sensor LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 546 of 1672
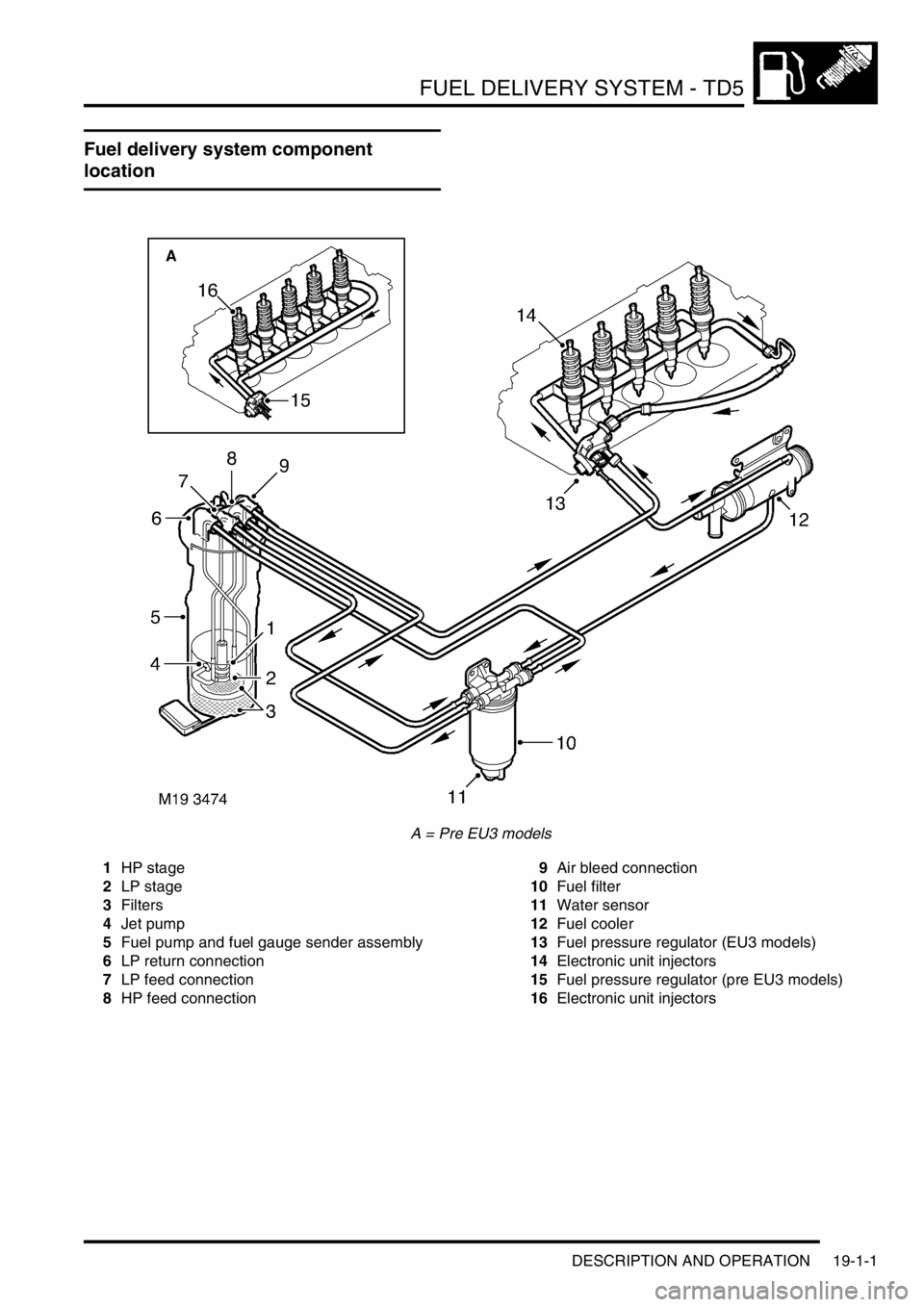
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-1-1
FUEL DELIVERY SYST EM - Td5 DESCRIPTION AND OPERAT ION
Fuel delivery system component
location
A = Pre EU3 models
1HP stage
2LP stage
3Filters
4Jet pump
5Fuel pump and fuel gauge sender assembly
6LP return connection
7LP feed connection
8HP feed connection9Air bleed connection
10Fuel filter
11Water sensor
12Fuel cooler
13Fuel pressure regulator (EU3 models)
14Electronic unit injectors
15Fuel pressure regulator (pre EU3 models)
16Electronic unit injectors
Page 548 of 1672

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-1-3
Description
General
The fuel delivery system comprises a fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, five injectors and a fuel filter. The
system is controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM) which energises the fuel pump relay and controls the
operation and timing of each injector solenoid.
Unlike other Diesel engines, the Td5 engine has no injection pump. The diesel direct injection system receives fuel
at pressure from a two stage fuel pump located in the fuel tank. The system incorporates a fuel return to the fuel pump,
via a fuel cooler attached to the inlet manifold and a fuel filter. A fuel pressure regulator is located in a housing on the
rear of the cylinder head. The regulator maintains the fuel delivered to the injectors at a constant pressure and returns
excess fuel back to the fuel filter and pump via the fuel cooler.
