check engine LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 1999, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 1999Pages: 1529, PDF Size: 34.8 MB
Page 278 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-45
Flow Test (P Codes P1414 and P1417)
When the Leak test has been passed successfully, the SAI control valves are then opened while the SAI pump is still
operational. Flow should now begin to enter the exhaust system. By monitoring the HO2S sensor voltage output, the
ECM determines if sufficient flow is being introduced into the exhaust system. Depending on which bank of the engine
detects the fault, one or both P codes can be stored.
Fault Finding Methodology
Malfunctions can be broadly categorised into two different categories: Flow Faults or Leak Faults.
Additionally, they also differ depending if the corresponding P code exists for both cylinder banks simultaneously or
is unique to one bank, for example:
Faults of each of the four basic types should be investigated in a different priority order, starting with the most logically
plausible cause or component.
Fault Finding Flow Charts
The following flow charts show the order of investigation that should be performed depending on the type of fault
present. These should be treated as guidelines to ensure that the most likely and plausible causes are addressed first.
However, the flow charts assume that no clear or obvious reason for failure exists. If the cause of the malfunction is
immediately obvious, then the flow charts should not be followed.
Once a malfunction is identified, it should be rectified as necessary and the system checked as per the instructions
in the following 'Checking Malfunctions' section.
NOTE: It is not necessary to follow the remainder of the flow chart once a potential root cause has been identified.
Flow Fault Finding chart
1Fault codes P1412, P1414, P1415 or P1417 present
2Insufficient flow detected
3Is fault present on both cylinder banks?
If 'NO' proceed to step 4
If 'YES' proceed to step 8
4Vacuum supply – Check for: blockage and/or vacuum line disconnected from SAI valve
5SAI Valve – Check for: jam / diaphragm leak or blockage
6Delivery Hoses to SAI Valve – Check for: blockage / leaks
7SAI Pipes to Cylinder Head – Check for: blockage / leaks
8Electrical Issue – Check for: Related P code (relay/fuse/solenoid), rectify as necessary and check connectors
9Vacuum Supply – Check for: Blocked/leaking vacuum lines or correct solenoid operation (open/closed)
10Delivery Hoses – Check for: Blocked/leaking hoses
11SAI Pump – Check for: Correct operation using TestBook/T4 or pump blockage/failure
12SAI Valves – Check for: Both SAI Valves jammed/blocked/leaking diaphragms
Leak Fault Finding Chart
1Fault codes P1413 or P1416 present
2SAI system leak detected
3Is fault present on both cylinder banks?
If 'NO' proceed to step 4
If 'YES' proceed to step 5
4SAI Valve – Check for: leakage
5Vacuum supply – Check for: solenoid stuck open (mechanical failure) or stuck open (electrical failure)
6SAI Valve – Check for: leakage from one or both valves
P Code Type One Bank Only Both Banks
FlowIII
LeakIII IV
Page 280 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-47
The following table shows the components itemised on the above illustration and the test applicable to each
component.
Test 1– Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Pump
Power Supply and Relay
Check all wiring and connections.
Functional Check of SAI Pump
The ECM checks the engine coolant temperature when the engine is started in addition to checking the elapsed time
since the last engine start. The engine coolant temperature must be below 55°C (131°F) and the ambient temperature
above 8°C (46°F) for the SAI pump to run. Also, depending on the long term 'modelled' ambient temperature
determined by the ECM, the minimum time elapsed required since the last engine start can be up to 8.25 hours. The
period of time that the SAI pump runs for depends on the starting temperature of the engine and varies from
approximately 95 seconds for a start at 8°C (46°F) to 30 seconds for a start at 55°C (131°F).
With a warm engine which is switched off and the SAI pump relay removed, the SAI pump can be supplied with power
by bridging terminals 87 and 30 at the relay socket.
CAUTION: Ensure that terminals 87 and 87a are not connected or bridged in any way, a short circuit will
occur.
NOTE: TestBook/T4 can also be used to force the SAI system to perform an SAI active diagnostic routine. During this
routine the SAI pump will run for approximately 10 seconds.
