check engine LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 827 of 1529
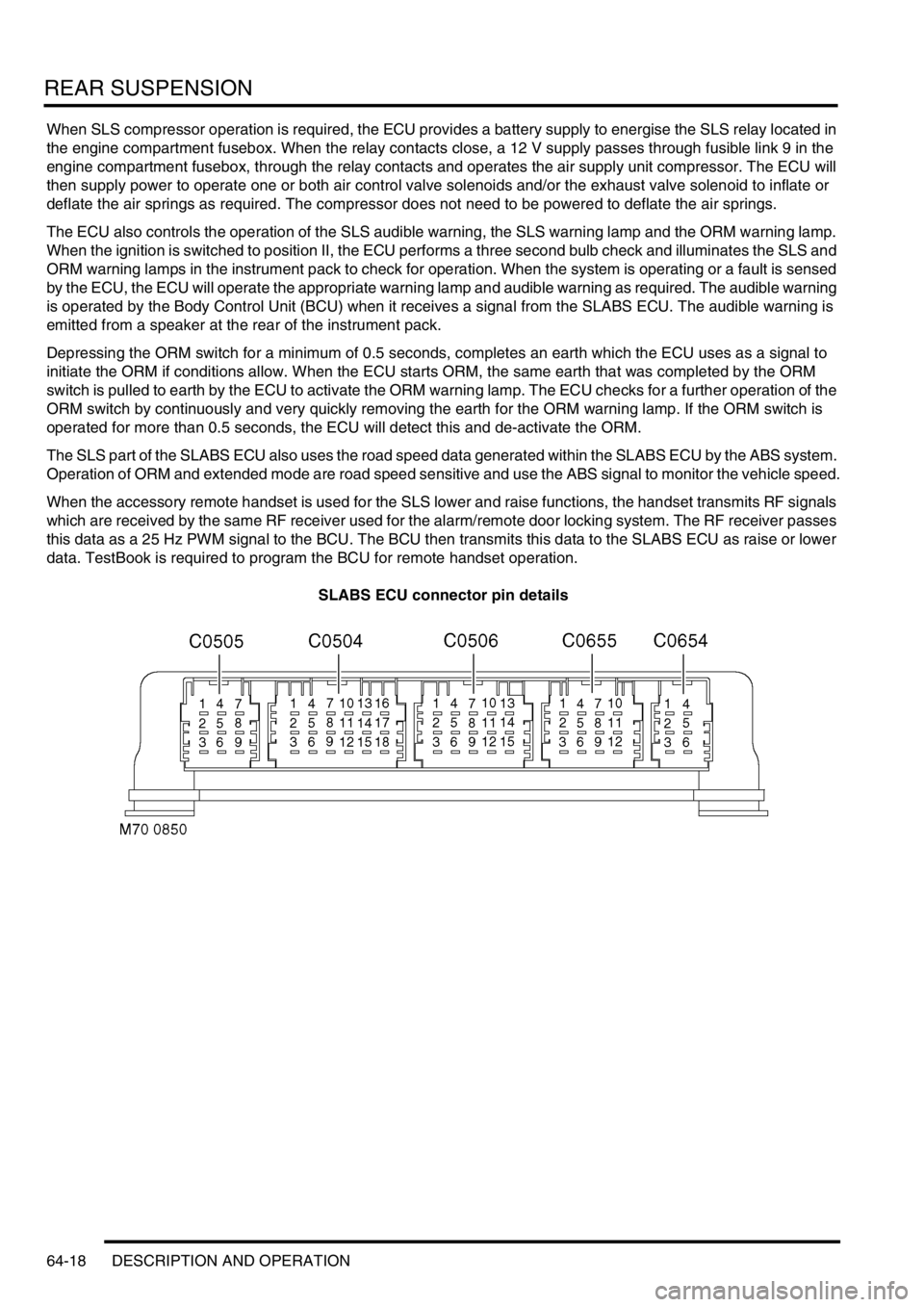
REAR SUSPENSION
64-18 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
When SLS compressor operation is required, the ECU provides a battery supply to energise the SLS relay located in
the engine compartment fusebox. When the relay contacts close, a 12 V supply passes through fusible link 9 in the
engine compartment fusebox, through the relay contacts and operates the air supply unit compressor. The ECU will
then supply power to operate one or both air control valve solenoids and/or the exhaust valve solenoid to inflate or
deflate the air springs as required. The compressor does not need to be powered to deflate the air springs.
The ECU also controls the operation of the SLS audible warning, the SLS warning lamp and the ORM warning lamp.
When the ignition is switched to position II, the ECU performs a three second bulb check and illuminates the SLS and
ORM warning lamps in the instrument pack to check for operation. When the system is operating or a fault is sensed
by the ECU, the ECU will operate the appropriate warning lamp and audible warning as required. The audible warning
is operated by the Body Control Unit (BCU) when it receives a signal from the SLABS ECU. The audible warning is
emitted from a speaker at the rear of the instrument pack.