A fuel filter is positioned on the chassis to the right of the fuel tank. The fuel feed and return to and from the engine
passes through the filter. The filter also incorporates a water sensor which illuminates a warning lamp in the
instrument pack.
A moulded fuel tank is located at the rear underside of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals. The tank
provides the attachment for the fuel pump and fuel gauge sender unit which is located inside the tank.
Fuel tank and breather
The fuel tank and breather system is a major part of the fuel delivery system. The fuel tank and breathers are located
at the rear of the vehicle between the chassis longitudinals.
Fuel tank
The moulded fuel tank is made from High Molecular Weight (HMW) High Density Polyethylene (HDPE). The diesel
tank is manufactured using a proportion of recycled plastic.
The tank is retained in position by a metal cradle which is secured to the chassis with two nut plates and bolts at the
rear and a stud plate and two nuts at the front. A strap above the tank is bolted to the chassis and restrains the tank
from moving upwards. The fuel tank has useable capacity of approximately 95 litres (25 US Gallons).
An aperture in the top surface of the tank allows for the fitment of the fuel pump and fuel gauge sender unit which is
retained with a locking ring.
A reflective metallic covering is attached to the tank with two scrivets to shield the tank from heat generated by the
exhaust system.
The fuel filler is located in the right hand rear quarter panel, behind an access flap. The flap is opened electrically
using a switch on the fascia which operates a release solenoid.
The filler is closed by a threaded plastic cap which screws into the filler neck. The cap has a ratchet mechanism to
prevent overtightening and seals against the filler neck to prevent the escape of fuel vapour. The filler cap has a valve
which relieves fuel pressure to atmosphere at approximately 0.12 to 0.13 bar (1.8 to 2.0 lbf.in
2) and opens in the
opposite direction at approximately 0.04 bar (0.7 lbf.in2) vacuum.
A moulded filler tube, made from HMW HDPE, connects the filler to the tank via a flexible hose. The filler tube is
connected at its top end behind the filler flap.
Page 551 of 1672
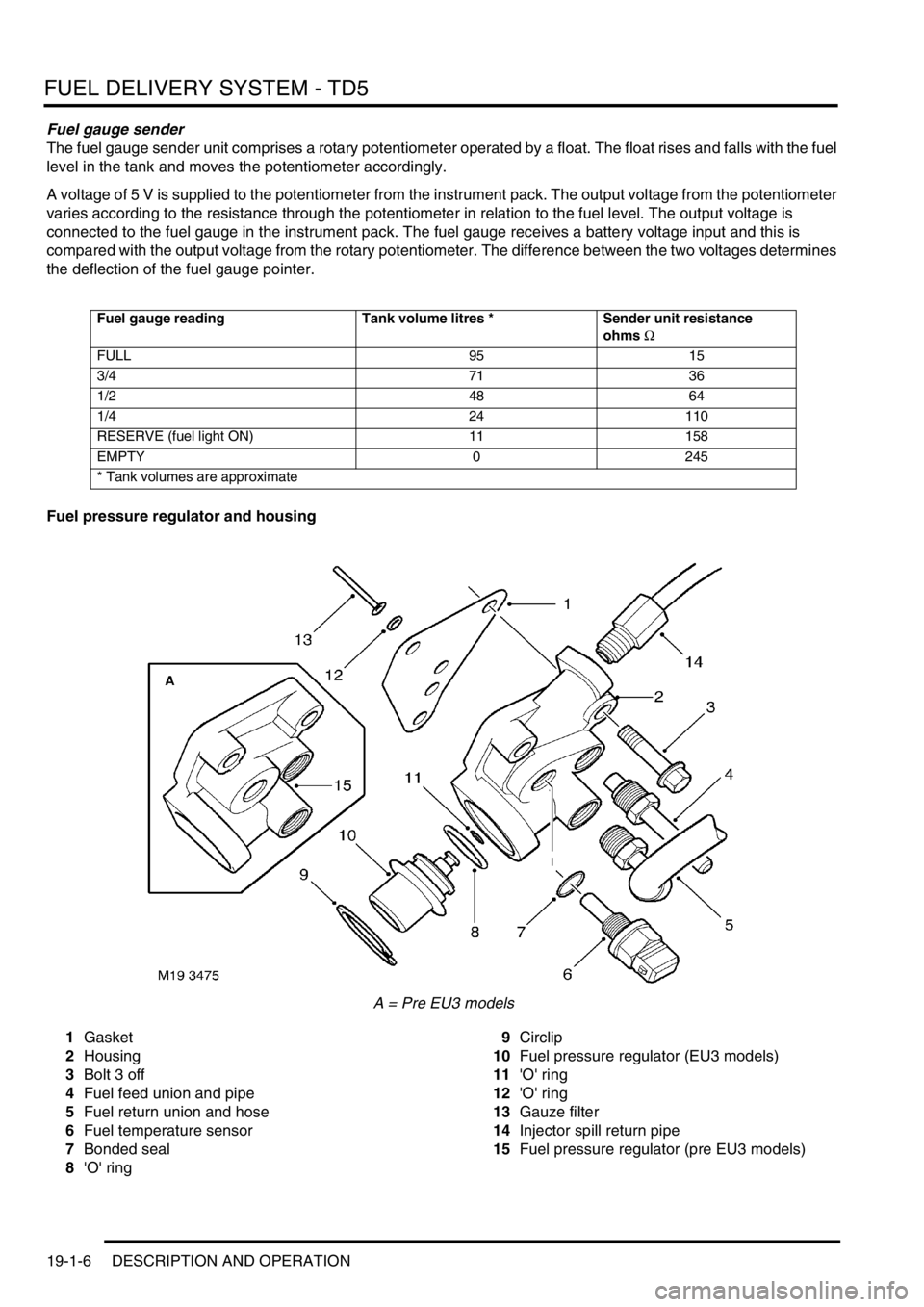
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
19-1-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Fuel gauge sender
The fuel gauge sender unit comprises a rotary potentiometer operated by a float. The float rises and falls with the fuel
level in the tank and moves the potentiometer accordingly.