When the terminals are bridged or the diagnostic routine initiated, the pump must run when requested which will be
noticeable by the running noise of the pump. Only allow the SAI pump to run for a maximum of 90 seconds and allow
sufficient time for the pump to cool down before running again.
If the SAI pump does not run or makes a scraping noise, it must be replaced. In this case, all other system components
must also be checked.
Noise Complaints
If the SAI pump runs but the operating noise is excessively loud, the external components of the pump, cable, hose
line, and decoupling segments, must be checked. Check the decoupling segments and hose line for distortion and
the cable and hose line for contact with the pump body.
If excessive noise still occurs, the SAI pump must be replaced.
NOTE: Before a new SAI pump is fitted, the SAI control valves must checked for correct function and tightness – Refer
to Test 2 – Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Control Valves.
When fitting a new SAI pump, ensure that the hose lines, the cable and the decoupling segments are fitted without
tension and contact with the pump body.
Item No. Component Description Applicable Test
1 SAI Pump Test 1 – Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Pump
2 SAI control valves (1 per engine bank) Test 2 – Secondary Air Injection (SAI) Control
Valves
3 Vacuum solenoid valve Test 3 – Vacuum Solenoid Valve
4 Delivery hoses to SAI control valves Test 4 – Delivery Hoses to Secondary air
Injection (SAI) Control Valves
5 Connection to air manifold (SAI rail) Test 5 – Connection to Air Manifold
6 Vacuum line (intake manifold to vacuum solenoid valve) Test 6 – Vacuum Lines
7 Vacuum lines (vacuum solenoid valve to SAI control valves) Test 6 – Vacuum Lines
Page 282 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-49
Test 3 – Vacuum Solenoid Valve
Function
The vacuum solenoid valve is energised for the duration of the secondary air injection. The valve is open when
energised, the intake manifold vacuum acts on the diaphragm of the SAI control valve and the control valve opens.
The solenoid valve is closed when de-energised.
Power Supply
Remove the harness connector from the vacuum solenoid valve and check the voltage between the connection
terminals. No voltage must be present at the connector after switching off the SAI pump.
Opening/Tightness
Disconnect the vacuum line at one of the SAI control valves and connect a hand vacuum pump to the line. With the
engine running at idle, a pressure difference of a minimum of 390 mbar (5.65 lbf/in
2) must measurable on the hand
vacuum pump gauge with the vacuum solenoid valve energised.
The vacuum solenoid valve must be sealed when de-energised. If the Opening/tightness test fails, replace the
vacuum solenoid valv.
Test 4 – Delivery Hoses to Secondary air Injection (SAI) Control Valves
Visually inspect the delivery hoses to the SAI control valves for damage or blockage. If damage, condensate or
deposits are found the delivery hoses must be replaced. Check the hoses for correct connection and leaks.
Test 5 – Connection to Air Manifold
Check the connection for leaks visually or by using a leak detection spray. Reseal the connection if necessary.
Test 6 – Vacuum Lines
Visually inspect the vacuum lines for damage. Check each line for leaks or blockages using the vacuum hand pump.
Check the lines for correct connection.
Page 319 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
There are three types of ECT sensor diagnostic checks:
lThe ECT sensor signal is within limits, but is inaccurate – the engine has to be running and the signal indicates
a coolant temperature below 40°C (104°F). The signal differs too much from the coolant temperature model for
longer than 2.53 seconds.
lThe ECT sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold value – the ECM has to be powered up to perform
the diagnostic, but the engine does not need to be running.