Depressing the ORM switch for a minimum of 0.5 seconds, completes an earth which the ECU uses as a signal to
initiate the ORM if conditions allow. When the ECU starts ORM, the same earth that was completed by the ORM
switch is pulled to earth by the ECU to activate the ORM warning lamp. The ECU checks for a further operation of the
ORM switch by continuously and very quickly removing the earth for the ORM warning lamp. If the ORM switch is
operated for more than 0.5 seconds, the ECU will detect this and de-activate the ORM.
The SLS part of the SLABS ECU also uses the road speed data generated within the SLABS ECU by the ABS system.
Operation of ORM and extended mode are road speed sensitive and use the ABS signal to monitor the vehicle speed.
When the accessory remote handset is used for the SLS lower and raise functions, the handset transmits RF signals
which are received by the same RF receiver used for the alarm/remote door locking system. The RF receiver passes
this data as a 25 Hz PWM signal to the BCU. The BCU then transmits this data to the SLABS ECU as raise or lower
data. TestBook is required to program the BCU for remote handset operation.
SLABS ECU connector pin details
Page 876 of 1529
BRAKES
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 70-23
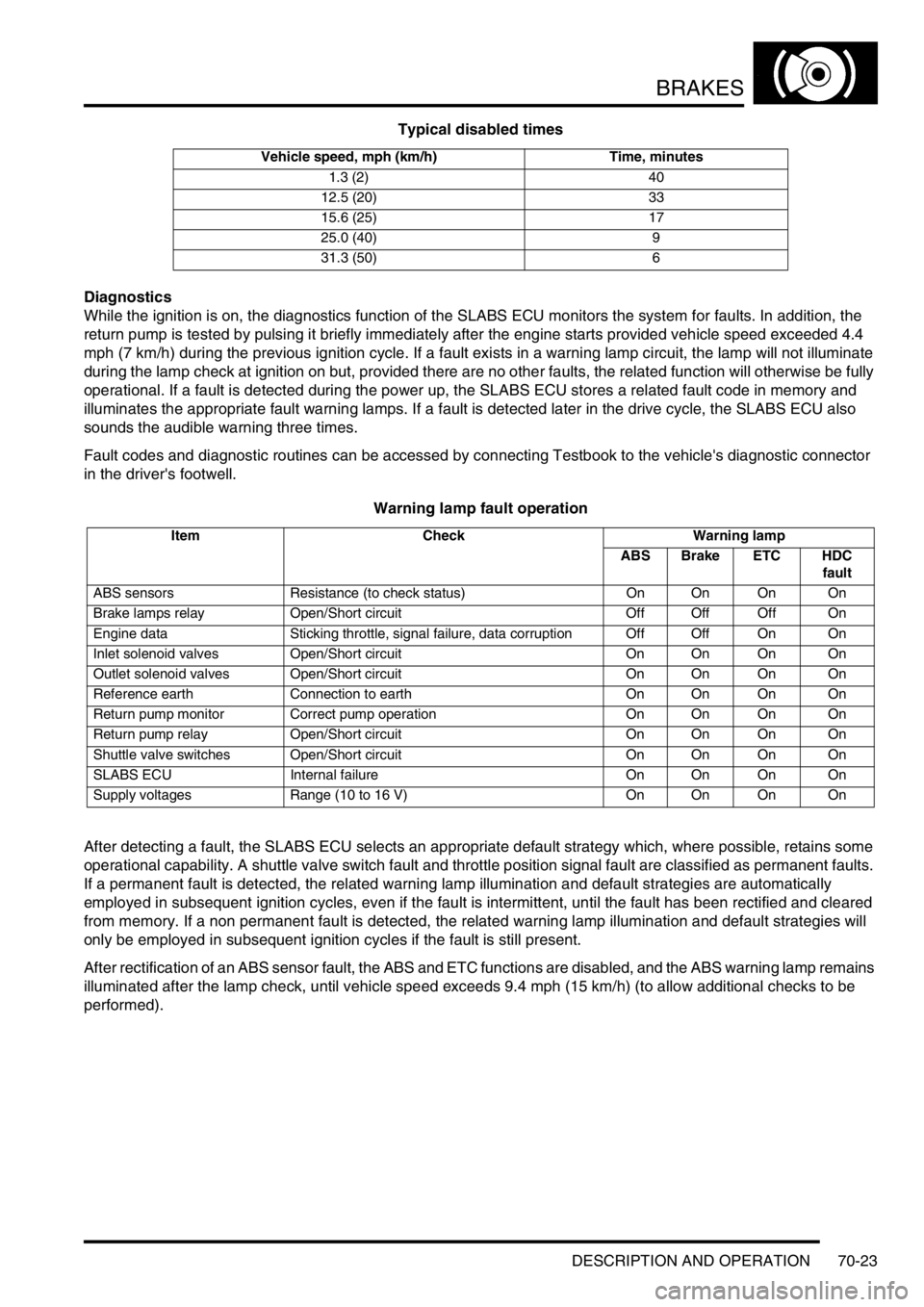
Typical disabled times
Diagnostics
While the ignition is on, the diagnostics function of the SLABS ECU monitors the system for faults. In addition, the
return pump is tested by pulsing it briefly immediately after the engine starts provided vehicle speed exceeded 4.4
mph (7 km/h) during the previous ignition cycle. If a fault exists in a warning lamp circuit, the lamp will not illuminate
during the lamp check at ignition on but, provided there are no other faults, the related function will otherwise be fully
operational. If a fault is detected during the power up, the SLABS ECU stores a related fault code in memory and
illuminates the appropriate fault warning lamps. If a fault is detected later in the drive cycle, the SLABS ECU also
sounds the audible warning three times.
