10% exposure to the cold coolant return from the radiator bottom hose.
At engine speeds below 1500 rev/min, the by-pass valve is closed only allowing the small flow through the sensing
holes. As the engine speed increases above 1500 rev/min, the greater flow and pressure from pump overcomes
the light spring and opens the by-pass flow valve. The flow valve opens to meet the engine’s cooling needs at
higher engine speeds and prevents excess pressure in the cooling system. With both thermostats closed,
maximum flow is directed through the heater circuit.
The heater matrix acts as a heat exchanger reducing the coolant temperature as it passes through the matrix.
Coolant emerges from the heater matrix and flows to the fuel cooler’T’connection via the heater return hose.
From the fuel cooler the coolant is directed into the coolant pump feed pipe and recirculated around the heater
circuit. In this condition the cooling system is operating at maximum heater performance.
Coolant Flow - Engine Hot
As the coolant temperature increases the main thermostat opens. This allows some coolant from the outlet
housing to flow through the top hose and into the radiator to be cooled. The hot coolant flows from the left tank in
the radiator, along the tubes to the right tank. The air flowing through the fins between the tubes cools the coolant
as it passes through the radiator.
A controlled flow of the lower temperature coolant is drawn by the pump and blended with hot coolant from the
by-pass and the heater return pipes in the pump feed pipe. The pump then passes this coolant, via the cylinder
block, to the oil cooler housing, cooling the engine oil before entering the block to cool the cylinders.
When the fuel temperature increases, the heat from the fuel conducts through the fuel cooler’T’connection and
causes the fuel thermostat to open. Coolant from the cylinder block flows through the oil cooler and via a pipe and
hose enters the lower radiator. The lower temperature coolant from the oil cooler housing is subjected to an
additional two passes through the lower radiator to further reduce the coolant temperature. From the lower radiator
the coolant flows , via a hose, to the fuel cooler.
As the hot fuel cools, travelling slowly forwards through the cooler, it meets the progressively colder coolant
travelling in the opposite direction from the lower radiator.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 302 of 667

COOLING SYSTEM
1
ADJUSTMENT DRAIN AND REFILL
Service repair no - 26.10.01
WARNING: Hot coolant
Drain
1.Remove engine acoustic cover.
2.Visually check engine and cooling system for
signs of coolant leaks.
3.Examine hoses for signs of cracking, distortion
and security of connections.
4.Position drain tray to collect coolant.
5.Remove expansion tank filler cap.
6.Loosen clip screws securing air inlet hose to
intercooler and inlet manifold, release and
remove hose.
7.Release clip and disconnect bottom hose from
radiator.
8.Allow cooling system to drain.
9.Disconnect bottom hose from radiator.Refill
1.Flush system with water under low pressure.
2.Do not use water under high pressure as it could
damage the radiator.
3.Connect bottom hose to radiator and secure
hose with clip.
4.Prepare coolant to required concentration.
5.Position heater temperature control to maximum
hot position.
6.Remove bleed screw from top hose.
7.Fill system slowly through coolant expansion
tank until a steady flow of coolant is emitted from
the bleed hole in top hose.
8.Fit bleed screw to top hose.
9.Continue filling system until coolant level
reaches’MAX’mark on expansion tank.
10.Fit expansion tank filler cap.
11.Position air intake hose and tighten clip screws.
12.Start and run engine until normal running
temperature is reached.
13.If fitted, DO NOT operate air conditioning.
14.Switch off engine and allow to cool.
15.Check for leaks and top-up coolant to’MAX’
mark on expansion tank.
ProCarManuals.com