A voltage of 5 V is supplied to the potentiometer from the instrument pack. The output voltage from the potentiometer
varies according to the resistance through the potentiometer in relation to the fuel level. The output voltage is
connected to the fuel gauge in the instrument pack. The fuel gauge receives a battery voltage input and this is
compared with the output voltage from the rotary potentiometer. The difference between the two voltages determines
the deflection of the fuel gauge pointer.
Fuel pressure regulator and housing
A = Pre EU3 models
1Gasket
2Housing
3Bolt 3 off
4Fuel feed union and pipe
5Fuel return union and hose
6Fuel temperature sensor
7Bonded seal
8'O' ring9Circlip
10Fuel pressure regulator (EU3 models)
11'O' ring
12'O' ring
13Gauze filter
14Injector spill return pipe
15Fuel pressure regulator (pre EU3 models)
Fuel gauge reading Tank volume litres * Sender unit resistance
ohms Ω
FULL 95 15
3/4 71 36
1/2 48 64
1/4 24 110
RESERVE (fuel light ON) 11 158
EMPTY 0 245
* Tank volumes are approximate
Page 552 of 1672
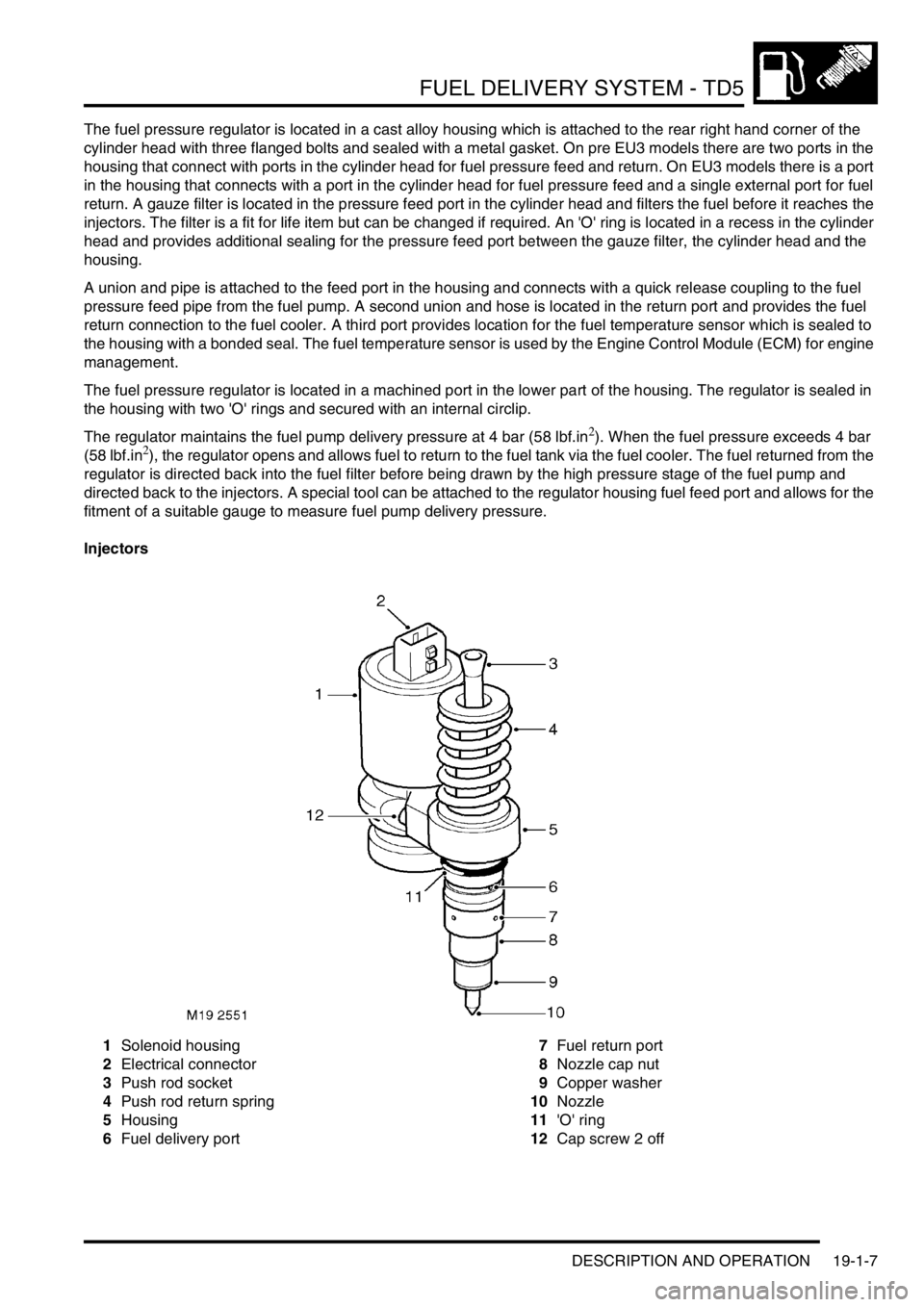
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-1-7
The fuel pressure regulator is located in a cast alloy housing which is attached to the rear right hand corner of the
cylinder head with three flanged bolts and sealed with a metal gasket. On pre EU3 models there are two ports in the
housing that connect with ports in the cylinder head for fuel pressure feed and return. On EU3 models there is a port
in the housing that connects with a port in the cylinder head for fuel pressure feed and a single external port for fuel
return. A gauze filter is located in the pressure feed port in the cylinder head and filters the fuel before it reaches the
injectors. The filter is a fit for life item but can be changed if required. An 'O' ring is located in a recess in the cylinder
head and provides additional sealing for the pressure feed port between the gauze filter, the cylinder head and the
housing.