Fault codes and diagnostic routines can be accessed by connecting Testbook to the vehicle's diagnostic connector
in the driver's footwell.
Warning lamp fault operation
After detecting a fault, the SLABS ECU selects an appropriate default strategy which, where possible, retains some
operational capability. A shuttle valve switch fault and throttle position signal fault are classified as permanent faults.
If a permanent fault is detected, the related warning lamp illumination and default strategies are automatically
employed in subsequent ignition cycles, even if the fault is intermittent, until the fault has been rectified and cleared
from memory. If a non permanent fault is detected, the related warning lamp illumination and default strategies will
only be employed in subsequent ignition cycles if the fault is still present.
After rectification of an ABS sensor fault, the ABS and ETC functions are disabled, and the ABS warning lamp remains
illuminated after the lamp check, until vehicle speed exceeds 9.4 mph (15 km/h) (to allow additional checks to be
performed).
Vehicle speed, mph (km/h) Time, minutes
1.3 (2) 40
12.5 (20) 33
15.6 (25) 17
25.0 (40) 9
31.3 (50) 6
Item Check Warning lamp
ABS Brake ETC HDC
fault
ABS sensors Resistance (to check status) On On On On
Brake lamps relay Open/Short circuit Off Off Off On
Engine data Sticking throttle, signal failure, data corruption Off Off On On
Inlet solenoid valves Open/Short circuit On On On On
Outlet solenoid valves Open/Short circuit On On On On
Reference earth Connection to earth On On On On
Return pump monitor Correct pump operation On On On On
Return pump relay Open/Short circuit On On On On
Shuttle valve switches Open/Short circuit On On On On
SLABS ECU Internal failure On On On On
Supply voltages Range (10 to 16 V) On On On On
Page 912 of 1529

RESTRAINT SYSTEMS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 75-9
Operation - SRS
The diagnostic and control unit (DCU) controls the SRS system. The DCU is located beneath the centre console close
to the handbrake area. The DCU contains both an electronic deceleration sensor as well as an electromechanical
safing sensor. When the electronic deceleration sensor within the DCU detects rapid deceleration of the vehicle, it
compares the deceleration rate with stored values in its' memory. If the deceleration rate exceeds the stored value
and the electromechanical safing sensor triggers, the DCU deploys the airbag and the seat belt pretensioners. The
DCU will not deploy the airbags and seat belt pretensioners unless both sensors trigger.
The SRS has diagnostic capabilities through TestBook. In the event that a fault is detected, the DCU alerts the driver
by illuminating a warning lamp in the instrument cluster.
The DCU controls the following:
lSRS warning lamp.
lDrivers airbag module.
lPassenger airbag module (where fitted).
lDriver seat belt pretensioner.
lPassenger seat belt pretensioner.
WARNING: The integrity of the SRS system are critical for safety reasons. Ensure the following precautions
are always adhered to:
lNever install used SRS components from another vehicle or attempt to repair an SRS component.
lWhen repairing an SRS system only use genuine new parts.
lNever apply electrical power to an SRS component unless instructed to do so as part of an approved test
procedure.
lSpecial Torx bolts are necessary for installing the airbag module - do not use other bolts. Ensure bolts
are tightened to the correct torque.
lAlways use new fixings when replacing an SRS component.
lEnsure the SRS Diagnostic Control Unit (DCU) is always installed correctly. There must not be any gap
between the DCU and the bracket to which it is mounted. An incorrectly mounted DCU could cause the
system to malfunction.
System deployment
The airbag and seat belt pretensioners deploy to protect the front seat occupants when the DCU senses a rapid
vehicle deceleration. The system deploys when the following conditions are met:
lThe ignition switch is on.
lThe vehicle decelerates beyond a threshold defined within the DCU.
lThe electromechanical safing sensor within the DCU triggers.
When all of the above conditions are met, the DCU deploys the airbag(s) and seat belt pretensioners. If the above
conditions are not met, the DCU will not deploy the system.
Component replacement policy
After an impact which deploys the airbags and pretensioners, the following components must be renewed:
lDCU.
lDriver and passenger airbag modules.
lDriver and passenger buckle pretensioners.
lRotary coupler.
lFlyleads (where applicable) connecting airbags and pre-tensioners to SRS harness
SRS warning lamp
The SRS warning lamp illuminates for 5 seconds during system readiness check on starting the engine. The SRS
warning lamp extinguishes for one second after the system readiness check is performed. If a fault is present the
warning lamp then illuminates continuously. If no fault is present, the SRS warning lamp remains extinguished. If a
system fault occurs in excess of two seconds after the readiness check has been completed, the SRS warning lamp
illuminates for that ignition cycle. It remains illuminated for a minimum of 12 seconds ± 4 seconds for all fault
conditions.