lThe ECT sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold value – the ECM has to be powered up to perform
the diagnostic, but the engine does not need to be running.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0116 Engine coolant temperature circuit/range
performance problemSignal differs too much from temperature model for
longer than 2.53s
P0117 Engine coolant temperature circuit low input Open circuit or short circuit to battery supply
P0118 Engine coolant temperature circuit high input Short circuit to earth
Page 321 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-22 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
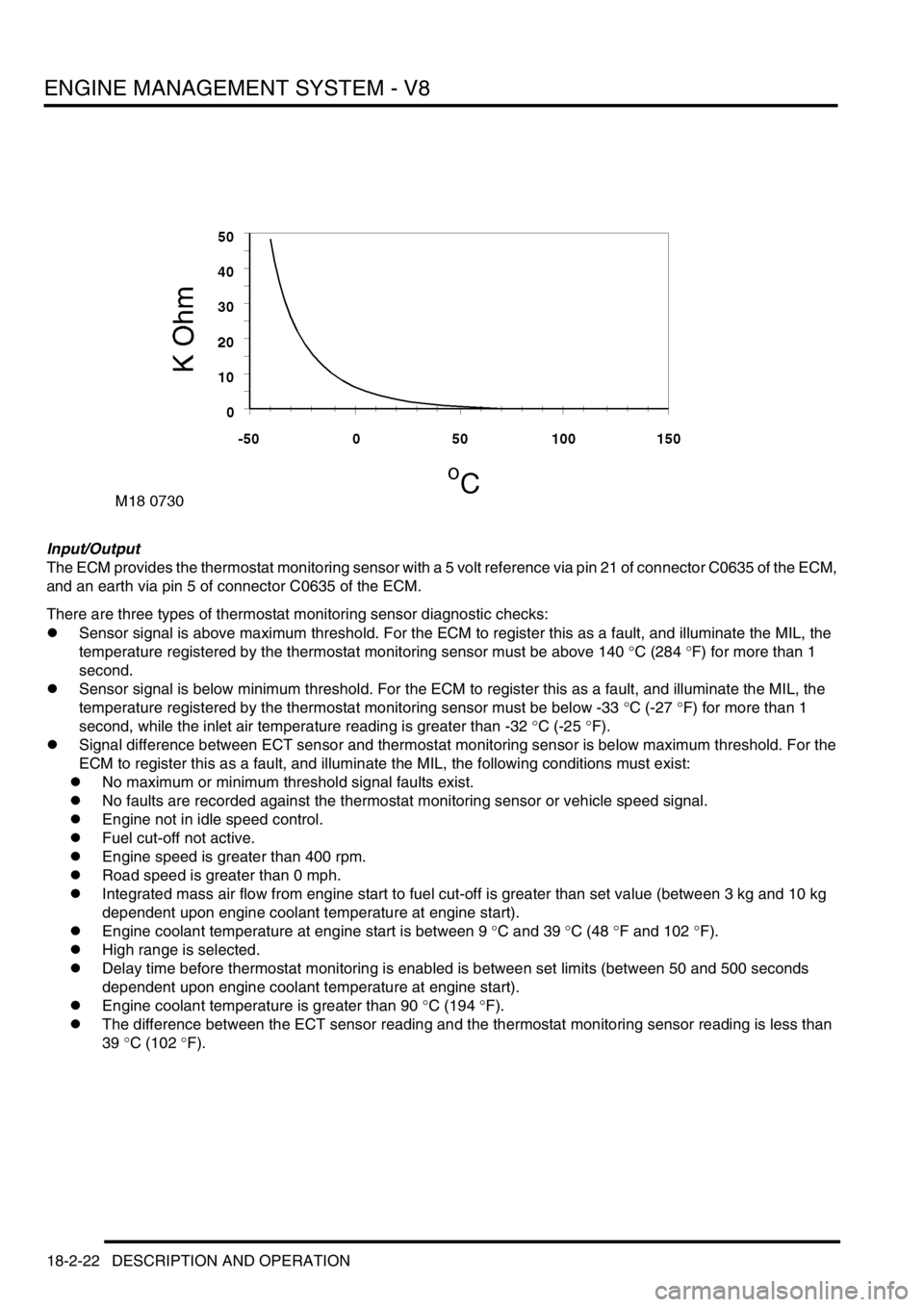
Input/Output
The ECM provides the thermostat monitoring sensor with a 5 volt reference via pin 21 of connector C0635 of the ECM,
and an earth via pin 5 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
There are three types of thermostat monitoring sensor diagnostic checks:
lSensor signal is above maximum threshold. For the ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the
temperature registered by the thermostat monitoring sensor must be above 140 °C (284 °F) for more than 1
second.
lSensor signal is below minimum threshold. For the ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the
temperature registered by the thermostat monitoring sensor must be below -33 °C (-27 °F) for more than 1
second, while the inlet air temperature reading is greater than -32 °C (-25 °F).