A union and pipe is attached to the feed port in the housing and connects with a quick release coupling to the fuel
pressure feed pipe from the fuel pump. A second union and hose is located in the return port and provides the fuel
return connection to the fuel cooler. A third port provides location for the fuel temperature sensor which is sealed to
the housing with a bonded seal. The fuel temperature sensor is used by the Engine Control Module (ECM) for engine
management.
The fuel pressure regulator is located in a machined port in the lower part of the housing. The regulator is sealed in
the housing with two 'O' rings and secured with an internal circlip.
The regulator maintains the fuel pump delivery pressure at 4 bar (58 lbf.in
2). When the fuel pressure exceeds 4 bar
(58 lbf.in2), the regulator opens and allows fuel to return to the fuel tank via the fuel cooler. The fuel returned from the
regulator is directed back into the fuel filter before being drawn by the high pressure stage of the fuel pump and
directed back to the injectors. A special tool can be attached to the regulator housing fuel feed port and allows for the
fitment of a suitable gauge to measure fuel pump delivery pressure.
Injectors
1Solenoid housing
2Electrical connector
3Push rod socket
4Push rod return spring
5Housing
6Fuel delivery port7Fuel return port
8Nozzle cap nut
9Copper washer
10Nozzle
11'O' ring
12Cap screw 2 off
Page 554 of 1672
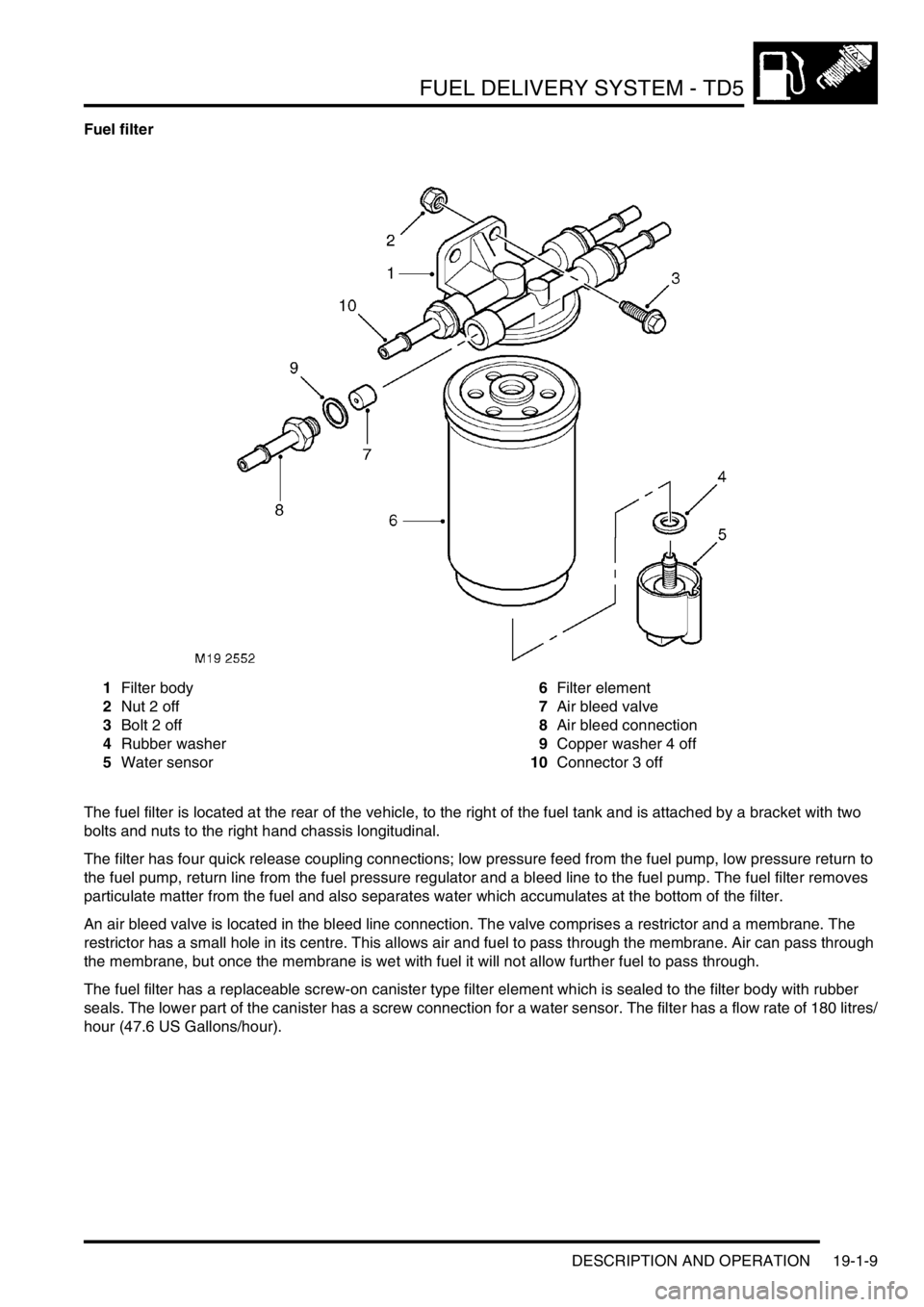
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-1-9
Fuel filter
1Filter body
2Nut 2 off
3Bolt 2 off
4Rubber washer
5Water sensor6Filter element
7Air bleed valve
8Air bleed connection
9Copper washer 4 off
10Connector 3 off
The fuel filter is located at the rear of the vehicle, to the right of the fuel tank and is attached by a bracket with two
bolts and nuts to the right hand chassis longitudinal.
The filter has four quick release coupling connections; low pressure feed from the fuel pump, low pressure return to
the fuel pump, return line from the fuel pressure regulator and a bleed line to the fuel pump. The fuel filter removes
particulate matter from the fuel and also separates water which accumulates at the bottom of the filter.
An air bleed valve is located in the bleed line connection. The valve comprises a restrictor and a membrane. The