The SRS warning lamp will only illuminate for low voltage concerns while the low voltage condition is present. If the
low voltage condition is corrected, the SRS warning lamp extinguishes and the fault is recorded in the DCU's memory.
Page 957 of 1529
EXTERIOR FITTINGS
76-2-10 REPAIRS
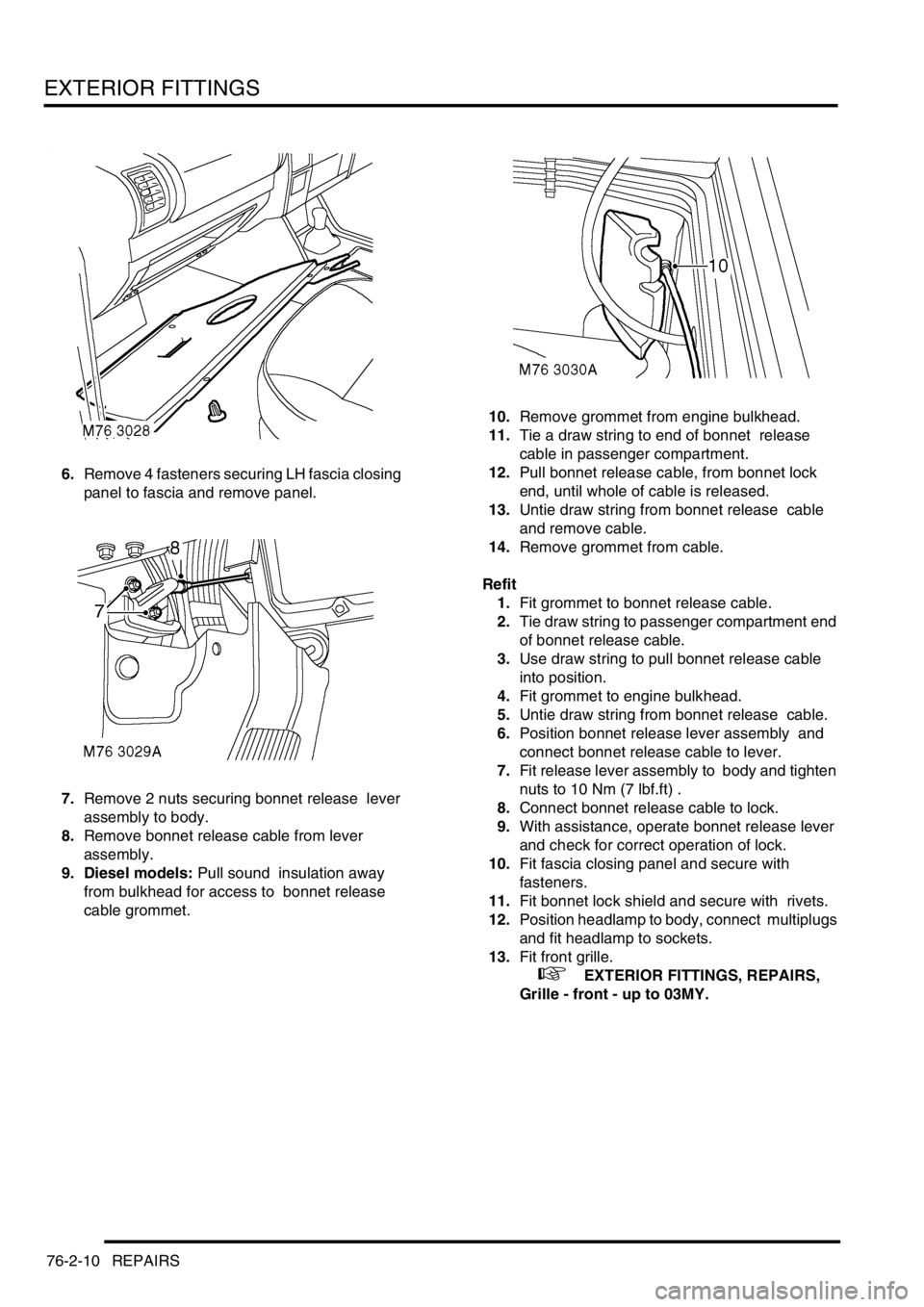
6.Remove 4 fasteners securing LH fascia closing
panel to fascia and remove panel.
7.Remove 2 nuts securing bonnet release lever
assembly to body.
8.Remove bonnet release cable from lever
assembly.
9. Diesel models: Pull sound insulation away
from bulkhead for access to bonnet release
cable grommet. 10.Remove grommet from engine bulkhead.
11.Tie a draw string to end of bonnet release
cable in passenger compartment.
12.Pull bonnet release cable, from bonnet lock
end, until whole of cable is released.
13.Untie draw string from bonnet release cable
and remove cable.
14.Remove grommet from cable.
Refit
1.Fit grommet to bonnet release cable.
2.Tie draw string to passenger compartment end
of bonnet release cable.
3.Use draw string to pull bonnet release cable
into position.
4.Fit grommet to engine bulkhead.
5.Untie draw string from bonnet release cable.