lSignal difference between ECT sensor and thermostat monitoring sensor is below maximum threshold. For the
ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the following conditions must exist:
lNo maximum or minimum threshold signal faults exist.
lNo faults are recorded against the thermostat monitoring sensor or vehicle speed signal.
lEngine not in idle speed control.
lFuel cut-off not active.
lEngine speed is greater than 400 rpm.
lRoad speed is greater than 0 mph.
lIntegrated mass air flow from engine start to fuel cut-off is greater than set value (between 3 kg and 10 kg
dependent upon engine coolant temperature at engine start).
lEngine coolant temperature at engine start is between 9 °C and 39 °C (48 °F and 102 °F).
lHigh range is selected.
lDelay time before thermostat monitoring is enabled is between set limits (between 50 and 500 seconds
dependent upon engine coolant temperature at engine start).
lEngine coolant temperature is greater than 90 °C (194 °F).
lThe difference between the ECT sensor reading and the thermostat monitoring sensor reading is less than
39 °C (102 °F).
Page 324 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-25
In the event of a MAF sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDuring driving engine rev/min may dip, before recovering.
lDifficult starting.
lEngine stalls after starting.
lDelayed throttle response.
lEmissions control inoperative.
lIdle speed control inoperative.
lReduced engine performance.
lMAF sensor signal offset.
There are two types of MAF sensor diagnostic check:
lThe MAF sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold for specific speed range – the engine must have
exceeded 200 rev/min for longer than 300 ms and remain above 400 rev/min. The signal must be less than the
threshold mapped against engine speed for longer than 500 ms.
lThe MAF sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold for specific speed range – the engine must have
exceeded 200 rev/min for longer than 10 ms. The signal must be greater than the threshold mapped against
engine speed for longer than 300 ms.
If the MAF sensor fails the following fault codes will be produced and can be retrieved by TestBook:
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0102 Mass or volume air flow low input MAF signal < minimum threshold, which is speed
dependent
P0103 Mass or volume air flow circuit high input MAF signal > maximum threshold, which is speed
dependent
Page 326 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-27
There are two types of IAT sensor diagnostic checks:
lThe IAT sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold – the engine has to have been running for longer than
180 seconds, and idle speed control must have been operational for longer than 10 seconds. No fuel cut off is
active. The IAT sensor signal must be less than -35°C (-31°F) for longer than 200 ms.
lThe IAT sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold – the ECM has to be powered up (engine does not
need to be running), and the signal must be greater than 140°C (284°F) for longer than 200 ms.
If the IAT sensor fails the following fault codes will be produced and can be retrieved by TestBook:
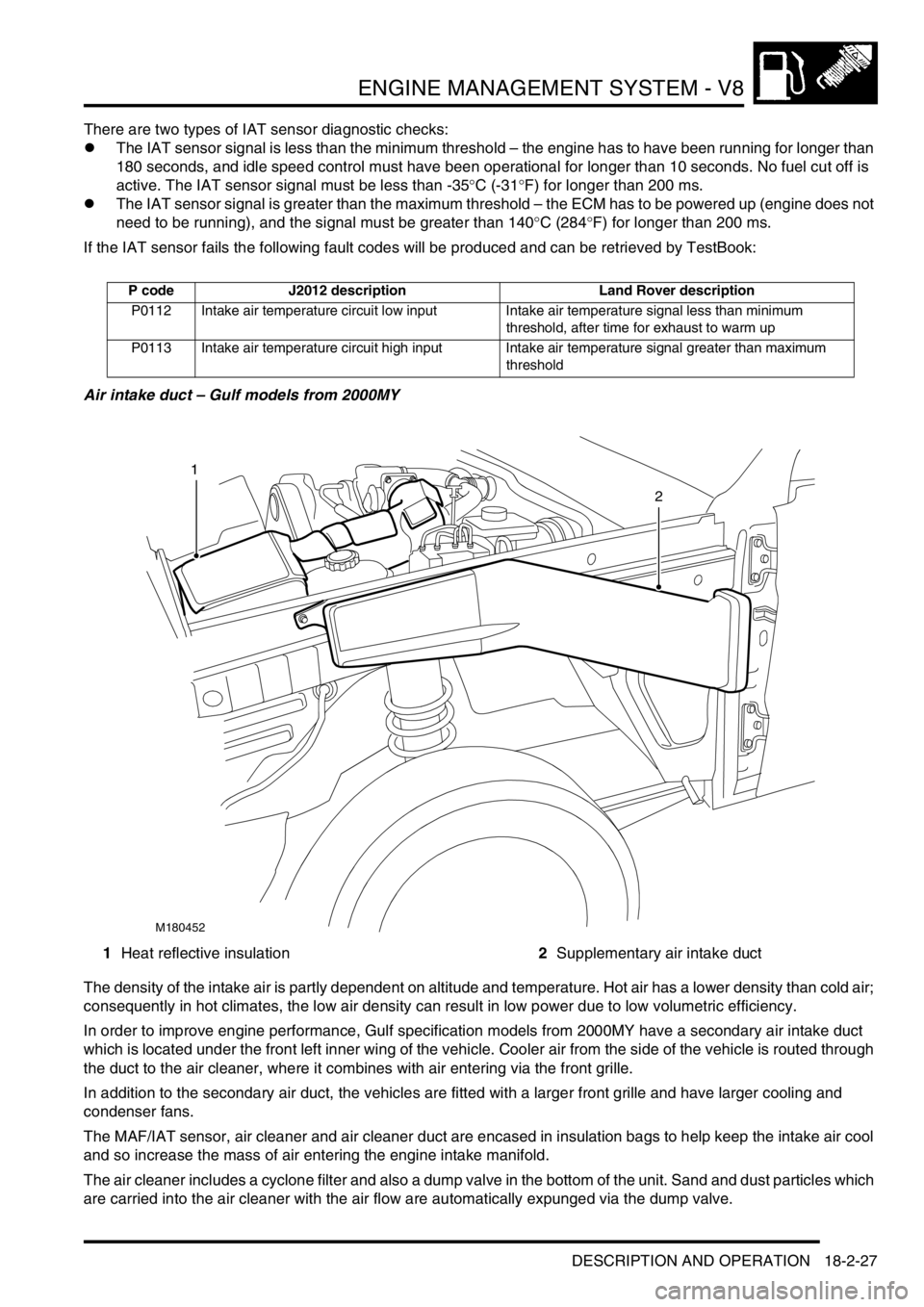
Air intake duct – Gulf models from 2000MY
1Heat reflective insulation2Supplementary air intake duct
The density of the intake air is partly dependent on altitude and temperature. Hot air has a lower density than cold air;
consequently in hot climates, the low air density can result in low power due to low volumetric efficiency.
In order to improve engine performance, Gulf specification models from 2000MY have a secondary air intake duct
which is located under the front left inner wing of the vehicle. Cooler air from the side of the vehicle is routed through
the duct to the air cleaner, where it combines with air entering via the front grille.
In addition to the secondary air duct, the vehicles are fitted with a larger front grille and have larger cooling and
condenser fans.
The MAF/IAT sensor, air cleaner and air cleaner duct are encased in insulation bags to help keep the intake air cool
and so increase the mass of air entering the engine intake manifold.
The air cleaner includes a cyclone filter and also a dump valve in the bottom of the unit. Sand and dust particles which
are carried into the air cleaner with the air flow are automatically expunged via the dump valve.
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0112 Intake air temperature circuit low input Intake air temperature signal less than minimum
threshold, after time for exhaust to warm up
P0113 Intake air temperature circuit high input Intake air temperature signal greater than maximum
threshold
M180452
1
2
Page 328 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-29
In the event of a TP sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine performance concern.
lDelayed throttle response.
lFailure of emission control.
lClosed loop idle speed control inoperative.
lAutomatic gearbox kickdown inoperative.
lIncorrect altitude adaptation.
lMIL illuminated (NAS only).