restrictor has a small hole in its centre. This allows air and fuel to pass through the membrane. Air can pass through
the membrane, but once the membrane is wet with fuel it will not allow further fuel to pass through.
The fuel filter has a replaceable screw-on canister type filter element which is sealed to the filter body with rubber
seals. The lower part of the canister has a screw connection for a water sensor. The filter has a flow rate of 180 litres/
hour (47.6 US Gallons/hour).
Page 555 of 1672

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - TD5
19-1-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Water sensor
The water sensor has a three pin electrical connector. When the sensor detects water in the filter it illuminates a
warning lamp in the instrument pack .
+ INSTRUMENTS, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
The water sensor attachment thread has a slot machined down one side. The filter can be purged of water by partially
unscrewing the sensor which aligns the slot in the threads with a corresponding hole in the sensor. When aligned,
water and fuel can flow down the slot and flows from a small cast tube on the side of the sensor. Re-tightening the
sensor misaligns the slot and stops the flow of fuel.
The water sensor receives a battery supply from the fuel pump relay in the engine compartment fusebox on one of
the electrical connector pins. The two remaining pins are connected to the instrument pack and an earth header joint.
The sensor operation uses the measurement of resistance between two electrodes submerged in the fuel and
activated by the presence of water.
When the ignition is moved to position II the warning lamp will illuminate for approximately two seconds to check
warning lamp functionality. TestBook can also illuminate the warning lamp to check its functionality.
When the filter is full with fuel and no water is present the resistance of the Diesel fuel will show a reading of 15 mA
maximum on the feed wire to the instrument pack. This current will not illuminate the water sensor warning lamp in
the instrument pack. When sufficient water surrounds both electrodes the resistance of the water will show a reading
of 130 mA maximum. This will supply sufficient voltage to the instrument pack to illuminate the warning lamp to alert
the driver to the presence of water in the fuel system.