6.Position bonnet release lever assembly and
connect bonnet release cable to lever.
7.Fit release lever assembly to body and tighten
nuts to 10 Nm (7 lbf.ft) .
8.Connect bonnet release cable to lock.
9.With assistance, operate bonnet release lever
and check for correct operation of lock.
10.Fit fascia closing panel and secure with
fasteners.
11.Fit bonnet lock shield and secure with rivets.
12.Position headlamp to body, connect multiplugs
and fit headlamp to sockets.
13.Fit front grille.
+ EXTERIOR FITTINGS, REPAIRS,
Grille - front - up to 03MY.
Page 1139 of 1529

CORROSION PREVENTION AND SEALING
77-4-6 CORROSION PREVENTION
Corrosion prevention
Factory treatments
During production, vehicle bodies are treated with the following anti-corrosion materials:
lA PVC-based underbody sealer which is sprayed onto the underside of the main floor, rear floor, front and rear
wheelarches and the front valance assembly;
lAn application of cavity wax which is sprayed into the sill panels, 'A' post, 'B-C' post, fuel filler aperture, body rear
panel and the lower areas of the door panels;
lA coating of underbody wax which is applied to the entire underbody inboard of the sill vertical flanges, and
covers all moving and flexible components EXCEPT for wheels, tyres, brakes and exhaust;
lA coat of protective wax applied to the engine bay area.
Whenever body repairs are carried out, ensure the anti-corrosion materials in the affected area are repaired or
renewed as necessary using the approved materials.
+ BODY SEALING MATERIALS, MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS, Approved materials.
Precautions during body repairs and handling
Take care when handling the vehicle in the workshop. Underbody sealers, seam sealers, underbody wax and body
panels may be damaged if the vehicle is carelessly lifted.
+ LIFTING AND TOWING, LIFTING.
Proprietary anti-corrosion treatments
The application of proprietary anti-corrosion treatments, in addition to the factory-applied treatment, could invalidate
the Corrosion Warranty and should be discouraged. This does not apply to Rover approved, compatible, preservative
waxes which may be applied on top of existing coatings.
Fitting approved accessories
When fitting accessories ensure that the vehicle's corrosion protection is not affected, either by breaking the protective
coating or by introducing a moisture trap.
Do not screw self-tapping screws directly into body panels. Fit suitable plastic inserts to the panel beforehand. Always
ensure that the edges of holes drilled into panels, chassis members and other body parts are protected with a suitable
zinc rich or acid etch primer, and follow with a protective wax coating brushed onto the surrounding area.
Do not attach painted metal surfaces of any accessory directly to the vehicle's bodywork unless suitably protected.
Where metal faces are bolted together always interpose a suitable interface material such as weldable zinc rich
primer, extruded strip, or zinc tape.
Steam cleaning and dewaxing
Due to the high temperatures generated by steam cleaning equipment, there is a risk that certain trim components
could be damaged and some adhesives and corrosion prevention materials softened or liquified.
Adjust the equipment so that the nozzle temperature does not exceed 90° C (194° F). Take care not to allow the steam
jet to dwell on one area, and keep the nozzle at least 300 mm (11.811 in) from panel surfaces.
DO NOT remove wax or lacquer from underbody or underbonnet areas during repairs. Should it be necessary to
steam clean these areas, apply a new coating of wax or underbody protection as soon as possible.
Inspections during maintenance servicing
It is a requirement of the Corrosion Warranty that the vehicle body is checked for corrosion by an authorised Land
Rover Dealer at least once a year, to ensure that the factory-applied protection remains effective.
Service Job Sheets include the following operations to check bodywork for corrosion:
lWith the vehicle on a lift, carry out visual check of underbody sealer for damage;
lWith the vehicle lowered, inspect exterior paintwork for damage and body panels for corrosion.
It will be necessary for the vehicle to be washed by the Dealer prior to inspection of bodywork if the customer has
offered the vehicle in a dirty condition.
Page 1140 of 1529
CORROSION PREVENTION AND SEALING
CORROSION PREVENTION 77-4-7
The checks described above are intended to be visual only. It is not intended that the operator should remove trim
panels, finishers, rubbing strips or sound-deadening materials when checking the vehicle for corrosion and paint
damage.
With the vehicle on a lift, and using an inspection or spot lamp, visually check for the following:
lCorrosion damage and damaged paintwork, condition of underbody sealer on front and rear lower panels, sills
and wheel arches;
lDamage to underbody sealer. Corrosion in areas adjacent to suspension mountings and fuel tank fixings.
NOTE: The presence of small blisters in the underbody sealer is acceptable, providing they do not expose bare metal.
Pay special attention to signs of damage caused to panels or corrosion protection material by incorrect jack
positioning.
WARNING: It is essential to follow the correct jacking and lifting procedures.
With the vehicle lowered, visually check for evidence of damage and corrosion on all visible painted areas, in
particular the following:
lFront edge of bonnet;
lVisible flanges in engine compartment;
lLower body and door panels.
Rectify any bodywork damage or evidence of corrosion found during inspection as soon as is practicable, both to
minimise the extent of the damage and to ensure the long term effectiveness of the factory-applied corrosion
prevention treatment. Where the cost of rectification work is the owner's responsibility, the Dealer must advise the
owner and endorse the relevant documentation accordingly.