There are three throttle position sensor diagnostic checks:
lTP sensor signal is greater than the maximum threshold value – the engine speed must be greater than 400 rev/
min for longer than 2 seconds and the signal must be greater than 96% for longer than 50 ms.
lTP sensor signal is less than the minimum threshold – the engine speed must be greater than 400 rev/min for
longer than 2 seconds and the signal must be less than 4% for longer than 50 ms.
lRatio of throttle position to mass of air flow – the calculated throttle angle must be outside limits when the engine
speed is between 800 rev/min and 4000 rev/min, the engine load is between 2 and 6.5 and the coolant
temperature is above -10°C (14°F).
Should a malfunction of the TP sensor occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0101 Mass or volume air flow circuit range/
performance problemLoad monitoring, the ratio of throttle position to air flow
P0122 TPS a circuit low input Signal < minimum threshold
P0123 TPS a circuit high input Signal > maximum threshold
Page 333 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-34 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
In the event of fuel injector signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lRough running.
lDifficult starting.
lEngine misfire.
lPossible catalyst damage.
lHigh emissions.
lAdaptive fuelling disabled.
lAdaptive idle speed control disabled.
The ECM performs three types of fuel injector diagnostic check:
lOutput short circuit to earth
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage
lOutput open circuit
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0201 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 1 Injector 1 open circuit
P0261 Cylinder 1 injector circuit low Injector 1 short circuit to earth
P0262 Cylinder 1 injector circuit high Injector 1 short circuit to battery supply
P0301 Cylinder 1 misfire detected Injector 1 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0202 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 2 Injector 2 open circuit
P0264 Cylinder 2 injector circuit low Injector 2 short circuit to earth
P0265 Cylinder 2 injector circuit high Injector 2 short circuit to battery supply
P0302 Cylinder 2 misfire detected Injector 2 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0203 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 3 Injector 3 open circuit
P0267 Cylinder 3 injector circuit low Injector 3 short circuit to earth
P0268 Cylinder 3 injector circuit high Injector 3 short circuit to battery supply
P0303 Cylinder 3 misfire detected Injector 3 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0204 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 4 Injector 4 open circuit
P0270 Cylinder 4 injector circuit low Injector 4 short circuit to earth
P0271 Cylinder 4 injector circuit high Injector 4 short circuit to battery supply
P0304 Cylinder 4 misfire detected Injector 4 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0205 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 5 Injector 5 open circuit
P0273 Cylinder 5 injector circuit low Injector 5 short circuit to earth
P0274 Cylinder 5 injector circuit high Injector 5 short circuit to battery supply
P0305 Cylinder 5 misfire detected Injector 5 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0206 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 6 Injector 6 open circuit
P0276 Cylinder 6 injector circuit low Injector 6 short circuit to earth
P0277 Cylinder 6 injector circuit high Injector 6 short circuit to battery supply
P0306 Cylinder 6 misfire detected Injector 6 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0207 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 7 Injector 7 open circuit
P0279 Cylinder 7 injector circuit low Injector 7 short circuit to earth
P0280 Cylinder 7 injector circuit high Injector 7 short circuit to battery supply
P0307 Cylinder 7 misfire detected Injector 7 excess emissions/catalyst damaging level of
misfire
P0208 Injection circuit malfunction - cylinder 8 Injector 8 open circuit
P0282 Cylinder 8 injector circuit low Injector 8 short circuit to earth
P0283 Cylinder 8 injector circuit high Injector 8 short circuit to battery supply
Page 336 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-37
There are eight IACV diagnostic checks performed by the ECM:
lOutput short circuit to earth – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to battery supply – opening coil
lOutput open circuit – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to earth – closing coil
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage – closing coil
lOutput open circuit – closing coil
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error low (engine speed must be 100 rev/min less than the target speed, engine load
less than 2.5 and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h less than the expected air flow for a fault condition to
be flagged).
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error high (the engine speed must be more than 180 rev/min greater than the target
speed and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h greater than the expected air flow for a fault condition to be
flagged).
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1510 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - opening winding
P1513 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - opening winding
P1514 IACV opening coil malfunction Open circuit - opening winding
P1553 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - closing winding
P1552 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - closing winding
P1551 IACV closing coil malfunction Open circuit - closing winding
P0505 Idle control system malfunction Blocked IACV - high or low rev/min error