Page 568 of 1672
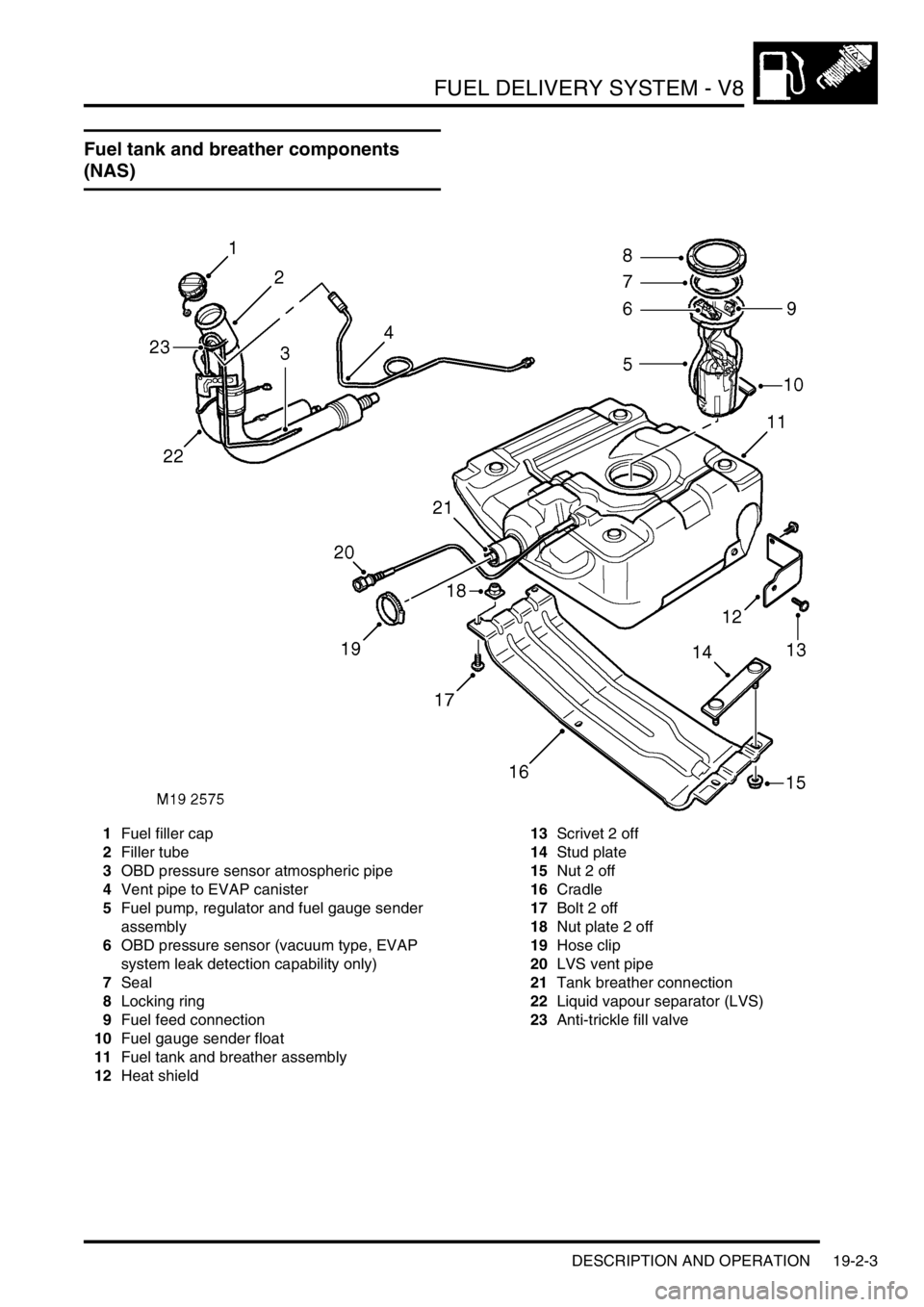
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-2-3
Fuel tank and breather components
(NAS)
1Fuel filler cap
2Filler tube
3OBD pressure sensor atmospheric pipe
4Vent pipe to EVAP canister
5Fuel pump, regulator and fuel gauge sender
assembly
6OBD pressure sensor (vacuum type, EVAP
system leak detection capability only)
7Seal
8Locking ring
9Fuel feed connection
10Fuel gauge sender float
11Fuel tank and breather assembly
12Heat shield13Scrivet 2 off
14Stud plate
15Nut 2 off
16Cradle
17Bolt 2 off
18Nut plate 2 off
19Hose clip
20LVS vent pipe
21Tank breather connection
22Liquid vapour separator (LVS)
23Anti-trickle fill valve
Page 570 of 1672

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-2-5
NAS markets: A fabricated filler tube, made from stainless steel, connects the filler to the tank via a flexible rubber
hose. The filler tube is connected at it's top end behind the filler flap.
On all vehicles that use unleaded fuel, the filler neck is fitted with an inhibitor. The inhibitor is a tapered nozzle in the
mouth of the filler neck which will only allow the use of a standard unleaded fuel filler gun. A spring loaded flap valve
prevents the incorrect fuel from being trickle filled from an incorrect filler gun.
Fuel tank breather system (all markets except NAS)
The filler tube incorporates a tank vent which allows air and fuel vapour displaced from the tank when filling to vent to
atmosphere via the filler neck. A relief valve in the vent line to the EVAP canister prevents vapour escaping through
the canister during filling. This prevents the customer overfilling the tank and maintains the correct fuel cut-off level.
The filler tube also incorporates an integral Liquid Vapour Separator (LVS). During normal driving excess fuel vapour
is passed via the vent line into the EVAP canister. To prevent the canister from being overloaded with fuel vapour,
especially in hot climates, the vapour is given the opportunity to condense in the LVS. Fuel which condenses in the
LVS flows back into the tank through the ROV's.
A breather spout within the tank controls the tank 'full' height. When fuel covers the spout it prevents fuel vapour and
air from escaping from the tank. This causes the fuel to 'back-up' in the filler tube and shuts off the filler gun. The
position of the spout ensures that when the filler gun shuts off, a vapour space of approximately 10% of the tanks total
capacity remains. This vapour space ensures that Roll Over Valves (ROV's) are always above the fuel level and the
vapour can escape and allow the tank to breathe.
The pressure relief valve fitted in the vent line to the EVAP canister prevents the customer trickle filling the tank.