Where corrosion has become evident and is emanating from beneath a removable component (e.g. trim panel,
window glass, seat etc.), remove the component as required to permit effective rectification.
Underbody protection repairs
Whenever body repairs are carried out, ensure that full sealing and corrosion protection treatments are reinstated.
This applies both to the damaged areas and also to areas where protection has been indirectly impaired, as a result
either of accident damage or repair operations.
Remove corrosion protection from the damaged area before straightening or panel beating. This applies in particular
to panels coated with wax, PVC underbody sealer, sound deadening pads etc.
WARNING: DO NOT use oxy-acetylene gas equipment to remove corrosion prevention materials. Large
volumes of fumes and gases are liberated by these materials when they burn.
NOTE: Equipment for the removal of tough anti-corrosion sealers offers varying degrees of speed and effectiveness.
The compressed air-operated scraper (NOT an air chisel) offers a relatively quiet mechanical method using an
extremely rapid reciprocating action. Move the operating end of the tool along the work surface to remove the material.
The most common method of removal is by means of a hot air blower with integral scraper.
Another tool, and one of the most efficient methods, is the rapid-cutting 'hot knife'. This tool uses a wide blade and is
quick and versatile, able to be used easily in profiled sections where access is otherwise difficult.
Use the following procedure when repairing underbody coatings:
1Remove existing underbody coatings
2After panel repair, clean the affected area with a solvent wipe, and treat bare metal with an etch phosphate
material
3Re-prime the affected area
CAUTION: DO NOT, under any circumstances, apply underbody sealer directly to bare metal surfaces.
4Replace all heat-fusible plugs which have been disturbed. Where such plugs are not available use rubber
grommets of equivalent size, ensuring that they are embedded in sealer
5Mask off all mounting faces from which mechanical components, hoses and pipe clips, have been removed.
Underbody sealer must be applied before such components are refitted
6Brush sealer into all exposed seams
7Spray the affected area with an approved service underbody sealer
8Remove masking from component mounting faces, and touch-in where necessary. Allow adequate drying time
before applying underbody wax
Page 1141 of 1529

CORROSION PREVENTION AND SEALING
77-4-8 CORROSION PREVENTION
After refitting mechanical components, including hoses and pipes and other fixtures, mask off the brake discs and
apply a coat of approved underbody wax.
NOTE: Where repairs include the application of finish paint coats in the areas requiring underbody wax, carry out paint
operations before applying wax.
Cavity wax injection
Areas treated with cavity wax are shown in the previous figures. After repairs, always re-treat these areas with an
approved cavity wax. In addition, treat all interior surfaces which have been disturbed during repairs whether they
have been treated in production or not. This includes all box members, cavities and door interiors. It is permissible to
drill extra holes for access where necessary, provided these are not positioned in load-bearing members. Ensure that
such holes are treated with a suitable zinc rich primer, brushed with wax and then sealed with a rubber grommet.
Before wax injection, ensure that the cavity to be treated is free from any contamination or foreign matter. Where
necessary, clear out any debris using compressed air.
Ensure that cavity wax is applied AFTER the final paint process and BEFORE refitting any trim components.
During application, ensure that the wax covers all flange and seam areas and that it is adequately applied to all
repaired areas of both new and existing panels.
It should be noted that new panel assemblies and complete body shells are supplied without wax injection treatment.
Ensure that such treatment is carried out after repairs.
Effective cavity wax protection is vital. Always observe the following points:
lComplete all paint refinish operations before wax application;
lClean body panel areas and blow-clean cavities if necessary, before treatment;
lMaintain a temperature of 18° C (64° F) during application and drying;
lCheck the spray pattern of injection equipment;
lMask off all areas not to be wax coated and which could be contaminated by wax overspray;
lRemove body fixings, such as seat belt retractors, if contamination is at all likely;
lMove door glasses to fully closed position before treating door interiors;
lTreat body areas normally covered by trim before refitting items;
lCheck that body and door drain holes are clear after the protective wax has dried;
lKeep all equipment clean, especially wax injection nozzles.
Underbody wax
The underbody wax must be reinstated following all repairs affecting floor panels. The wax is applied over paints and
underbody sealers.
Remove old underbody wax completely from a zone extending at least 200 mm (7.874 in) beyond the area where new
underbody sealer is to be applied.
Engine bay wax
Reinstate all protective engine bay wax disturbed during repairs using an approved material.
Where repairs have involved replacement of engine bay panels, treat the entire engine compartment including all
components, clips and other fixtures with an approved underbonnet lacquer or wax.
+ BODY SEALING MATERIALS, MATERIALS AND APPLICATIONS, Approved materials.
Page 1290 of 1529
BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-3
BCU outputs
The BCU processes the input signals it receives and uses the information to determine the control outputs that need
to be established for any given set of conditions. The BCU provides controlled outputs for the following systems:
lInterior courtesy lamps.
lFuel flap release actuator.
lAnti-theft status LED.
lEngine Control Module.
lDoor lock actuators.
lDirection indicators and hazard warning lamps.
lHeadlamps.
lAlarm sounder.
lVehicle horns.
lBattery backed sounder.
lStarter relay.
lPassive re-mobilisation exciter coil.
Simultaneous switching of outputs in different units is limited by the bus transfer time, but the skew is no longer than
100 ms for either the BCU or the IDM. When the processor is reset, all outputs are switched off until the inputs have
been read for the first time to check current condition.
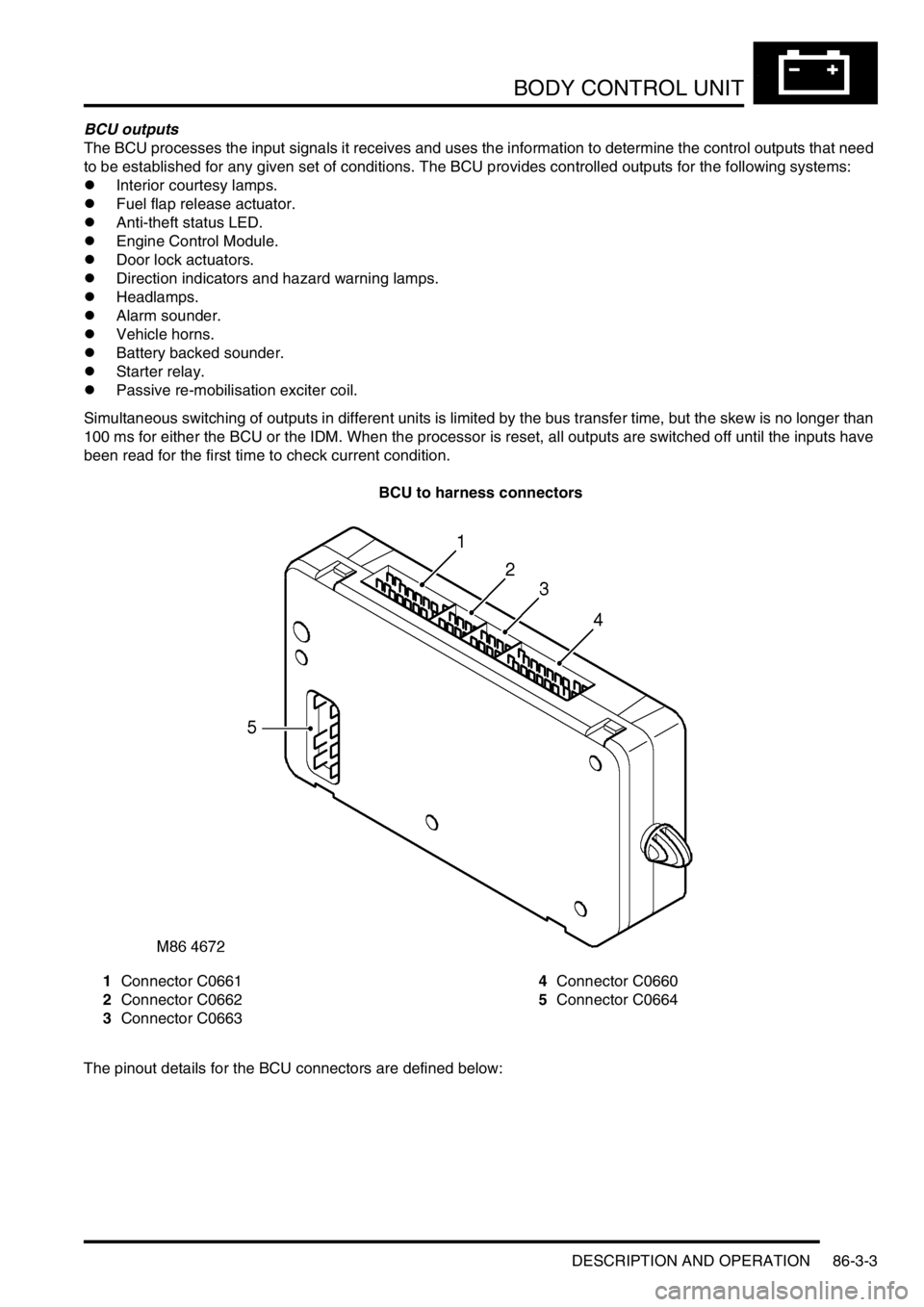
BCU to harness connectors
1Connector C0661
2Connector C0662
3Connector C06634Connector C0660
5Connector C0664
The pinout details for the BCU connectors are defined below:
Page 1304 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-17
The existence of an intermediate state causes a fault code to be detected by the BCU. To reduce the chances of the
fault condition occurring while changing selector lever position, the inputs are debounced and only considered valid
when they have existed for at least 33 ms.
Transmission neutral selector
The transmission neutral sensor provides an earth signal to the BCU when the transfer box is in neutral. The earth
signal causes the BCU to operate an audible warning when the transfer box is in neutral with the ignition switched on.
+ TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Self levelling suspension and ABS
The BCU communicates with the SLABS ECU for several functions:
lAn output is provided from the SLABS ECU to the BCU to provide the logic conditions for issuing the SLS audible
warning.
lThe BCU receives an input from the SLABS ECU relating to the raise/ lower command from the remote handset.