Trickle filling greatly reduces the vapour space in the tank which in turn affects the tank's ability to breathe properly,
reducing engine performance and safety. When filling the tank, the pressures created are too low to open the pressure
relief valve, preventing the customer from trickle filling the tank. Vapour pressures created during driving are higher
and will open the valve allowing vapour to vent to the EVAP canister.
Four ROV's are welded onto the top surface of the tank. Each ROV is connected by a tube to the main vent line to
the EVAP canister. The ROV's allow fuel vapour to pass through them during normal vehicle operation. In the event
of the vehicle being overturned the valves shut-off, sealing the tank and preventing fuel from spilling from the vent line.
Fuel tank breather system (NAS)
The filler tube incorporates a tank vent which allows air and fuel vapour displaced from the tank when filling to vent to
atmosphere via the filler neck. A filler cap operated valve within the fuel filler neck prevents vapour escaping through
the EVAP canister during filling. This prevents the customer overfilling the tank and maintains the correct fuel cut-off
level.
The filler tube also has an 'L' shaped, stainless steel Liquid Vapour Separator (LVS). During normal driving excess
fuel vapour is passed via the vent line into the EVAP canister. To prevent the canister from being overloaded with fuel
vapour, especially in hot climates, the vapour is given the opportunity to condense in the LVS. Fuel which condenses
in the LVS flows back into the tank via the LVS vent line and through the Roll Over Valves (ROV's).
For NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability, a small tube is located alongside the filler
tube and terminates near to the filler neck. The tube is connected to the On Board Diagnostics (OBD) pressure sensor
in the fuel pump and provides the sensor with a reading of atmospheric pressure to compare against the tank
pressure.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Emission Control Systems.
A breather spout within the tank controls the tank 'full' height. When fuel covers the spout it prevents fuel vapour and
air from escaping from the tank. This causes the fuel to 'back-up' in the filler tube and shuts off the filler gun. The
position of the spout ensures that when the filler gun shuts off, a vapour space of approximately 10% of the tanks total
capacity remains. This vapour space ensures that the ROV's are always above the fuel level and the vapour can
escape to the LVS and allow the tank to breathe.
Page 571 of 1672
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
19-2-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The filler cap operated valve closes the vent line to the EVAP canister to prevent the customer trickle filling the tank.
Trickle filling greatly reduces the vapour space in the tank which in turn affects the tank's ability to breathe properly,
reducing engine performance and safety. When filling the tank, the removal of the filler cap closes the valve and the
vent line preventing the customer from trickle filling the tank. When the cap is installed the valve is opened by the cap
allowing vapour to vent to the EVAP canister.
The four ROV's are welded inside the top surface of the tank. Each ROV is connected internally in the tank by a tube
to the LVS. The ROV's allow fuel vapour to pass through them during normal vehicle operation. In the event of the
vehicle being overturned the valves shut-off, sealing the tank and preventing fuel from spilling from the vent line into
the LVS.
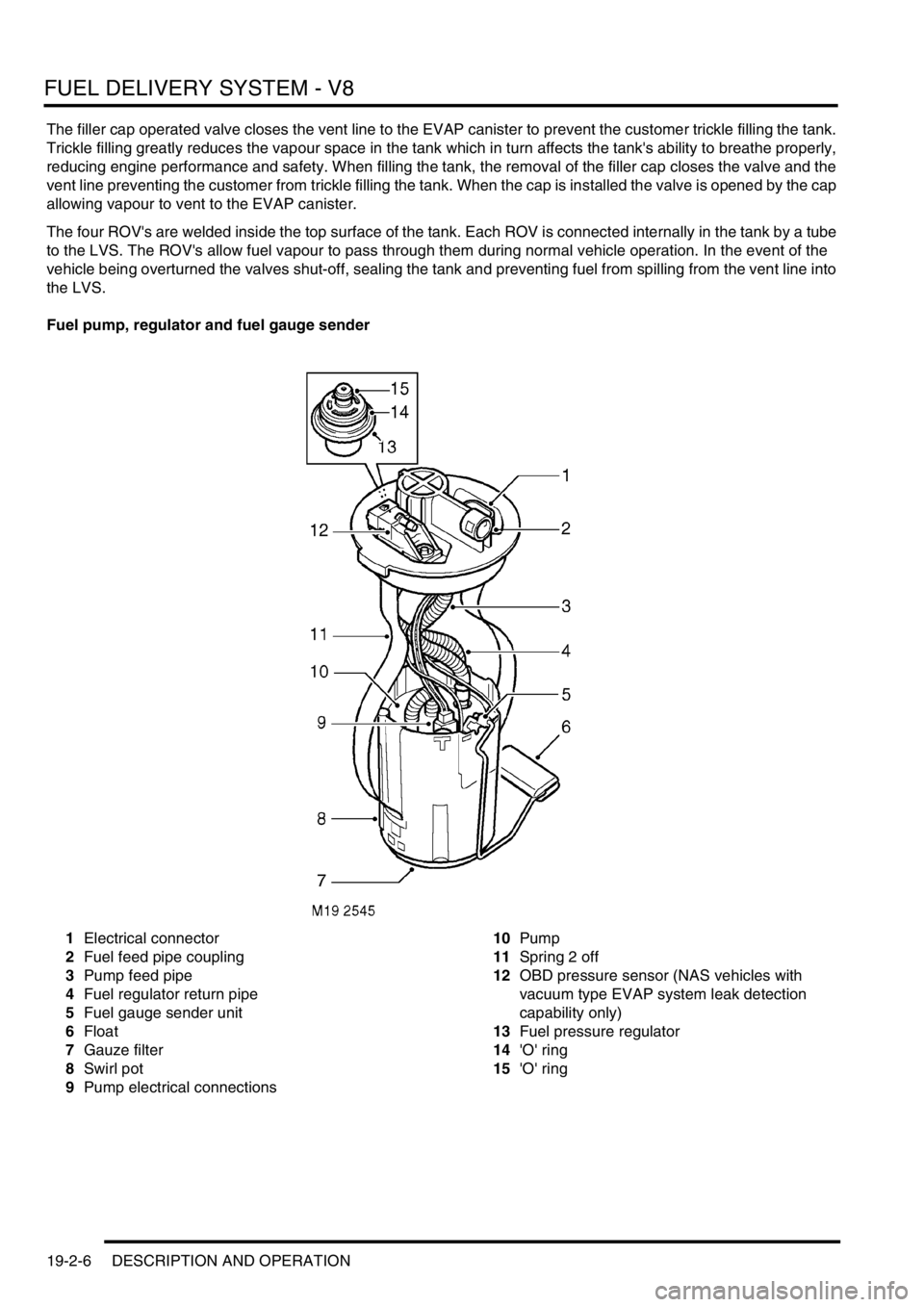
Fuel pump, regulator and fuel gauge sender
1Electrical connector
2Fuel feed pipe coupling
3Pump feed pipe
4Fuel regulator return pipe
5Fuel gauge sender unit
6Float
7Gauze filter
8Swirl pot
9Pump electrical connections10Pump
11Spring 2 off
12OBD pressure sensor (NAS vehicles with