+ REAR SUSPENSION, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - SLS.
Hill descent control
The BCU provides an output signal to the SLABS ECU for automatic transmission in neutral for HDC control. The
BCU checks the status of the ignition and 'gearbox state' inputs and provides a 'Neutral selected' output. If the ignition
is on and 'gearbox state' is Neutral, the 'Neutral selected' output is on, otherwise 'Neutral selected' is off.
+ BRAKES, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Heated screens
The Heated Front Screen (HFS) is fitted for some market destinations and is operated from a non-latching switch
located on the instrument pack cowl. The BCU will only allow the heated front screen to operate when the engine is
running and controls the time-out period for switching the circuit off.
The heated front screen operation can also be controlled from the Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) ECU on
vehicles fitted with air conditioning.
The heated rear window will only function when the engine is running, and is operated by a non-latching switch on the
instrument pack cowl. The heated rear window can also be operated by the ATC ECU on vehicles fitted with air
conditioning.
Interior courtesy lamps
The BCU controls the operation of the interior courtesy lamps. The courtesy lamps are situated in the front, mid and
rear areas of the headlining.
Fuel flap actuator
The BCU provides an earth path to the fuel flap release solenoid to allow the fuel filler flap to be opened. This is only
allowed if the alarm system is not set and all other conditions have been satisfied. The fuel flap release switch is
located in the fascia switch pack on vehicles up to 2003 model year or in the instrument pack binacle on vehicles from
2003 model year. The switch receives a voltage supply from the passenger compartment fuse box.
Page 1306 of 1529

BODY CONTROL UNIT
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 86-3-19
Operation
For IDM inputs which are also inputs for BCU functions, the delay before the BCU recognises the change in input
status is less than 250 ms. The BCU uses a debounce algorithm to ignore changes in input having a duration less
than 100 ms with the exception of automatic gearbox W, X, Y, Z inputs, which have a debounce period of 33 ms.
Transit mode
To prevent excessive battery drain during transit to overseas markets, the vehicle is placed in a transit mode.
To exit the transit mode, simultaneously hold down the heated rear window switch and the rear fog lamp switch, turn
the ignition switch from 0 to II and, after a minimum of 2 seconds, release the switches.
Transit mode can be entered using TestBook. When TestBook communicates with the BCU for diagnostics related to
BCU operation, it first checks that the vehicle is not in transit mode.
Anti-theft system
The BCU uses the driver's door key lock and unlock switches to activate and deactivate the security system. The
driver's door lock is also used for entering the EKA.
+ ALARM SYSTEM AND HORN, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Immobilisation
For immobilisation, the BCU disables the starter motor relay. When the engine is cranking, the ECM looks for a coded
signal from the BCU. If the signal is not received within one second of cranking, the fuel supply to the engine is
stopped and the injectors are disabled. This also prevents unburnt fuel from entering the catalyst.
If the BCU is disconnected, the engine starter motor will remain isolated by the starter motor relay and the ECM will
remain immobilised. The main wiring for the system is contained within the main harness which is relatively
inaccessible, so preventing intruders from disabling the system by cutting the wires for the immobilisation system.
Once the immobiliser has been activated, destruction of the trigger device or the wiring to it will not disarm the system.
The RF transmitter communicates to the BCU via the RF receiver using a 70 bit code. Pressing the unlock button on
the transmitter will re-mobilise the vehicle. The RF transponder is integrated into the metal key assembly, inserting
the key into the ignition switch will induce a signal in the exciter coil to re-mobilise the vehicle.
Anti-theft alarm
The alarm system provides a warning of unauthorised access to the vehicle and includes perimetric and volumetric
monitoring under the control of the BCU.
The perimetric protection system detects opening of all doors, tail door and bonnet and will also detect the operation
of the ignition key switch. The following conditions must be satisfied before the BCU will operate all of the functions
of perimetric protection:
lAll doors and hinged panels are in the closed position.
lIgnition key out of the ignition switch.
lInertia switch is not tripped.
If all conditions are not satisfied the BCU will enter a mislock condition.
The volumetric sensor uses two ultrasonic sensors mounted in the headlining to detect movement within the vehicle.
The alarm will trigger when the sensor signals the BCU for 200 ms or greater. Within a single setting period the alarm
system will allow a maximum of 10 triggers as a result of any combination of sensor inputs. It is possible to lock the
vehicle without enabling the volumetric alarm by using the key. The same conditions needed to satisfy enabling of the
perimetric protection system is also needed to enable volumetric protection.
When the alarm system is set the BCU checks the status of all the inputs from the door and bonnet switches to ensure
the integrity of the vehicle before setting the alarm system into operational mode. In some markets, when the alarm
is set the BCU sends a signal to the IDM which will cause the direction indicators to flash three times for a duration of
3 seconds.
If the sensors are triggered the BCU will activate an alarm sounder to provide an audible warning of a theft attempt.
The activation period of the alarm sounder is 25 to 30 seconds. The duty cycle of the alarm sounder is 50:50 ± 10%.