vacuum type EVAP system leak detection
capability only)
13Fuel pressure regulator
14'O' ring
15'O' ring
Page 572 of 1672

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 19-2-7
The fuel pump is a 'self priming' wet type pump which is immersed in fuel in the tank. The fuel pump operates at all
times when the ignition switch is in position II. If the engine is not started, the ECU will 'time-out' after 2 seconds and
de-energise the fuel pump relay to protect the pump. The pump receives a feed from the battery via fuse 10 in the
engine compartment fusebox and the fuel pump relay. The relay is energised by the ECM when the ignition switch is
moved to position II.
The fuel pump is retained with a locking ring and sealed with a rubber seal. The locking ring requires a special tool
for removal and fitment. An access panel for the fuel pump is located in the loadspace floor below the loadspace
carpet. The access panel is sealed to the floor with a rubber seal and retained by six self-tapping screws.
The fuel gauge sender is integral with the fuel pump. The sender is submerged in the fuel and is operated by a float
which moves with the fuel level in the tank.
Fuel pump
The fuel pump assembly comprises a top cover which locates the fuel pressure regulator, electrical connector and
fuel pipe coupling. The top cover is attached to a plastic cup shaped housing by two metal springs. The housing
locates the pump and the fuel gauge sender unit.
The lower part of the housing is the swirl pot, which maintains a constant fuel level at the fuel pick-up. A feed pipe
from the pump to the coupling connection and a return pipe from the regulator connect between the top cover and the
housing.
A coarse filter is attached to the base of the housing and prevents the ingress of large contaminants into the swirl pot.
A gauze filter prevents particles entering the fuel pump.
Surrounding the pump is a large fine paper filter element which further protects the fuel pressure regulator, engine
and injectors from particulate contamination. The paper filter is not a serviceable item and removes the requirement
for an external in-line filter.
A non-return valve is located in the base of the housing. When the fuel tank is full, fuel pressure keeps the valve lifted
from its seat allowing fuel to flow into the swirl pot. As the tank level reduces, the fuel pressure in the tank reduces
causing the valve to close. When the valve is closed fuel is retained in the swirl pot, ensuring that the swirl pot remains
full and maintains a constant supply to the fuel pump.
A four pin electrical connector is located on the top cover of the pump and provides power feed and return for fuel
pump and fuel gauge rotary potentiometer operation. A single quick release coupling connects the fuel feed pipe to
the outer top surface of the pump.
Two metal springs are attached to the top cover and the housing of the pump. When the pump is installed it seats on
the lower surface inside the tank. The springs exert a downward pressure on the pump and ensure that the pump is
located positively at the bottom of the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a maximum current draw of 6.5 A at 12.5 V.
On NAS vehicles with vacuum type EVAP system leak detection capability only, the fuel pump top cover is fitted with
an On Board Diagnostics (OBD) pressure sensor. This sensor has a three pin electrical connector which provides a
connection between the sensor and the ECM. The sensor is sealed in the top cover with an 'O' ring and secured with
a clip. The sensor monitors tank pressure during OBD tests of the fuel evaporation system integrity. A hose is
connected to the sensor and is routed across the top of the fuel tank and terminates at the top of the fuel filler tube.
The pipe is open to atmosphere and provides atmospheric pressure for the sensor operation.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.